Hecol 268 - chapter 10 - french revolution, french directoire (1795-1799), consulat (1799-1804), republique/empire (1804-1815) and english regency (1811-1820)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
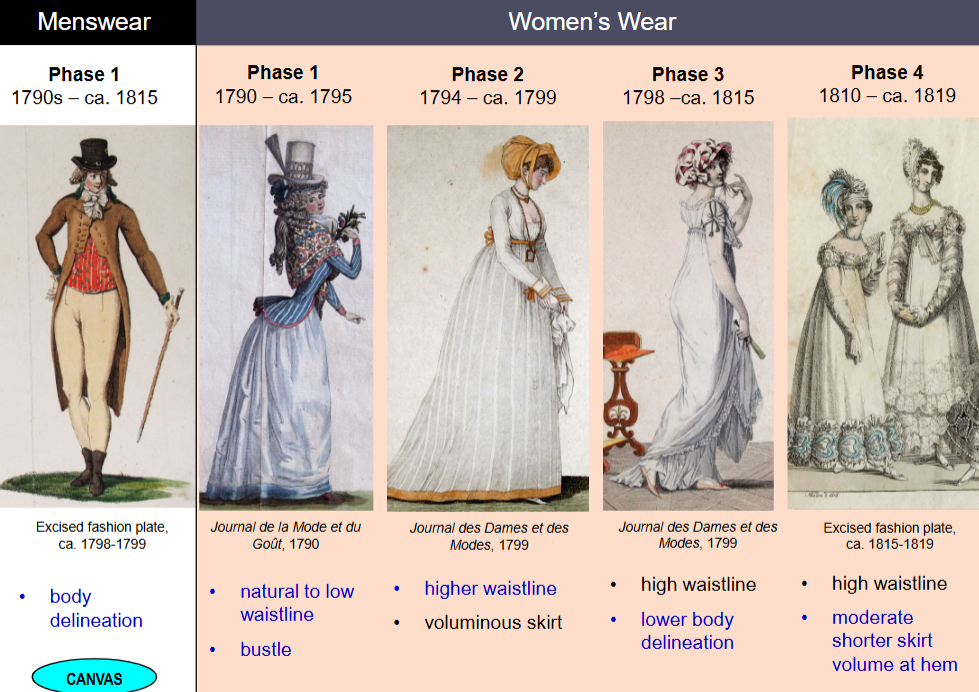
menswear vs. womenswear (1790-1815)
men have one phase while women have 4
what happened during the french revolution (1789-1794)?
1789 - bankruptcy of the government estates-general are called national assembly declared
Money troubles? Print more! Assignat: paper bill issued in france as currency from 1789 - 1796
Storming of the bastille
completion of a constitution
women's march on versailles
Constitutional monarchy fails
legislative assembly 1791 - 1792
Execution of louis the 16th in 1793
1789: poufs are banned
1792: ban on wigs - “ en oreilles de chien” (in dog ears)
Reign of terror 1793-1794 lead by Robespiere, standing out with fashionable clothing could lead to arrest or execution, so many people avoided extravagant styles to stay safe.
what happened during the directoire (1795-1799)?
Directoire period (1795-1799) had executive power held by five "directors" and a new constitution.
The parliament consisted of 500 representatives and 250 senators, with limited suffrage based on property, replacing the 1793 universal suffrage.
To fund expenses, the government relied on war plunder.
In 1799, a coup led by General Napoléon Bonaparte ended the Directoire.
what happened during the Consulante and empire 1799-1814/1815 ?
During the Consulate (1799), executive power was held by three consuls, with Napoleon Bonaparte as the first consul.
The government was republican but became increasingly conservative, authoritarian, autocratic, and centralized.
In 1804, Napoleon crowned himself emperor, famously taking the crown from the pope during the ceremony. His reign lasted until 1814/1815.
what garments were seen during the revolution and what was the reason for the certain fashion?
Supporters of the revolution could adopt elements of dress that symbolizes their political views
Red, white, and blue colors
The revolutionary cockade (mandatory by 1793)
The bonnet rouge or “red cap of liberty”
Trousers of the working man replaced the knee breeches of the aristocratic old regime
Shoes with laces instead of buckles
Les san-culottes, Culottes = french for knee breeches
Working class men did not wear san-culottes,They wore trousers or pantaloons
They could also wear: a carmagnole (short jacket of dark color, hip length, not well fitted with black fullness), Often with a red waistcoat, Wooden sabots (clogs)

