Histology & Tissues Characteristics
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
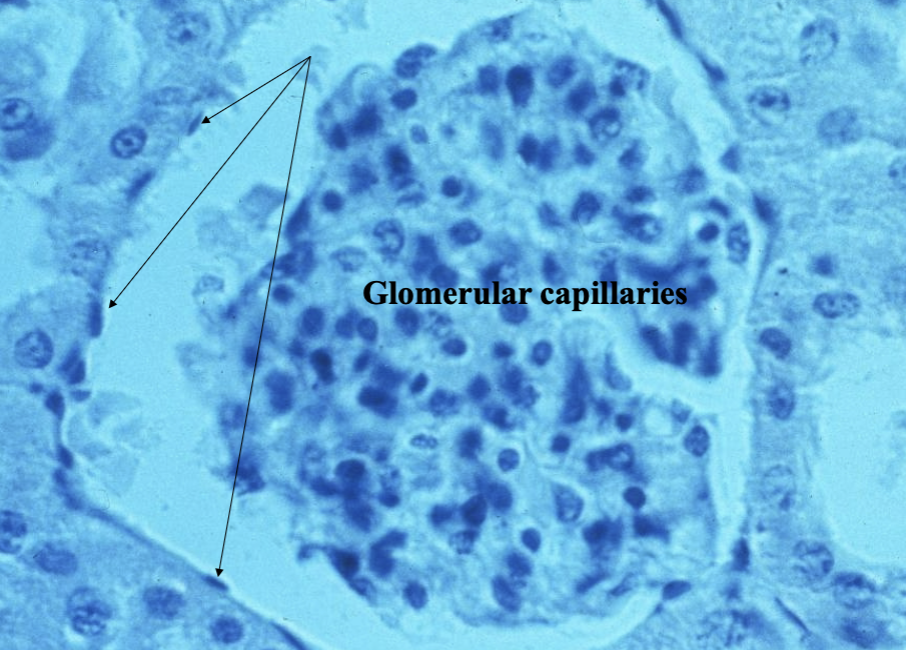
What are the arrows pointing at?
Simple Squamous Epithelial tissue
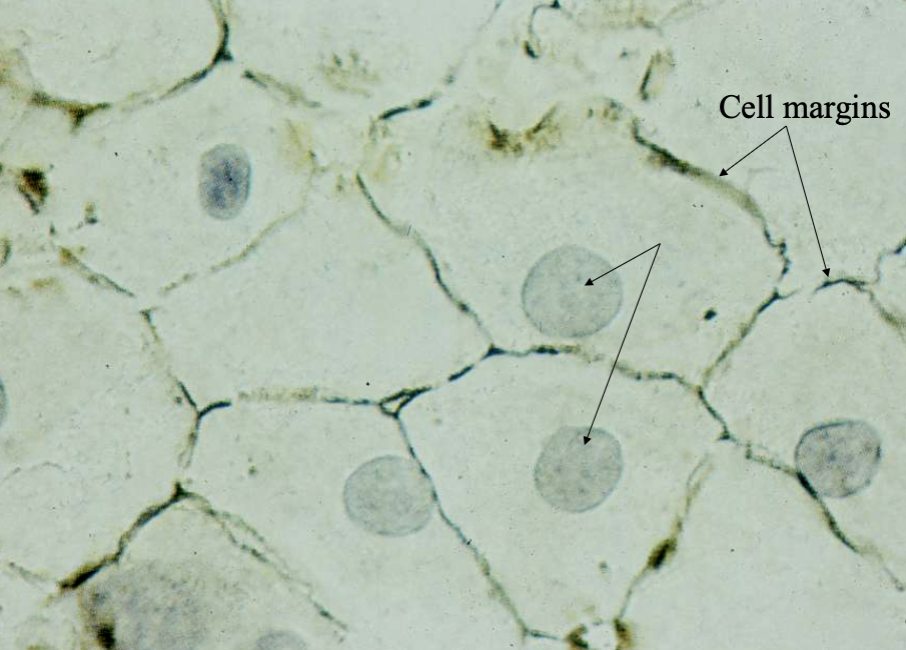
What is this? What are the arrows pointing at?
Simple Squamous mesothelium
Nuclei & cell margins
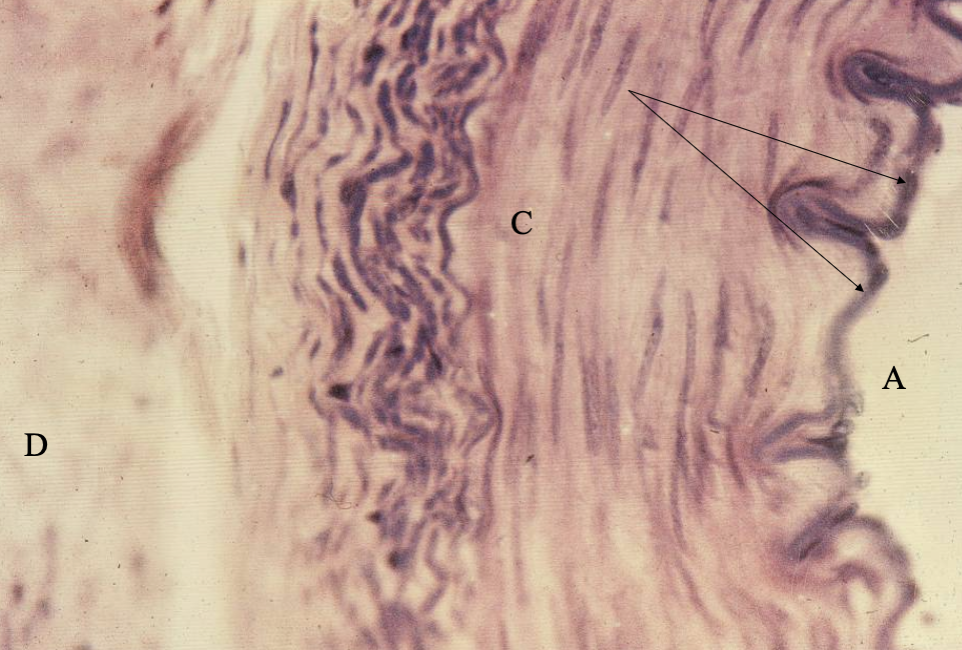
What are the arrows pointing at? And what is A, C & D?
Simple squamous Endothelium tissue
Lumen
smooth muscle
connective tissue
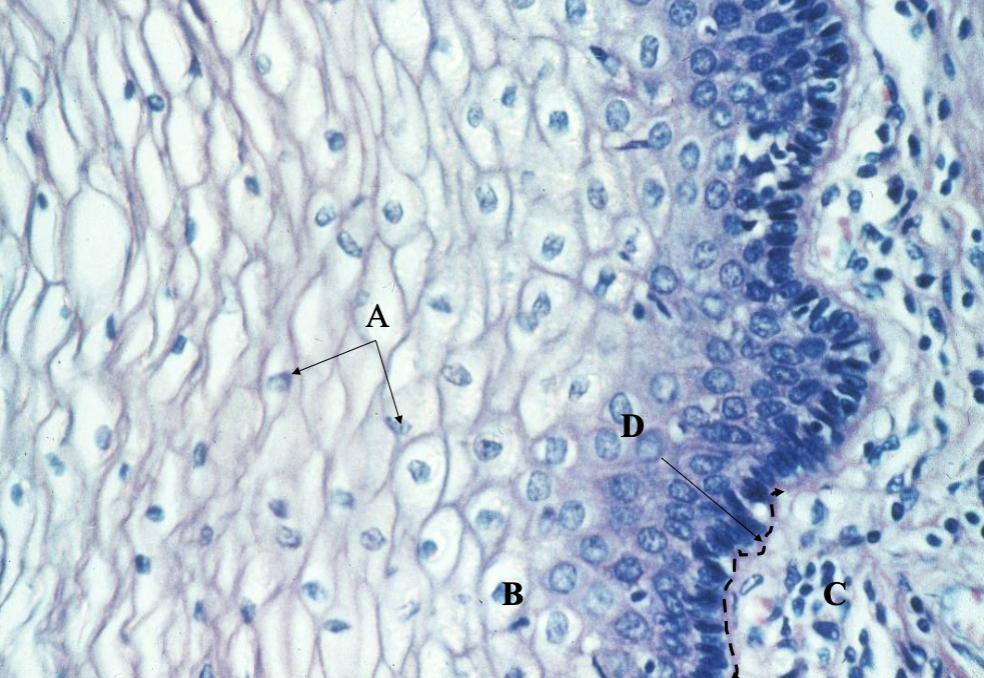
What cell structure is this? What’s A, B, C & D?
