Lec 3
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Theme 1: Membrane transport of ions & water
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Every cell maintains intracellular concentrations of ________ solutes that are very different from those of the extracellular environment
inorganic
What type of gradient across the cell membrane is important to the cells function it uses a great deal of energy to maintain them?
Ionic gradient
Ex.
Na+/K+-ATPase
What is simple diffusion?
Molecules move constantly and randomly
Over time, more molecules move at random from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (Passive, no energy needed)
What is Ficks Law of Diffusion?
The net rate of diffusion of a solute across a membrane
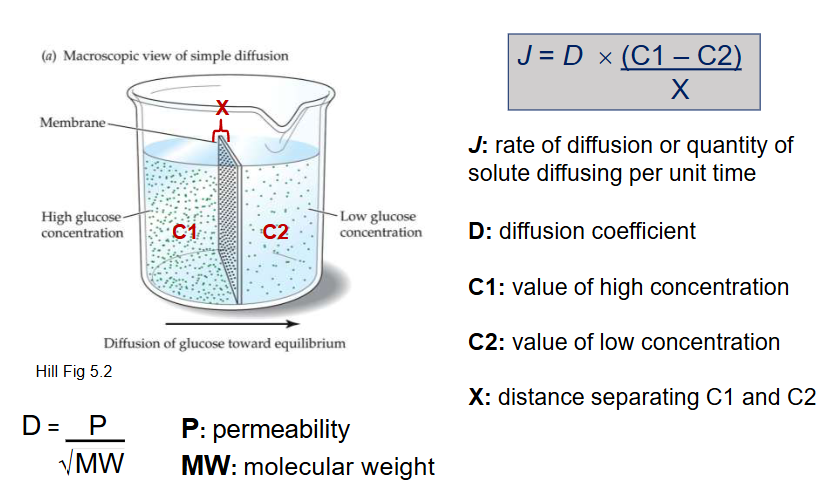
What 5 factors effect diffusion rate (J)?
Concentration gradient of substance (J+)
Permeability of membrane substance (J+)
Molecular weight of substance (J-)
Distance separating C1 from C2 (J-)
Temperature (J+)
Movements of solutes across a permeable membrane is determined by the _________ gradient
electrochemical
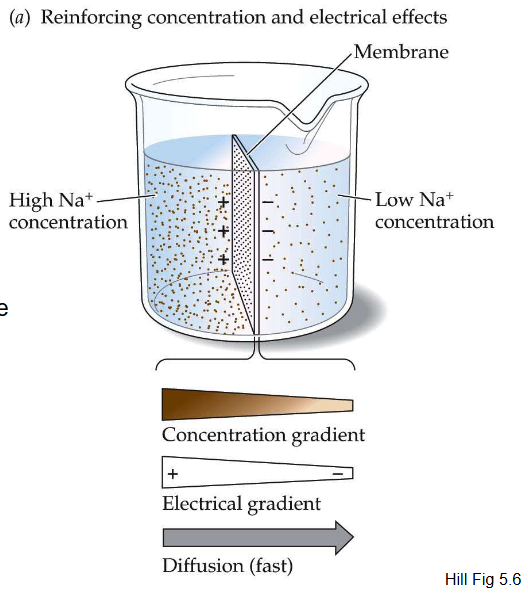
When the chemical and electrical gradients are in the same direction, diffusion is _____
fast
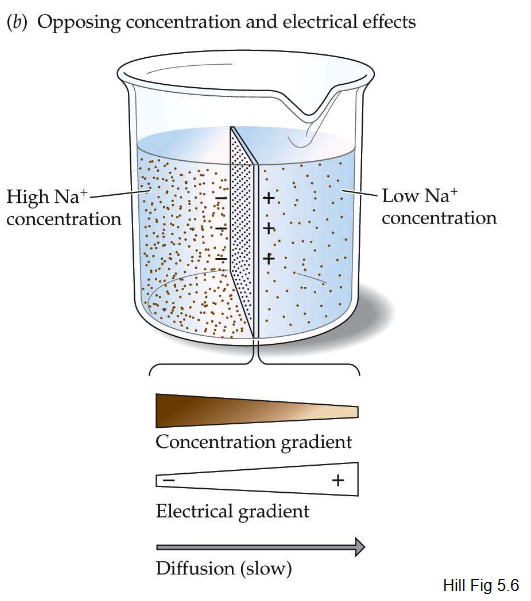
When the chemical and electrical gradients are in opposite directions, diffusion is ____
slow
What is Osmosis? And what does it depend on?
