Health Psychology: Eating and Weight Management
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
To provide nutrients and energy to run the body, starting with chewing and saliva in the mouth.
What are the three activities that use available energy from ingested food?
1. Processing newly ingested food (80% of calories), 2. Basal metabolism (9-10% of calories), 3. Active behavioral processes (approximately 250 calories).
What does stable weight depend on?
Stable weight occurs when energy intake (calories) equals energy output (physical activity and basal metabolism).
What was the goal of Ancel Keys' starvation experiment in the 1940s?
To reduce the weight of individuals by 25%.
What psychological effects were observed in participants after starvation in Keys' experiment?
Participants became irritable, aged, and had a lack of trust in themselves regarding food.
What is the 'yo-yo effect' in relation to dieting?
It refers to the cycle of losing weight and then regaining it, often due to metabolic adaptations.
What was the outcome of the Brownell et al. (1986) experiment on rats regarding metabolism?
Rats that were made obese then put on a calorie-restricted diet showed a decrease in metabolism and difficulty in maintaining weight loss.
What happens to basal metabolism during extreme caloric restriction?
Basal metabolism declines, making weight loss more difficult.
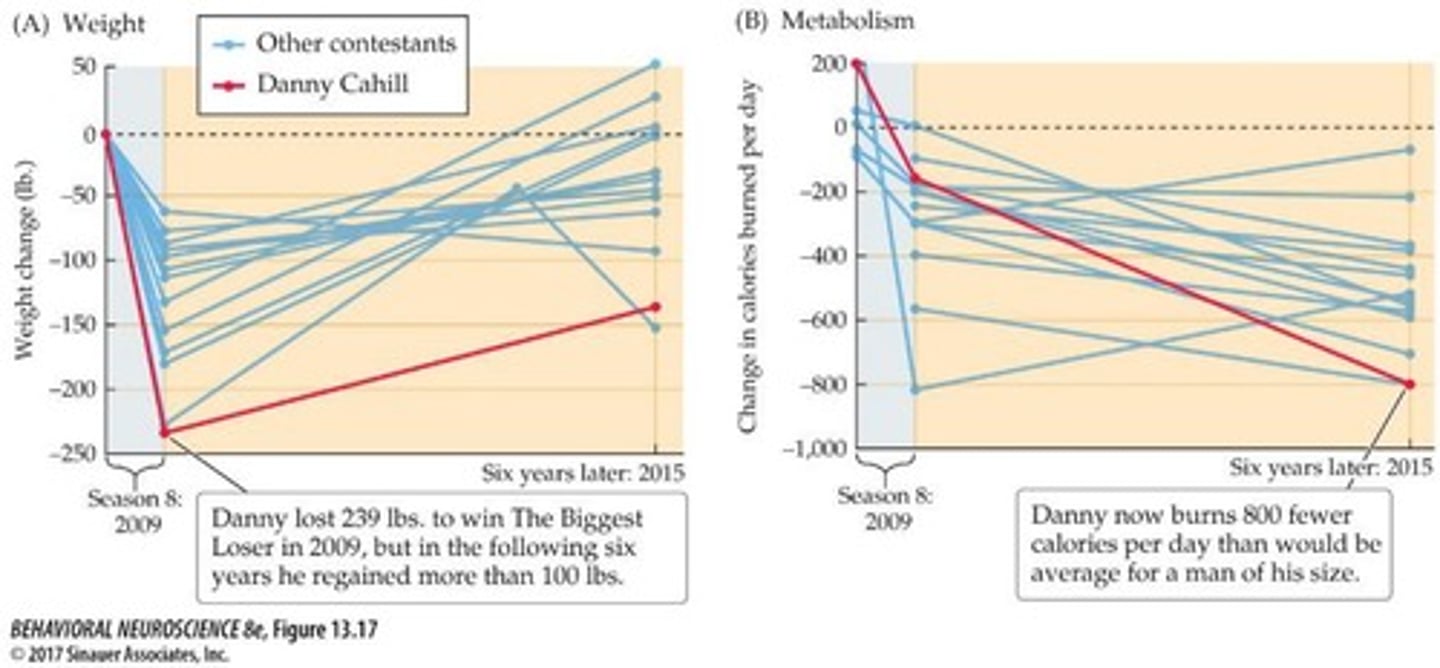
What was the significant finding regarding contestants from Season 8 of The Biggest Loser?
