word-retrieval difficulties
Word-retrieval models are largely derived from ___________
________ errors
________ errors
________ errors
neurotypical speech errors
phonological
morphological
semantic
exchanges
We can exchange consonants for consonants and vowels for vowels
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Word-retrieval models are largely derived from ___________
________ errors
________ errors
________ errors
neurotypical speech errors
phonological
morphological
semantic
exchanges
We can exchange consonants for consonants and vowels for vowels
In case she decide_ to hits it”
this is an example of?
morphological shifts
"Nunique New York"
this is an example of?
anticipation
“Unique Yew York"
this is an example of?
perseveration
clarefully
this is an example of?
additions
fazzled
this is an example of?
deletions
slickery, gluttony + sloth → sluttony
this is an example of?
blends
“You look absolutely ugly.”
this is an example of?
semantic substitutions
types of semantic relationships
contrasts
similarity
sub/super-ordination
coordination
part-whole
completion
egocentrism
word derivatives
predication
contrasts
day-night
most common error
sad-unhappy
similarity
family-sister; vehicle-car
sub/superordination
superordinate vs subordinate
super: category
sub: under category
sister-brother; apple-peach
coordination
bird-feather; year-month
part-whole
gin-tonic; big-mac
completion
republican-rich
egocentrism
deep-depth
word derivatives
baby-cry; dog-bark (syntagmatic associations)
predication (more common in children)
discrete-stage model
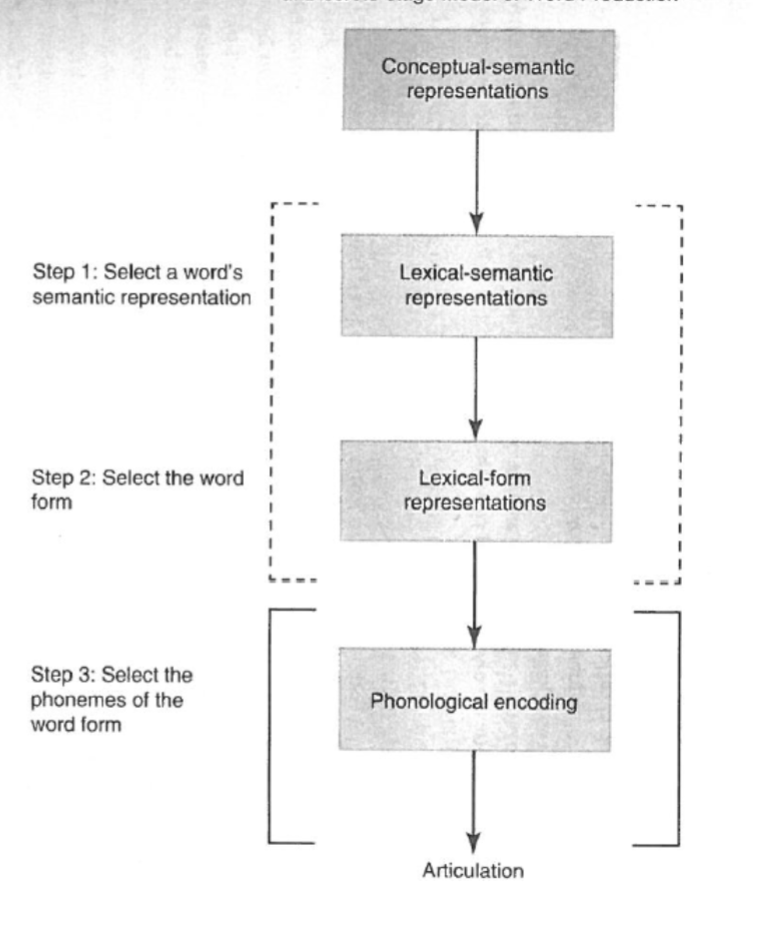
interactive (la) model
step 1: word form selection, semantic feedforward and phonological feedback activation determine what lexical representation will be selected
step 2: phonological encoding
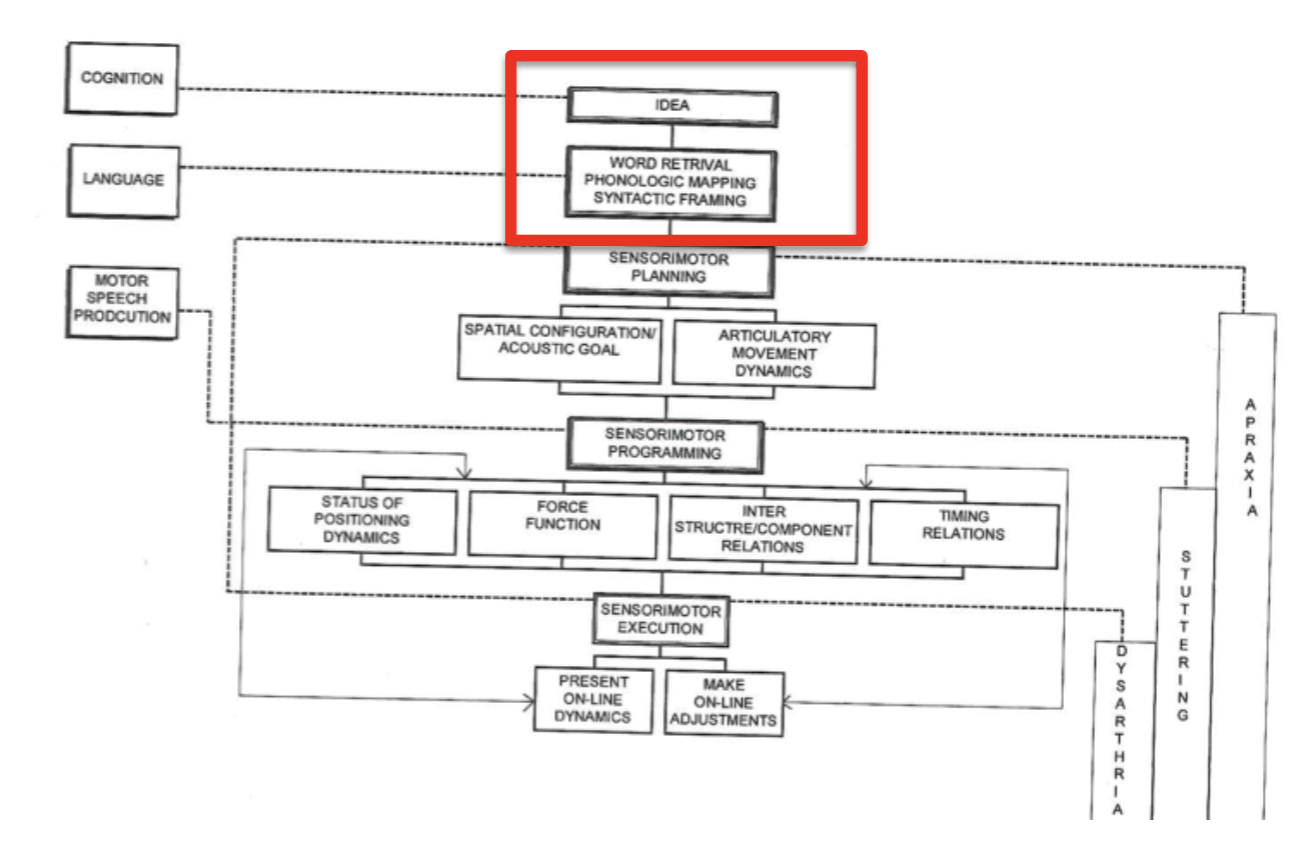
language vs speech production (be careful)
in AD (and svPPT) the concepts are gone not language,
