6: Population ecology: age-structured populations and life histories
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what are Allee effects
Difficulty in survival and reproduction at low population densities due to reduced cooperation or assistance among individuals, hindering essential activities like finding food, mating, and defending against predators.
Net reproductive rate, R0
Average (“expected”) # of daughters a female has in her lifetime = net reproductive rate = R0
R0 = Σ lx m x
x = age class
mx (or bx) = # daughters born to a female
of age x during the interval x to x + 1
lx = probability of being alive at age x
“Survivorship curve” = a graph of lx vs. x
lx necessarily declines with x
compare R0 with λ,
time units of one generation
rather than one time interval
Generation time, T (Average age at which a female gives birth)
T = Σ x lx m x / R0

Relationships among R0 , λ, r
parameters indicate the factor by
which a population changes during a discrete
interval of time, but those intervals are
different
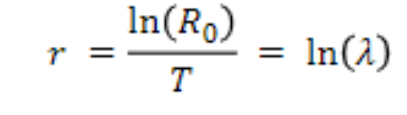
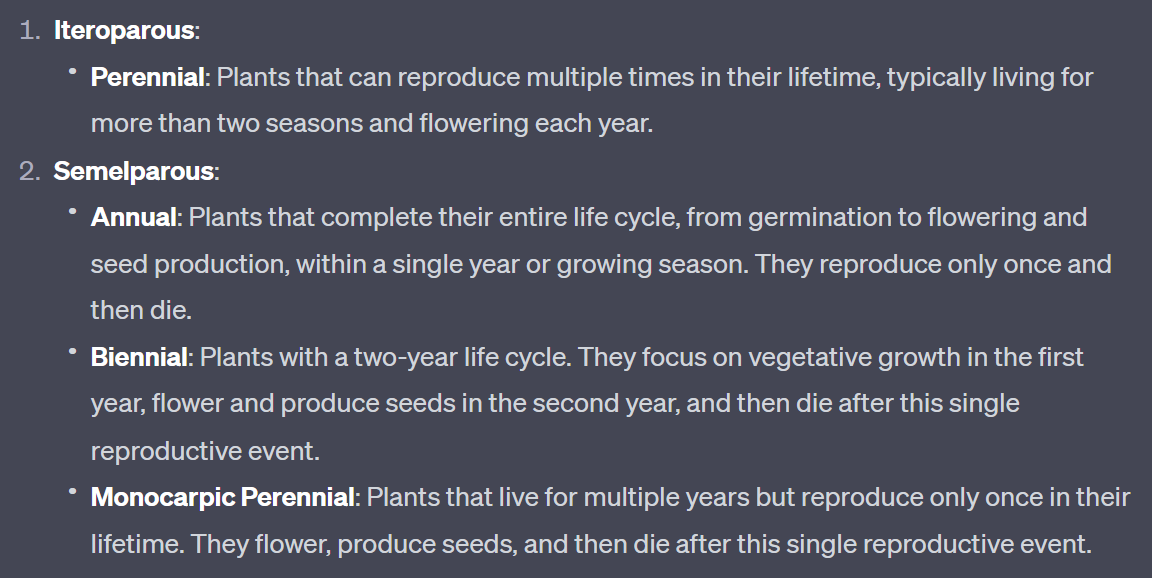
what are semelparous organisms
Species that reproduce only once in their lifetime, investing most of their energy in a single, intense reproductive event.
what are iteroparous organisms
Species that have the ability to reproduce multiple times during their lifetime, allocating resources for reproduction over several reproductive events
Plant life history categories
(iteroparous and semelparous)
When does natural selection favour
semelparity?
When reproductive output is increased by
accumulating resources for longer
In plants, if:
• Massive flower/fruit displays attract more beneficial animals
what is the Advantage of synchrony? (organisms within a population reproducing or releasing offspring at the same time)
having infrequent, synchronized reproductive pulses is a tactic used by certain organisms when they produce a large number of offspring all at once (a pulse) to potentially overwhelm predators. increases the chances of a portion of the offspring surviving to adulthood, as predators may not be able to consume all the offspring
K and r strategies
K-selected (K strategy): The "K" in K-selected refers to the carrying capacity of an environment for a particular species, representing the maximum population size that the environment can sustain over the long term. K-selected species have evolved to adapt to stable, predictable environments near their carrying capacity.
r-selected (r strategy): The "r" in r-selected refers to the intrinsic rate of population growth. r-selected species have a high intrinsic growth rate and are adapted to unstable or unpredictable environments. They tend to produce a large number of offspring, but with less investment in each individual.

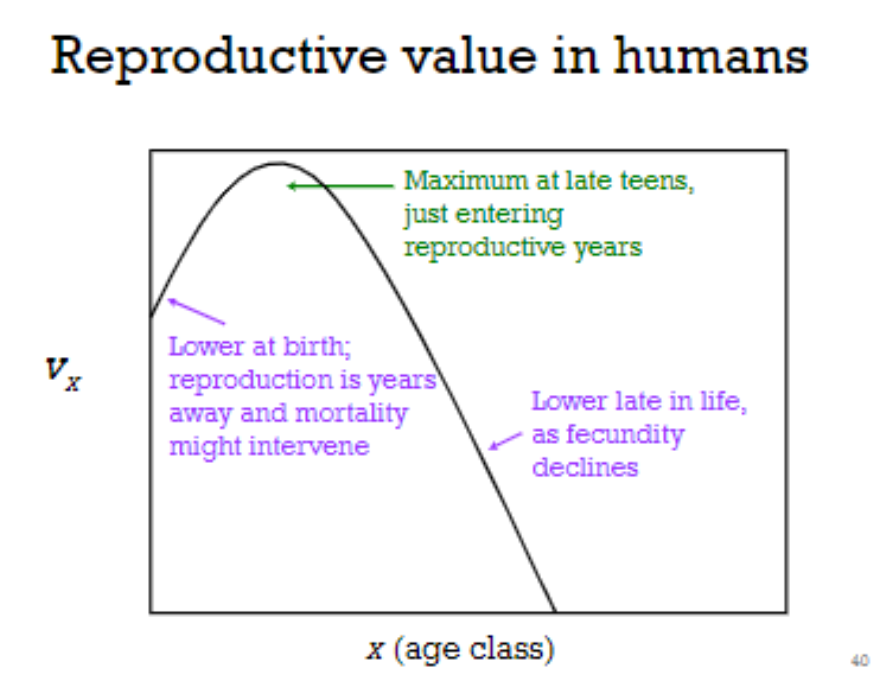
Reproductive value, v x
expected number
of future daughters left to an individual of
age x