Session 4: Energy Storage - Carbohydrates & Lipids
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Which tissues have an absolute requirement for glucose as an energy source?
- Erythrocytes and leukocytes
- Testes
- Kidney medulla
- Lens and cornea of the eye
Stable blood glucose levels are absolutely essential for normal ____ function
Stable blood glucose levels are absolutely essential for normal brain function
What is the most severe outcome of SEVERE hypoglycaemia (~0.6mmol/L)?
Brain damage, death
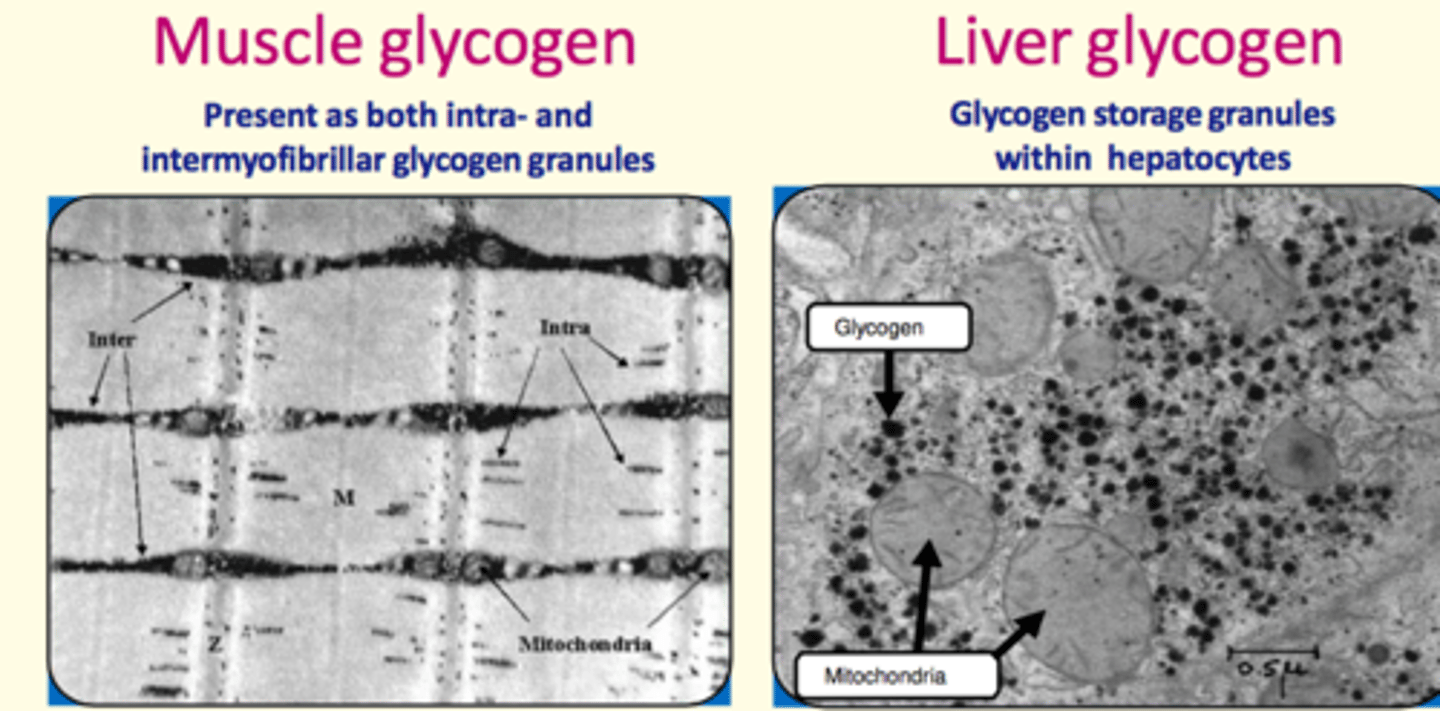
How is glucose granules stored in the liver and muscle?
Glycogen
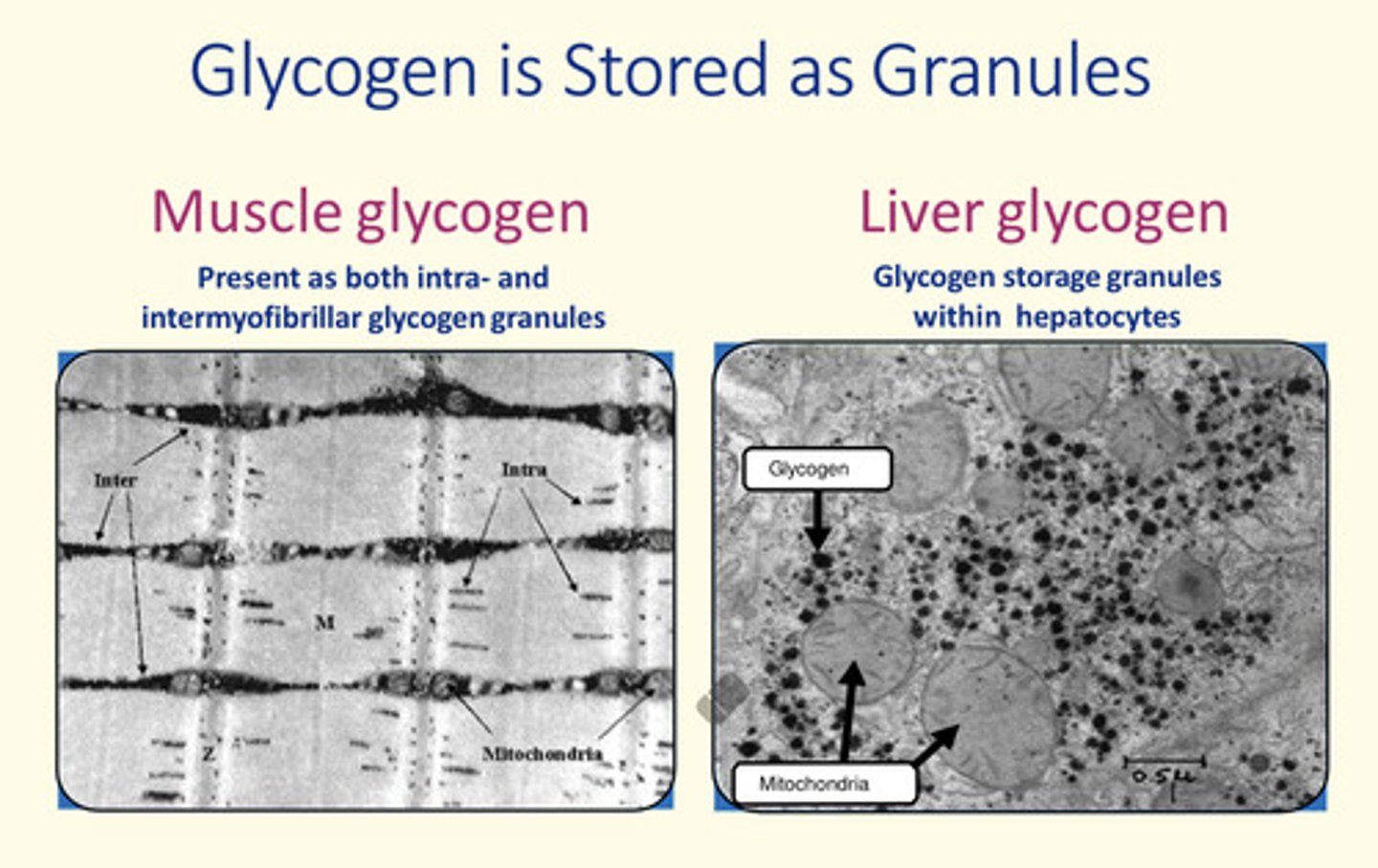
Describe the structure of glycogen
- Polymer of glucose (polysaccharide)
- Highly branched originating from dimer glycogenin
- Chains linked by α-1-4 glycosidic bonds
- Branch points = α-1-6 glycosidic bonds
What types of bonds can be found in glycogen?
The α-1-6 glycosidic bonds = form branching points
The α-1-4 glycosidic bonds = join the chains
What is glycogenin?
Glycogenin is a core protein that glycogen uses as its core and starting synthesis point.
