Pulmonary Embolism: Pathophysiology, Virchow's Triad, and Genetic Factors
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
BOTH blood flow and ventilation
the mechanical and humoral reflex consequences of embolic obstruction cause alterations in
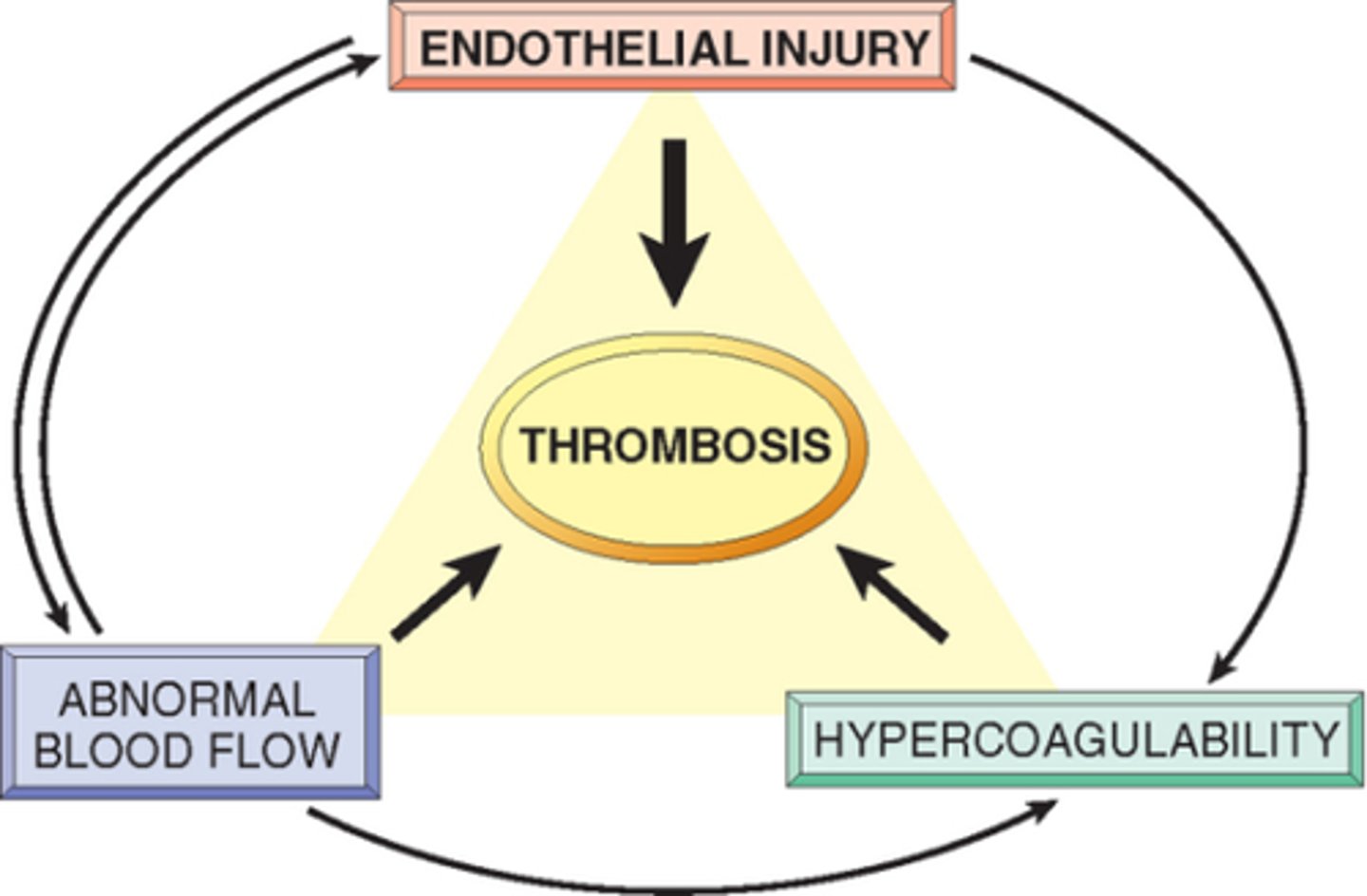
stasis, hypercoagulability, enothelial injury
Virchow's triad
it has a mutation that causes resistance to protein C which normally inactivates clotting factors V and VIII
How does Factor V Leiden relate to PE and DVT
increased plasma prothrombin concentrations, inherited hypercoagulability
prothrombin gene mutation leads to
It increases. pulmonary embolism creates a ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch, where blood clots block blood flow to parts of the lung. As a result, oxygenated air reaches the alveoli, but deoxygenated blood cannot pass through those areas to pick up oxygen, leading to a larger-than-normal difference between the oxygen levels in the alveoli and the arterial blood.
