Drake University Bio 13: Exam 2
1/99
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of body parts.
Physiology
The study of how body parts function and work.
Gradient
A change in distribution over time or space that creates different regions and driving forces for diffusion.
Phospholipid bilayer
A cell membrane structure composed of two layers of phospholipids that is critical for cellular function.
Chemical Gradient
A difference in the concentration of particles across a space, driving diffusion from high to low.
Osmotic Pressure
The pressure required to prevent the flow of water across a semipermeable membrane, influenced by the number of solute particles.
Hydrostatic Pressure
The pressure exerted by a fluid at rest; relevant in the context of blood pressure within vessels.
Partial Pressure
The pressure exerted by a single gas in a mixture of gases; important for gas exchange in respiration.
Epithelial Tissue
A type of tissue characterized by closely packed cells that line surfaces and cavities, and may have specialized structures such as microvilli or cilia.
Connective Tissue
The most varied type of tissue, characterized by widely spaced cells embedded in an extracellular matrix.
Muscle Tissue
Specialized tissue responsible for movement, containing actin and myosin filaments.
Nervous Tissue
Tissue specialized for rapid communication within the body, consisting primarily of neurons and glial cells.
Negative feedback
A control mechanism that reduces any difference from the set point to maintain homeostasis.
Positive feedback
A control mechanism that amplifies a response or process in the body.
Cardiac Cycle
The sequence of events in one complete heartbeat, including contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of the heart chambers.
Stroke Volume
The amount of blood pumped by the heart in one contraction.
Cardiac Output
The volume of blood the heart pumps in one minute, calculated as stroke volume multiplied by heart rate.
Autorhythmic cells
Pacemaker cells in the heart that spontaneously generate electrical impulses driving heart contractions.
Pacemaker Potentials
Automatic spontaneous electrical signals from pacemaker cells that initiate heartbeats.
Hydrostatic Pressure Gradient
The difference in pressure within a fluid that drives fluid movement, significant in the cardiovascular system.
Cuboidal epithelia
A type of epithelial tissue characterized by cube-shaped cells, often involved in secretion and absorption processes in glands and organs.
Columnar epithelia
A type of epithelial tissue composed of tall, column-like cells that are primarily involved in absorption and secretion functions, commonly found in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract.
Squamous epithelia
A type of epithelial tissue made up of thin, flat cells that facilitate diffusion and filtration, often found in areas such as the alveoli of the lungs and the lining of blood vessels.
Pseudostratified epithelia
A type of epithelial tissue that appears to be stratified due to varying cell heights but is actually a single layer of cells, typically found in the respiratory tract and often contains cilia and goblet cells.
Epithelial junctions
Structures that connect adjacent epithelial cells, providing strength and communication between cells, including tight junctions, adhering junctions, and gap junctions.
striated tissue
Muscle tissue marked by a striped appearance due to the arrangement of myofibrils. It is involved in voluntary movements and includes skeletal and cardiac muscle.
skeletal tissue
A type of muscle tissue that is striated and voluntary, responsible for the movement of bones and posture, typically attached to the skeleton.
cardiac tissue
A type of muscle tissue that is striated and involuntary, found exclusively in the heart, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
smooth tissue
A type of muscle tissue that is non-striated and involuntary, found in various organs including the intestines and blood vessels, responsible for regulating movements within those organs.
glial cells
Supportive cells in the nervous system that protect and maintain neurons, playing essential roles in their function and homeostasis.
Nervous and Endocrine systems
Control and regulate all of the other systems.
stimulus
Any change in the environment that triggers a response from an organism or cell.
conformers
Organisms that maintain internal conditions that vary with environmental changes; they rely on the external environment to regulate their physiological processes.
regulators
Organisms that maintain internal conditions relatively constant, regardless of external environmental changes; they actively regulate their physiological processes.
Intrinsic conduction system
A group of specialized cardiac muscle cells that initiate and propagate electrical impulses, controlling the heart's rhythm and rate.