the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration
Depends on the number of dissolved entitles in the solution, not on what those entities are
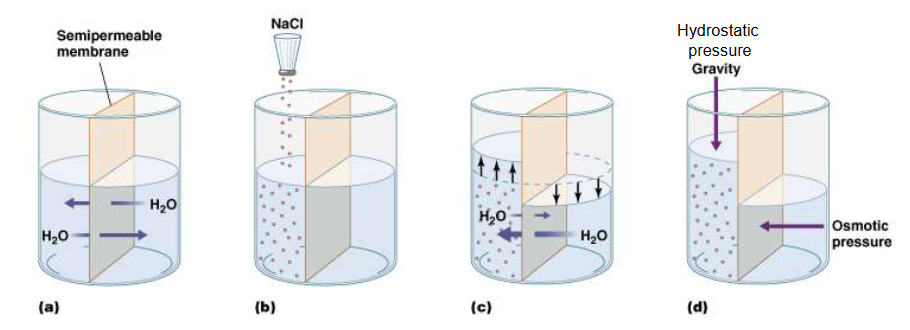
What is osmotic pressure?
property of a solution that allows you to predict which way water will move
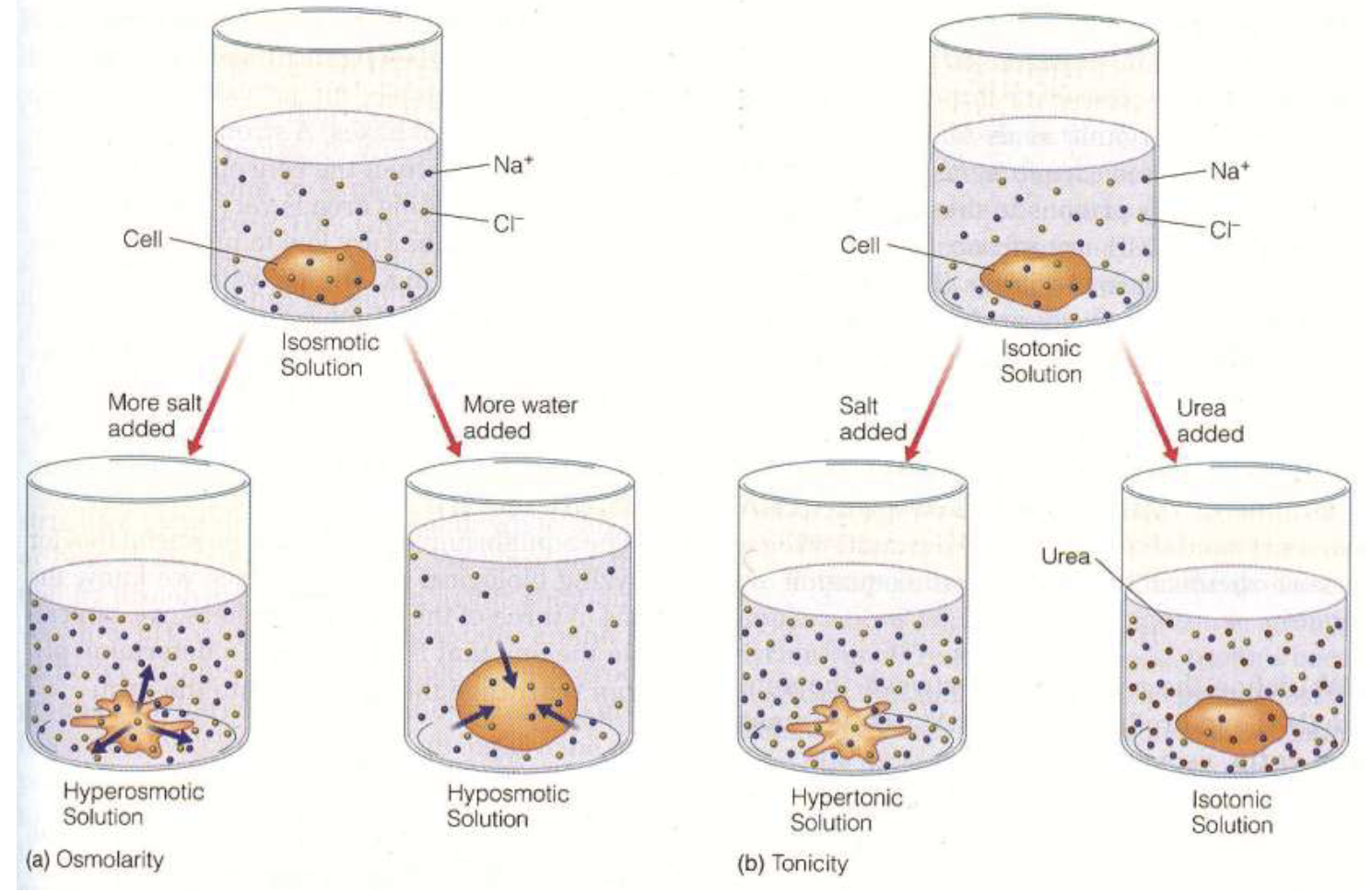
What is Osmolarity?
total dissolved entities per liter
What is Tonicity?
the effect of a solution on cell volume
Depends on differences in osmolarity but also on the permeability of the membrane to the solutes (whether or not the solute can enter the cell)
What is the difference between osmosis and tonicity?