what happens to the A-a gradient in PE
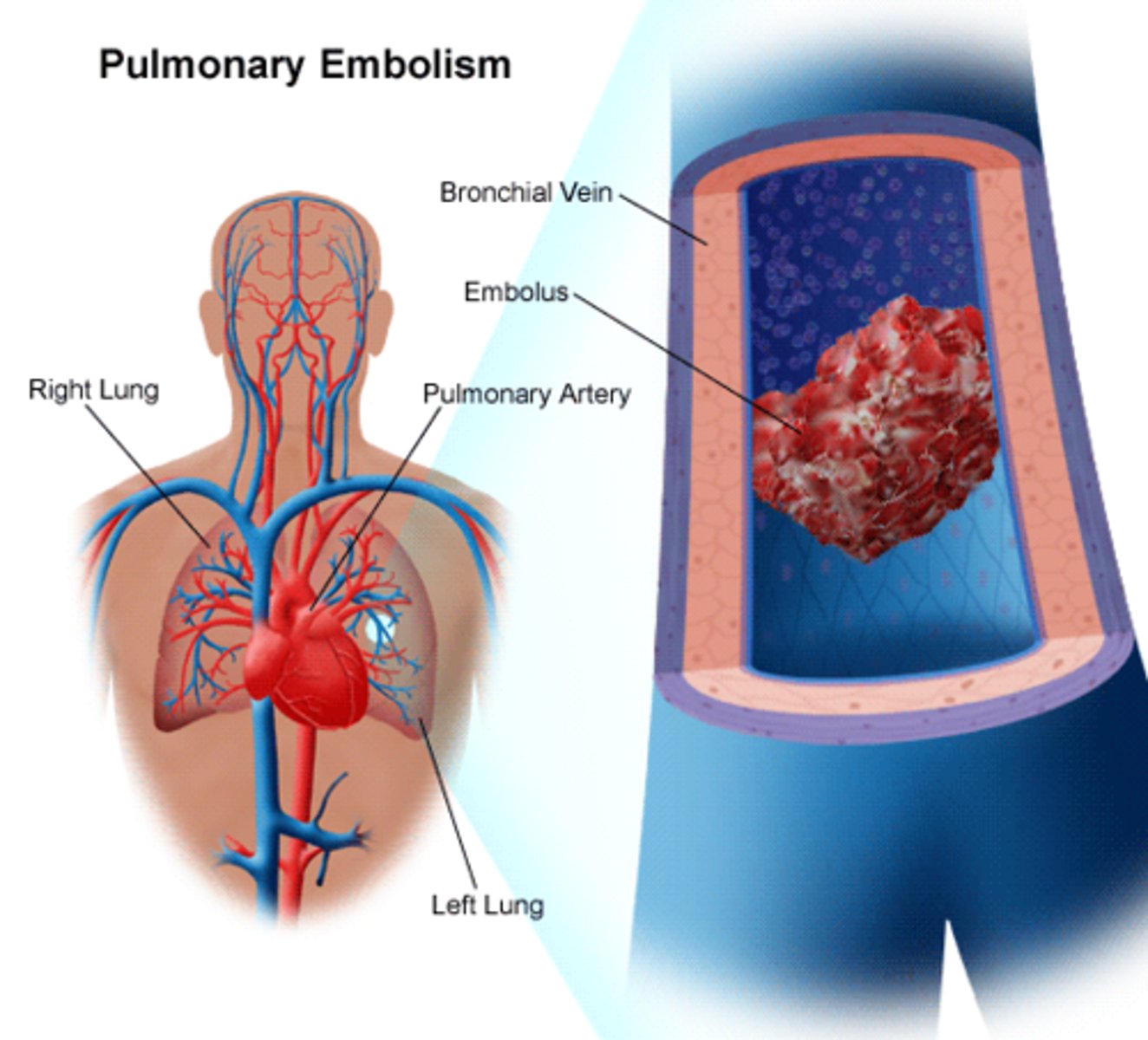
lung ischemia/infarct (blood supply cut off)
increase vascular resistance/RV afterload
may lead to RV dilation, hypokinese, tricuspid insuff/failure
hemodynamic effects of PE
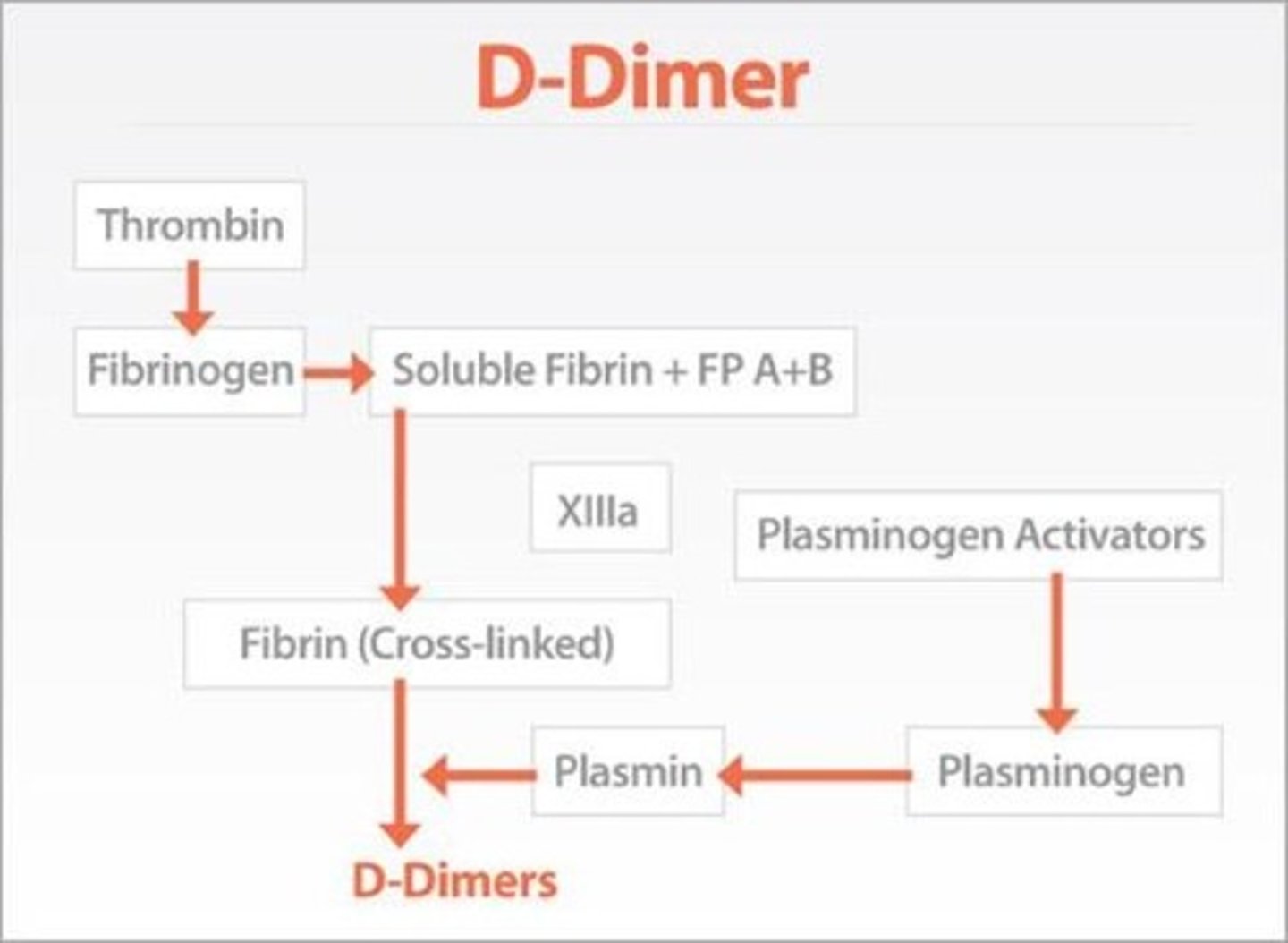
in a patient with low moderate likelihood of DVT. can rule out but cannot rule in (nonspecific)
when to use d-dimer test
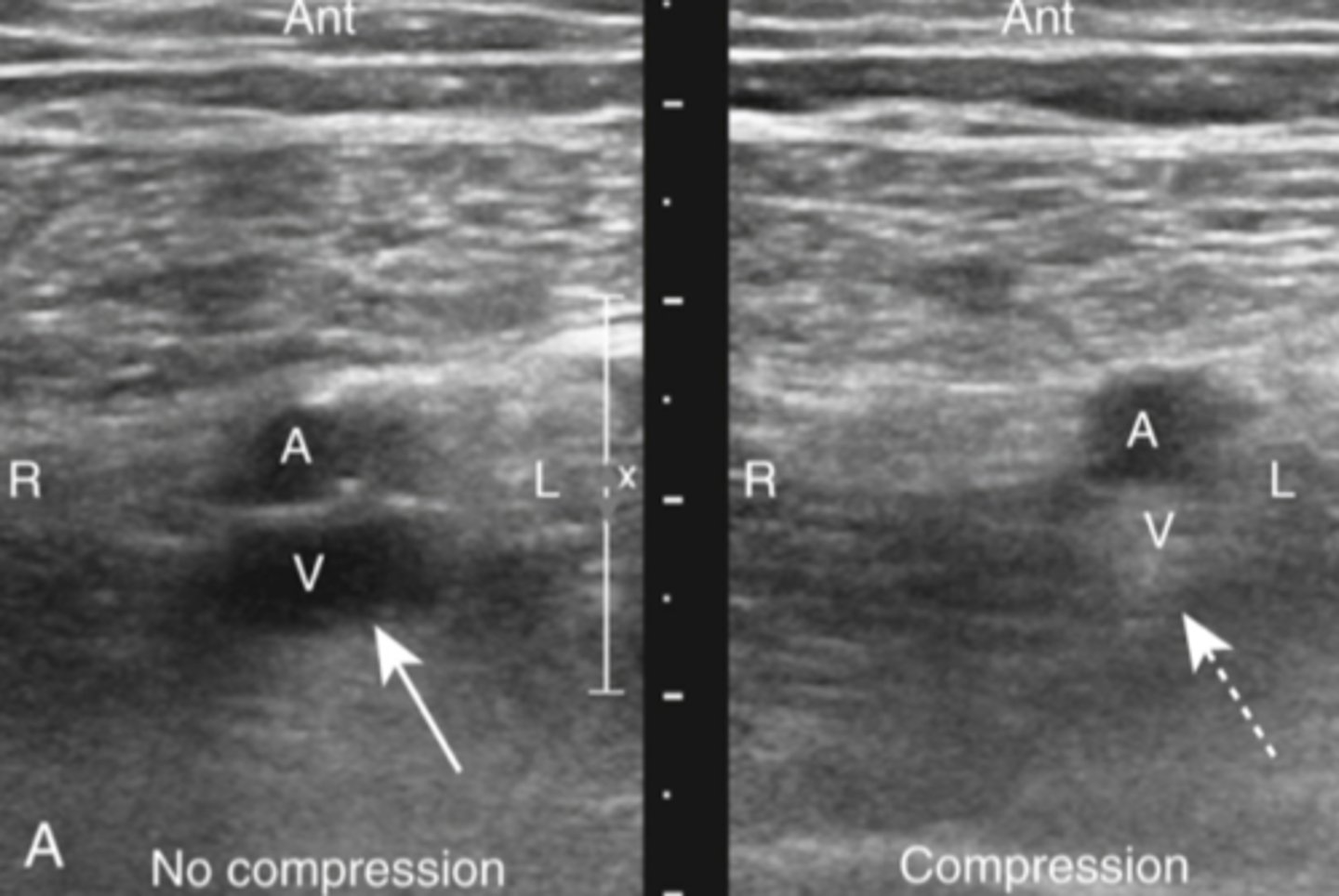
can ID DVT (assoc with PE)