13 out of 14 contestants regained significant weight over the following 6 years, with metabolic suppression persisting and even increasing over time.
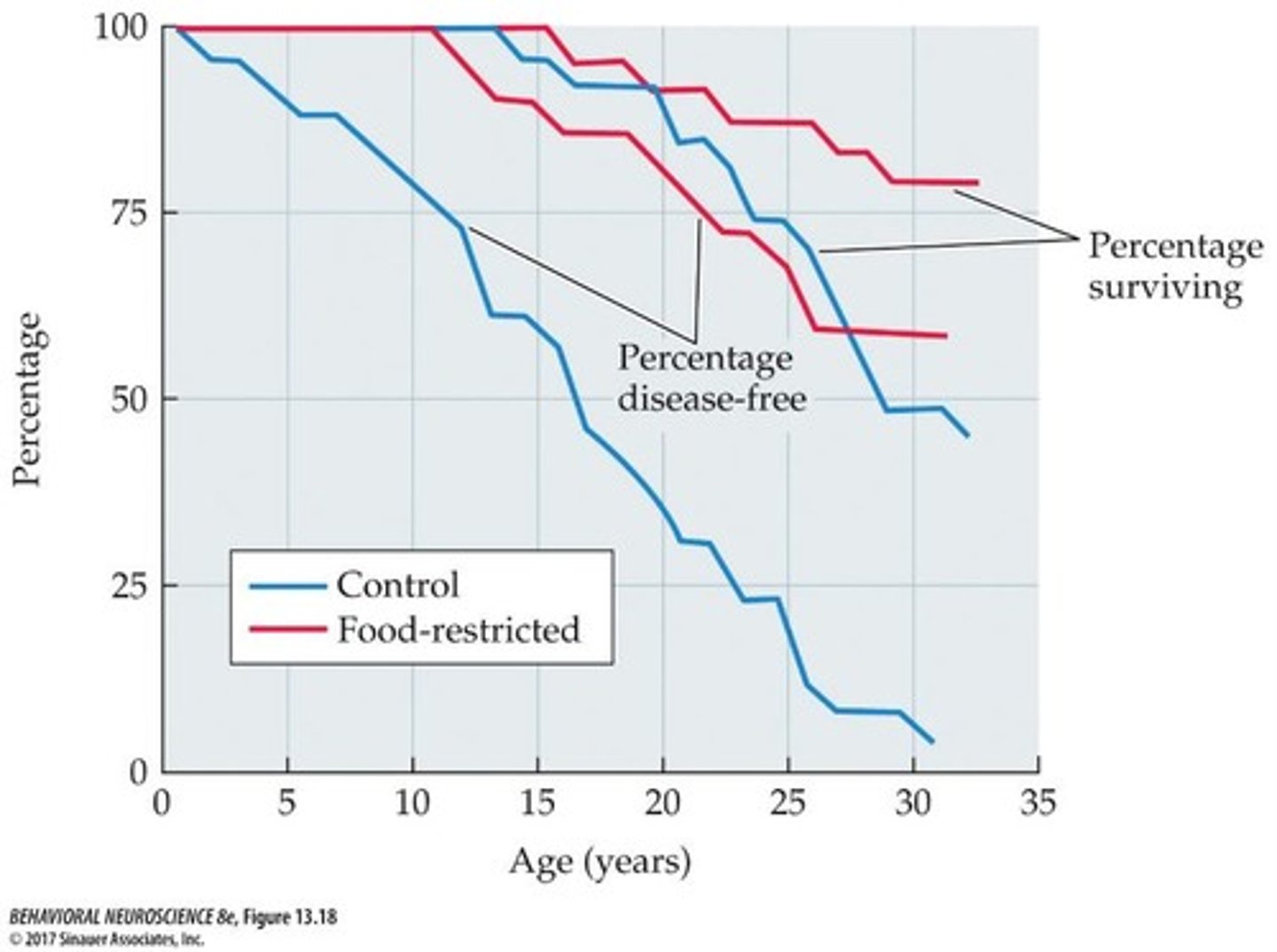
What are the benefits of caloric restriction observed in rhesus monkeys?
Moderate caloric restriction over 20 years resulted in significant reductions in age-related diseases and associated mortality.
What did the 1970s experiment on overeating reveal about weight gain?