Muscle cells
Have the ability to shorten and contract.
Intercalated discs
Specialized connections between cardiac muscle cells that enable rapid communication and synchronization of contractions.
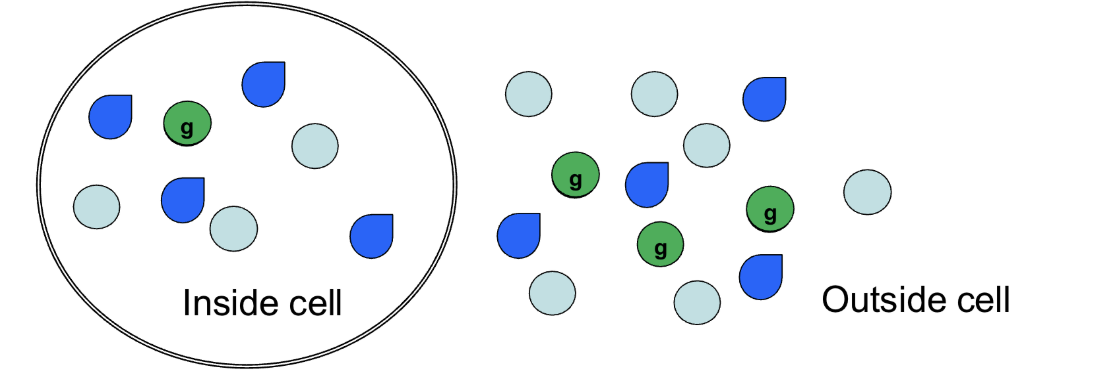
concentration gradient
What kind of gradient is shown if we consider only the bright green spheres?
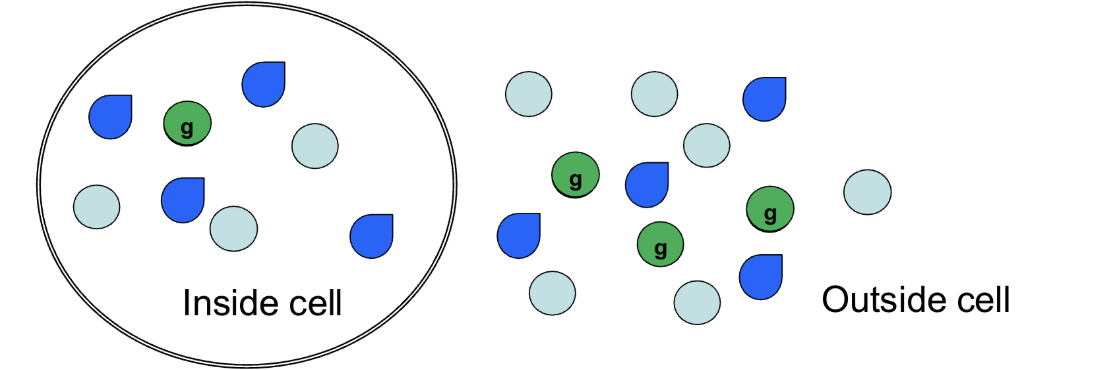
Yes, into the cell
If we consider only the bright green spheres, will there be any movement? If so, which way?
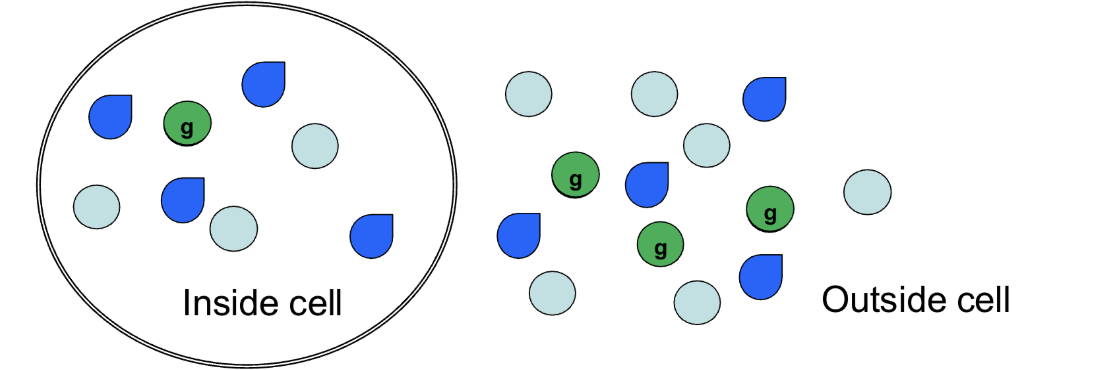
One
How many bright green spheres will move into the cell?