can visualize the thombus directly, otherwise relies on loss of vein compressability
detects change in venous flow
how can ultrasound help diagnose DVT/PE
90% cases have hypoxia, hypocapnia, and respiratory alkalosis
Increased A-a gradient (most >20)
how can ABG help diagnose
PE (hamptoms hump and westermark sign)
most often normal, but when not it looks like this
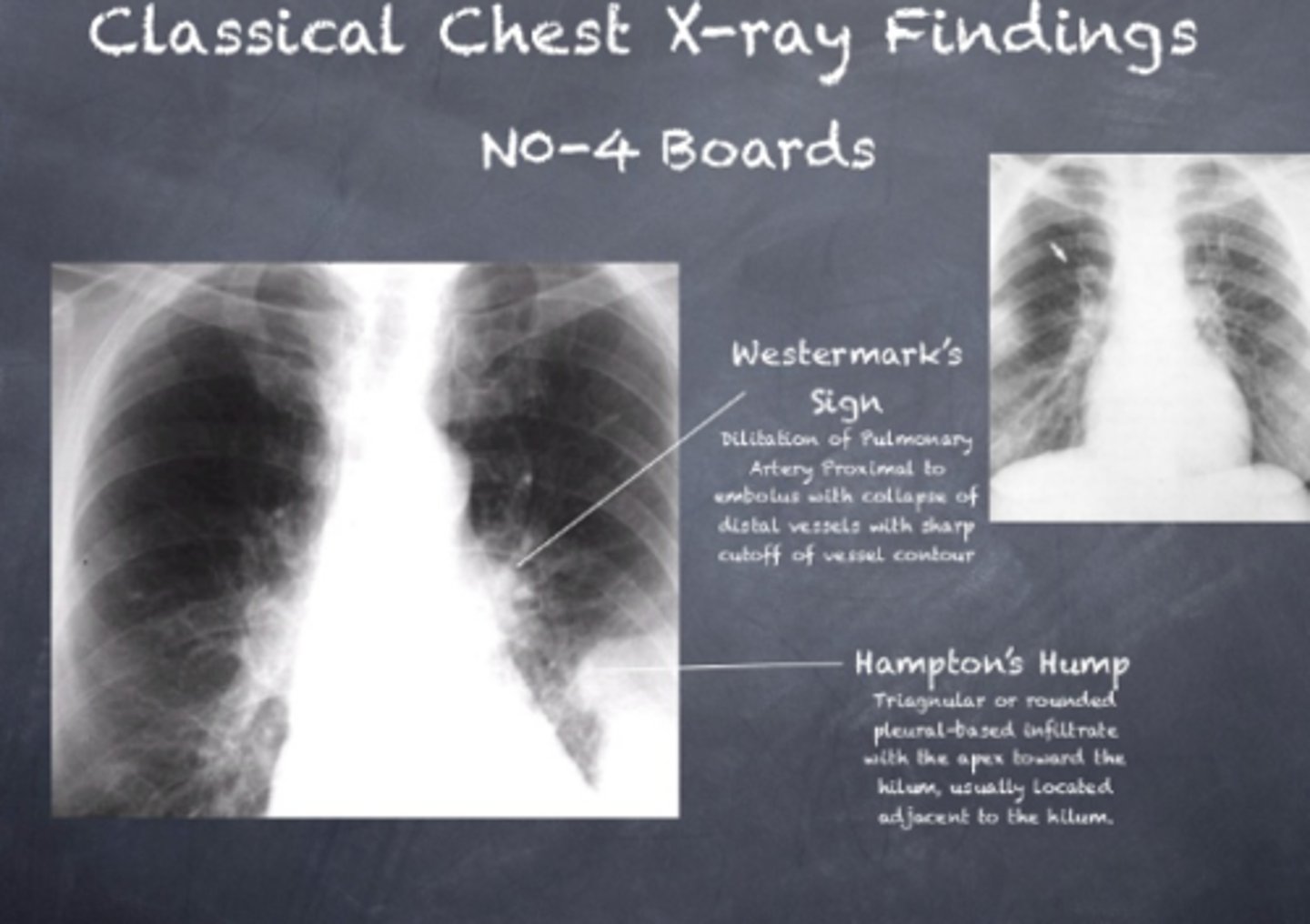
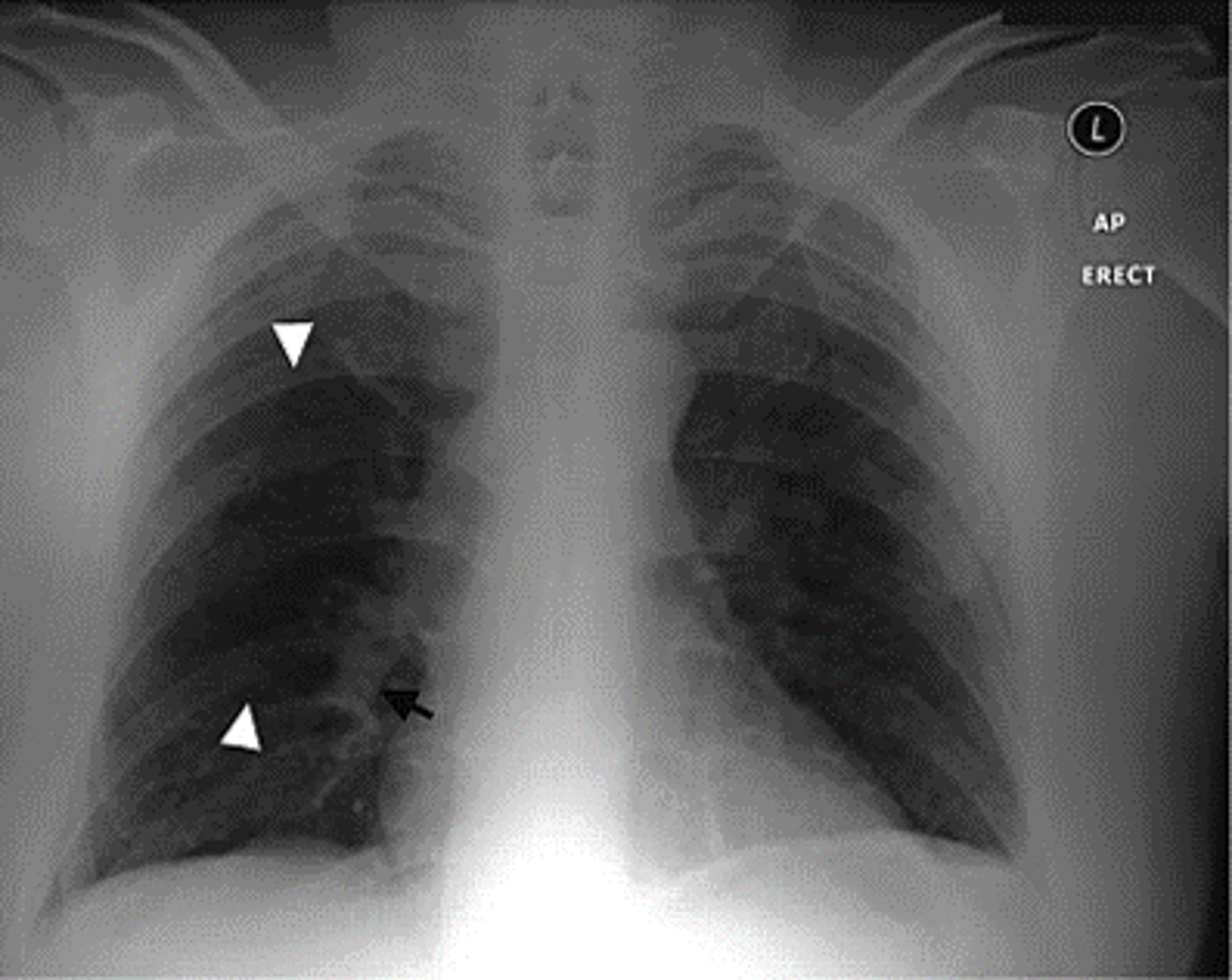
lack of vascular markings downstream of clot
westermark sign
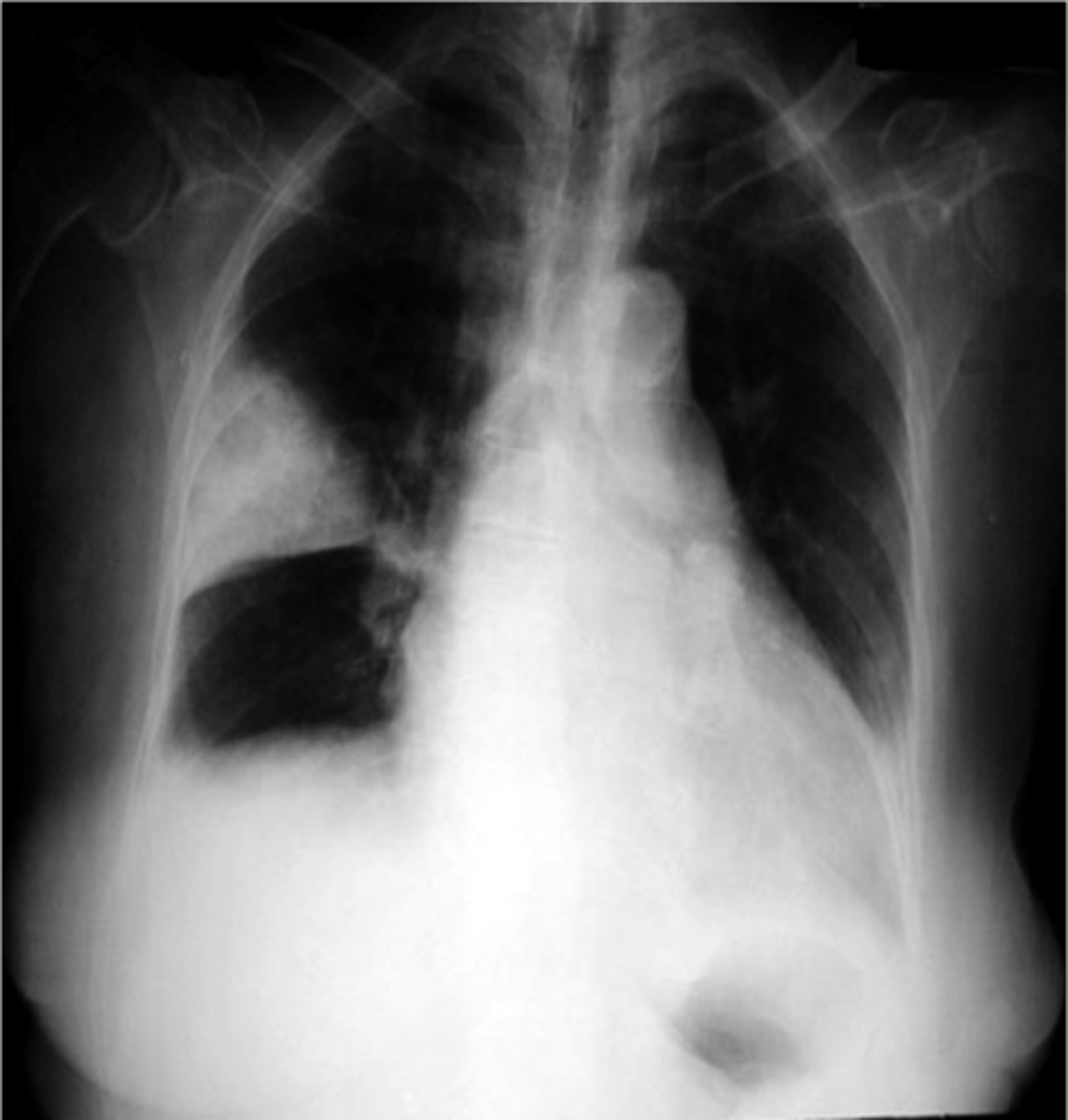