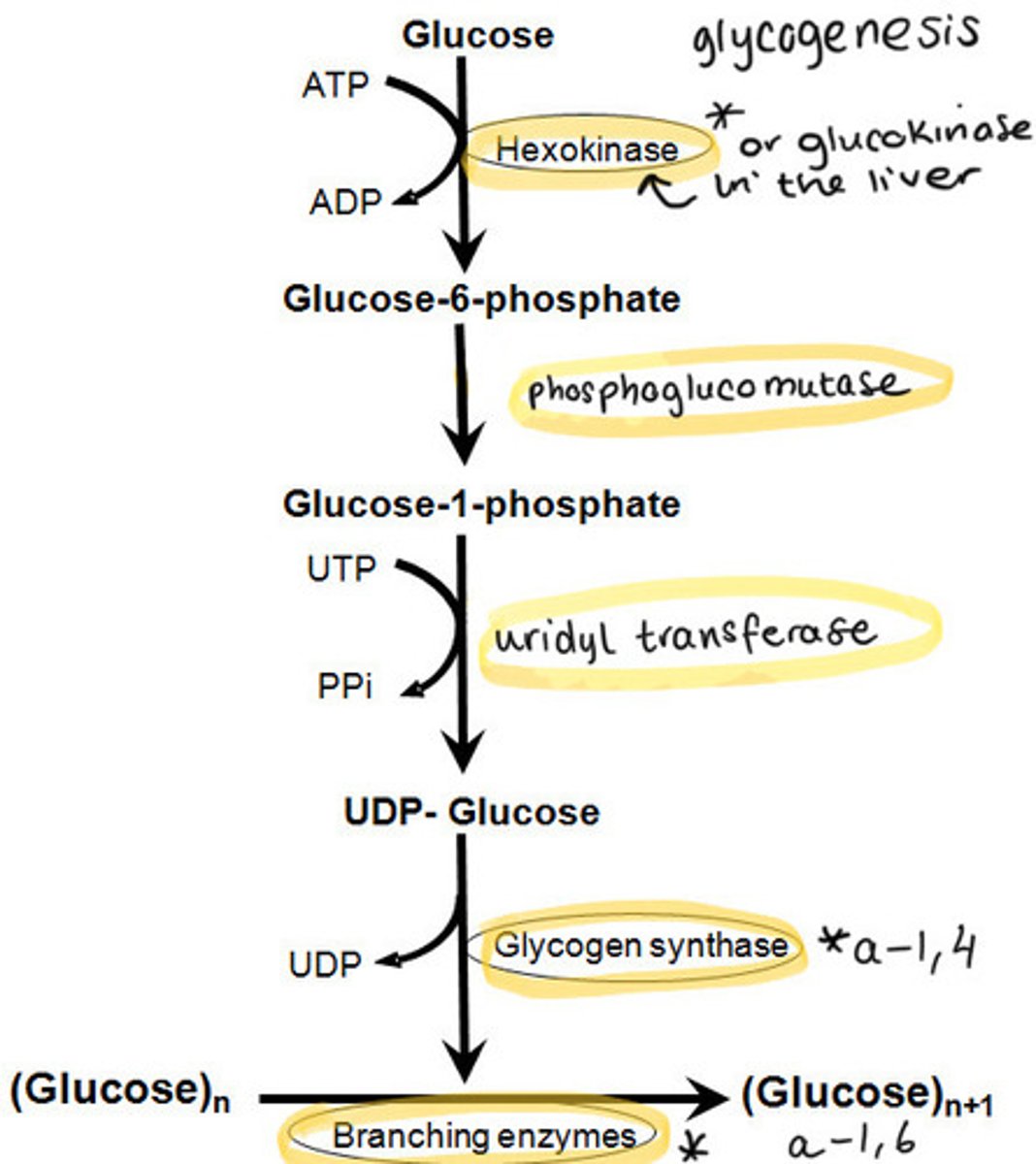
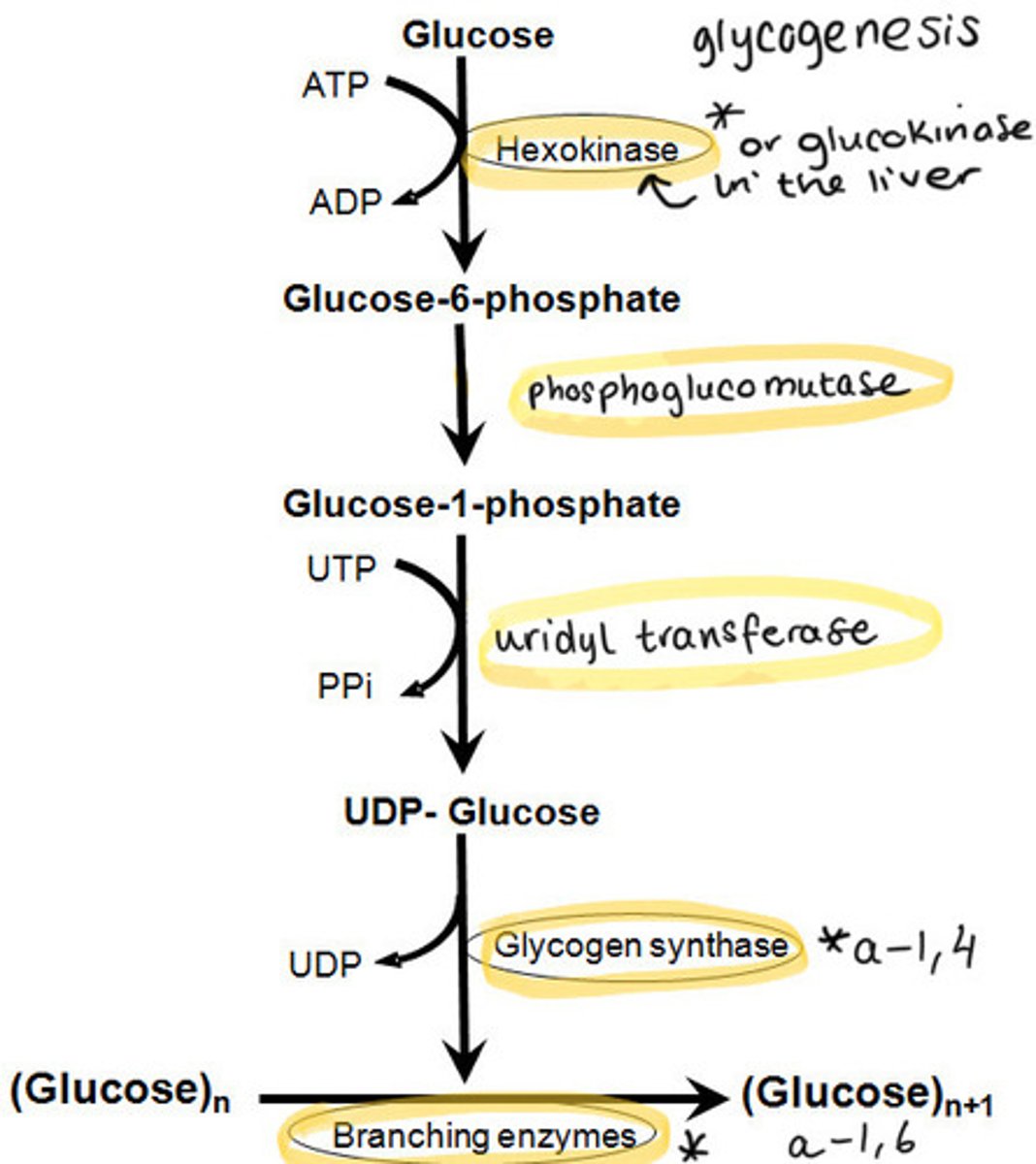
What is glycogenesis and where does it occur?
The conversion of glucose to the storage form of glycogen
It occurs in the muscle and liver
What is the first reaction in glycogenesis?
Glucose converted to glucose-6-phosphate
Catalysed by hexokinase (most cells) or glucokinase (in liver)
What is glycogenolysis? Where does it occur?
The breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate
It occurs in the hepatocytes and muscle cells
What is the second reaction in glycogenesis?
Glucose-6-phosphate is converted to glucose-1-phosphate
Catalysed by phosphoglucomutase
Different enzymes allow for catalysis of glycogen in glycogenolysis - what are these enzymes?
Glycogen phosphorylase = alpha-1-4 glycosidic bonds
De-branching enzyme = alpha-1-6 glycosidic bonds
What is the third reaction in glycogenesis?
Glucose-1-phosphate is converted to UDP-glucose
Catalysed by uridyl transferase
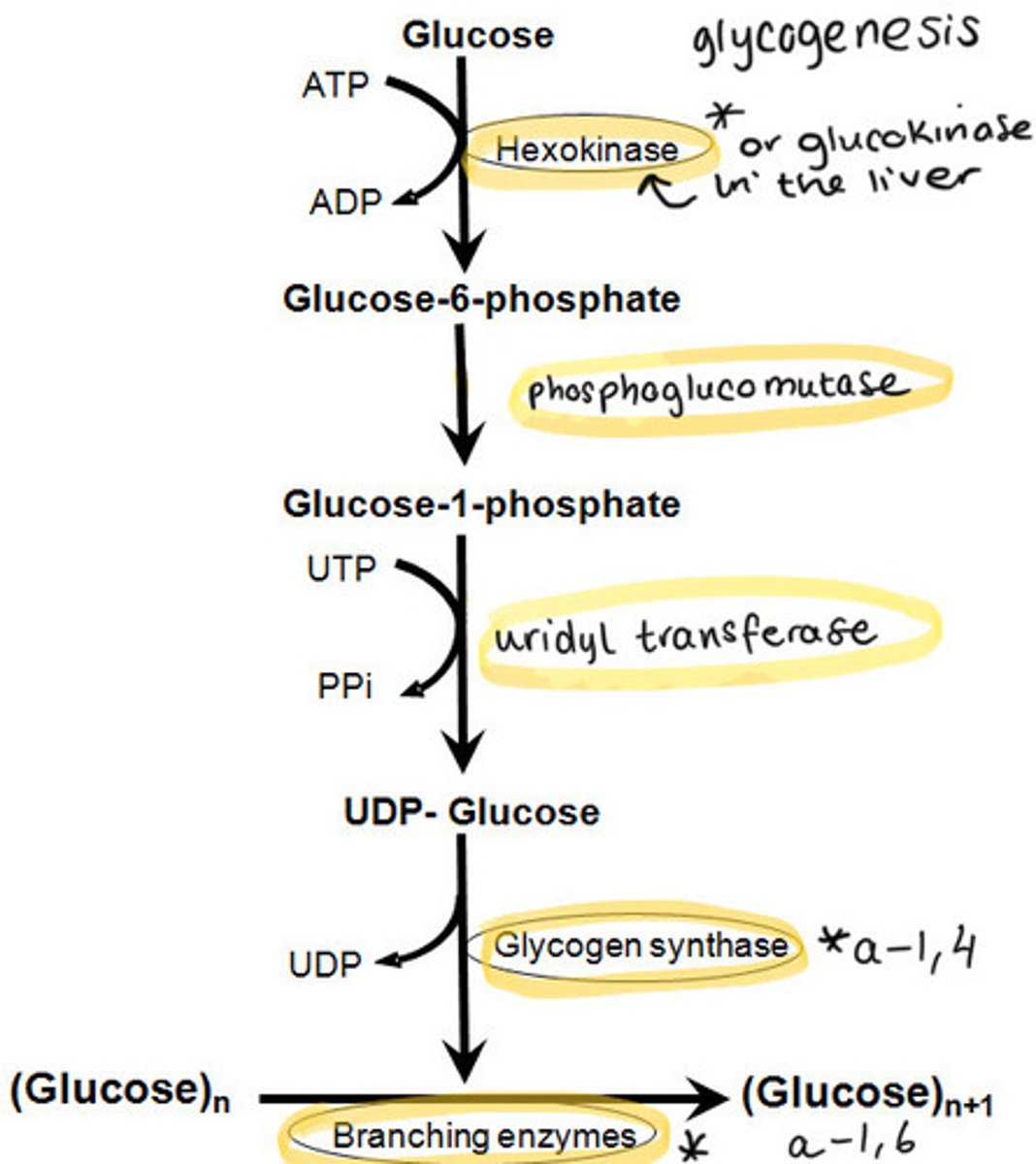
What is the fourth and final step in glycogenesis?
