3.3.2 Costs
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What does the short run mean?
Think FofP
When at least one FofP is fixed
→ We tend to assume the FofP that is fixed is capital
Since capital is fixed, additional labour can be added, but this leads to..?
Diminishing marginal productivity - where for every additional worker added, total output increases but marginal output falls
What are fixed costs?
Costs that don’t vary with the level of output
→ Remains constant regardless of quantity of output
→ Usually associated with operations of businesses - they don’t change in the short run
E.g. rent, marketing costs, insurance
What does total fixed cost look like on a diagram?

What are average fixed costs (AFC)?
Formula?
Fixed costs per unit
TFC/Q
→ Higher the output, lower the AFC
TFC and AFC plotted on curve together?
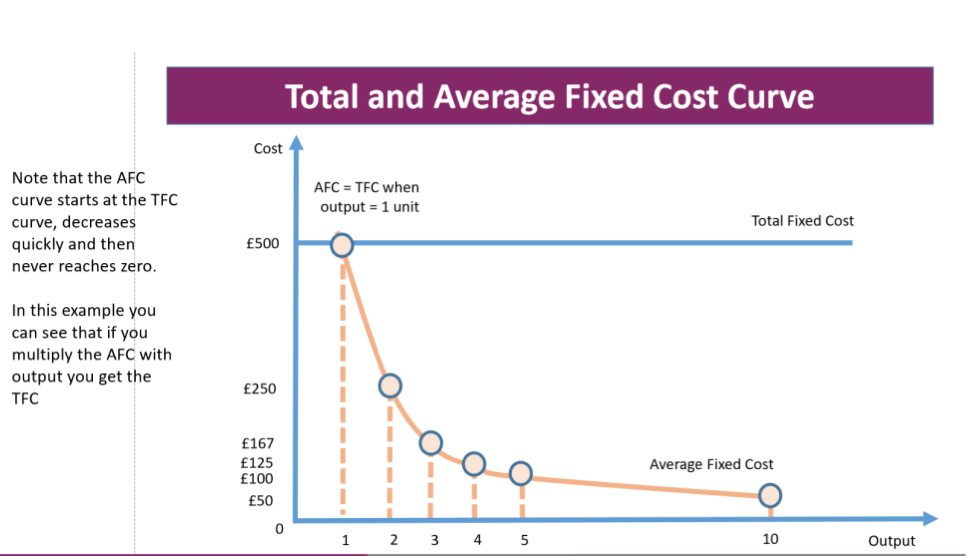
If short run production increases, total fixed costs remain the same - therefore what happens to AFC..?
AFC must fall (just think of formula, makes sense) → TFC/Q
Why is this cost concept important? Important to who in particular?
Important for start-up + challenger businesses
→ If they can ramp up sales + output fairly quickly, they can bring down AFC + hopefully lower their average total costs to make them more cost + price competitive
→ Many businesses try to operate with lean production systems, keeping fixed costs as low as poss.
E.g. hiring out machinery rather than buying, employing workers on flexible short-term contracts
What are variable costs?
Costs that change directly with level of production e.g. raw materials/number of workers /wages
What is the difference between salaries and wages?
Salaries: An annual cost for a business to pay a worker - fixed cost
Wages: Payment per hour worked - seen as a variable cost as firms need more workers on an hourly rate when output increases
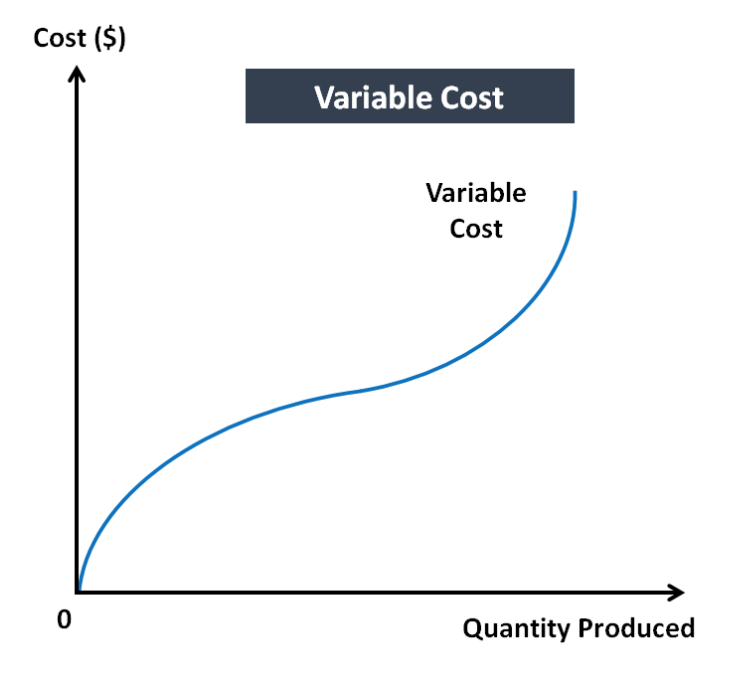
What does the variable costs curve look like?
Kind of like tan diagram
Heavily influenced by diminishing marginal productivity
Curve is steep as labour begins to be employed, but is not using capital effectively
As curve flattens, productivity of labour is at highest (more can be produced without adding cost)
Costs increase quicker than output when we see diminishing returns + an over utilisation on capital + worker productivity falls
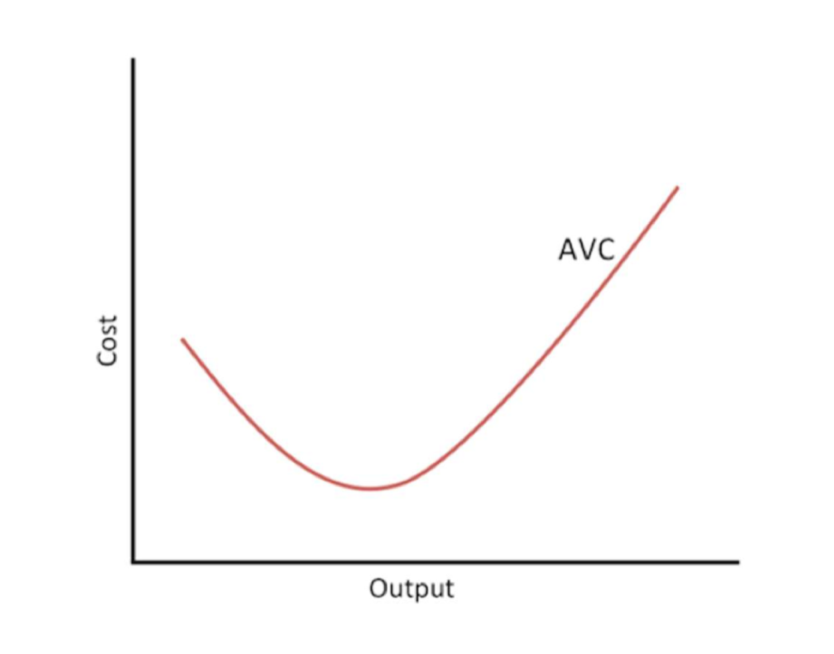
Formula for AVC?
What does the curve look like?
