Reactivity of Metals
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Define a chemical reaction
a process in which one or more substances, called reactants, are transformed into one or more different substances, know is the products, through the rearrangment of their atoms.
Chemical reactions are a type of process known as —————— where bonds are broken & reformed.
chemical change
What is the law of conservation of mass
The law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction mass is neither created nor destroyed.
Thus the no. of atoms present in the reactants are equal to the no. of atoms in the product.
Define reactivity
Reactivity refers to how easily and quickly a substance reacts chemically with other substances.
Define metal reactivity
Metals are considered reactive if they easily lose electrons to form positive ions when they come in contact with other substances, such as water or acids.
Evidence of Reaction
change in colour
release of gas
formation of a precipitate
change in temperature
emission of light
change in amount of reactants or products
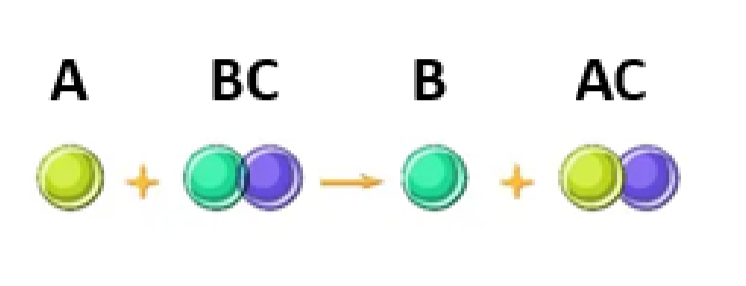
define a single displacement reaction
When metakl A is more reactive that metal B, is will displace B by breaking the covalent bonds between B & C and forming a new covalent bond with element C.
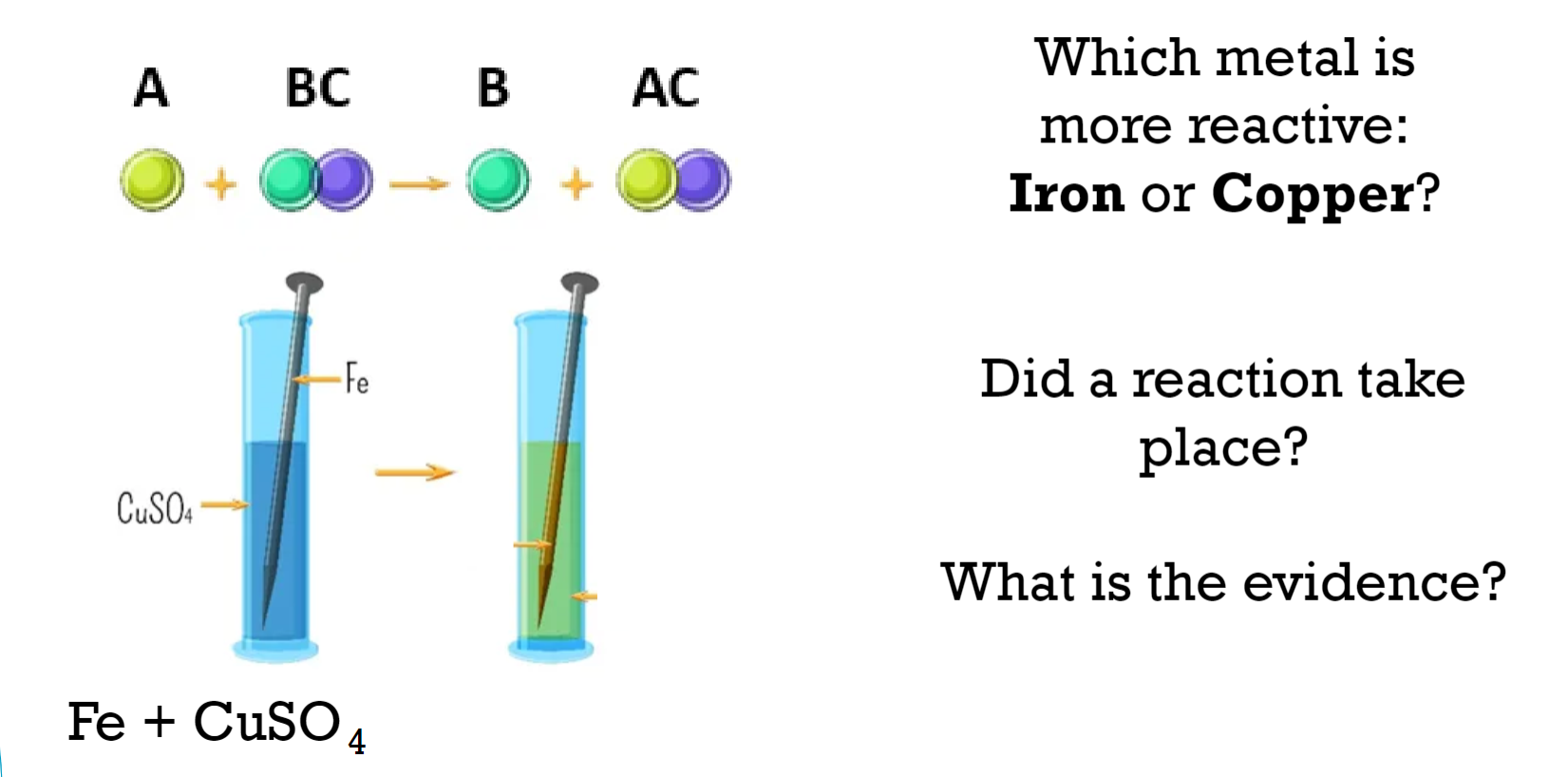
