Kins 309-Exam 1 Review
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
Physical Activity
any bodily movement produced by contracting skeletal muscles
resulting in an increase in energy expenditure
resulting in an increase in energy expenditure
2
New cards
Exercise
PA that is planned, structured, repetitive, and purposeful activity to improve or maintain any component of fitness for life or sport
3
New cards
Health
a human condition with physical, social, and psychological dimensions, each characterized on a continuum with positive and negative poles
Positive health- wellness
Negative health- morbidity and mortality
Positive health- wellness
Negative health- morbidity and mortality
4
New cards
Physical Fitness
“a set of attributes” that people can have or achieve that relates to the ability to perform physical activity
5
New cards
Morbidity
relative incidence of a particular disease in a specific locality.
Ex. diabetes, hypertension, depression, heart disease
Ex. diabetes, hypertension, depression, heart disease
6
New cards
Mortality
a measure of the number of deaths (frequency) in a given population
7
New cards
What does MET stand for?
metabolic equivalent of a task
8
New cards
Why are MET’s important?
are used to estimate the energy expenditure for many common physical activities.
9
New cards
MET- Light Exercise
1\.6-2.9 METs
standing in line, walking slowly, washing dishes
standing in line, walking slowly, washing dishes
10
New cards
MET- moderate exercise
3-5.9 METs
golf, tennis, walking quickly 3 mph
golf, tennis, walking quickly 3 mph
11
New cards
MET- vigorous exercise
>= to 6 METs
jogging, running, fast walking, soccer, basketball
jogging, running, fast walking, soccer, basketball
12
New cards
CMR
Cardiovascular, Metabolic, Renal Disease
13
New cards
S/S of cardiovascular, metabolic or renal disease
pain discomfort in chest, neck, jaw, arms
shortness of breath at rest or mild exertion
dizziness (during exercise)
orthopnea (breathlessness while laying down)
ankle edema (swelling evident at night)
palpitations or tachycardia
intermittent claudication
known heart murmur
unusual fatigue with usual activities
shortness of breath at rest or mild exertion
dizziness (during exercise)
orthopnea (breathlessness while laying down)
ankle edema (swelling evident at night)
palpitations or tachycardia
intermittent claudication
known heart murmur
unusual fatigue with usual activities
14
New cards
PAR-Q+
the physical activity readiness questionnaire for everyone
15
New cards
When to use PAR-Q+
self-screening for entry into moderate intensity exercise programs
16
New cards
How many questions on PAR-Q+
7 on the first page
17
New cards
ACSM Exercise Guidelines for Healthy Adults 18-65
should accumulate at least 150 min/week of moderate intensity exercise. (30-60 min a day)
OR
at least 75 min of vigorous intensity exercise (20-60 min a day) PLUS resistance train 2 days per week
OR
at least 75 min of vigorous intensity exercise (20-60 min a day) PLUS resistance train 2 days per week
18
New cards
Why is overall physical activity an important part of exercise prescription?
their are lots of health benefits associated with increasing physical activity.
19
New cards
What part of US has the biggest increase in these trends?
mid south
Louisiana, Oklahoma, mississippi, arkansas, kentucky, alabama
Louisiana, Oklahoma, mississippi, arkansas, kentucky, alabama
20
New cards
Difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
In diabetes type 1, the pancreas does not make insulin, because the body's immune system attacks the islet cells in the pancreas that make insulin. In diabetes type 2, the pancreas makes less insulin than used to, and your body becomes resistant to insulin.
21
New cards
Health-related Components of fitness
ability to perform daily activities with vigor.
* cardiovascular fitness
* muscular endurance
* muscular strength
* body composition
* flexibility
* cardiovascular fitness
* muscular endurance
* muscular strength
* body composition
* flexibility
22
New cards
Skill-related Components of fitness
sport, motor skill performance
* power\*\*
* speed
* agility
* balance
* reaction time
* coordination
* power\*\*
* speed
* agility
* balance
* reaction time
* coordination
23
New cards
Basic Training Principles
principles of
overload
progression
recovery
overuse
specificity
reversibility
individual differences
overload
progression
recovery
overuse
specificity
reversibility
individual differences
24
New cards
principle of overload
muscles adapt to a greater resistance
25
New cards
principle of progression
amount and intensity of your exercise should be increased gradually
26
New cards
principle of recovery
components
* rest
* hydration
* nutrition
* mobility/flexibility
* mental health/stress reduction
* high quality sleep
* rest
* hydration
* nutrition
* mobility/flexibility
* mental health/stress reduction
* high quality sleep
27
New cards
principle of specificity
physiological and metabolic responses and adaptations to exercise training are specific to type of exercise and muscle groups involved
28
New cards
principle of overuse
violating the principle of overload; overdoing it
may result in injuries
may result in injuries
29
New cards
principle of reversibility
use or lose it
positive physiological effects and health benefits of regular PA and exercise are reversibile
positive physiological effects and health benefits of regular PA and exercise are reversibile
30
New cards
Individual differences
varying age, fitness levels, and varied responses to a given exercise stimulus.