AVC= TVC/Q
→ AVC falls when there are increasing returns to labour (labour productivity is rising)
→ When diminishing marginal returns sets in, AVC increases as labour productivity decreases + marginal returns diminishes
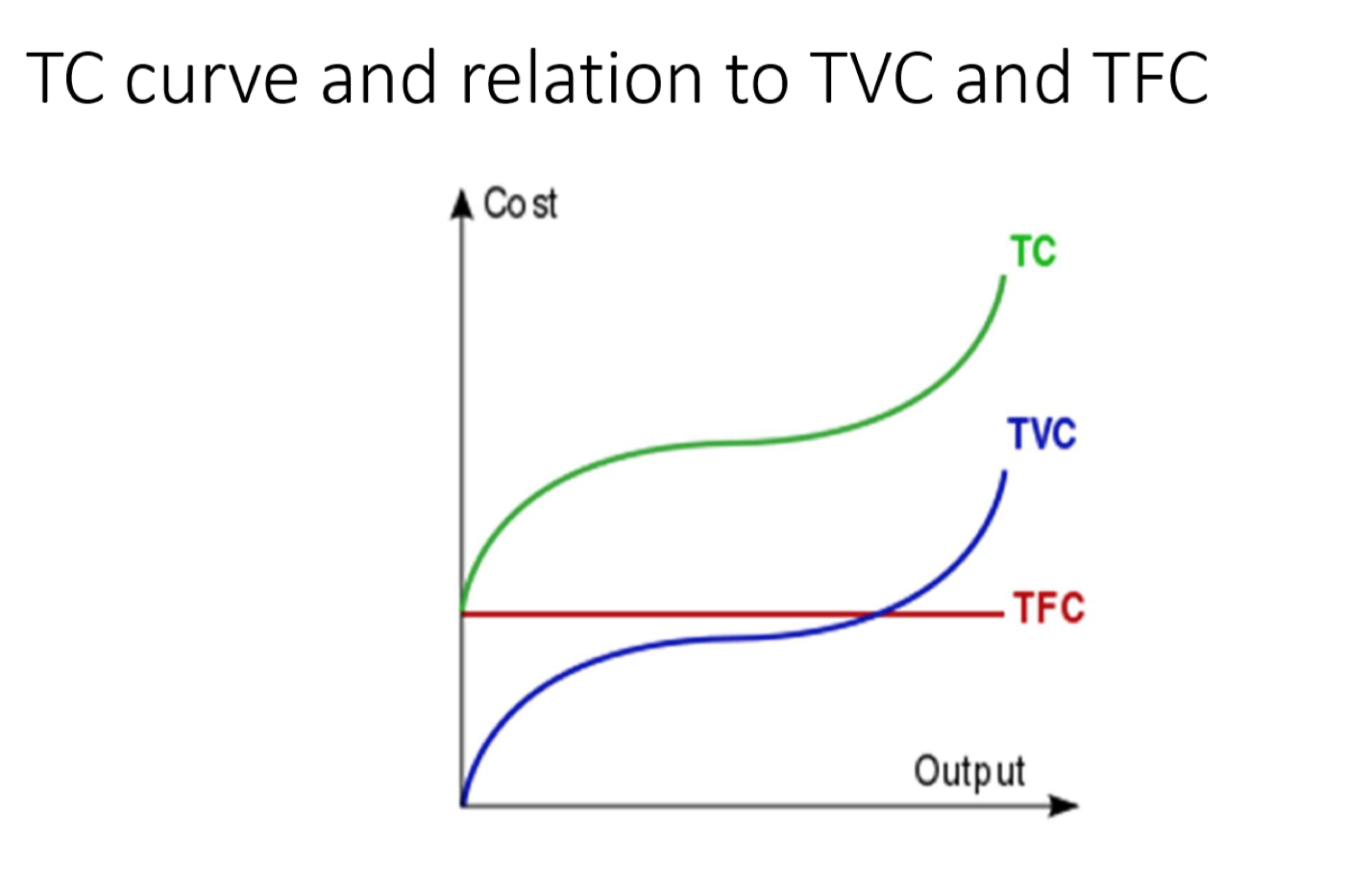
Total costs formula?
Total costs= TFC + TVC
TC curve relation to TVC and TFC curves?
What is marginal cost?
Formula?
The change in total cost for a business as a result of a one-unit change in output / cost to produce one extra unit
MC= Change in TC/ change in Q
Why is marginal cost an important concept to understand?