Stratified squamous of the lower strata (skin)
Nuclei
Epidermis
Dermis
Basement membrane
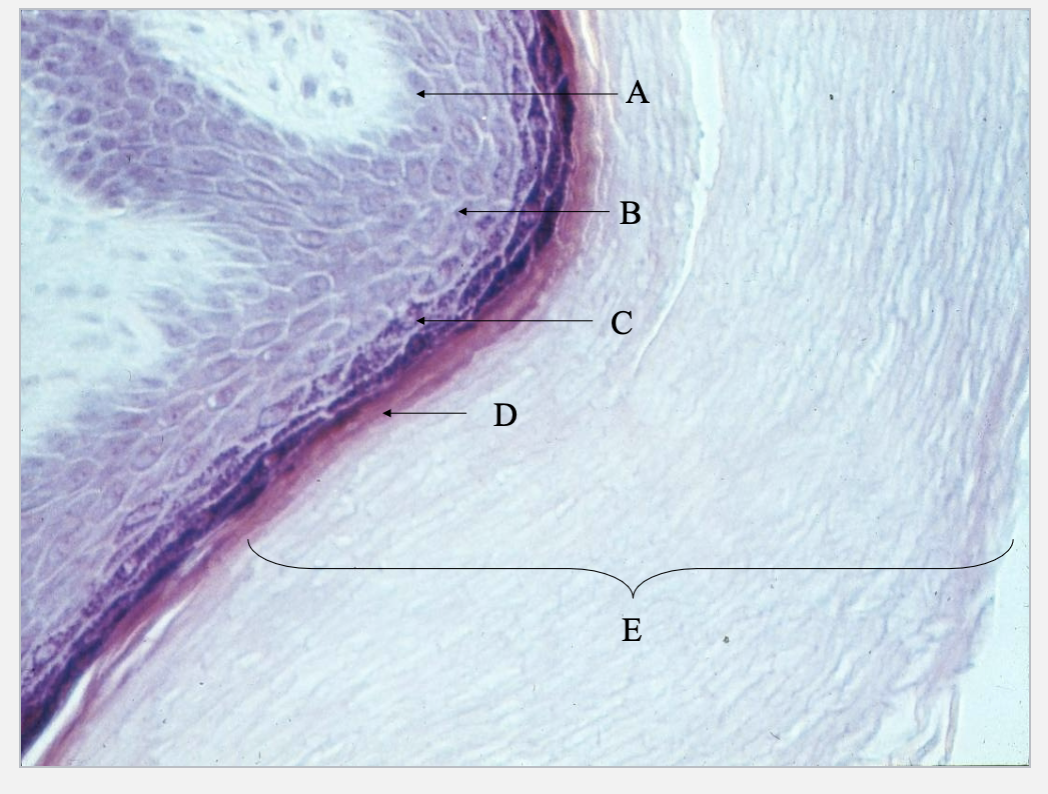
What is A, B, C, D & E?
Stratum basale
Stratum spinous
Stratum granulosum
Stratum lucid
Stratum corneum
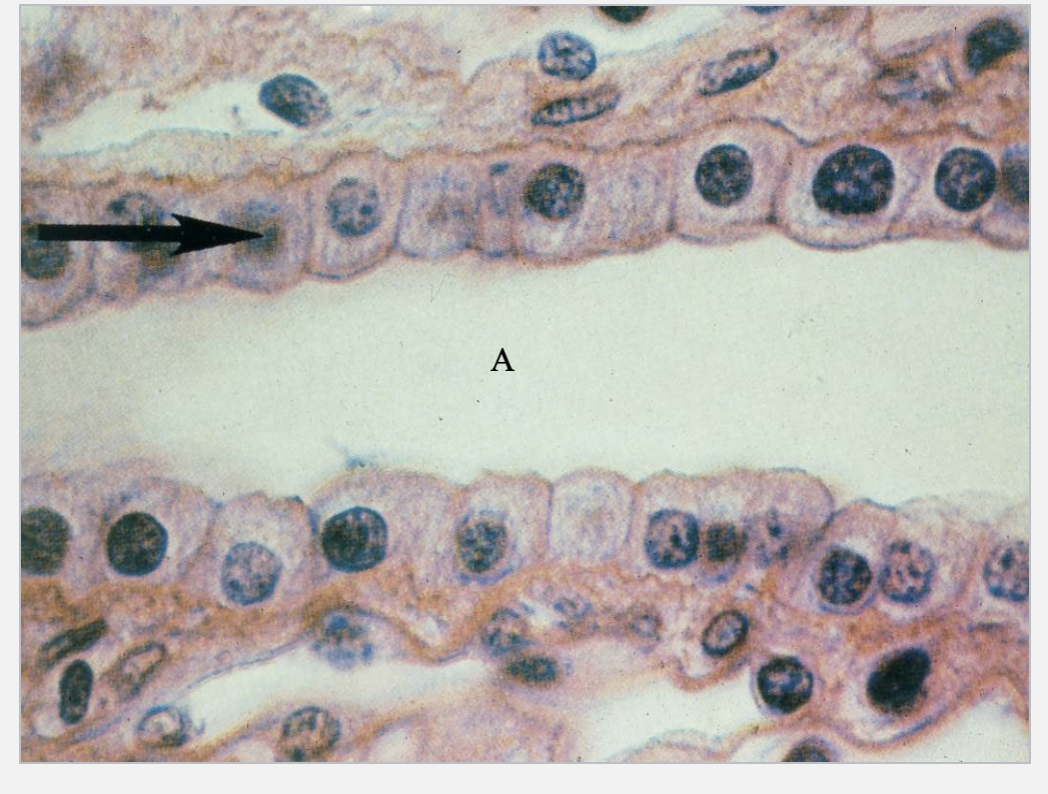
What tissue type is the arrow pointing at? What’s A?
Simple cubdioal epithelial tissue
lumen
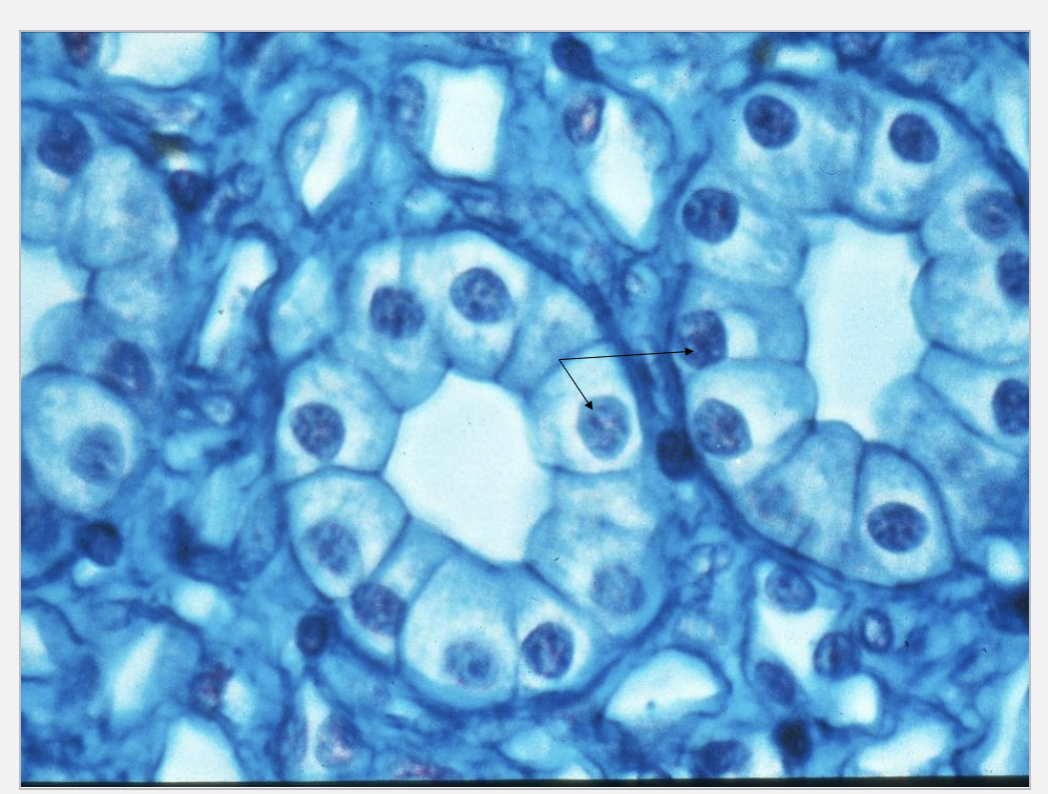
What tissue type is seen & what are the arrows pointing at?
simple cuboidal tissue
nuclei
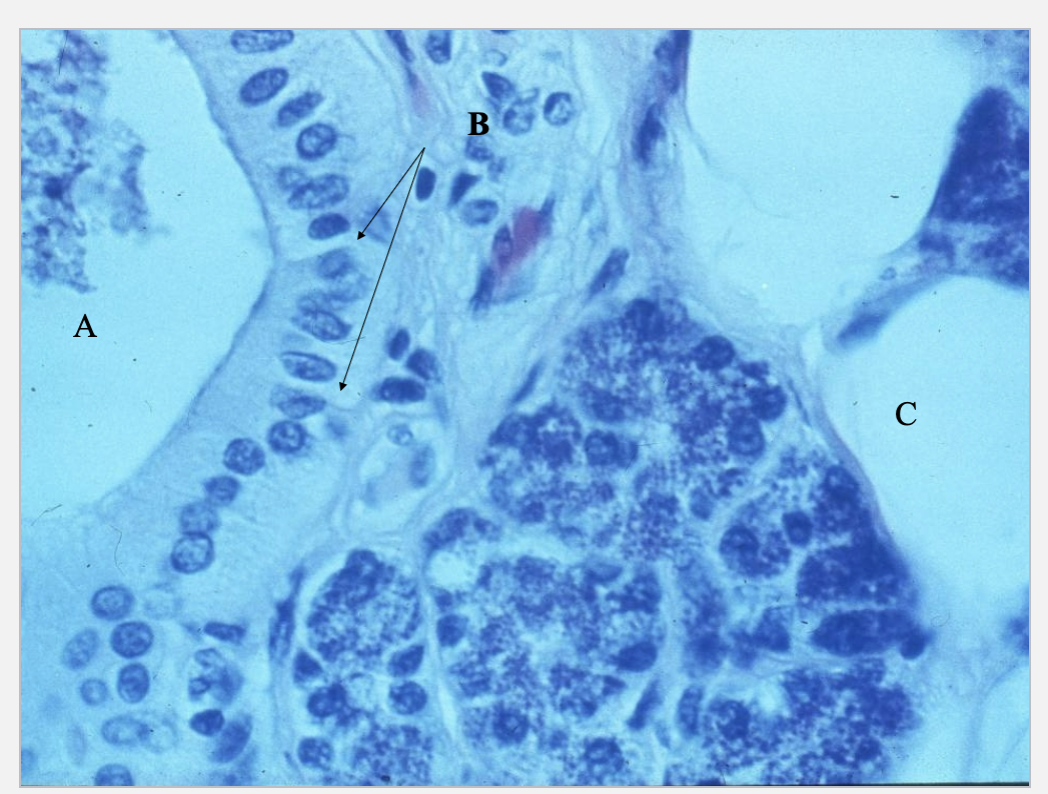
What is A, B & C?
Lumen
Simple columnar epithelium salivary gland duct
Adipocyte
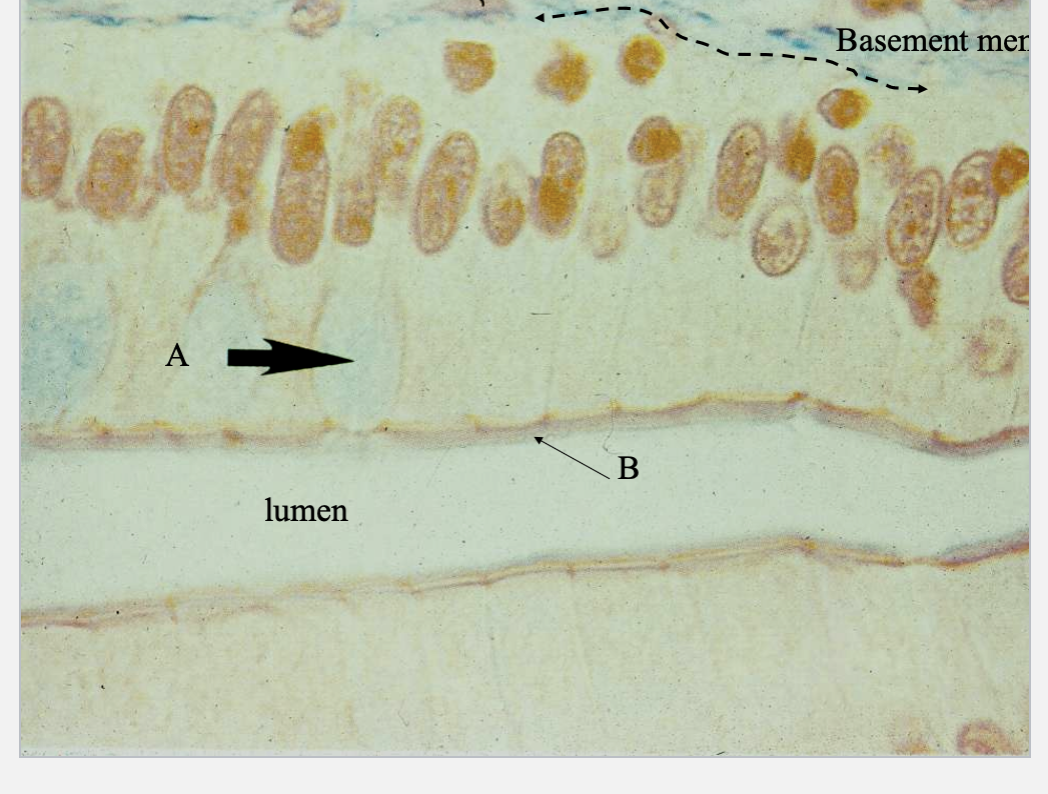
What Tissue type is this? Where is it? & What’s A &B?
Simple Columnar epithelium in small intestine
Goblet cell
Microvilli
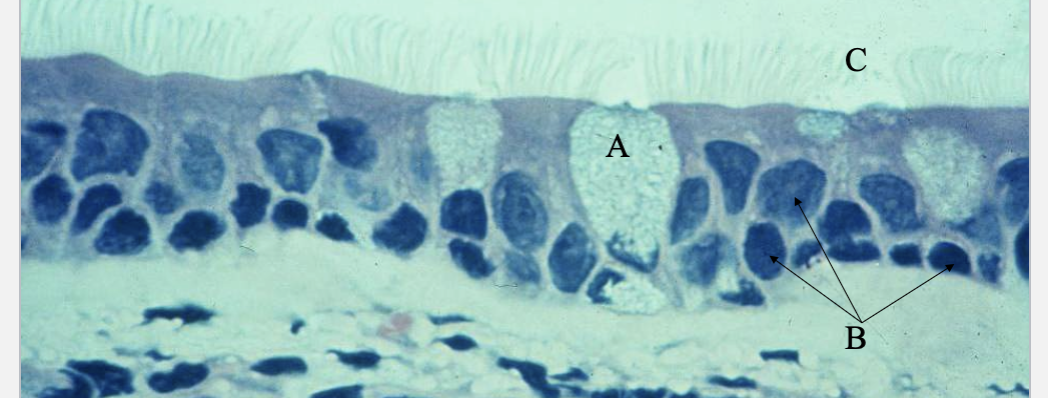
What is this tissue type? where is it? What’s A, B & C?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium in trachea
Goblet cell
nuclei
cilia
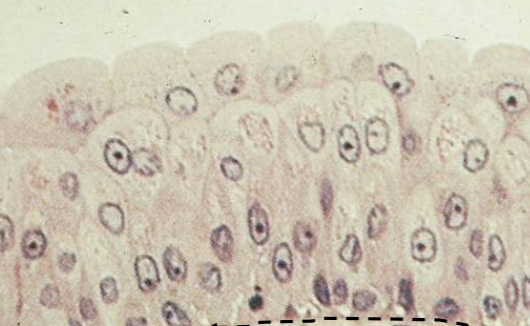
What tissue type is this? where is it found?
Transitional epithelium
found in unrinary bladder
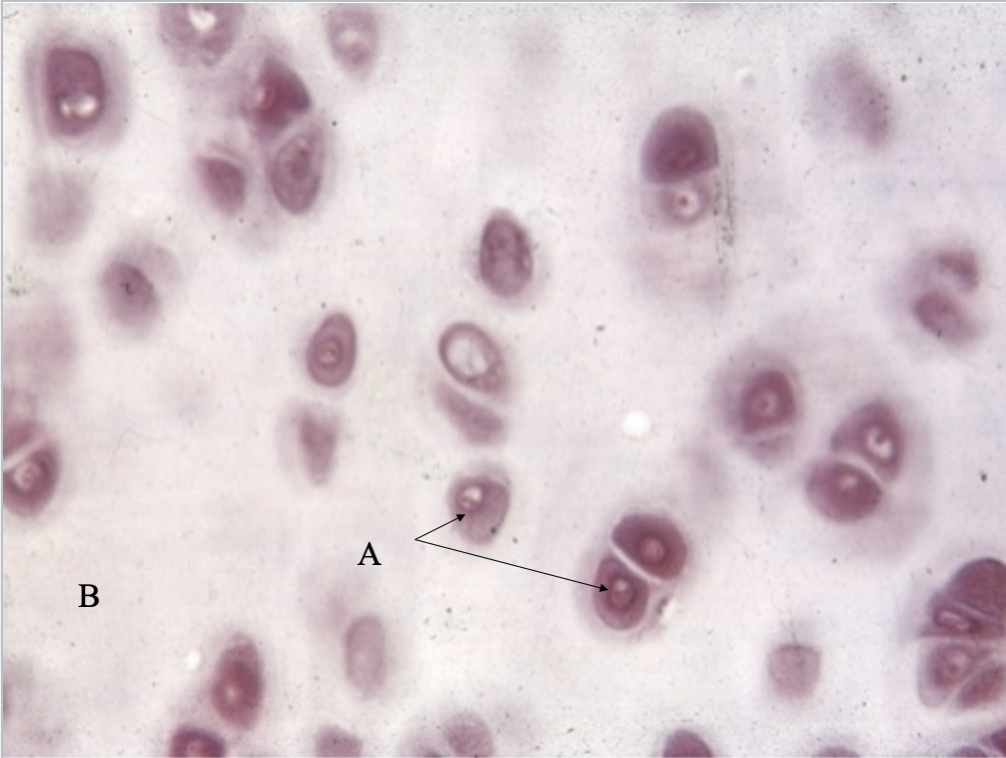
What’s this tissue? & what is A & B?