Osmolarity considers the total concentration of penetrating and non-penetrating solutes
Tonicity relates only to the total concentration of non-penetrating solutes
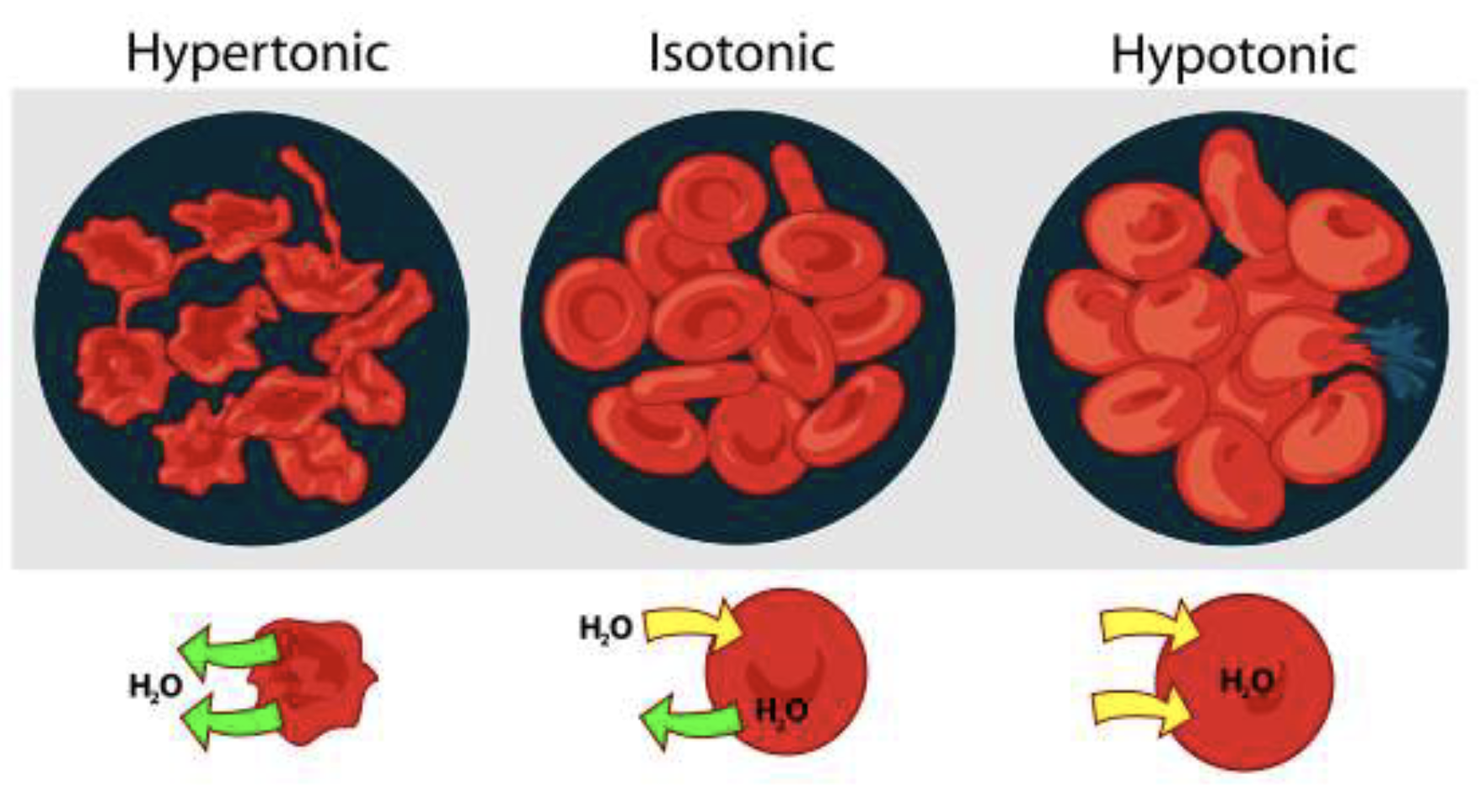
What are the 3 different forms of red blood cells in solutions? And what happens to them?
Hypertonic: Excessive water leaves cell
Isotonic: Balanced in and exit of water
Hypotonic: Excessive water into cell
Osmosis depends on the _____ of solute particles in solution NOT the _____ of particles
Number, Type
What is Donnan Equilibrium?
Predicts that the distribution of ions across a membrane will be unequal if the membrane is impermeable to one or more types of charged particles