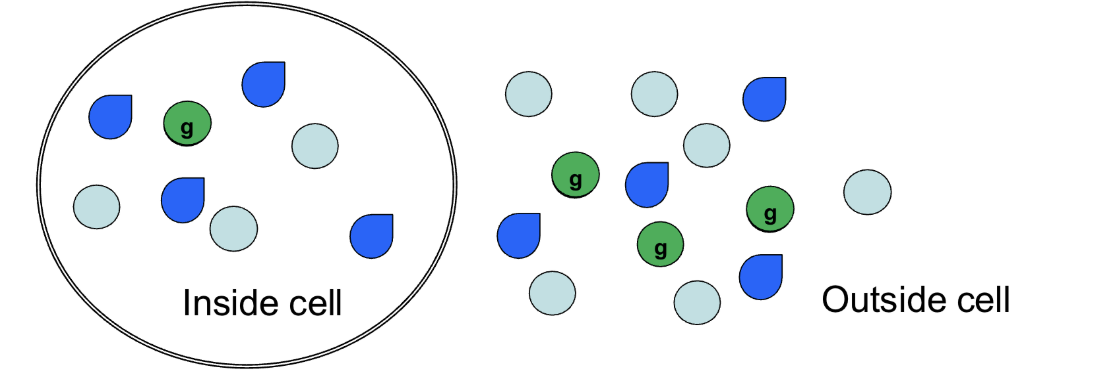
Osmotic pressure gradient
What kind of gradient is shown if we consider all of the spheres together?
Yes, water will move out of the cell
Will there be any movement? If so, what will move and which way will it go?
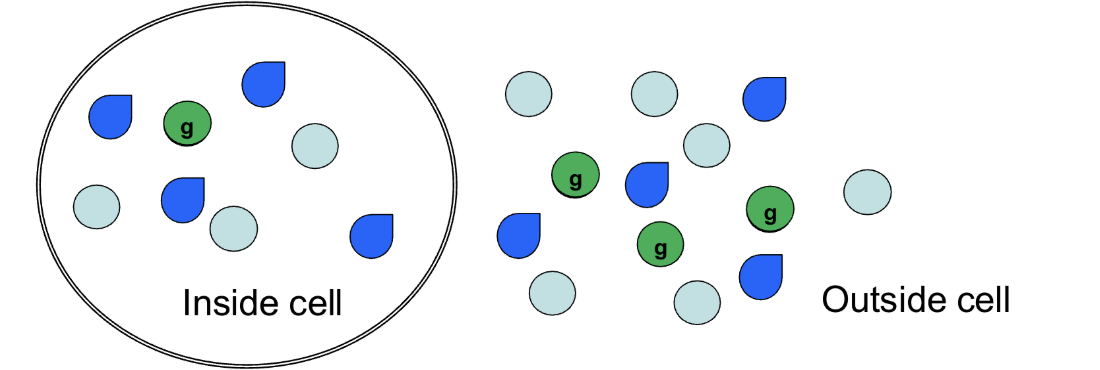
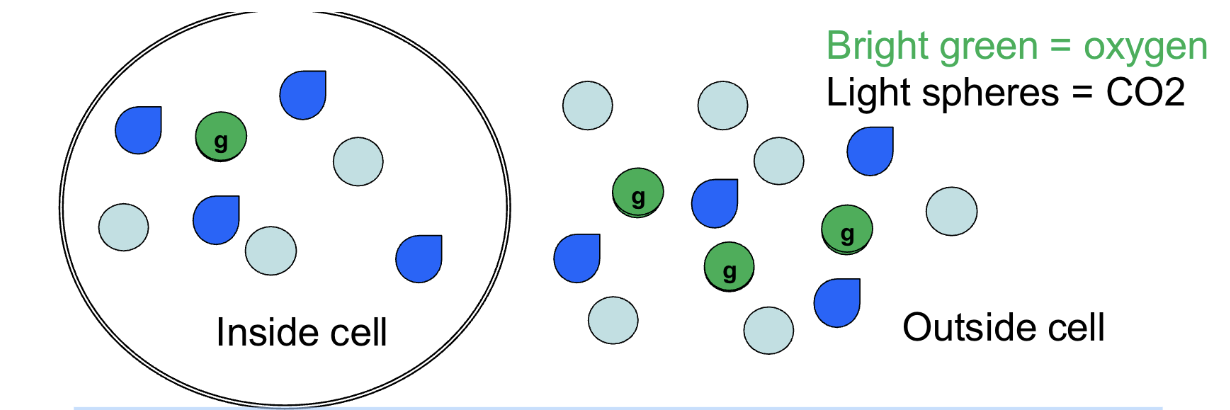
