Neuroanatomy Midterm 2
1/331
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
332 Terms
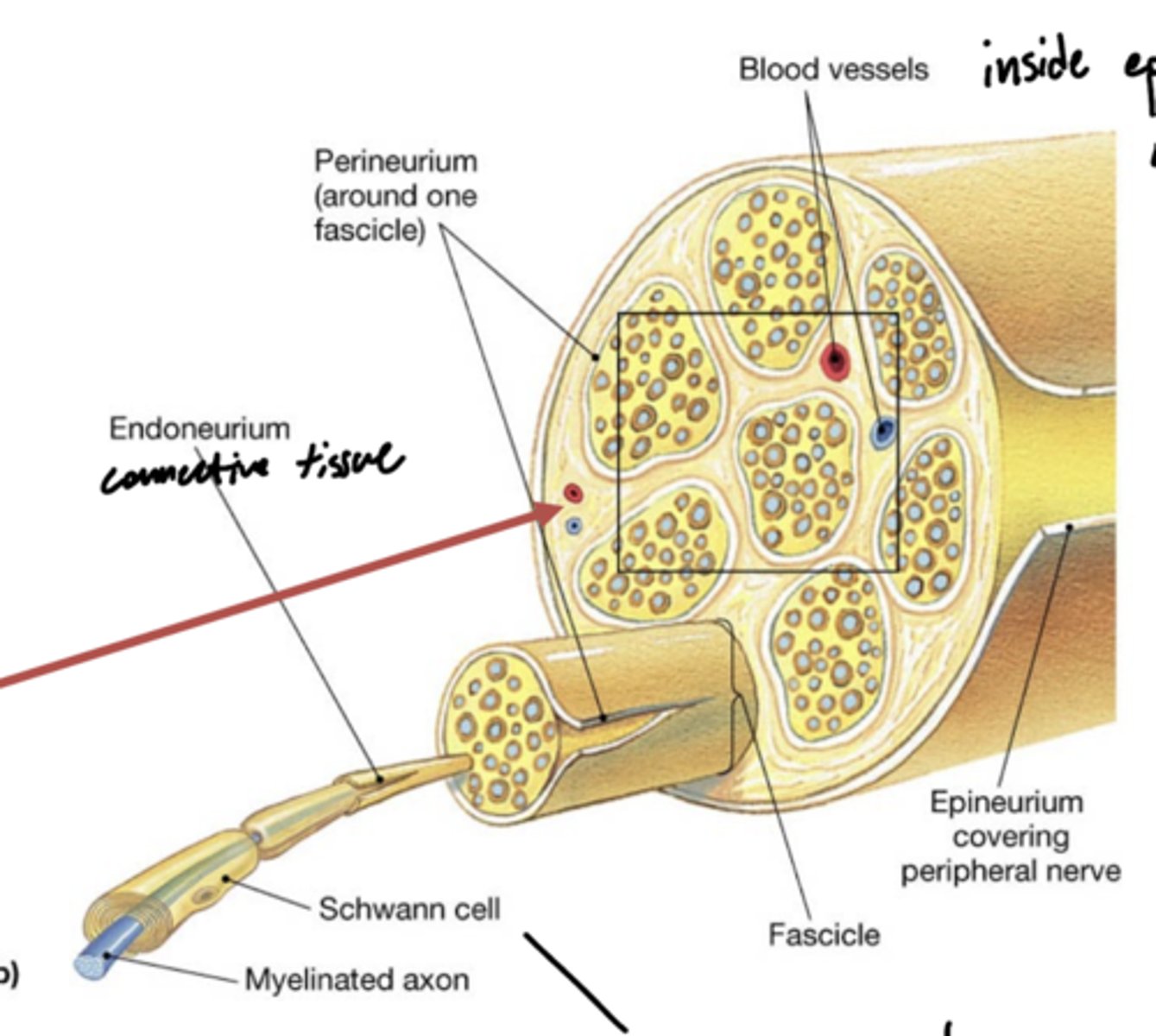
What are the layers of peripheral nerves (superficial to deep)?
1. epineurium
2. perineurium
3. endoneurium
4. neurolemma
5. axon cylinder
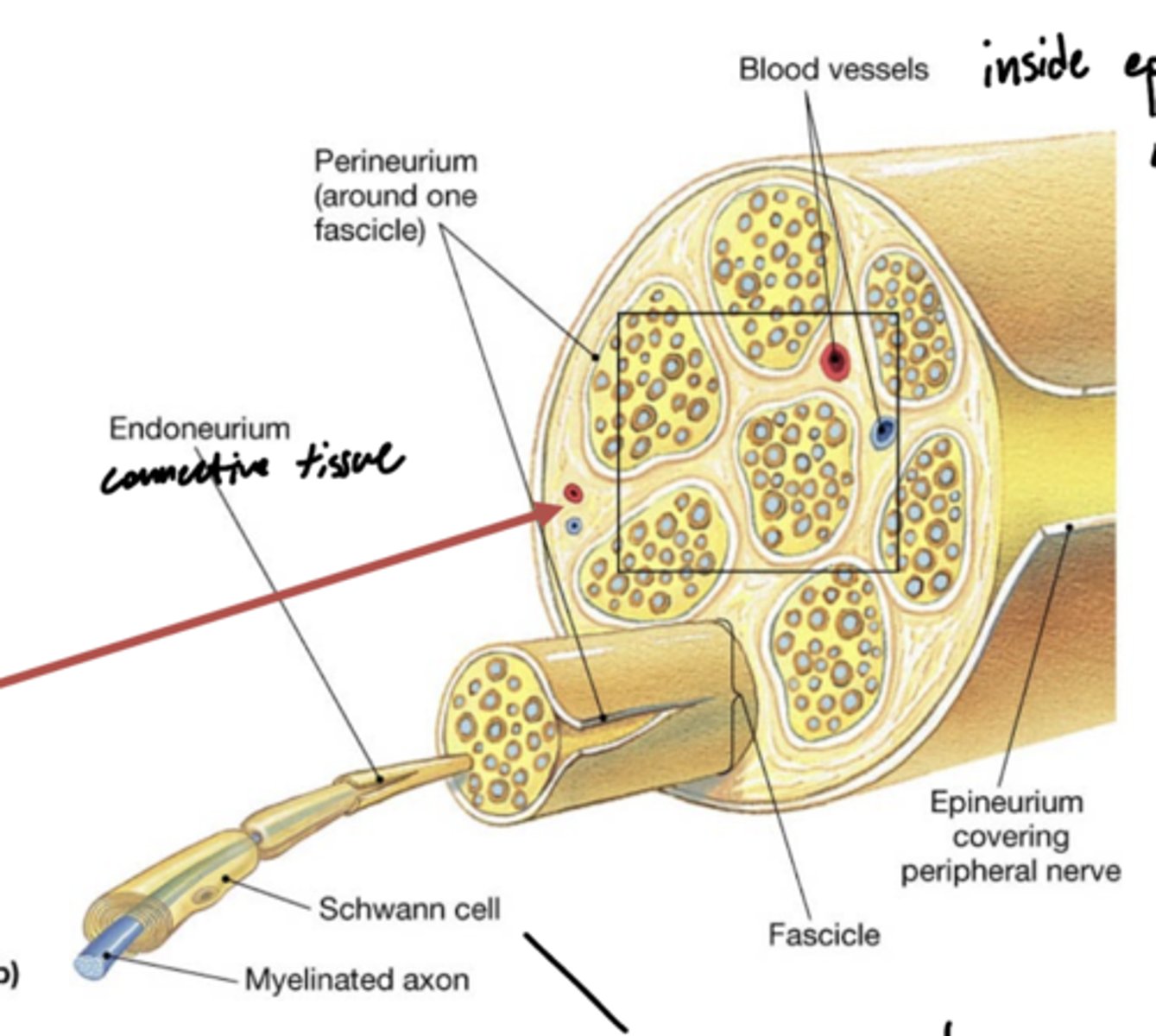
What layer of peripheral nerves participates in the blood brain barrier?
perineurium
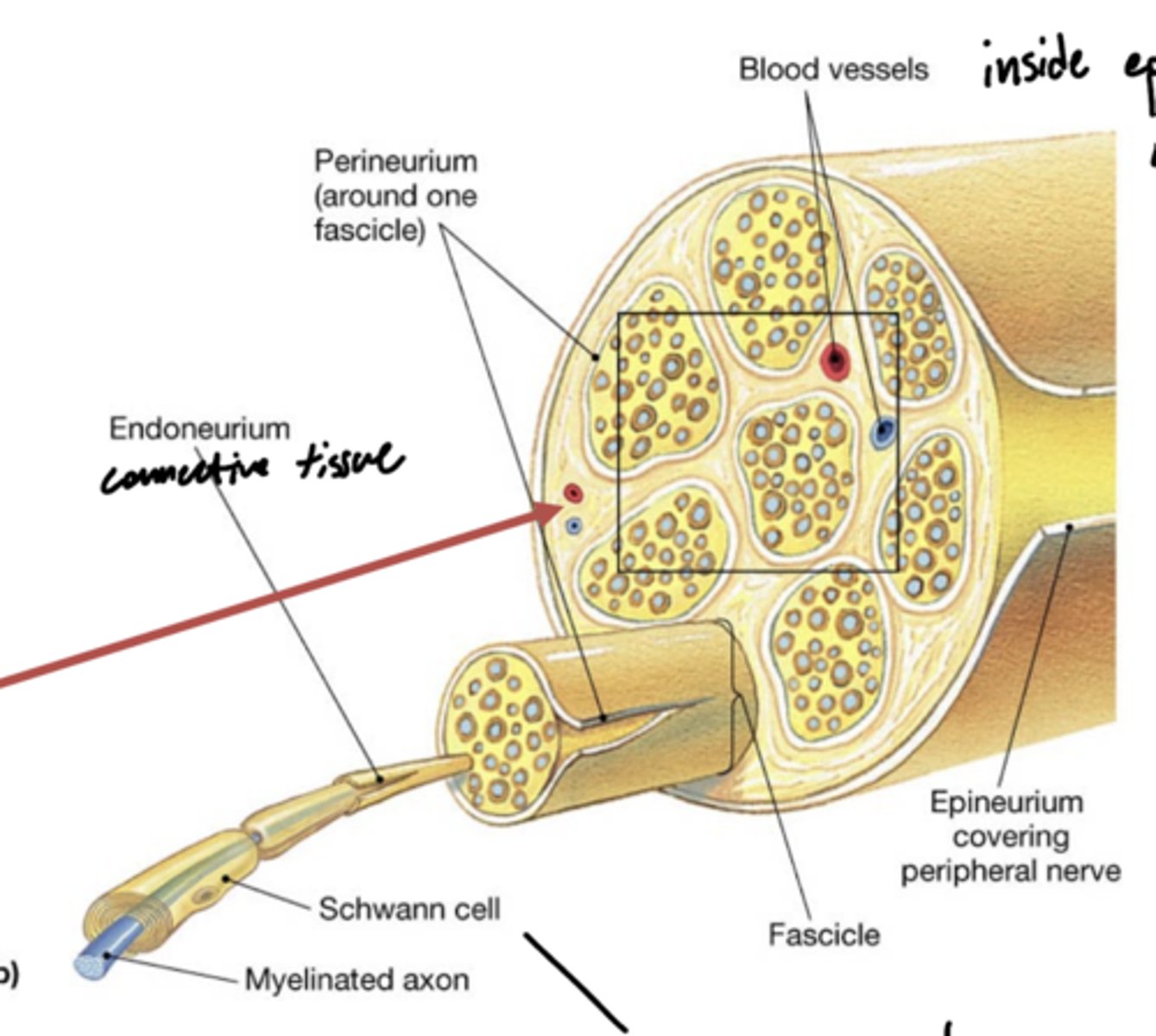
What are vasa nevorum?
latin for blood vessels of the nerves -- red arrow
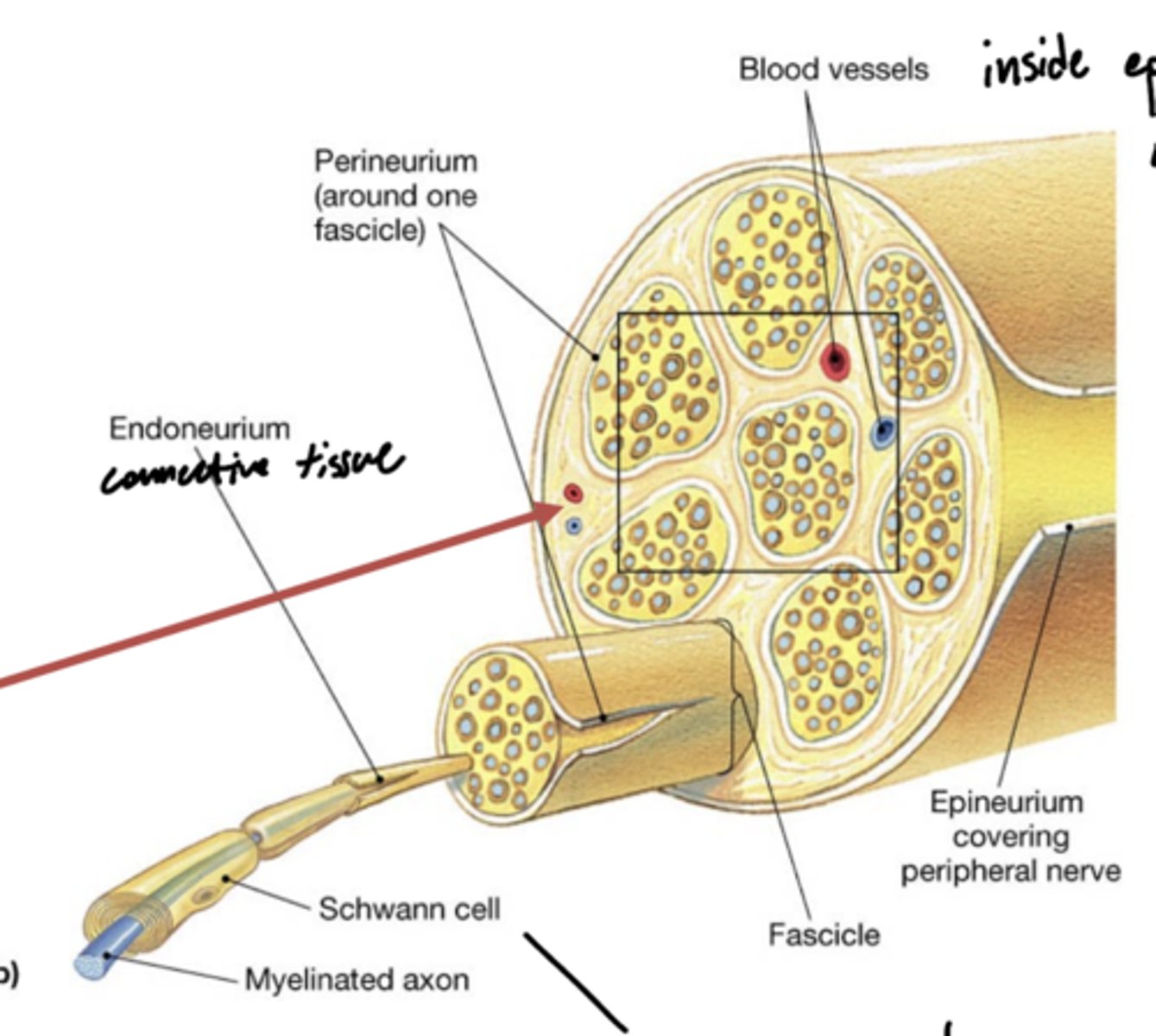
What layers do vasa nevorum reside between?
epineurium -- outside
perineurium -- inside
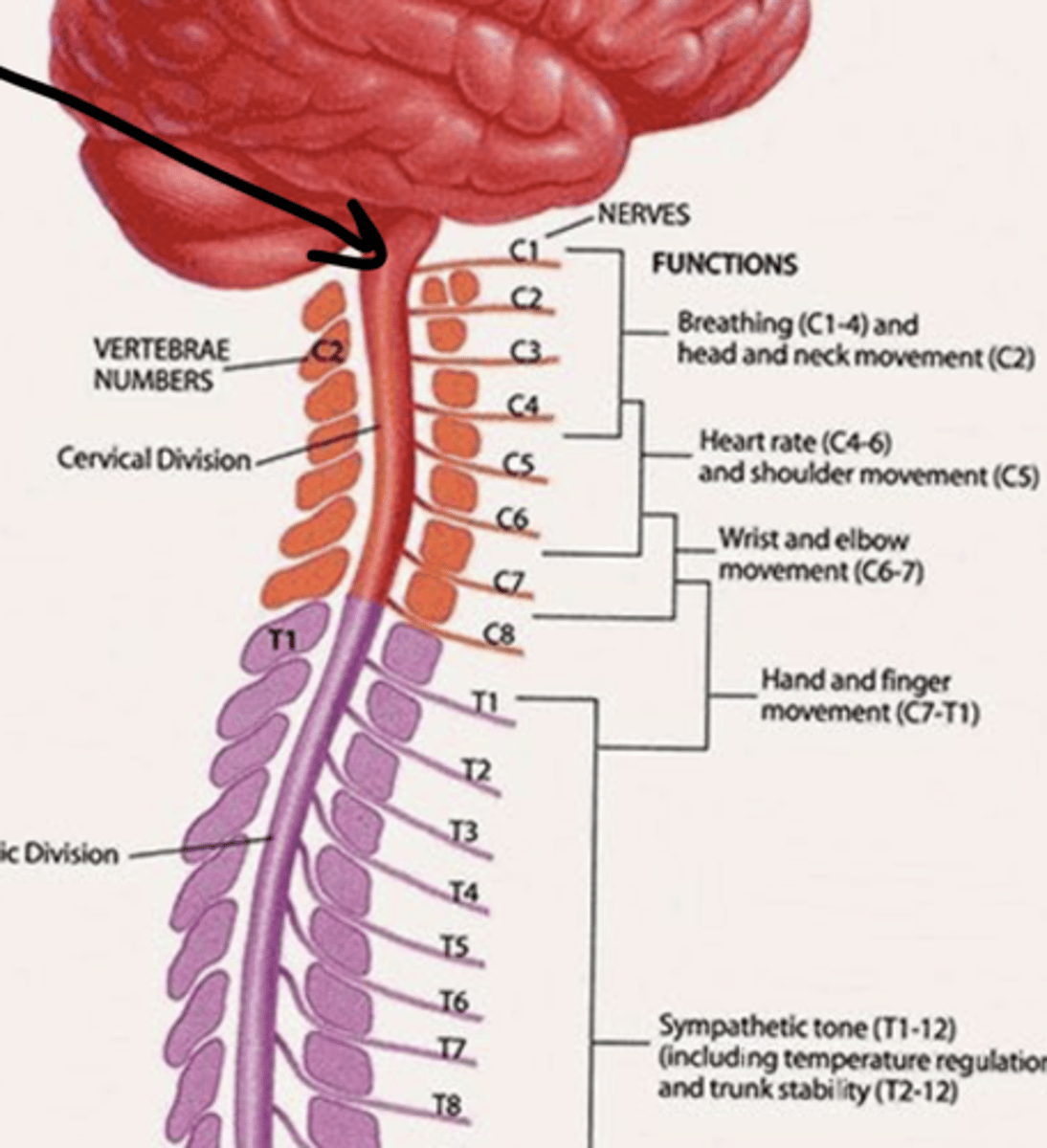
Which vertebrae do spinal nerves travel above their respective vertebrae?
C1 - C7
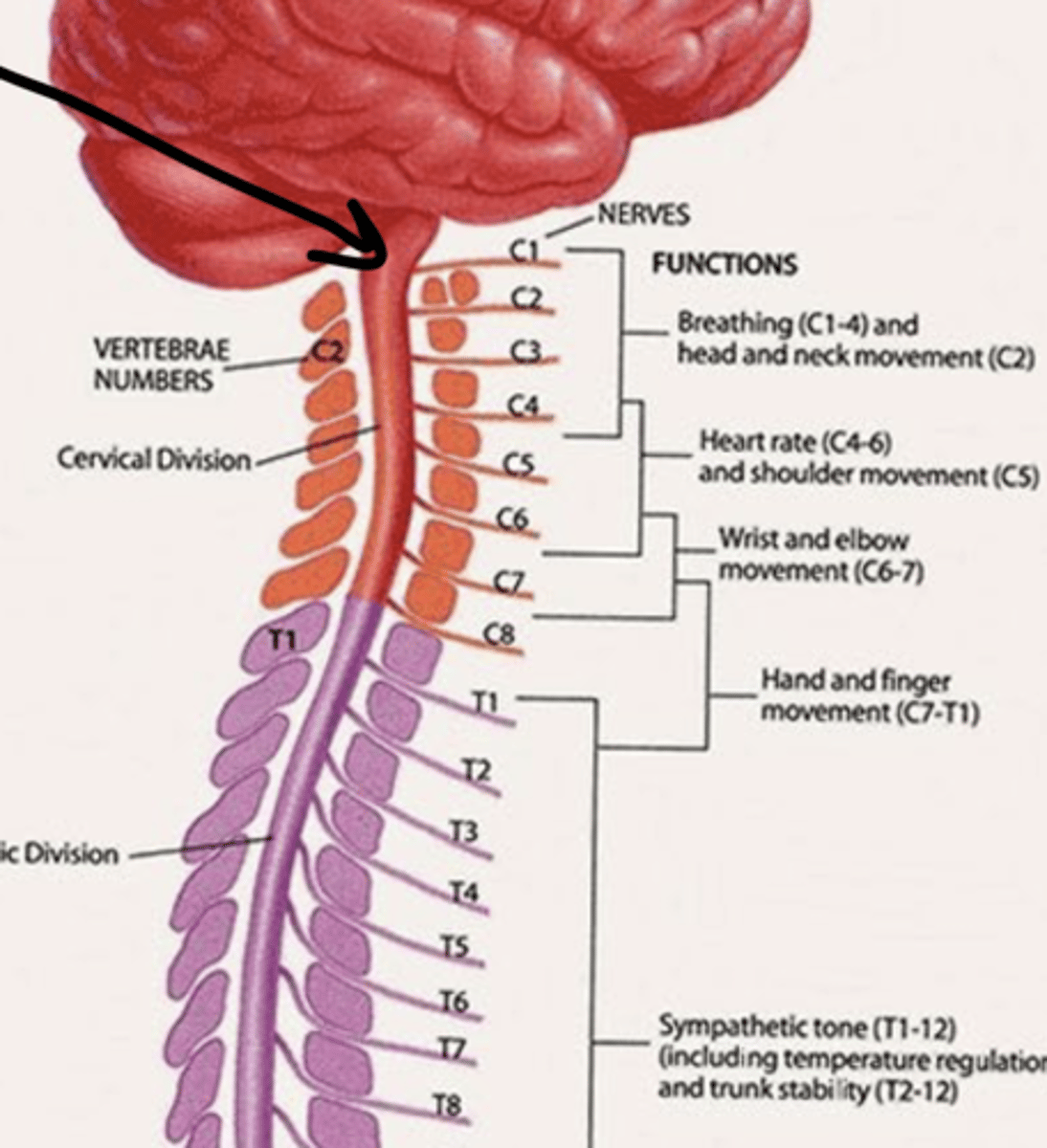
Which vertebrae do spinal nerves travel below their respective vertebrae?
T1 down
why? -- extra cervical nerve C8
How is the gray and white matter organized in the spinal cord?
white matter -- largely peripheral
gray matter -- central
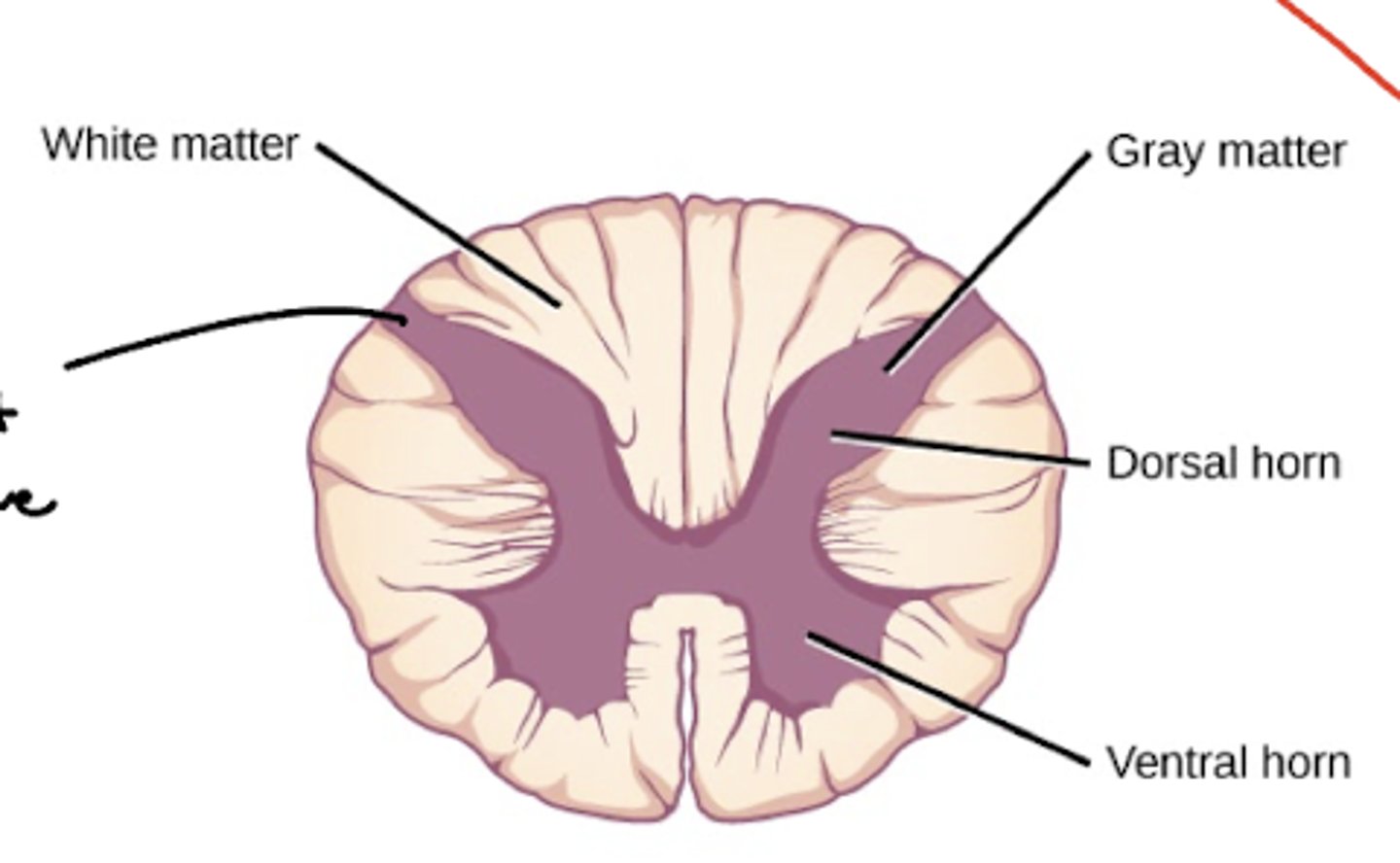
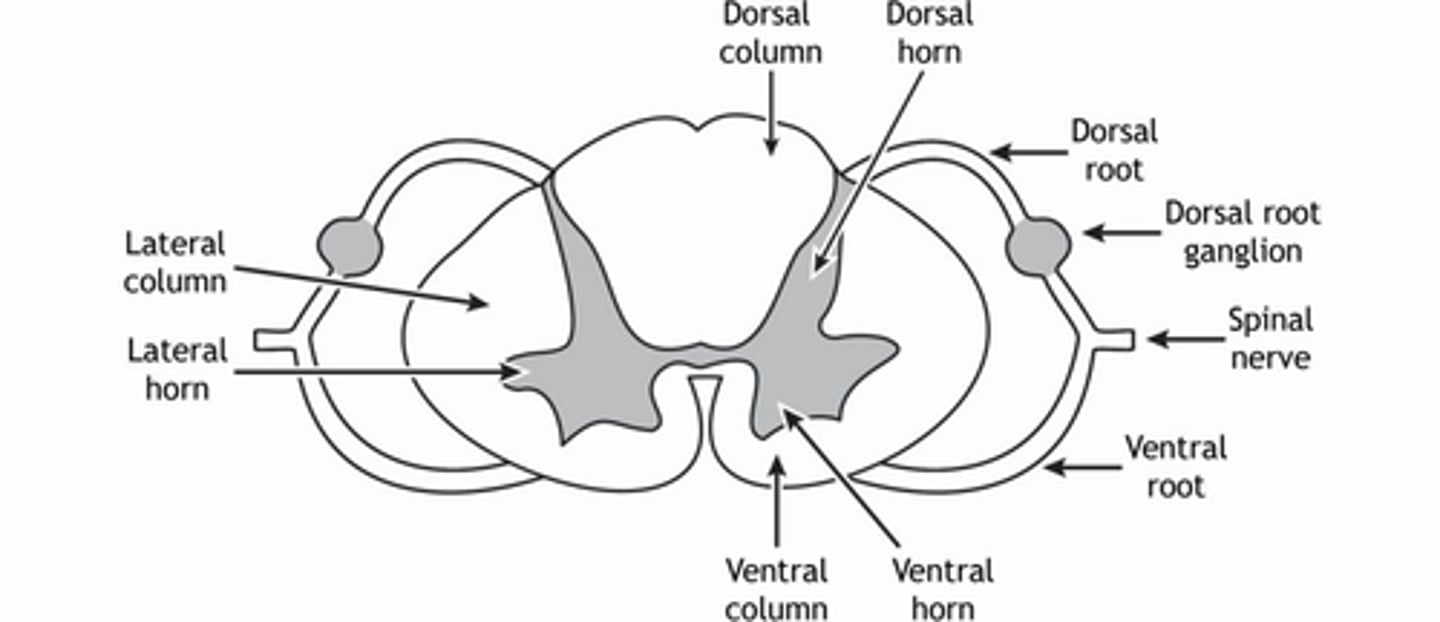
What are the divisions of the gray matter in the spinal cord?