pleural based opacities with convex medial margins, wedge-shaped, suggest infarct
hamptom hump
sinus tachy most often
complete/incomplete RBBB
Right axis deviation
famous "s1-q3-t3"
EKG findings in PE
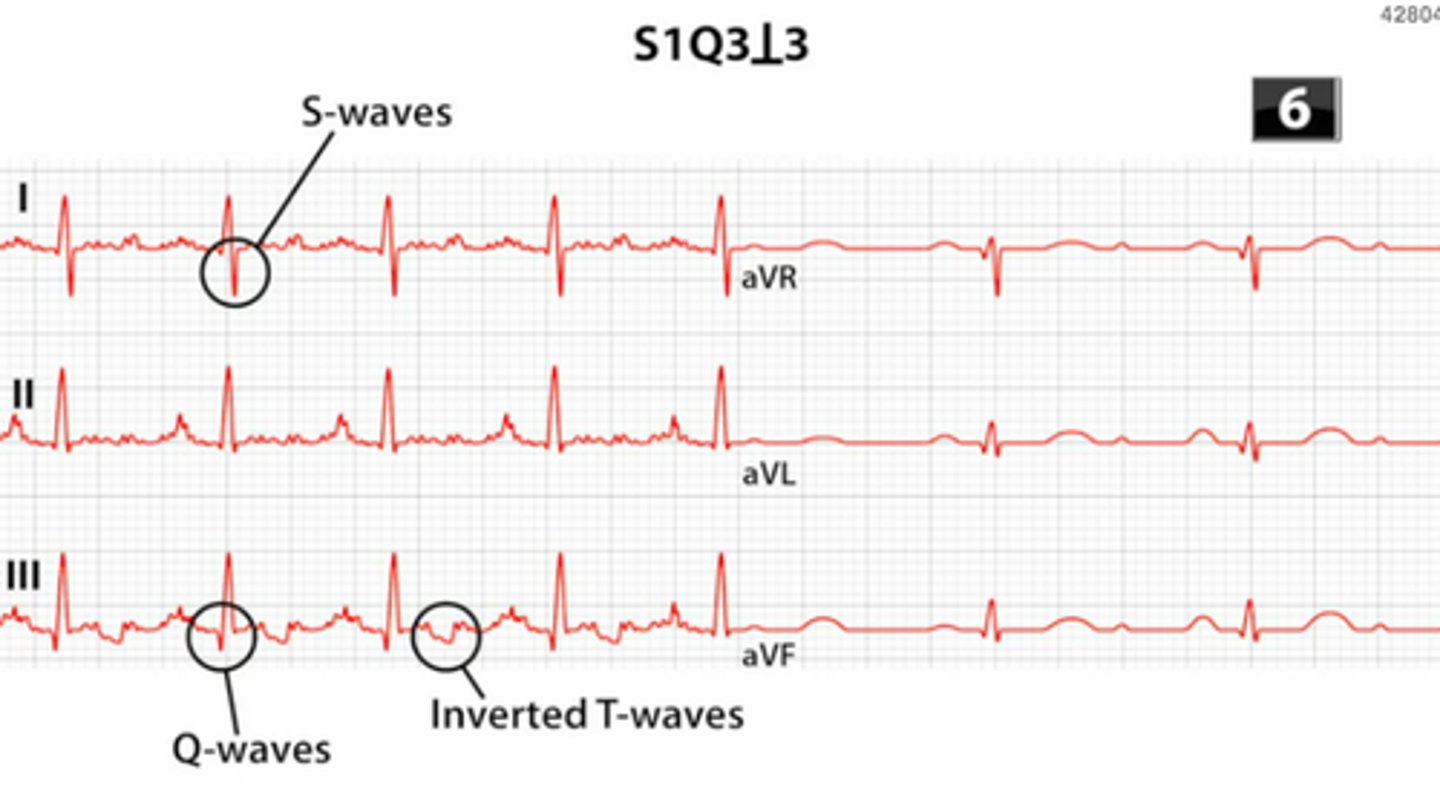
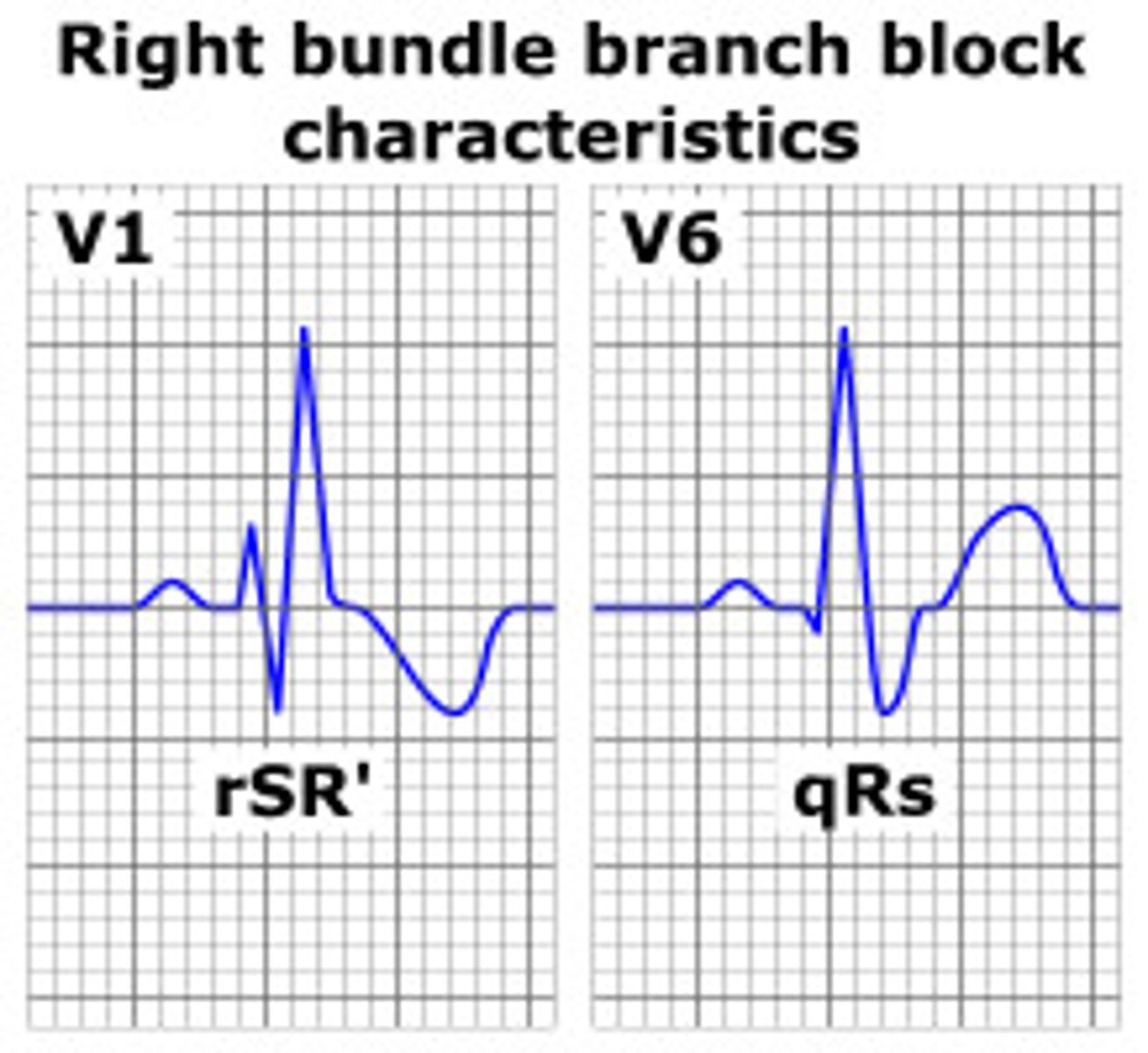
RBBB, seen in PE
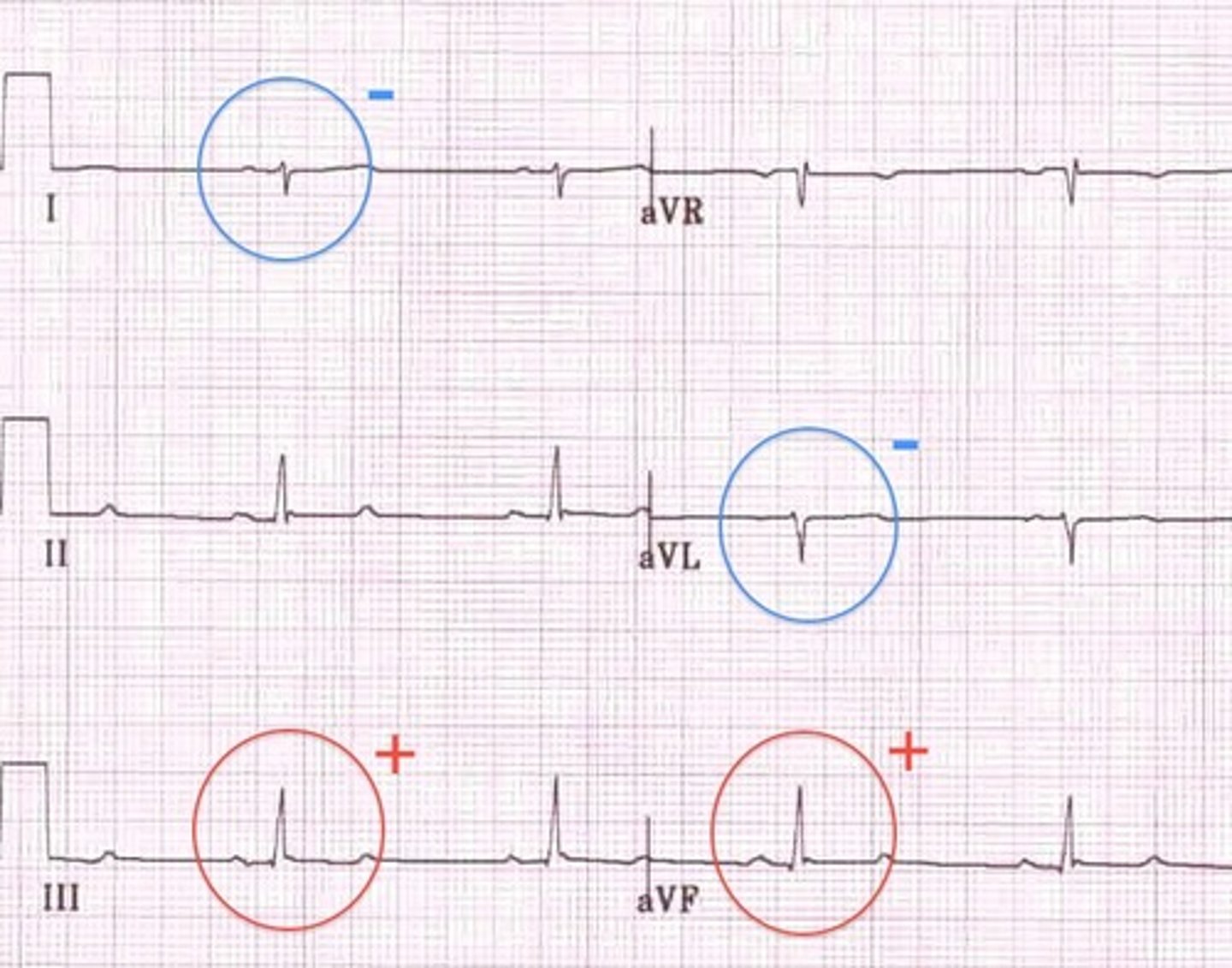
Right axis deviation, seen in PE
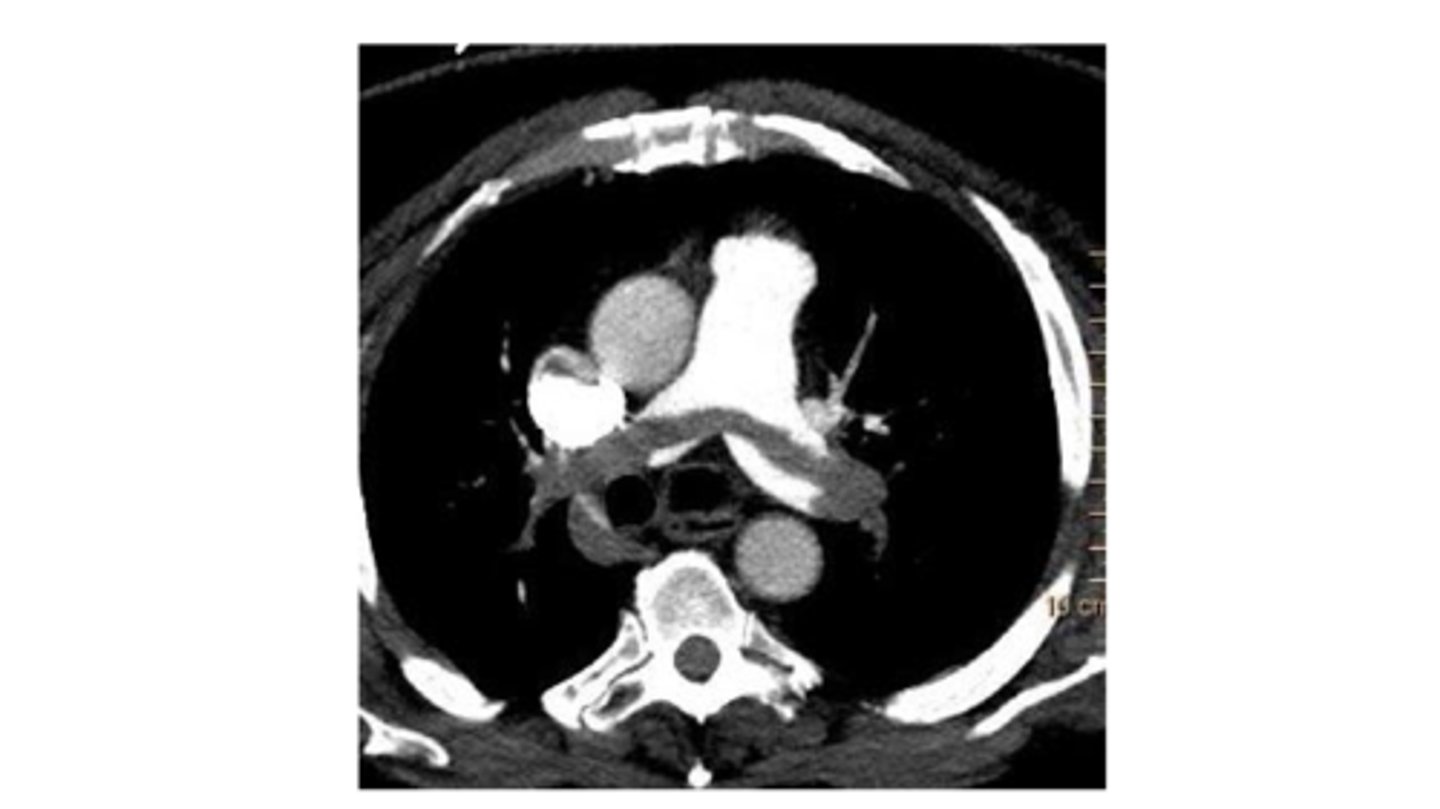
new standard of diagnosis for PE, neg predictive value of 99%. accurate as invasive angiography
