Pathophysiology of heart failure
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
WHAT IS HF?
impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood
HF in turn leads to the cardinal clinical symptoms of ________&________ and signs of HF, namely edema and rales
dyspnea and fatigue
______is the volume of blood (liters) pumped from ventricles per time (minutes)
cardiac output (CO)
Heart Rate BPM Affected by:
Autonomic innervation
Hormone regulation
Fitness level
Age
STROKE VOLUME (L) Affected by:
•Preload
•Afterload
•Contractility
•Heart size (gender)
•Fitness level
Age
CARDIAC OUTPUT =
HEART RATE (BPM) X STROKE VOLUME (L)
Preload “stretch”
•Volume of blood inside ventricles during diastole
•Quantify: left ventricle end-diastolic volume (LVEDV or EDV)
•Average adult male at rest: 120 mL
preload
end of diastole
afterload
resistance needed to overcome to force blood out
EF
% of blood being pumped out
Afterload “squeeze”
•Resistance ventricles must overcome to force blood into systemic circulation
•Quantify: systemic vascular resistance (SVR), pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), end-systolic volume (ESV)
Average adult male at rest: 50 mL
Contractility “strength”
•Contraction of the myocardium through the actin-myosin cross bridge cycle
•Quantify: ejection fraction (EF)
•EF = EDV – ESV à “stroke volume”
EDV
•Average adult male at rest: 50-70%
Preload “stretch” Affected by:
•Heart rate
•Ventricle compliance
•Atrial contraction
•Venous/aortic pressure
Total blood volume
Afterload “squeeze” Affected by:
•Aortic pressure
•Systemic vascular resistance
•Ventricle wall thickness
•Ventricle radius
Contractility “strength” Affected by:
•Sympathetic nervous system
•Heart rate
•Ca2+
•Rhythm
WHAT IS AN AVERAGE CO FOR AN ADULT MALE? CO = HR x SV
-70bpm * (70ml/1000)=4.9L/min
Average adult CO: 4-8 L/min at rest
What about Cardiac Index? (BSA of 1.9 m2)
Average adult CI: 2.5-4.0 L/min/m2 at rest
-CO/BSAà4.9L/min/1.9m2=2.6L/min/m2
preload looking at LVEDPàhow much LV is filled at end of diastole. If you increase the LVEDP, it will _______stroke volume ànot exactly how our body works bc of hemodynamics. If u were to keep filling the heart, it would burst bc there’s a finite amount of volume u can put in the heart
increase
how much blood going out in reality is going to be dependent on how ________ is, how much EP ur blood is releasing at one point.
high ur BP
a scenario lets say u have low BP, so decrease afterload but keep same amount of volume. The SV is going to increase bc _______
it doesn’t have resistance.
Whats happening w/ HF over time is you have very weak ventricles and ur body is trying to compensate by increasing how much is being filled in there, but bc ventricles are weak u have _______ contractility
Decrease
another compensatory mechanism is high BP. Doesn’t matter if u put in a whole bucket of blood. If something is smacking the blood from coming out and it can’t squeeze to go out, the volume _______
won’t change at all
in HF, do a right heart cathàgoing thru inferior vena cava (sometimes superior VC) but going thru a vein. Both of the veins dump into _________ and these pressures are very important bc we can figure out what the underlying problem is in our patients w/ HF
right atria
high on both sides of the heart usually signs of _______à blocked up left side and has no where to go, so starts overfilling onto other side
acute decompensated HF
WHAT CAN IMPACT INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES?
•Heart failure (hypervolemia)
•Pulmonary arterial hypertension
•Pleural effusion
•Cardiac tamponade
•Hypovolemia
•Shock
•Systolic failure (heart contraction) HF with reduced ejection fraction
HFrEF
•Diastolic failure (heart relaxation) HF with preserved ejection fraction
HFpEF
Types of HF Course of disease
•Acute (congestive/decompensated)
•Chronic
Types of HF Location of disease
•Right sided (left-sided HF is most common cause)
•Left sided
•Biventricular
HFREF works
•Loss of intrinsic contractility
•Overstretched ventricles
•Weak and thin ventricles
•Pumping (systolic) dysfunction
HFPEF works
•Failure of ventricles to relax properly
•Thick and stiff ventricles
•Reduced ventricle volume in diastole
•Filling (diastolic) dysfunction
Classification of HF Based on the ejection fraction of the_______
left ventricle
midrange/mildly reduced
HFmrEF
-just bc you have HFpEF, doesn’t mean you will never have HFrEF but u cannot go from ________ bc those are 2 separate problems
HFrEF to HFpEF
What can cause an acute decrease in cardiac output?