horns
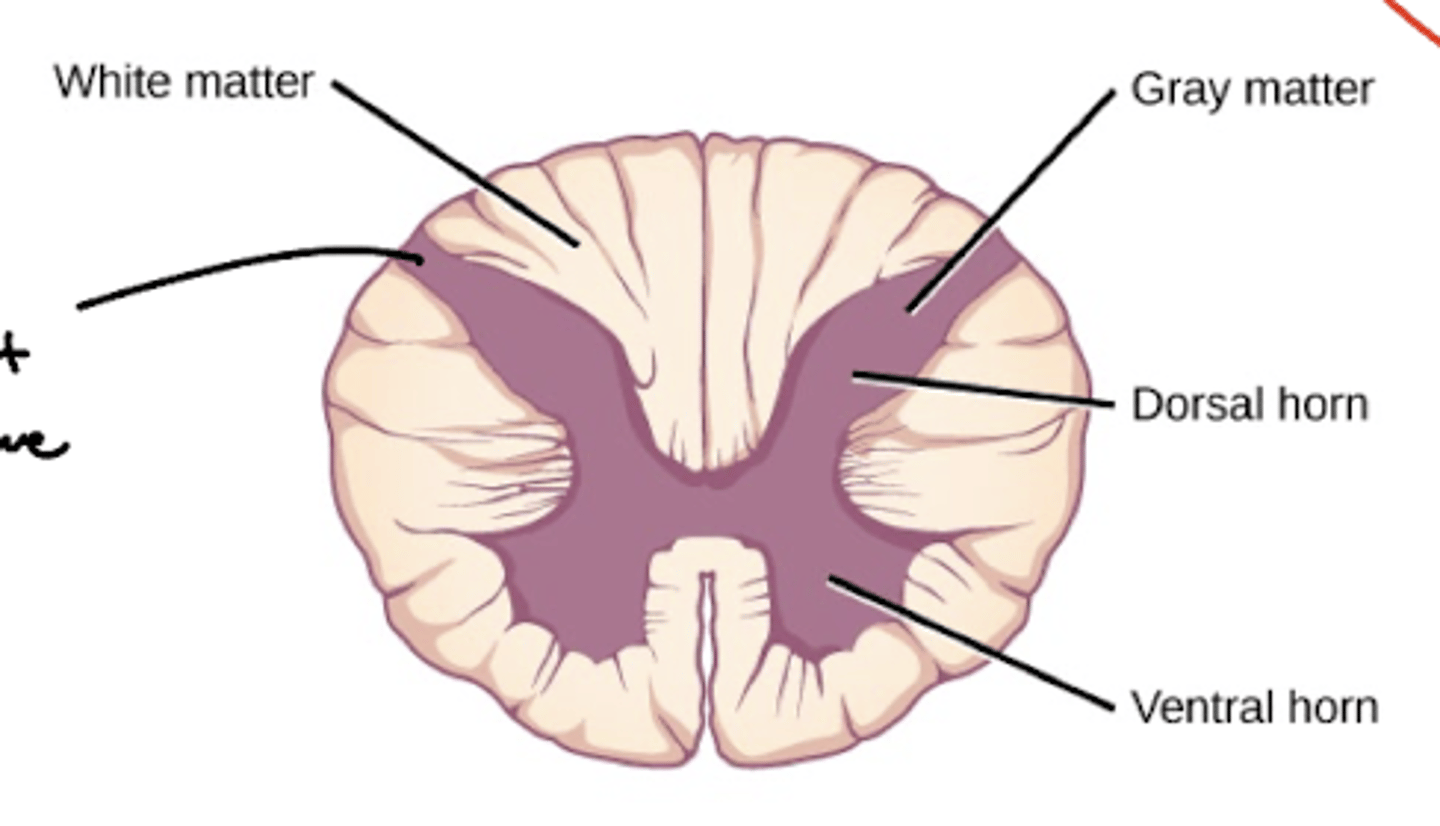
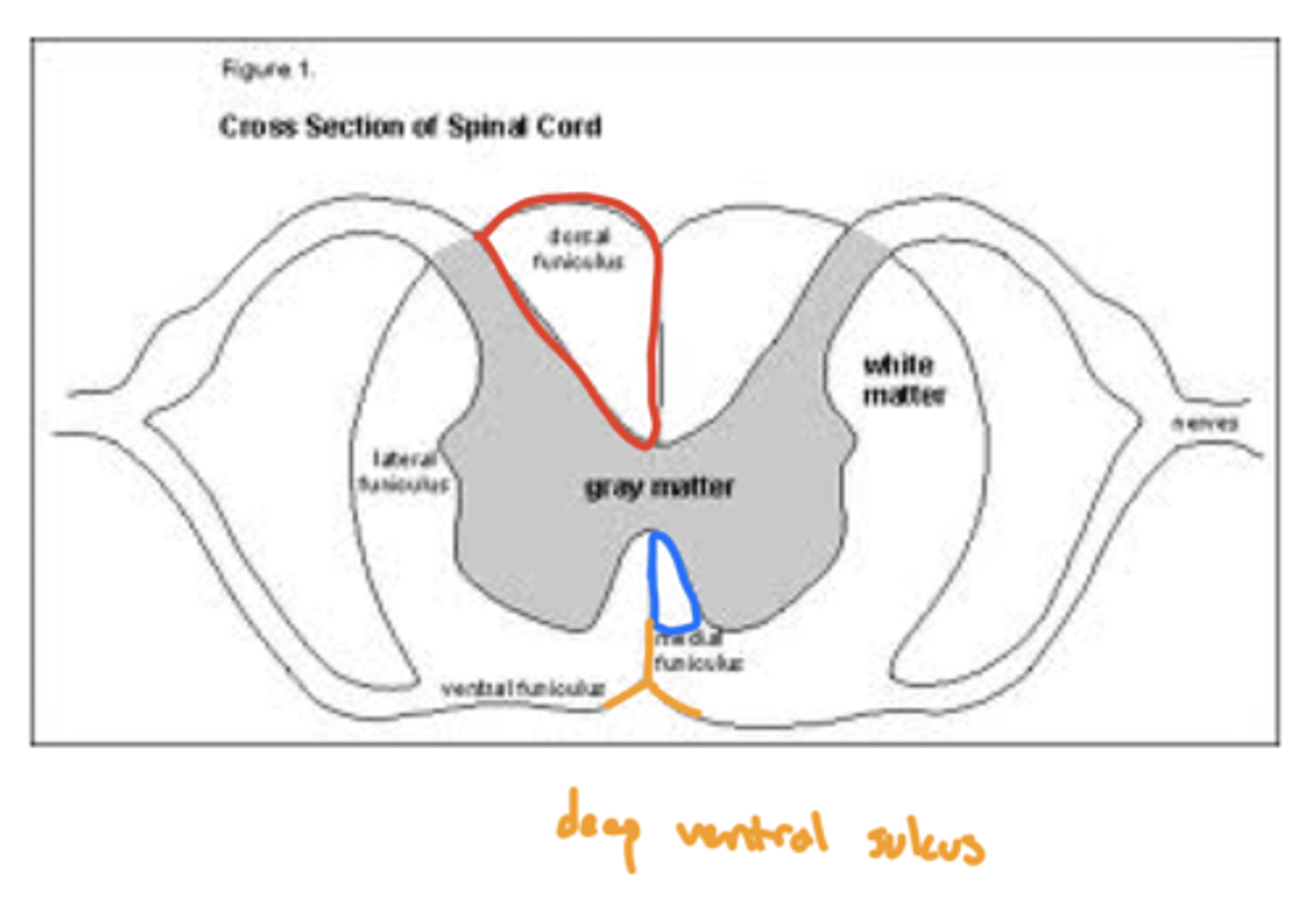
What are the divisions of the white matter in the spinal cord?
funiculi (funiculus)
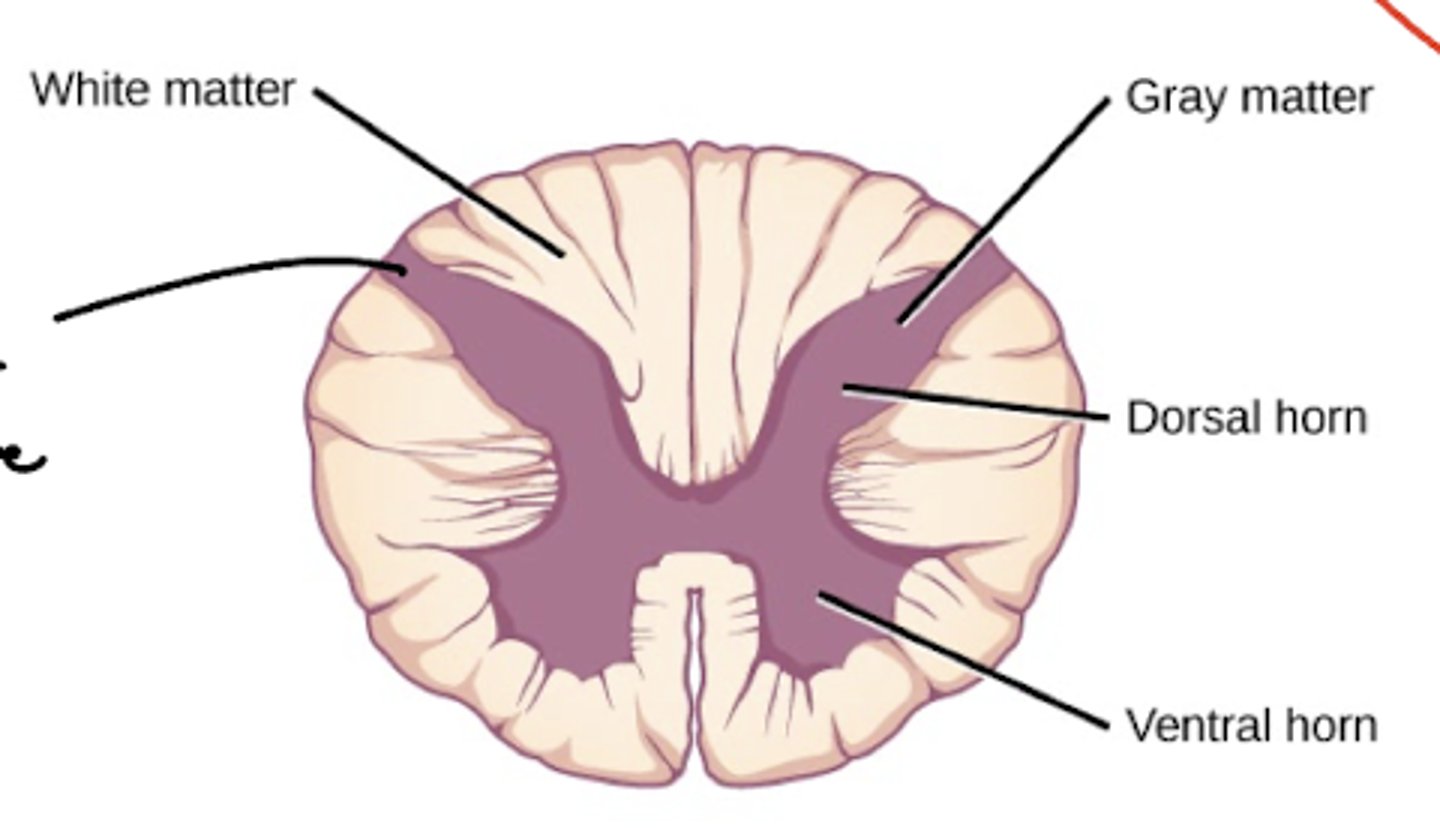
What parts of the spinal cord DON’T have two distinct lateral horns?
1. cervical C1-C8
2. L3-S1
3. S5
Which parts of the spinal cord has three distinct horns?
1. T1-L2 (very obvious)
2. S2-S4 (not very obvious)
ventral, dorsal, and lateral horns
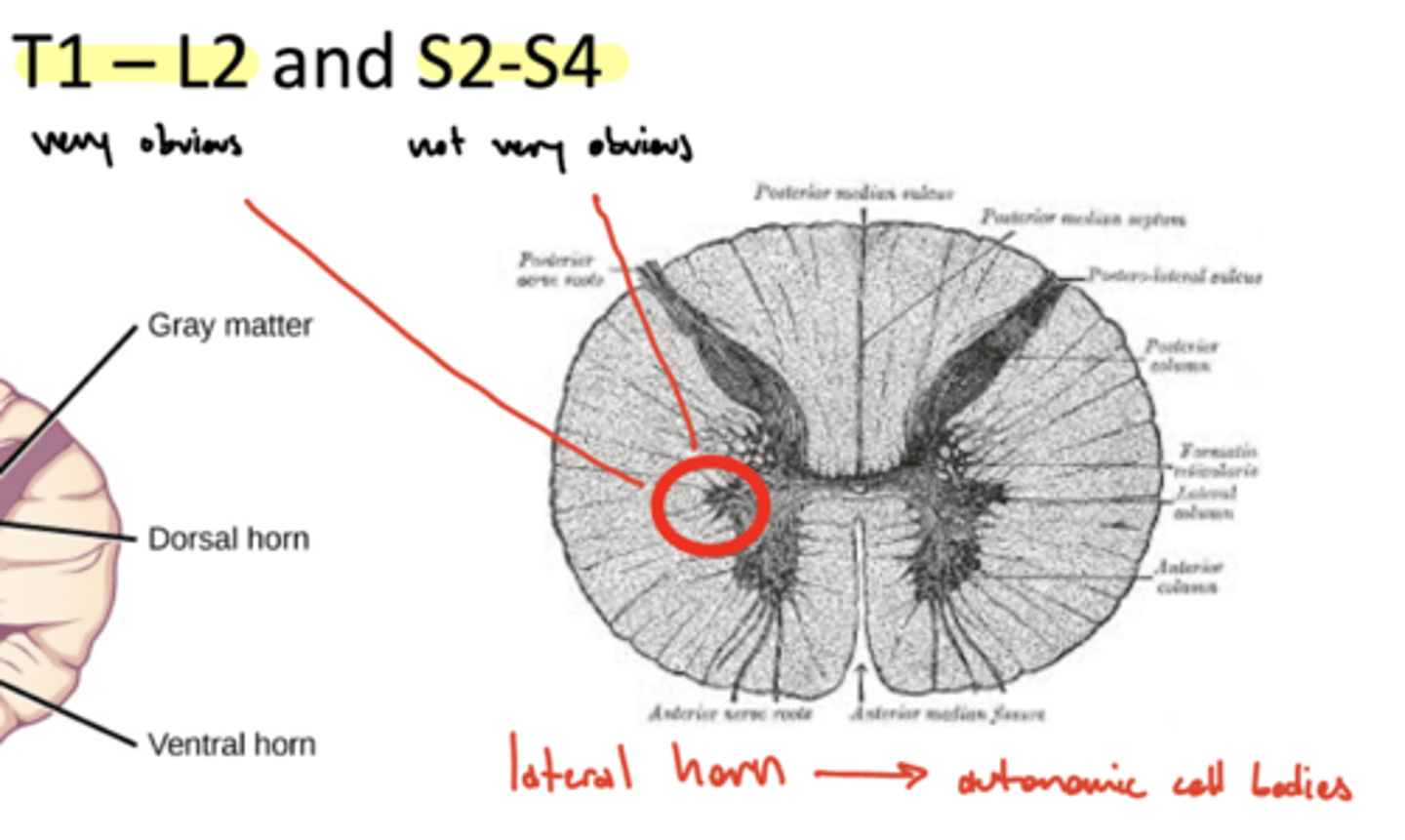
What is the function of the lateral horn of the spinal cord?
autonomic cell bodies -- central component of the ANS
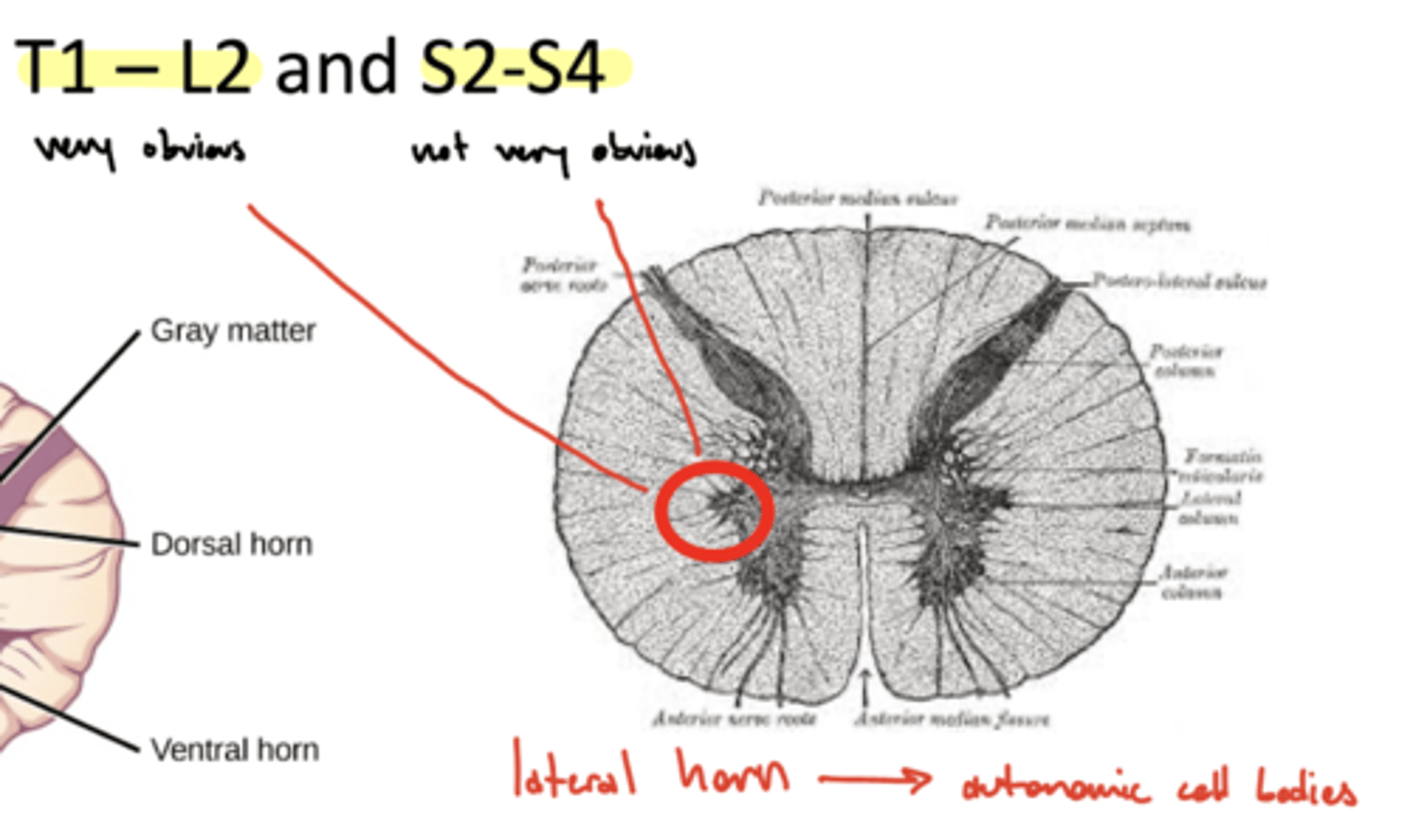
What is another name for the lateral horn of the spinal cord?
intermediate cell column
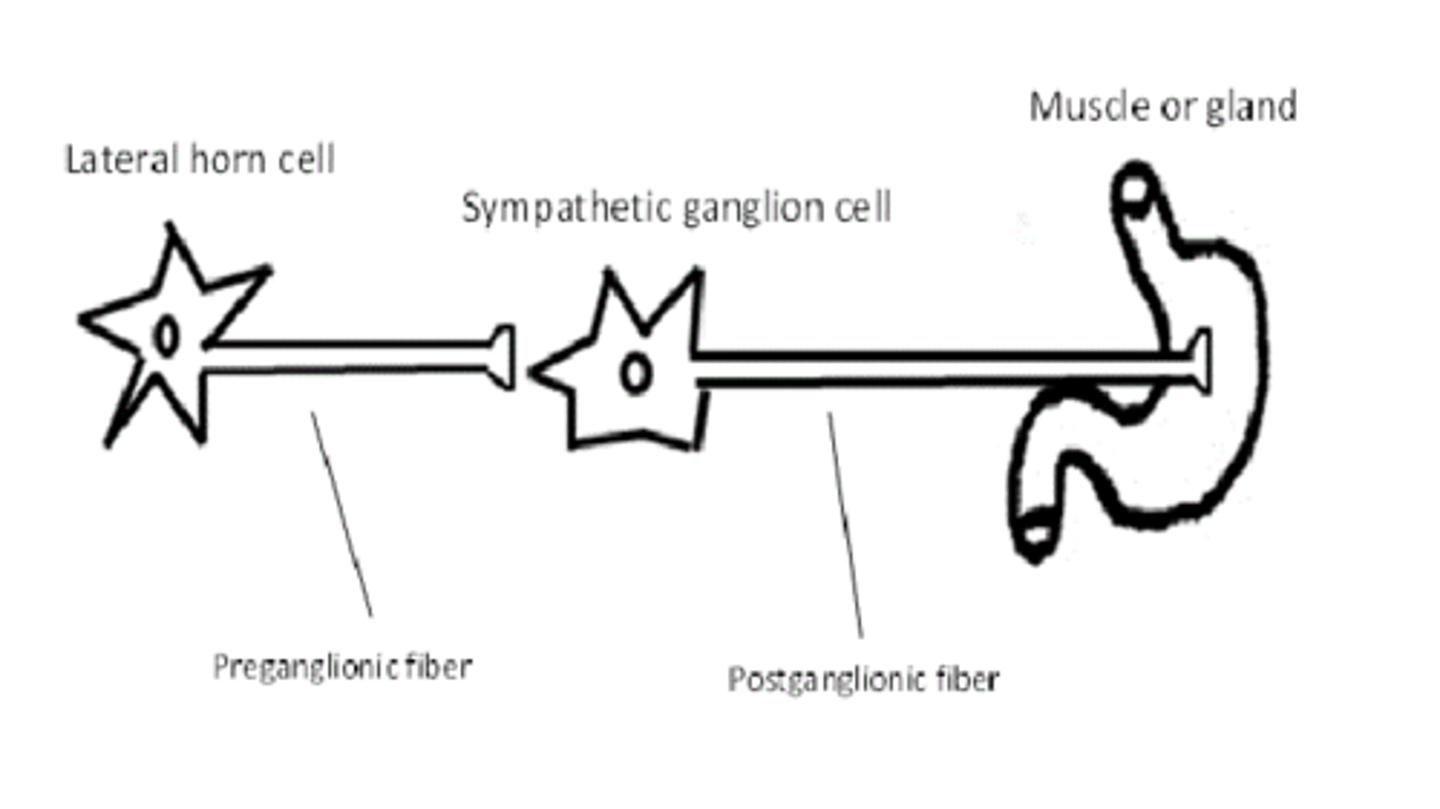
What are the cell bodies of the lateral horn through T1-L2?
sympathetic preganglionic cell bodies
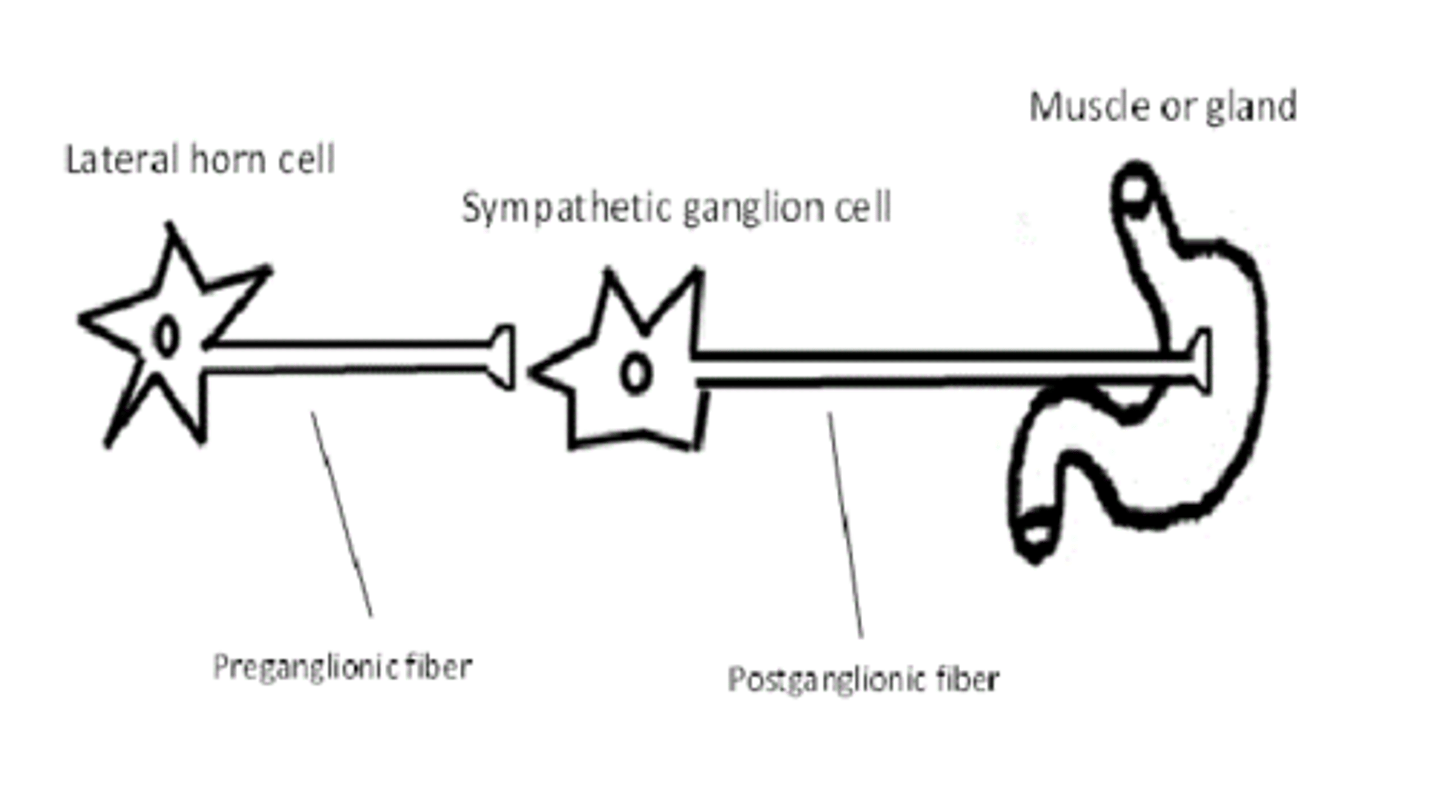
What are the cell bodies of the lateral horn through S2-S4?
parasympathetic preganglionic cell bodies
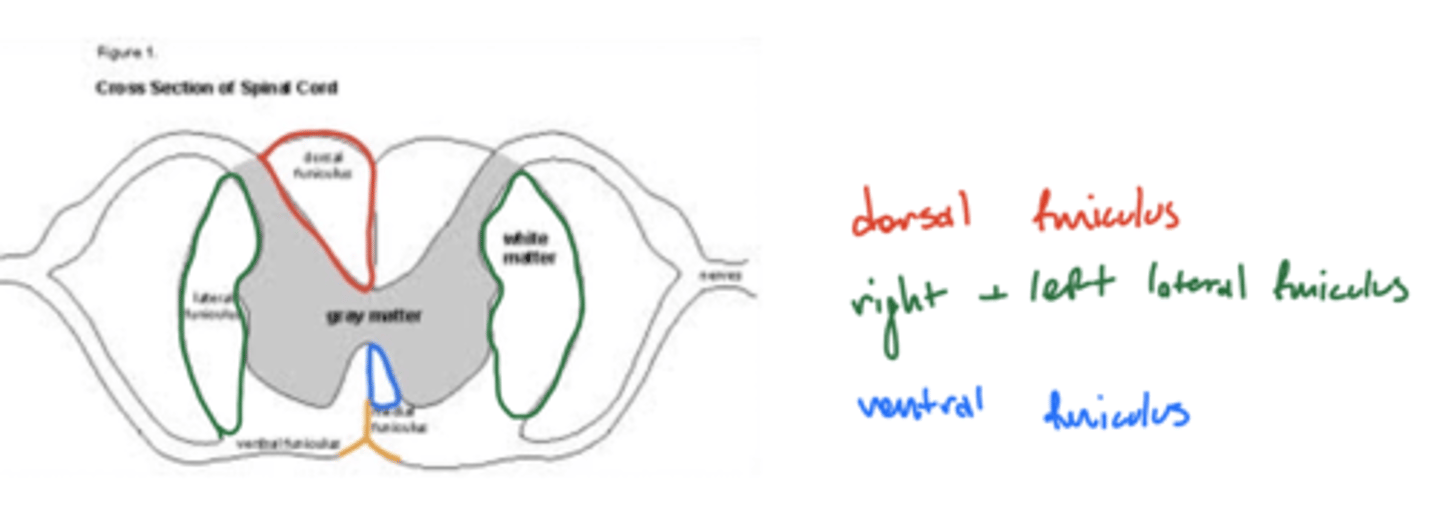
What are the four funiculi of the spinal cord?
1. dorsal funiculus
2. ventral funiculus
3. right lateral funiculus
4. left lateral funiculus
image -- ventral is much smaller, not as much laterally
What are the divisions of the dorsal funiculus?
