Review Sheet: Barron's AP Environmental Science 2023
1.0(1)Studied by 15 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/361
Last updated 4:12 AM on 2/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
362 Terms
1
New cards
Ecosystem
Community of living organisms interacting with non-living components
2
New cards
Organisms
A living thing that can function on its own
3
New cards
Species
Organisms that resemble each other
4
New cards
Population
Same species occupying a specific area.
5
New cards
Community
Population of different species.
6
New cards
Symbiosis
Any type of close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms of the same or different species
7
New cards
Amensalism
One species suffers, other is not affeced
8
New cards
Commensalism
One species benefits, and the other isn’t.
9
New cards
Competition
Rivalry of species over same resources
10
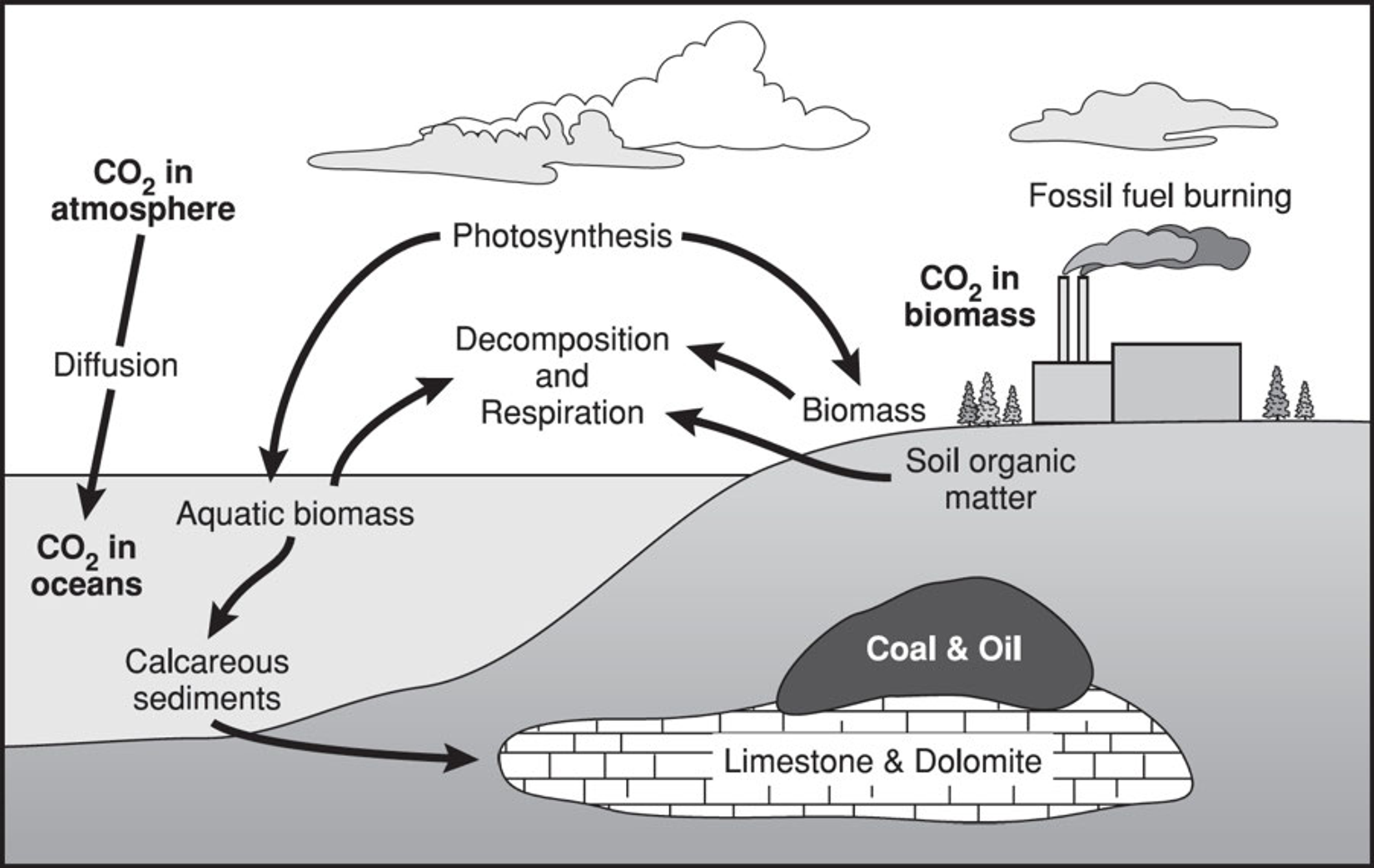
New cards
Mutualism
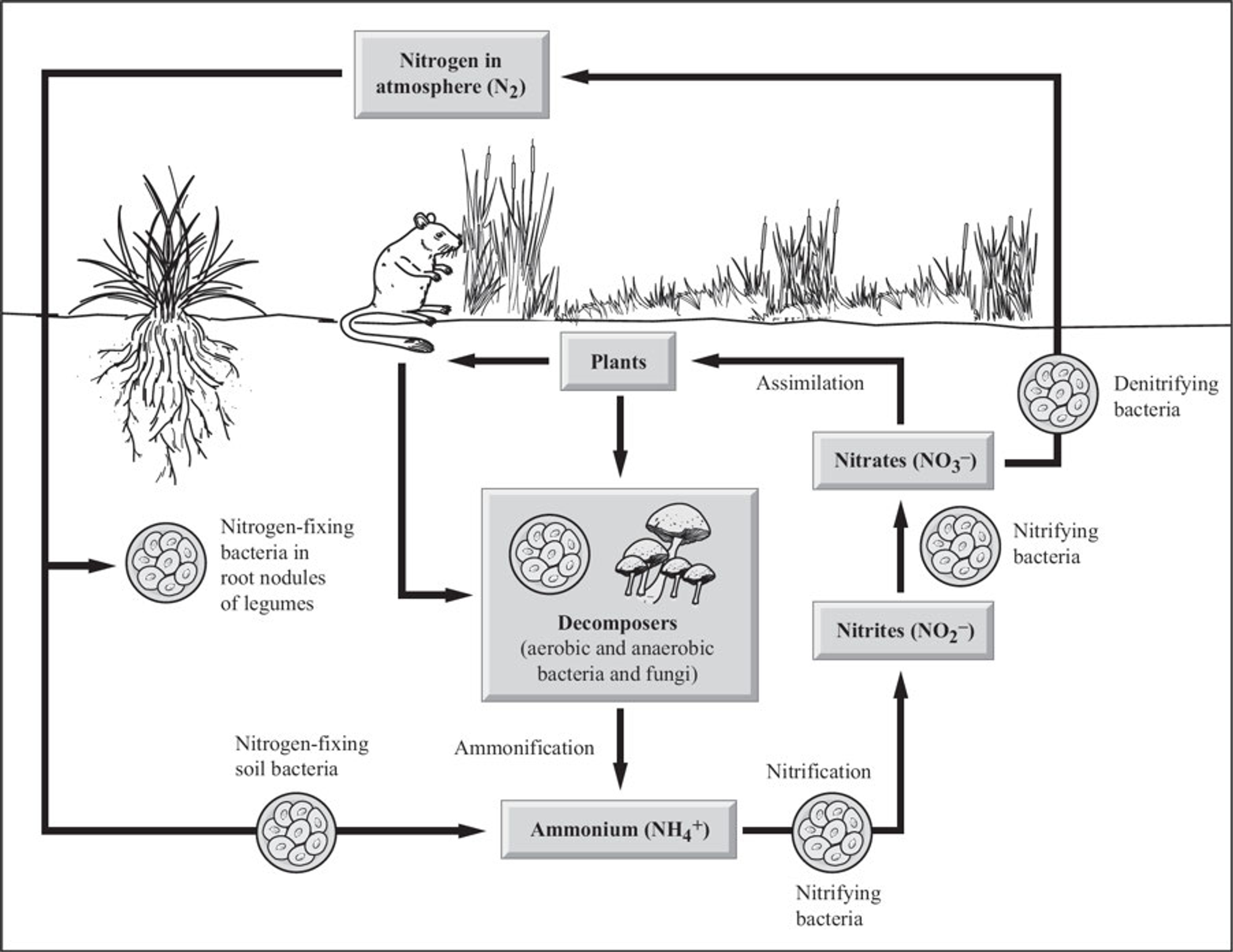
Both species benefit
11
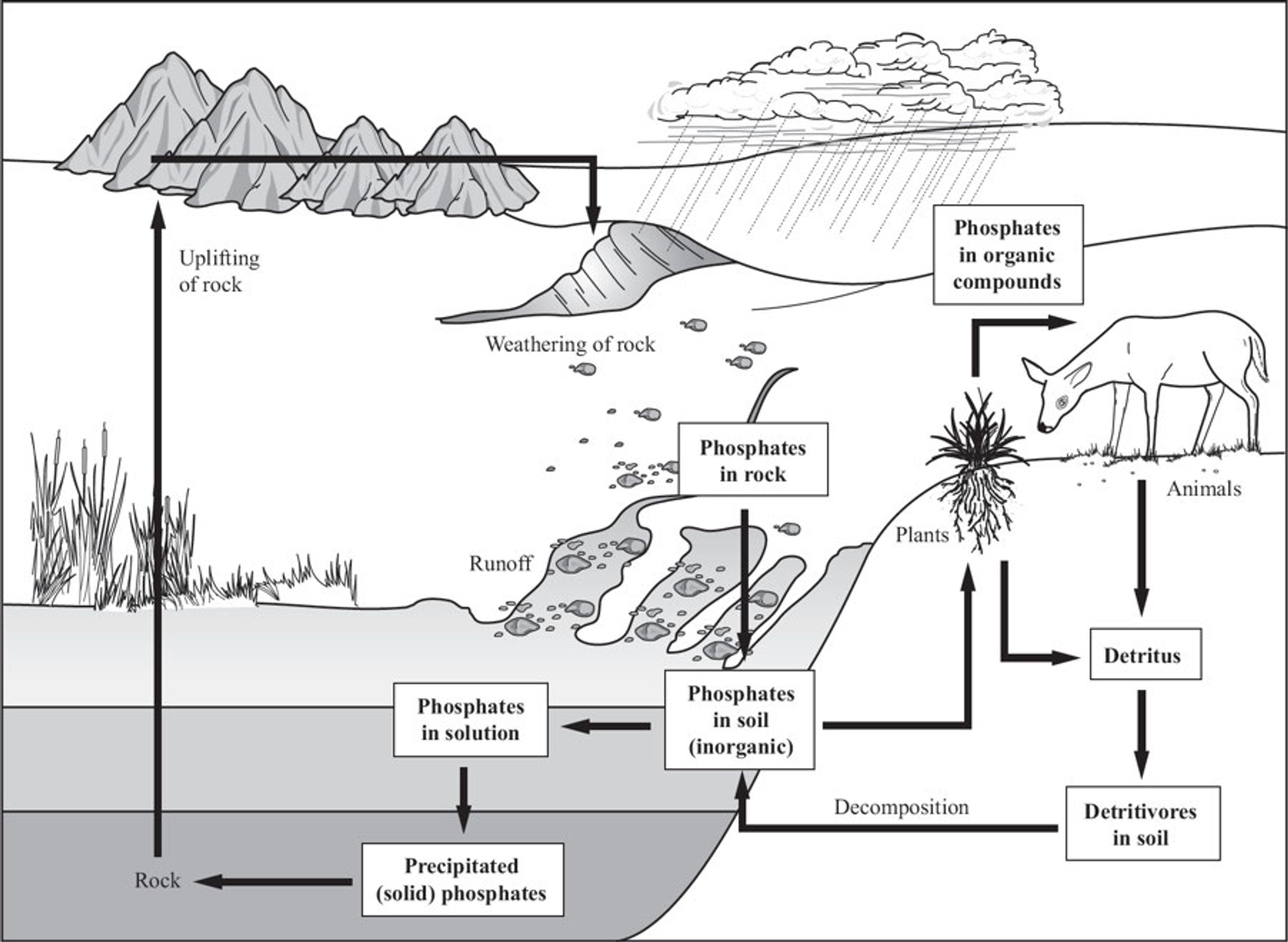
New cards
Parasitism
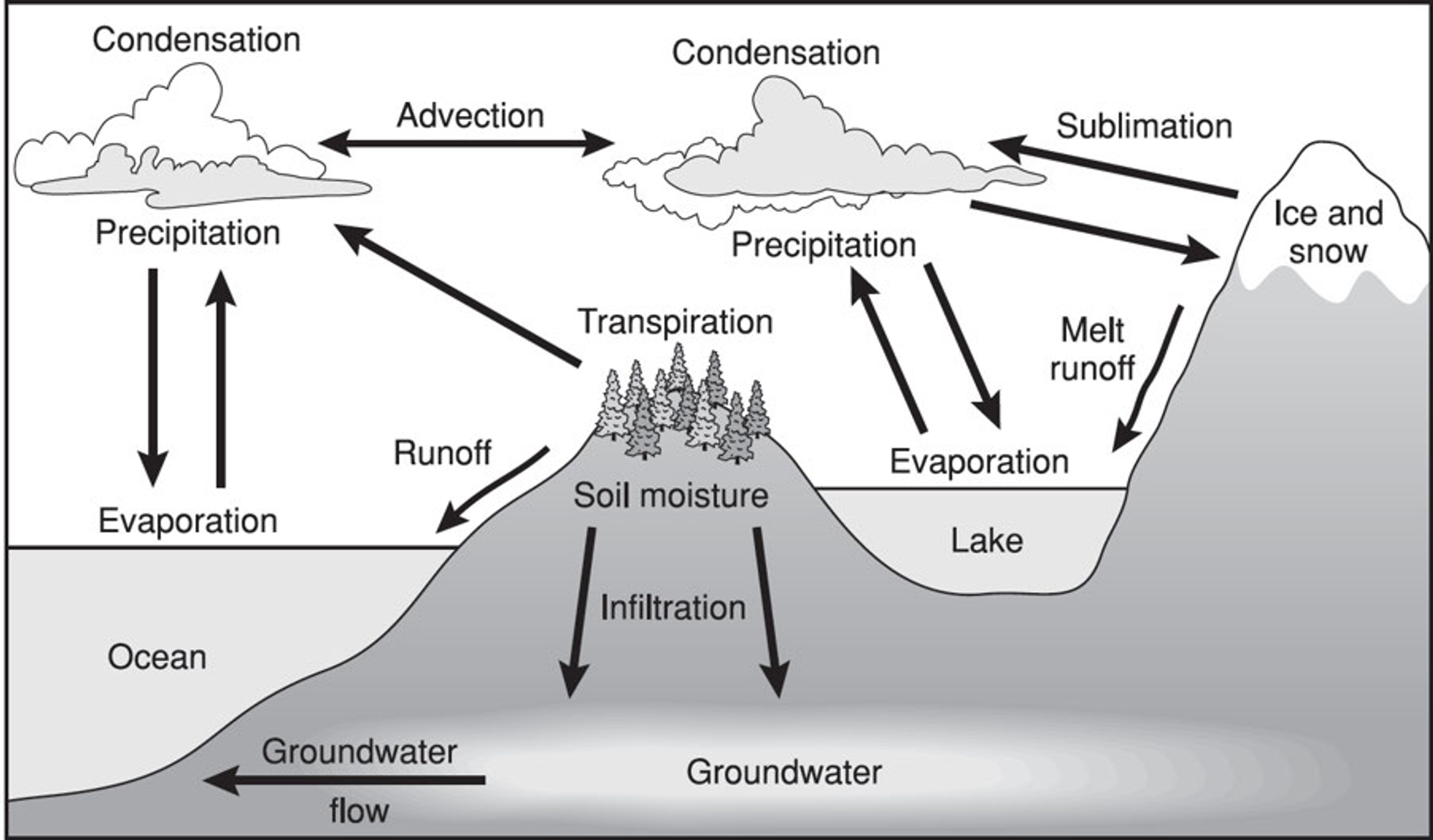
One species benefits and the other is harmed
12
New cards
Predation
Predator kills and eat their prey
13
New cards
Saprottrophism
Organism that feeds on nonliving organic matter.
14
New cards
Morphological partitioning
Two species shares same resources; evolved slightly different structures
15
New cards
Spatial partitioning
Species use same resource occupying different areas.