Donnan equilibrium or Gibbs–Donnan equilibrium, explains how nonpermeating anions inside the cell can lead to unequal concentrations across the membrane of permeating ions
What are the 3 rules for Donnan Equilibrium?
Principle of Electroneutrality; total (+) charge = total (-) charge
The product of the concentration of permeant ions inside the cell = the product of the concentration of permeant ions outside the cell
Osmolarity inside and outside must balance
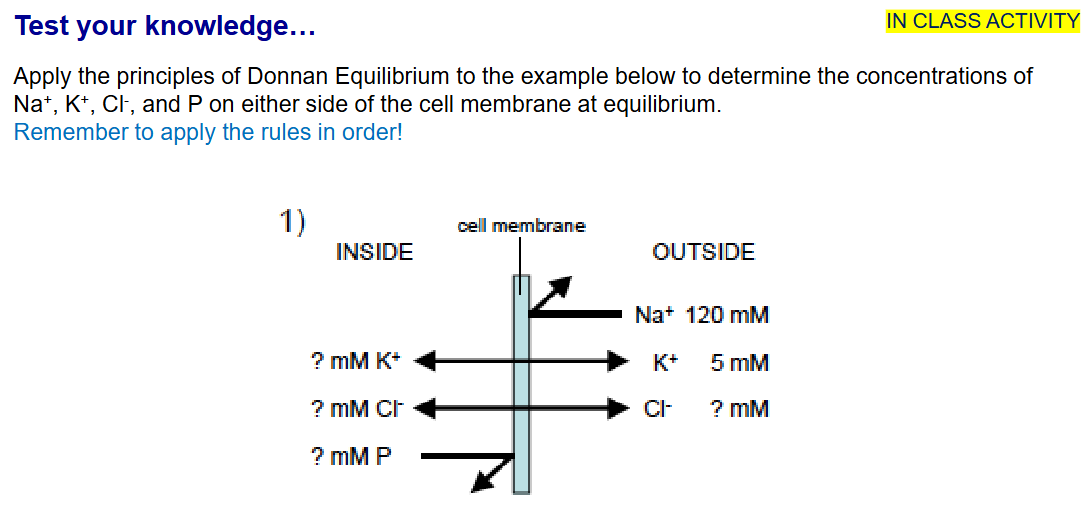
Inside:
25 mM K+
25 mM Cl-
200 mM P
Outside:
125 mM Cl-