each person has a different response to exercise
experience
genetics
exercise history
risk factors
each person has a different response to exercise
experience
genetics
exercise history
risk factors
31
New cards
Health Concerns with Overweight/Obese Individuals
coronary heart/artery disease
stroke
hypertension
dyslipidemia
osteoarthritis
sleep apnea
type 2 diabetes
some cancers
stroke
hypertension
dyslipidemia
osteoarthritis
sleep apnea
type 2 diabetes
some cancers
32
New cards
Society Concerns with Overweight/Obese Individuals
Could not find
33
New cards
Mental benefits of PA and Exercise
increased:
self-esteem
self-confidence
overall cognitive performance
creativity
sleep quality
\
reduced:
stress
depression
anxiety
cognitive decline
self-esteem
self-confidence
overall cognitive performance
creativity
sleep quality
\
reduced:
stress
depression
anxiety
cognitive decline
34
New cards
physical benefits of PA and exercise
improved:
ADLs
muscular strength endurance
bone density
mobility
weight management
balance
reduced:
CVD
hypertension
type 2 diabetes
some cancers
chronic health conditions/disabilities
ADLs
muscular strength endurance
bone density
mobility
weight management
balance
reduced:
CVD
hypertension
type 2 diabetes
some cancers
chronic health conditions/disabilities
35
New cards
Dose-Response Concept
relationship between the dose of exercise required to elicit the desired response
dose- amount= total weekly energy expenditure
frequency, intensity, or duration
response- relative risk reduction of morality, physical fitness benefits, risk factor reduction
dose- amount= total weekly energy expenditure
frequency, intensity, or duration
response- relative risk reduction of morality, physical fitness benefits, risk factor reduction
36
New cards
Sudden Cardiac Death
the abrupt loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness
37
New cards
HCM
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
heart muscle becomes thickened makes it harder to pump blood.
heart muscle becomes thickened makes it harder to pump blood.
38
New cards
Common cause of SCD in younger athletes
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
39
New cards
ACSM Pre-participation Flowchart
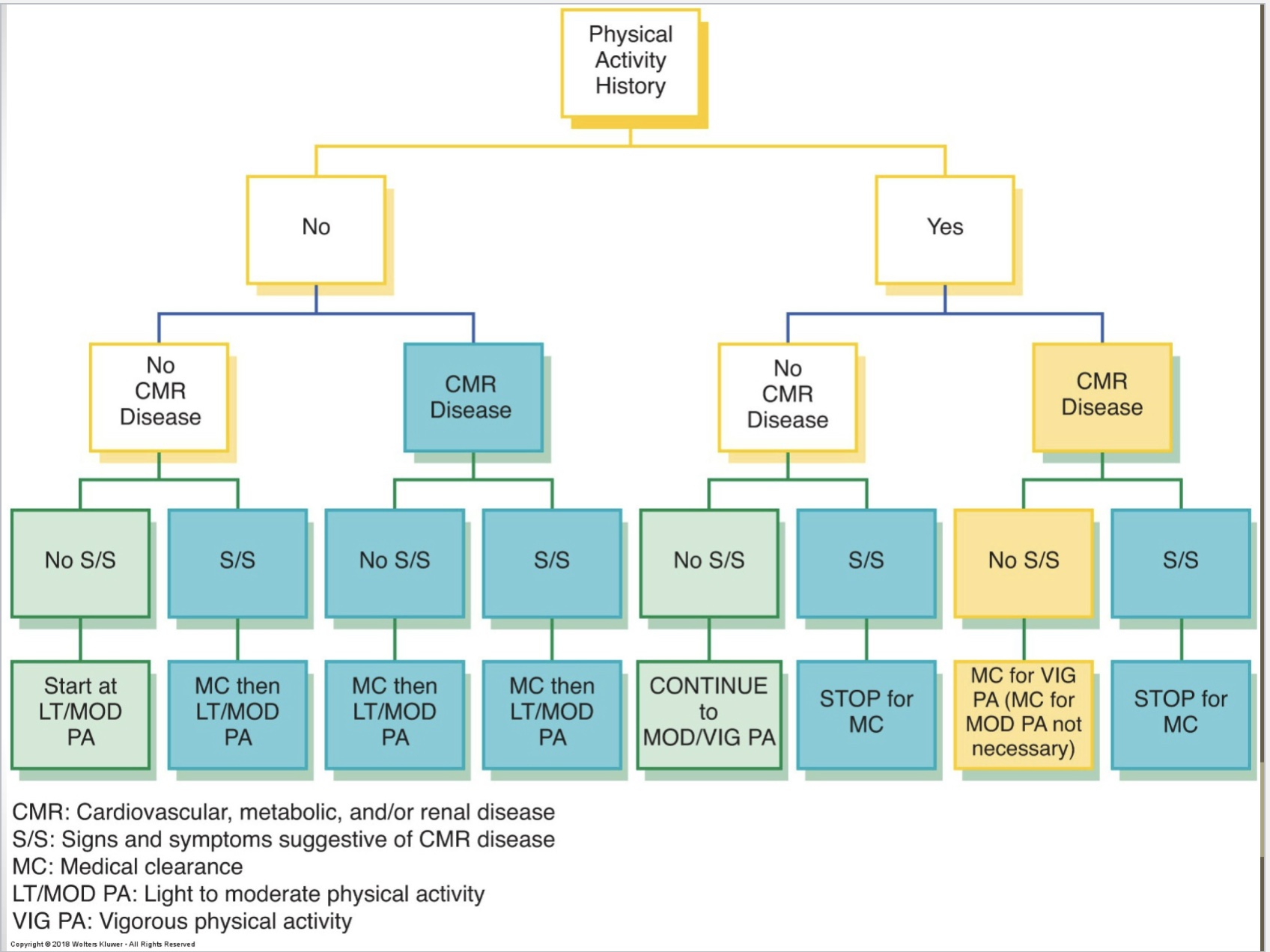
40
New cards
CVD Risk Factors
Age
family history
smoking
physical inactivity
body mass/waist circumference
hypertension
dyslipidemia
blood glucose
\
if one risk factor isn’t known it counts as risk factor
family history
smoking
physical inactivity
body mass/waist circumference
hypertension
dyslipidemia
blood glucose
\
if one risk factor isn’t known it counts as risk factor
41
New cards
Age
men over 45