-decr HR – bradycardia
-decr in volume –hypovolemia
-incr in BP-HTN
-arrthymias can decr output
-ACS
-medications
-shock
CARDIOMYOPATHY
An acquired or inherited disease of the myocardium associated with mechanical or electrical disfunction, leading to an enlarged/rigid heart muscle
Cardiomyopathy doesn't mean _____ (BUT can be an etiology for it)
HF
w/ non-_____________, there are are issues that are not directly affecting the heart but are going to impact it overtime (ex. obesity)
ischemic cardiomyopathies
COMMON ETIOLOGIES BY TYPE OF HF: HFrEF
CAD/ACS
HTN
COMMON ETIOLOGIES BY TYPE OF HF: HFpEF
HTN
-w/ CAD/ACSà w/ an infarct have ______, tissue is going to get weak and stretched out
tissue dying
HTN more of a cause w/ HFpEF bc if u have a very high pressure system the heart ventricles have to get stronger to overcompensate for thatànot going to actually over-compensate, its just going to make ______so less volume can go in. Body thinks it’s helping out but acc doing more damage in long run
ventricles thicker/stiffer
_________ is the most common cause of HFrEF, accounting for up to 75% of case
Coronary artery disease
The cause of _______ can be singular, multifactorial or unknown
heart failure
HFREF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
1.SNS: neurohormonal activation
2.Frank-Starling mechanism
3.RAAS: neurohormonal activation
4.Ventricular hypertrophy and remodeling
COMPENSATORY MECHANISMS
•Initiated by acute reductions in BP or reduced renal perfusion (due to low CO)
•Purpose is to provide short-term support to maintain circulatory homeostasis (a normal cardiac output)
•Long term activation results in functional, structural, biochemical, and molecular changes in the heart
•Further stress results in deterioration of ventricular function
SNS ACTIVATION ↓ in CO causes _______ which decrease parasympathetic tone
unloading of baroreceptors
SNS ACTIVATION ↑ in sympathetic tone which releases __________, and arginine vasopressin (AVP)
norepinephrine (NE), renin
SNS ACTIVATION ↓ β1 receptor sensitivity, ___ stimulation overtime
reduces
Neurohormones:
•NE: ________
tachycardia, vasoconstriction, contractility
Neurohormones:
AVP & Renin: ________
vasoconstriction, water retention
CARDIOMYOCYTE CONTRACTION
•↑ HR, ↓ diastole time, ↑ intracellular Ca2+
•↑ actin-myosin interaction, ↑ rate of contraction
•↓ lusitropy (ability to relax)
•Creates greater filament interaction during systole (force), ↑ wall tension
Decreased output alerts the kidney due to ______, kidneys think there is not enough blood volume, activates RAAS
reduced perfusion
RAAS ACTIVATION Neurohormones
Angiotensin II:
•Binds to AT1 receptor, releases AVP and ET-1 and releases NE
•Promotes sodium retention, free water retention, and stimulates aldosterone release
•Vasoconstriction of efferent glomerular arteriole maintains renal perfusion pressure
RAAS ACTIVATION Neurohormones
Aldosterone:
•Increased due to stimulation of the adrenal cortex by angiotensin II , not cleared as well due to decreased hepatic clearance from reduced hepatic perfusion
•Promotes sodium retention and water retention
•Causes interstitial cardiac fibrosis by increasing collagen deposition in the extracellular matrix
KALLIKREIN-KININ SYSTEM Cross talks with RAAS to cause _______
vasodilation
__________ increases release of other vasodilatory molecules (NO, PGI2, EDHF)
Bradykinin
in HF, heart is trying to stretch out, increase the _____, but if actual ventricle is weak and it cannot contract, it doesn’t matter. The amount of blood its going to pump out will still not be good
volume
causes an increase in LV volume and pressure (preload)
Fluid retention
Sarcomeres are stretched and force of ______ is enhanced
contraction
Frank starling mechanism: preload can only be increased to a certain point before it causes ______
congestion
__________ released from the ventricle in response to pressure/volume overload
Purpose is to promote natriuresis/diuresis and inhibit RAAS and SNS
-only natural response from ur body that is good
Natriuretic peptides (NP)
Natriuretic peptides
Atrial NP (ANP):
high affinity, short half life
Natriuretic peptides
Brain or B-type (BNP):
lower affinity but longer half life
Natriuretic peptides
N-terminal (NT-proBNP):
biologically inactive, longest half life
in HF, when u have that vasoconstriction and u have a ton of volume, ur heart releases natriuretic peptides that cause _______à trying to get rid of volume
diuresis
use BNP and _______ (BNP precursor)
NT-proBNP
-important to get _________ if u can to know if its elevated bc of renal failure, Afib, or HFà not perfect biomarker but can trend it to see if its getting worse
baseline BMP
_______change in myocardial cells causing change in size, shape, structure and function of heart
VENTRICULARREMODELING
Which biomarkers are involved with each of the compensatory mechanisms in HF?