Firms aiming to make profits need to have an indication of the MC of supplying extra output
→ Can make higher profits if MC is less than marginal rev
*MC can be hard to measure → might produce batches of extra output but hard to increase in single units
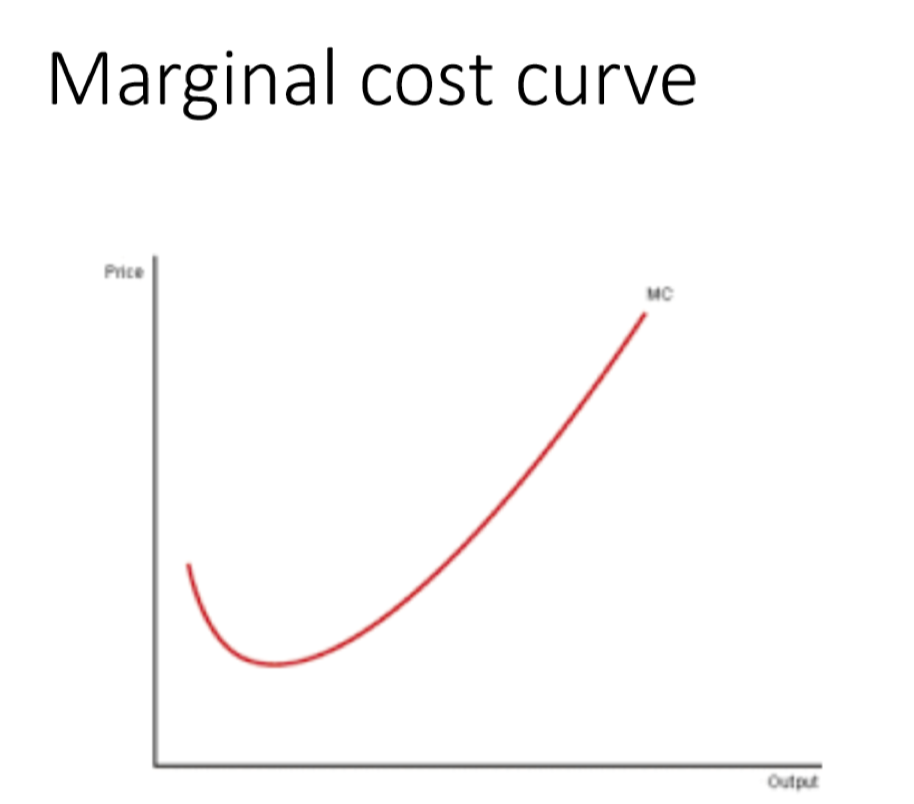
What does the MC curve look like?
When curve is downwards sloping: marginal productivity increases