Hyaline cartilage CT
Chonodrocytes
Matrix
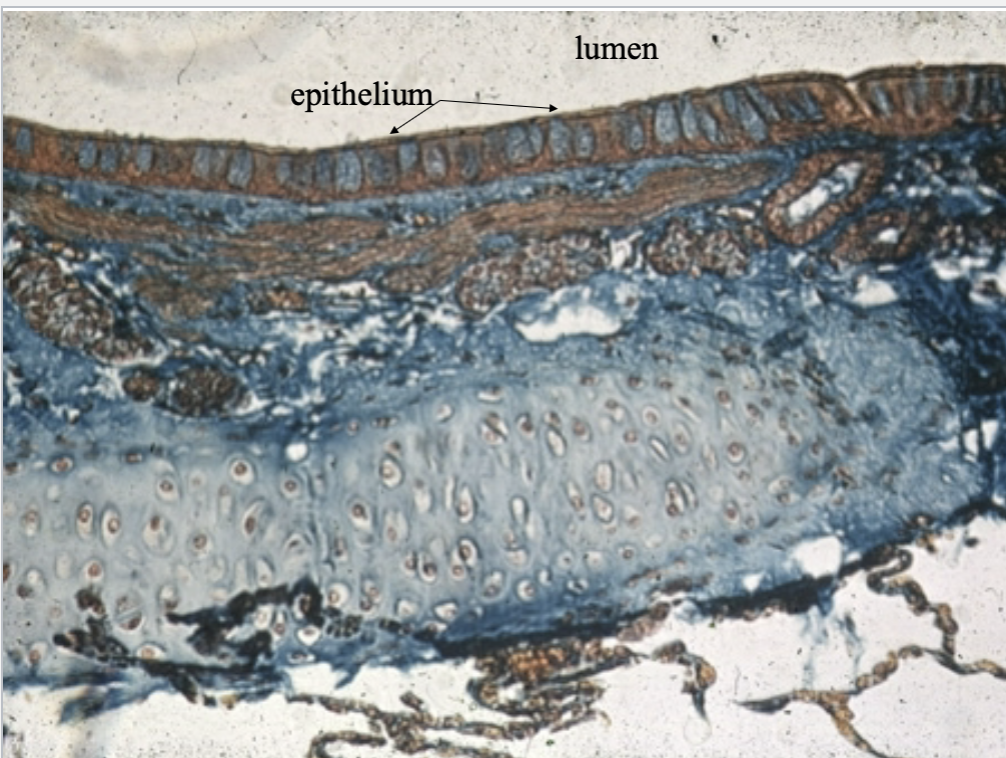
What is this tissue? where can it be found?
Hyaline cartilage CT
trachea
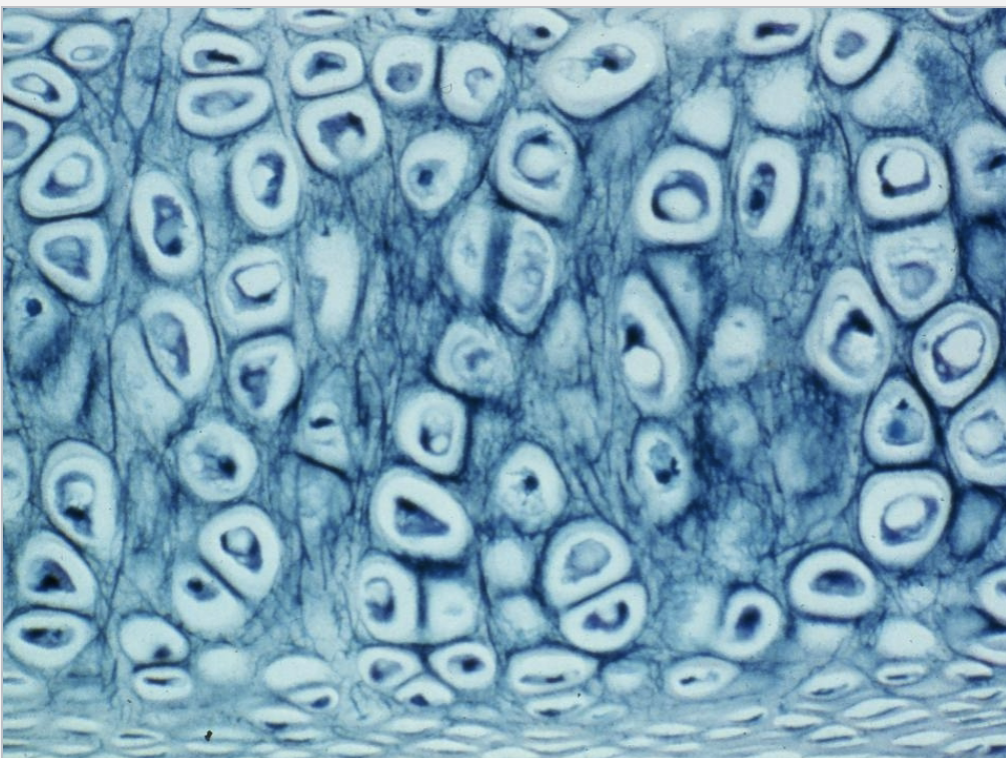
What is this tissue?
Elastic cartilage
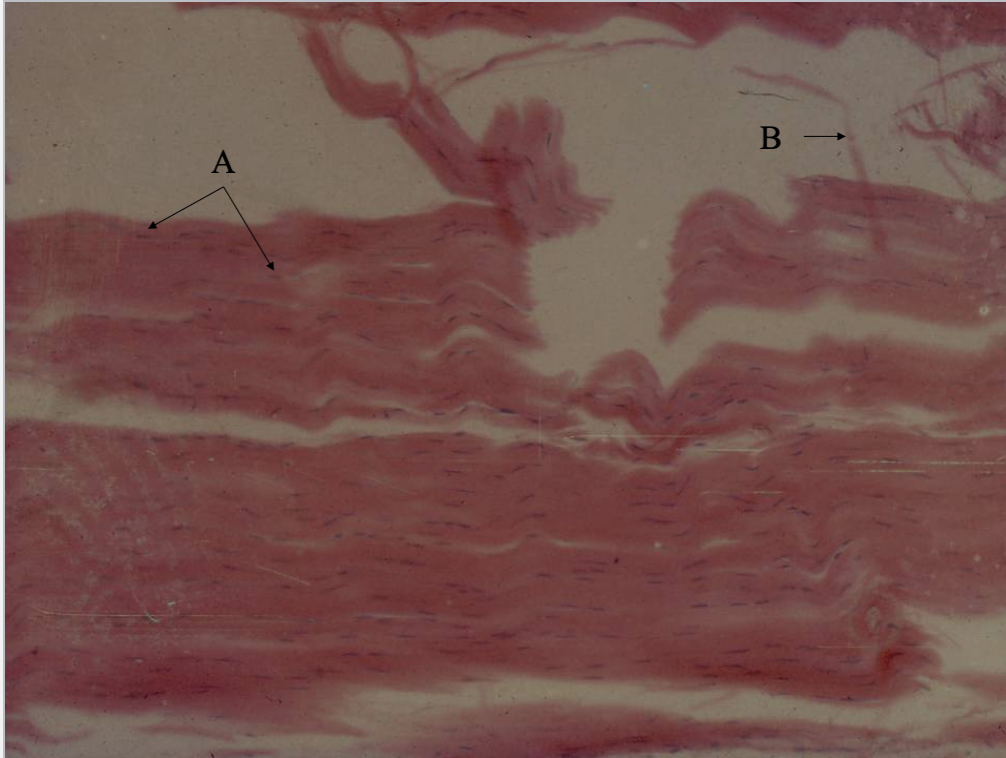
What tissue type is this? What’s A & B?
White fibrous CT in tendon
Nuclei
Collagen fiber
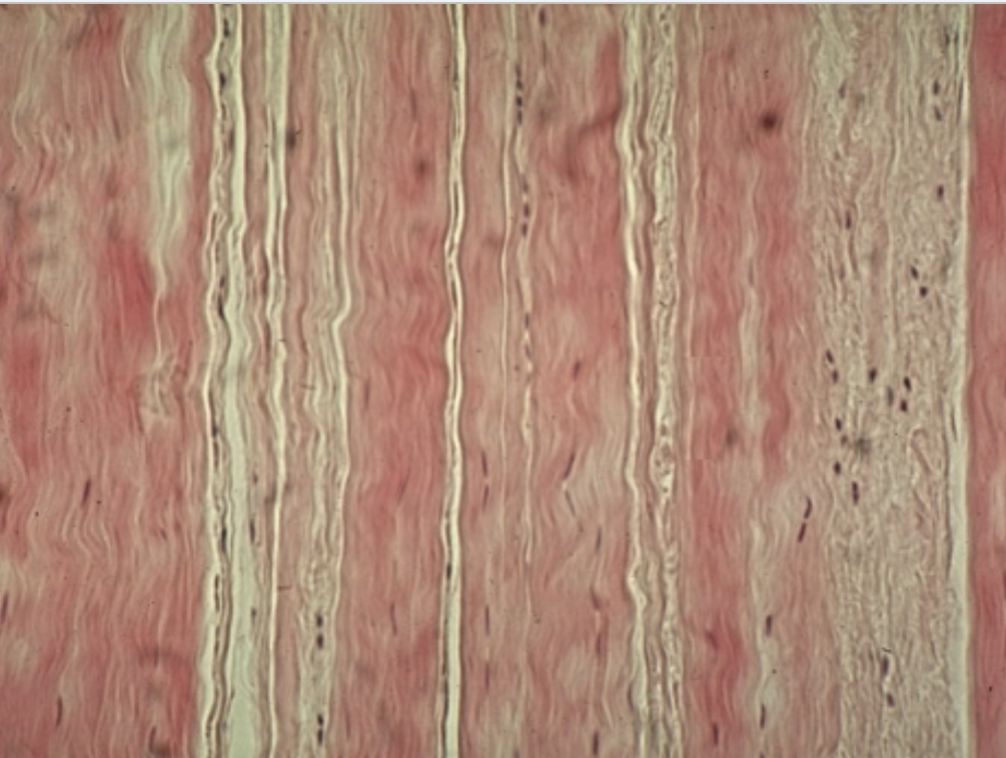
What tissue type is this? Where can it be found?