Partial pressure gradient
What kind of gradient is shown if the spheres are gases?
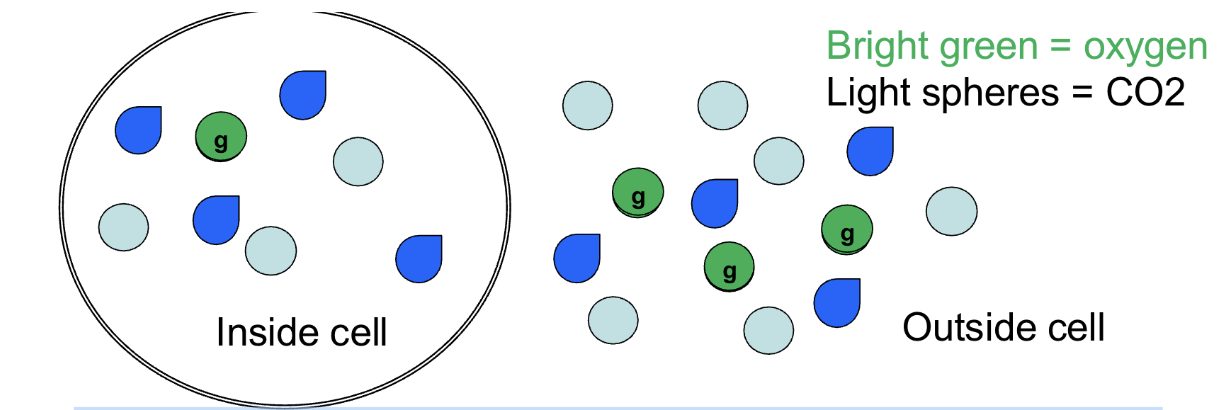
It will enter the cell
Which direction will CO2 move in this scenario?
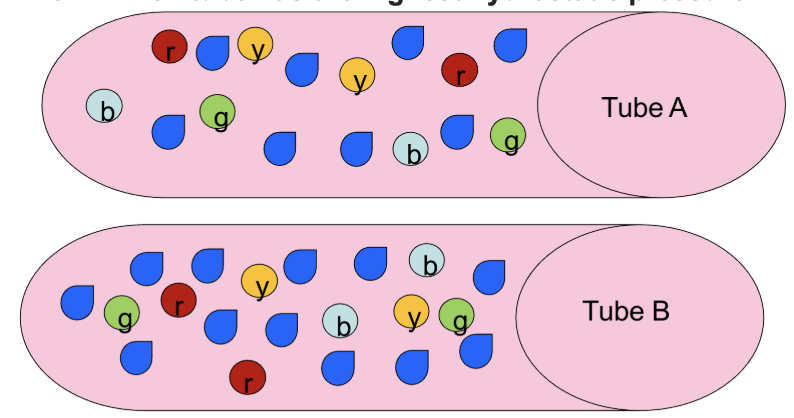
Tube B because it has more fluid
Which tube has the highest hydrostatic pressure?