what were the origins of the bonnet rougue?
Revolutionaries believed the cap had historical roots in ancient Greece and Rome, where it symbolized liberty.
In the Middle Ages, a similar cap marked the end of apprenticeship
true or false, if was hard at times to distinguish the wealthy class and people who had money from the working class because the wealthy class dressed like workers.
true
how were hairstyles during the revolution?
à la Titus haircut (also called à la victime), which mimicked the short hair of individuals heading to the guillotine.
This hairstyle became fashionable, with women also adopting short cuts, symbolizing the grim and radical times of the Revolution.

menswear phase 1 (1790s-1815)
focused on body delineation, with English styles dominating but proportions changing.
Key features included wide revers, high neck stocks, top hats or bicornes, and turned-over collars.
French elements refined the look, with breeches made of doe skin, tight to the body, adding polish to the attire.

how was hair like in phase 1 for men?
Disheveled
long
Gray powdered natural colour
short
Sideburns (no facial hair in 18th century till now)
who is “Beau” Brummell (george bryan brummell)?
DANDY - a man who puts importance into fashion with elegance
understated, impeccable, cravat savant (precursor to modern tie)
<< bathed in milk to have whiter skin>>
how did the coat change for men?
Frock(window for their groin) coat becomes the morning coat: has a high folder collar (worn just for riding becomes informal and worn everyday)
Revers with “M” notch
lower body garments in men phase 1
Knee breeches: full dress, dress, undress
Pantaloons: dress, undress, closely fitted (could be knit), might have instep
Trousers: dress, undress, fuller and reached the ankle, might have instep, << cossack trousers>

boots for men in phase 1
Spencer and coat jockey boots: may be knitted fabrics
Jockey boots
Hessian boots
Greatcoat and hessian boots
Womenswear in Phase 1: 1790–1795
Natural to low waistline
Bustle
Extreme undress (look like you woke up in the morning, indian shawl worn over)
Open and close gowns, Jackets and skirts
womenswear in Phase 2: 1794-1799
Higher waistline, Voluminous skirt
Simpler ‘democratic styles in dress’
No panniers (UK (except court) and france): 1794 UK: waist level rises (<< back has a roll so you can anchor the petticoat>>), Padded roll in back, Petticoats still worn
1795: UK and france: Short sleeves
1796: france: Natural hair in curls (circle of david 1798: image), Hair flattened with “huile antique”
Undergarments: Transitional stays: shorter, contours breasts, padded roll/tabs
what happened during the late directoire?
<<age of terror ends, age of dancing>>
2nd half of the directoire: Co-existing silhouettes
Fashion extremists were called Merveilleuses (women)(the marvelous ones) and Incroyables(men)(the incredible ones)
Caricatures: << based on reality but pushing it>>
Fashion plates (show more legs for women)
<<Fabrics for the elite are cotton, instead of linen>>
?? - normative or atypical?
“Robe trousse” (lifted dress)
A return to freedom of the press?
More delineation, but men are lineation
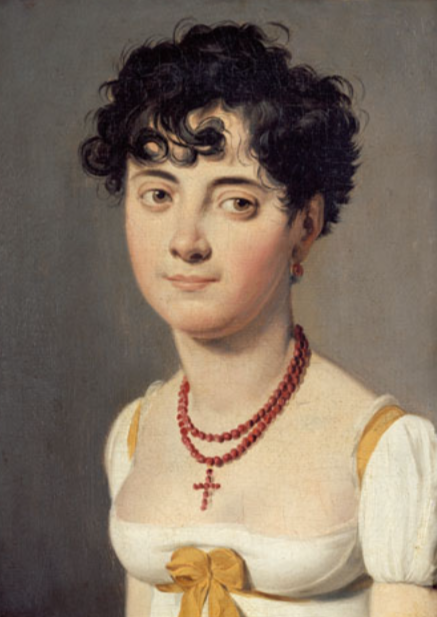
how was womenswear(merveilleuses) in the late directoire (second-half, 1797-1799)?
simple and natural aesthetic
sheerest fabrics, deep necklines that reached the waist, Hair in shaggy, unkempt looks.
Women wore very little underwear and no corsets
columnal skirts replacing voluminous petticoats.
little or no sleeves
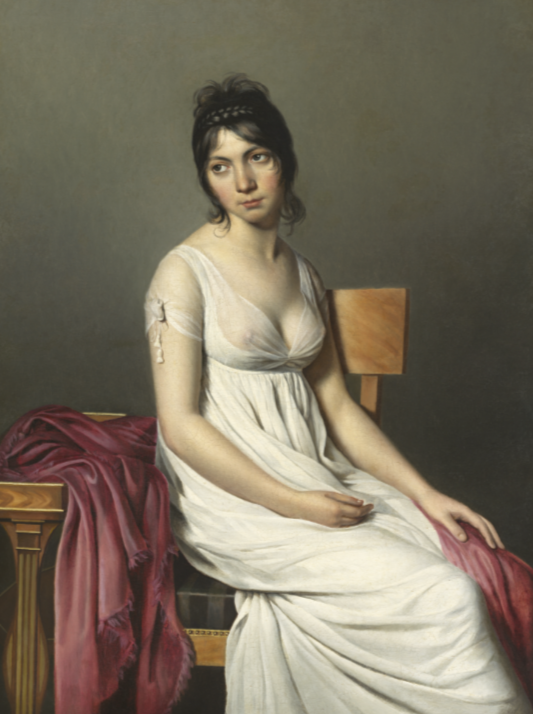

