exam 3 112
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:45 PM on 3/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
1
New cards
green algae is
the protist that gave rise to land plants
2
New cards
how long ago to algae split to land plants
405 mya
3
New cards
what are some major issues with life on land
exposure to sun, different nutrients, lack of water different temperatures
4
New cards
advantages of life on land
increased survival chances, less competition, new potential food options
5
New cards
4 main land plant features
multicellular haploid and diploid life
offspring contain all genetic info=diploid
embryo protection
small haploid portion of life cycle
offspring contain all genetic info=diploid
embryo protection
small haploid portion of life cycle
6
New cards
how did plants jump from water to lan
adaptation
7
New cards
exapmples of adaptations
cuticle, stomata, tracheid, diploid genome, haploid
8
New cards
cuticle
waxy thing that keeps water in
9
New cards
stomato
allows for gas echange
10
New cards
tracheids
tubes that move nutrients throughout a plant
11
New cards
bryophytes nonvascular
closest and oldest living descendants of first land plants, dominant gametophyte (n) no roots have rhizoid
12
New cards
under bryo liverworts nonvascular
flattened haploid (n) gametophyte, moist env, sexual reproduction(gametangia) water moves sperm to egg
13
New cards
archegonia does?
egg producer
14
New cards
antheridia does?
sperm producer
15
New cards
asexual reproduction of liverworts
gemmae cups
16
New cards
under bry moss nonvascular
gametophyte (n) leaflike structures around stemlike axis, rhizoids to anchor and pull in nutrients
17
New cards
sporophyte of moss

18
New cards
gametophyte of moss

19
New cards
under bryo nonvascular hornworts
origin is unclear, sporophyte is photosynthetic, stomata for gas exchange
20
New cards
non vascular plant life time
most spent in gametophyte as (n)
21
New cards
parts of moss
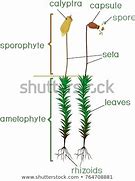
22
New cards
vacsuclar seed less plant
tracheophyte
23
New cards
under tracheophyte vasc seedless cooksonia
oldest and first vascular plant, appeared 410 myo, only a few cm tall
24
New cards
key features of tracheophytes
homorsporous
vascular tissue
cuticle
stomata
leaves
vascular tissue
cuticle
stomata
leaves
25
New cards
homosporous
produce 1 type of spore increase survival of offspring
26
New cards
vascular tissue
increase nutrient absorption and size of plant
27
New cards
another positice of cuticle
helps decrease water loss
28
New cards
stomata
regulate gas exchange, water can leave but not enter
29
New cards
positive of leaves
allows for more photosynthesis
30
New cards
evolution of vascular system
1. stems size increase
2. roots established anchor, nutrient absorption
3. leaves increase photo
4. seeds protect embryo increase survival
1. flowers increase pollination
31
New cards
seedless vasc spend most time
as sporophyte and diploid
32
New cards
seedless vac plants include
tracheophytes, lycophytes(club mosses), pterophytes(whiskferns ferns horsetails),
33
New cards
lycophytes (club mosses)
worldwide distribution, abundant in tropics, dominant sporophyte, strolois=houses spores(repro structure)
34
New cards
pterophytes
still sorting out relatedness, all form antheridia and archegonia, all require free water for flagellated sperm
35
New cards
under ptero whisk ferns
found in tropics, forking green stems, symbiosis with fungi, gametophyte is underground
36
New cards
under ptero horsetails
sporophyte, photosynthetic stems, cells walls with silica known as scouring rush, strobilus contains spores
37
New cards
conditions for spore release
dry hot, unfavorable
38
New cards
why do plants release in poor conditions
so their offspring have the best chance of survival
39
New cards
advantage of having silica
structural integrity, protection against predators, enables taller plant
40
New cards
under ptero ferns
largest group, most diverse group of seedless vascular plants, large sporophyte, low light levels, cool, damp
41
New cards
rhizoid
stem of fern
42
New cards
rhizome
rootlike structure of fern
43
New cards
where are the spores of a fern
under the blade inside of the sporangium
44
New cards