SNS
epinephrine
calcium
arginine Vasopressin
Which biomarkers are involved with each of the compensatory mechanisms in HF?
RAAS
renin
aldosterone
angiotensin I/II
Which biomarkers are involved with each of the compensatory mechanisms in HF?
Frank Starling
Natriuretic peptides
ANP
BNP
Which biomarkers are involved with each of the compensatory mechanisms in HF?
ventricular Remodeling
cytokines
Increase preload volume
(Frank-Starling)
benefit:
increase stroke volume (CO)
Harm:
Pulmonary and systemic congestion (edema)
Myocardial O2 demand
Vasoconstriction
(RAAS - Neurohormonal Activation)
benefit:
increase SVR to increase BP
Shunts blood to vital organs (CO)
harm:
increase Myocardial O2 demand
decrease stroke volume (activates compensatory mechanism)
Tachycardia/Increased contractility
(SNS - Neurohormonal Activation)
benefit:
increase HR (CO)
harm:
increase Myocardial O2 demand
decrease Diastole time (less volume)
increase Risk of arrhythmias
increase Myocardial cell death
decrease Β1 receptor regulation
Ventricular Remodeling
(Hypertrophy)
benefit:
increase CO
decrease myocardial wall stress
decrease myocardial O2 demand
harm:
Diastolic/Systolic dysfunction
increase myocardial cell ischemia/death
increase fibrosis and arrhythmias
AMYLOID CARDIOMYOPATHY PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
•Over 30 proteins attributable to amyloidosis
•Most common protein is transthyretin (TTR)
•Deposition of abnormal proteins into the extracellular space of the myocardium
•ATTR-CM can be inherited (ATTRm-hereditary mutant) or part of the aging process (ATTRwt - wild-type)
•Commonly causes HFpEF
•Novel drug therapy to target TTR protein
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
•Most common genetic cardiac disease
•Commonly causes HFpEF
•Myosin protein defects are most often observed
•Mutant sarcomere genes trigger myocardial changes
•Leads to hypertrophy and fibrosis
_________ are common causes of HF with specific pathophysiology that do not respond to standard HF treatment
ATTR-CM and HCM
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Dyspnea
•Chronic lung disease
•Pulmonary arterial hypertension
•Anemia
•Pulmonary embolism
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Edema
•Venous insufficiency
•Nephrotic syndrome
•Deep vein thrombosis
•Lymphedema
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Jugular venous distention
•Constrictive pericarditis
•Pericardial effusion
•Pulmonary embolism
•Tension pneumothorax
SYMPTOMS OF HF
F:
A:
I:
L:
fatigue
abdominal pain, appetite loss, anorexia
impaired memory (confusion)
lower ability to exercise/do daily activities
SYMPTOMS OF HF
U:
R:
E:
urination at night (nocturia)
respiration issues (dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, cough
edema (pulmonary, lower extremities, hepatic)
SIGNS OF HF
H:
E:
A:
R:
T:
hepatomegaly, hepatojugular reflux
edema (pulmonary/peripheral)
ascites
regurgitation (mitral), S3 gallop
tachypnea, tachycardia
SIGNS OF HF
C:
M:
P:
cool extremities, cardiomegaly, cachexia
mental status changes
pulmonary rates, pleural effusion, positive JVD
Why are these signs/symptoms occurring?