When curve is upwards sloping: every additional unit produced costs more than the last due to diminishing marginal productivity
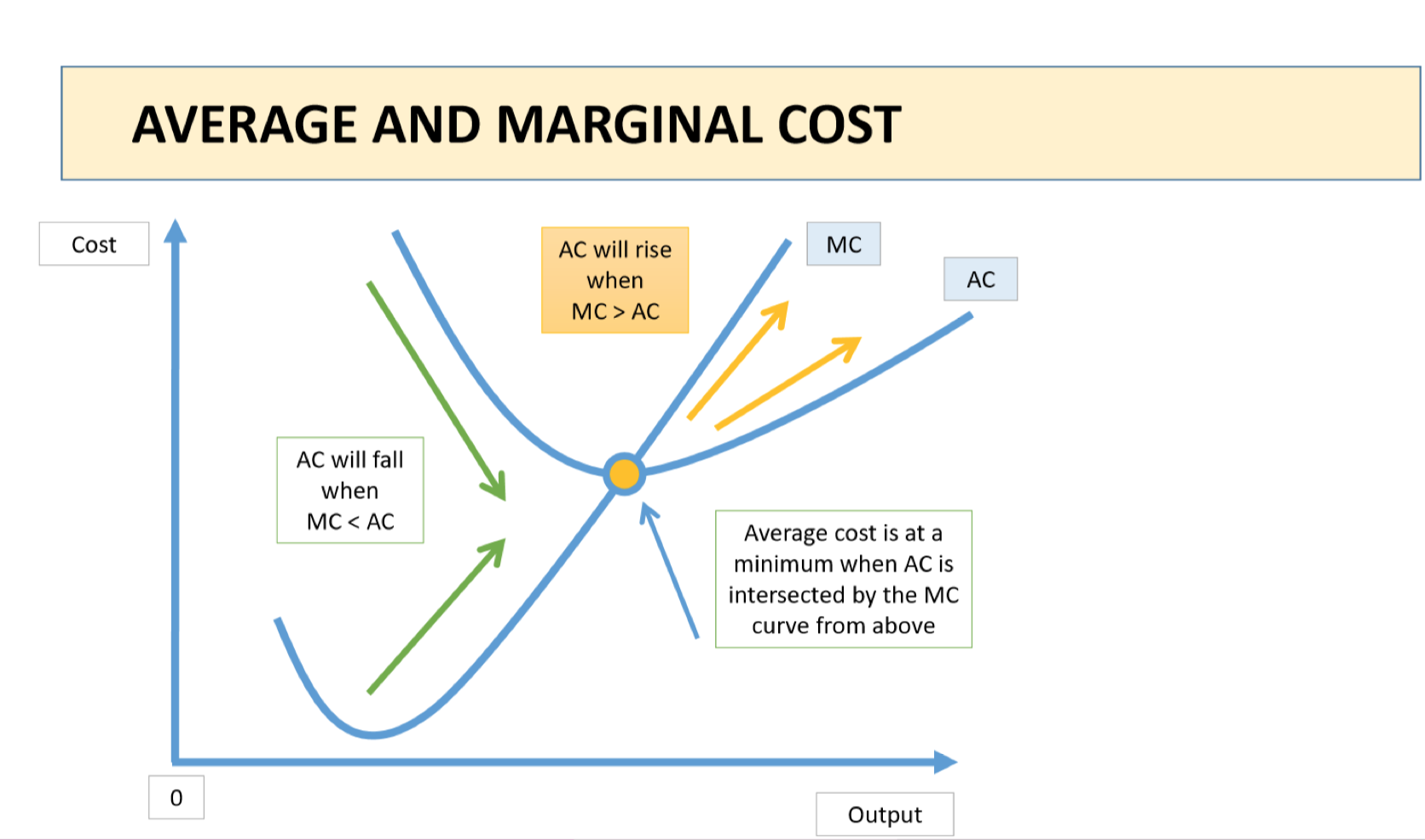
What is the relationship between AC and MC?
This relationship is crucial for understanding a firm’s cost behaviour
When MC<AC, what happens to AC?
→ When MC<AC - AC gets pulled down. The last unit produced adds less to the TC than the AC per unit, lowering the average
