chapter 1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts as well as their relationship to one another.
Gross Anatomy
What you see with your eyes. Examples: Surface, Organs
Physiology
The study of how the body and its parts work or function.
Chemical level
Atoms, molecules, and organelles
Cellular level
Single cell
Tissue level
Groups of similar cells
Organ level
Contains two or more types of tissues
Organ system level
Organs that work closely together
Organismal level
All organ systems combined to make the whole organism
Organ Systems
composed of groups of organs that cooperate to perform a major body function.
Integumentary System
Skin; external body covering. Protects deeper tissue from injury. Helps regulate body temperature.
Skeletal System
Bones, cartilage, joints. Protects and supports body organs. Provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement. Forms blood cells.
Muscular System
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles. Allow movement and facial expression, maintain posture, produce heat.
Nervous System
Brain, spinal cord & nerves. Fast-acting control system of the body; responds to internal and external changes.
Endocrine System
Glands secrete chemicals called hormones that regulate many processes such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
Cardiovascular System
Heart & blood vessels. Heart pumps blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, and other materials to and from cells.
Lymphatic System
Lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels. Returns fluid leaked from blood vessels to blood and cleans lymphatic fluid of bacteria and foreign matter.
Respiratory System
Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs. Exchanges gases with the external environment; keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen & removes carbon dioxide.
Digestive System
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines. Breaks food down into simple units that can be absorbed by the blood for distribution to body cells and eliminates undigested food as solid waste.
Urinary System
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra. Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body and regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood.
Reproductive System
Males: penis, testes / Females: ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes. Overall function is the production of offspring.
Homeostasis
The tendency of the body to maintain internal stability or a dynamic equilibrium.
“dynamic steady state”
Adjustments in physiological systems that preserve homeostasis.
Receptor
Senses a particular change or stimulus
Control center
Receives and processes information from the receptor.
Effector
Cell or organ that responds to commands from the control center.
Negative Feedback
An imbalance is corrected by a response that restores balance.
Positive Feedback
The body initiates a response that increases the imbalance until a specific goal is reached.
