suspension
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the primary goal of a suspension system in a Formula Student car?
To maintain maximum tire grip by keeping the tire in optimal contact and alignment with the road during cornering, acceleration, and braking.
What does the suspension try to keep as constant as possible during motion?
The tire contact patch size and wheel alignment (especially camber) to maximize friction.
What happens if the tire contact patch becomes smaller during cornering?
Grip decreases because less rubber touches the road, leading to understeer or oversteer.
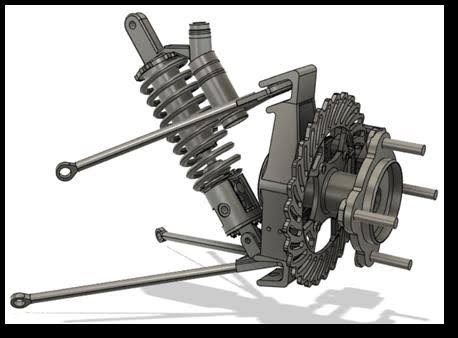
Why do Formula Student cars almost always use a Double Wishbone suspension?
Because it allows precise control over camber gain and roll center location, keeping the tire flat on the road during cornering.
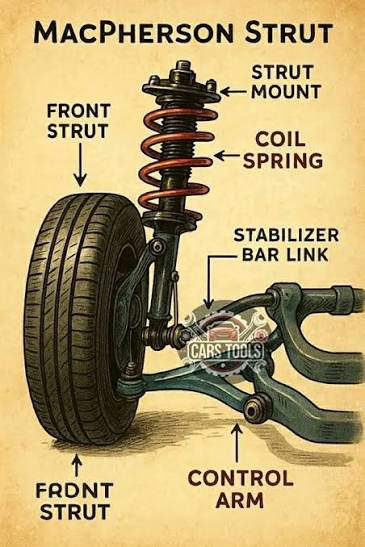
Why is MacPherson strut rarely used in FS cars?
It has poor camber control during chassis roll, reducing grip in corners.
Why is Multi-link suspension not ideal for FS?
It is heavy, complex, harder to design and package, and offers no performance advantage at FS scale.
Lateral acceleration
When you take a fast corner and you feel your body being pushed to the side — that is lateral acceleration.
how fast you can turn without losing control.
Negative acceleration
This is called deceleration or braking deceleration — it’s how quickly the car slows down when you apply the brakes.
chassis torsional stiffness
Nm/° tells you how much torque is required to twist the chassis by 1 degree.
What is the Instant Center (IC) in suspension geometry?
The Instant Center is the point where the projected upper and lower control arms (or suspension links) of a wheel side intersect. It represents the center about which the wheel is “rotating” at that instant during suspension travel.
Why is the Instant Center important?
The position of the Instant Center determines how the suspension transfers forces, how the tire maintains contact with the ground, and how the car responds under cornering.
What is the Roll Center (RC)?
The Roll Center is a theoretical point about which the vehicle chassis rolls during cornering. It is calculated using the geometry of the suspension and instant centers.
How is the Roll Center found?
Draw lines from each tire contact patch to its instant center. The point where these lines intersect the vehicle centerline vertically is the roll center.
Why are front and rear roll centers different?
Different front vs. rear roll center heights control how the car rotates mid-corner.
Higher rear RC → encourages rotation (oversteer tendency)
Higher front RC → reduces front roll → can limit steering response or cause understeer.