When MC>AC, what happens to AC?
→ When MC>AC, AC gets pushed up. The last unit produced adds more to the TC than the AC per unit, increasing the average
What happens to AC when MC=AC?
AC remains constant
AC and MC curve?
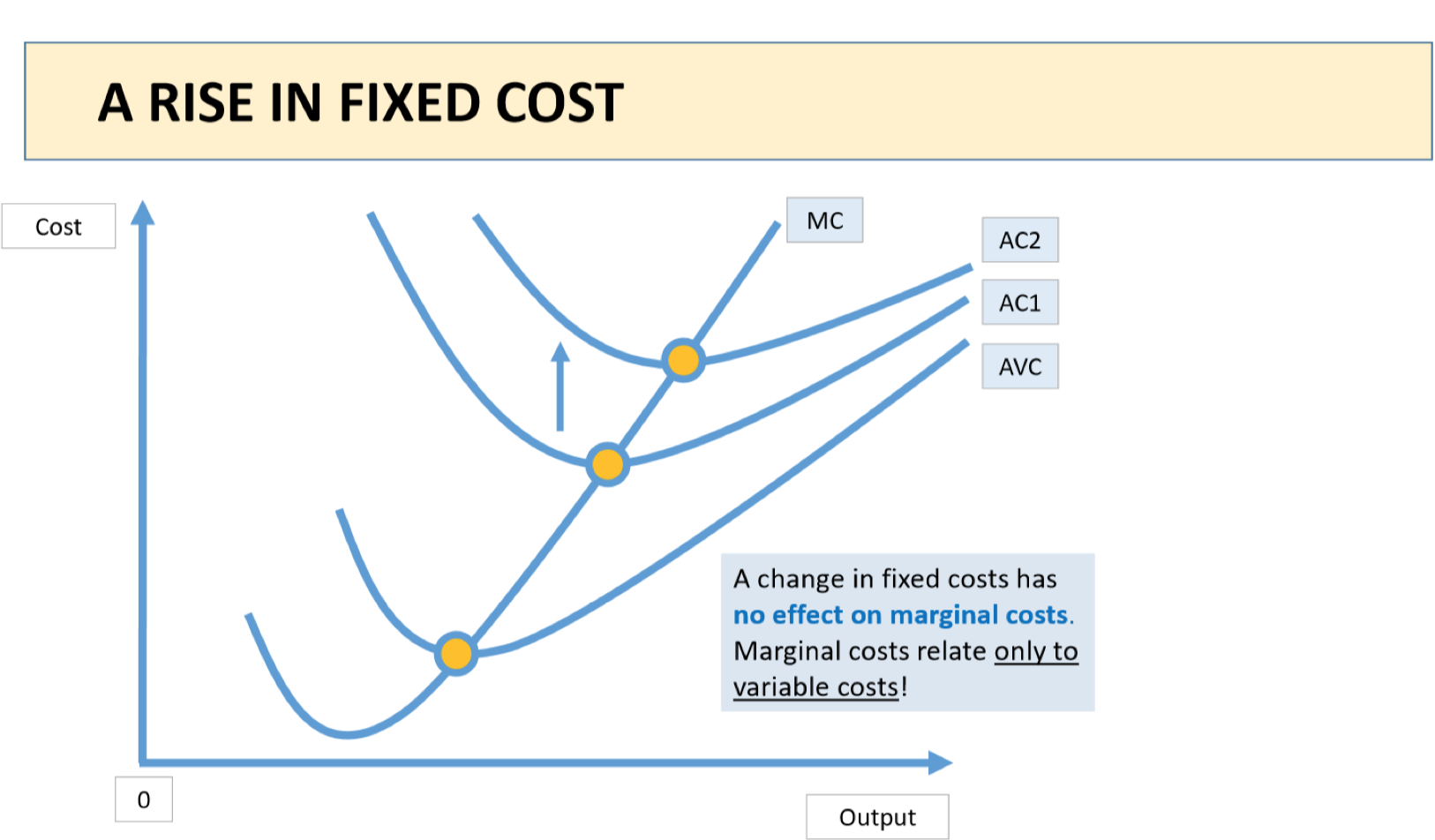
If there is a rise in fixed costs, what effect will there be on marginal costs?
A change in fixed costs has no effect on marginal costs
→ MC relate only to variable costs!