1. fasciculus gracilis
2. fasciculus cuneatus
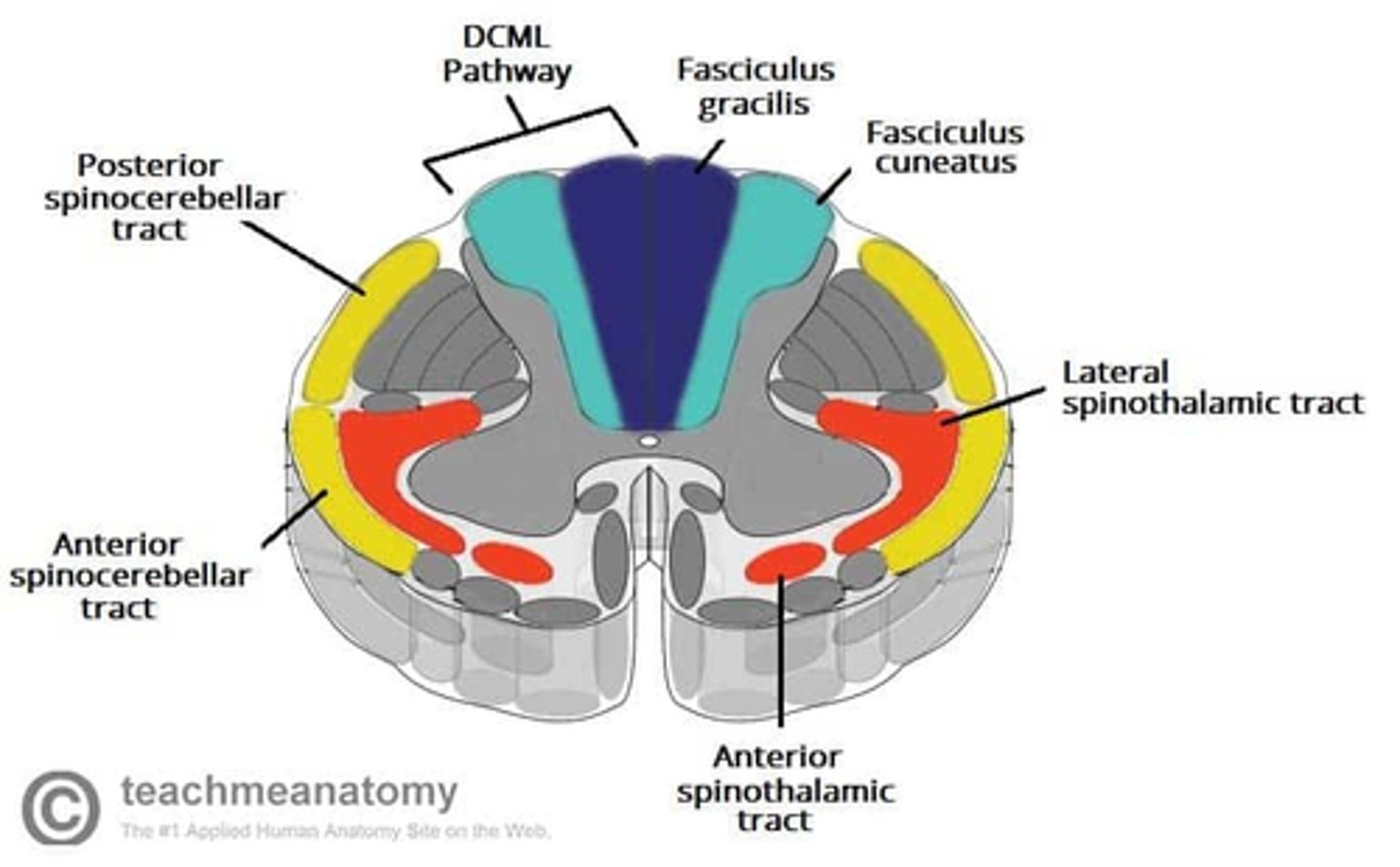
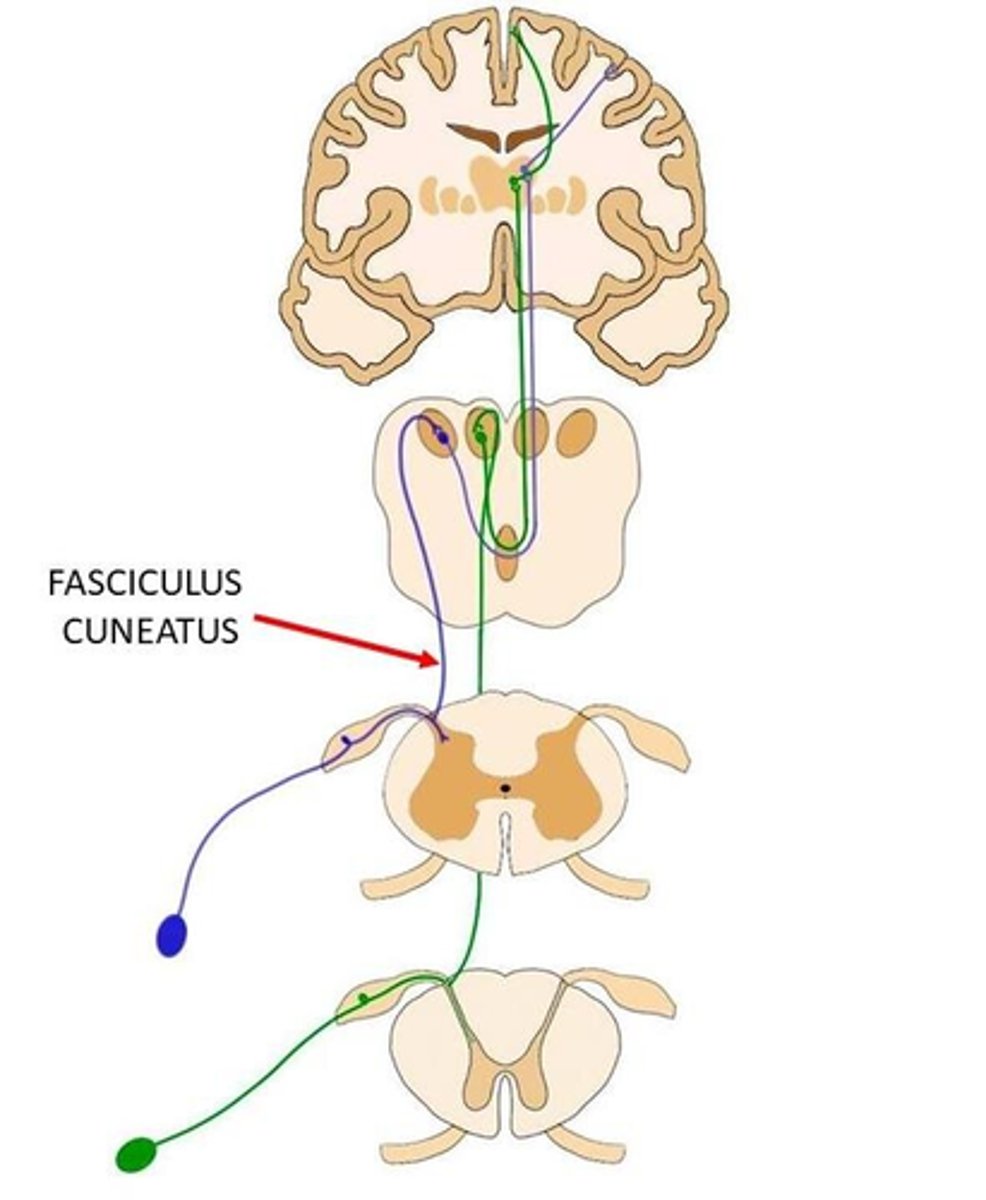
What is the function of the fasciculus gracilis?
ascending (sensory) lower limbs
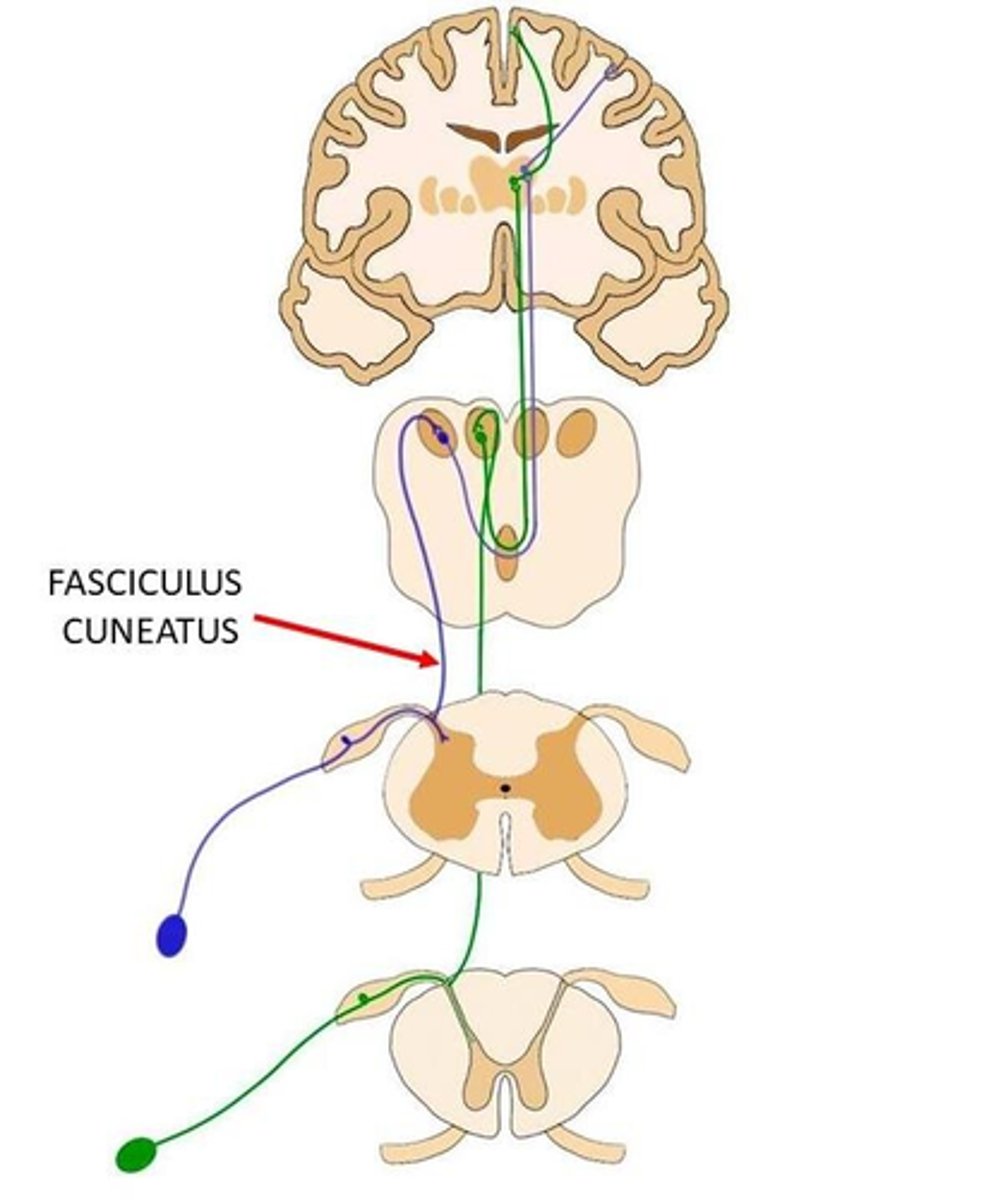
What is the function of the fasciculus cuneatus?
ascending (sensory) upper limbs
What are spinal nerves a fusion of?
1. ventral root (motor)
2. dorsal root (sensory)
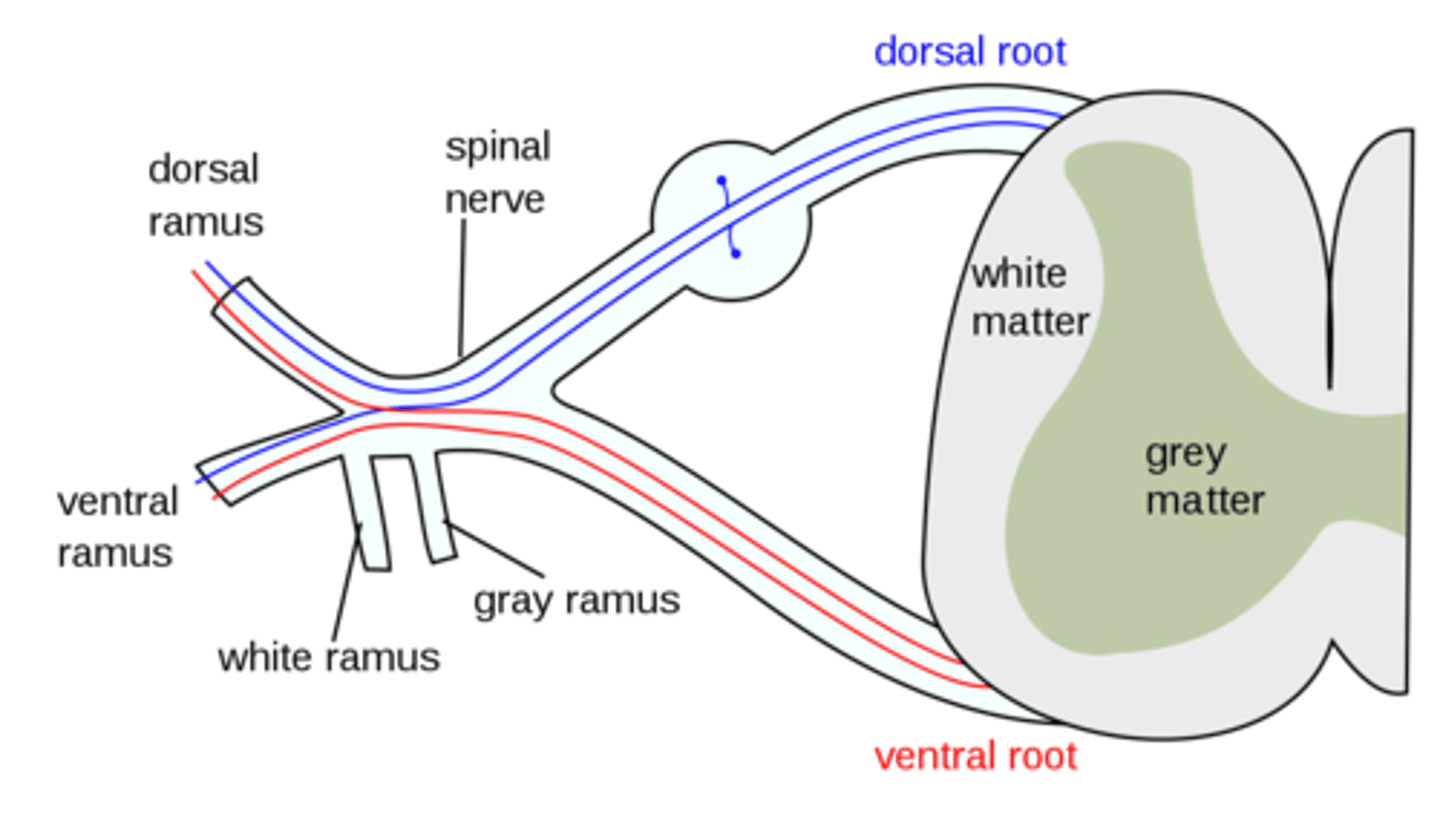
Which ANS innervation does white and gray rami (communicans) carry?
sympathetic innervation
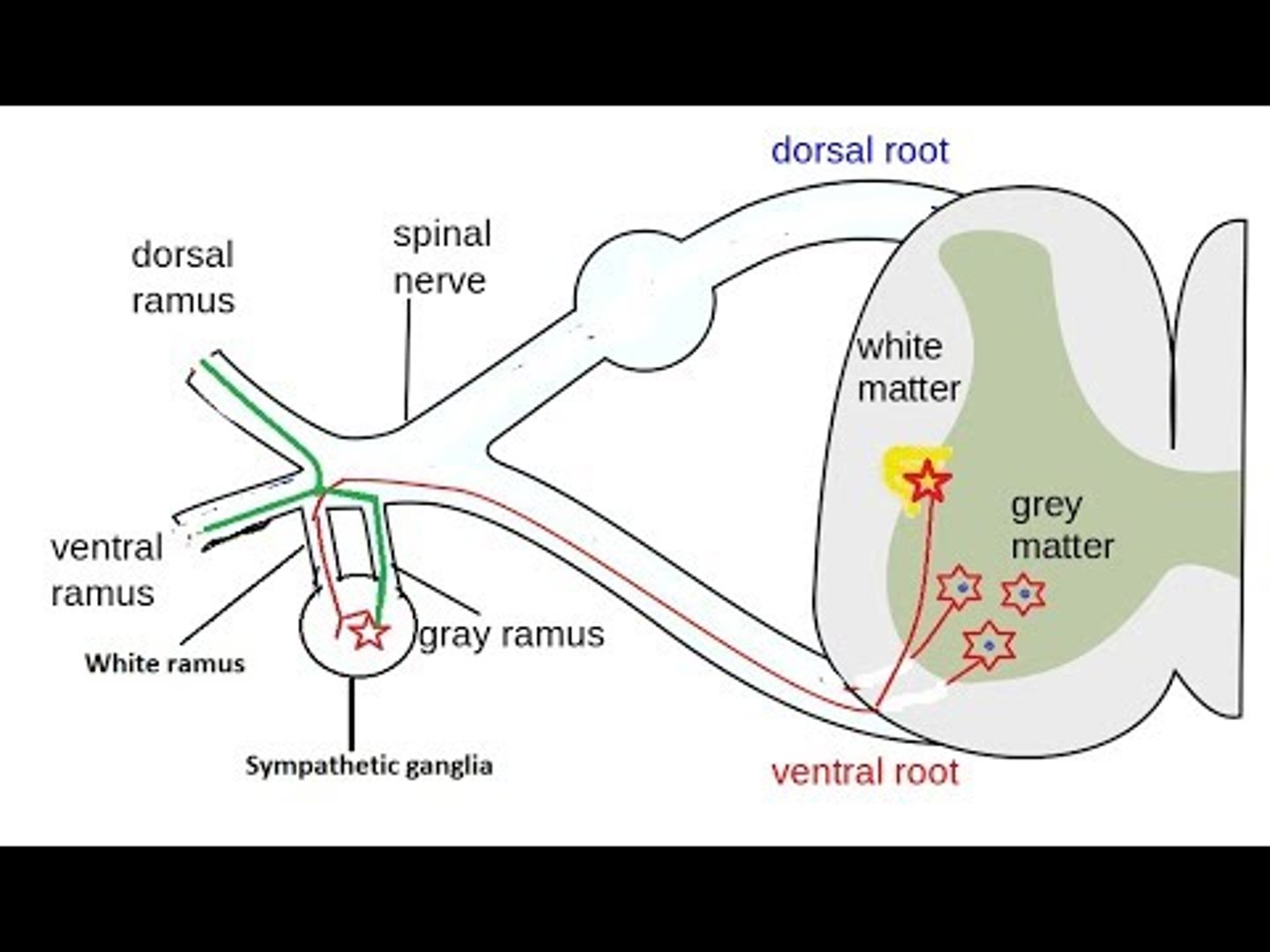
What do gray rami (functionally) connect?
sympathetic chain ganglion to target tissue (postganglionic) (entire spinal cord)
image -- dotted lines
What do white rami (functionally) connect?
spinal cord to chain ganglion
image -- solid lines (T1 - L2)
Does gray rami (communicans) carry preganglionic or postganglionic fibers?
postganglionic
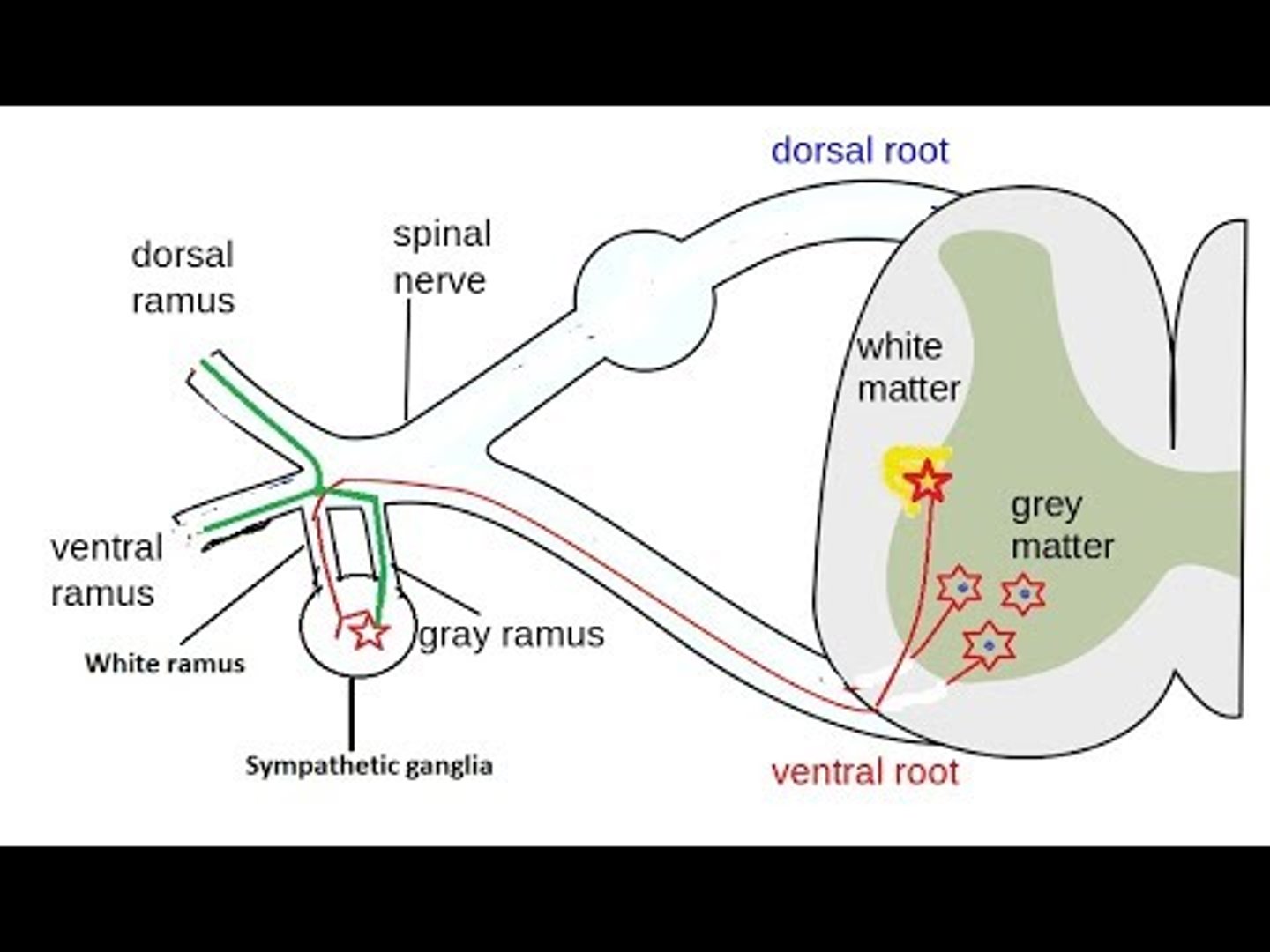
Does the white rami (communicans) carry preganglionic or postganglionic fibers?
preganglionic
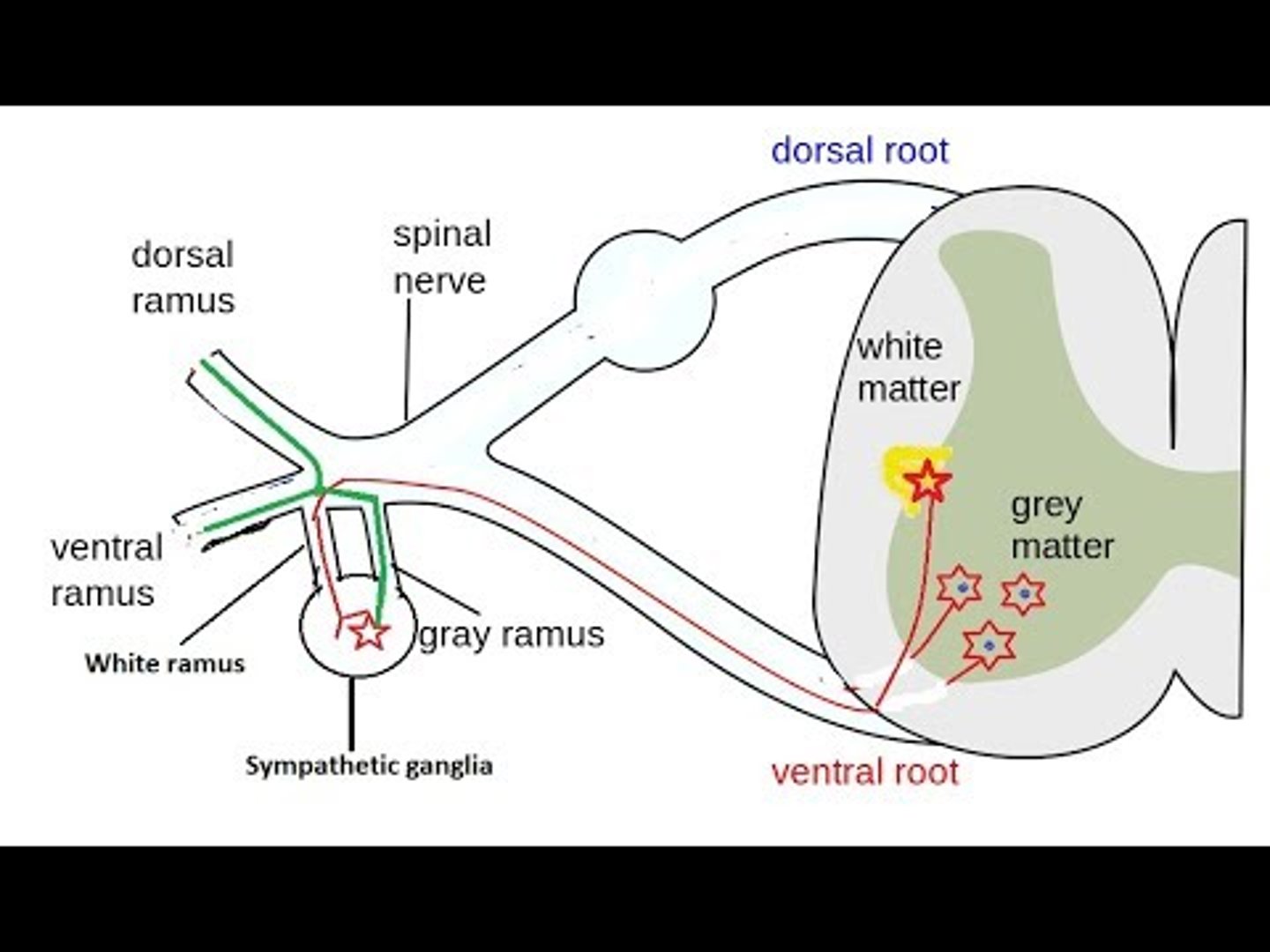
Where are the cell bodies of the gray rami (communicans) located?
sympathetic chain ganglion, or paravertebral
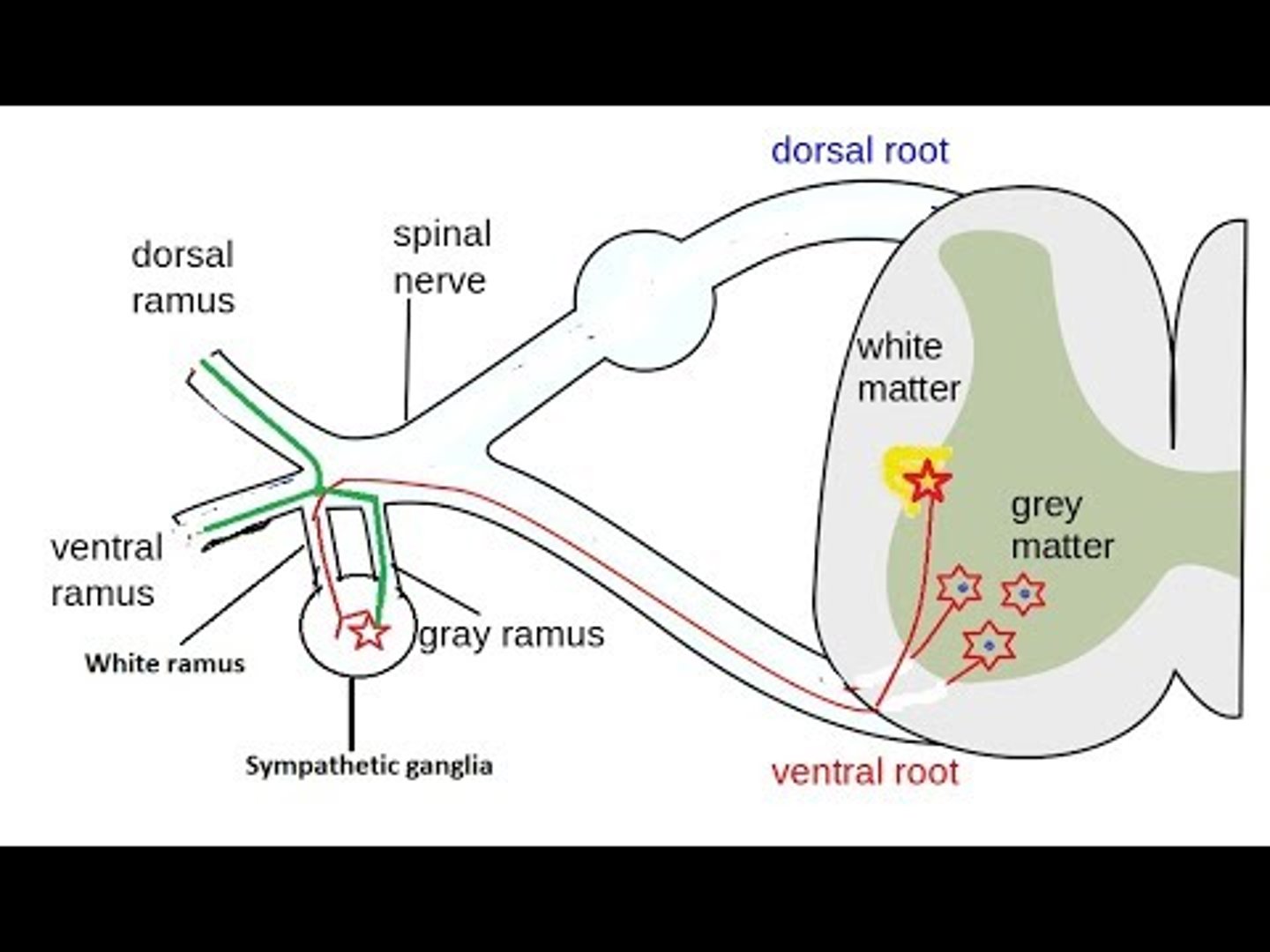
Where are the cell bodies of the white rami (communicans) located?
gray matter of the spinal cord (lateral horn T1-S2)
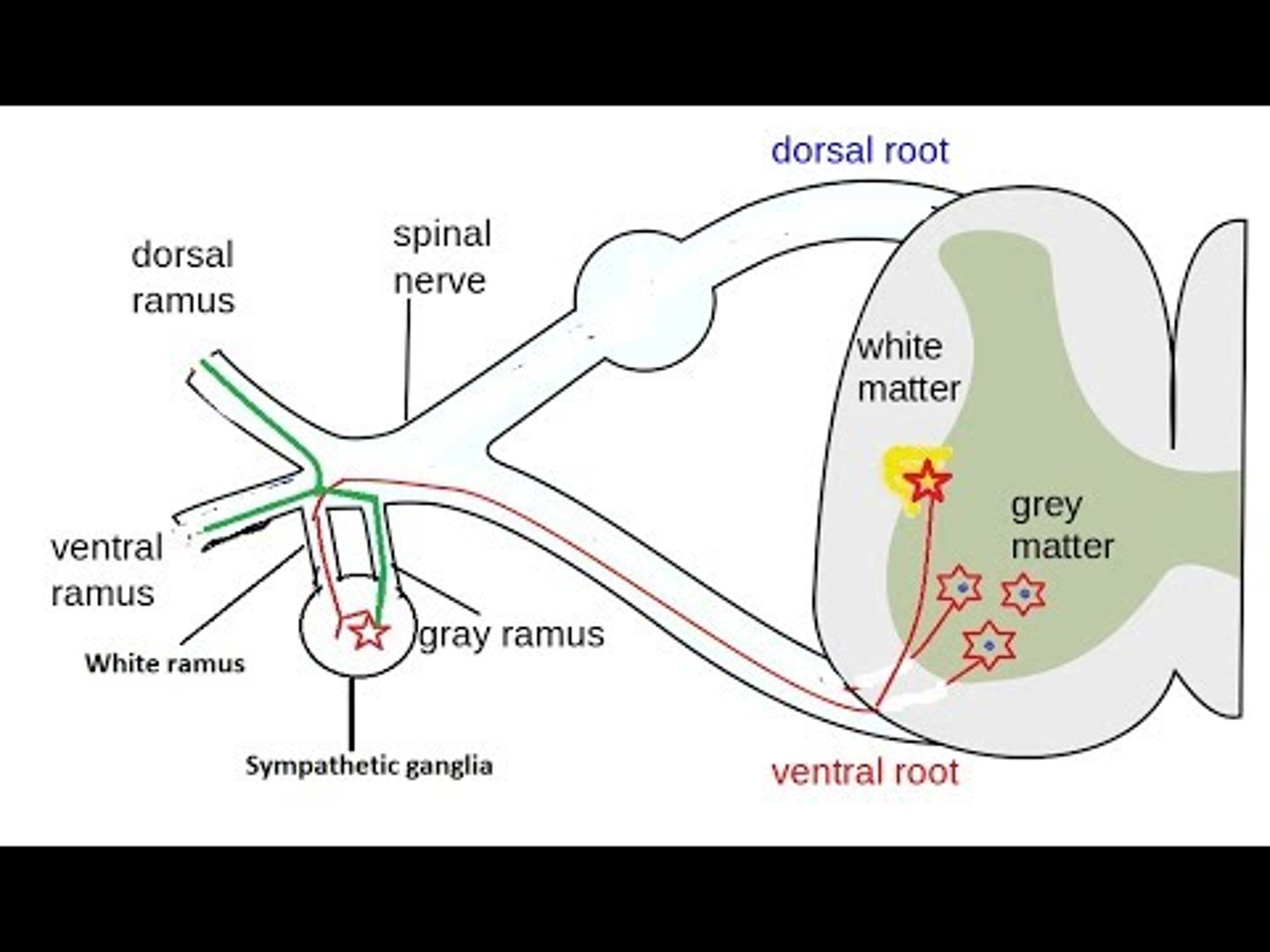
Where (level of spinal cord) are gray rami located?
whole spinal cord
why? -- postganglionic sympathetic fibers can exit everywhere!