Glycogen (n residues) + UDP-glucose produces = glycogen (n+1 residues) + UDP
Two enzymes are involved...
Glycogen synthase = formation of α-1-4 glycosidic bonds
Branching enzyme = formation of α-1-6 glycosidic bonds
What enzyme catalyses the conversion of glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate in glycogenolysis?
Phosphoglucomutase
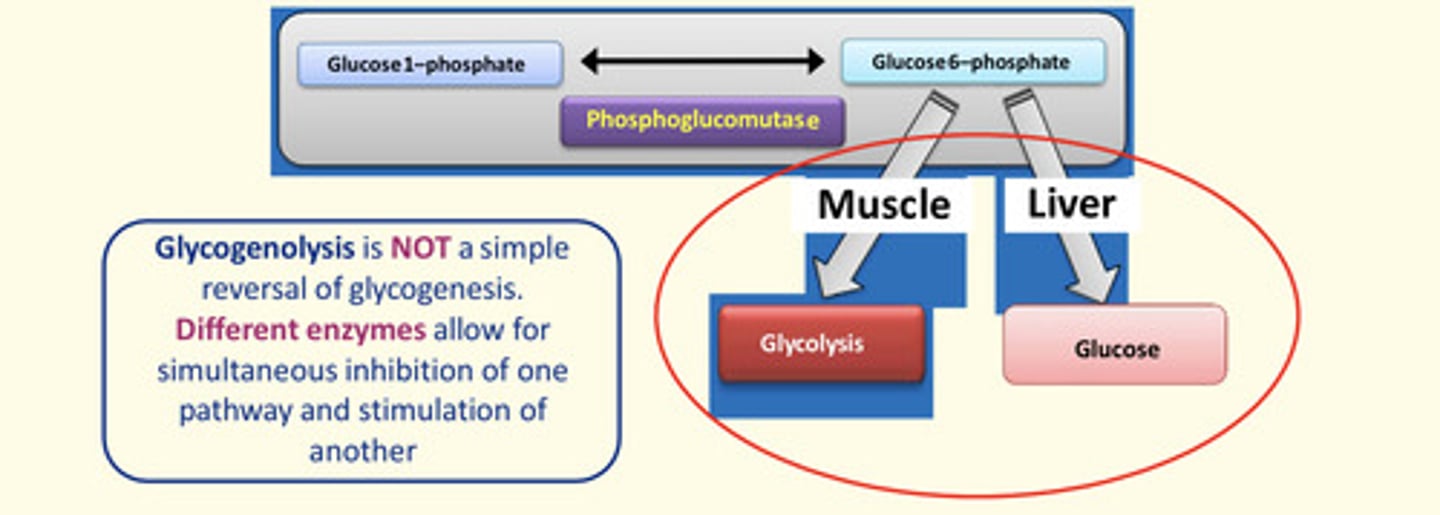
Why can't glucose-6-phosphate from glycogenolysis be broken down into free glucose in the muscle?
The muscle lacks the glucose-6-phosphatase enzymes - so the glucose-6-phosphate must enter glycolysis to produce ATP
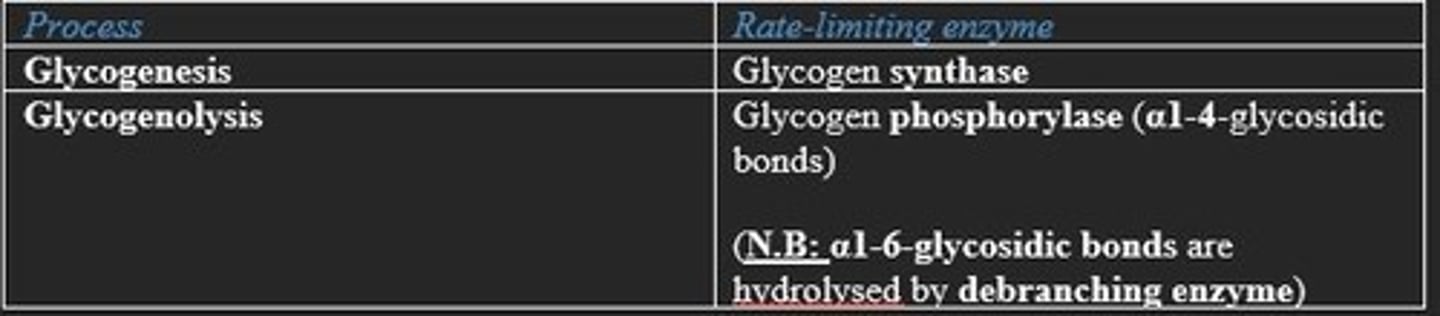
What are the rate-limiting enzymes in glycogen synthesis (glycogenesis)?
Glycogen synthase
What are the rate-limiting enzymes in glycogen degradation (glycogenolysis)?
Glycogen phosphorylase
Hormones that regulate glycogen metabolism
Glucagon, adrenaline, insulin
Hormones that stimulate glycogen breakdown
- Glucagon
- Adrenaline
Hormones that stimulate glycogen synthesis
- Insulin

Major precursors of gluconeogenesis
1) Lactate = cori cycle via lactate dehydrogenase
2) Glycerol
3) Pyruvate
4) Glucogenic amino acids = alanine
5) Galactose
6) Fructose
Triacylglycerols are hydrophobic and therefore stored in an anhydrous form in specialised tissue known as _______.
Triacylglycerols are hydrophobic and therefore stored in an anhydrous form in specialised tissue known as white adipose tissue.
In what organ does fatty acid synthesis mainly occur?
liver
Glucose is stored in the body as...
Glycogen
Name two processes which lead to increased availability of glucose in the body
1. Glycogenolysis
2. Gluconeogenesis
Glycogen synthesis requires energy in a form of…
UTP and ATP
What are two enzymes with key regulatory roles in gluconeogenesis
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)
Name the important enzyme in glycogen metabolism which catalyses this reversible reaction…
Glucose 1-phosphate ⇔ Glucose-6-phosphate
Phosphoglucomutase
Name two rate-limiting enzymes which play key role in glycogen metabolism
Glycogen synthase
Glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen is stored in granules in myocytes and hepatocytes. There are more granules in the liver but muscles stores more glycogen molecules.
True or false?
True
Glucose obtained from glycogenolysis is processed differently in liver and muscle because cells of one of these tissues do not have this enzyme...
Muscle does not have glucose-6-phosphatase
Glycerol is hydrophobic and fatty acid is hydrophilic
True or false?
False
Precursors for gluconeogenesis
Lactate
Glucogenic amino acids (mainly alanine)
Glycerol
Galactose and Fructose
Insulin inhibits gluconeogenesis through inhibition of the amount and/or activity of PEPCK and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
True or false?
True
Name enzyme playing important role in the regulation of the fatty acid synthesis
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
The lipid which may accumulate in the liver is...
Triglyceride
Fatty acids travel complexed with ___ to muscle and other tissues
Fatty acids travel complexed with albumin to muscle and other tissues
What are the names of the hormones which influence hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) and adipose triacylglycerol lipase (ATGL)?
Hormones that ACTIVATE HSL and ATGL (lipolysis)
- Glucagon
- Adrenaline
Hormones which INHIBIT HSL and ATGL (lipolysis)
Insulin = INHIBITS HSL and ATGL
Where does fatty acid synthesis occur?
Liver
Name of the process where fatty acids are catabolised?
Beta-oxidation
Triacylglycerols are hydrophobic and are stored in their anhydrous form in specialised tissues known as ____ tissue
Triacylglycerols are hydrophobic and are stored in their anhydrous form in specialised tissues known as white adipose tissue
What are the major precursors of gluconeogenesis?
Lactate
Glycerol
Pyruvate
Glucogenic amino acids such as alanine
Galactose
Fructose
Give an example of a disorder which arises from excess glycogen storage (excess glycogenesis)
Von Gierke disease
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency in liver
Give an example of a disorder which arises from insufficient glycogen degradation
McArdle disease
Glycogen phosphorylase enzyme deficiency in muscle
What are the "rate-limiting" enzymes involved in glycogen metabolism?
Glycogen synthesis = glycogen synthase
Glycogen degradation = glycogen phosphorylase
Which enzyme is lacking in muscle that leads to substrate entering into glycolysis as free glucose is not readily produced?