Initially, weight gain was easy, but it became increasingly difficult, requiring participants to eat more to continue gaining weight.
What hormone is secreted from fat cells and is relevant to weight maintenance?
Leptin.
What is the impact of metabolic adaptation on weight loss?
Metabolic adaptation can lead to a decrease in metabolic rate, making it harder to maintain weight loss after dieting.
What is the significance of the energy balance equation in weight maintenance?
It highlights the importance of balancing calories consumed with calories burned to achieve stable weight.
How does the body respond to significant weight loss in terms of metabolism?
The body compensates by decreasing metabolic rate to regain lost weight.
What is the role of basal metabolism in energy expenditure?
Basal metabolism accounts for a significant portion of energy expenditure, even at rest.
How does caloric restriction affect longevity?
Caloric restriction has been linked to increased longevity and reduced disease risk.
What psychological challenges do individuals face after significant weight loss?
They may struggle with maintaining their weight loss due to changes in metabolism and psychological factors.
What is the relationship between caloric intake and weight gain?
Consuming calories above the body's energy needs leads to weight gain.
What factors can influence an individual's metabolism?
Nutrition, physical activity, and hormonal regulation can all influence metabolism.
What are the potential long-term effects of extreme dieting?
Extreme dieting can lead to metabolic suppression and difficulties in maintaining weight loss.
What is the significance of the setpoint theory in weight management?
The setpoint theory suggests that the body has a natural weight range it tries to maintain, which can complicate weight loss efforts.
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis is the active process of maintaining a relatively stable internal environment.
What are the two appetite centers proposed in the dual-center hypothesis?
The ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) and the lateral hypothalamus (LH).
What happens when the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) is lesioned?
Rats with VMH lesions overeat and gain weight.
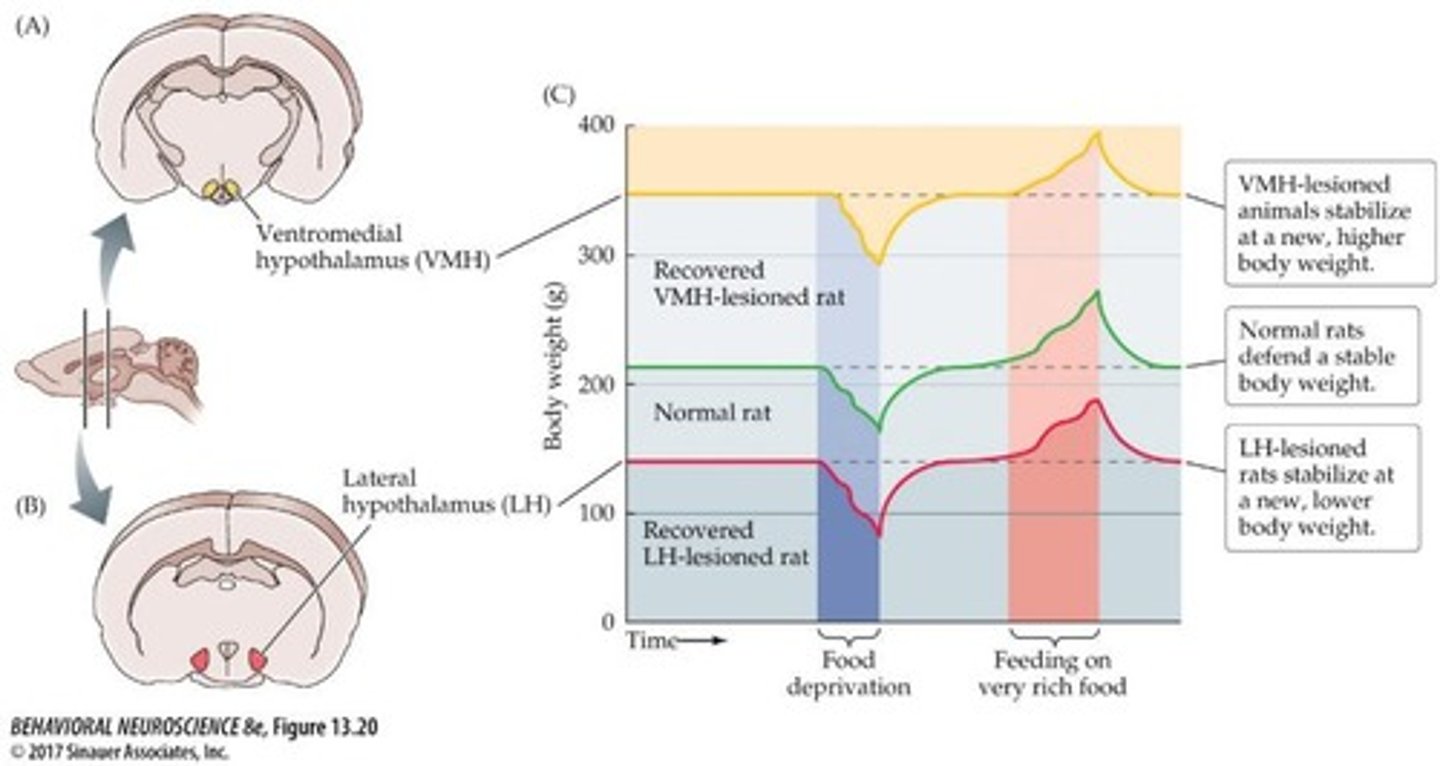
What happens when the lateral hypothalamus (LH) is lesioned?