16
New cards
Temporal partitioning
Two species eliminate direct competition; utilizing same resource at diffrent times
17
New cards
Deserts
An area that receives no more than 25 centimeters of rainfall a year
18
New cards
Forests
Area with large number of trees
19
New cards
Tropical Rainforests
Occurs in tropical areas of heavy rainfalls.
20
New cards
Temperate Deciduous Forests
Occurs in association of seasonally wet and dry or monsoon climates
21
New cards
Temperate Coniferous Forests
Occurs in low levels of precipitation
22
New cards
Grasslands
Lands dominated by grasses.
23
New cards
Southern Taiga
Also known as boreal forest
24
New cards
Northern Taiga
Approaches tree line and tundra biome
25
New cards
Grasslands
Lands dominated by grasses
26
New cards
Savannas
A grassy plain with scattered individual trees
27
New cards
Arctic tundra
Circles North Pole extending South to the Taiga; cold, dry, desert-like.
28
New cards
Alpine tundra
Located in mountains where trees cannot grow
29
New cards
Antarctic
Cold, remote area in the Southern Hemisphere
30
New cards
Photic Zone
Uppermost layer of water.
31
New cards
Neretic Zone (Sublittoral)
Extends to the edge of continental shelf.
32
New cards
Littoral Zone (Intertidal)
Closest to the shore.
33
New cards
Corals
Marine invertebrates that typically live in compact colonies
34
New cards
Fringing Reefs
Grow near the coastline.
35
New cards
Barrier Reefs
Similar to the coastline but separated by deeper lagoons
36
New cards
Attols
Rings of coral that create protected lagoons; found in the middle of the sea
37
New cards
Lakes
Formed where precipitation or runoffs fills depressions in Earths surface
38
New cards
Benthic Zone
Bottom of the Lake
39
New cards
Limnetic Zone
Well lit, open surface water
40
New cards
Littoral Zone
Close to the shore that extends to depth penetrated by sunlight.
41
New cards
Profundal Zone
No light regions
42
New cards
Oligotrophic
Young Lake; deep cold; nutrient poor
43
New cards
Mesotrophic
Middle-Aged Lake; moderate nutrient content.
44
New cards
Eutrophic
Old lake; shallow, warm, large surface area
45
New cards
Source Zones
Headwater streams; often begins as springs or snowmelt
46
New cards
Transition Zone
Slower, warmer, wider, and lower-elevation moving streams
47
New cards
Floodplain Zone
Result of large amounts of sediment and nutrients
48
New cards
Riparian Areas
Lands adjacent to creeks, lakes, rivers, and streams that support vegetation
49
New cards
Law of Tolerance
It states that the existence, abundance, and distribution of species depend on the tolerance level of each species to both physical and chemical factors
50
New cards
Limiting Factor
Any abiotic factor that limits or prevents the growth of a population
51
New cards
Carbon Cycle
The process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere
52
New cards
Carbon Cycle
53
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle
A process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere
54
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle
55
New cards
Phosphorous Cycle
A cycle that describes the movement of phosphorus through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere
56
New cards
Phosphorous Cycle
57
New cards
Hydrologic Cycle
It involves the continuous circulation of water in the Earth-Atmosphere.
58
New cards
Hydrologic Cycle
59
New cards
Aquifer
Contains water in quantities sufficient to support a well or spring
60
New cards
Recharge zone
The surface area above an aquifer that supplies water to the aquifer
61
New cards
Unsaturated zone
The zone immediately below the land surface
62
New cards
Water table
The level below which the ground is saturated with water
63
New cards
Biomass pyramid
It shows how much organic mass is within each trophic level
64
New cards
Energy Pyramids
These show the proportion of energy passed from one trophic level to the next-level consumers in an ecosystem
65
New cards
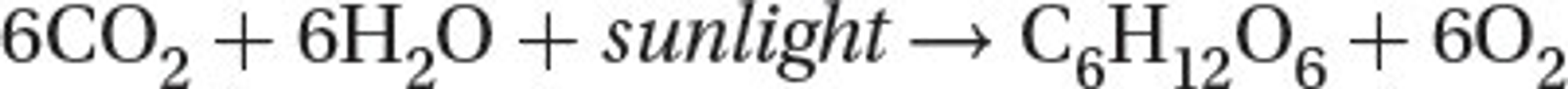
Photosynthesis
66
New cards
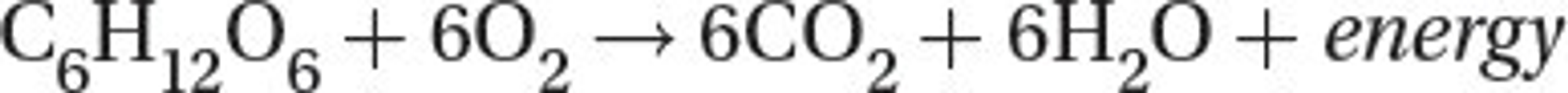
Cellular respiration
67
New cards
Gross primary production (GPP)
The rate at which plants capture and fix a given amount of chemical energy as biomass in a given length of time.