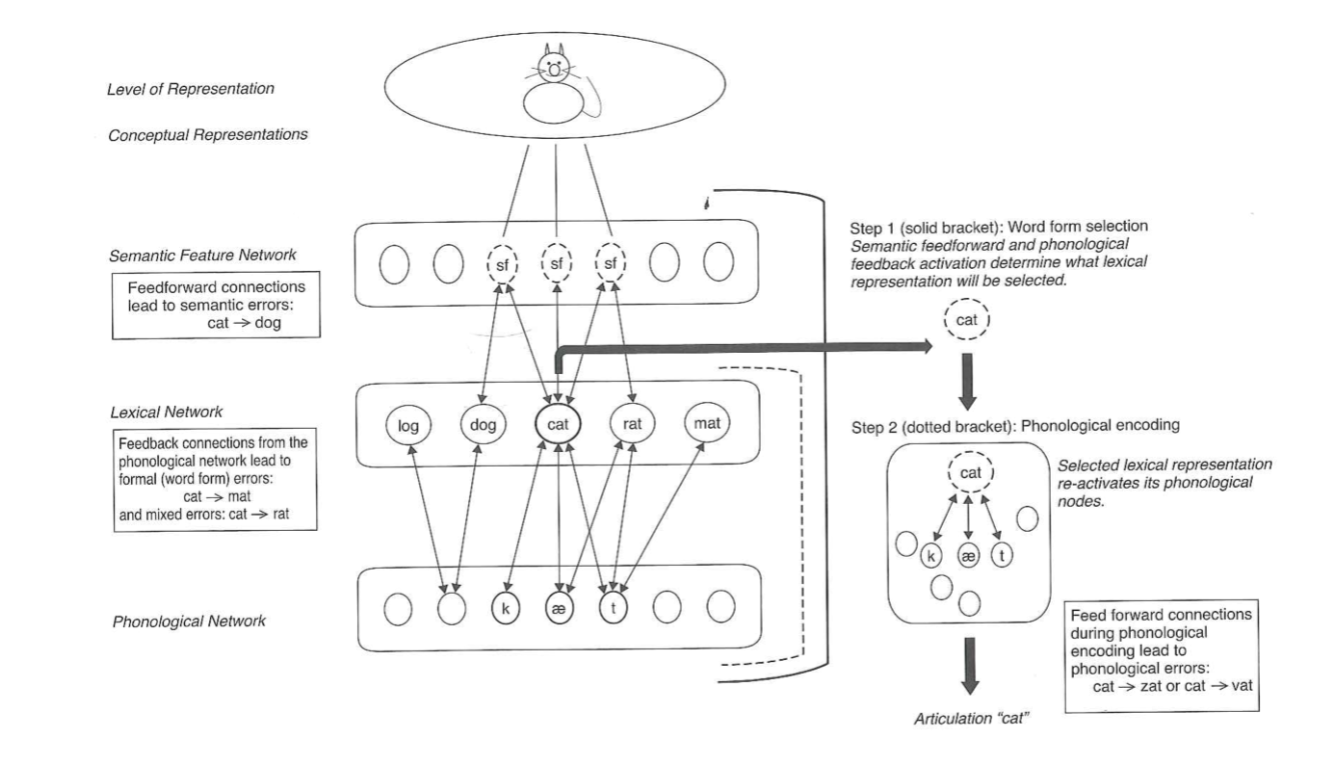
what must be reached for the correct semantic and phonologic representation to be retrieved?
then what happens?
a threshold level of activation
Competitor targets (even from L2) should decay.
After being produced, the target itself should decay.
→ if not, you end up with perseverated responses
The level of impairment is identifiable with _________________
testing/observation (error analysis)
Impaired/degraded semantic features or concepts (more common in AD or svPPA)
what step?
Semantic anomia (semantic features)
step 1
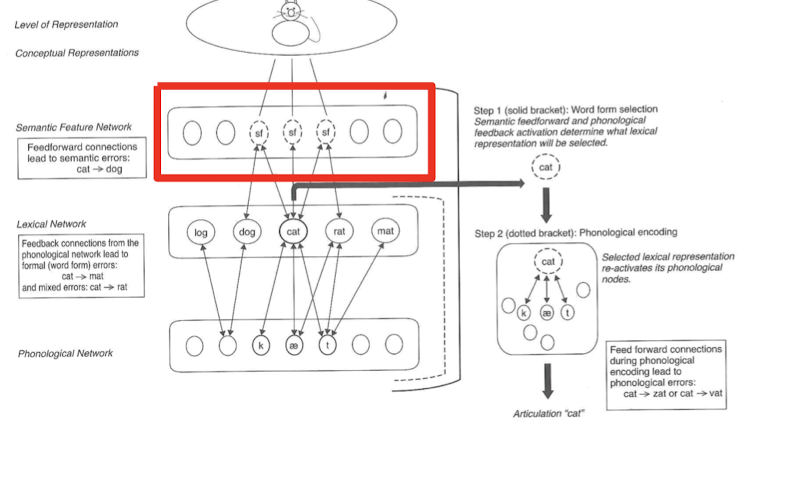
Impaired interactive activation between semantic feature and lexical networks AND/OR between lexical and phonological network levels
what step?
Word form anomia (lexical-phonological or lexical-semantic)
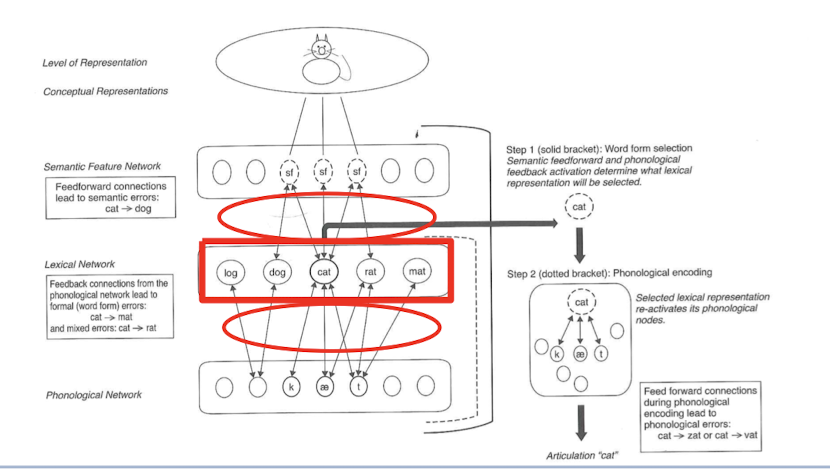
semantic paraphasias, phonologically-related targets, real-word substitutions are examples of?