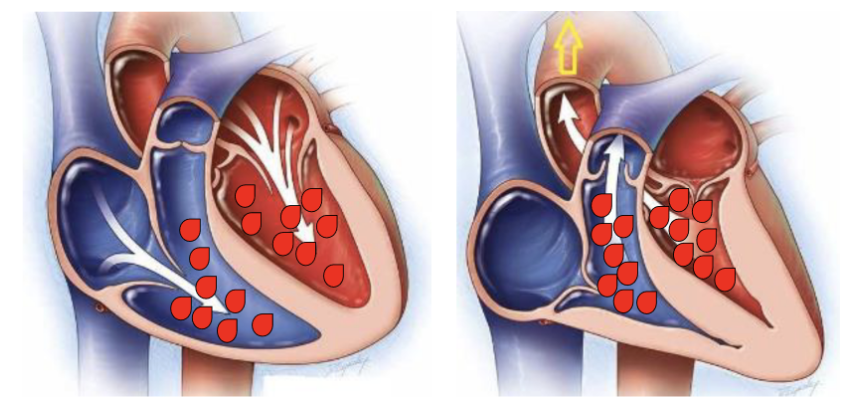
Right
Which heart has the highest hydrostatic pressure in the ventricles?
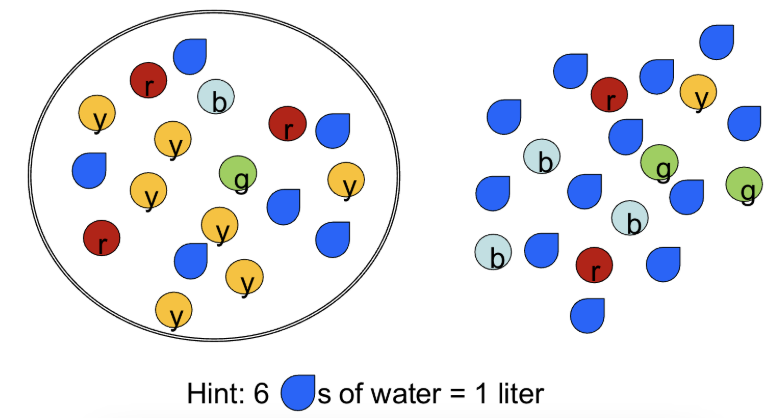
The outside
Which region has the highest hydrostatic pressure? (Assume volumes are equal between the inside and outside of the cell.)
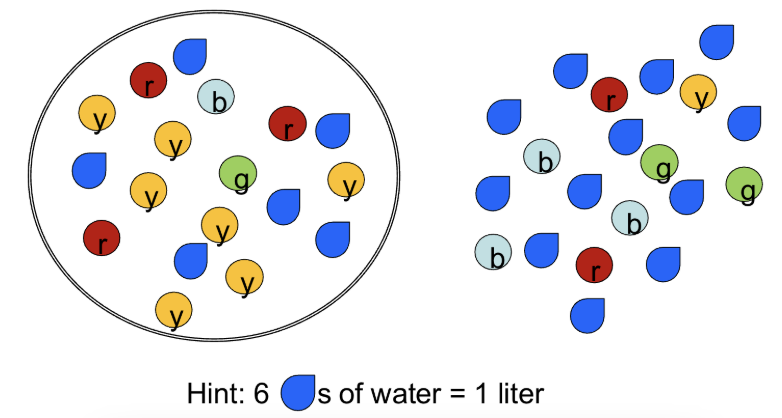
12 miliosmles
What is the osmotic pressure inside the cell?