Dense regular connective tissue. it can be found in tendons
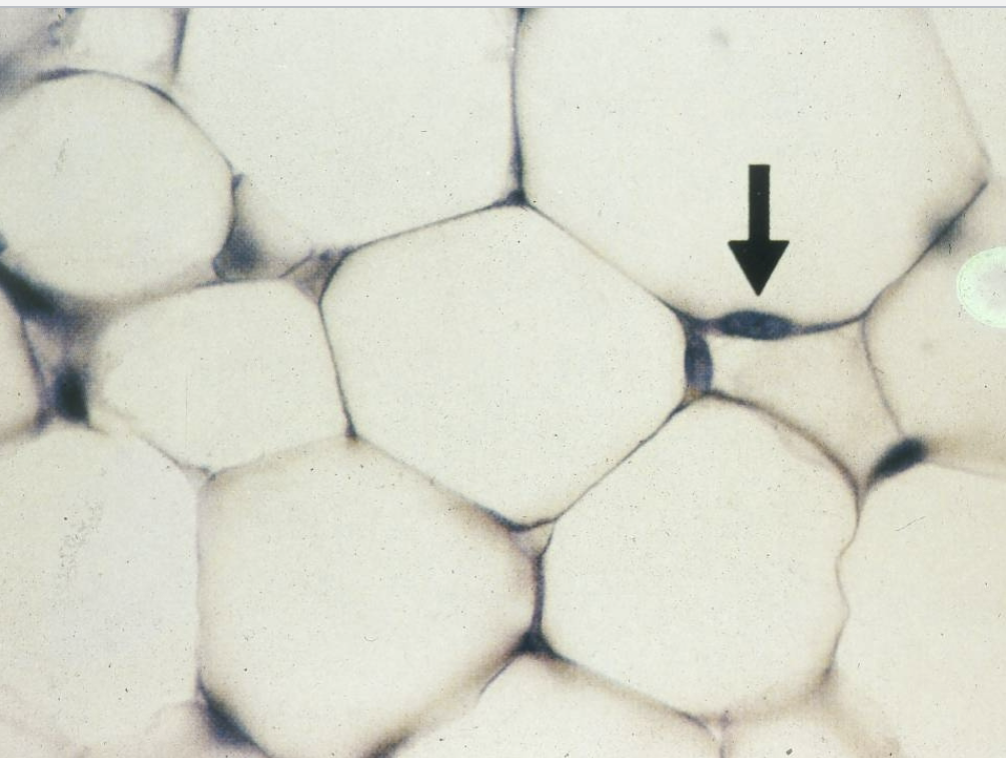
What tissue is this? What is the arrow pointing to?
Adipose CT tissue
nucleus
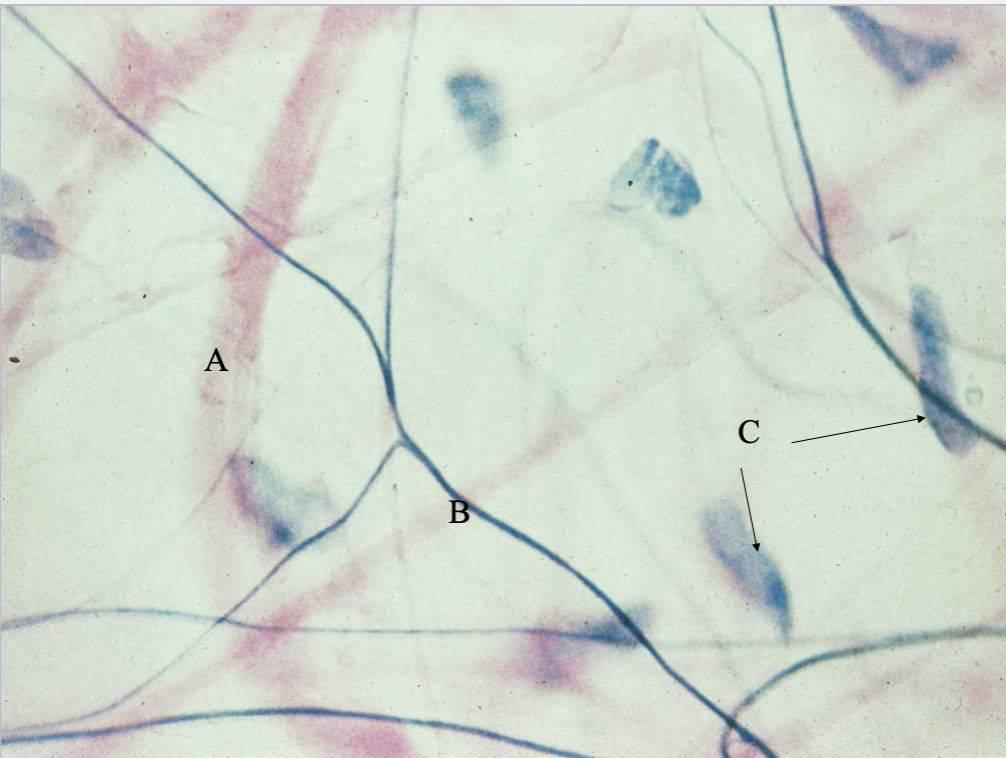
What tissue type is this? What is A, B & C?
Areolar CT in the Hyodermis
Collagen fiber
Elastic fiber
nuclei
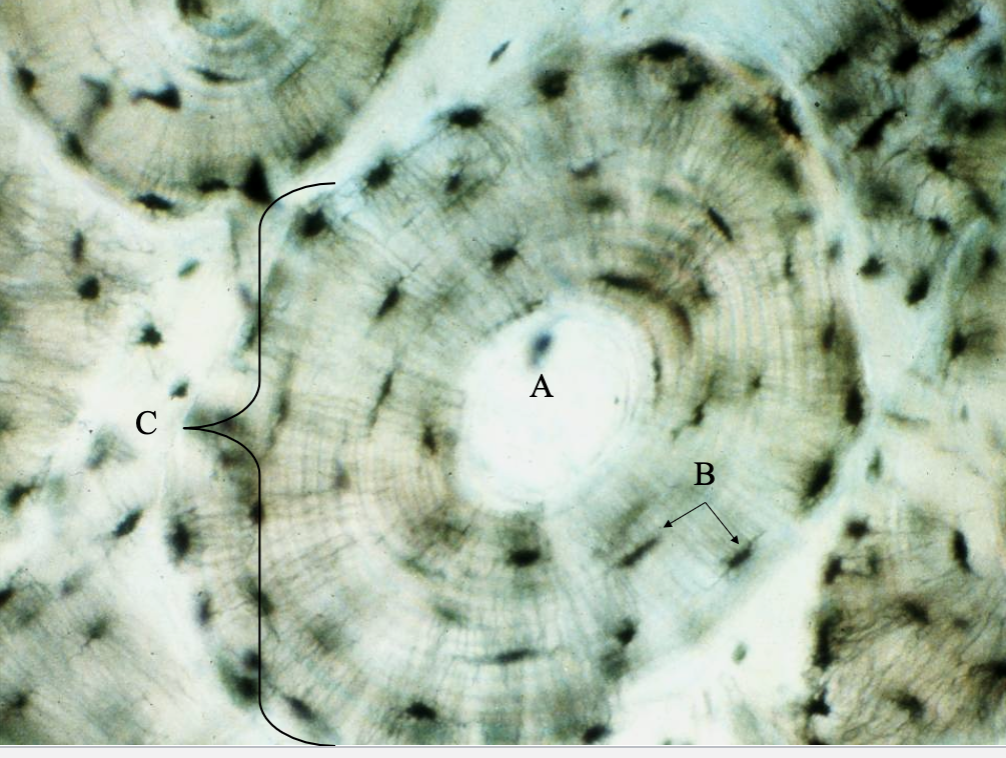
What tissue type is this? What’s A, B & C?
Compact Bone
central canal
Osteocytes
Osteon
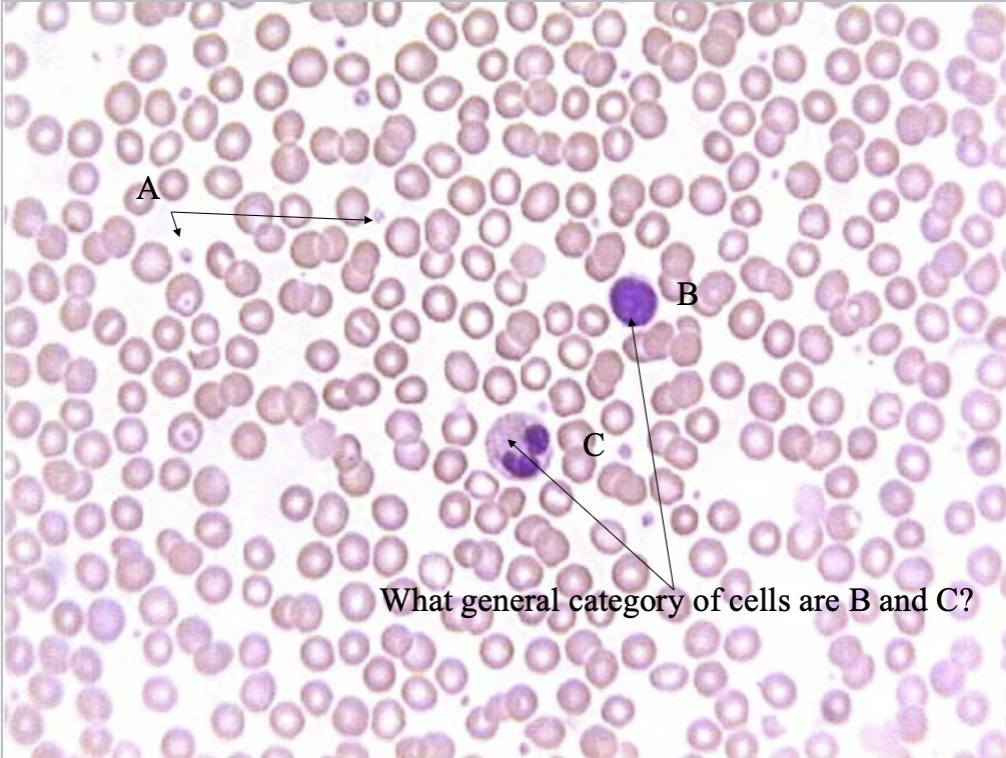
What tissue type is this? what’s A, B & C?