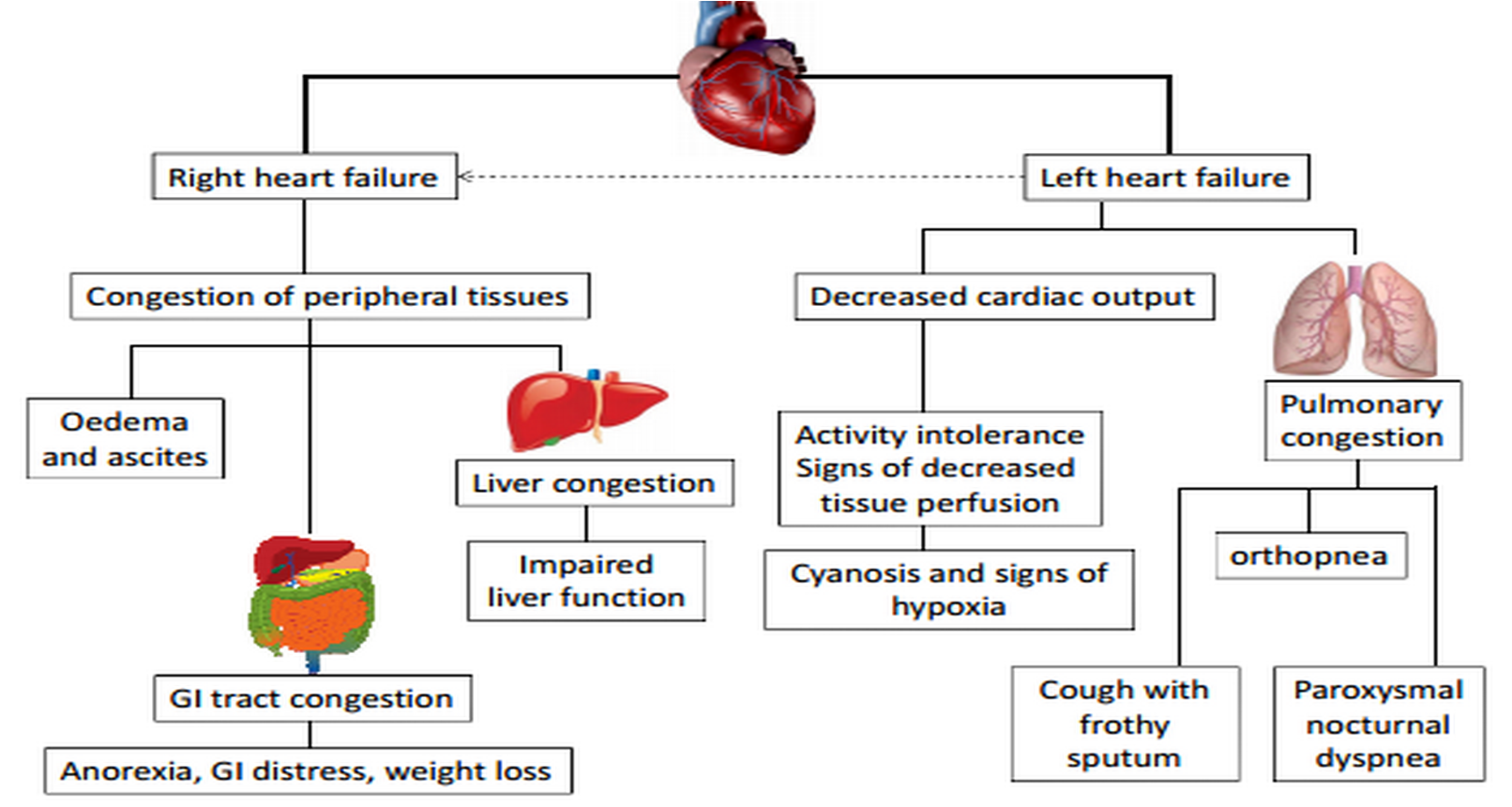
Class 1
Limitation of Physical Activity
None
Clinical Assessment
Ordinary physical activity does NOT cause undue fatigue, dyspnea, palpitations, or angina
Class II
Limitation of Physical Activity
Mild
Clinical Assessment
Comfortable at rest, ordinary physical active may cause symptoms
Class III
Limitation of Physical Activity
Moderate
Clinical Assessment
Comfortable at rest, less than ordinary physical activity leads to symptoms
Class IV
Limitation of Physical Activity
Severe
Clinical Assessment
Symptoms present at rest and worsened with any activity
Stage A At Risk
No objective evidence of cardiovascular disease and no symptoms or limitations in ordinary physical activity
Stage B Pre-HF
No symptoms/signs of HF, but objective evidence of cardiovascular disease
Stage C Symptomatic HF
Structural heart disease with current or previous signs/symptoms of HF
Stage D Advanced HF
Marked HF symptoms interfering with daily life and with recurrent hospitalizations
Who is “at risk”?
HTN, CVD, DM, obesity, hereditary cardiomyopathies, exposure to cardiotoxins
What is “evidence of CVD”?
structural heart disease, increased filling pressures, OR risk factor(s) AND elevated BNP or persistent elevated cardiac troponin levels (in absence of a competing diagnosis, like ACS, MI)
DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS IN HF: NON-INVASIVE
Echo
•LV size, ejection fraction
•Valve function
•Wall motion abnormalities
•Pericardial effusion
ACUTE DECOMPENSATION OF HF (ADHF)
What is ADHF?
Acute worsening of chronic HF requiring medical intervention