how was menswear (incroyables) during the late directoire?
excessively tight breeches
cravats or collars that covered much of the chin
shaggy unkept hair (“en oreille de chien”)
woolen English-style coat
jockey boots with pointed toes
walking stick
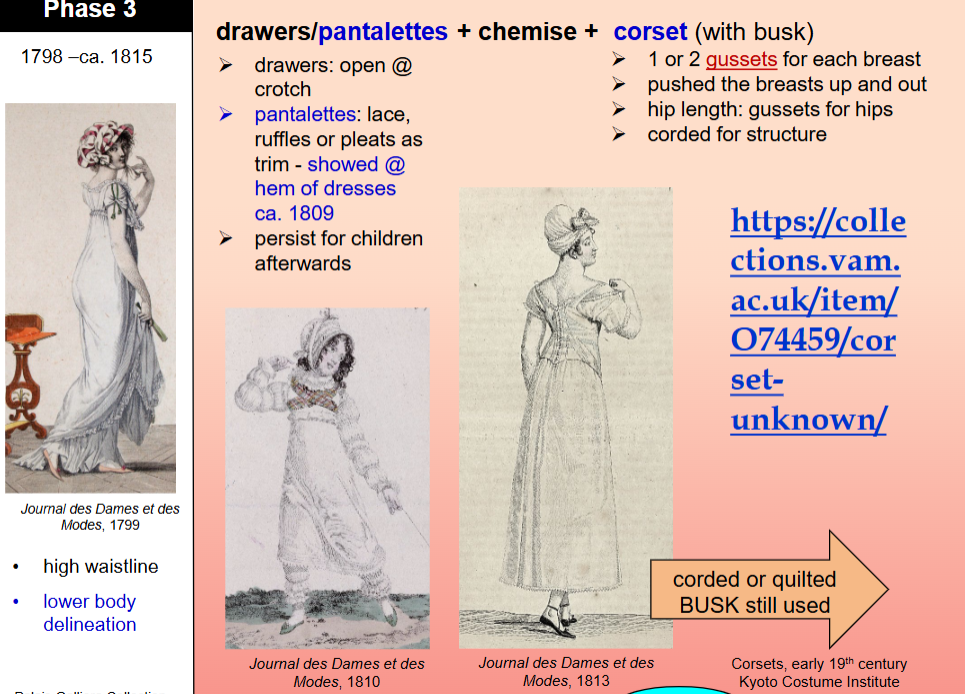
how was womenswear in phase 3?
High waistline
Lower body delineation
Frenetic dancing “the age of nudity”, a “new” aristocracy
Supremacy of styles based on the ancient greeks
The “natural body”, Buttocks - new erogenous zone (<< not wearing voluminous petticoat so people can see the shape of the buttocks>>)
the chemise dress continues to be important
trying to show the leg in the cloth
drawers, pantalettes, chemise and corset
what did napolean do during his reign?
puts a stop to extreme dress behaviours which he considers immoral
Attempts to recreate the elegance of court to stimulate the economy and gain credibility (pushes silk instead of wool)
in 10 years, he instituted legal and educational reforms, reorganized the government, making it more efficient, competent, and honest
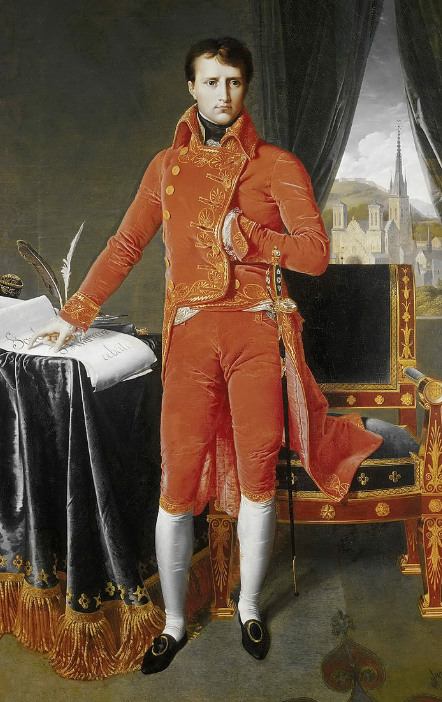