why are the spores of ferns under the blade
protection, gravity helps release spores
45
New cards
more things about ferns
developmental independence & dominance of sporophyte, gametophyte lacks vacsular tissue, water moves sperm to egg
46
New cards
fiddlehead
tight coiled tips of ferns
47
New cards
caboniferous period
360-295 mya horsetails, whiskferns, ferns===fossil fuels
48
New cards
ex of vacs seed plant
maple
49
New cards
maple syrup come from
phylum anthophyta
50
New cards
maple syrup process
leaves run photosynthesis, in the winter sugar travels down through phloem, in the warmer months the sugar travels back up via the xylem where it is tapped
51
New cards
gal syruphow many gallons of sap have to be boiled to create one
60-70
52
New cards
faster method for syrup instead of boiling
filtering water out
53
New cards
acorn germination
oak mature 5-10 years after they
54
New cards
pollination
move pollen(sperm) to egg
55
New cards
fertilization
sperm fuses with egg=zygote
56
New cards
oak trees best friends
squirels, deer, turkeys, woodpeckers
57
New cards
what stragey do oak trees use when dispersing thousands of babies
something with R
58
New cards
vasc seed herbaceous
short life cycle, short lived
59
New cards
under herb annuals
die every year, regrow from seed/root base
60
New cards
under herb perinials
year after year, long lived
61
New cards
under herb evergreen
leaves year rounds
62
New cards
under herb decidous
looses leaves in major drop
63
New cards
seed vac woody
long lived, long life cycle
64
New cards
shoot system
stem part, repoduction, support, produce nutrients
65
New cards
root system
get water, nutrients, anchor
66
New cards
which group partners with root systems
mychorizzae
67
New cards
ground tissue
muscle/flesh stores nutrients bulk of plant body
68
New cards
vascular tissue
moves fluid and nutrients
69
New cards
dermal tissue
skin protection, decreases water loss
70
New cards
ground=parenchyma
most common tissue type, stores nutrients, photosynthesis, secretions
71
New cards
ground=collenshyma
durable, tough, string, felxibility and structural support
72
New cards
ground=schlerenchyma
hard, gritty, support, small level of protection, wood fibers, paper
73
New cards
what does grit do for a pear
protect developing cells
74
New cards
vascular tissues
xylem and phloem
75
New cards
xylem contains
dissolved minerals, water roots to shoots
76
New cards
ploem contains
sugar, shoots to roots
77
New cards
tracheid
back flow preventers (pits)
78
New cards
dermal tissues from top down
upper epidermis, palisade, xylem, phloem, lower epidermis
79
New cards
upper epidermis
cuticle, dead cells
80
New cards
palisade
mesophyll cell-photosynthetic
81
New cards
lower epidermis
opening for stoma
82
New cards
guard cells
regulate movement in and out located on side of stoma
83
New cards
stoma in heat
close, but doesn’t allow for gas exchange
84
New cards
trichomes
on dermal layer, hairs, protection against predation, trap evaporated water back into roots
85
New cards
woody plants
periderm epidermis that ages into hard swollen layer of dead cells decreases water loss\`
86
New cards
primary growth patterns
apical and lateral
87
New cards
apical
meristem tissue, growth from tip
88
New cards
lateral
width/girth
89
New cards
199-167 mya
angiosperms
90
New cards
what led to evolution of vasc seedless
hot dry environment
91
New cards
seedless vasc dominated during
mesozoic era relied on wind for pollination of seed
92
New cards
angio pollination
use animals that eat fruit
93
New cards
endosperm
nutrients for developing embryo
94
New cards
kay features for seed plants
vascular
sporophyte dominant
heterosporous
some are dioescous 1 gender
some are monodioesco
sporophyte dominant
heterosporous
some are dioescous 1 gender
some are monodioesco
95
New cards
gymnosperm facts
\~319 mya bear naked seeds
96
New cards
unger gymno phylum coniferophyta
cone trees
304 mya
evergreens producing
needle
monocious
304 mya
evergreens producing
needle
monocious
97
New cards
pollen cones
micrsporangium
98
New cards
seed cones
megasporangium
99
New cards
how long does it take a conifer tree to grow and produce cones
3 years
100
New cards
pollinations for the tree
7-10 days