Word form anomia (lexical-phonological or lexical-semantic)
Impaired phonological selection OR impaired phonological encoding (choosing the wrong phoneme)
what step?
Phoneme assembly (phonological output)
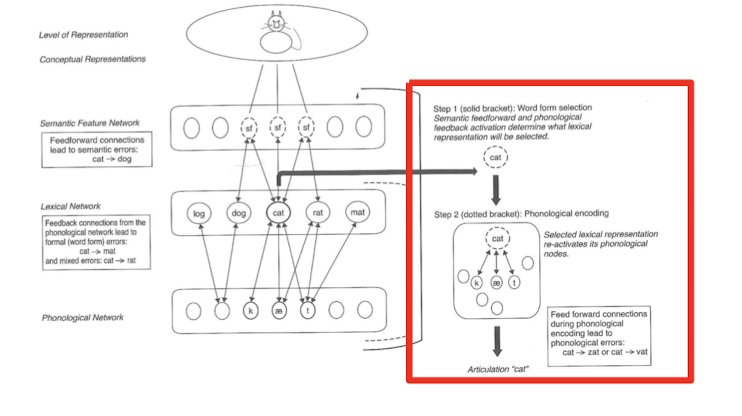
non-word errors, or close (phonologically-related) to target are examples of?
Phoneme assembly (phonological output)
includes i don’t know and nonresponses as well as vague responses “that thing”
nonresponse
whole-part responses where part of the target is names (e.g., “building” for city; “furniture” for office; “ducks” for follow). also includes responses that are visually similar to the target and from a different semantic category (e.g., “snake” for rope)
visual errors
error that could be perceptually or semantically based as responses are from the same semantic category and are visually similar (e.g., “fox” for dog)
ambiguous visual/semantic category errors
responses from the same category and are typically not usually visually similar (e.g., “world map” for globe")
semantic-within category errors (coordinate errors)
response is correct but too general (e.g., “room” for office; “animal” for dog)
semantic superordinate errors
thematically-related response with an obvious semantic association with the target that can include statements of action or function (e.g., “bing bang” for bell), physical attributes (e.g., “glass for vase; “hemp” for rope) contextual associations (e.g., “route” for road), and specific subordinate or proper noun examples of the target (e.g., “putter” for club)
semantic-associative errors
multiword responses that indicate accurate identification of the target (e.g., “outside of a house to walk through” for door). also included in this category were acceptable slang terms. the error had to provide some uniquely-specifying information.
semantic circumlocutionary errors
deletions, insertions, transpositions, or insertions of phonemenes of the target word with at least one syllable correct (e.g, “ven” for oven)
phonemic/phonological errors
response repetition (either correct or incorrect) which has been used to name 1 of the previous 5 pictures
perseverations
responses with no clear connection between the response and the target, or incoherent responses (e.g., “man?” for dag; or “pusska” for radio)
unrelated errors
“can you hand me the… er…. remote"?”
anomic pause
“can you hand me the TV?”
semantic paraphasia
“can you hand me the rebote?”
phonemic paraphasia
“can you hand me the …other there… the clicker…for the TV?”
anomic circumlocution
“can you hand me the jazzlepam?”
neologism
“griss me the jazzlepam”
jargon
“you…uh…remote?”
agrammatism
fast the jazzleman on the choose.”
paragrammatism/empty speech
word-retrieval neuroanatomy
WHAT: Areas affecting semantics
anterior temporal lobe
MCA lesions affecting the temporal lobe
WHERE: Areas affecting phonology
Anterior: LIFG, anterior insula, SMA
Posterior: middle posterior temporal lobe, angular or supramarginal gyr
stimuli and assessment considerations
word frequency
word length
semantic categories
task demands
Frequency effects (high vs. low) in repetition are apparent: may signal impaired __________ vs ________ level
phonological versus semantic
Word length
– Affects which level of impairment?
– If the phonological network is impaired, shorter words may result in …
-any
-more paraphasias (because there are more phonologically-related neighbors)
Semantic categories
– __________ may be inaccessible/affected by the lesion
Specific categories
task demands
confrontation naming vs. discourse, non-propositional speech
which level is targeted in SFA?
lexical-semantic level
which level is targeted in PCA?
phonological-lexical/phonological output
which level is targeted in Verb network strengthening treatment (VNeST)?
lexical-semantic
which level is targeted in Lexical Retrieval Cascade (LRC)?
phonological-semantic-lexical
Generalization considerations at the semantic level
Atypical → typical- prototypicality effect
Abstract → concrete
Infrequent → frequent
Be creative about categories: Goal-derived/ad hoc categories
cueing hierarchies