Glucose-6-phosphatase lacking in the muscle
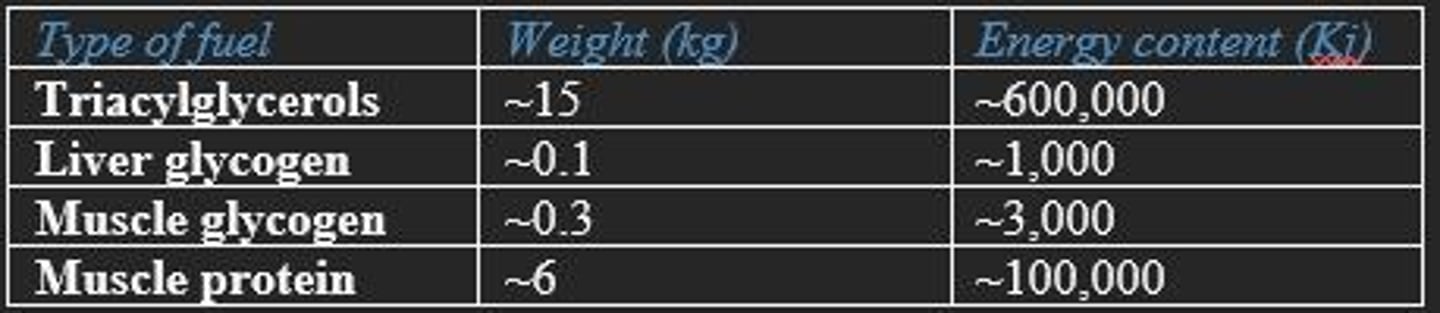
Major energy sources in a 70kg man
triaglycerols
liver glycogen
muscle glycogen
muscle protein
Hypoglycaemia symptoms and plasma levels (mmol/L)
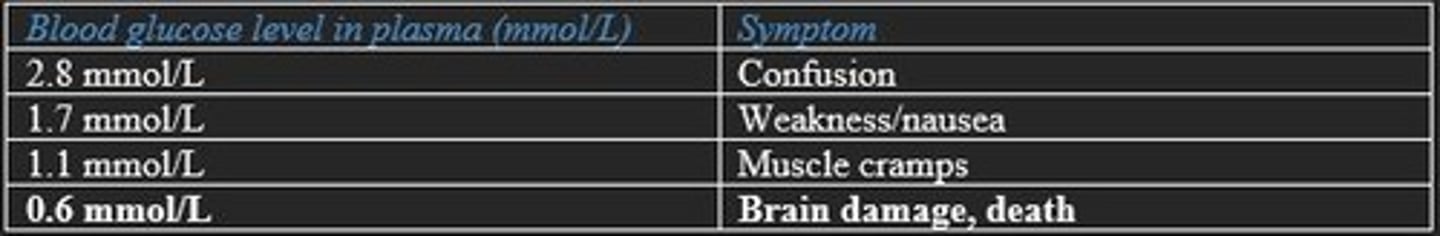
At what blood glucose plasma level (mmol/L) does hypoglycaemia lead to brain damage and death?
0.6 mmol/L
Symptoms of hypoglycaemia
Confusion, weakness, nausea, muscle cramping
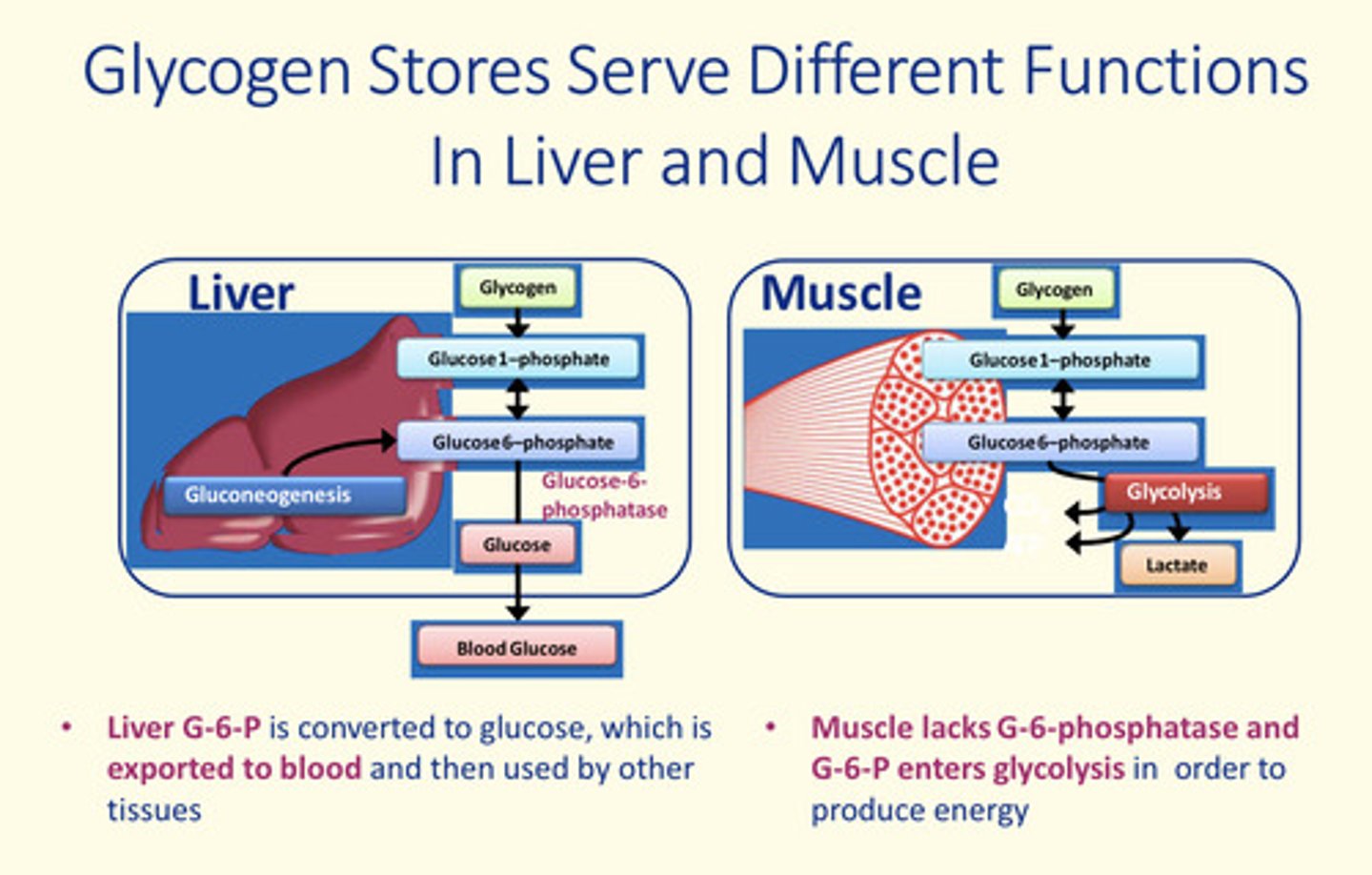
Major difference between glycogen metabolism between liver and muscle
In the liver =
Glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme present
In the muscle =
LACK of glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme means that glucose-6-phosphate is not turned into free glucose. Instead, glucose-6-phosphate enters glycolysis to produce ATP instead

Compare glycogen metabolism in liver and muscle
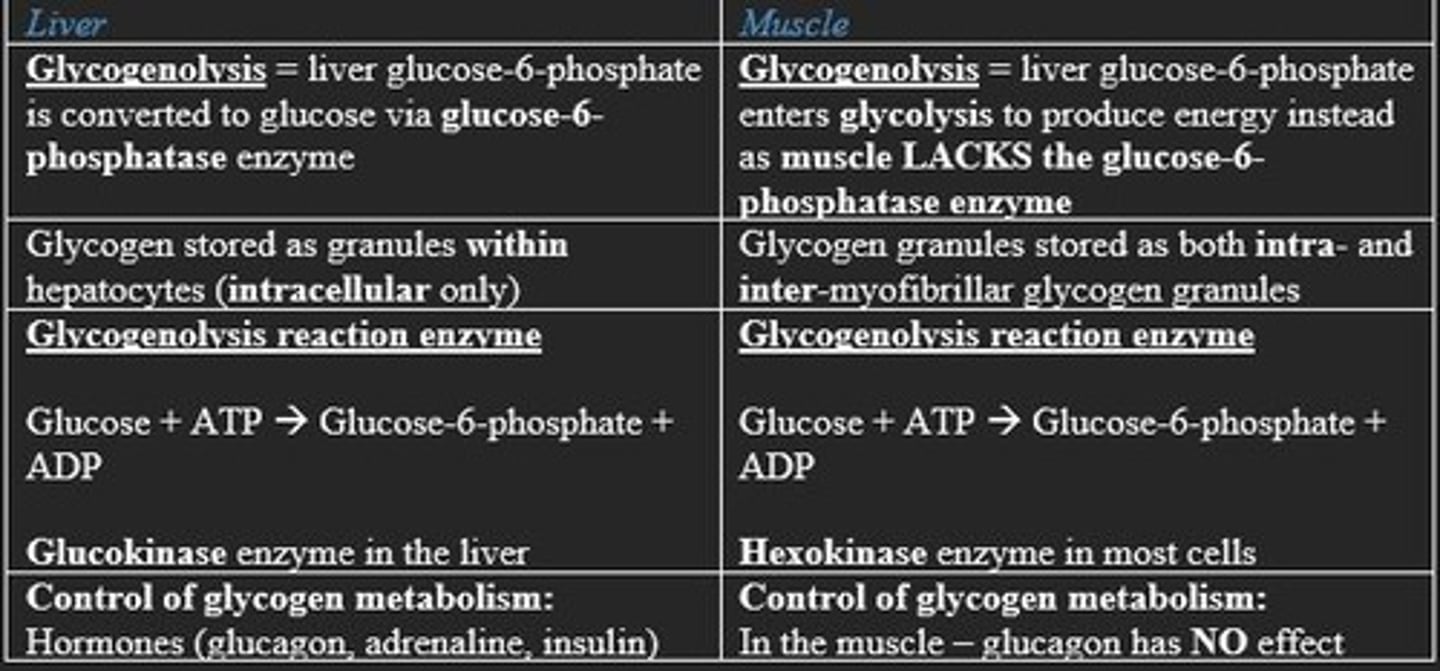
Glucagon has ___ effect on metabolism of glycogen in the muscle
NO
Rate-limiting enzymes for glycogenesis and glycogenolysis (glycogen metabolism)?
Name two Glycogen Storage Diseases (GSDs)
Von Gierke disease
McArdle disease
Von Gierke Disease (GSD)
Deficiency in liver glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme

McArdle Disease (GSD)
Deficiency in muscle glycogen phosphorylase enzyme

There are over ___ types of GSD
15
When does gluconeogenesis occur?