Blood CT
Platelets
White blood cells
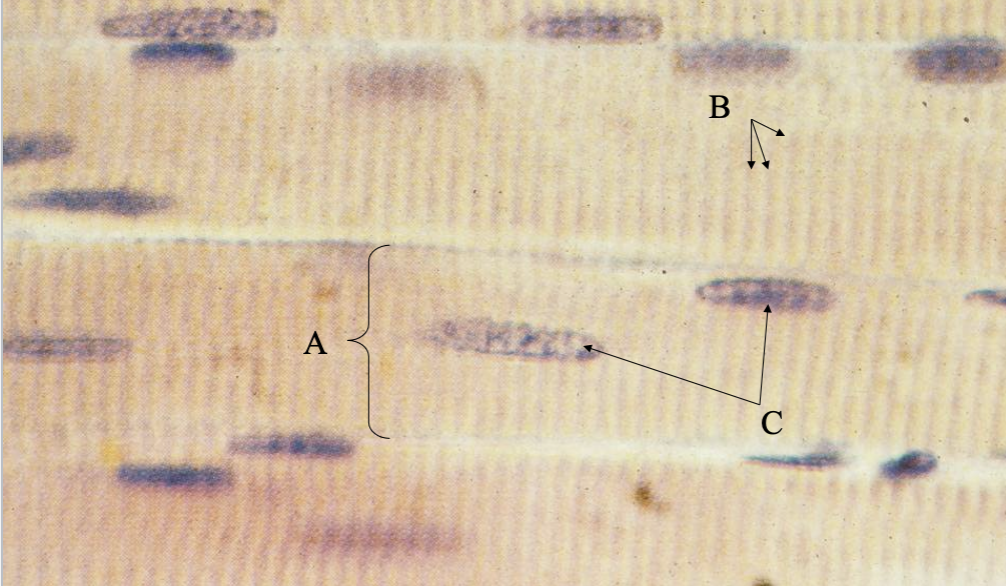
What tissue is this? what's A, B & C?
Skeletal Muscle
Muscle Cell
Strations
Nuclei
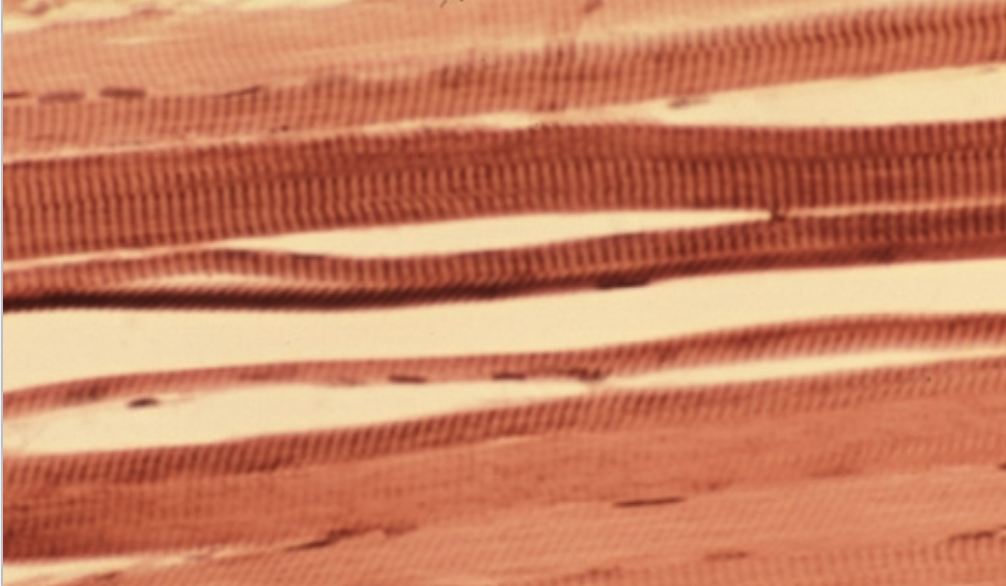

What tissue is this?
Skeletal muscle
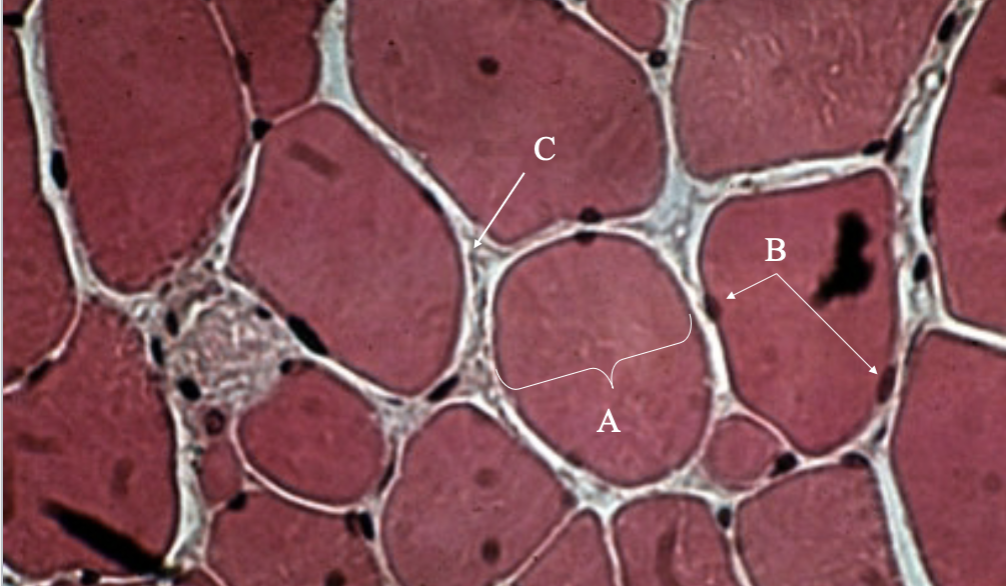
What tissue is this? What’s A, B & C?
Cross Section of Skeletal Muscle Tissue
muscle cell
nuclei
endomysium
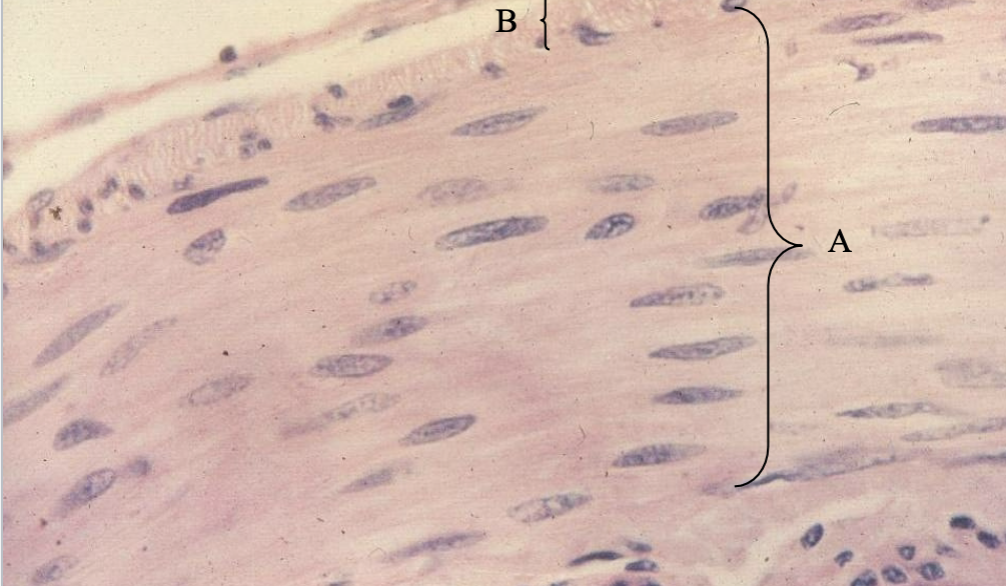
What tissue is this? What’s A & B?