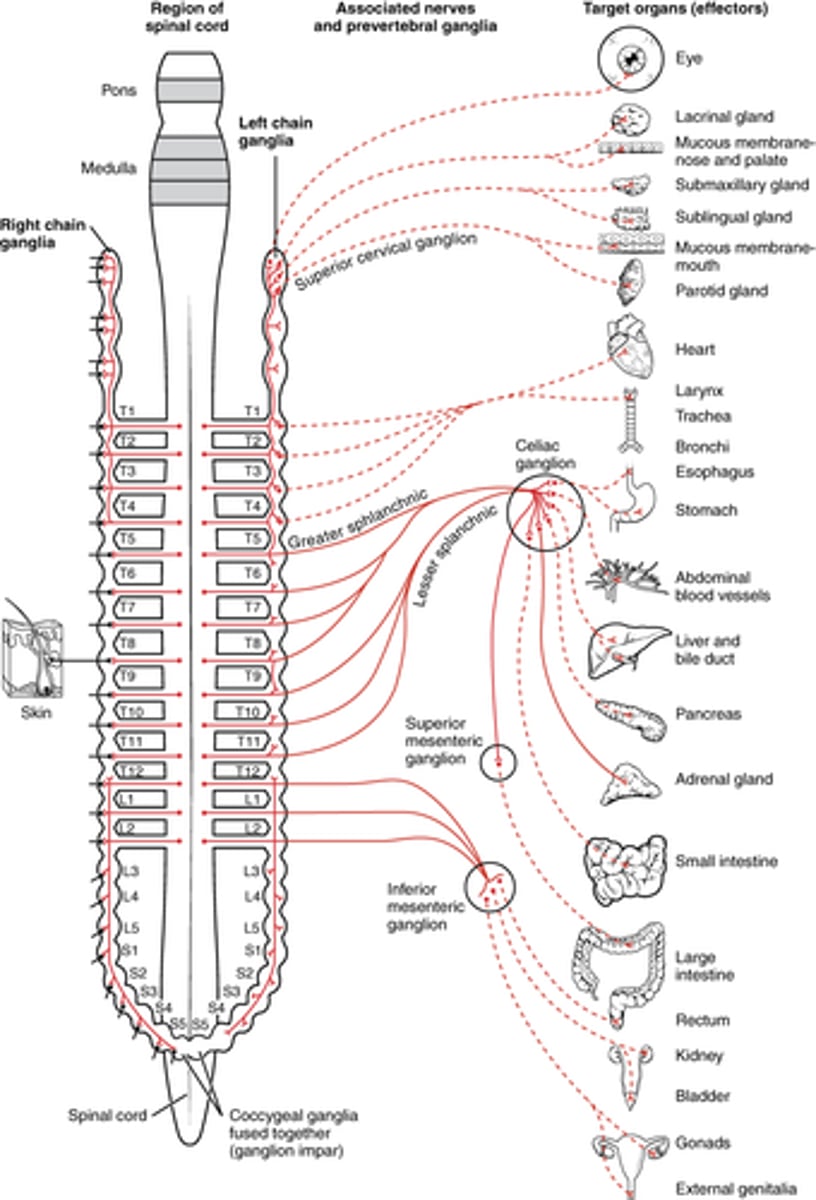
Where (level of spinal cord) are white rami located?
T1 - L2
why? -- where preganglionic exit the spinal cord
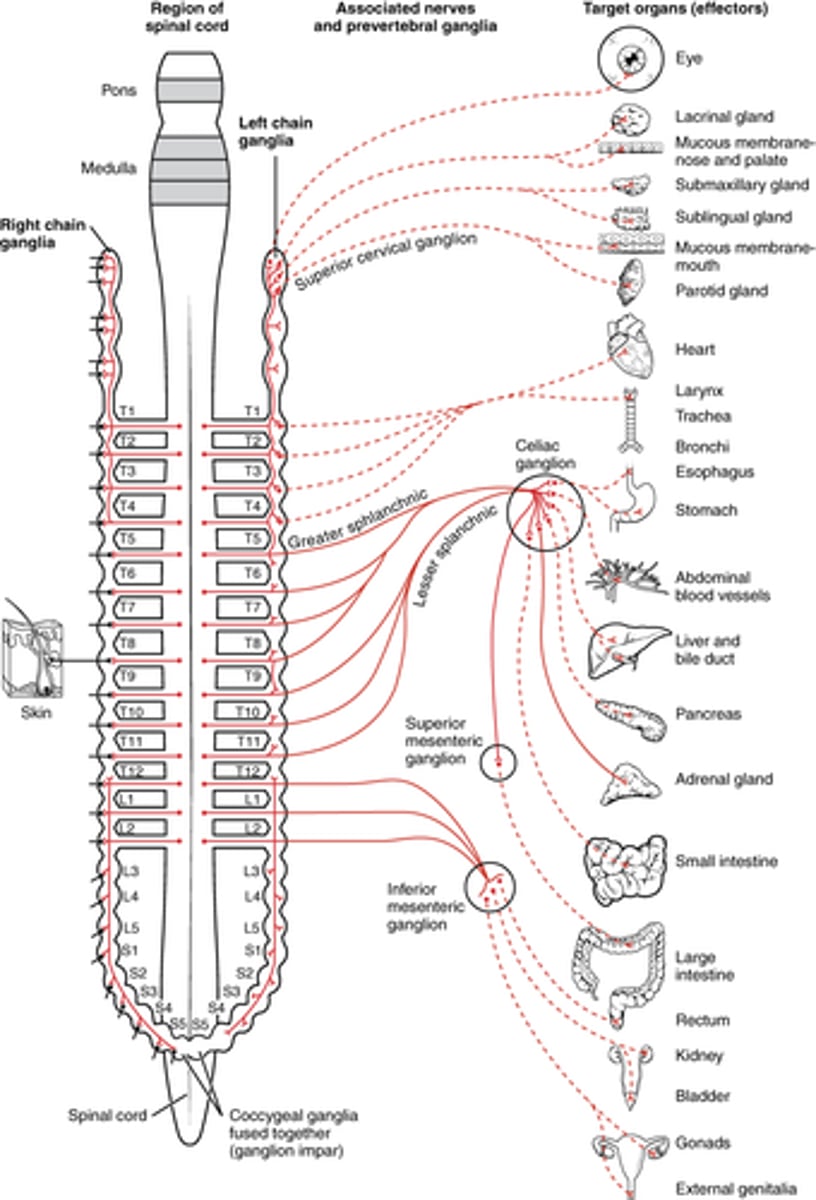
Where can postganglionic sympathetic fibers exit sympathetic chain?
everywhere! -- sympathetic chain
image -- dotted is postganglionic
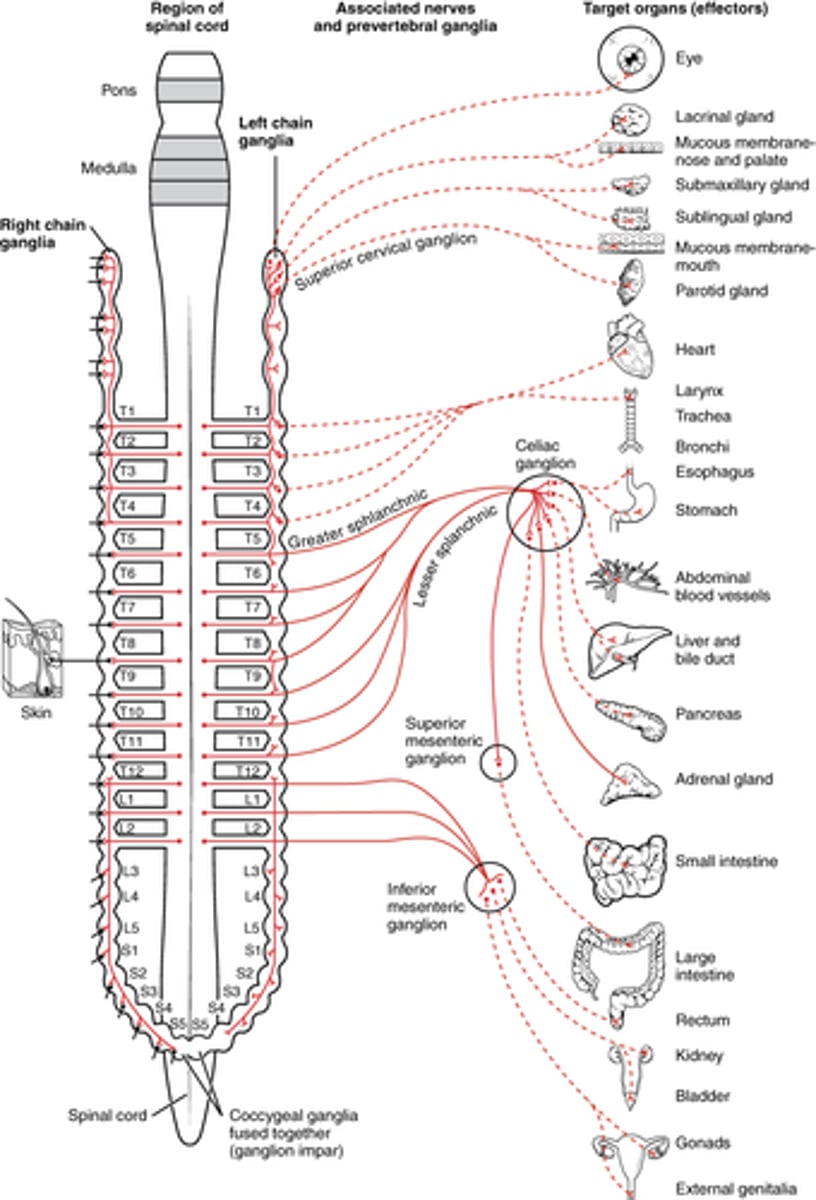
Where can preganglionic sympathetic fibers exit the spinal cord?
T1 - L2
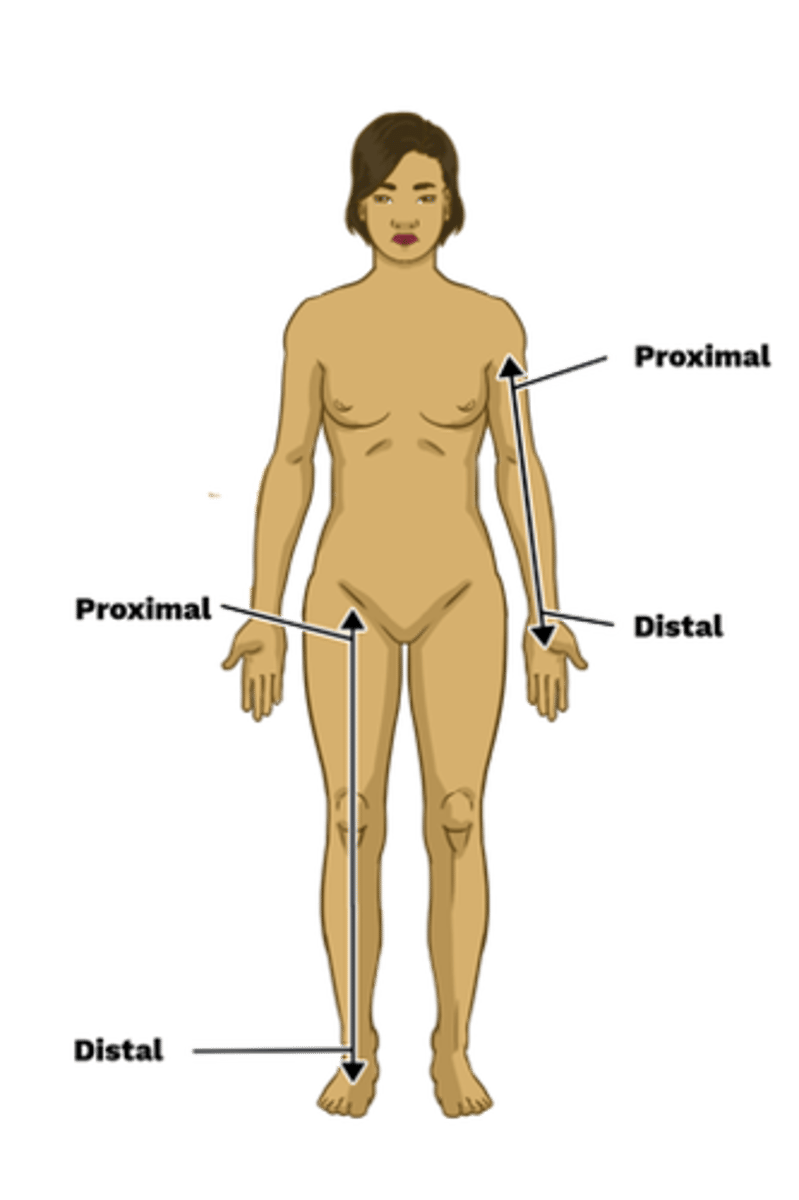
What is the difference between proximal and distal?
proximal means closer to the origin, while distal means further away
Why are the gray and white rami those colors?
gray rami (postganglionic) -- unmyelinated
white rami (preganglionic) -- myelinated
Where do the preganglionic sympathetic nerves synapse in relation to what they innervate and why?
nerve synapses where the nerve is impacting (i.e. whatever structure it innervates)
for example... preganglionic may enter at T1, but synapse (postganglionic) at the sympathetic ganglion near C6 for the arms
What do spinal nerves bifurcate into?
1. ventral primary ramus (larger)
2. dorsal primary ramus
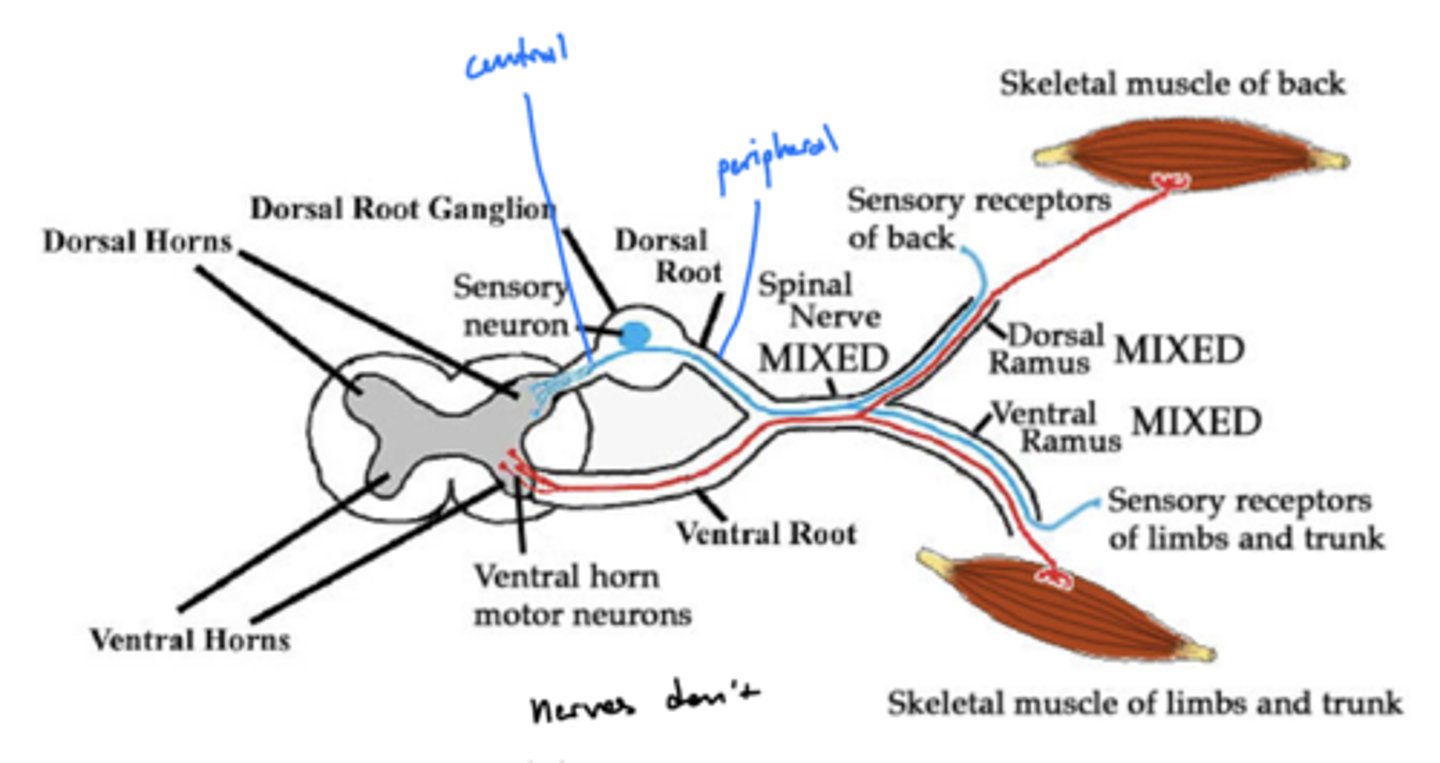
What does the ventral ramus nerves innervate?
skeletal muscles of limbs and trunk
What does the dorsal ramus nerves innervate?
GSE, GSA, and sympathetics of the back and the back of the head
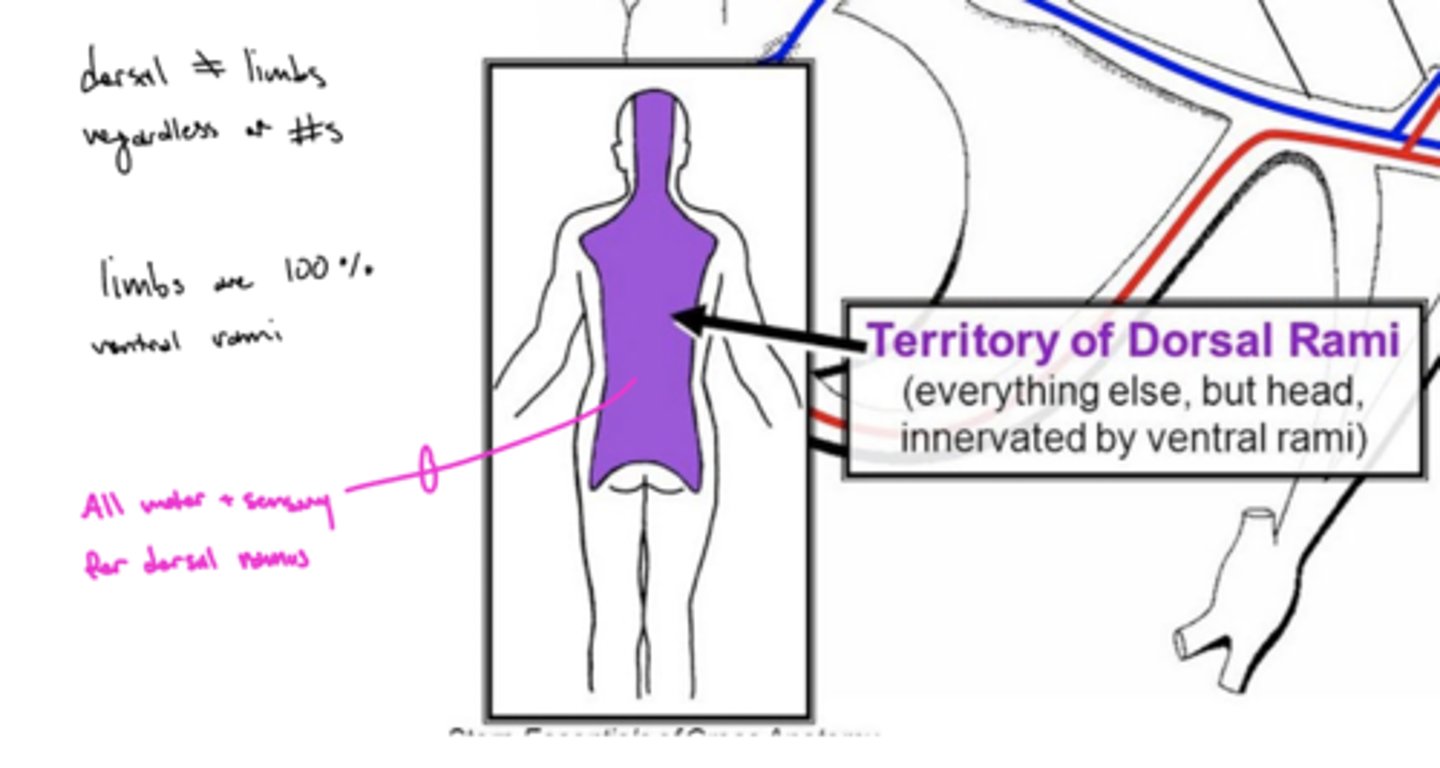
What type of sensations (motor, touch, ANS, etc.) do the ventral/dorsal rami carry?
1. motor (GSA)
2. sensory (GSE)
3. sympathetic
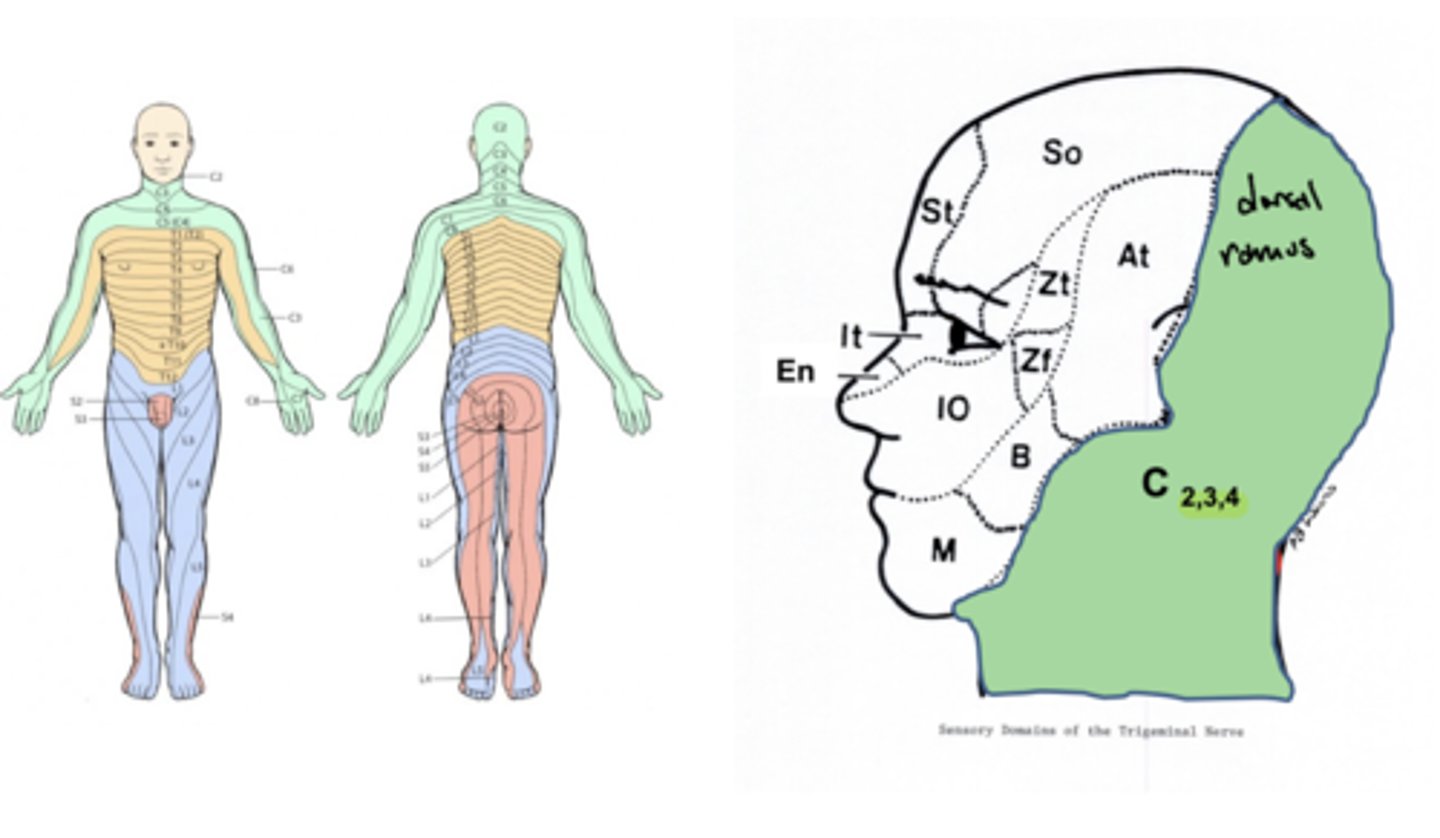
How does sympathetic innervation reach the distal regions (extremities) of the body?
along ventral/dorsal rami from the spinal cord
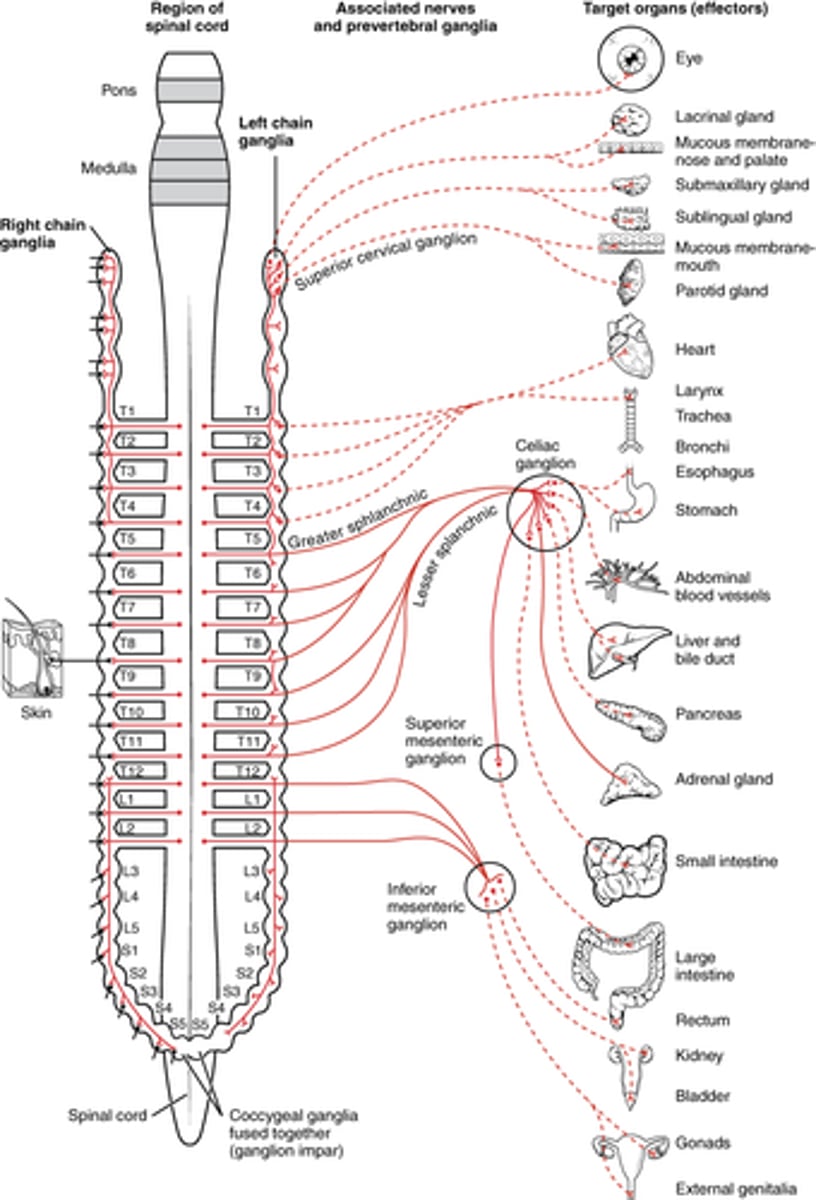
How does parasympathetic innervation reach the distal regions (extremities) of the body?
1. cranial nerves
2. pelvic splanchnic efferent preganglionic nerve cell bodies
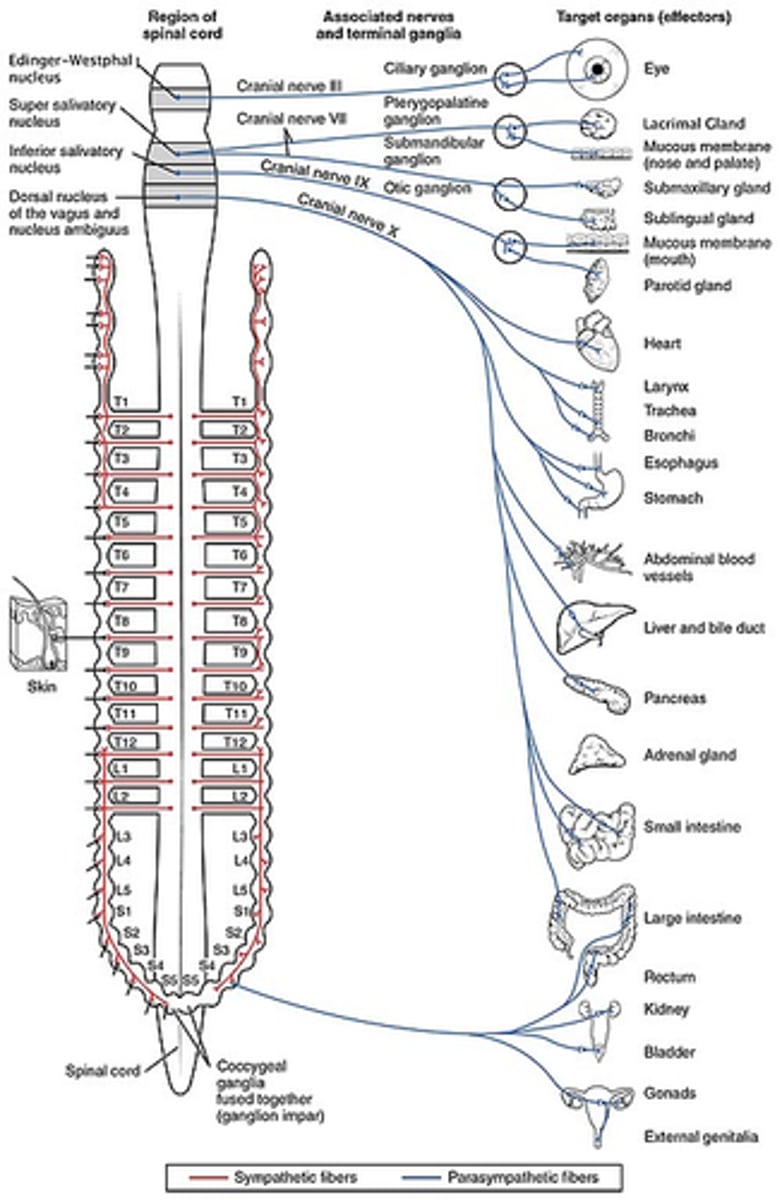
What are the peripheral nerves of the body?
1. all spinal nerves (another name)
2. CN III - XII (3-12)
What are all of the cranial nerves?