Anatomical position
Standing, face-front, feet parallel, arms at sides with palms facing forward
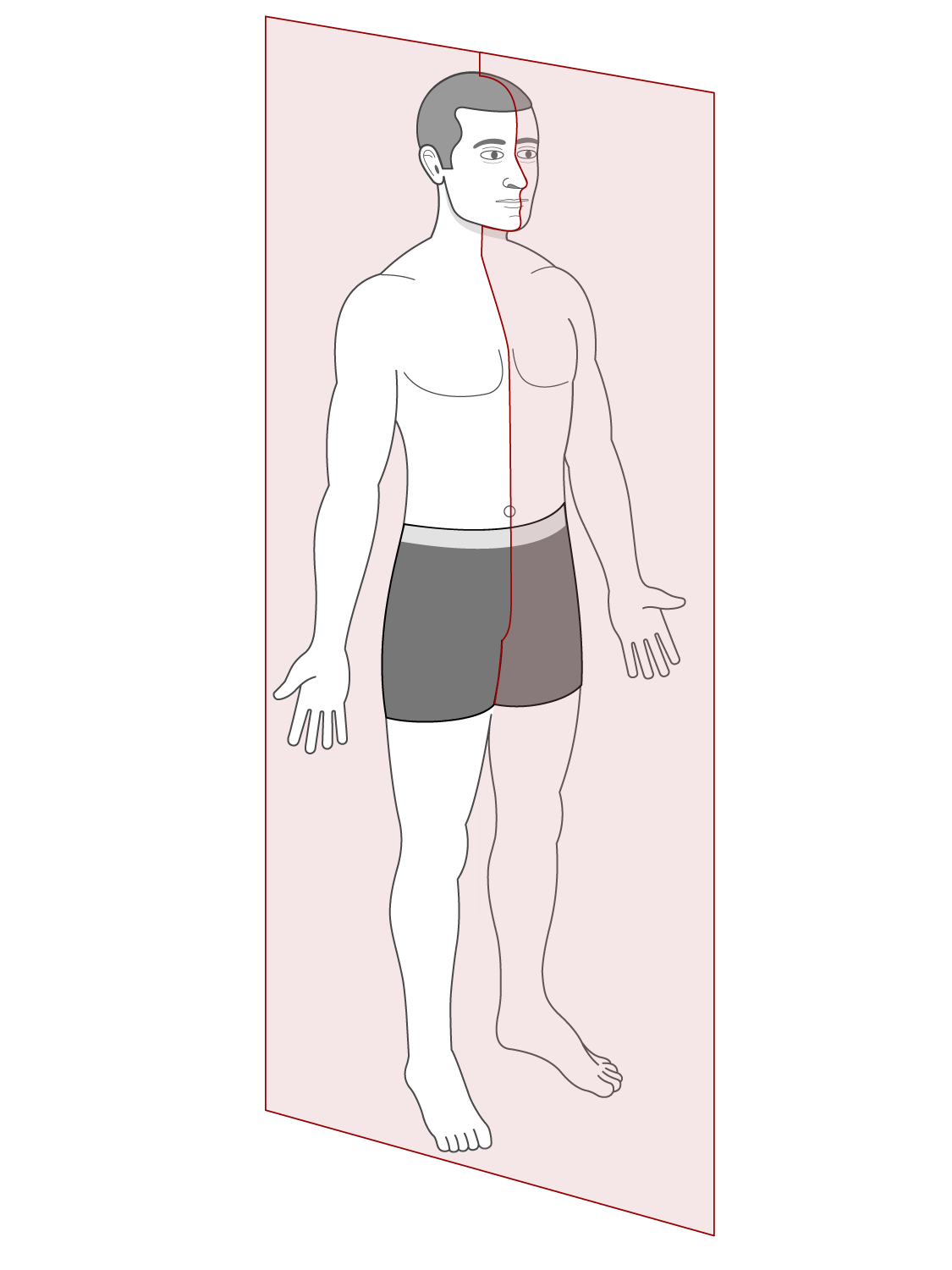
Sagittal Plane
Lengthwise or longitudinal; split left and right
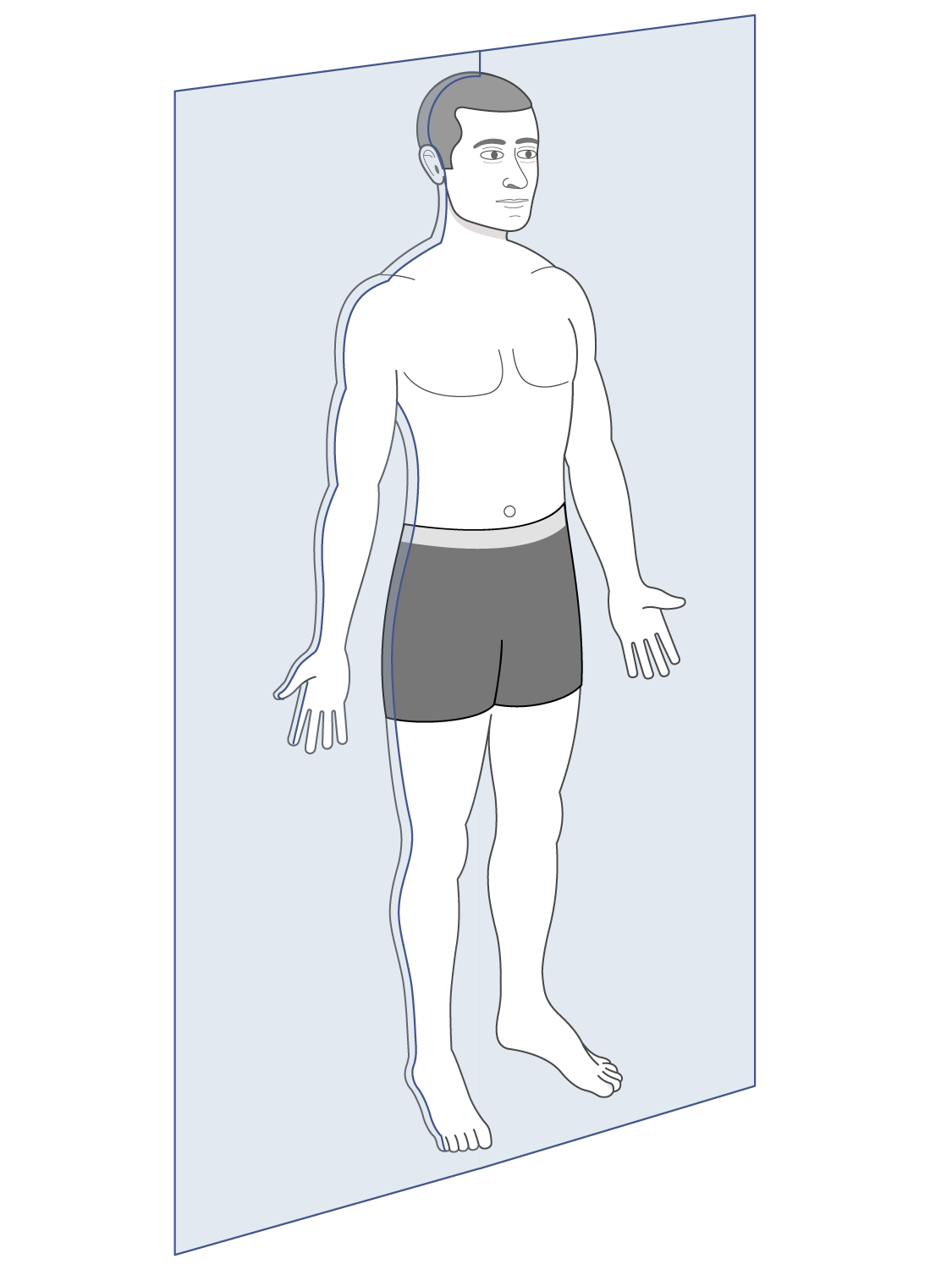
Frontal Plane
Divides into anterior or posterior parts
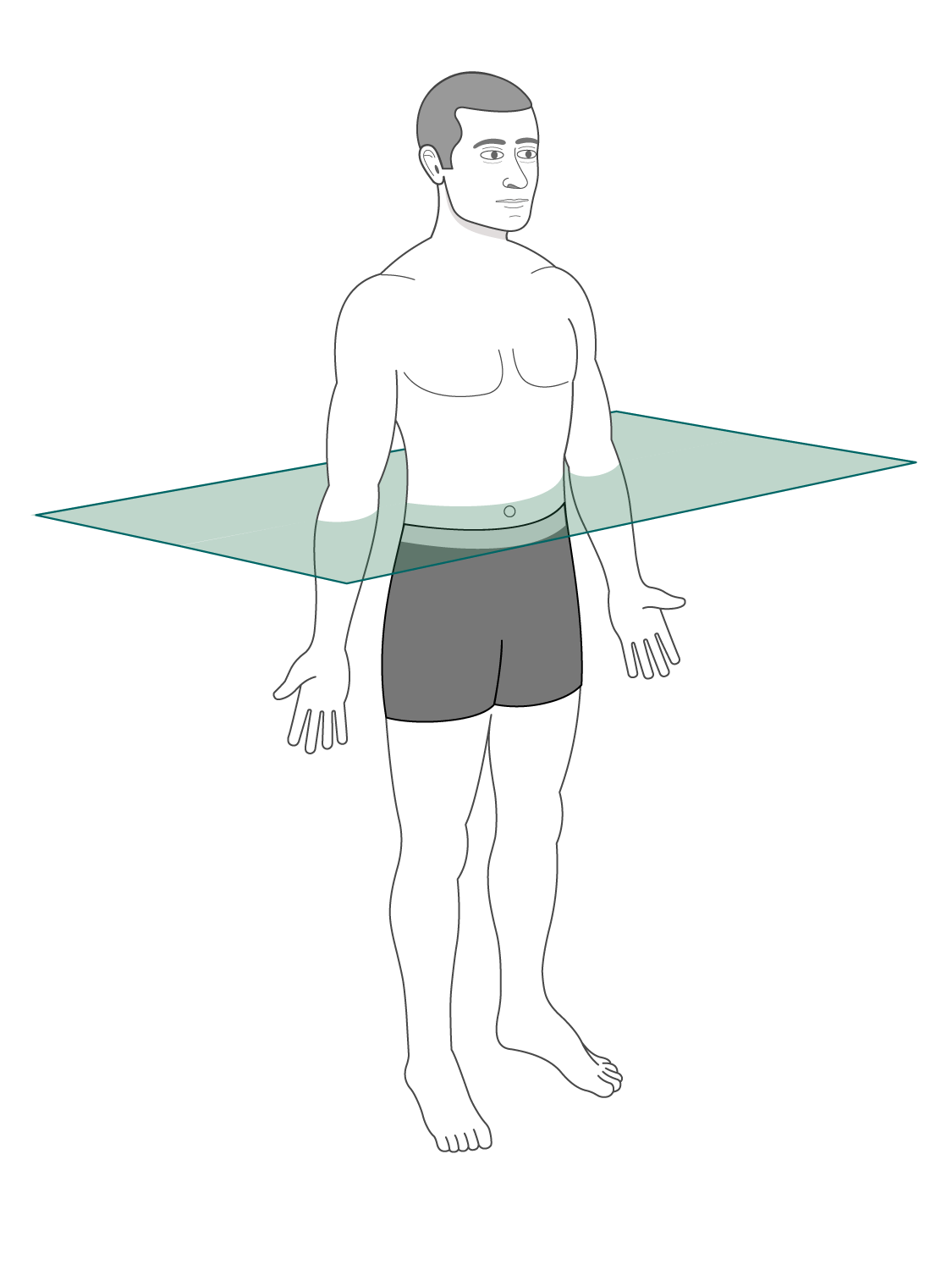
Transverse Plane
Horizontal; divides superior and inferior halves
Cranial cavity
Encases brain
Vertebral cavity
Encases spinal cord
Ventral Body Cavity
Houses the internal organs (collectively called viscera)
Pleural Cavity
Each cavity surrounds one lung
Pericardial cavity
Encloses heart
Abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver
Pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
Serosa (Serous Membrane)
Thin, double-layered membranes that cover surfaces in ventral body cavity
Parietal serosa
Lines internal body cavity walls
Visceral serosa
Covers internal organs
Pericardium
Heart
Pleurae
Lungs
microscopic anatomy
seeing individual cells (cytology) and tissues (histology)
general physiology
fundamental principles of how living organisms function at various levels, from cells and tissues to entire systems
pathophysiology
study of the functional changes that occur in the body as a result of disease or injury
body cavity
a fluid-filled space inside the body that holds and protects internal organs
principal cavities
ventral and dorsal cavity
dorsal cavity subdivisions
cranial and vertebral cavity
ventral cavity subdivisions
thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity
Mediastinum
Contains pericardial cavity; Surrounds other thoracic organs, such as esophagus, trachea, etc.
internal environment
the fluid medium surrounding cells within the body
extracellular fluid
all the body fluids that are outside the cells
intracellular fluid
the fluid contained within cells, representing a major portion of the body's total water
interstitial fluid
the fluid found in the spaces surrounding cells in the body
plasma
liquid component of blood that suspends blood cells
cytosol
fluid portion of the cytoplasm in which organelles of the cell reside
cytoplasm
the jelly-like substance inside of a cell
feedback mechanism
a process where the output of a system influences its input, creating a loop that can be either positive or negative
feedforward mechanism
anticipatory adjustment of muscles or systems before a movement or change occurs, preparing the body for an action or response
negative feedback examples
thermoregulation (body temperature control) and blood glucose/pressure regulation
positive feedback examples
childbirth(uterine contractions) and blood clotting
homeostatic regulation of a body function
The pancreas releasing insulin to maintain blood sugar levels within a narrow range
homeostasis leading to disease states
hyperthermia/hypothermia
Imbalances in blood pressure, heart rate, and blood flow can contribute to heart failure, stroke