electrical charge and currents
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Name one thing needed for electrical charge to flow through a circuit
Potential difference
Equation for charge flow, time and current
Charge flow = current x time
Describe current in a single loop circuit
The same at any given point
What does current through a component depend on
Resistance of the component and the potential difference across it
Greater resistance =
Smaller current for a given potential difference across a component
Current, potential difference and resistance equation
Potential difference = current x resistance
Outline resistance of a wire practical
*
Variables in resistance of a wire practical
Dependant = resistance
Independent = length of wire
Control = material of wire, temperature and cross sectional area of wire
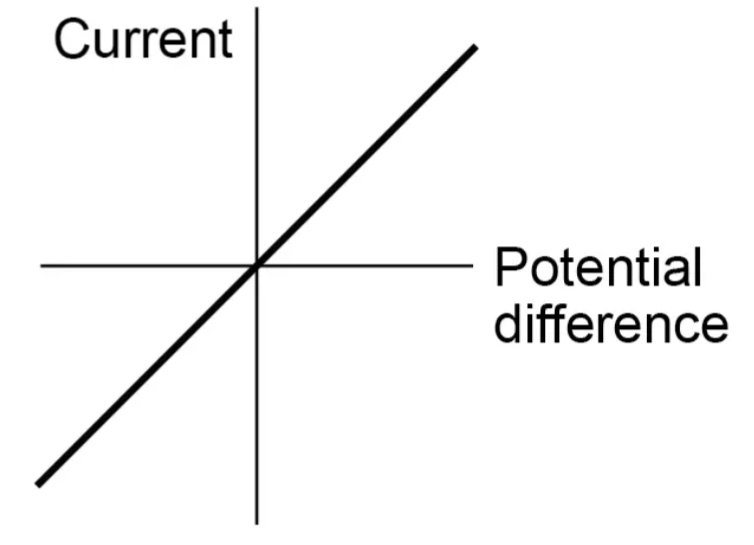
Resistor / ohmic conductor graph
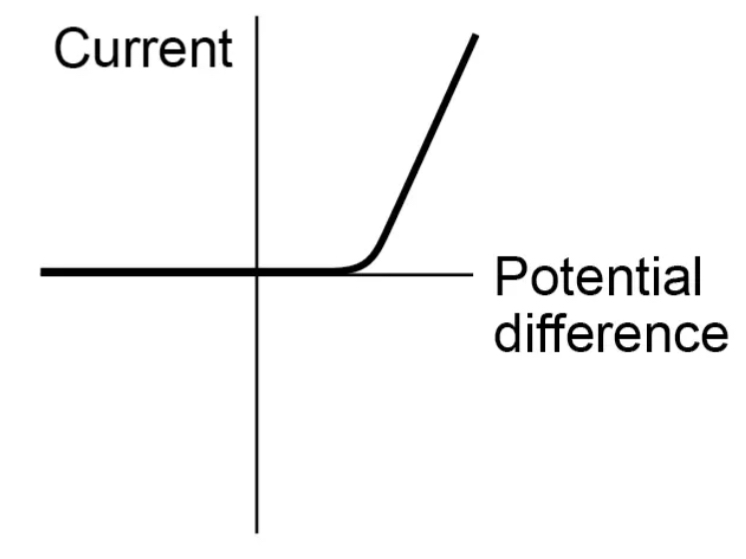
Filament lamp graph
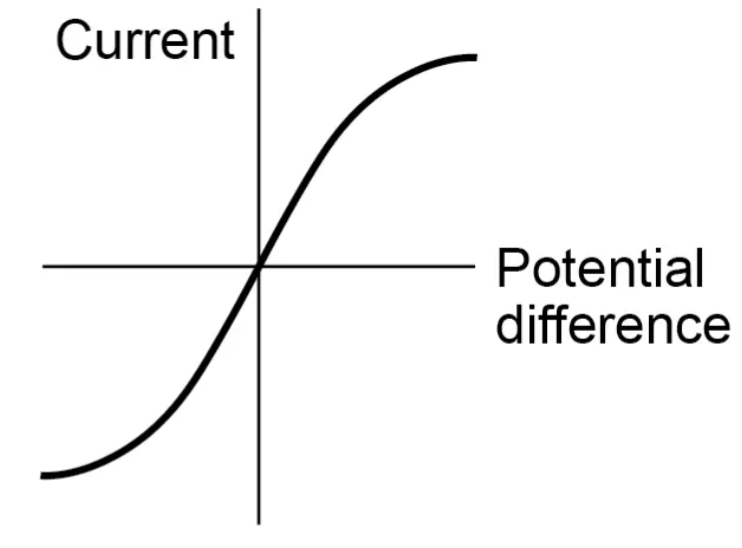
Diode graph
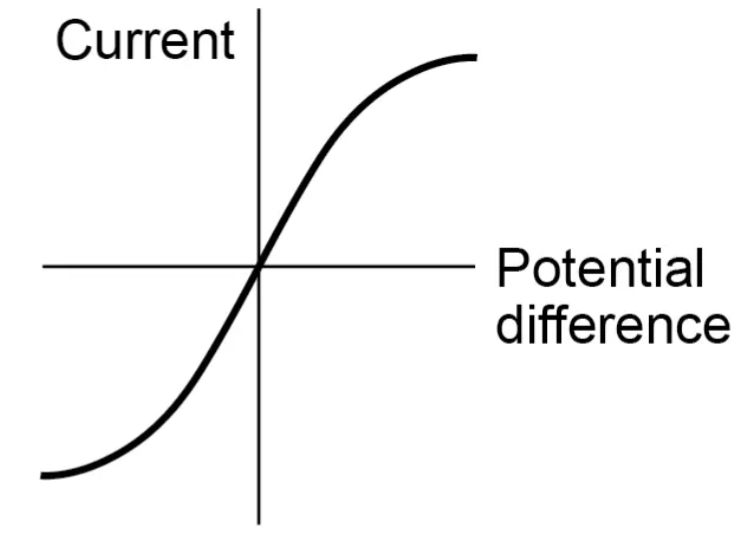
Explain a diode graph
The current can only flow in one direction as the resistance the other way is very high so remains at 0 current until it sharply increases at a voltage of around 0.7. This threshold means the resistance drops significantly and current begins to flow
Explain an ohmic conductor graph
The current through an ohmic conductor (at a constant temperature) is directly proportional to the potential difference across the resistor. This means that the resistance remains constant as the current changes.
Explain a filament lamp graph
Curved because the resistance is not constant and increases alongside temperature. As temperature rises, atoms in metal filament vibrate so free electrons struggle to get through, increasing resistance again and flattening the graph.
The resistance of a thermistor _______ as the temperature increases.
Decreases
The resistance of an LDR decreases as light intensity _______
Increases
Explain the required practical for the iv graphs
What are the variables in the iv graph practical
Potential errors in length of wire practical
Zero error
Ruler not clipped at 0 as wore thick or inaccurate
Switch is overused and temperature increases