1. Olfactory
2. Optic
3. Oculomotor
4. Trochlear
5. Trigeminal
6. Abducens
7. Facial
8. Vestibulocochlear
9. Glossopharyngeal
10. Vagus
11. Spinal Accessory
12. Hypoglossal
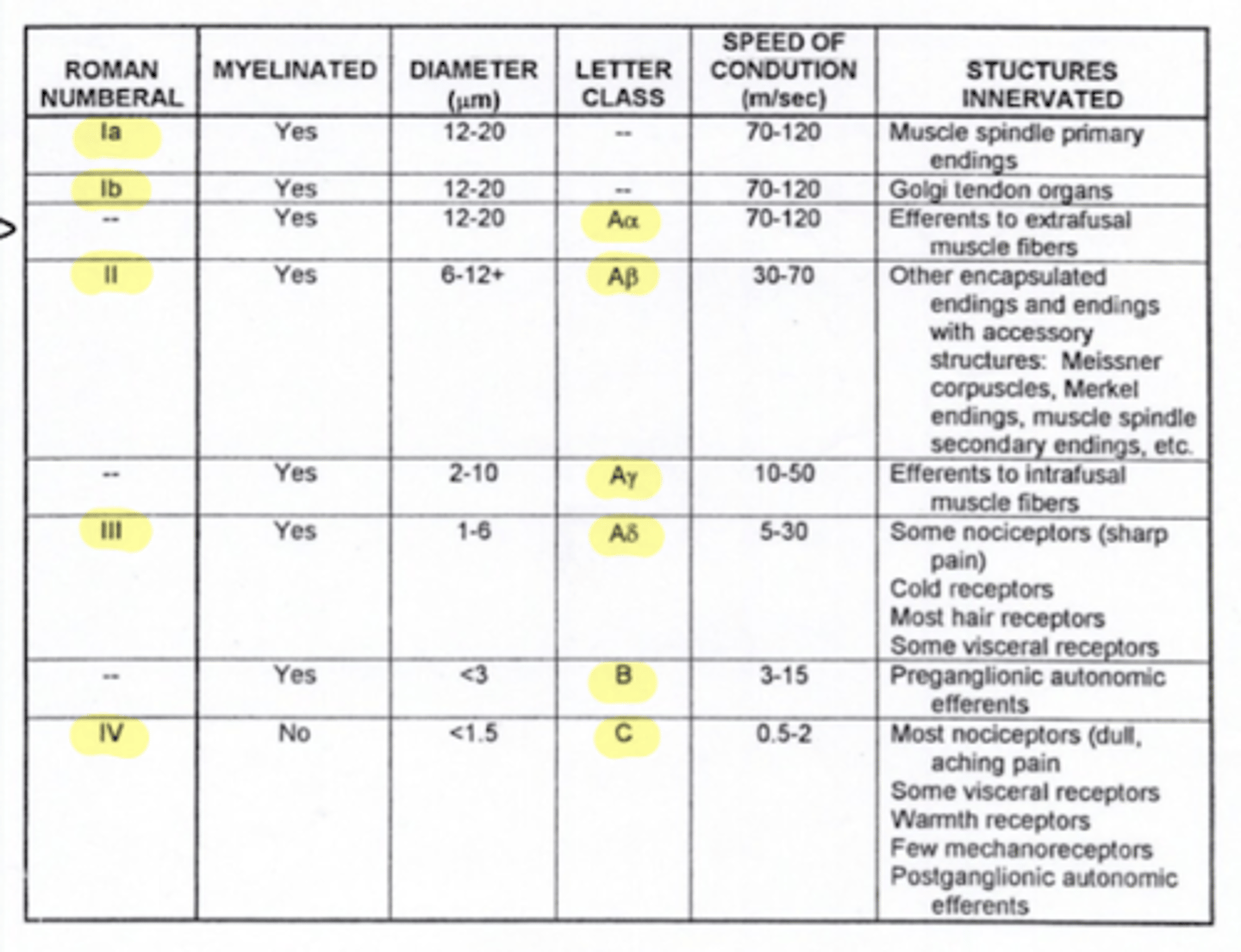
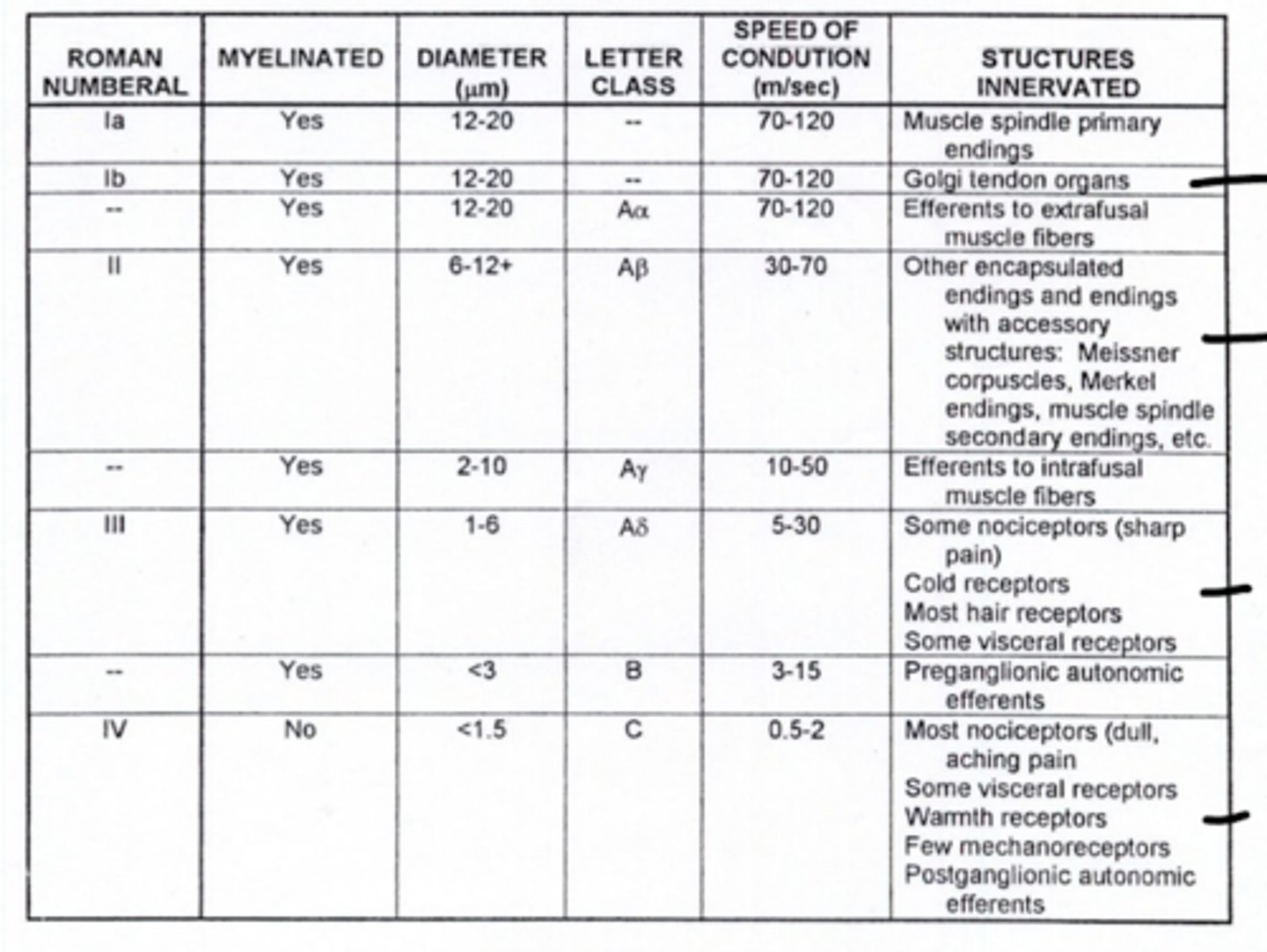
What is the fiber type of alpha motor neurons (lower motor neuron)?
Aα
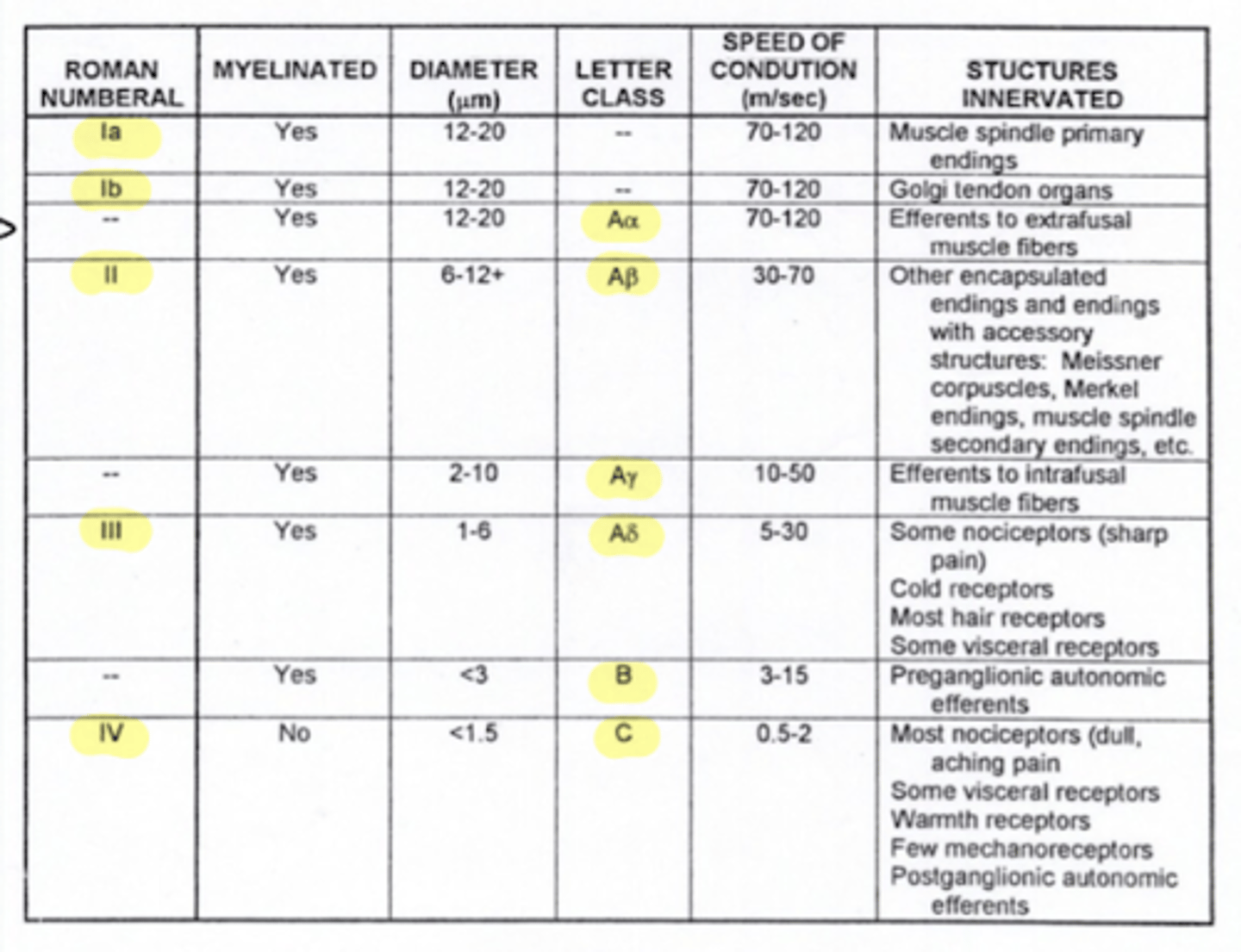
Where are Aα fibers located?
efferent to extrafusal muscle fibers (lower motor neurons or alpha motor neurons)
What does extrafuscle mean?
when fired, muscle shortens and moves bones
What is the alpha motor unit?
a population of muscle fibers that are innervated by a single alpha motor neuron (AMN)
1. one motor neuron
2. many muscle fibers
smaller motor unit = precision movement
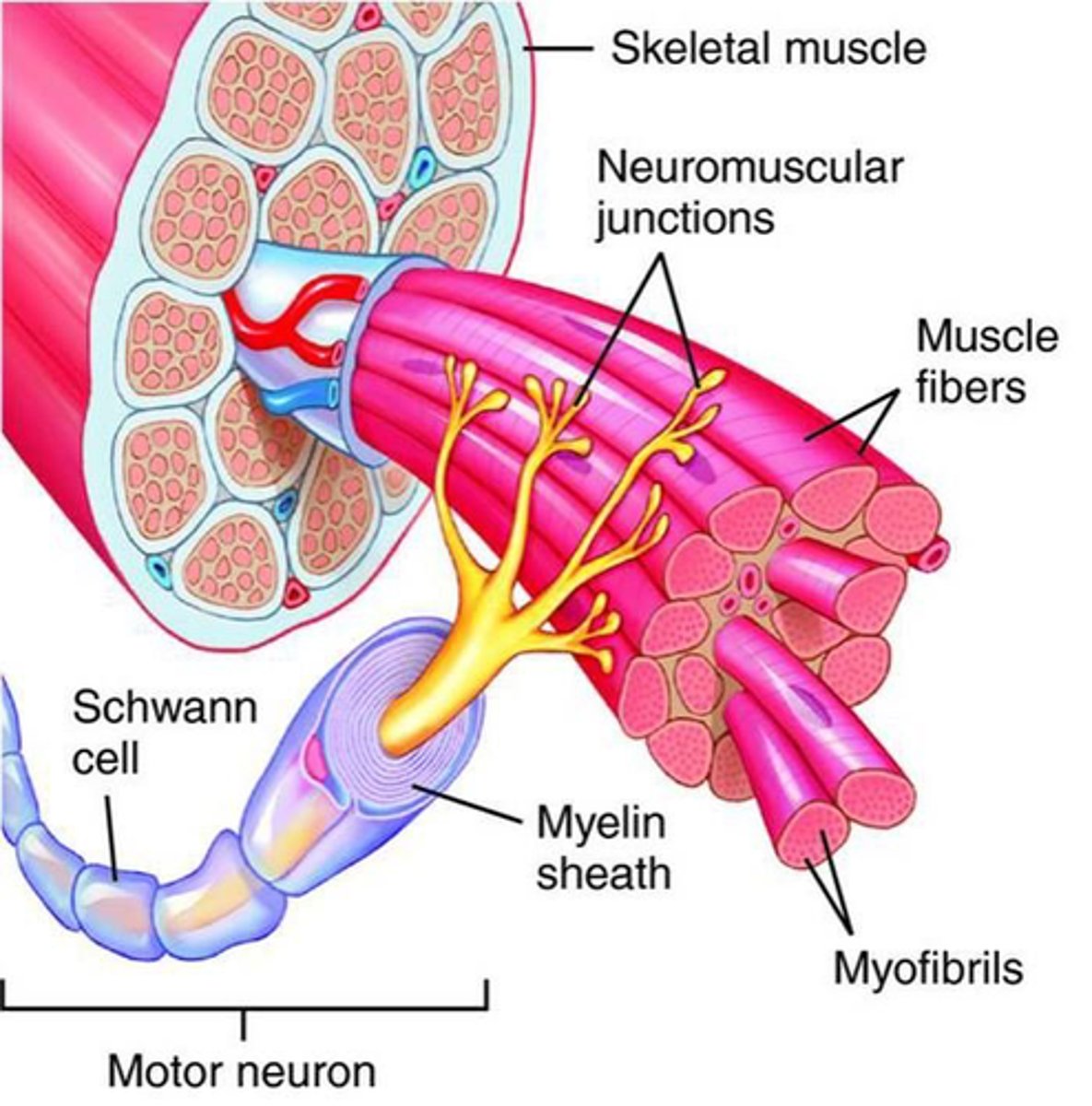
What does it mean to talk about alpha motor size?
how many fibers a motor unit innervates
What determines the size of an alpha motor unit?
size of the homunculus for that organ
face = huge = small size = many alpha motor neurons = precise
legs = small = large size = few alpha motor neurons = not precise
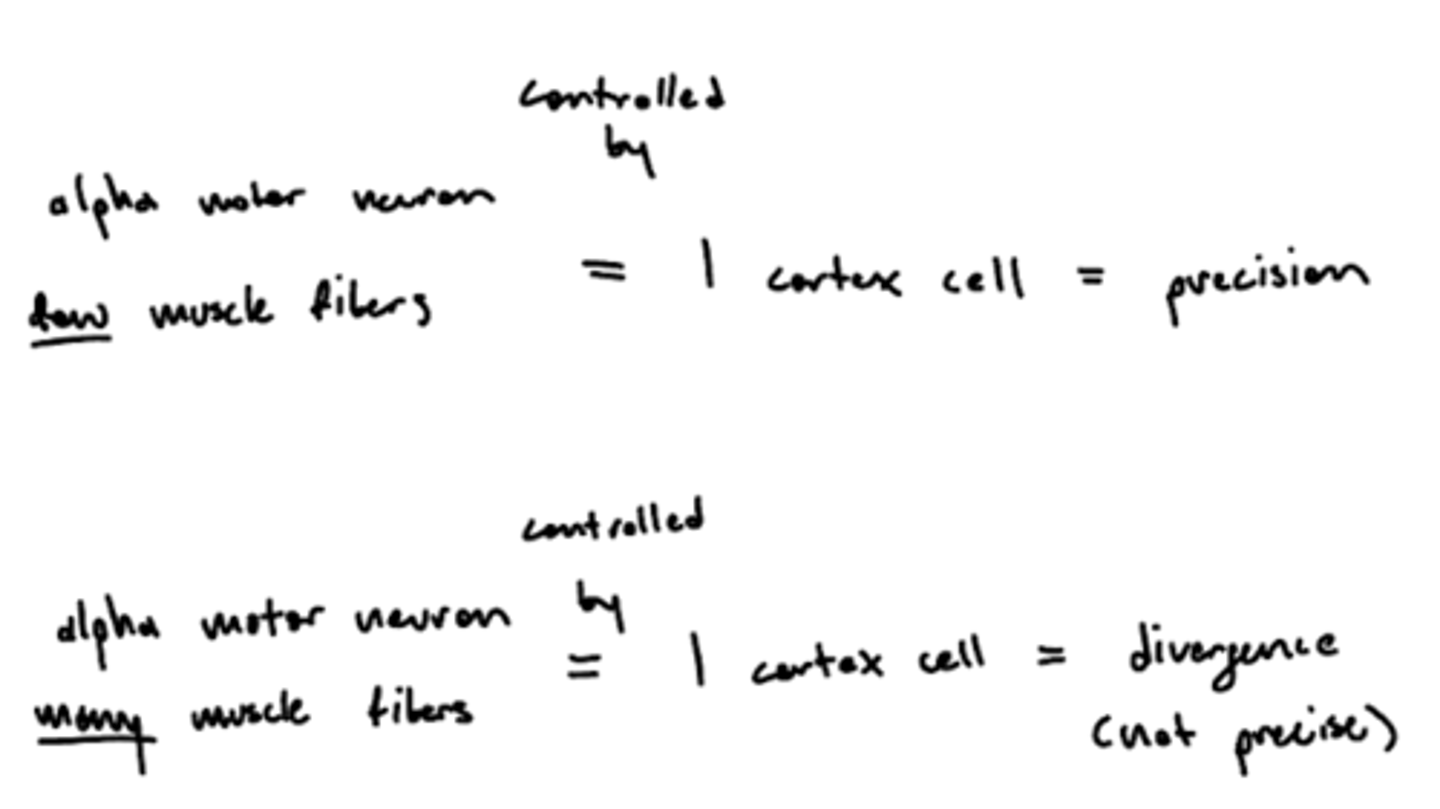
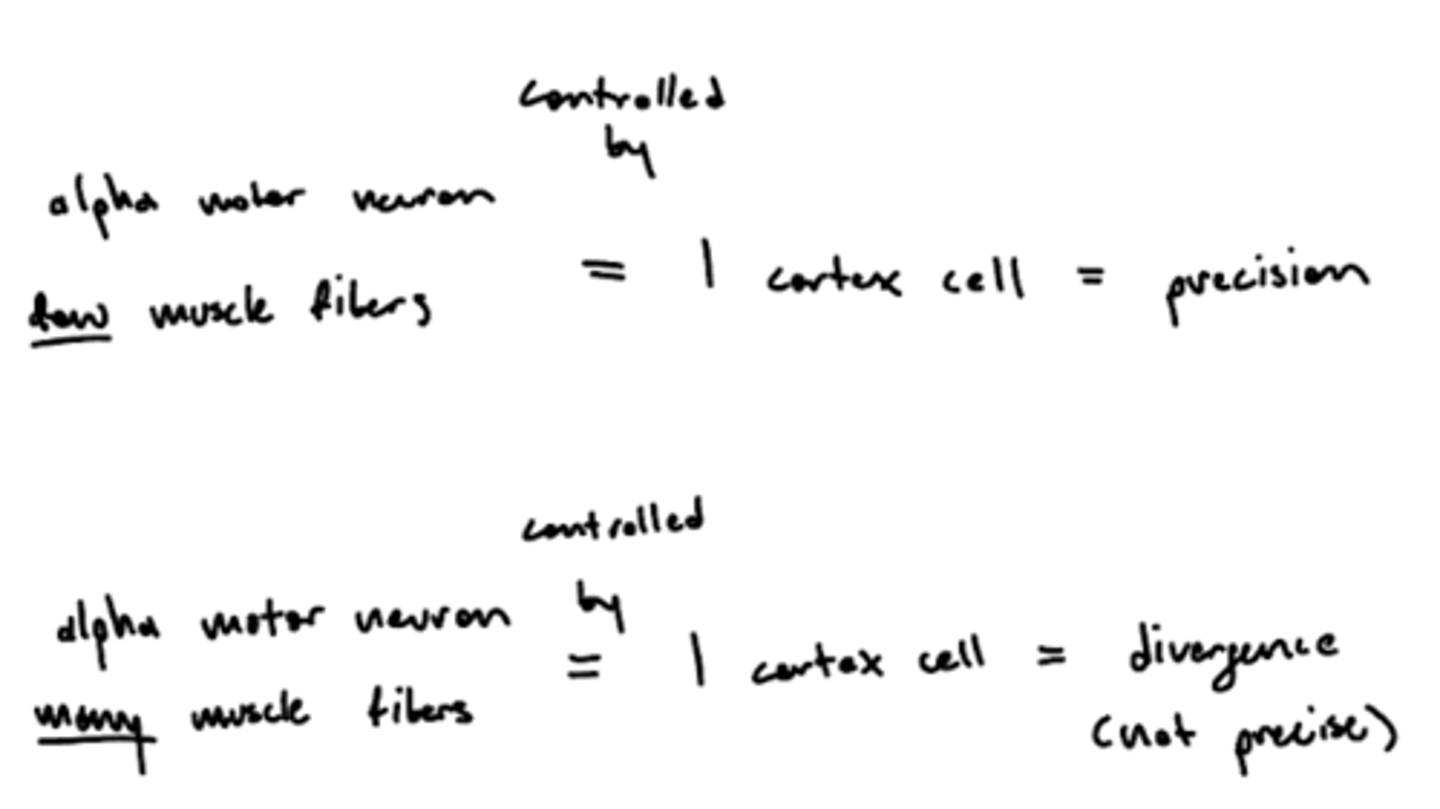
Why are smaller alpha motor units more precise?
1 cortex cell controls 1 alpha motor unit, fewer muscle fibers (smaller alpha motor unit) innervated allow for precise movement
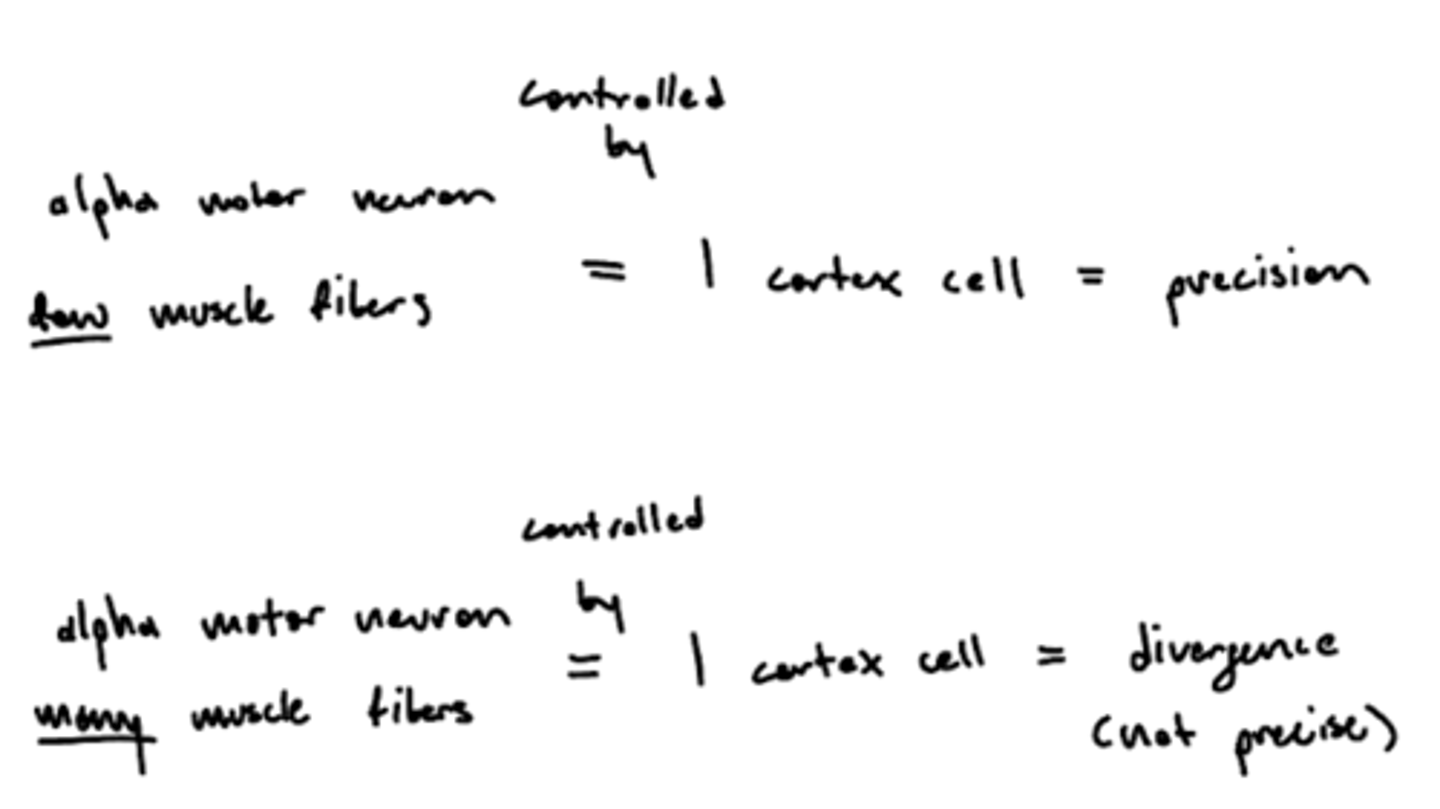
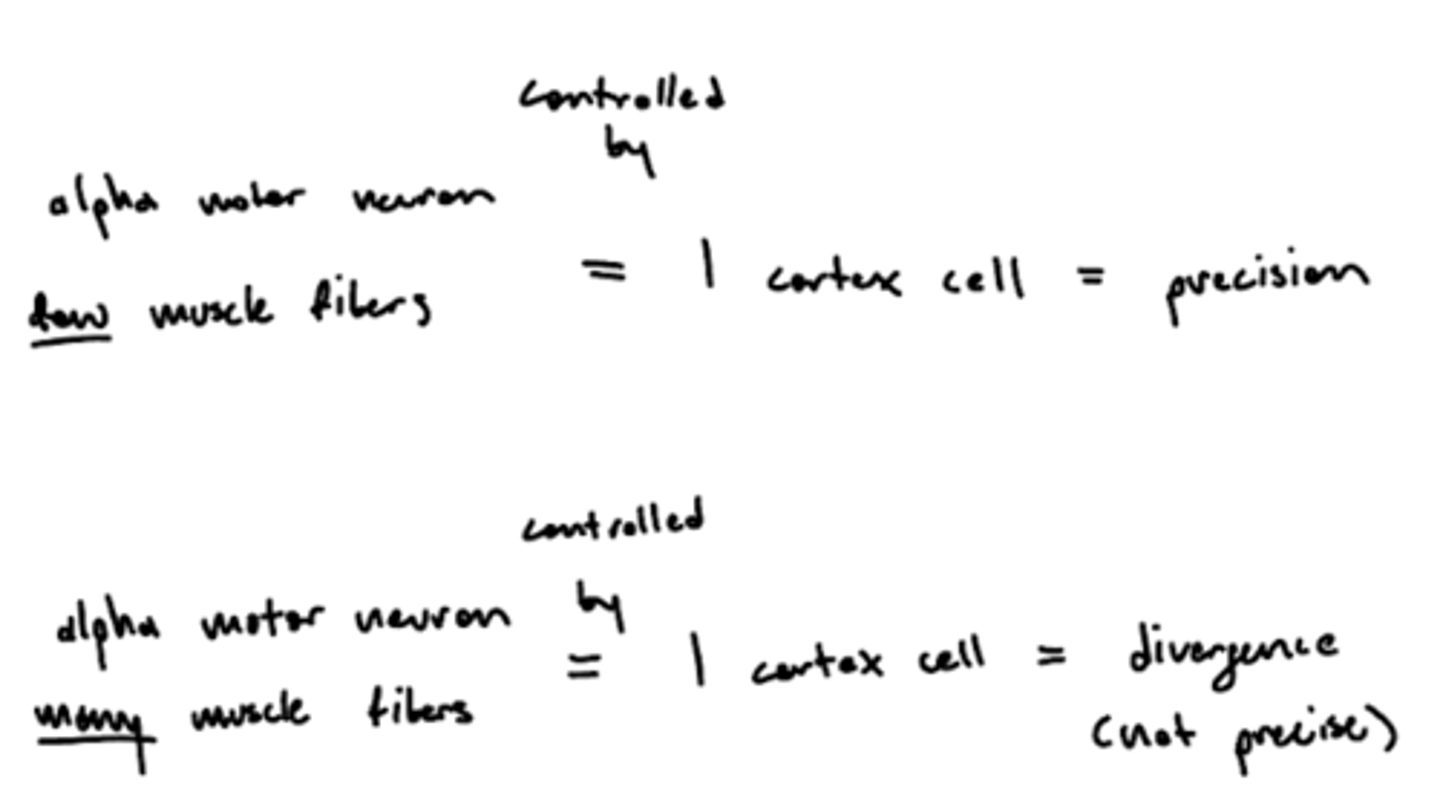
Why are larger alpha motor units less precise?
