Intro to Evolution
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Evolution
gradual change over time
When the Earth first formed, what type of atmosphere was there?
primitive atmosphere
What did the primitive atmosphere contain?
Methane gas (CH4)
Ammonia (NH3)
Hydrogen (H2)
Water vapor (H2O)
What released atoms to form simple organic molecules?
UV rays and lightning bombarded the atmosphere, breaking the bonds in gas molecules
What led to the first heterotrophs?
Membranes formed around organic compounds → lead to the primitive cell that uses anaerobic respiration for energy = first heterotrophs!
Heterotrophs
an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter.
similar to present day bacteria
What was the result of simple organic molecules used for food being used up?
a competition for food
cells evolved to make their own food →leading to the first autotrophs
Autotrophs
produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis
What happened as a result of photosynthesis evolving?
oxygen would become available/abundant, changing the course of life forever
What did lightning convert?
free O2 to ozone molecules
The ozone layer blocking the UV rays allowed for what?
evolution of new organisms
What is an acquired trait caused by?
It arises during an organism’s lifetime as a result of the organism’s experience or behavior
NOT CAUSED BY GENES
Summary of Darwinian Evolution
Overproduction: a production will produce an overabundant number of offspring
Limited resources → not all offspring will survive
Variation exists in a population and is inherited
Organisms with better traits in environment live
longer and reproduce
Gradual change in population =
favorable characteristics more
frequent over time
Overproduction
a production will produce an overabundant number of offspring
As a result of limited resources, …
not all offspring will survive
What exists in a population?
variation
What is inherited?
variations
Individuals that have the best traits to fit into their environment will…
live longer
leave more offspring
What accumulates over generations?
gradual change in a population with favorable characteristics
Where do variations come from?
Mutations – can be favorable
Recombination (crossing over) – during meiosis
Natural Selection
the process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change
What type of phenotypes do organisms adapt to?
phenotypes that are favorable to their environment to help improve their fitness
Fitness
the ability for an organism to survive and reproduce in their environment
What is an Example of Natural Selection?
Insecticide Resistance– DDT
Humans spray crops with insecticide
Resistant insects survive
Frequency of resistant insects will grow
Gene Pool
entire collection of genes among a population
Population Genetics
the study of gene pools and the change they undergo
Adaptations
a change or the process of change by which an organism/species becomes better suited to its environment
How are adaptations possible?
due to variations
- the variations may improve or reduce fitness
What types of variations are preserved by natural selection?
variations that aid in survival
What happens when over time, all members have inherited the variation?
it becomes an adaptation
What are the types of adaptations?
Structural
Physiological/Behavioral
Structural adaptations
Woodpeckers tongue is long and narrow to get food out of small openings in trees
Physiological/Behavioral adaptations
Poison venom of a snake
Birds migrate in search of food
Species
a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature
the offspring needs to be fertile in order for it to be considered a species
ex. female horse + male donkey = mule (sterile). A mule cannot reproduce → it’s not a species
What are the Types of Evolution? (5)
Convergent evolution
Divergent evolution
Coevolution
Gradualism
Punctuated equilibrium
Convergent Evolution
2 species evolve similar characteristics due to common environmental conditions, not common ancestry
ex: wings of bat and bird
ex: fins of shark and dolphin
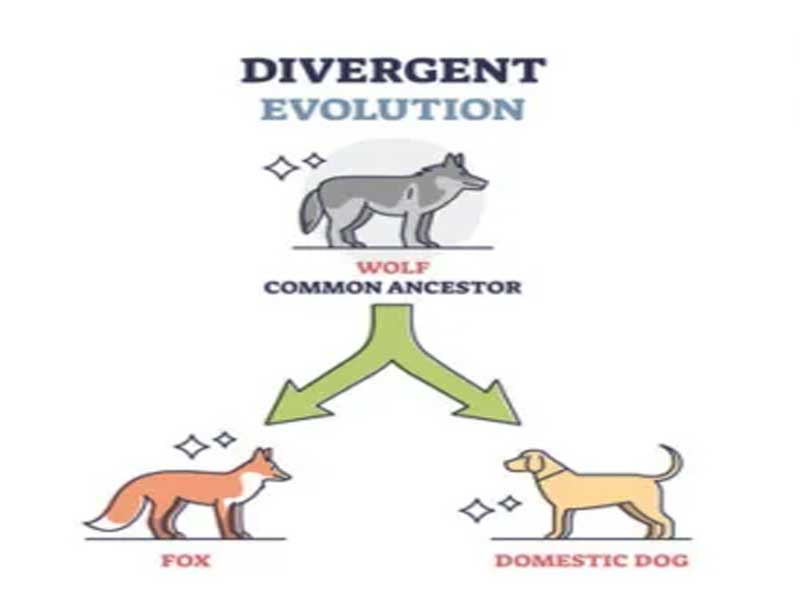
Divergent Evolution (aka adaptive radiation):
2 or more species arise from a common ancestor
Can be a result of geographic isolation, driven by particulars of the location
ex: fox and dogs
ex: Darwin's finches
Coevolution
process where two or more species influence each other's evolution
Ex: predator and prey
What's a specific example of coevolution?