During 8-10 hours of fasting (liver glycogen stores are depleted at this point via glycogenolysis) and more glucose is now required
Where does gluconeogenesis occur?
Liver and kidney cortex (cytosol)
What two key enzymes regulate gluconeogenesis?
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
In what situations does gluconeogenesis occur?
- Starvation/fasting
- Prolonged exercise
- Stress (fight or flight)
What three hormones increase activity of enzymes (below) that regulate gluconeogenesis?
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
- Glucagon
- Cortisol
- Adrenaline
What hormone decreases the activity of enzymes (below) that regulate gluconeogenesis?
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
Insulin
TGs is a highly ___ energy store
efficient
Are TGs hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobic
Triglyceride utilisation occurs during...
- Exercise
- Stress
- Starvation
- Pregnancy
The energy content of triglycerides per gram is ___ that of carbohydrate or proteins
twice
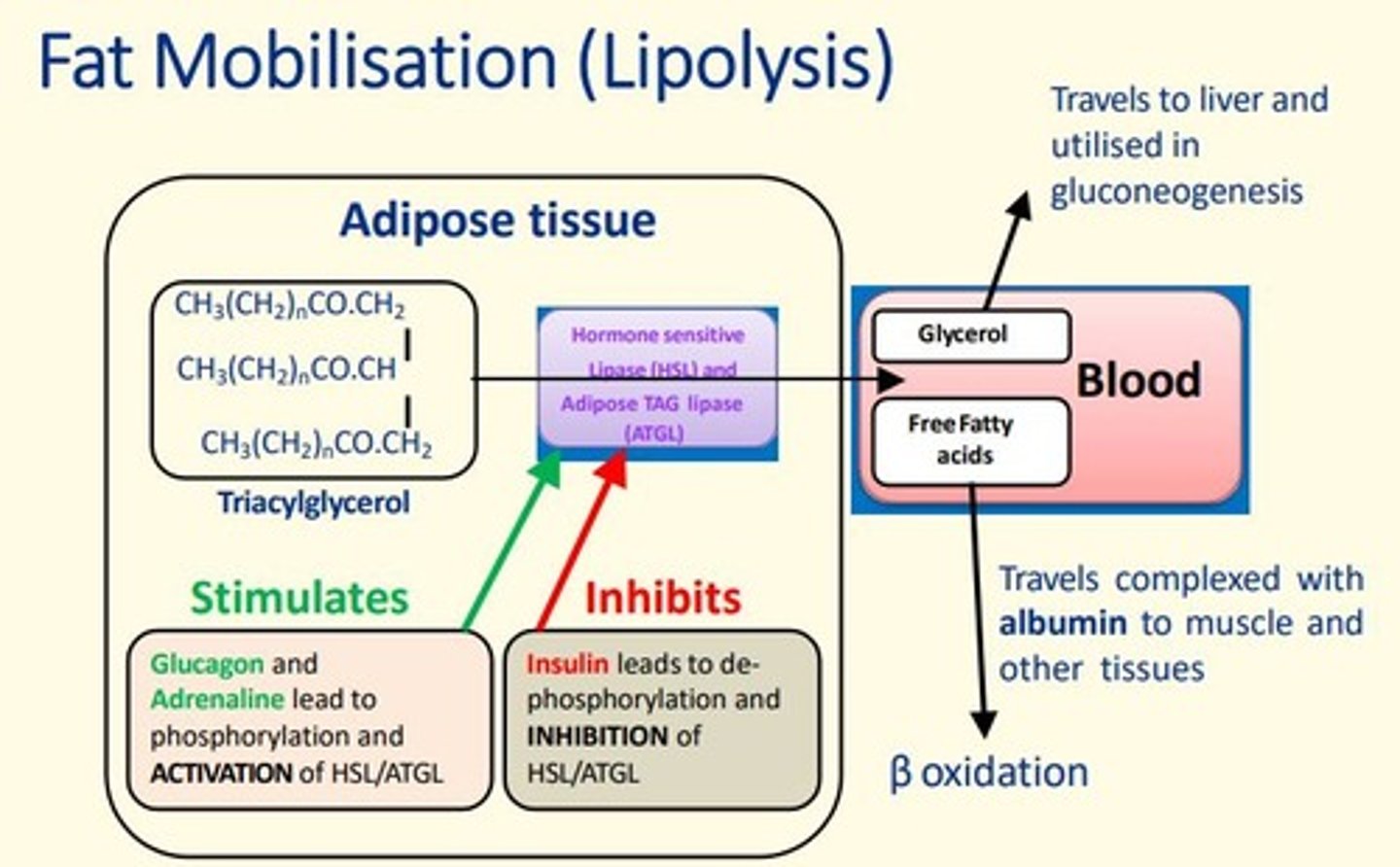
Fat mobilisation is called
Lipolysis
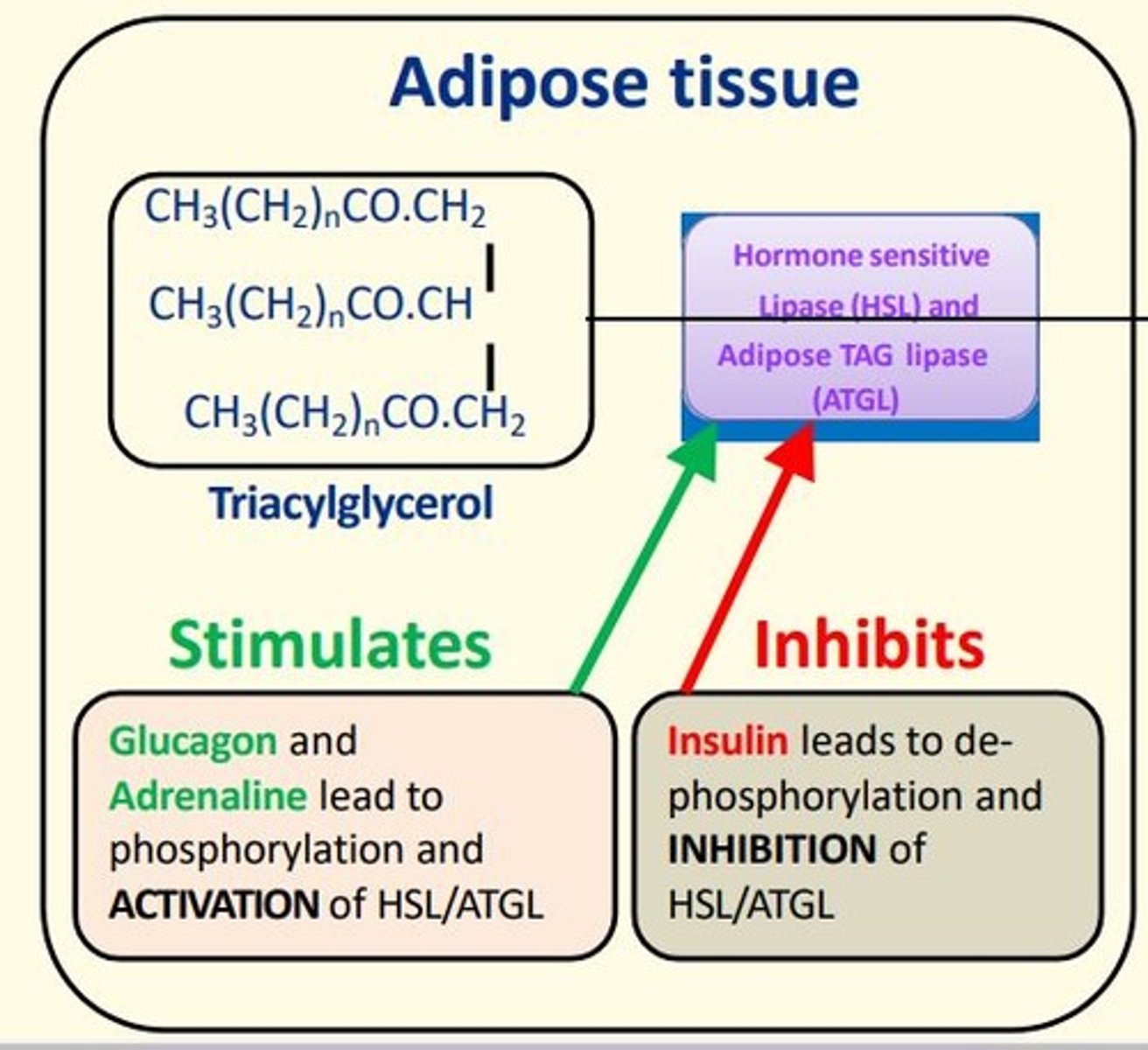
What enzymes regulate fat mobilisation (lipolysis) in adipose tissue?
Hormone Sensitive Lipase (HSL)
Adipose TAG Lipase (ATGL)
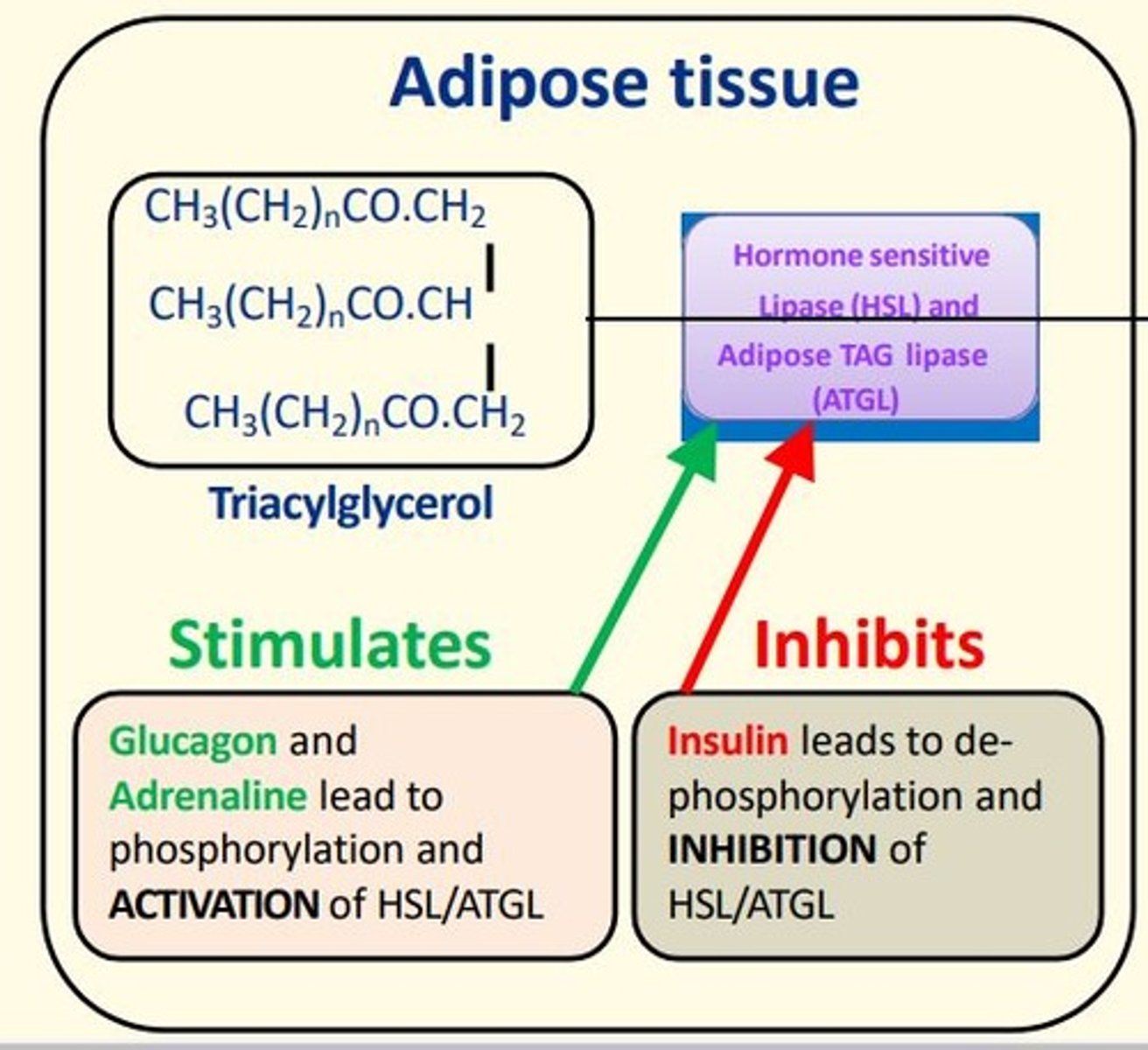
Hormones that stimulate LIPOLYSIS enzymes HSL + ATGL by phosphorylating them?
Glucagon
Adrenaline
leads to phosphorylation and activation of HSL/ATGL
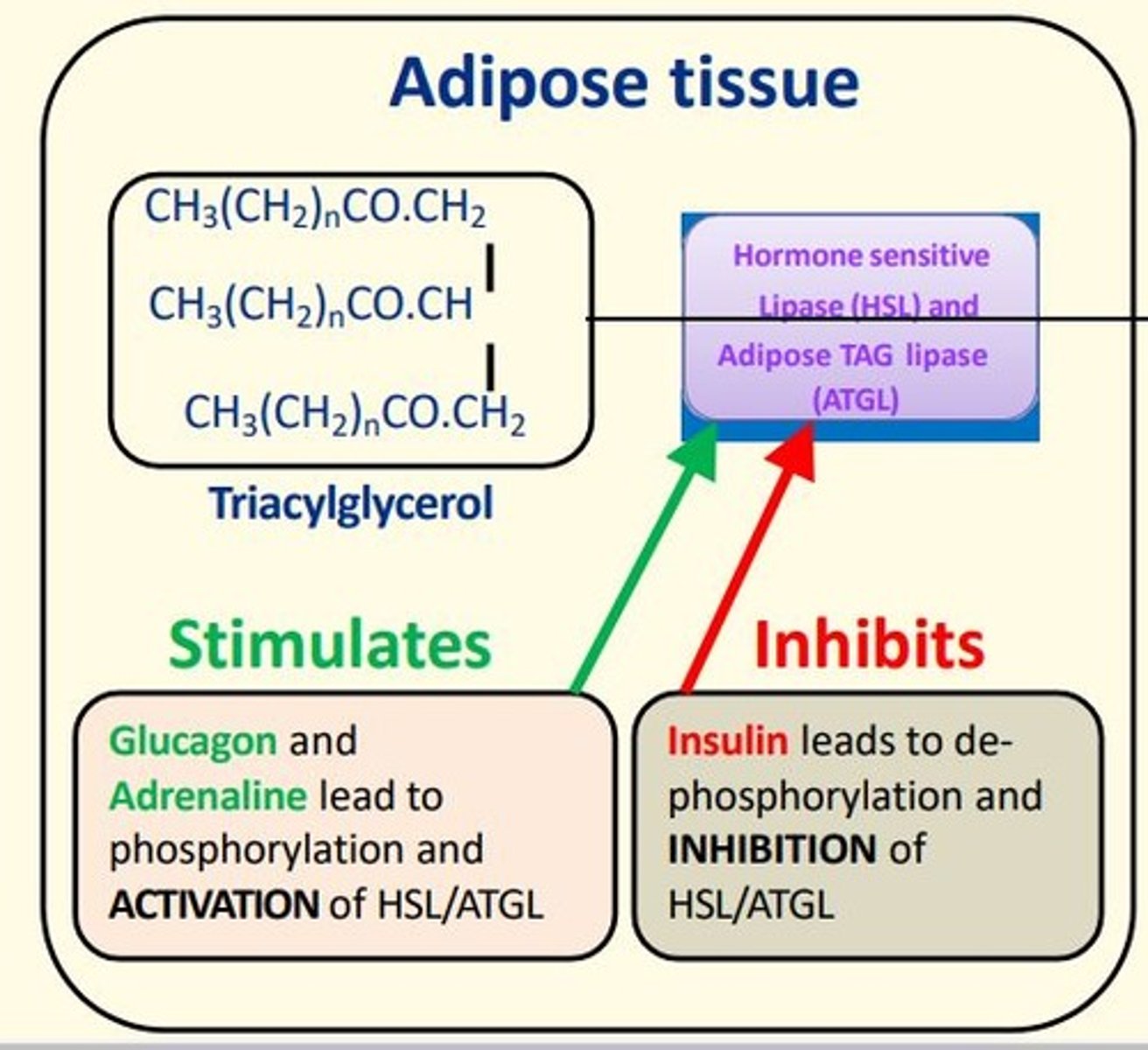
Hormones that inhibit LIPOLYSIS enzymes HSL + ATGL by de-phosphorylating them?
