5.4 active transport
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is the definition of active transport?
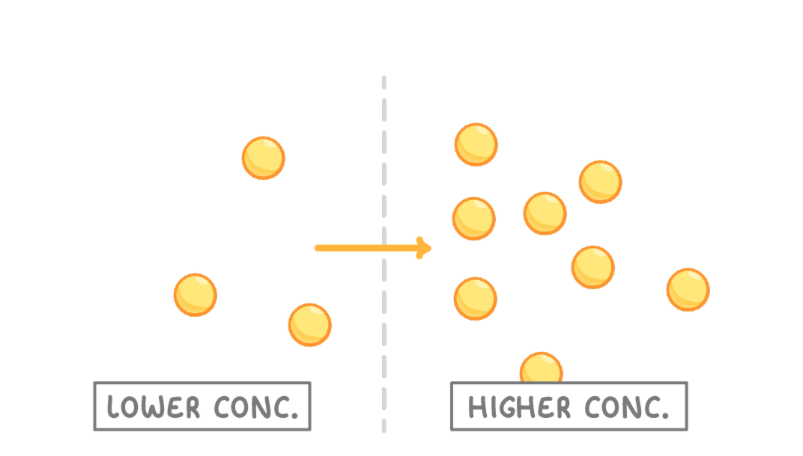
Active transport is the movement of molecules across a membrane, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.
This requires energy (in the form of ATP) from respiration.
What do we mean by against the concentration gradient?
'Against the concentration gradient' means that substances are moving from an area of lowerconcentration to an area of higher concentration.
Is active transport an active or passive process?
Active transport is an active process because it requires energy.
What type of protein is used in active transport?
Active transport uses carrier proteins
Explain how molecules enter cells via active transport.
The molecule, and ATP, binds to the carrier protein. ATP is hydrolysed to ADP and phosphate which causes the carrier protein to change shape.
This releases the molecule on the opposite side of the membrane. The phosphate is released from the carrier protein, causing it to return to its original shape.
Name 4 factors that affect the rate of active transport.
Temperature
Thickness of membrane
Number of carrier proteins
Rate of respiration
Explain how the number of carrier proteins affects the rate of active transport.
The more carrier proteins, the faster the rate of active transport.
Name the two types of bulk transport.
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Describe the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis.
Endocytosis is the bulk transport of material into cells, whereas exocytosis is the bulk transport of material out of cells.
Name the two types of endocytosis.
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis