Gen 4100 Exam 1 - Iowa State University
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), the two alleles for a given trait separate from each other, so that each gamete only receives one allele
Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
different genes are sorted into gametes independently. This means that the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not affect the allele it receives for another gene.
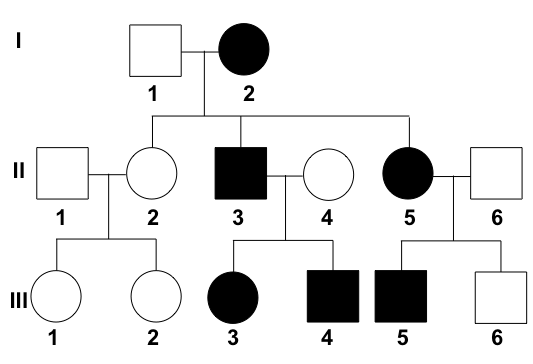
Pedigree
a chart that shows the relationships between family members or animals
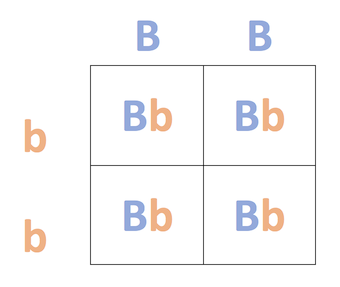
Testcross
a breeding experiment that determines an organism's genotype
Carriers
an individual who carries and is capable of passing on a genetic mutation associated with a disease and may or may not display disease symptoms
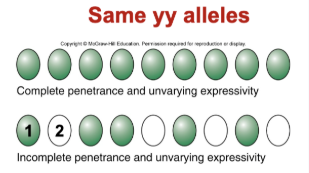
Complete Penetrance
an affected individual carries at least one dominant allele of a dominant trait or two recessive alleles of a recessive trait
Rare-In-Population
individuals who marry into the pedigree in the second and third generations; are not carriers
Not Y-Linked
the causative genes in these problems may be autosomal or X-linked but are not Y-linked
Recessive Trait
a trait that is only expressed when both inherited copies of a gene are recessive
any affected individual has two unaffected parents
example: a → aa
Dominant Trait
a characteristic that is passed down from a parent to their child, and is expressed when at least one dominant allele is inherited
every affected child has an affected parent
two affected parents can produce unaffected children
example: Aa or AA
Autosomal Recessive
a pattern of genetic transmission where a mutated gene is located on an autosome (non-sex chromosome)
if any affected daughter has two unaffected parents
no obvious bias between males and females
X-Linked Recessive
a pattern of passing down genetic traits or disorders that are caused by mutations on the X chromosome
when an affected son has two unaffected parents (daughter normally unaffected)
traits appear more in males (mother carrier to son transmission)
Complete Dominance
a genetic phenomenon where one allele of a gene completely masks the other allele
hybrid resembles one of the two parents
Incomplete Dominance
a genetic phenomenon where the phenotype of a heterozygote is a blend of the phenotypes of its parents
hybrid resembles neither parent (intermediate phenotype)
Codominance
a genetic pattern where two different versions of a gene (alleles) are both expressed in an individual
hybrid shows traits from both parents
Pleiotropy
the phenomenon of a single gene/allele determining several distinct and seemingly unrelated characteristics. Occurs when one gene influences two or more seemingly unrelated phenotypic traits
Pleiotropic Genes - Recessive Lethal Alleles
pairs of identical alleles that cause death when present in both copies in an organism
can code for either dominant or recessive traits
do not always cause death
Penetrance
the percentage of individuals with a particular genotype that show the expected phenotype
Novel Phenotypes
a unique visual characteristic of an organism that differs from its parents
Complementary Gene Action
occurs when two or more genes must work together to produce a specific phenotype
Epistasis
an allele at one gene masks the phenotype of alleles at another gene
Hypostatic
one whose phenotype is altered by the expression of an allele at a separate locus in an epistasis event
Complementary Gene Action
a genetic interaction where two separate genes must both have a dominant allele present in order to produce a specific phenotype
Redundant Genes
multiple genes in an organism that perform the same function
How Do Mutations Effect Gene Expression and Function?
Alters the DNA sequence, potentially leading to changes in the produced protein, including: no protein production, a non-functional protein, or a protein with altered activity, which can result in various phenotypic effects depending on the gene involved, ranging from no noticeable change to severe disease states; the effects can include complete loss-of-function, gain-of-function, or altered regulation of gene expression depending on the nature of the mutation and its location within the gene
Loss-of-Function
the function of a gene is reduced or eliminated
this can be due to decreased expression or impaired protein function
usually recessive
Gain-of-Function
a gene acquires increased or new function
this can be due to altered expression or altered protein function
usually dominant
Types of Mutations
insertional mutagens: fragment of DNA is inserted into a chromosome or near a gene
substitution: the base is replaced by one of the other bases
deletion: block of one or more DNA pairs is lost
insertion: block of one or more DNA pairs is added
chromosomal rearrangements: affect many genes at one time (inversion/translocation)
Loss-of-Function Mutations
usually recessive to wild-type
null (amorphic mutations): completely block the function of a gene product
hypomorphic mutations: gene product has weak but detectable activity
Gain-of-Function Mutations
usually dominant
hypermorphic mutations: generate more gene product or the same amount of a more efficient gene product
neomorphic mutations: generate gene product with a new function or that is expressed at an inappropriate time or place
Complementation Test
a genetic procedure that determines if two mutations are in the same gene or different genes. It's used to understand how genetic strains interact
a cross between two mutations in the same gene (usually) fails to complement (ex., mutant phenotype)
a cross between two mutations in separate genes (usually) do complement (ex., wild-type progeny)
Types of Genetic Approaches
CRISPR/Cas9
transgenic reporter
gene/Enhancer trap
conditional mutants
gene drive
CRISPR/Cas9
gene-editing technology that uses RNA and a protein to modify DNA
A guide RNA binds to a specific DNA sequence
The Cas9 protein follows the guide RNA to the DNA
The Cas9 cuts both strands of the DNA
The cell repairs the damaged DNA
scientists use this process to change genes
it can be used in gene activation
Can cause unwanted mutations and it’s not super efficient
Transgenic Reporter
a gene that produces a protein that can be used to identify a cell type, protein, or circuit
Gene/Enhancer Trap
An insertion element (ex., transposon) contains a splice acceptor (SA) site and a reporter gene (GFP, LacZ, etc.) using CRISPR/Cas9
Upon insertion into a gene, the reporter becomes spliced to an exon in the mRNA of the trapped gene
The GFP reporter now shows the expression pattern of the trapped gene
In addition, the trapped gene is also mutated
Gene Drive
a genetic system that promotes the inheritance of a particular gene to increase its prevalence in a population
Conditional Mutants
an organism with a genetic change that only results in a mutant phenotype under certain environmental conditions
Forward Genetics
the approach of determining the genetic basis responsible for a phenotype
natural and induced mutations → phenotypic selection → mapping of candidate genes
to identify mutants and genes that control a trait of interest through genetic screening
Reverse Genetics
the approach to study the function of a gene by targeted mutation and phenotypic characterization
mutations in a gene of interest → phenotypic analysis
to study the function of a gene of interest through mutational analysis