Insulin
leads to de-phosphorylation and inhibition of HSL/ATGL
Free fatty acids travel complexed to ___ to muscle and other tissues where they undergo B-oxidation
albumin
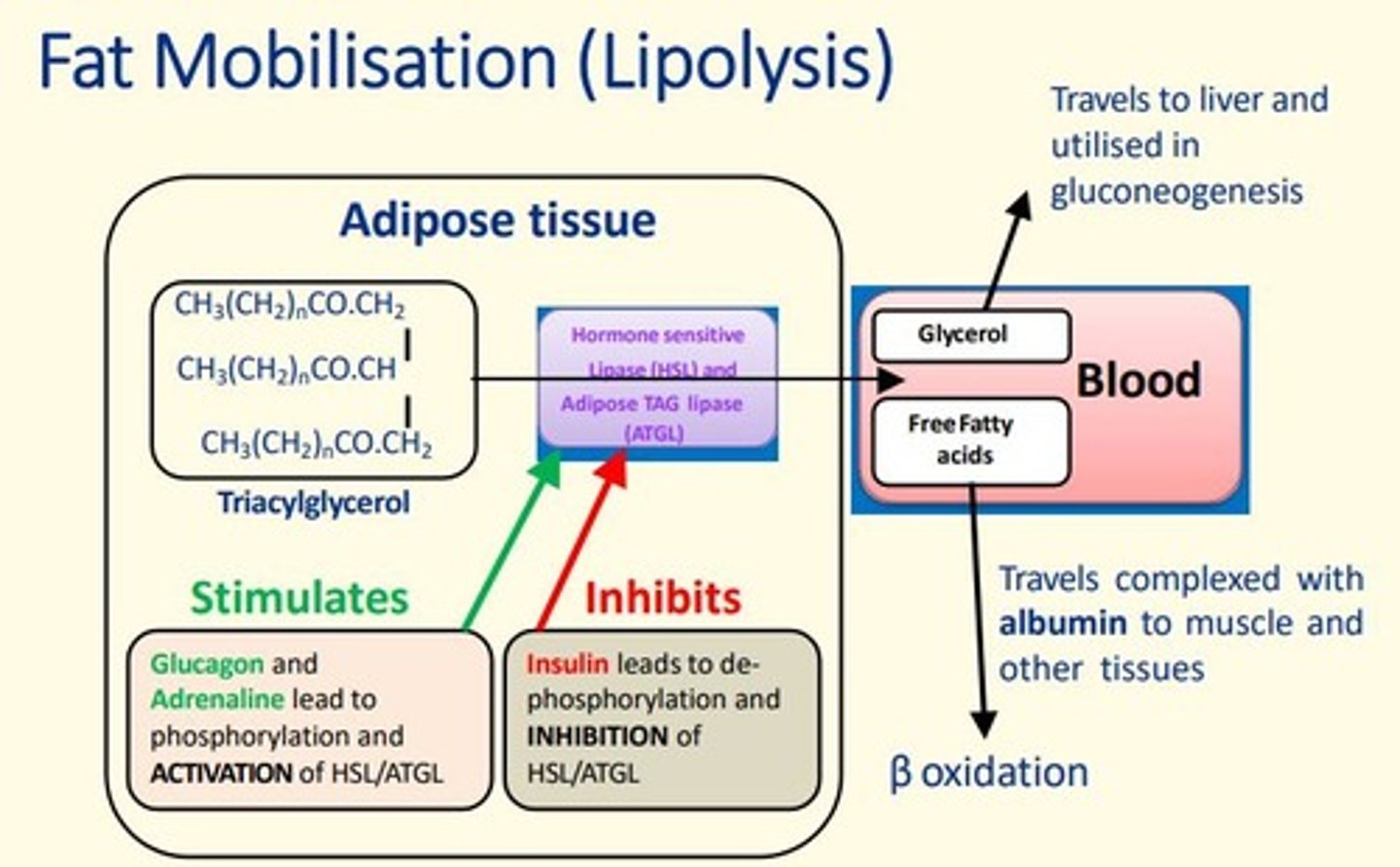
Glycerol travels to ___ and is utilised in gluconeogenesis
liver
The key regulatory enzyme in fatty acid synthesis in the liver
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase

Insulin and ___ increase the activity of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (fatty acid synthesis regulating enzyme)
Citrate

Glucagon and ___ and AMP decrease the activity of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (fatty acid synthesis regulating enzyme)
Adrenaline

Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (key regulator) produces ___ from acetyl-CoA in fatty acid synthesis
malonyl-CoA

Fatty acid synthase complex builds fatty acids by the sequential addition of 2 carbon units provided by ___ in fatty acid synthesis
malonyl-CoA

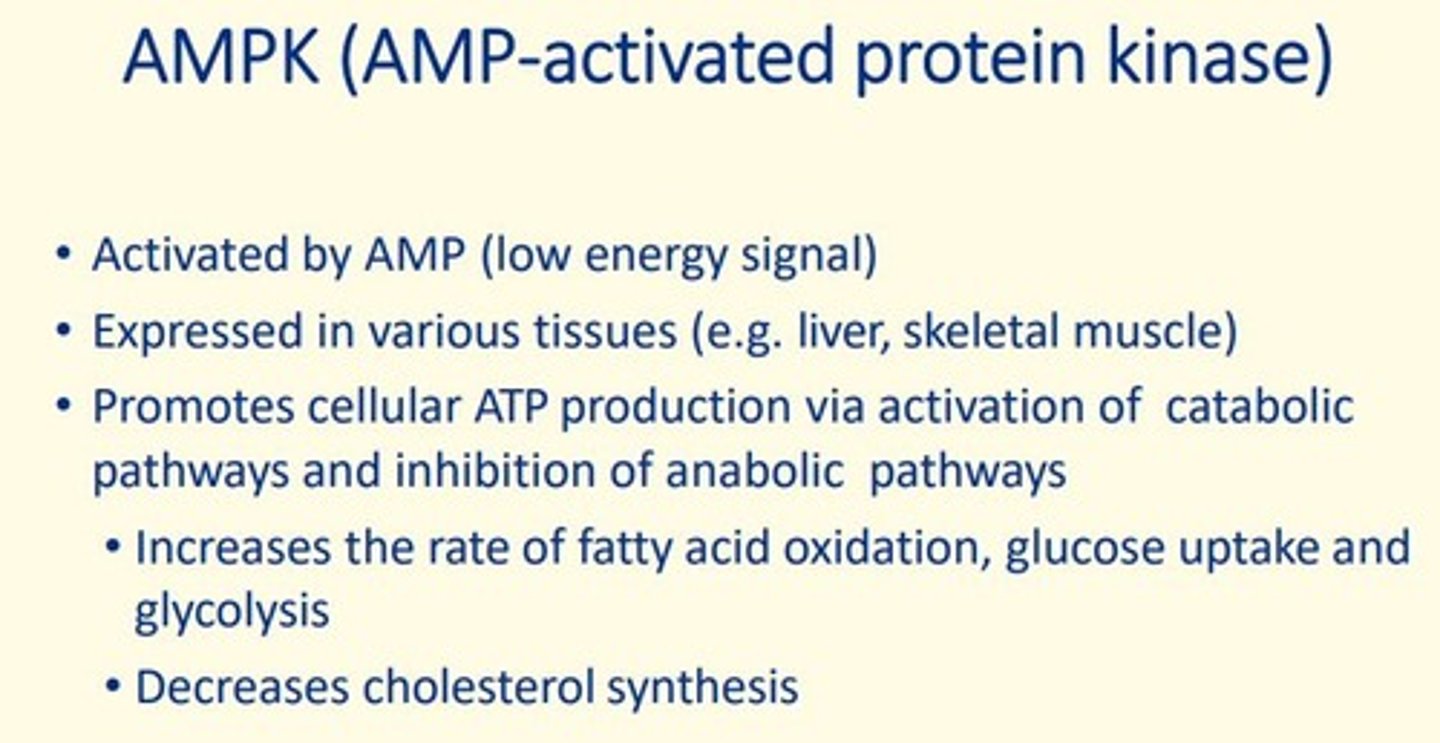
AMPK
AMP-activated protein kinase
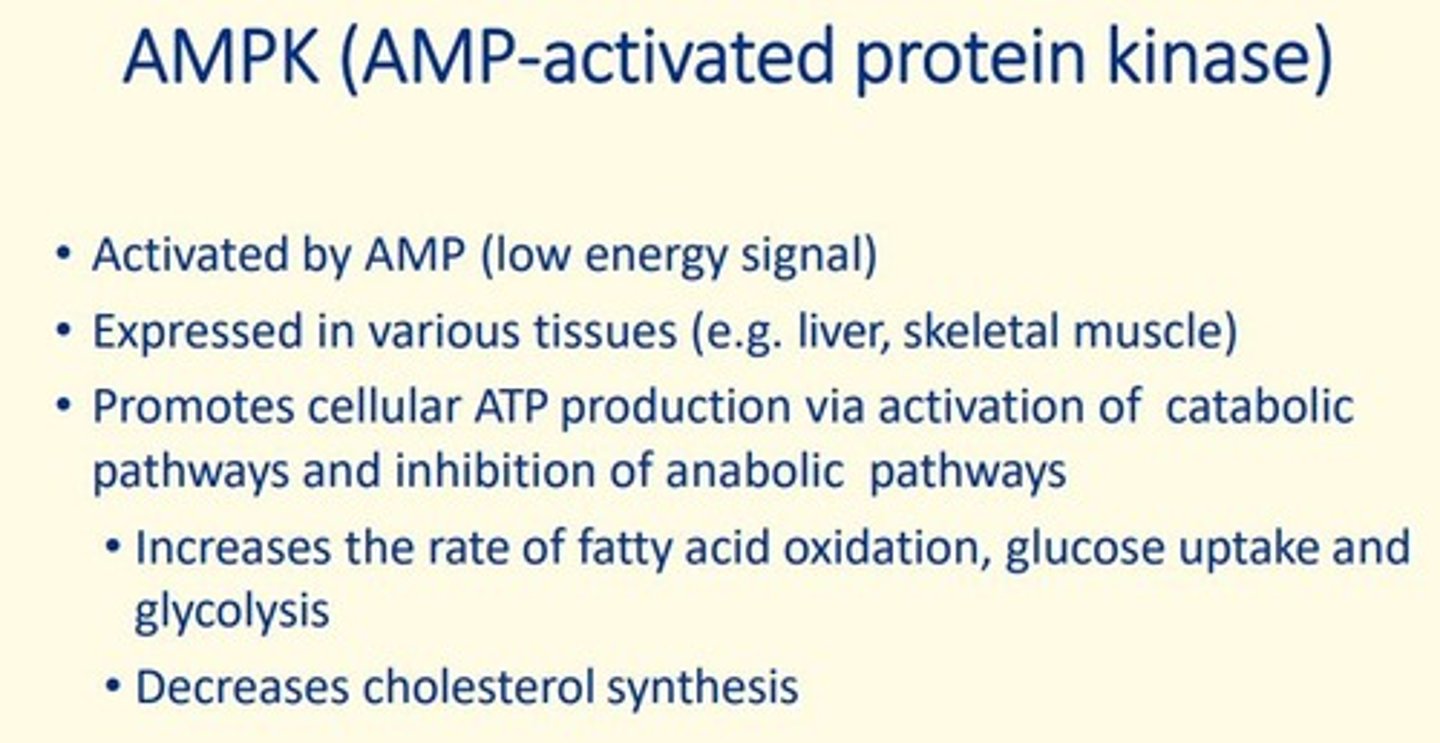
What is AMPK activated by?