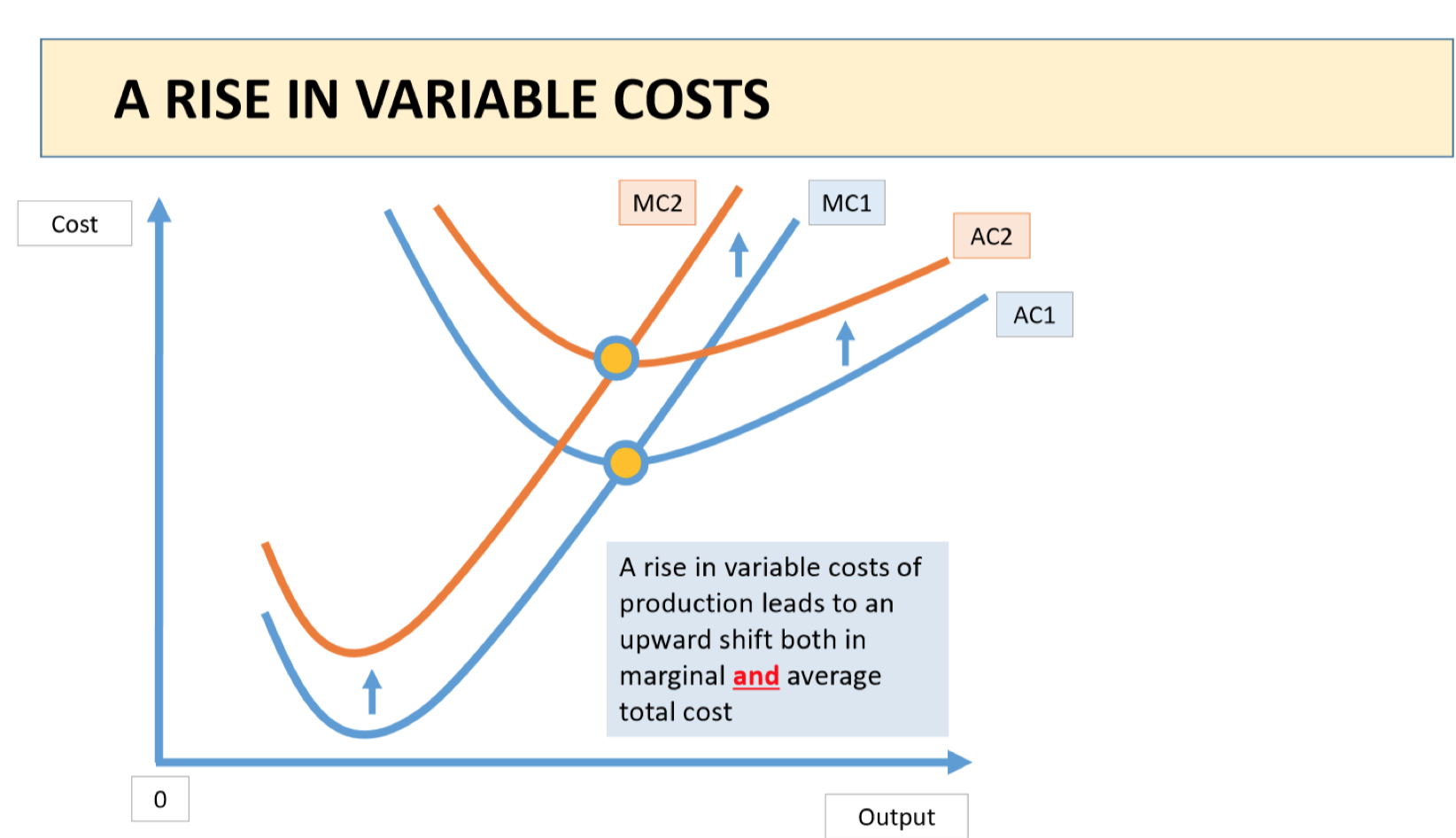
If there was a rise in variable costs e.g. number of workers, what would the effect be on the MC and AC curve?
*Think shifts
Leads to an upwards shift of AC and an inwards shift of MC
AFC formula?
AFC= TFC/Q
ATC formula?
ATC= AVC + AFC
What is meant by average product?
Measures output per-worker-employed or output-per-unit of capital
What is meant by marginal product?
The additional output produced by adding one more unit of a variable input, like labor, while keeping all other inputs fixed
Implicit costs
The opportunity costs of using resources a firm already owns. They represent the income or benefit forgone by not using those resources in their next best alternative use
E.g.
The salary a business owner gives up by running their own business instead of working for someone else.
The rent a company could have earned by leasing out a building it owns but instead uses for its own production.
Explicit costs
The direct, out-of-pocket physical payments a firm makes for factors of production. They are tangible and easily recorded in a company's financial accounts
E.g.
Wages and salaries paid to employees.
Rent for a factory or office.
Raw materials purchased for production.
Economic costs of production?
X + Y= Economic costs of production
What is X and Y?
The total cost of a firm's production, including both the direct, monetary payments and the opportunity costs of using resources
Economic costs of production= implicit costs + explicit costs