Smooth muscle from the intestine
inner circular layer
outer longitudinal layer
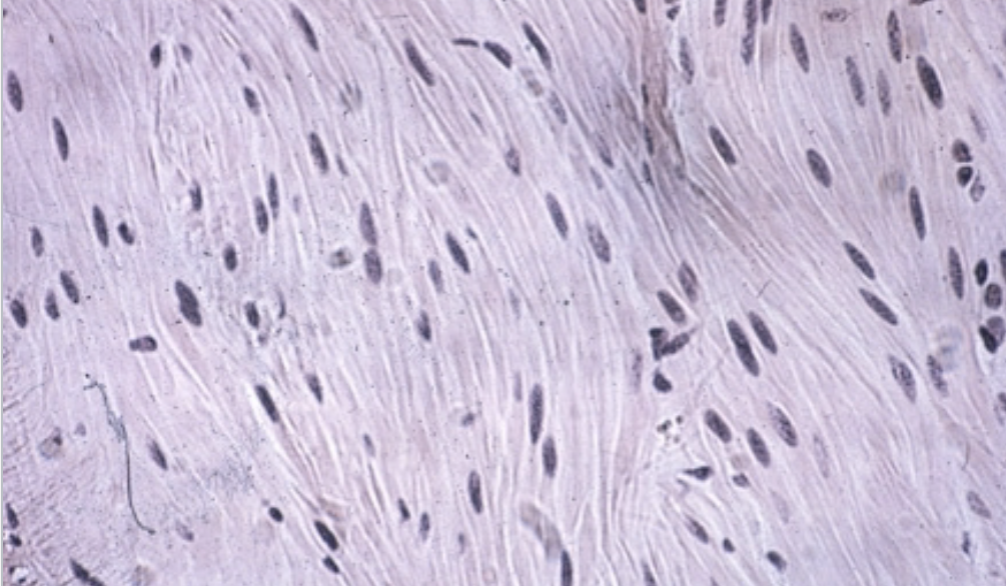
What tissue is this?
Smooth muscle
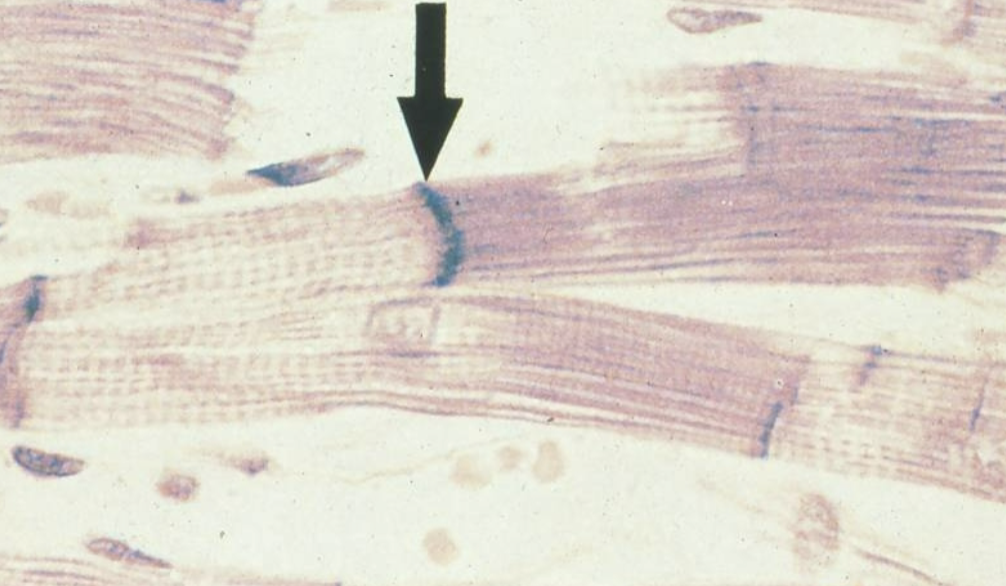
What tissue is this? What’s the arrow pointing at?
Cardiac muscle
intercalated disks
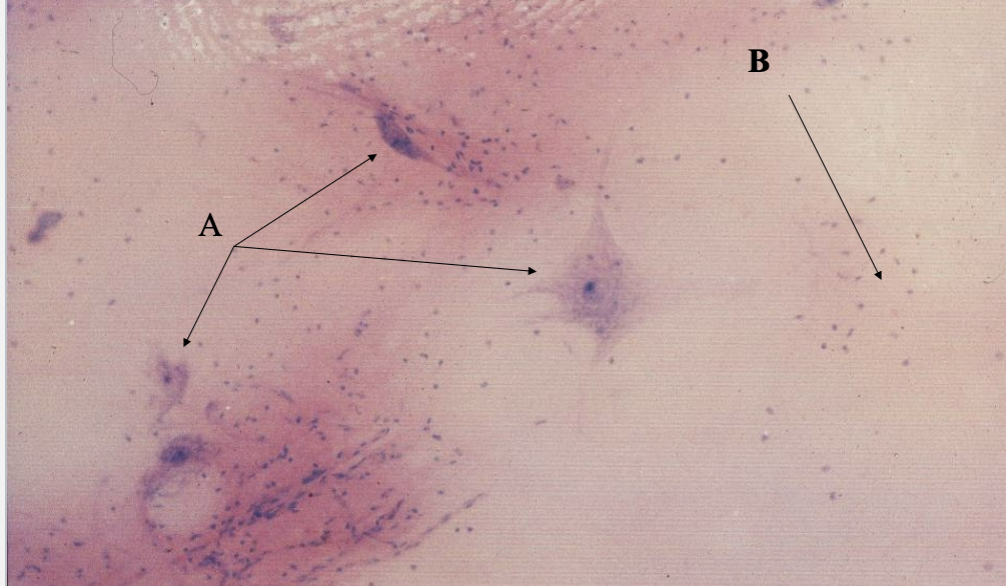
What tissue is this? What is A & B?
Multipolar neuron (spinal cord smear)
neurons
Neuroglia
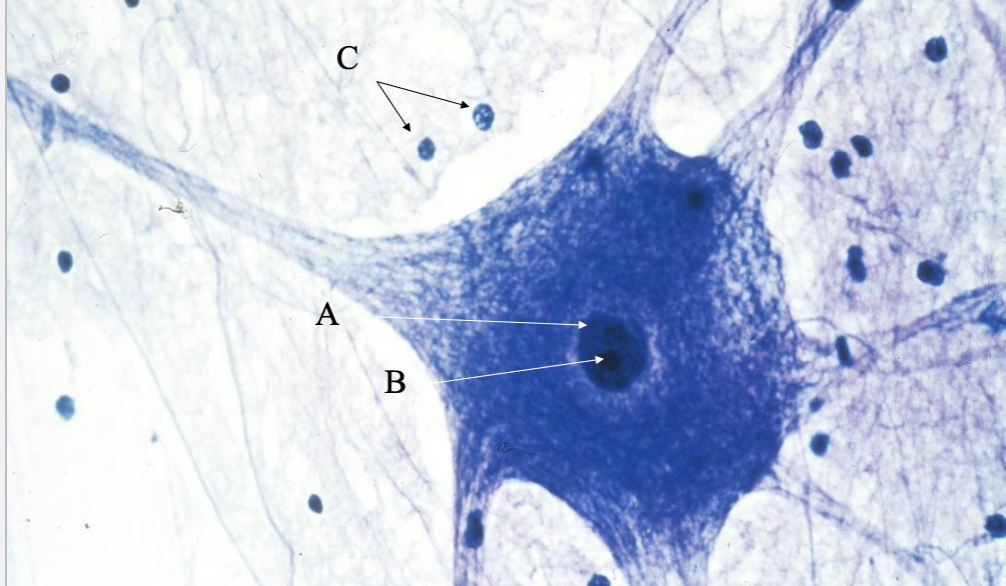
What’s this? What’s A, B & C?
Multipolar neuron.
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Neurgolia
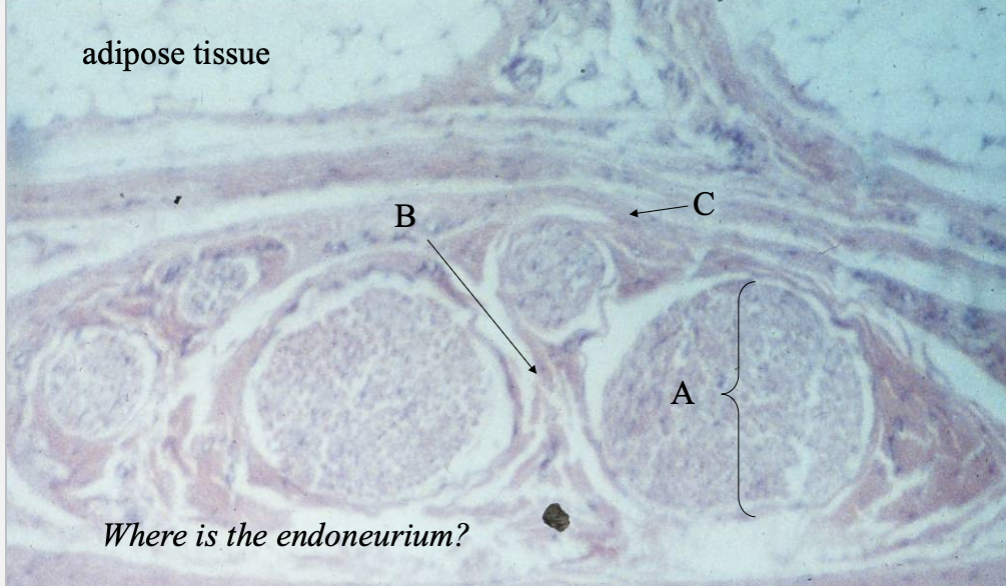
What’s A, B & C?
fascicle
perineurium
epinerium
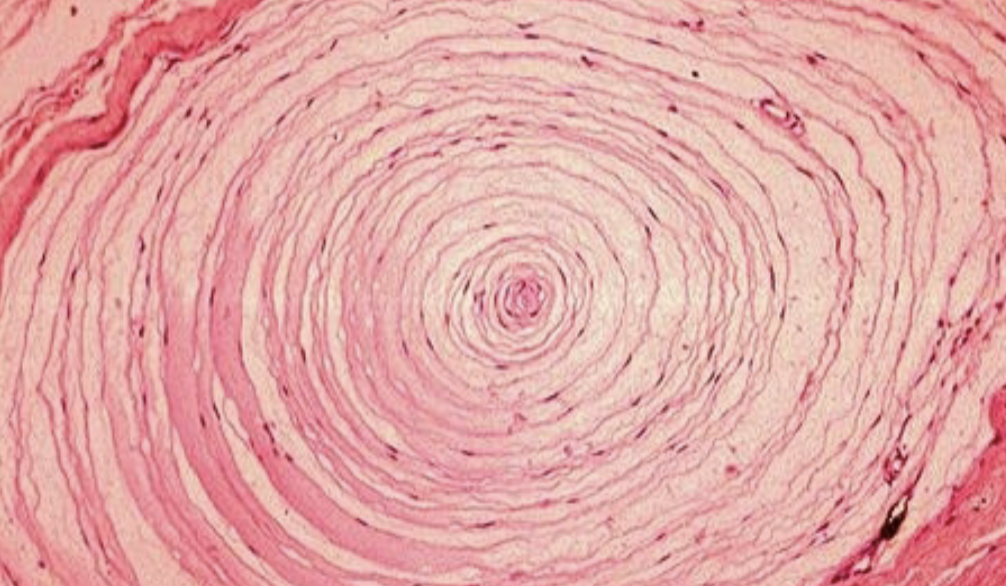
What’s this?