women over 55
women over 55
42
New cards
family history
any heart condition including; myocardial infarction, bypass surgery/angioplasty, sudden death
before the age of 55 in male relatives
before the age of 65 in male relatives
must by 1st degree relative
before the age of 55 in male relatives
before the age of 65 in male relatives
must by 1st degree relative
43
New cards
smoking
current smoker
those that quit within previous 6 months
exposure to environmental tobacco smoke
those that quit within previous 6 months
exposure to environmental tobacco smoke
44
New cards
physical inactivity
not meeting 75-150 min/week of moderate to vigorous physical activity
45
New cards
body mass/waist circumference
BMI greater or equal to 30kgm2
Waist circumference over
102 cm /40 in for men
88 cm/ 35 in for women
Waist circumference over
102 cm /40 in for men
88 cm/ 35 in for women
46
New cards
hypertension
systolic blood pressure greater than 130mmHg
diastolic blood pressure greater than 80 mmHg
diastolic blood pressure greater than 80 mmHg
47
New cards
dyslipidemia
LDL above 130
taking lipid lowering medication
total cholesterol over 200
\
HDL is positive risk factor. it cancels out other risk factors if over…
40 in men and 50 in women
taking lipid lowering medication
total cholesterol over 200
\
HDL is positive risk factor. it cancels out other risk factors if over…
40 in men and 50 in women
48
New cards
blood glucose
pre-diabetes if over 100
diabetes if over 126
diabetes if over 126
49
New cards
Transtheoretical Model of Change
change as a process involving progress through five stage. describes how people either modify a problem behavior or acquire a positive behavior
50
New cards
stage 1- pre contemplation
\-not ready to take action
\-no intention to take action in next 6 months
\-cons outweigh pros of being active
\-misinformed or uninformed
\-denial
\-unaware
\-several failed attempts- demoralized
\-no intention to take action in next 6 months
\-cons outweigh pros of being active
\-misinformed or uninformed
\-denial
\-unaware
\-several failed attempts- demoralized
51
New cards
stage 2-contemplation
intending to be active in the next 6 months
\-thinking about taking action
\-intend to start in next 6 months
\-more aware of pros/cons of engaging in PA
\-convinced but not fully committed
\-costs may still outweigh the benefits doubt/delay
\-thinking about taking action
\-intend to start in next 6 months
\-more aware of pros/cons of engaging in PA
\-convinced but not fully committed
\-costs may still outweigh the benefits doubt/delay
52
New cards
stage 3- preparation
planning- beginning an activity but may be irregular.
