Cell physiology of solute recovery
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a nephron?
It is a single filtering unit in the kidney
What are the different parts of the nephron called?
Renal corpuscle
Proximal tubule
Henle’s loop
Distal tubule
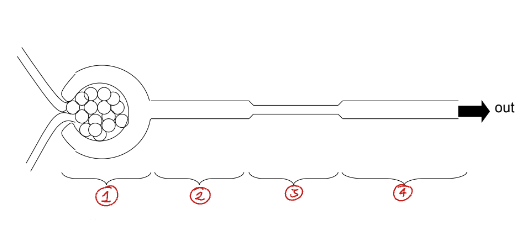
Label this diagram of the nephron
Renal corpuscle
Proximal tubule
Henle’s loop
Distal tubule
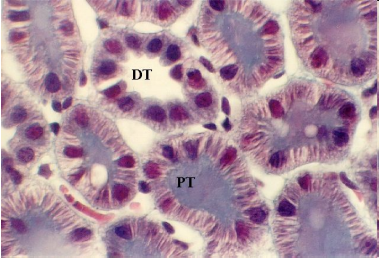
How can the distal tubule be distinguished from the proximal tubule on a histology slide?
Proximal tubules have villi while distal tubules don’t.
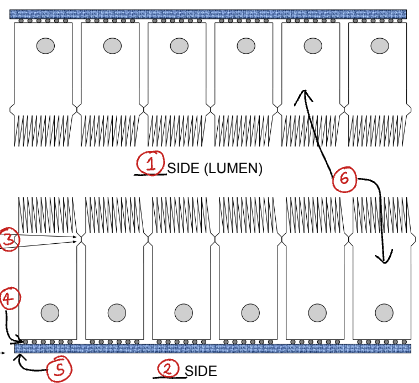
Label this diagram showing the epithelial structure
Apical side
Basal side
Tight and adherens junctions
Adhesions
Basement membrane
Epithelial cells
What is different about the adherens junctions between epithelial cells in the proximal tubule?
They are 10x more leaky than usual.
What molecules do the nephron epithelia recover?
Na +
K +
Ca 2+
Mg 2+
C l-
HCO3 -
PO4 2-
H2O
Amino acids
Glucose
Proteins
Is there a water pump in the kidneys?
NO
What structures help reabsorb molecules in the nephron epithelia?
Primary active transporters
Solute Carrier family (SLC) proteins
Aquaporins
Ion channels
Protein endocytosis receptors
Aquaporins
water channels
What are the most commonly found Primary Active Transporters
Na+/K+ ATPase
H+ ATPase
How many different types of SLC are found in the kidney?
About 300
Why are kidney cells packed with mitochondria?
A lot of energy is needed to move molecules from the filtrate to the plasma. This is due to the fact that the filtrate and plasma will be around equilibrium.
What is the name of the ‘engine’ that creates a gradient for passive transport in the nephron epithelia?
Na+/K+ ATPase
How does sodium recovery happen in the proximal tubule?
Na+/K+ ATPase and Na+/H+ exchangers work together to get sodium back into the blood.
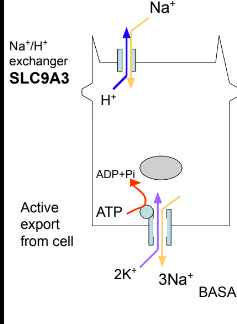
Does the Na+/H+ exchanger need energy to function?
No, export of H+ out of the epithelial cells provides energy for the transport of sodium into the cell.
How does sodium recovery happen in the distal tubule?
Sodium chloride co-transporters and Na+/K+ ATPase work together to transport sodium into the bloodstream.
Does the Sodium chloride cotransporter need energy to function?
No, the passive transport of chlorine down its concentration gradient into the cell provides energy that allows the Na+ to travel into the cell against its concentration gradient.
How does potassium recovery happen in the loop of Henle?
Na-K-Cl Cotransporters, Na+/K+ ATPase, and K+ channels work together to transport K+ back into the bloodstream.
How does the Na-K-Cl cotransporter work?
Na+, Cl- and K+ are all transported in the same direction by the co-transporter - into the cell. Na+/K+ ATPase allows this to happen by creating a concentration gradient that sodium can travel into the cell with, which allows the other two ions to also travel into the cell.
Once K+ has been transported from the loop of henle into the cell, how does it get back into the bloodstream?
It must travel through a potassium channel.
What does the ‘regulated leakage’ of potassium in the loop of henle mean?
There are ROMK channels (renal outer medullary K+ channels) through which potassium flows down a concentration gradient from inside the cell back into the loop of henle.
How does amino acid recovery in the proximal tubule happen?
where are amino acids reabsorbed in the kidney?
The proximal tubule