Example 1
Which metal is more reactive: Iron or Copper?
Iron (Fe) is more reactive than Copper (Cu). This is indicated by the reaction taking place where iron displaces copper from copper sulfate (CuSO₄), forming iron sulfate (FeSO₄) and copper (Cu). This type of reaction is known as a displacement reaction, and it occurs because iron is higher in the reactivity series than copper.
Did a reaction take place?
Yes, a reaction did take place.
What is the evidence?
When an iron nail is placed in a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO₄), a chemical reaction occurs. The solution changes color, and a layer of copper metal forms on the surface of the iron nail. This indicates that iron has displaced copper from the copper sulfate solution, forming iron sulfate and copper metal.
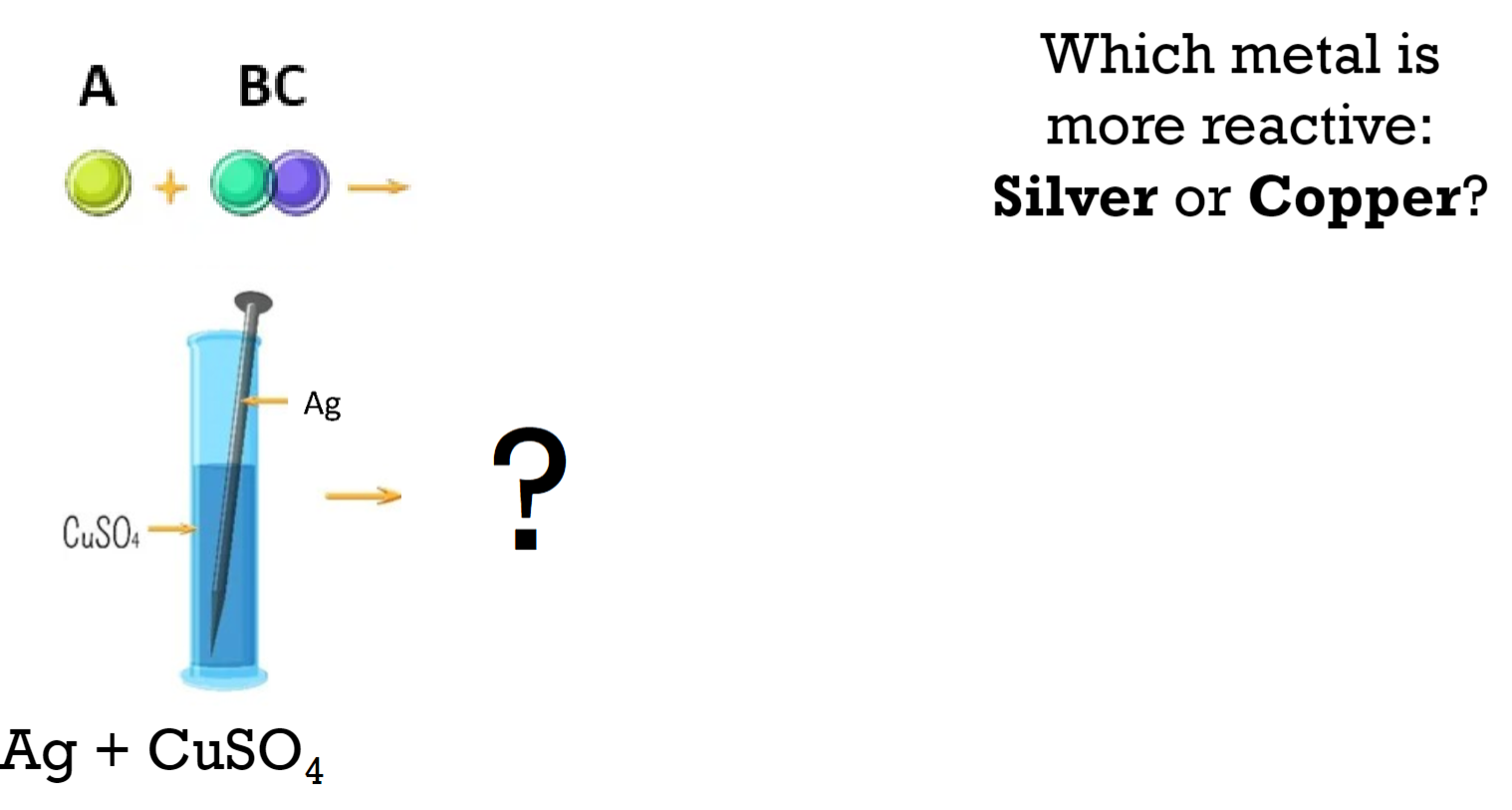
Example 2
Which metal is more reactive: Silver or Copper?
Copper (Cu) is more reactive than Silver (Ag). This is indicated by the fact that silver does not react with copper sulfate (CuSO₄) in the solution.
Did a reaction take place?
No, a reaction did not take place.
What is the evidence?
The evidence is that when a silver (Ag) strip is placed in a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO₄), there is no observable change. The solution remains blue, indicating that copper ions are still present in the solution, and no displacement reaction has occurred. This indicates that silver is less reactive than copper and cannot displace copper from its compound.