Pacinian corpuscle
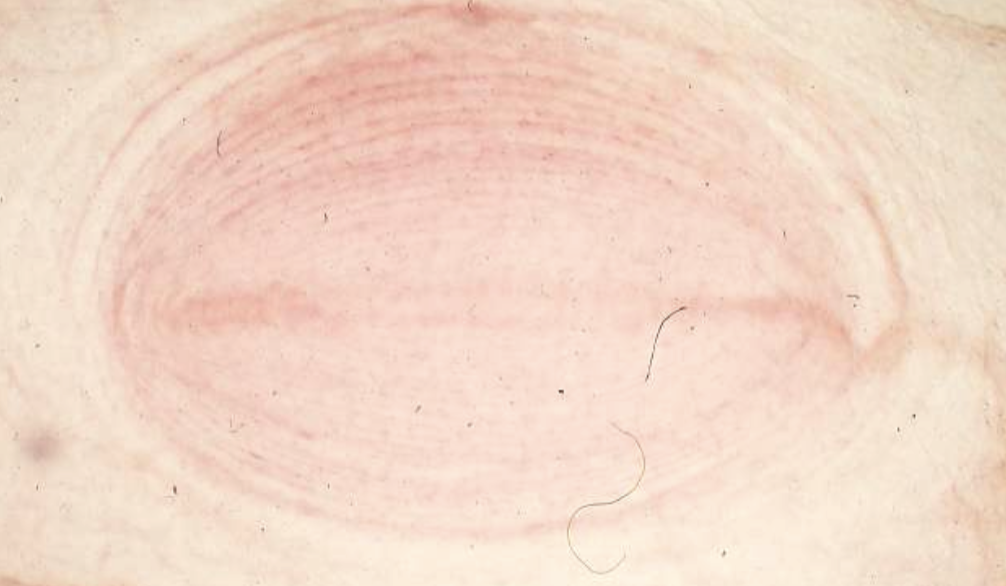
What’s this?
Pacinian corpuscle
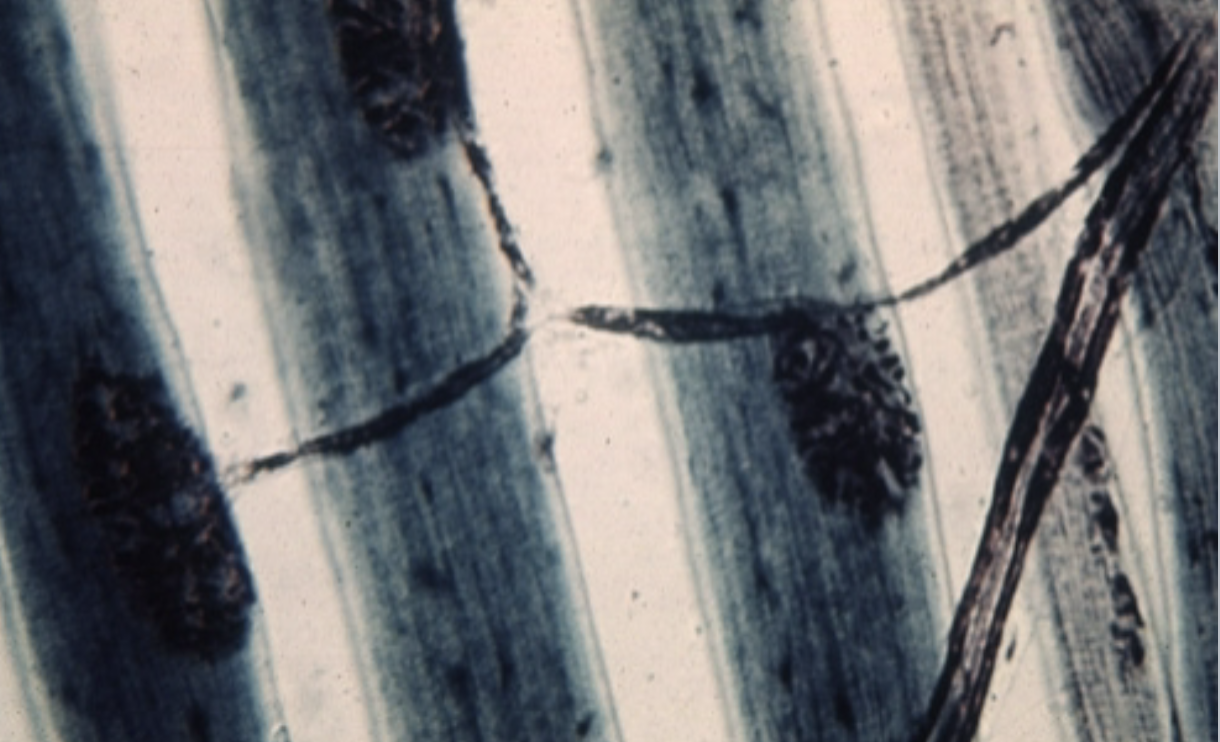
What’s this?
Neuromuscular junction motor end plate.
What’s the 4 Main tissue types in the Body??
Epithelial
Connective Tissue
Muscular Tissue
Nervous Tissue.
Simple Squamous Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Epithelial
Flat thin cell, looks similar to Adipose CT however is an epithelial tissue & has a nuclei in the middle.
Allows materials to pass through by diffusion, filtration absorption.
Lines Blood vessels like arteries, veins & capillaries.
Simple Cuboidal Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Epithelial
Cube shape cells that form a single layer connected to basement membrane.
Adsorption & secretion of substances.
in Kidney Tubules & Gonads
Simple Columnar Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Epithelium
Column shaped cells that form a single layer connected to basement membrane.
Secretion, Excretion & Absorption, can also be ciliated to make more surface area.
small intestine
Pseudostrafified Ciliated Columnar Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Epithelium
Different sized cells packed together, similar to stratified by its one layer connected to a basement membrane.
movement of particles & excretion.
Respiratory tract & nasal passage.
stratified squamous non keratinized Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
epithelium
layers of cells that progressively get flatter.
protection
covering for internal cavities & vulva.
stratified squamous keratinized Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Epithelium
layers of cells that progressively get flatter
prevent the loss of moisture & protect body.
Epidermis
Tranisitonal Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Epithelium
Can appeared stretched out and flatted layers or relaxed and lots of little ballon like layers.
can be stretchy & allow for expanding.
Bladder
Areolar Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Loose CT
Has Collagen & Elastic Fibers along with Fibroblasts cels.
provides support & protects organs.
Papillary region of the Dermis
Adipose Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Loose CT
Looks similar to simple squamous however the nuclei is appear on the border of the cells.
Energy storage, insulation & cushioning.
Hypodermis.
Dense Regular Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Dense CT
white, flexible tissue made of tightly packed bundles of collagen fibers.
Resitant in one direction
Tendons & Ligaments.
Dense irregular Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Dense CT
interwoven collagen fibers
Resistant in any direction
Found in Rectiluary region of Dermis.
Hyaline Cartilage Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
CT
Glassy appearance
helps bones move smoothly each each other.
Articulatory ends of bones.
Elastin Cartilage Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
CT
Tightly packed, with lots of elastic fibers.
supports parts of body that need to be bendy. (goes back to original shape)
Nose, & external ear.
Fibrocartilage Tissue type? Characteristics? Function? & Location?
CT
Looks like strips
resistant to compression
meniscus of knee, & between vertebrae
Skeletal Muscle Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Rod and very straight looking cells with striations & multiple nuclei pre cell.
Responsible for all volunaitry movements.
Everywhere
Cardiac Muscle Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Branch like structures with stations & one nuclei. Also have intercalated discs.
pumping blood through cardiovascular system.
Heart
Smooth Muscle Characteristics? Function? & Location?
Spindle shaped cells with 1 middle nuceli. No strations.
Steady contractions, in wave like manner.
Urterus, veins & arteries.
What are Goblet cells? Functions & location?
type of intestinal mucosal epithelial cell
synthesize & secrete mucus.
Airways & boundary organs.
What’s the difference between Cilia VS. Microvilli?
Can move things VS. Give more surface ares & increase absorption.
What’s glandular epithelium?
type of epithelium tissue that specializes in the release of substances in the body like mucous, digestive juices & hormones.