1 cortex cell controls 1 alpha motor unit, more muscle fibers (larger alpha motor unit) innervation creates divergent (not precise) movement
How does increased innervation to a muscle affect innervation to that muscle's antagonist?
bicep increased = tricep (antagonist) decreased
why? -- tells the brain (proprioception) where you are in space from the feeling of the length of the muscle spindles
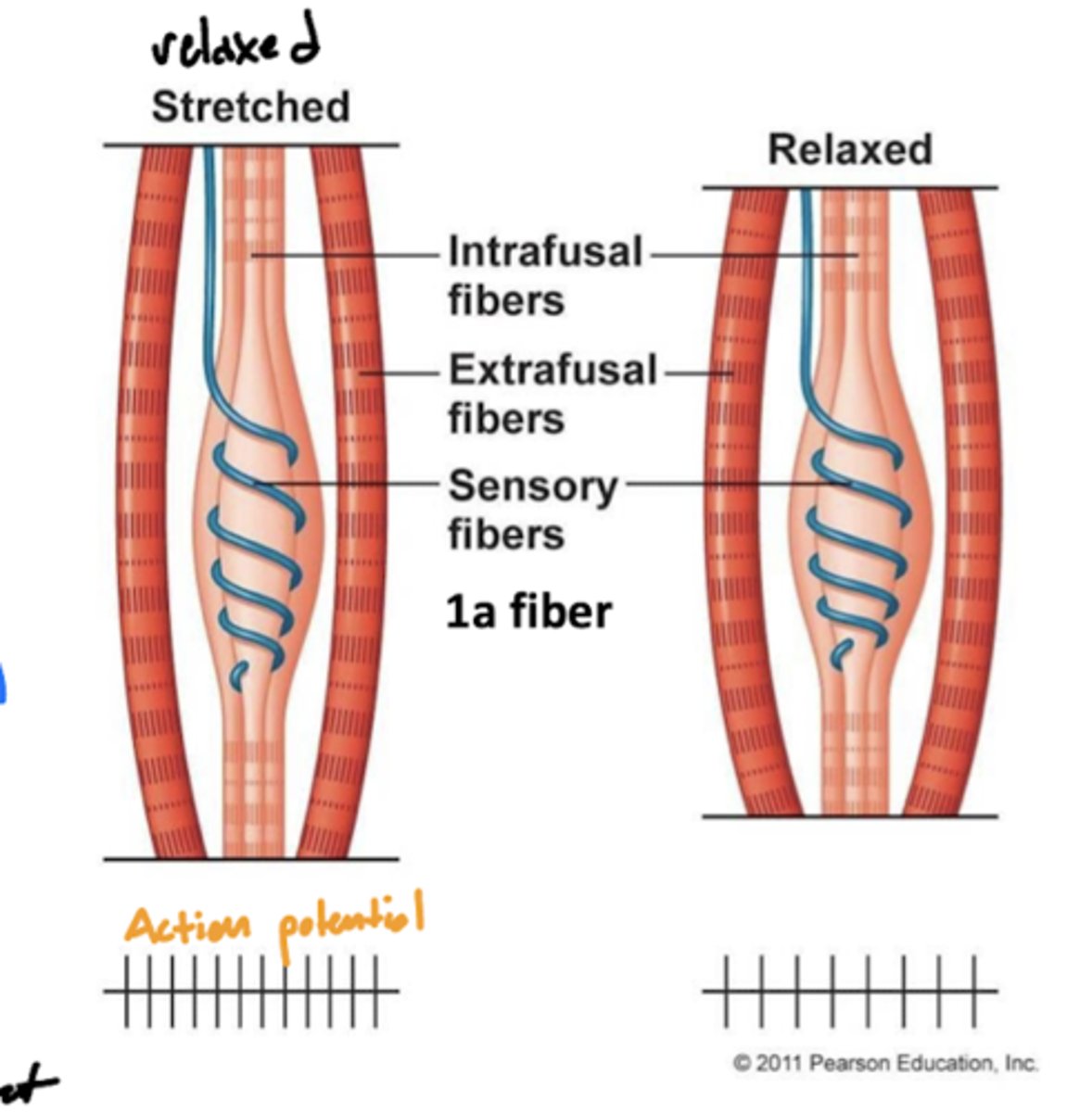
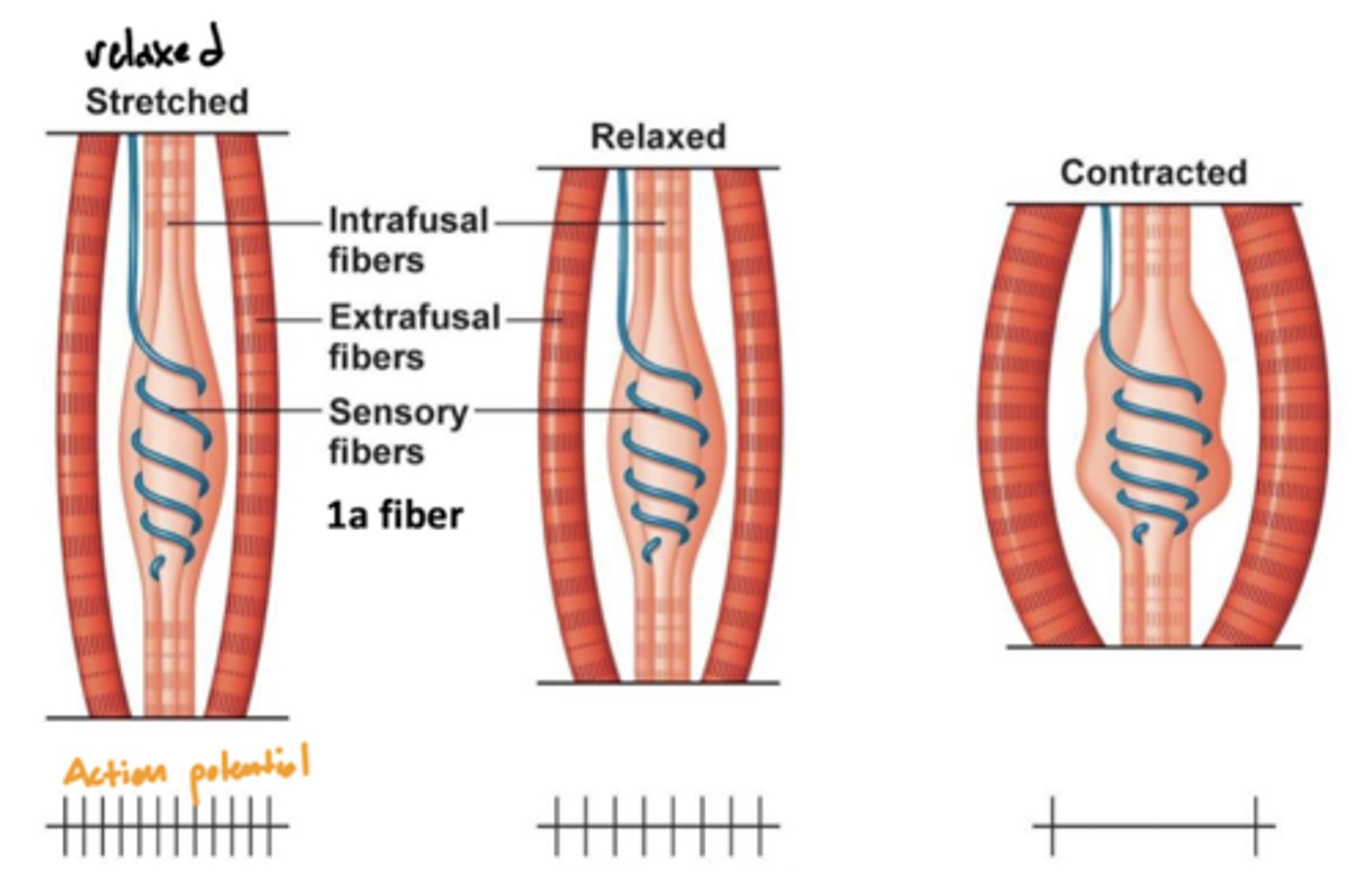
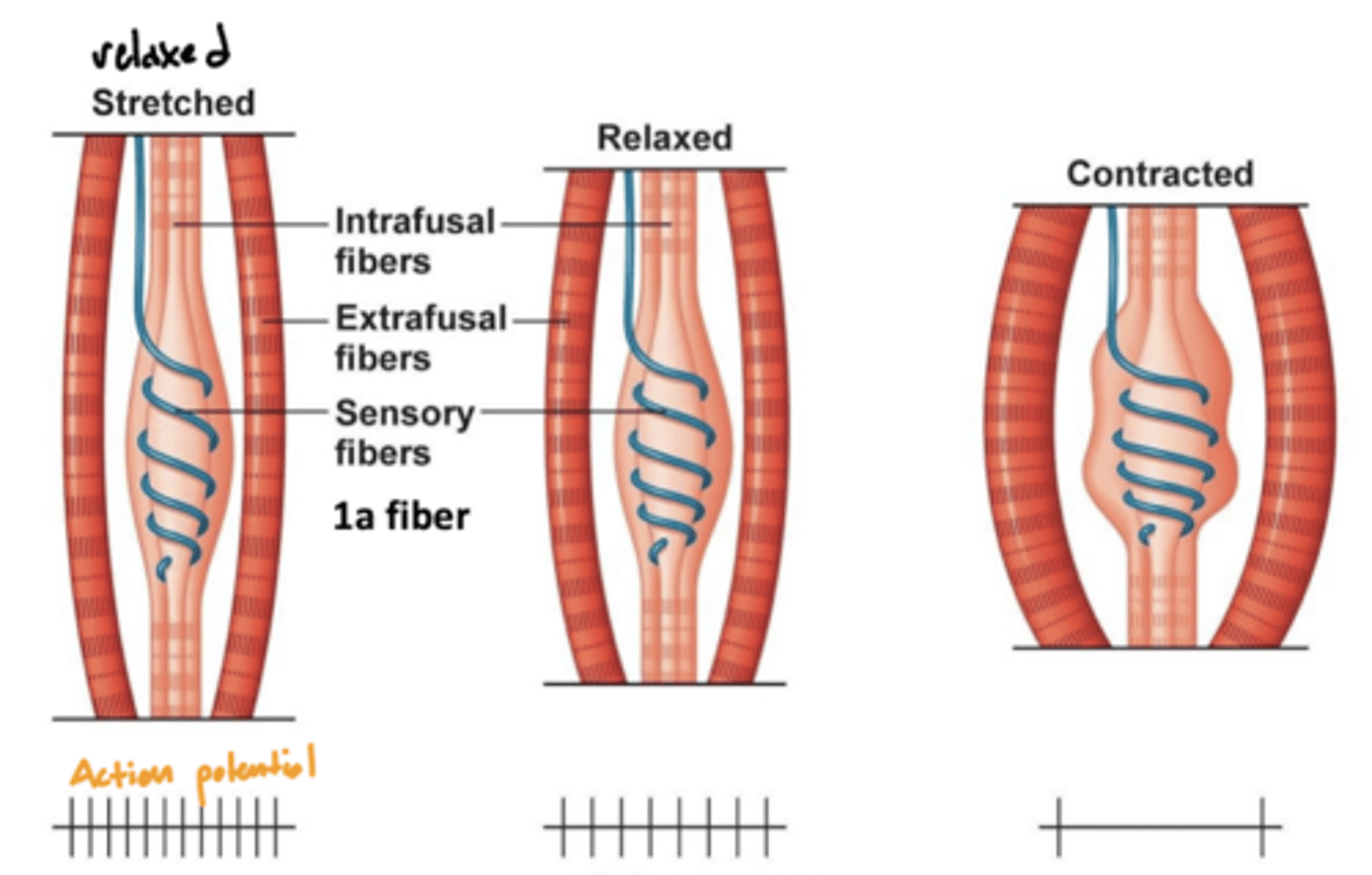
What is a muscle spindle?
a sensory receptor located in the muscle that senses how much the muscle is stretched
image -- blue line around the intrafusal muscle
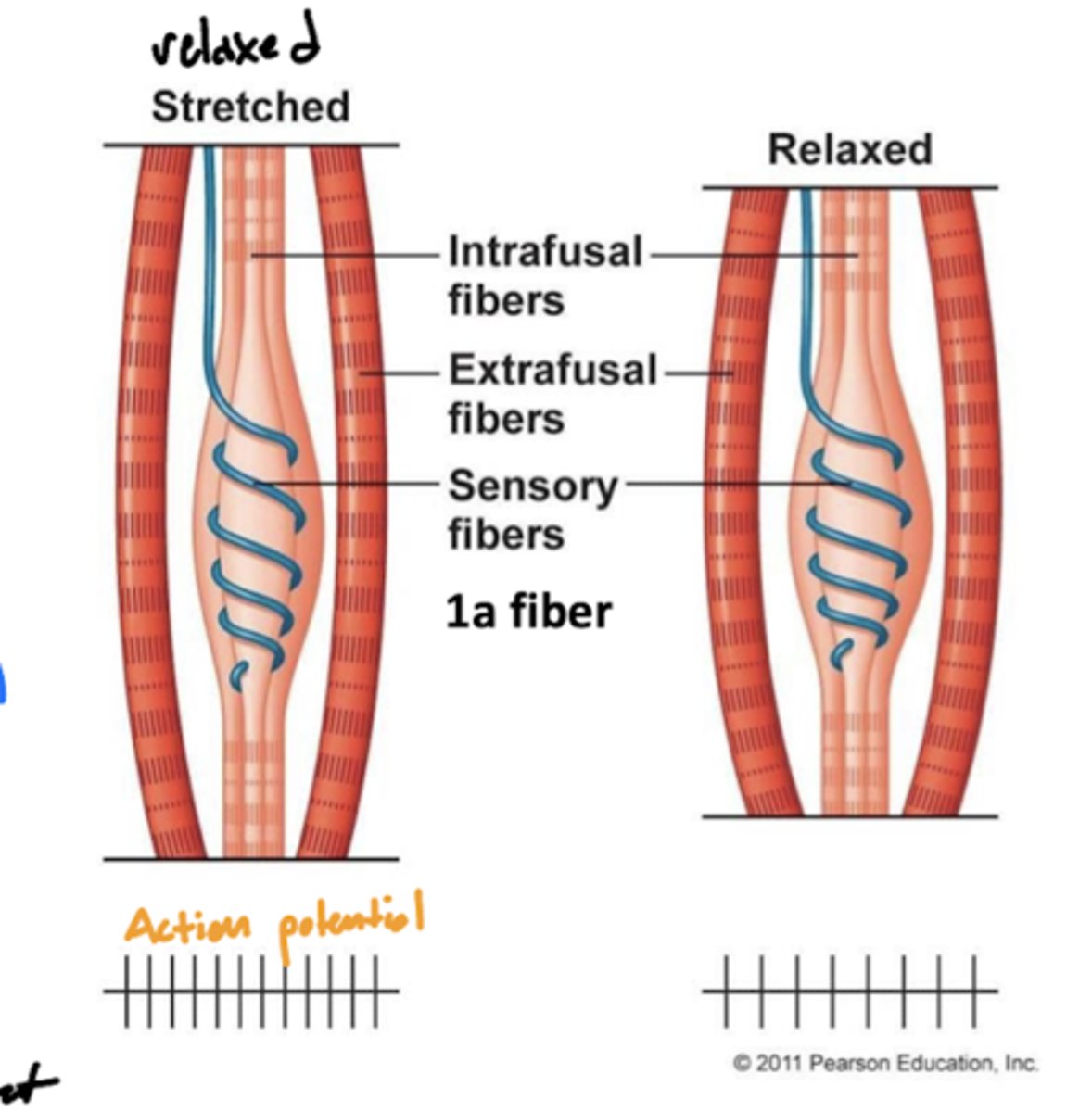
Where are muscle spindles?
wrapped around the intrafusal muscle (blue line labeled sensory fibers)
What is the function of intrafusal muscles?
1. sensory function by detecting changes in muscle length and the rate of change in length -- not directly involved in generating muscle force or movement
2. sets muscle tone
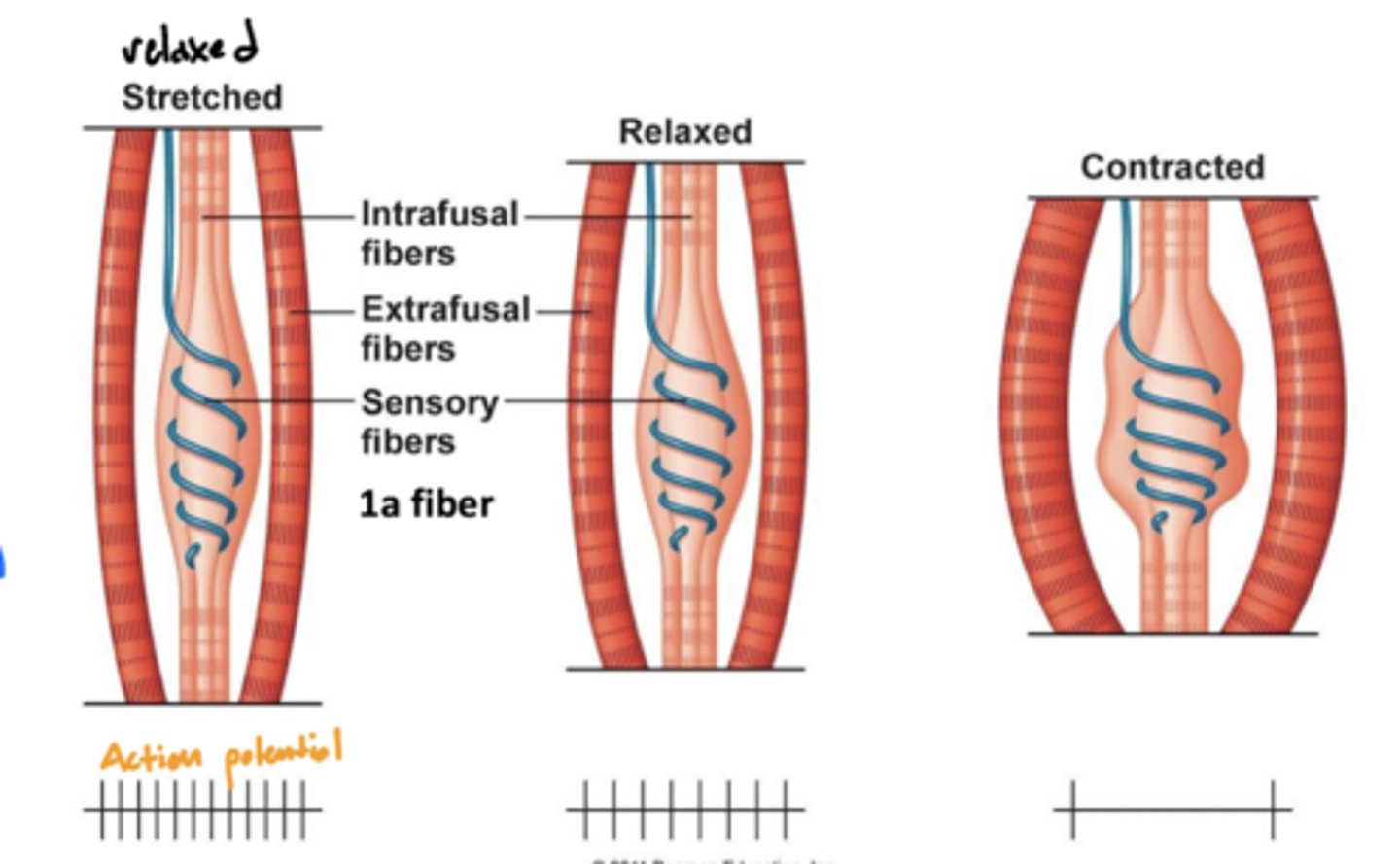
Where are intrafusal muscles?
found on the top and bottom of muscle spindle
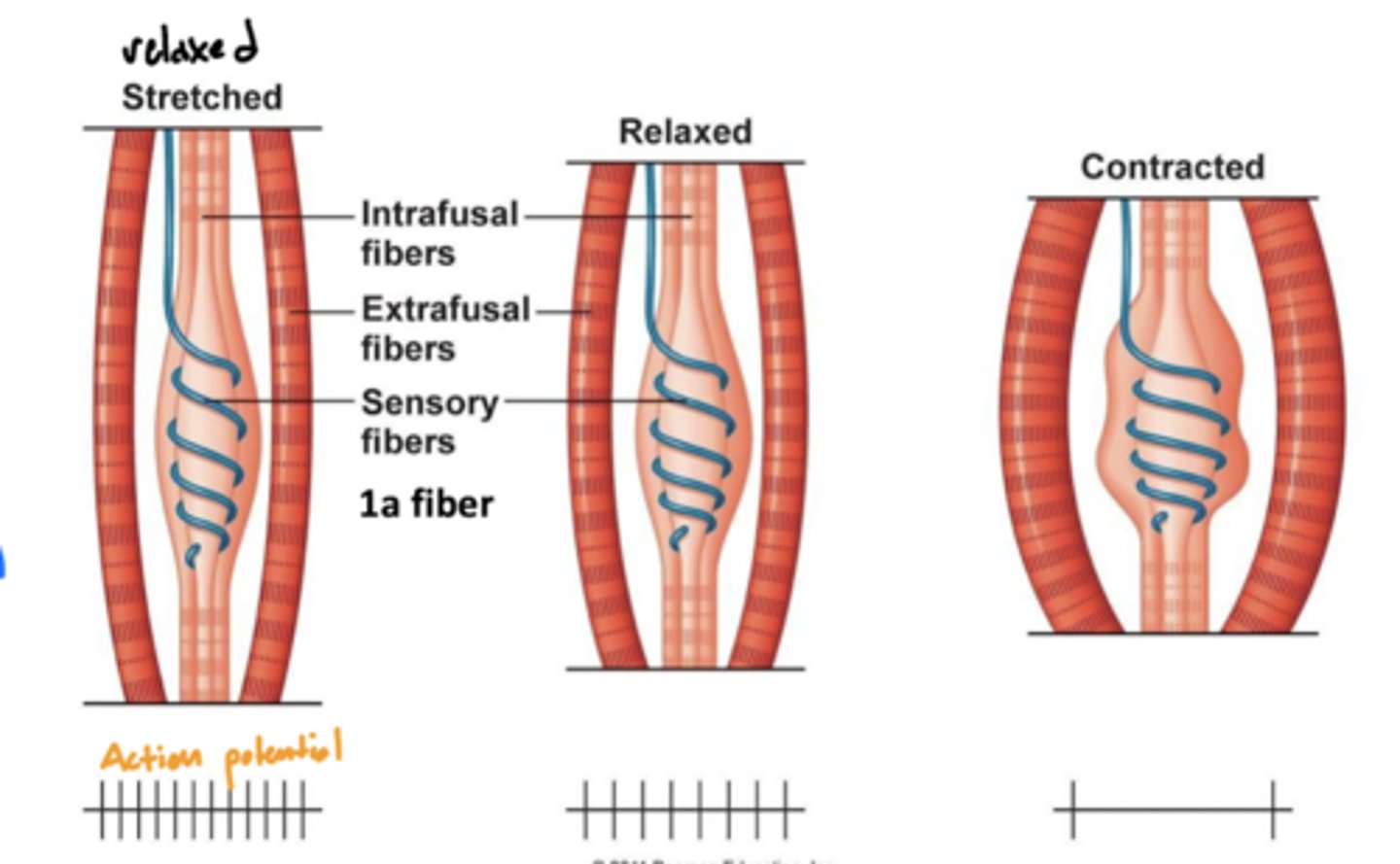
Are intrafusal or extrafusal muscles responsible for generating force?
extrafusal -- skeletal muscle fibers responsible for generating force and producing movement
When do you contract intrafusal muscles?
while setting muscle tone
What does intrafusal muscle contraction cause?
stretching of the muscle spindle
What is the relationship between muscle contraction and muscle spindle (action) potential?
when stretched (relaxed) -- high activity
when contracted (contraction) -- low activity
why? -- the function of muscle spindles is to initiate a spinal reflex when the muscle is being overstretched, therefore more action potentials will be sent when stretched
What does a hyper or hypo reflex indicate?
some type of pathology (flaccid or spastic paralysis)
What does hyperactivation of a spinal reflex indicate?
spastic paralysis (UMN problem) -- increased LMN receptors (hypersensitivity)
What does hypoactivation of a spinal reflex indicate?
flaccid paralysis -- no LMN or reduced
Do intrafusal muscles change muscle length?
NO direct impact on muscle length
What type of fibers are the sensory fibers of muscle spindles (also intrafusal muscle) during a spinal reflex?
1a fibers
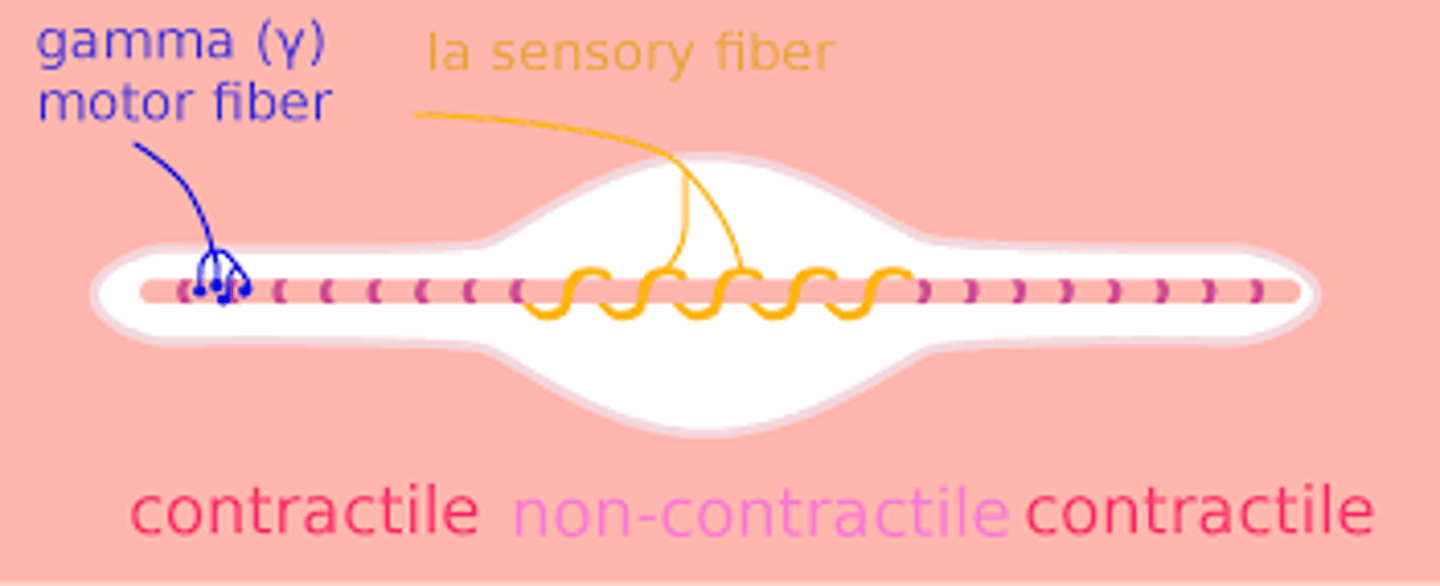
What type of fibers are efferent to intrafusal muscles?
Aγ fibers
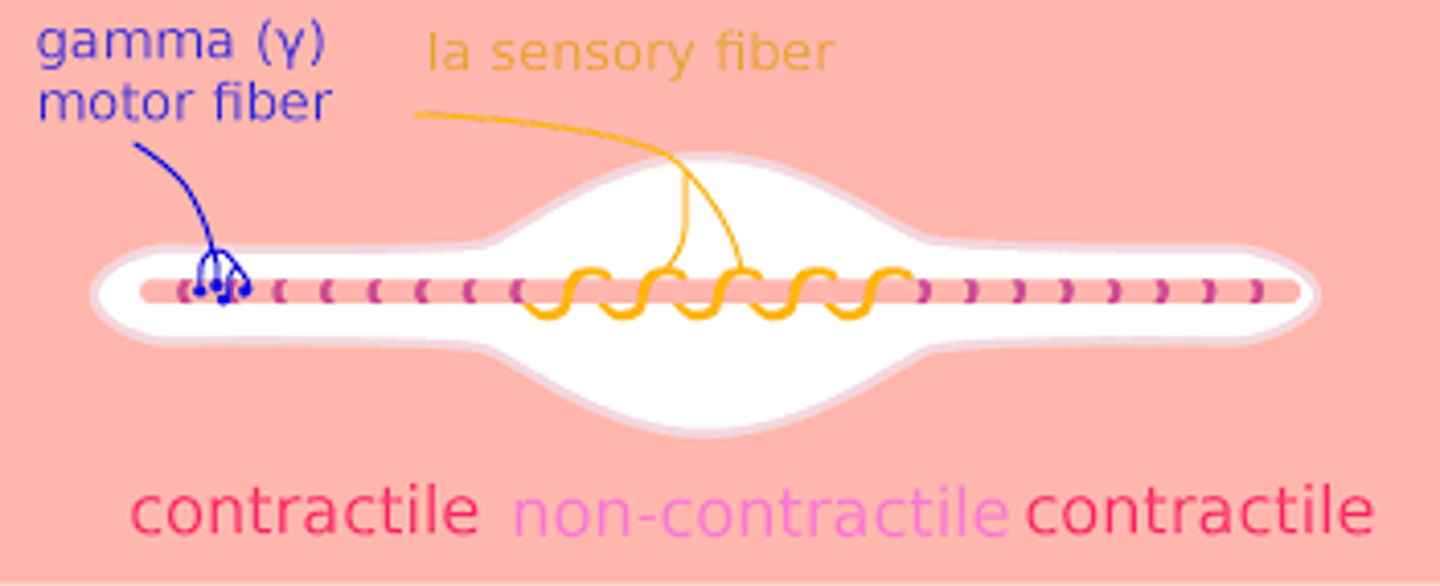
What type of fibers are efferent to extrafusal muscles?
Aα fibers
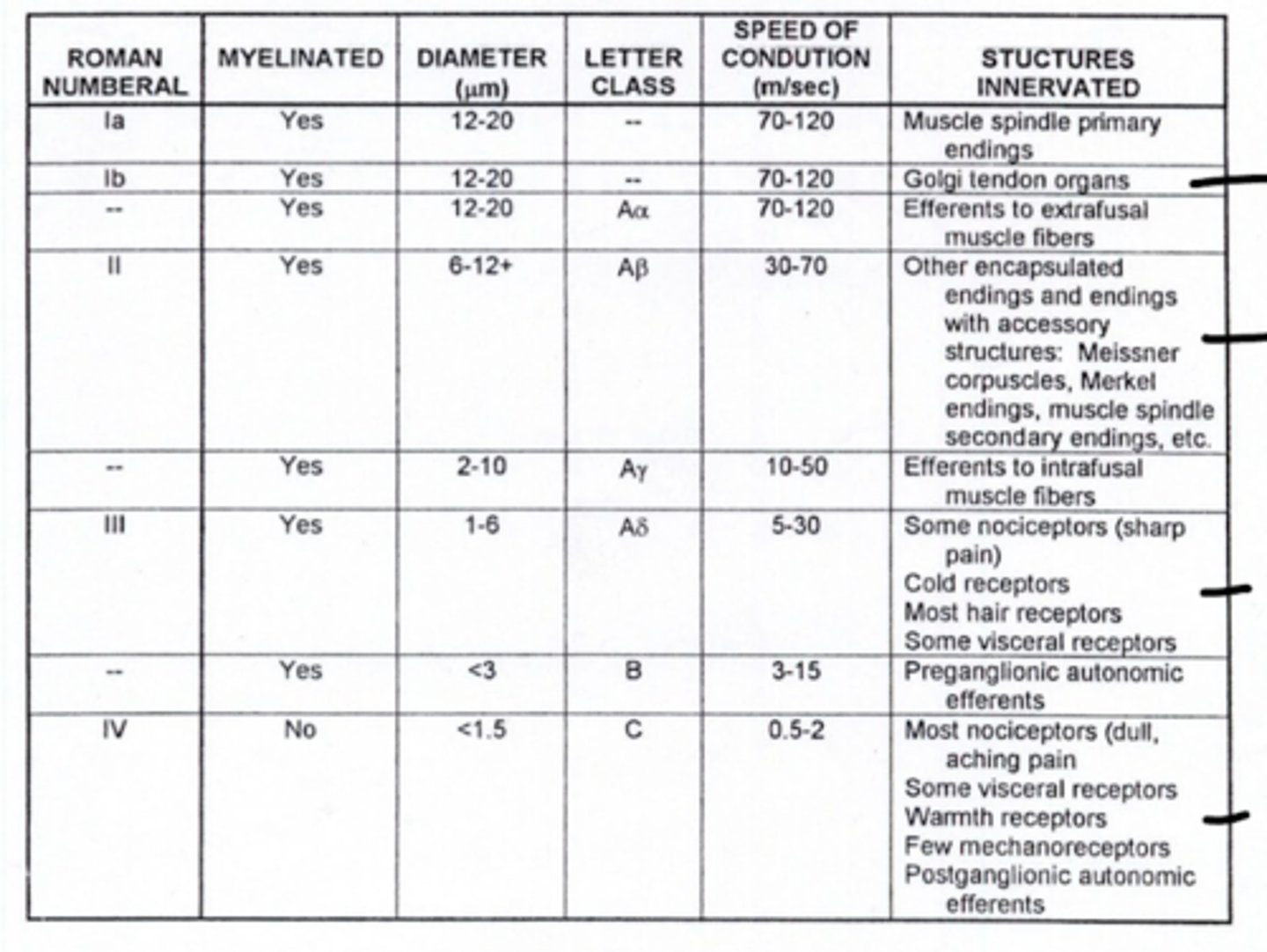
What is the mechanism of a spinal reflex?