Rats with LH lesions stop eating and lose weight.
What is glucagon and its role in the body?
Glucagon is a hormone that allows the release of stored energy from glycogen.
How do VMH- and LH-lesioned rats stabilize their body weight?
Both types of lesioned rats stabilize at a new body weight, which they defend against forced feeding or food deprivation.
What role does the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus play in hunger and satiety?
The arcuate nucleus signals hunger when the stomach is empty and suppresses appetite when full.
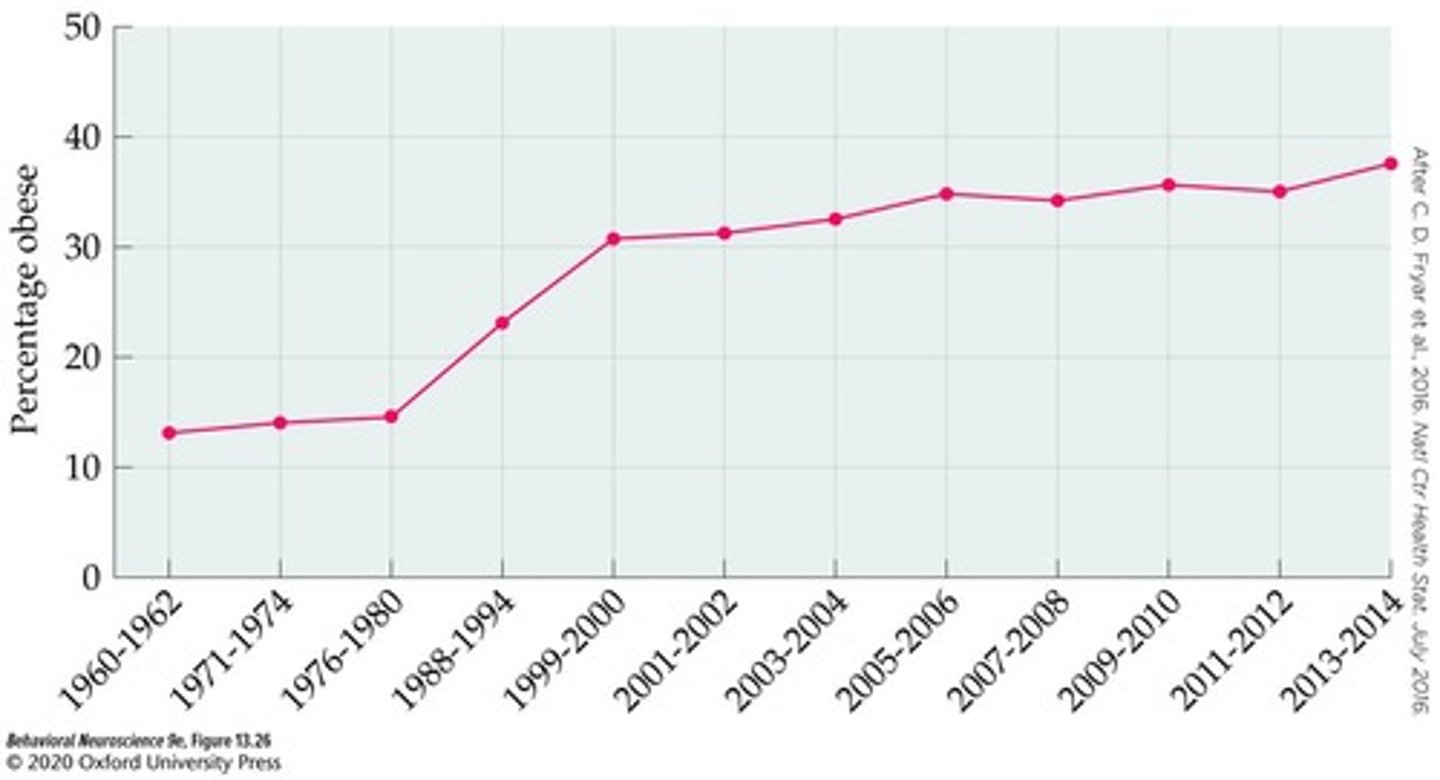
What is the prevalence of obesity in the United States?