CT chest with contrast
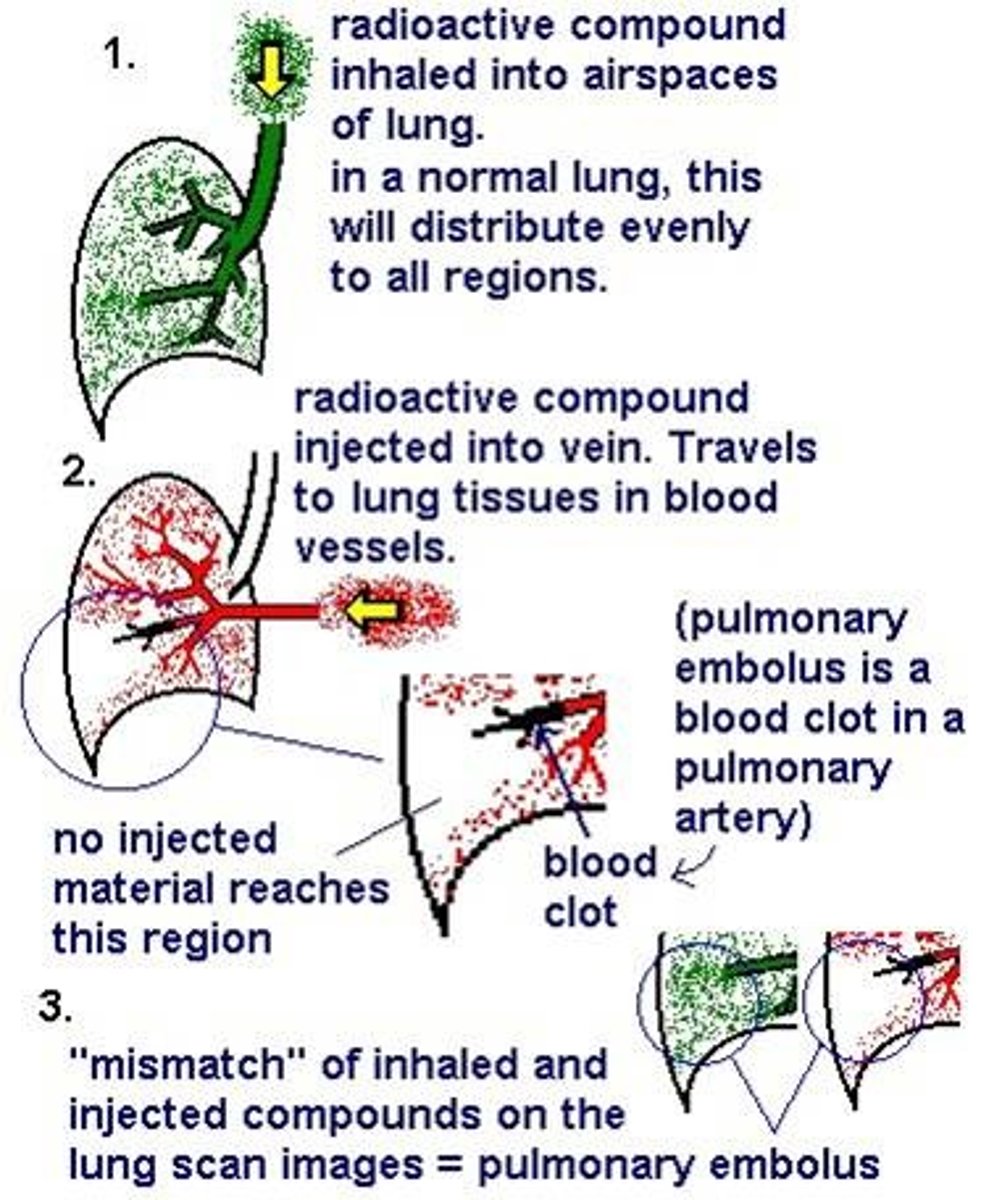
this is V/Q scan. use if renail impairment or IV contrast allergy
low prob (2% have), high probability (96% have)
intermediate, correlate with U/S for DVT
when would you use this instead of CT with iv contrast
clinical signs of DVT
alternative diagnosis less likely than PE (look at CXR, ABG, and EKG)
wells criteria - 3 pointers
HR > 100 (tachy)
surgery/immobilization in past 4 weeks
previous DVT/PE
wells criteria - 1.5 pointers
hemoptysis
malignancy