1. muscle spindle stretched
2. 1a fibers activated towards the spinal cord
3. interneuron activated (inhibitory or excitatory depending on reflex)
4a. Aγ activate, going to intrafusal muscles -- helps with contraction
4b. Aα active (or deactivate), going to the extrafusal muscle
why deactivate? -- some spinal reflexes deactivate antagonist muscles, like the flexor muscle
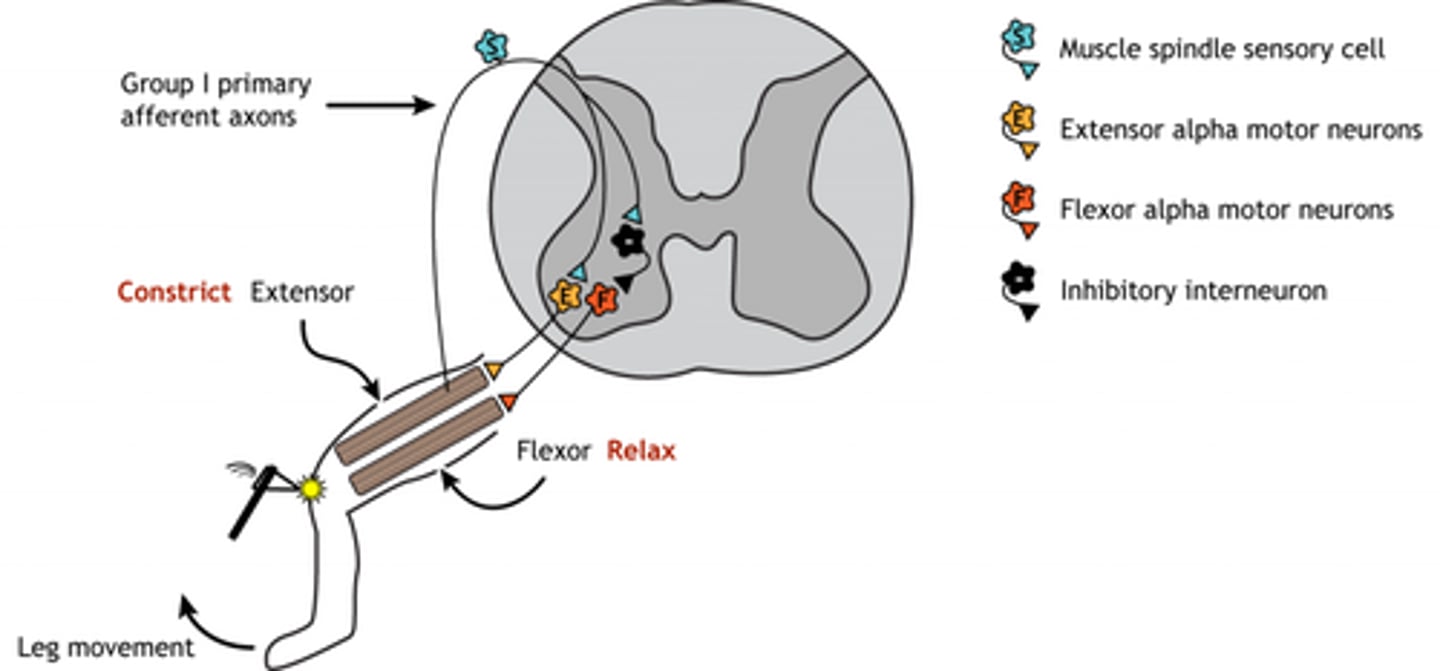
Why does the body set a muscle tone?
resist gravity -- doesn't want to decrease dynamic range of the cortex
What part of the body is responsible for regulating muscle tone?
cerebellum
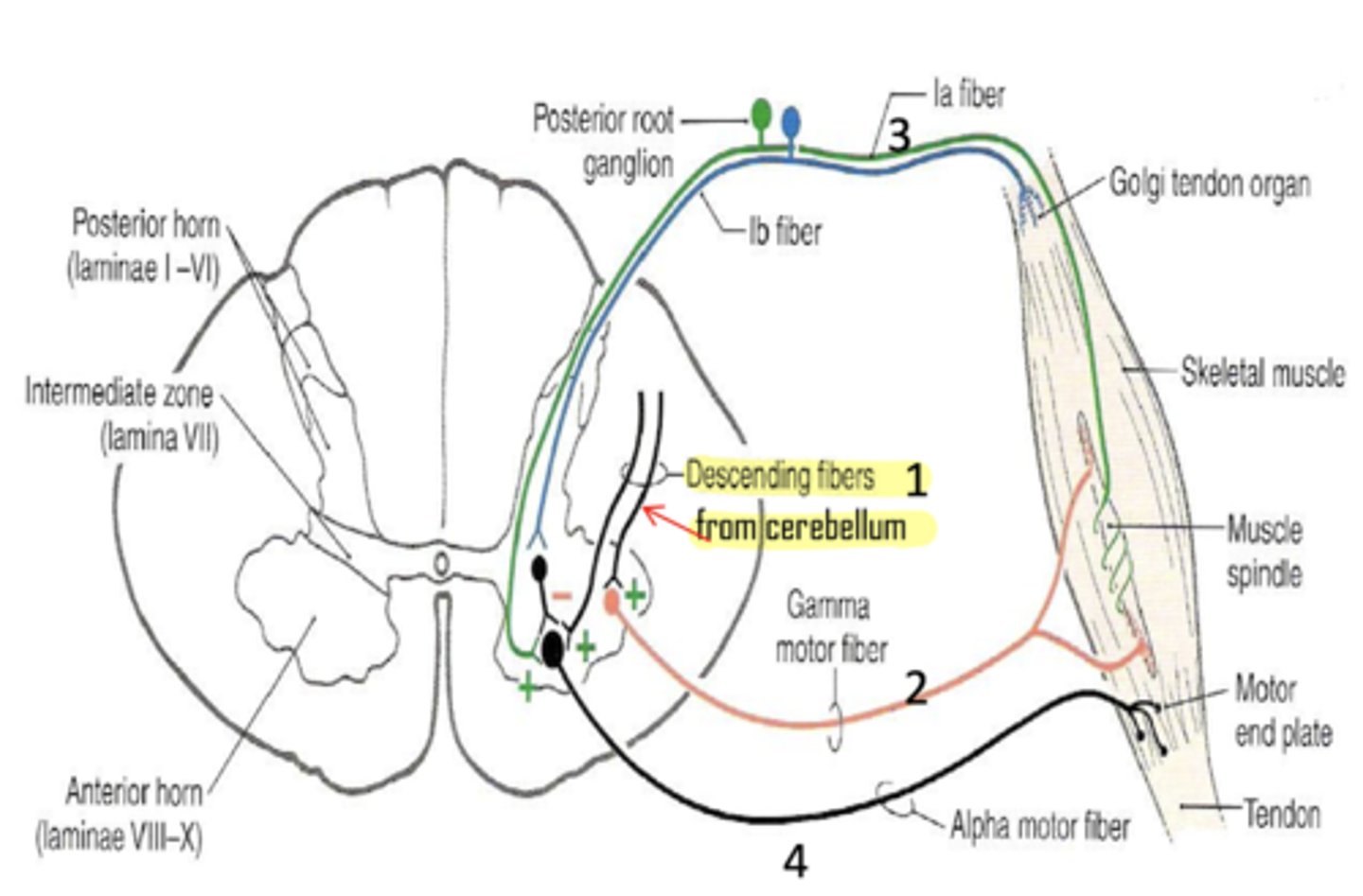
Why does muscle tone increase during spastic paralysis?
upper motor neuron (from BA 4) cannot inhibit descending cerebellar fibers
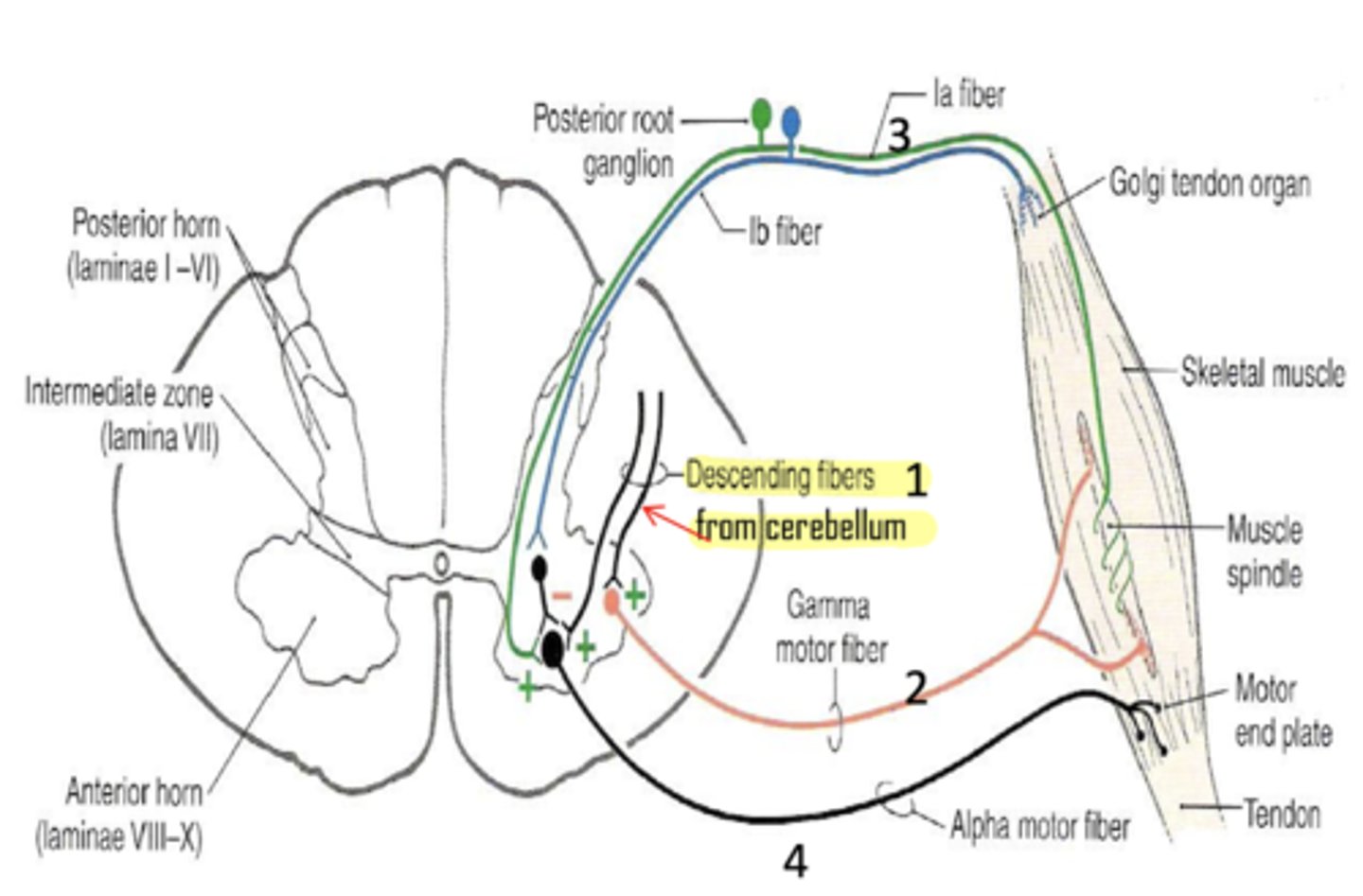
What is the golgi tendon organ?
a term that refers to a sensory receptor in a muscle tendon that monitors tension
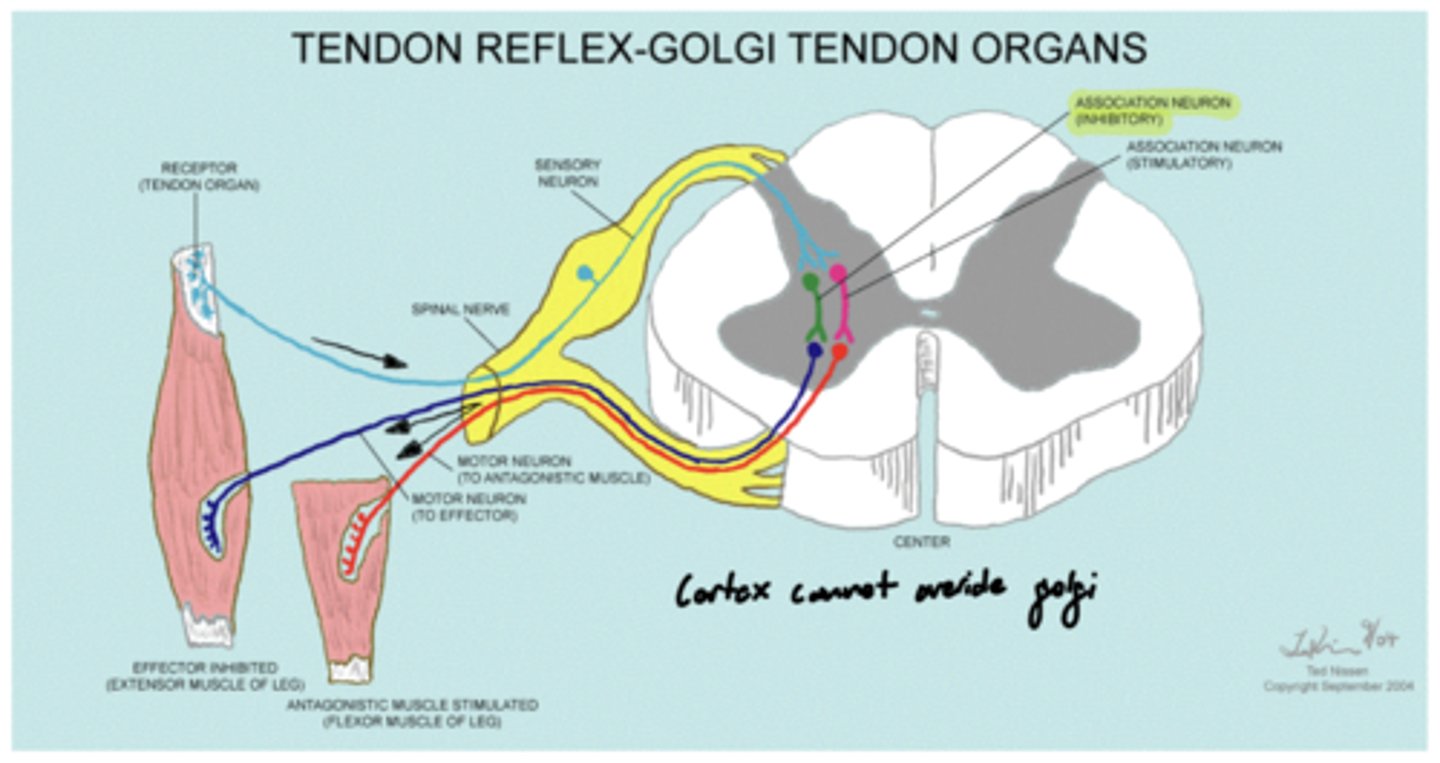
What type of afferent fibers do golgi tendon organs utilize?
1b
What is the function of the golgi tendon organ?
prevents muscle damage by inhibiting muscular tone when it is too great
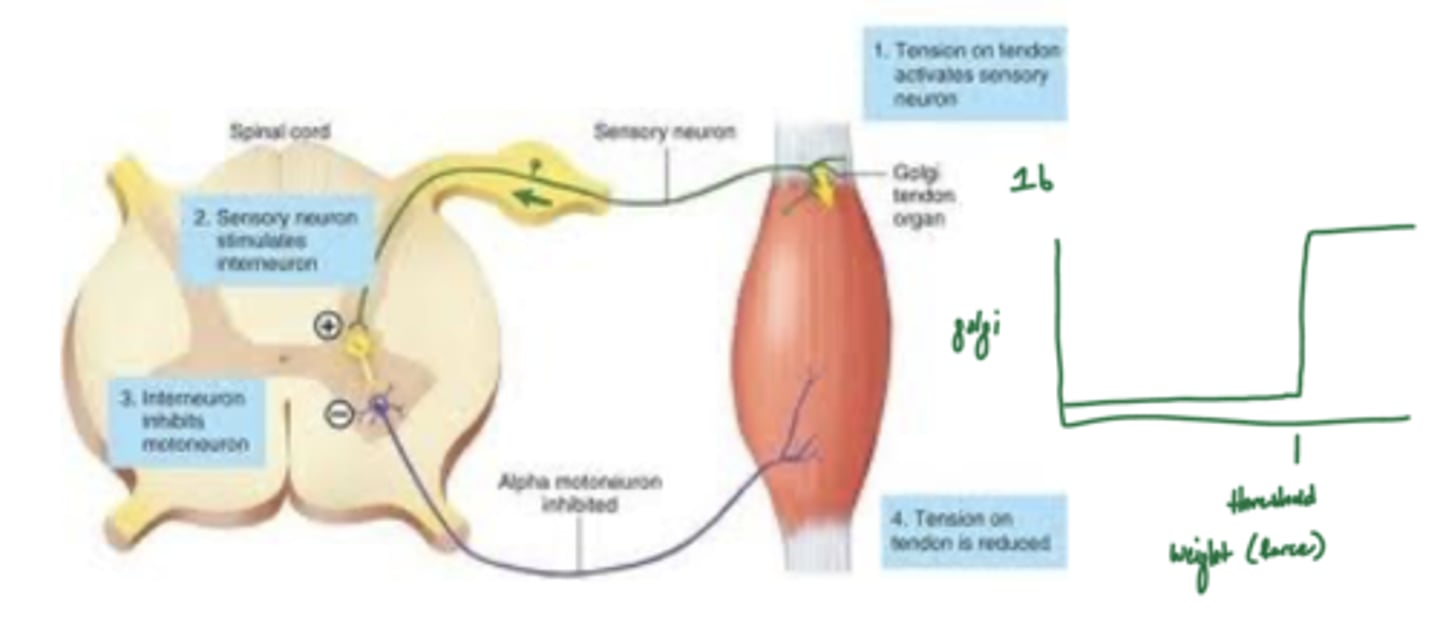
Can the cortex override the golgi tendon organ?
no -- if it did, danny's muscles would tear every time he goes to the gym

What are the classifications of peripheral nerve damage?
1. distal to injury (downstream)
2. proximal to injury (upstream)

What is the type of peripheral nerve damage that is distal to an injury?
Wallerian degeneration

What are the types of peripheral nerve damage that are proximal to an injury?
1. axon reaction or apoptosis
2. sprouting
3. regeneration

What is Wallerian degeneration?
removal of distal myelin following an injury
1. Schwann cell removes myelin via intracellular processes
2. phagocytes to clear neural debris -- leave behind neurolemma/endoneurial tube
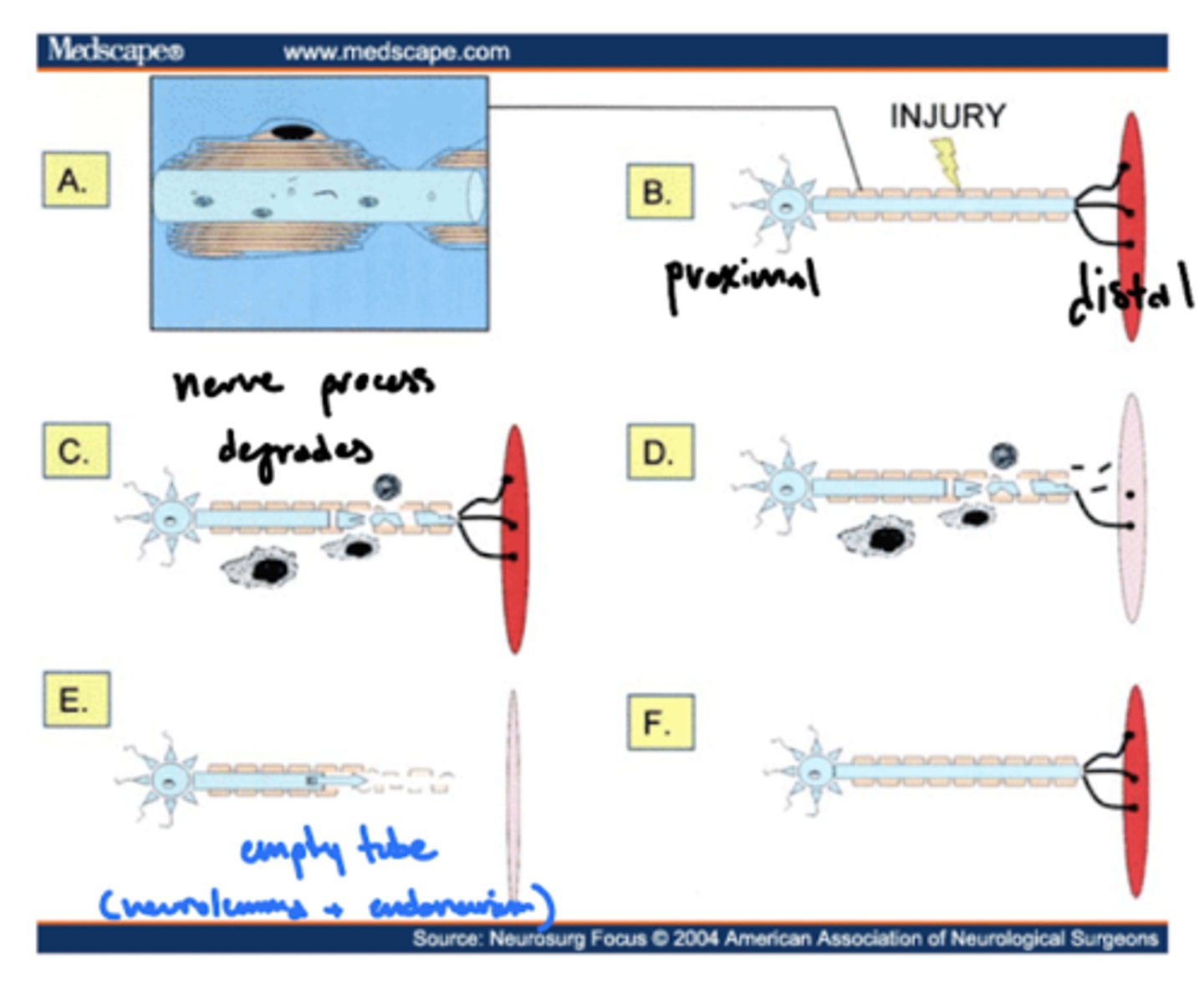
When do neurons undergo apoptosis or an axon reaction?
if damage is too near cell body
What is neuron regeneration?
sprouting of "growth cones" that are chemotactically drawn to empty tube
typically 80% of the original diameter
What is neuron sprouting?
attempted neuron regeneration by sprouting of "growth cones" towards the empty tube
What cranial nerve doesn't regenerate that well?
facial nerve (CN VII)
What is reactive synaptogenesis?
following injury, an uninjured axon sprouts to innervate a synaptic site that was lost due to a damaged neuron
why you can recover from CNS injuries, but have to relearn tasks
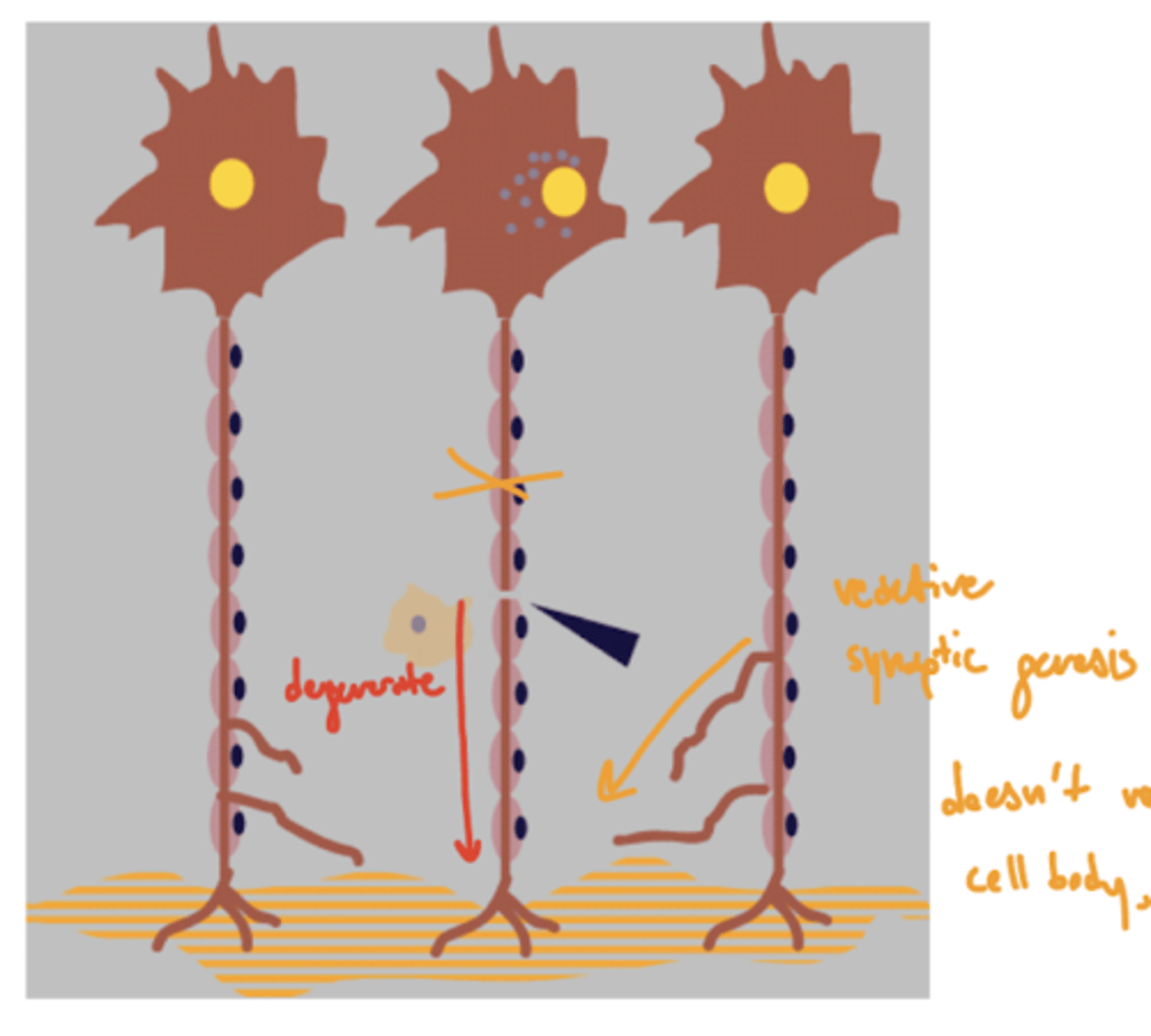
Why does the CNS undergo reactive synaptogenesis instead of regeneration via sprouting?
CNS secretes nogo
nogo -- inhibits axon regeneration
What is GVE stand for?
general visceral efferent
What is the function of GVE?
innervates internal organs
1. cardiac muscle
2. glands
3. smooth muscle (BVs, GI, bronchi)
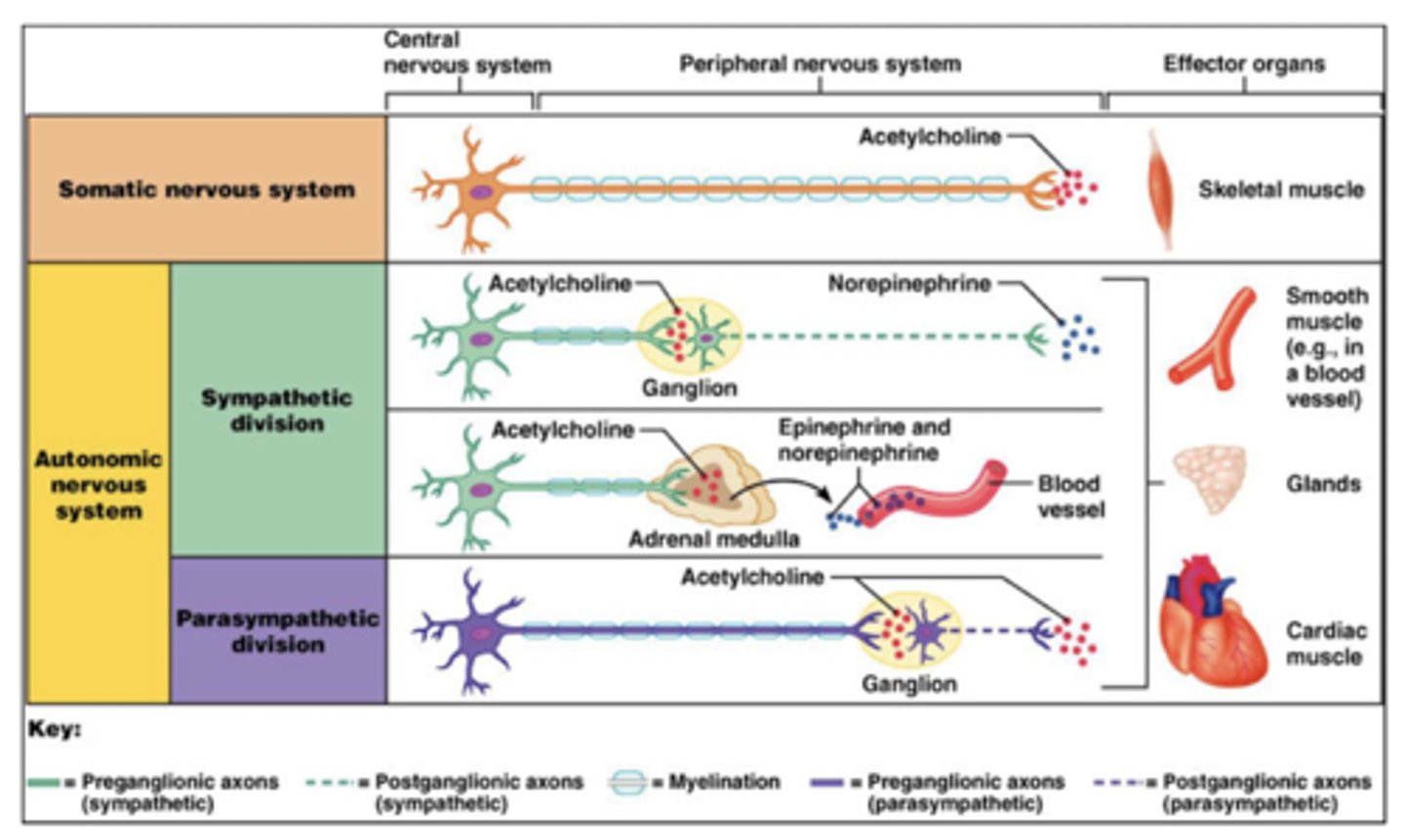
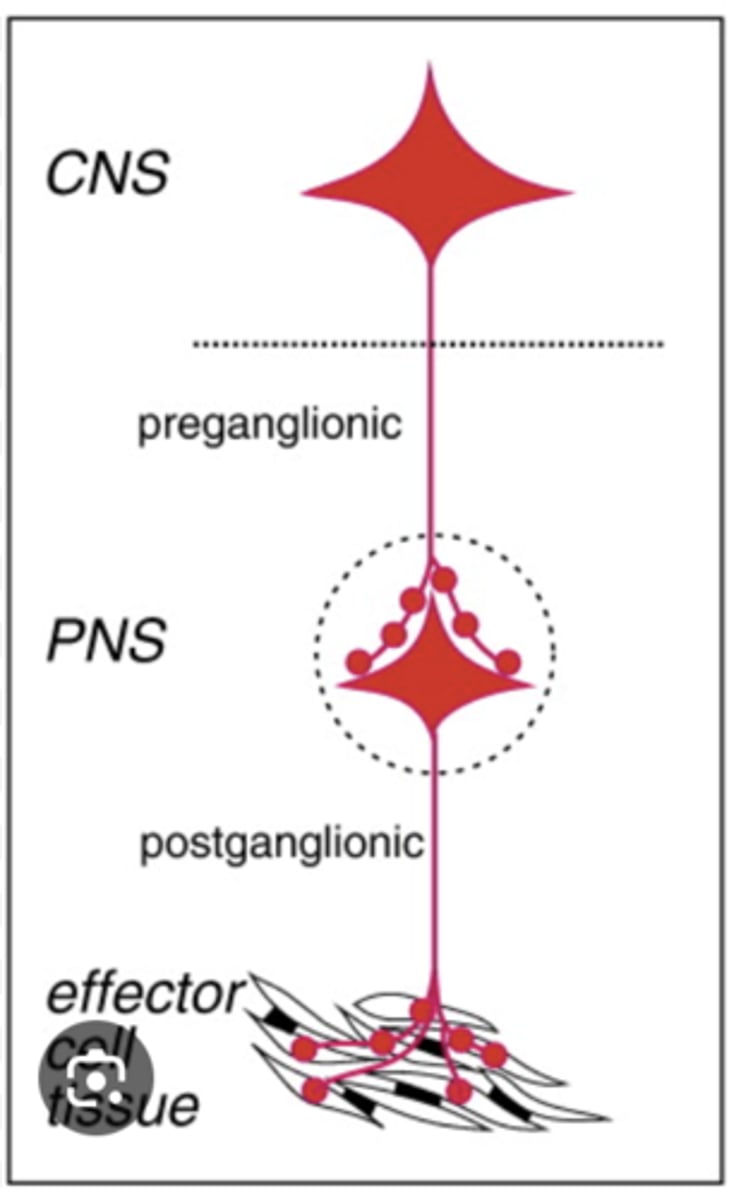
What is the basic wiring of the autonomic system?