getting ready to take action
intend to be active in next 30 days or immediate future
may have a specific plan to get started or are doing some PA but not meeting ACSM guidelines
smart goals
getting ready to take action
intend to be active in next 30 days or immediate future
may have a specific plan to get started or are doing some PA but not meeting ACSM guidelines
smart goals
53
New cards
stage 4-action
behavior change has recently started
actively involved but less than 6 months
“I’m doing it now”
actively involved but less than 6 months
“I’m doing it now”
54
New cards
stage 5- maintenance
regular participation for at least 6 months
“i’ve been doing it consistently for at least six months”
making PA a habit
becoming part of their identity
“i’ve been doing it consistently for at least six months”
making PA a habit
becoming part of their identity
55
New cards
Strategies to help clients move from one stage to next within TMC.
Having clients think of pros/cons
Helping clients make SMART goals
Helping clients to identify specific plans/people/places to support change
Follow-Up with client
support self-efficacy
non judgmental
motivation
discuss relapse
Helping clients make SMART goals
Helping clients to identify specific plans/people/places to support change
Follow-Up with client
support self-efficacy
non judgmental
motivation
discuss relapse
56
New cards
Social Cognitive Theory
key factor is self- efficacy. the more confident one feels in their capabilities and skills to succeed, the more likely they will engage in this behavior
57
New cards
reciprocal determinism
interaction between individuals and their environment. main factors
\-environment
\-individual personality characteristics/experiences
\-behavioral factors
\-environment
\-individual personality characteristics/experiences
\-behavioral factors
58
New cards
Self-Determination Theory
motivation exists on a continuum.
three psychosocial needs
\-self-determination or autonomy
\-competence
\-relatedness (meaningful social interactions with others)
three psychosocial needs
\-self-determination or autonomy
\-competence
\-relatedness (meaningful social interactions with others)
59
New cards
Intrinsic Motivation
as the doing of an activity for its inherent satisfaction rather than for some separable consequence.
60
New cards
Extrinsic Motivation
a motivation to participate in an activity based on meeting an external goal, garnering praise and approval, winning a competition, or receiving an award or payment.
61
New cards
Why we discourage adding extrinsic motivation if client is already intrinsically motivated?
Extrinsic rewards can undermine intrinsic motivation when used in certain situations or used too often. The rewards may lose their value when you reward behavior that was already intrinsically motivating. Some people also perceive extrinsic reinforcement as coercion or bribery.
62
New cards
Concept of cue/routine/reward when changing habit
the key to change- use the same cue, provide the same reward, change the routine
63
New cards
Barriers related to exercise adherence
lack of time or energy
lack of support, or workout partner, adequate facilities
poor health
self-conscious
lack of support, or workout partner, adequate facilities
poor health
self-conscious
64
New cards
Four strategies to help clients adhere to exercise
demonstrate support for client
help with organization and planning
helps client overcome barriers
gives praise and acknowledgement
motivates clients
helps set goals
positive feedback
help with organization and planning
helps client overcome barriers
gives praise and acknowledgement
motivates clients
helps set goals
positive feedback
65
New cards
How does exercise boost memory directly and indirectly?
directly- stimulating physiological changes (lower insulin resistance +inflammation. higher growth factors+ health of brain cells) brain part the controls thinking + memory is bigger
indirectly- improves mood + sleep. decreases stress + anxiety
indirectly- improves mood + sleep. decreases stress + anxiety
66
New cards
What exercise is usually studied in exercise/memory research?
walking
67
New cards
What did researchers find in study about tai chi?
had potential to enhance cognitive function in older adults w/ executive function. ( planning, working memory, attention, problem solving)
68
New cards
How long does it take to start seeing cognitive benefits of exercise?