wells criteria - 1 pointers
0-1 low
2-6 mod
6+ high
0-4 unlikely, >4 likely
wells low, mod, high prob scores
4
malignancy: 1
surgery in past 4 weeks: 1.5
tachy: 1.5
A 67 year old female with history of stage II lung cancer with resection 3 weeks ago presents to office with cough and shortness of breath. her CXR is clear and EKG demonstrates sinus tachy. ABG shows mild hypoxia. What is her wells score?
based on hemodynamic stability
elevated biomarkers like troponin, bnp?
RV strain on EKG?
risk stratification of PE
non-massive (70-75%)
Sub-mmassove (20-25%)
Massive (5-10%)
categories for PE
Sys BP >= 90 with NO signs of cardiac instability. excellent prognosis
non-massive PE
sys BP >= 90 with right ventricular strain pattern on EKG/echo and possible elevations in troponin/bnp
more likely to be detected clinically
submassive PE
sys BP <90 (obstructive/cardiogenic shock)
thrombosis affecting at least half of the pulmonary vasculature
dyspnea, syncope, hypotension, cyanoisis
massive PE
fondaparinux
can be used in HIT in pregnancy
II, VII, IX, X
what factors are prevented from being activated in heparin
life threatening or intracranial hemorrhage due to UFH or LMWH
what is protamine sulfate used for
dabigatran
idarucizumab neutralizes which anticoag
acitvated charcoal if last dose was recent
andexxa is a reversal agent.
Kcentra is a 4 factor complex concentrate
how to treat factor Xa inhibitor complications
3-6 months
duration of anticoag treatment for provoked DVT/PE
use LMWH or DOAC as monotherapy indefinitely
PE patients with cancer anticoagulants