1. central neuron
2. preganglionic
3. postganglionic
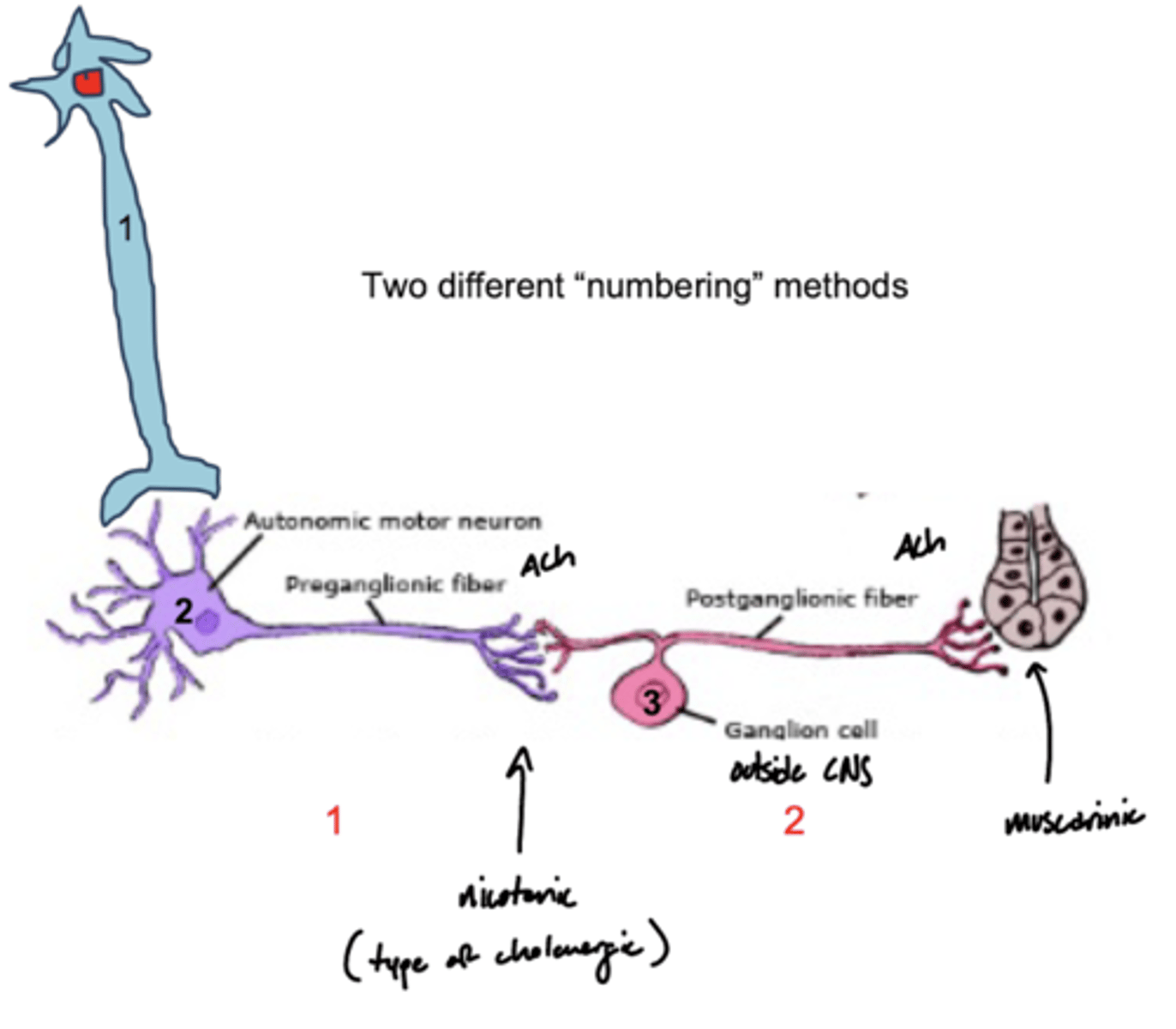
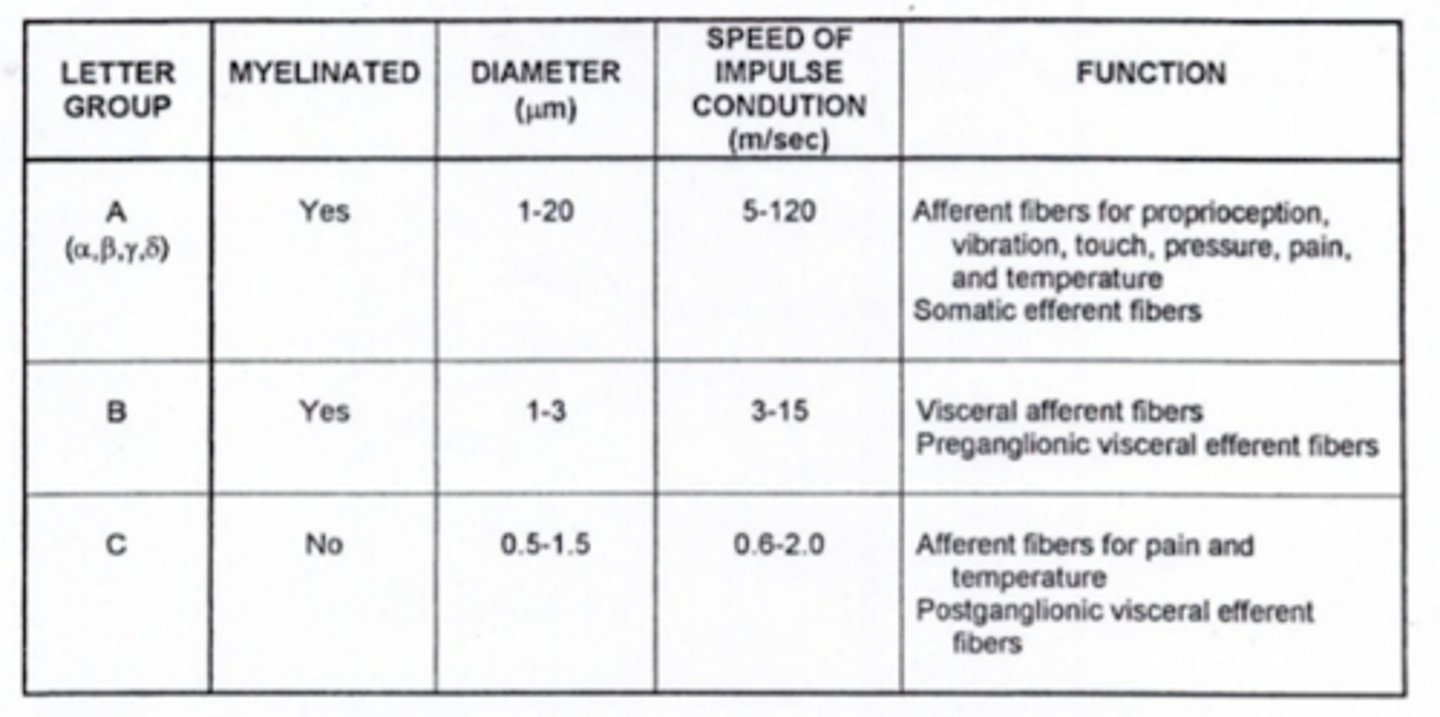
What type of fibers are preganglionic neurons?
type B fibers
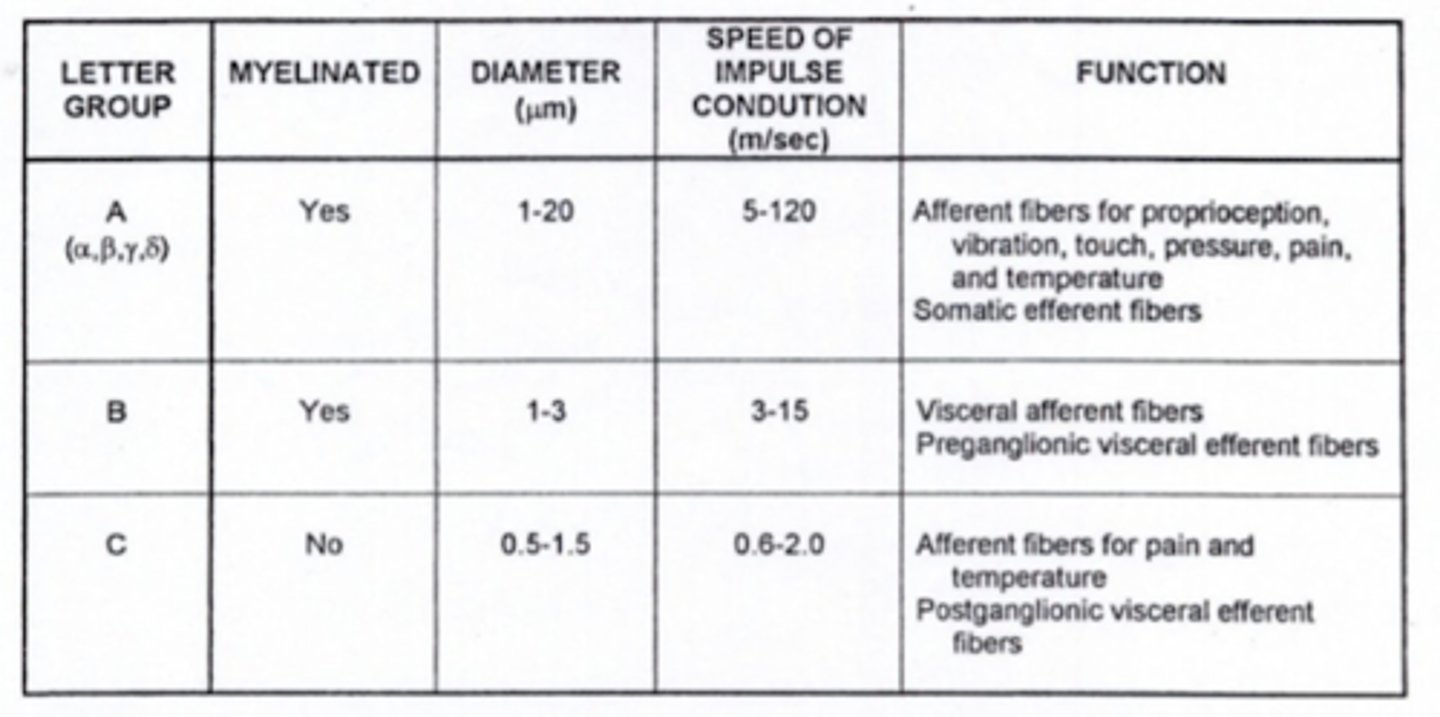
What type of fibers are postganglionic neurons?
type C fibers
Where are autonomic preganglionic cell bodies?
1. brainstem (with CNs)
2. lateral horn of spinal cord
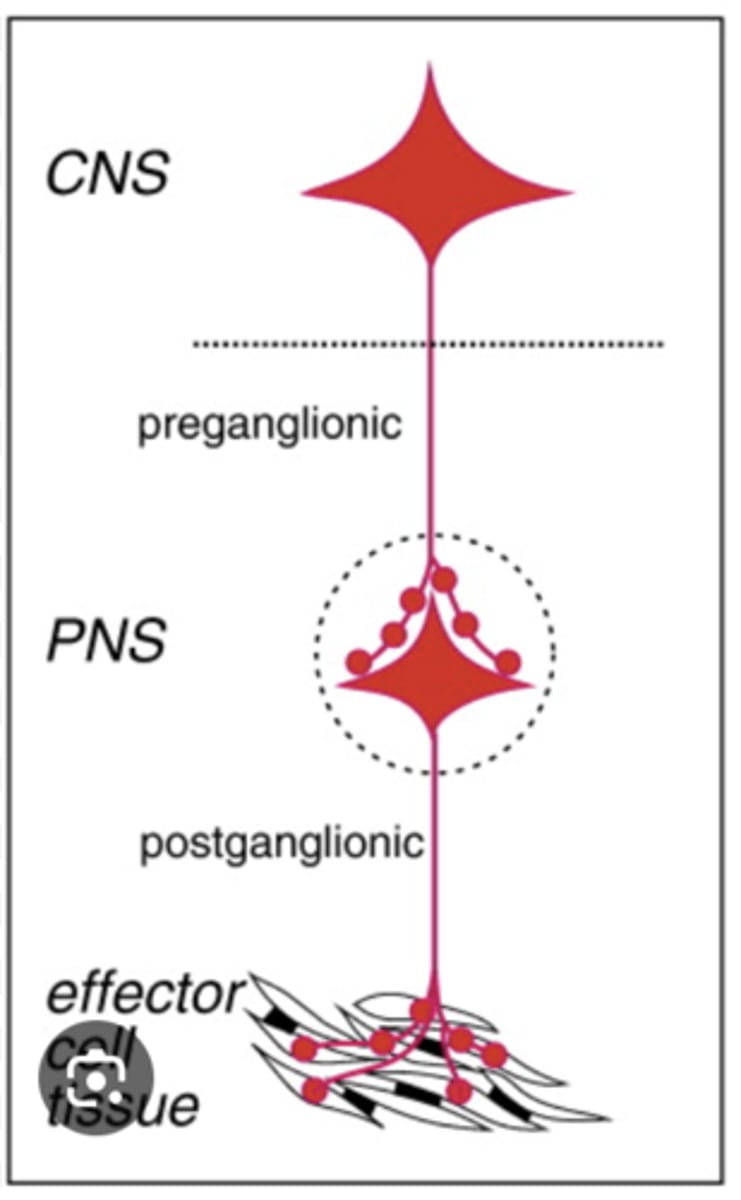
Where are the autonomic postganglionic cell bodies?
1. ganglia
2. wall of organs (part of GI)
Why does the parasympathetic system ALWAYS use acetylcholine (preganglionic and postganglionic)?
older phylogenically
ACh is the best NT
Which neurotransmitter do parasympathetic preganglionic neurons utilize?
acetylcholine
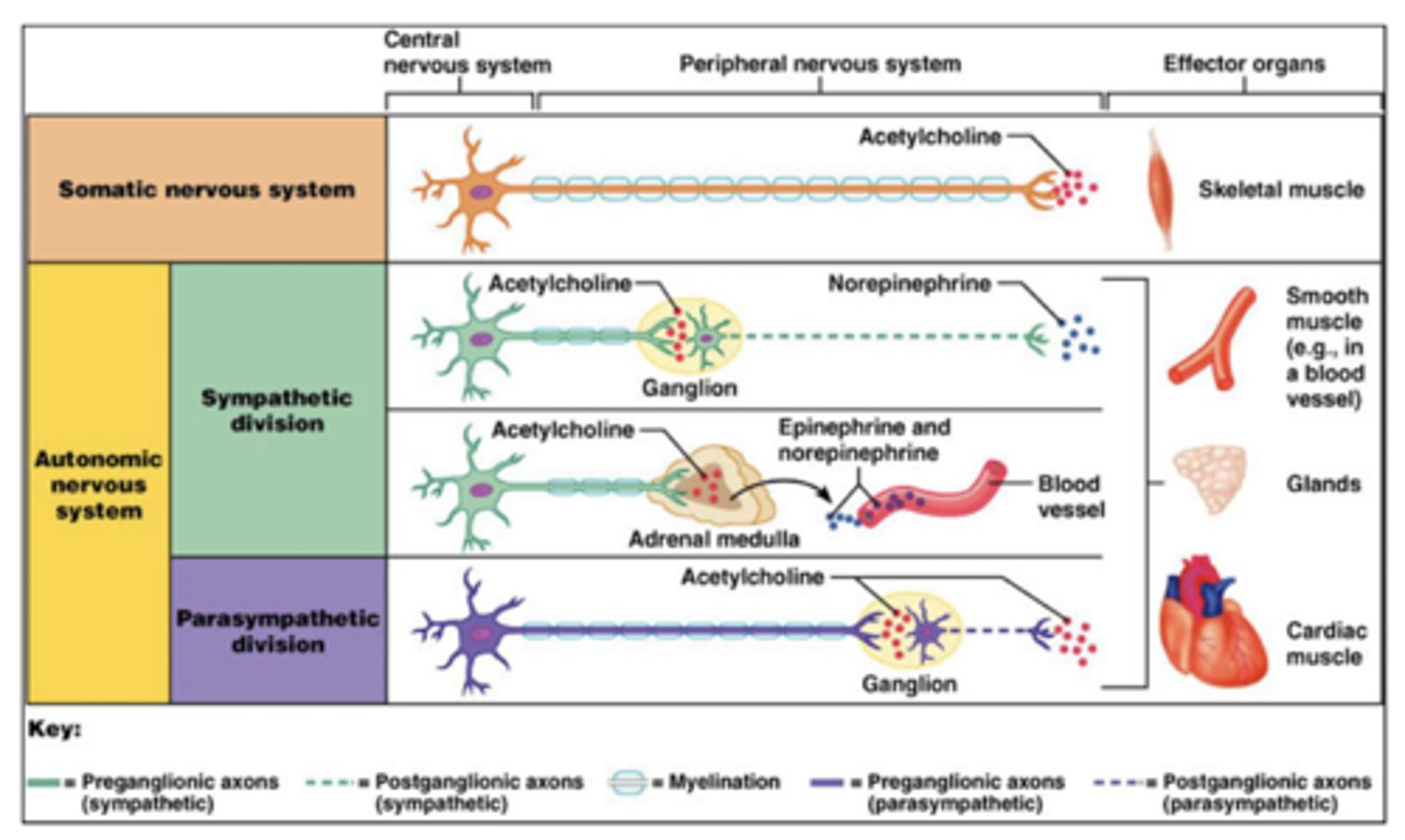
Which neurotransmitter do parasympathetic postganglionic neurons utilize?
acetylcholine
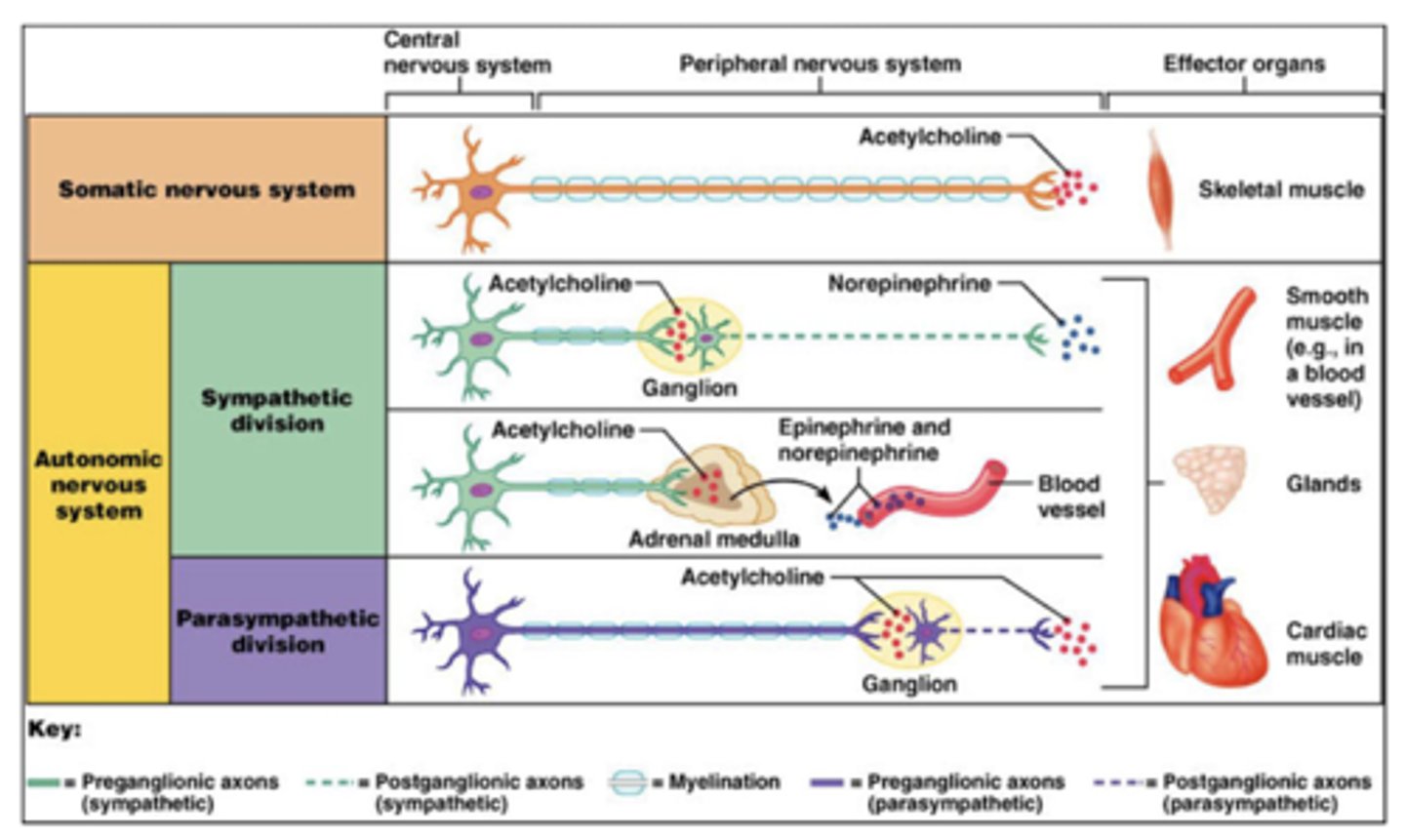
Which receptors do parasympathetic postganglionic neurons utilize?
nicotinic (nAChR)
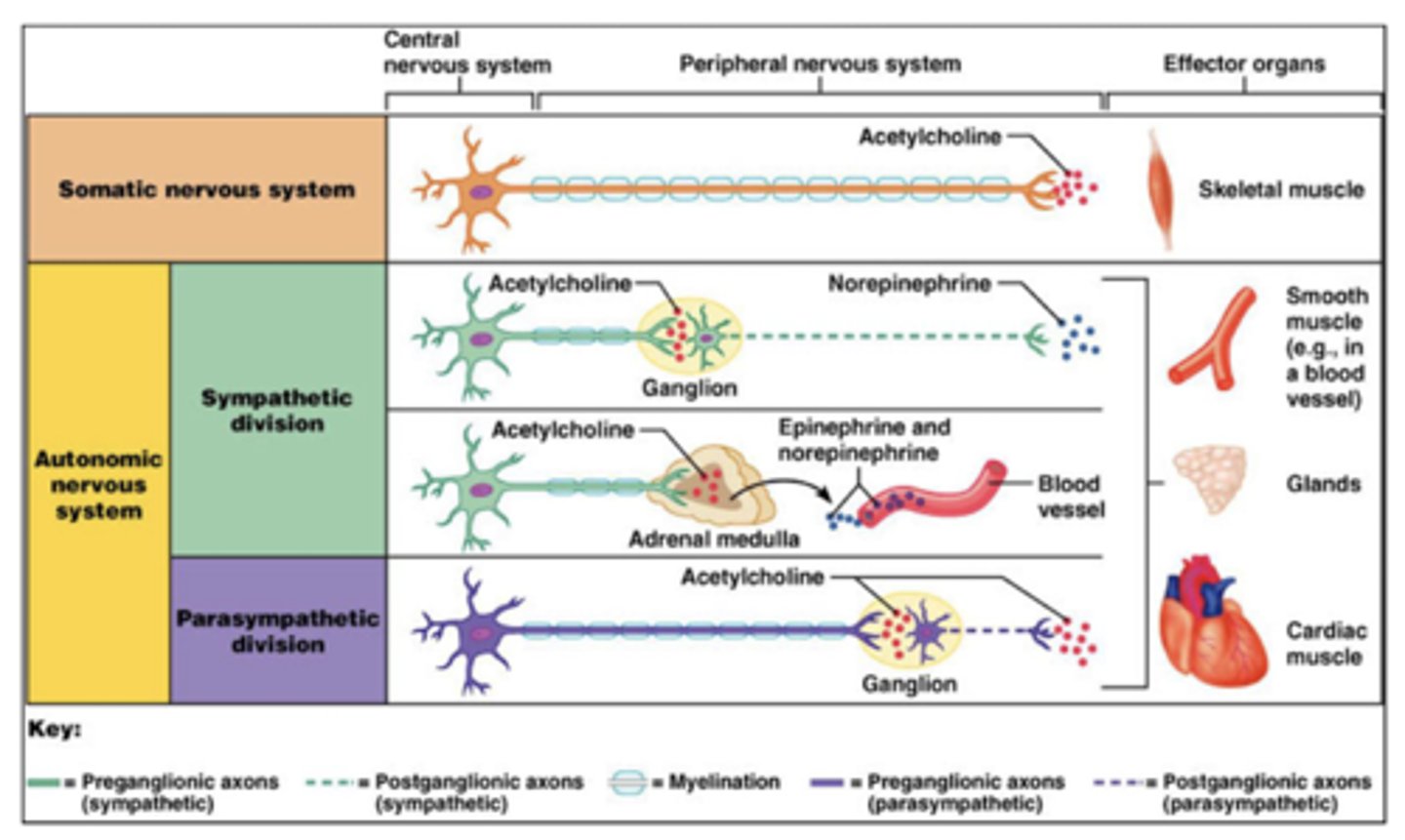
Which receptors do parasympathetic target tissue utilize?
muscarinic (M type)
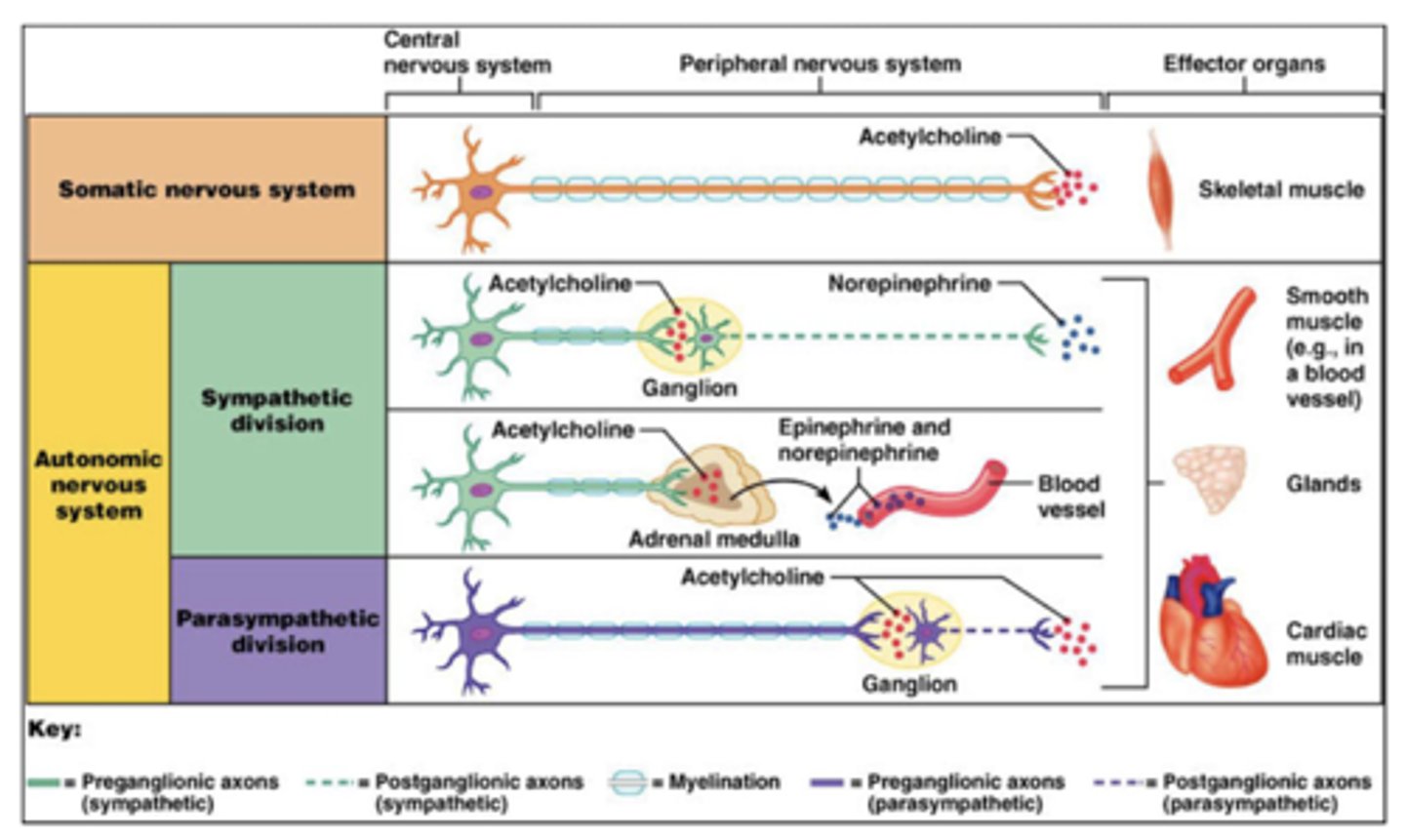
What type of receptor are muscarinic receptors?
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) via intracellular adenylate cyclase
What are the types of muscarinic receptors?
M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, etc.
Which neurotransmitter do sympathetic preganglionic neurons utilize?
acetylcholine
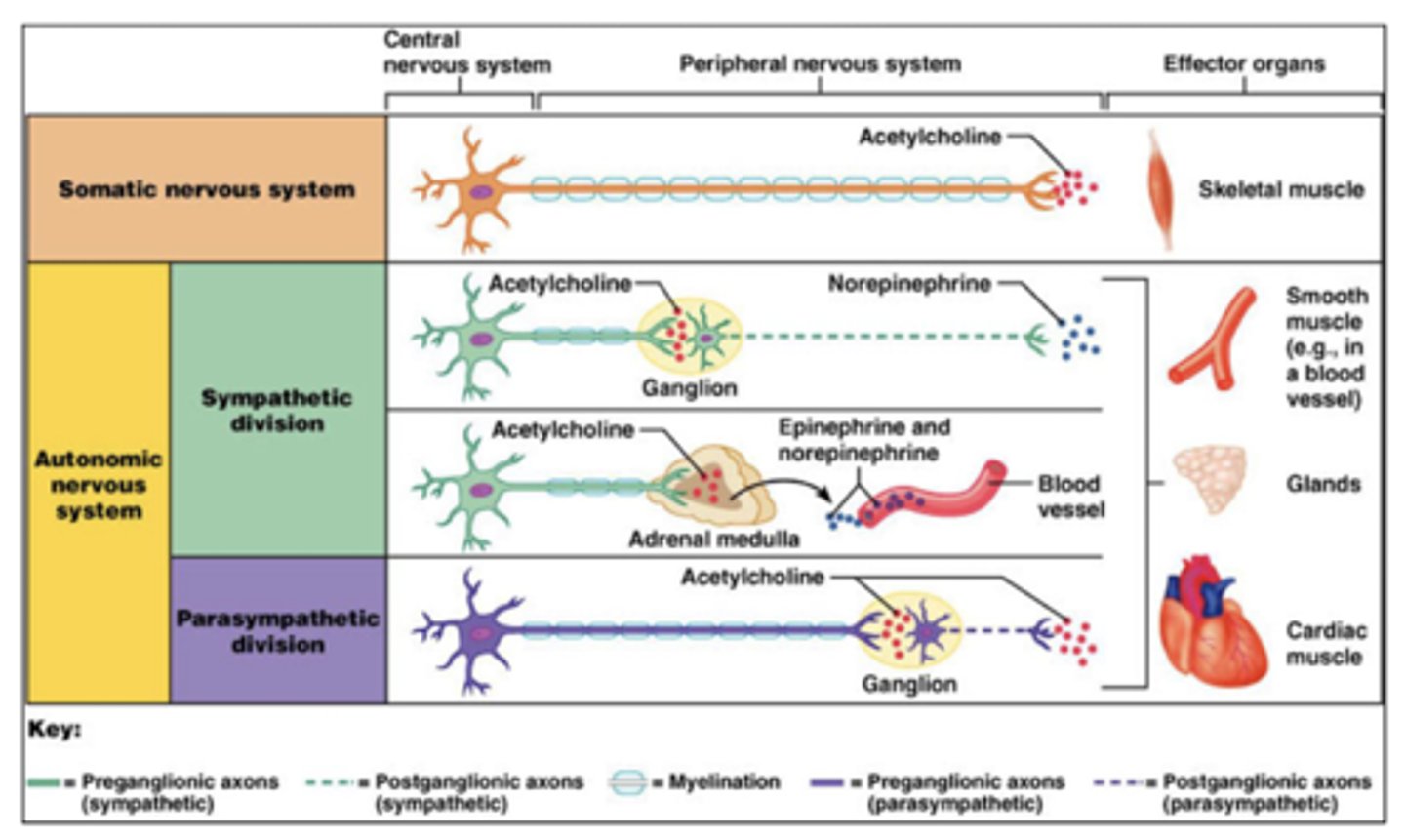
Which neurotransmitter do sympathetic postganglionic neurons utilize?
NorE