6 months
69
New cards
cholesterol
is a fat like substance. lipoproteins
70
New cards
sources of cholesterol
liver
food intake
food intake
71
New cards
3 reasons body needs cholesterol
make hormones
make vitamin D
make bile
make vitamin D
make bile
72
New cards
two types of proteins that carry cholesterol
low density lipoprotein
high density lipoprotein
high density lipoprotein
73
New cards
role of LDL
travels through bloodstream delivering cholesterol to cells that need it.
74
New cards
if body has too much LDL…
can build up on the walls of arteries
forms plaque
plaque buildup limits blood flow
causes coronary heart disease
^ risk of heart attack/stroke
forms plaque
plaque buildup limits blood flow
causes coronary heart disease
^ risk of heart attack/stroke
75
New cards
where is HDL made in body
liver
76
New cards
role of HDL
helps remove excess cholesterol from your cells, tissues, and plaque
returns excess to liver and then removes it
returns excess to liver and then removes it
77
New cards
blood pressue
the amount of force caused by blood pressing against the walls of arteries
78
New cards
role of right ventricle
pushes oxygen poor blood to lungs to pick up oxygen
79
New cards
role of left ventricle
pushes oxygen rich blood to your body
80
New cards
four main factors that affect pressure on artery walls.
proportional-
cardiac output
blood volume
blood viscosity
inverse-
resistance
cardiac output
blood volume
blood viscosity
inverse-
resistance
81
New cards
hypertension guidelines
new-
top # 130-139 or +
bottom # 80-89 or +
\
old-
top # 140 or more
bottom # 90 or more
top # 130-139 or +
bottom # 80-89 or +
\
old-
top # 140 or more
bottom # 90 or more
82
New cards
goal of these guidelines to decrease the risk of these diseases
heart attack, stroke, kidney disease
83
New cards
type 2 diabetes is more common in people with these characteristics
overweight, sedentary, middle age
84
New cards
relationship between glucose and insulin (healthy)
when blood glucose increases, pancreas secretes insulin. when insulin binds to its receptors it causes glucose transporters to come to surface of cell. facilitates entry of glucose into these cells
85
New cards
what goes wrong with type 2 diabetes
production of insulin is low and there can be resistance to insulin. circulating insulin fails to facilitate absorption of glucose into cells, and controls levels of blood sugar
86
New cards
common cause. of SCD in adults 20-30s
hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
87
New cards
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
genetic abnormality of the proteins used by heart muscle cells. the heart becomes abnormally thick in one area and when heart pumps, it has trouble ejecting blood past the thick part
88
New cards
why does this disease happen with exercise
w/ exertion and dehydration
blood volume decreases
blood volume decreases
89
New cards
why do runners die even with AED available
they go through ventricular tachycardia which can only be reversed by AED during 1- 2 minutes then it progresses to ventricular fibrillation. O2 is past return point.
90
New cards
prevention methods to detect symptoms of heart issue in younger adults
getting a cardiac echogram, echocardiogram or external exam of heart with ultrasound
91
New cards
self-determination theory
the more self-determined we are that is the more we’re doing what we want to do and aren’t being forced to do- the happier + more successful we tend to be
92
New cards
three basic needs of self-determination theory
autonomy- choice made by you
competence- know what your doing
relatedness- connects you to other people
competence- know what your doing
relatedness- connects you to other people
93
New cards
how did St.Johns football coach incorporate SD theory with his team
ditched the laps, calisthenics.
he let players get water between plays, choose plays to run, implemented autonomy + competence into practice
he let players get water between plays, choose plays to run, implemented autonomy + competence into practice
94
New cards
explain 2004 study related to intrinsic motivation
those who were intrinsic motivation after 6 months outnumbered extrinsically motivated people 3 to 1
95
New cards
5 ideas from positive psychology to keep clients upbeat/motivated
1. understand that pessimism is not a choice
2. make workouts fun
3. devise an engaging workout
4. frame progress in a positive way
5. remember that other people matter
96
New cards
two key points
having small successes
making a workout fun
making a workout fun
97
New cards
five areas that can motivate people to continue to exercise
1. demographic + biological factors
2. psychological, cognitive + emotional factors
3. behavioral attributes + skills
4. social + cultural
5. physical environment. + physical activity characteristics
\
98
New cards
most likely to dropout of exercise
\
* people who over estimate their expectancies
* people who smoke
* low self-worth
* bad body image
* people who over estimate their expectancies
* people who smoke
* low self-worth
* bad body image
99
New cards
what changed for linda
she joined a “life change” program w/ walking
100
New cards
what error did linda make before?
she skipped the preparation phase