Chemical Equilibria
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what are reversible reactions?
reactions that proceed in both the forward and backward directions
how are reversible reactions denoted
denoted by a double-headed arrow (⇌)
Are reversible reactions complete?
No. A state of dynamic equilibrium will be attained
What is the end result?
A mixture of both reactants and products
What is dynamic equilibrium
Dynamic equilibrium refers to a state in a reversible system where the forward and reverse processes occur at equal rates, resulting in no net change in macroscopic properties(conc, partial pressure).
forward rate = backward rate
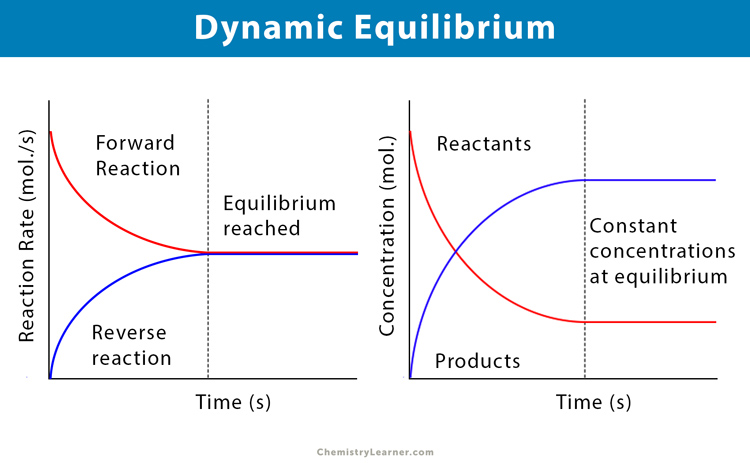
What are the conditions for dynamic equilibrium to occur?
Equilibrium can only be achieved in a closed system (does not allow matter to enter or leave but allows free transfer of energy)
Equilibrium can be attained from either direction of reactants or products
same equilibrium state can be attained starting from any amount of reactants and products if temperature remains constant
What is the reaction quotient Qc?
Ratio of the concentrations of the reactants and products raised to their stoichiometric ratios
products / reactants
When does equilibrium constant Kc occur?
when dynamic equilibrium is attained at a given temperature, concentration of reactant and product remain constant
Qc remains constant and is knows as Kc
units of Kc
mol dm^-3 (c+d -a+b)
What is eqm constant for gases
Kp (in terms of partial pressure)
What are the units for Kp
Pa (c+d - a+b)
What is the position of equilibrium
What is the relationship between rate constant and eqm constant
kf/kb = Kc
Variation if the forms of K
K(forward) = 1/K (backward)
K(backward) = 1/K(forward)
How do you calculate Kc value if there are 2 or more intermediate reactions?
K(overall) = K1 x K2
What happens to K if stoichiometric coefficients are multiplied by a factor n
K^n
What are the values of Kc/Kp not affected by
Changes in concentration of reactants and products (e.g. addition or removal of a reactant or products
Changes in total pressure