what kind of silhouettte for silk gowns during the consult and empire?
“A” line silhouette for silk gowns
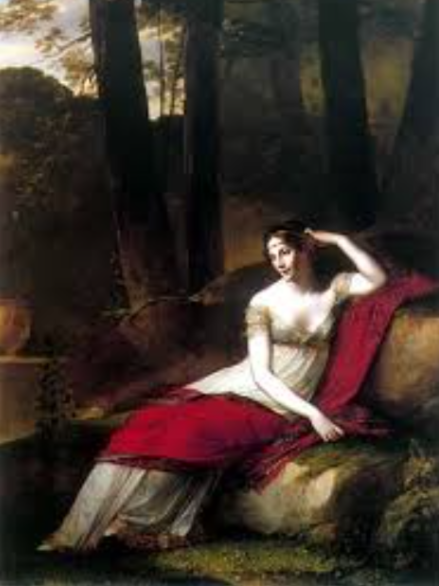

what are the importance of indian shawls during the consult and empire?
Napoleon bans the kashmir shawls, but his wife josephine will smuggle like 60 of them
what mechanization does the kashmir shawls lead to?
because of josephine wanting the shawls, napolean encourages the mechanization of making of them without importing it from anywhere else
The Jacquard loom was invented by Joseph Marie Charles Jacquard.
It used a binary system with punch cards to control the pattern, making it an early precursor to computer programming and technology.
garments and accessories in phase 3
A variety of sleeve and neckline styles could be seen: Short puffed sleeves most popular, Marie sleeve, Combined: short over long
Spencer jacket (men and women) (women is short)
Accessories of note: Reticule (<ancestor of handbag>), Cocakde fan, Bonnets, Slipper shoes with heel, “En cothurne” (pointed toes shoes)
how was phase 4 in womenswear?
Decorative hem treatments
Pelisse becomes coat dress
High waistline
Moderate shorter skirt volume at hem