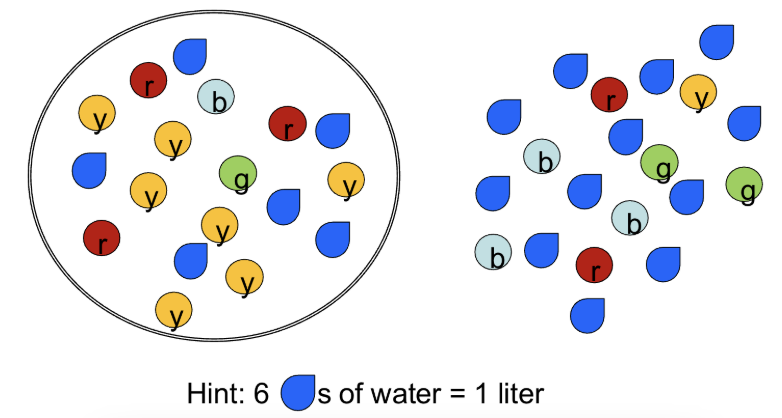
Water from the outside moving into the cell
Which way would this cause water to move?
Characteristics of epithelial tissue
Cells are close to each other
Cells have tight junctions that reduce leakiness
Cells have gap junctions that allow them to communicate with each other
Cells have an apical and basal surface that are different from each other
Cells line a body cavity or body space
Connective tissue
Which of the following tissue types is the most varied?
Tight junctions
A disorder which disrupts the ability of the vasculature to maintain a physiological barrier is most likely to involve which one of the following?
Connective tissue
During osteoarthritis, pain is caused when two bones come in direct contact with each other. What type of tissue has been lost or damaged in this condition?
Epithelial tissue
Gut microvilli are subjected to physical and chemical stresses, so the cells lining the GI tract are constantly undergoing repair and replacement. What type of tissue do these cells belong to?
Decreased ability to absorb nutrients (malnutrition), decreased ability to absorb water (diarrhea)
Gut microvilli are subjected to physical and chemical stresses, so cells lining the GI tract are constantly undergoing repair and replacement. What signs and symptoms would you expect someone with a decrease in gut microvilli to experience?
Damage to the myosin protein
A. Difficulty in walking
B. Difficulty in swallowing
C. Decreased gut motility (movement)
D. Decreased cardiac contraction
E. Decreased ability to regulate the amount of light entering the eye
Tight junctions, a blood-brain barrier
Delivery of drugs to retina and brain is difficult. Why might this be the case?
system specializing in communication
1. Sensory structures that can detect changes in the internal or external environment
2. Ability to synthesize & release a chemical signal
3. Means of delivering the chemical signal to a target cell
4. Receptors to the chemical signal on the target cells
5. Way to inactivate the signal
Sodium regulation
Extracellular sodium levels are normally 140 mEq/L. If sodium levels fall to 120 mEq/L, a hormone called aldosterone is released. Aldosterone causes extracellular sodium levels to increase. This is an example of which of the following?
Negative feedback
Extracellular sodium levels are normally 140 mEq/L. If sodium levels fall to 120 mEq/L, a hormone called aldosterone is released. Aldosterone causes extracellular sodium levels to increase. The increase in sodium causes aldosterone levels to then decrease. This is an example of which of the following?
Animals with a gastrovascular cavity lack
a. A cardiac pump
b. An atrium
c. Valves
d. Circulatory fluid that is separate and distinct from interstitial fluid
e. Vessels
Circulatory fluid that is separate and distinct from interstitial fluid
Animals with an open circulation lack which of the following?
Blood will not exit the atrium properly and blood will not enter the ventricle properly during ventricular diastole (AV)
What happens if the AV valve doesn’t open properly?
Blood will not exit the ventricle properly during ventricular systole
What happens if the semilunar valve doesn’t open properly?
Blood will flow back into the atrium during ventricular systole
What happens if the AV valve doesn’t close properly?