Nearly 40% of United States adults are considered obese.
What dietary change is believed to have contributed to the obesity epidemic since 1980?
The replacement of dietary fats with carbohydrates, especially sugar.
What is the epigenome?
The epigenome is a network of chemical compounds that surround DNA and influence gene expression without altering the DNA sequence.
How can parental obesity affect offspring?
Parental obesity may program metabolic disadvantages in offspring through epigenetic transmission.
What is the genetic explanation for obesity related to ob mice?
Ob mice have two copies of the ob gene and regulate their body weight at a higher level, resulting in larger and more numerous fat cells.
What is leptin and its function in the body?
Leptin is a hormone released by fat cells that signals the body about energy reserves.
What happens to ob mice regarding leptin?
Ob mice do not secrete leptin and cannot regulate their fat levels due to a defective leptin gene.
What effect does leptin have on the hypothalamus?
Leptin activates nuclei in the hypothalamus that help regulate appetite.
What is the effect of injecting obese rats with leptin?
Injecting obese rats with leptin causes them to lose weight.
Is there evidence of leptin defects in humans?
There is no real evidence for a defect in leptin in humans.
What brain peptide does leptin suppress the production of?
Leptin suppresses the production and release of neuropeptide Y.
What is the significance of the social view of fat?
The social view of fat has evolved over the years, impacting perceptions of obesity.
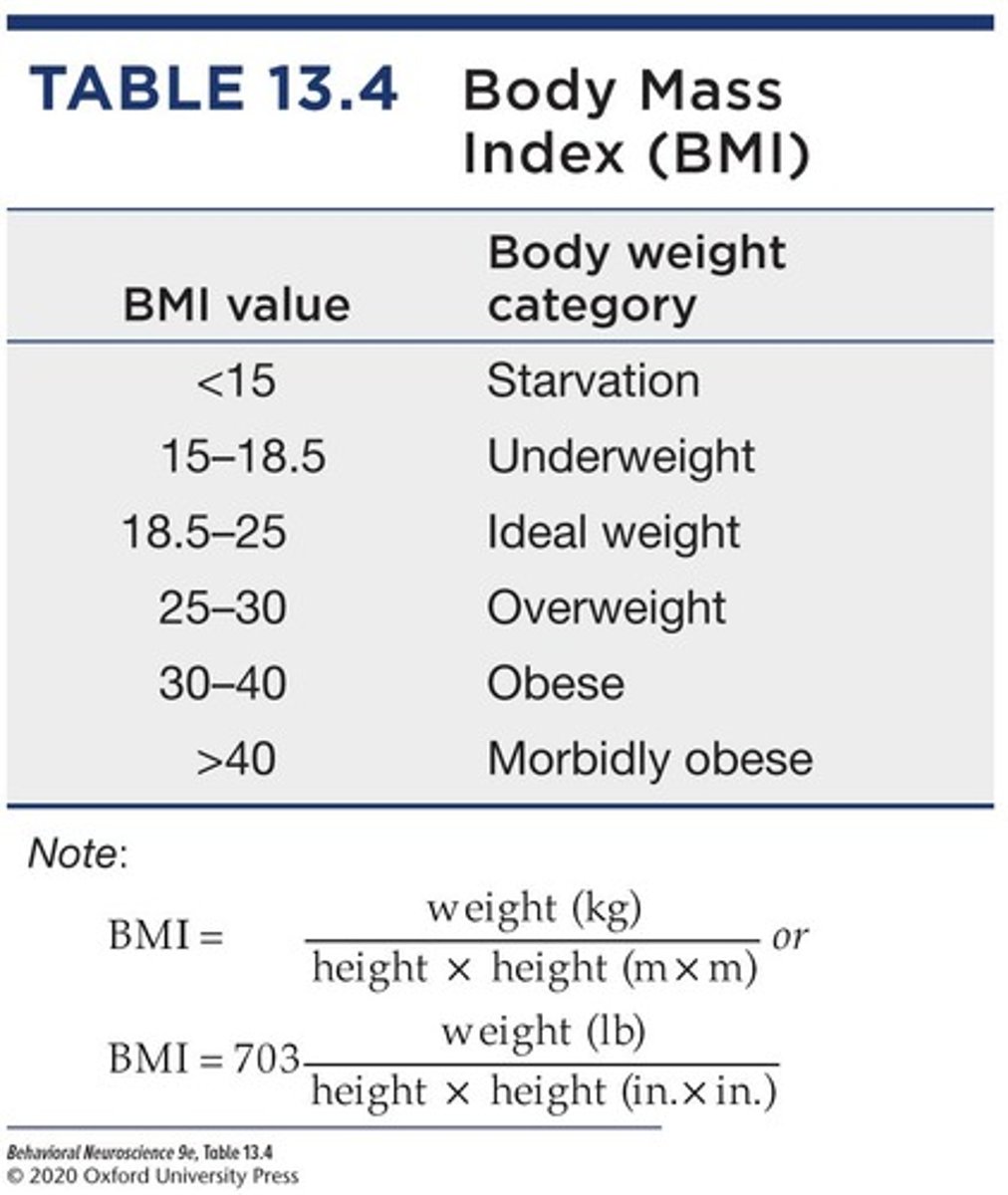
What is the relationship between obesity and body mass index (BMI)?
Obesity is often defined based on body mass index (BMI) and is considered an epidemic in the United States.
What is the role of glucagon-like peptide in appetite regulation?
Glucagon-like peptide mimics GLP-1 and counteracts ghrelin, helping to slow gastric emptying and promote feelings of fullness.
What is the impact of forced feeding or food deprivation on lesioned rats?
Lesioned rats defend their new body weight against both forced feeding and food deprivation.
What hormone is secreted by fat cells and plays a role in appetite regulation?
Leptin
What is the role of NPY neurons in appetite regulation?
NPY neurons promote increased feeding.
What do POMC neurons signal in terms of food intake?
POMC neurons signal a decrease in food intake.
What is the function of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)?
α-MSH signals satiety by suppressing appetite.
What is the effect of AgRP released by NPY neurons?
AgRP competes for melanocortin receptors, reducing the effectiveness of α-MSH in suppressing appetite.
What is sleeve gastrectomy?
A surgical procedure that reduces the stomach to a narrow tube, absorbing fewer nutrients and secreting less ghrelin.
What is the purpose of gastric bypass surgery?
To surgically reduce the stomach to a small pouch and connect it to the small intestine, bypassing part of the intestine to reduce nutrient absorption.