What is the reactivity series?
Reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in decreasing order of their reactivity (how fast they loose their valence electrons to form positive ions). Most reactive metals are at the top while the least reactive metals at the bottom.
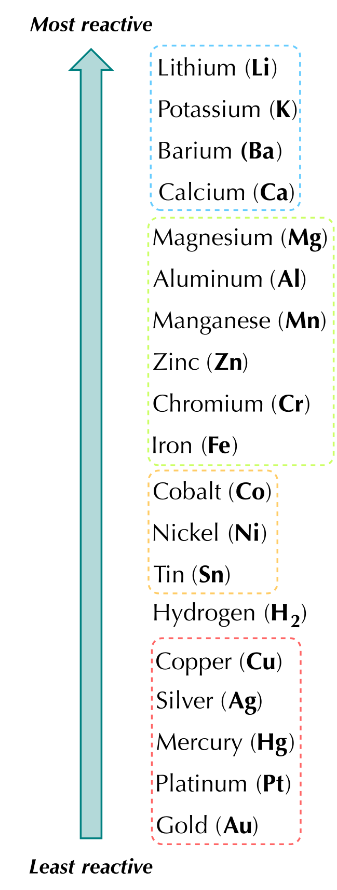
Observations about the reactivity series
the most reactive metals are the group 1 metals - alkali earth metals - larger atomic radii and low ionization energies.
group 2 metals are the second most reactive as they easily give up their two valence electrons to achieve a full outer energy level
transition metals are the least reactive as they fail to attain stable electron configuration
reacting a metal with acid (HCl) it will form a ——————
salt and hydrogen gas
This is a single displacement reaction, where a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive one from its compound.
the most reactive metals produce the most —————
heat
reacting a metal with water (H2O) it will form a ——————
metal hydroxide or metal oxide
This is a synthesis or combination reaction, where two simple substances react to form a more complex substance.