Blood will flow back into the ventricle during ventricular diastole
What happens if the semilunar valve doesn’t close properly?
Tricuspid AV valve
A valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle that prevents backflow of blood into the atrium during ventricular contraction.
Mitral (bicuspid) AV valve
A valve located between the left atrium and left ventricle that prevents backflow of blood into the atrium during ventricular contraction.
pulmonary semilunar valve
A valve located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery that prevents backflow of blood into the ventricle after contraction.
pulmonary artery
The major vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation.
aortic semilunar valve
A valve located between the left ventricle and the aorta that prevents backflow of blood into the ventricle after contraction.
aorta
The largest artery in the body, responsible for carrying oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body.
systole
The phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscles contract and pump blood out of the chambers.
diastole
The phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscles relax and fill with blood.
atrial depolarization
The electrical activation of the atria, resulting in their contraction and the initiation of blood filling into the ventricles.
p wave
The electrical activity that triggers atrial contraction, represented on an ECG as a small upward deflection (the first small hump on an ekg)
QRS
The electrical impulses that cause ventricular contraction, represented on an ECG as a sharp spike following the P wave.
ventricular repolarization
The process where the ventricles recover their electrical charge and relax after contraction, represented on an ECG as a T wave.
t wave
The part of an ECG that represents ventricular repolarization, following the QRS complex and preceding the next P wave.
myogenic hearts
Hearts that generate their own electrical impulses without external stimuli, typically found in certain fish, amphibians, and some reptiles.
simple epithelia
A type of tissue composed of a single layer of cells that covers body surfaces and lines cavities. They are involved in absorption, secretion, and filtration.
stratified epithelia
A type of tissue made up of multiple layers of cells, providing protection and typically found in areas subjected to abrasion, such as the skin and lining of the mouth.
ciliated epithelia
A type of tissue featuring cells with hair-like projections called cilia, which help in moving substances along surfaces, commonly found in the respiratory tract and fallopian tubes.
Endocrine system
Doesn’t have a dedicated road – wherever in the body the receptors are, that’s where the action will be and is responsible for producing hormones that regulate various physiological processes in the body, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
P-R interval
The time between the onset of atrial depolarization and the onset of ventricular depolarization, reflecting the conduction time through the AV node.
Ventricular depolarization order
AV node → bundle of His → bundle branches → Purkinje fibers → ventricular muscle
Extrinsic regulation of cardiac output
Autonomic nervous system modifies cardiac output
Parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digest)
Sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight)
stroke volume x heart rate = cardiac output
The amount of blood ejected by the heart in one beat multiplied by the number of beats per minute, resulting in the total volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
Tachycardia
An abnormally fast heart rate, typically defined as a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute.
Bradycardia
A slower than normal heart rate, typically defined as a resting heart rate below 60 beats per minute.
Stroke volume
The amount of blood pumped by the heart with each contraction.
Cardiac output (CO)
The total volume of blood the heart pumps per minute, calculated as the product of stroke volume and heart rate.
heart murmur
An abnormal sound during the heartbeat cycle, often indicative of an underlying heart condition, such as a valve issue.
atrioventricular valve (AV)
A valve located between the atria and ventricles of the heart, responsible for preventing backflow of blood during ventricular contraction.
semilunar valve
A type of heart valve located at the exits of the ventricles, preventing backflow of blood into the heart after contraction.
systemic circuit
The part of the circulatory system that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
breathing circuit
The system of airways and lungs involved in the process of respiration, facilitating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Single circulation
Blood only goes through the heart one time
Atrium: receiving chamber
Blood goes directly from getting oxygen into systemic circulation
Atrium → (valve) → ventricle → gills → systemic circulation → back to the heart
Double Circulation
Blood passes through the heart twice
Oxygenated blood is separated from deoxygenated blood
Common in mammals and birds, supporting higher metabolic rates.
Double circulation
A circulatory system where blood passes through the heart twice, ensuring oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are kept separate, facilitating efficient oxygen delivery to tissues.