plants and the animals that pollinate them
-Bats with slender, specialized tongues can feed on nectar of certain flowers, picking up pollen as they do
-The flowers coevolved with the bats, (attractive to bats)
-Bats transfer pollen from one flower to another
Gradualism
slow and steady change in a species
What is punctuated equilibrium?
an evolutionary theory stating that species remain stable for long periods and then experience rapid bursts of change (punctuated)
Stephen J Gould hypothesized that evolution is a “standstill” process punctuated by short revolutionary events of rapid evolution
During these evolution events, species become extinct and are replaced by other wholly new forms
Supported by the Fossil Record
Example of punctuated equilibrium
-A cheetah species has no spots. However, due to a gene mutation, a cheetah cub is born with spots.
-Because this adaptation helps the cheetah to hide and survive, more cheetahs are born with spots.
What hypothesis did Stanley Miller test?
If early gases are exposed to energy then organic compounds will form
He used the thinking that complex molecules formed from simple molecules
What did Lamark hypothesize?
Hypothesized that organisms strive to improve themselves and become more advanced
Principle of Use and Disuse from Lamark
Correct: organisms strive to improve themselves to become more evolutionarily advanced to survive in their environment
Incorrect: acquired traits are genetic
DISPROVEN bc August Wiesmann cut the tails off mice for 22 generations, but the mice continued to produce baby mice with normal tails
Darwin’s Voyage
Charles Darwin traveled on the Beagle
Darwin became interested in organisms on the Galapagos Islands
Darwin published a book based on his idea “descent with modification,” called the Origin of Species
Darwin’s Observations
Darwin collected 13 different species of finches
Each finch species had a distinctive beak
The Galapagos are relatively young
He hypothesized an original finch (or a few of the same species) had been blown off course from South America
Offspring of the original finch may have adapted to different environments and food sources
Over millions of years, large differences could have accumulated to create different species
Fossil
any trace of an organism that lived long ago
Types of fossils
Some organisms become trapped in ice or amber = VERY REVEALING
Most are in sand or clay = organism becomes petrified (turned to rock)
What does layering of sedimentary rock tell us?
when organisms existed
What does the fossil record support?
evolution
Fossils in lower rock layers are older than those in higher layers
What is an argument AGAINST evolution?
the fossil record is incomplete
Comparative Embryology
embryos of related organisms develop in similar ways
Comparative Biochemistry
the structure of hemoglobin in a chimpanzee strongly resembles the structure of hemoglobin in humans
What is common in all life forms?
Adenine
Tynine
Cytosine
Guanine
How identical is DNA between humans and chimps?
99% identical
How identical is DNA between humans and other mammals?
80% identical
Comparative Anatomy
the comparison of the structure (anatomy) of one animal or plant with the structure of a different animal or plant
Three ways to compare anatomy:
Homologous structures
Analogous structures
Vestigial organs
Homologous Structures
characteristics that are similar because they are inherited by a common ancestor and have similar embryological development
ex. a human arm and a chimp arm
Analogous Structures
features that serve identical functions, and look similar, but have very different embryological development
ex. wings of a bat and a butterfly
Vestigial Organs
inherited structures that may have been useful to an ancestor but have no use nowadays
ex. human tailbone, appendix, wisdom teeth
Rapid evolution
evolution that occurs over a shorter period of time
ex.
Bacteria builds resistance to antibiotics
Viruses: AIDS is one of the fastest evolving viruses today
COVID is quickly evolving
Artificial selection
evolutionary process in which humans consciously select for or against particular features in organisms
ex. dog breeders
What helped lead to the theory of natural selection?
Breeders generated new varieties of plants and animals by selecting parents with desirable traits
Major extinction event
65 million years ago an asteroid collided with earth and the dinosaurs died out
Mammals went on living because they were nocturnal and reproduced quickly
Causes of extinction
#1 cause = habitat destruction
#2 cause = invasive species
Extinction
termination of a species
Cambrian Explosion
when the first animals appeared → led to a breakthrough in the diversity of LIFE
What is the largest living mammal?
whale
Tree of Life
a model and research tool used to explore the evolution of life and describe the relationships between organisms, both living and extinct
Oxygen Revolution
After photosynthesis evolved, oxygen became available