68
New cards
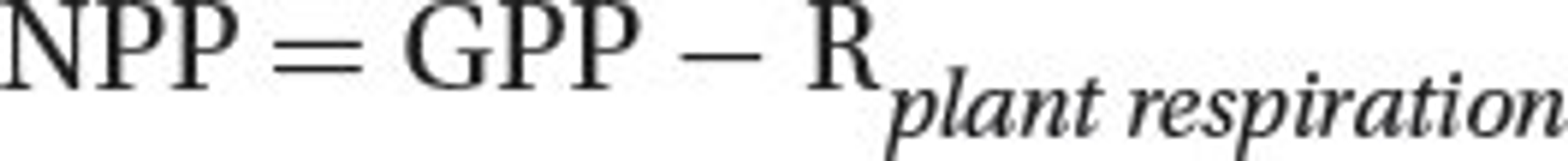
\
Net primary production Formula
69
New cards
Net primary production (NPP)
The remaining fixed energy is the rate at which all the plants in an ecosystem produce net useful chemical energy
70
New cards
Biodiversity
Variability among species, between species, and of ecosystems
71
New cards
Genetic diversity
Range of all genetic traits
72
New cards
Species diversity
Number of different species in a specific area
73
New cards
Ecosystem diversity
Range of habitats in specific area
74
New cards
Generalists
Live in different types of environments and have varied diets.
75
New cards
Specialists
Require unique resources and have limited diets
76
New cards
Pioneer
Earlier successional plants; generalists.
77
New cards
Keystone
Their presence contributes to the diversity of life; their extinction could lead to the extinction of other life forms
78
New cards
Indicator
Their presence, absence, or abundance reflects a specific environmental condition
79
New cards
Supporting Benefits
Provides more aid to the ecosystem.
80
New cards
Regulating Benefits
Provided that help moderate natural phenomena
81
New cards
Provisioning Benefits
Provides diversity of products.
82
New cards
Cultural Benefits
Supports recreational services.
83
New cards
Island Biogeography
It examines the factors that affect the richness and diversity of species living in these isolated natural communities
84
New cards
Island
A suitable habitat for a specific ecosystem that is surrounded by a large area of unsuitable habitat
85
New cards
Theory of Island Biogeography
It proposes that the number of species found on an "island" is determined by immigration and extinction of isolated populations
86
New cards
Physiological Adaptation
Methods of temperature control or how food are digested.
87
New cards
Behavioral Adaptation
Instincts, mating behavior, vocalizations.
88
New cards
Structural Adaptation
Physical features.
89
New cards
Short Term Adaptations
Develops from environments temporary changes
90
New cards
Long-term Adaptations
Develops over long periods of time in response to natural selection
91
New cards
Facilitation
Species modifies the environment, meeting the needs of others
92
New cards
Inhibition
Species modifies the environment, not suitable for the environment
93
New cards
Tolerance
Species are not affected by the presence of others
94
New cards
Primary Succession
Species first colonize a lifeless habitat.
95
New cards
Secondary Succession
Species recolonize a destroyed habitat
96
New cards
Episodic Process
Occurring occasionally and at irregular intervals
97
New cards
Periodic Process
Occurring at repeated intervals
98
New cards
Random Process
Lacking a regular pattern.
99
New cards
Generalists
Able to use a variety of environmental resources
100
New cards
Specialists
Use specific set of resources