AMP
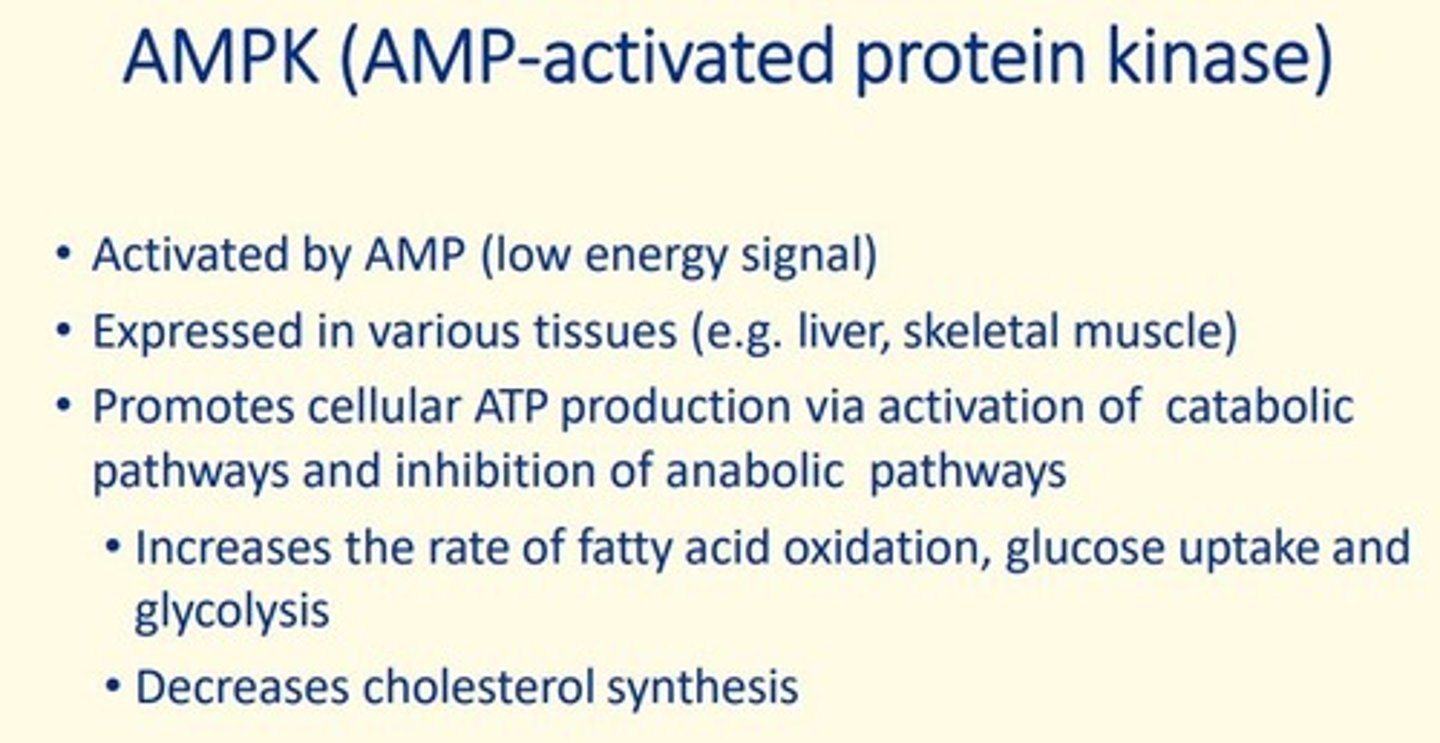
What tissues is AMPK expressed in?
liver, sketal muscle
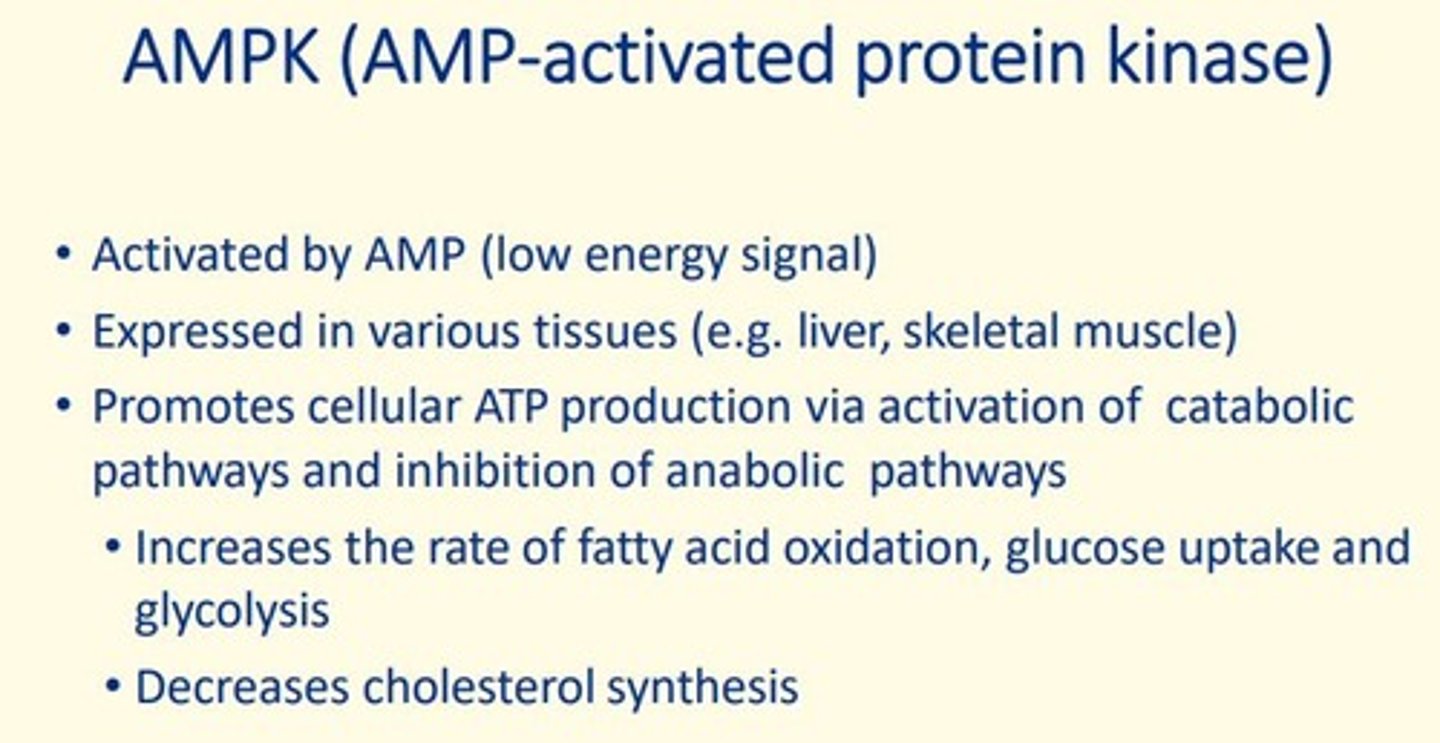
What does AMPK do?
1. Glucose uptake & glycolysis
2. Fatty acid oxidation
3. Decreases cholesterol synthesis
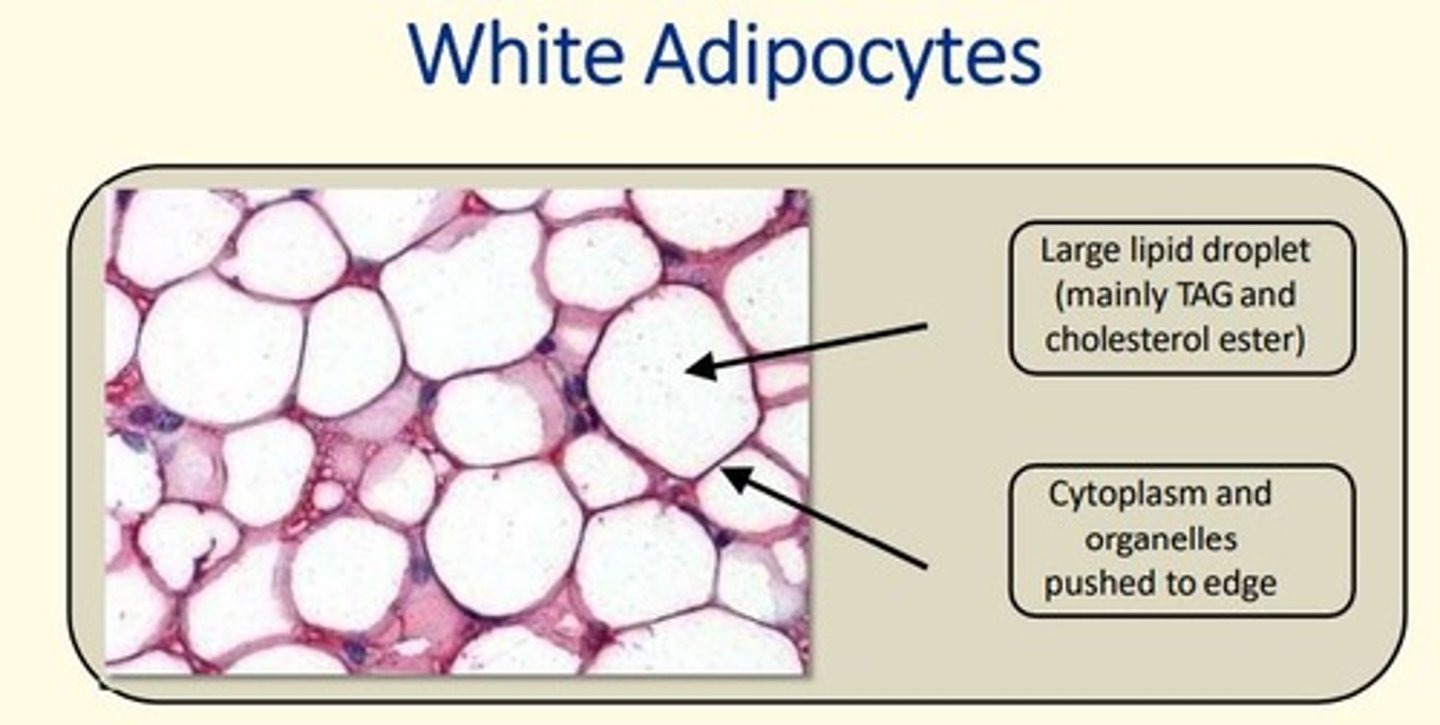
The average adult has ~30 billion fat cells weighing ___kg
15kg
White adipocytes can increase in size about ___ times during weight gain before dividing and increasing total number of fat cells
four
What enzyme can be found in small intestine that facilitates TG metabolism?
Pancreatic lipase
Lipoprotein lipase
an enzyme that sits on the outside of cells and breaks apart triglycerides (lipolysis), so that their fatty acids can be removed and taken up by the cell
Fatty acids do not easily pass the ___ barrier
blood-brain
Why is more glycogen stored in the muscles rather than liver?
In muscle =
- Glycogen stored both intra-cellularly and inter-cellularly