AQA GCSE Chemistry paper 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are all substances made out of?
atoms
What are atoms?
Smallest part of an element that can exist
What are atoms of each element represented by?
chemical symbol
How many different elements are there?
about 100
What are compounds?
substance formed from 2/more element chemically bind in fixed proportion
How are compounds formed?
elements react, atoms combine=chemical reaction
Features of a chemical reaction?
one/more new substance made, often change in energy
How can compounds be represented?
combination of numbers,chemical symbol,symbol of atom they came from=chemical formula
How can compounds be separated into elements?
chemical reactions
What is a mixture?
2/more elements/compounds not chemically bind
What are the chemical properties of each substance in a mixture?
unchanged from the beginning
How can mixtures be separated?
filtration, crystallisation, simple distillation, fractional distillation, chromatography=no chemical reaction/new substance made
What is chromatography good for?
separate compounds out of mixture
How to do chromatography?
draw line(pencil, insoluble) near bottom of filter paper.
ink spot to line, place paper in beaker of solvent(depends what’s tested).
ink no touch solvent or it’ll dissolve.
lid on breaker stop solvent evaporate.
let solvent seep up paper carry ink, each dye/compound in mixture(ink) move at diff rate, so dye will separate out, each dye form spot in diff place.
when solvent near top of paper, take out to dry,
What is the end result of chromatography?
pattern of spot called chromatogram
What is the point a solvent has reached as it moves up the paper called in chromatography?
solvent front
What is filtration?
separate insoluble solid from liquid, used to purify
How to do filtration?
turn paper to cone, place it in funnel, then over beaker, pour mixture in, and wait for complete separation.
What is evaporation?
separate soluble solid from liquid
How to do evaporation?
pour solution to evaporate dish, slow heat solution until solvent evaporate leaving dry crystals
What are 2 ways of separating a soluble solid from a liquid?
crystallisation, evaporation
How to do crystallisation?
pour solution to evaporate dish, slow heat it until some solvent/crystal form, remove dish from heat to let it cool, solid should start form crystal as it become insoluble in cold. Filter crystal from solution, then leave in warm place to dry.
What can you only use evaporation to make?
solid that doesnt decompose when heated
What should you use crystallisation to make?
nice big crystals, solid that doesnt decompose when heated
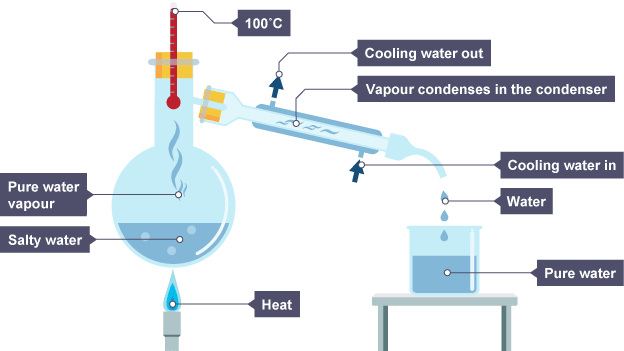
What is simple distillation?
separate liquid from solution with very diff boil point
How does simple distillation work?
solution heat, part of solution with lowest boil point evaporate first, vapour cool down in condenser, then condense to be collected.
What is the problem with simple distillation?
liquids mix again if liquid have similar boil point
What is fractional distillation?
separate liquid from solution even if boil point near each other
How does fractional distillation work?
mixture in flask, fractionating column on top, then heat. Liquids with low boil point evaporate first like simple distillation, except if other liquids with high boil point evaporate up the column, while the temp is at the boil point of the first liquid, they’ll condense down the column, since it’s cooler up there.

What does new experimental evidence lead to?
scientific model being replaced/changed
What were atoms thought to be before the discovery of electrons?
tiny spheres that could not divide
What did the discovery of the electron lead to?
plum pudding model of atom
What is the plum pudding model?
showed atom as ball of positive charge with electron stuck in it.
What did the results of the alpha particle scattering experiment lead to?
conclusion that mass of atom was concentrated at nucleus was charged
What did Ernest Rutherford call his results from the alpha particle scattering experiment?
nuclear model
What did the nuclear model replace?
plum pudding model
How did niels bohr adapt the nuclear model?
suggest that electrons orbit nucleus at specific distance.
What did Bohr’s theory of atomic structure gain and do?
agreed by experiments, helped explain observations
What did later experiments after Niels Bohr lead to the idea of?
+charge of nucleus subdivided into whole number of small particles, each have same amount +charge.
What was the name given to particles with the same +charge divided from a nucleus?
protons
What did the experimental work of James Chadwick provide?
evidence show existence of neutrons within nucleus.
What is the Bohr model?
an adapted nuclear model of atom, that suggest electron contained in shells, orbit nucleus in fixed shells(not in between).
What distance was each shell from the nucleus?
fixed