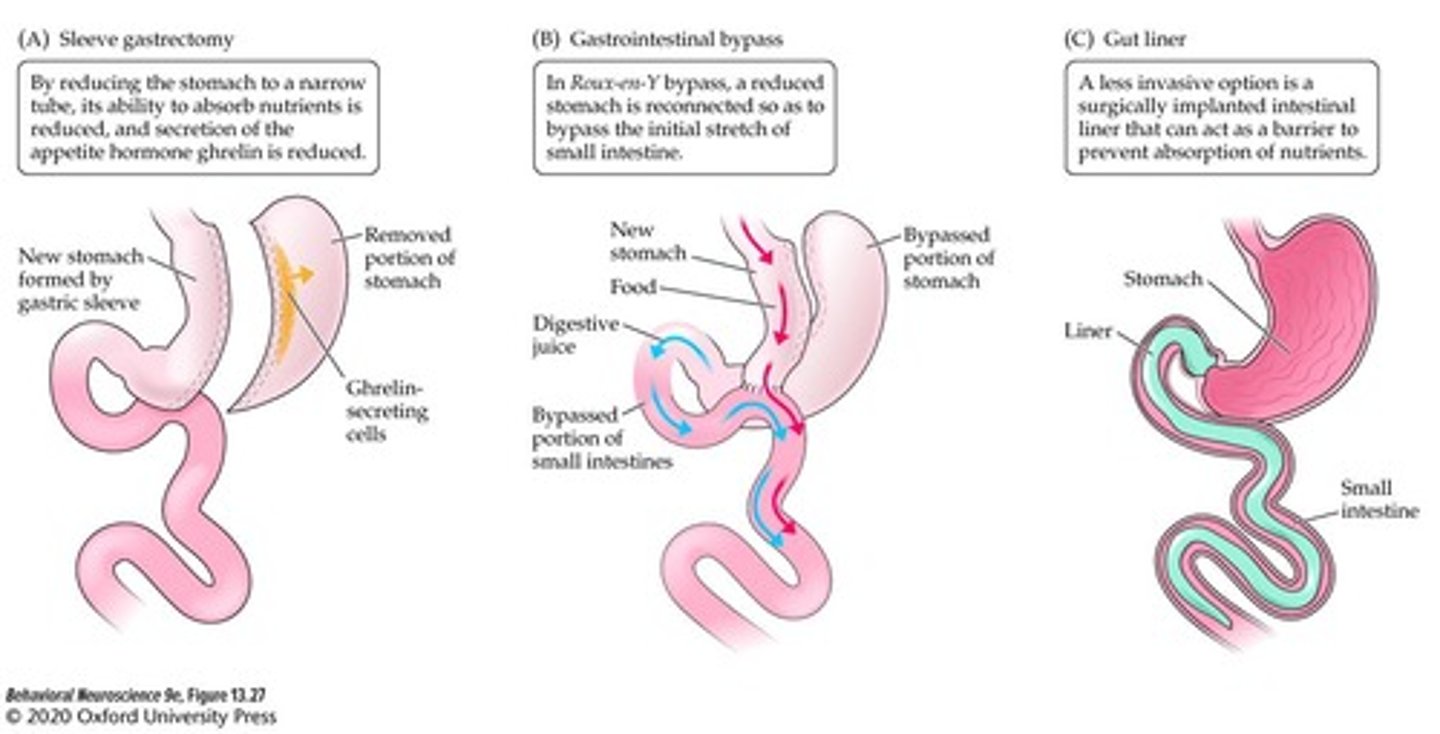
What is a less invasive option for obesity treatment mentioned in the notes?
Implantation of a plastic liner into the small intestine to prevent nutrient absorption.
What are some health risks associated with obesity?
Cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and osteoarthritis.
What is Anorexia Nervosa?
Intentional self-starvation for drastic weight loss, difficult to treat due to various contributing factors.
How does Anorexia Nervosa disproportionately affect individuals?
It disproportionately affects women compared to men.
What are the characteristics of Bulimia Nervosa?
Eating large quantities of food followed by purging through vomiting or laxatives.
What defines Binge Eating Disorder?
Uncontrollable intake of food beyond what is required at least once a week for three months, with a feeling of lack of control.
What are some potential health consequences of Binge Eating Disorder?
Anemia, esophageal damage, and obesity.
What is the relationship between childhood obesity and adult obesity?
Being overweight as a child increases the risk of being obese in adulthood.
What role do gut peptides play in appetite regulation?
Gut peptides like leptin, insulin, ghrelin, PYY3-36, and GLP-1 signal the brain to regulate appetite.
What is the significance of visceral and somatosensory information in appetite regulation?
They are transmitted via spinal nerves and the vagus nerve to help determine appetite.
What is the impact of obesity on mortality risk?
Obesity is associated with increased mortality risk.
What are the effects of surgical procedures for obesity on secondary health problems?
They result in weight loss and improvements in secondary problems like diabetes.
What is the role of the arcuate nucleus in appetite regulation?
It contains neurons that respond to peripheral signals to regulate food intake.
What happens to ghrelin levels after sleeve gastrectomy?
Ghrelin secretion decreases.
What is the psychological aspect of Binge Eating Disorder?
Individuals may not see their eating behavior as a problem and often do not seek treatment.
What is the relationship between obesity and fat distribution?
The distribution of fat can also be associated with health risks.
What is the significance of the vagus nerve in appetite signaling?
It transmits visceral and somatosensory information related to appetite.