Non-gravid Ovary Pathology
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are the 3 main categories of ovarian disease?
Anomalous/congenital
Metabolic (cysts)
Neoplastic
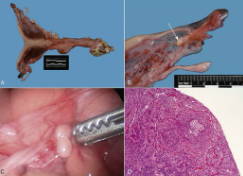
What are the 2 most common congenital conditions of the ovary and give brief description.
Ovarian hypoplasia
Ovarian dysgenesis - often linked to chromosomal abnormalities (monosomy or trisomy)
Ovaries are small and lack follicular activity
4 places cysts in the ovarian parenchyma can derive from
anovulatory Graafian follicles (luteal & follicular cysts)
cystic corpora lutea
cystic rete ovarii
cysts of subsurface epithelial structures
Most cause no problems but some can interfere with normal reproductive cycles
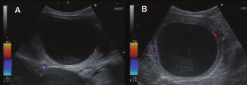
What is this in a cow?
Follicular cyst
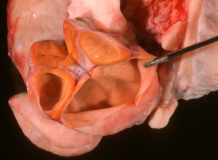
What are these in a cow
Left = follicular cyst
Right = luteal cyst
Behavioural and physiological changes associated with folicular cysts in cattle
Frequent intermittent oestrus
Nymphomania
Sexual quiescent/anoestrous
Follicular cysts can be 25-60mm
Steroidogenesis (oestrogens, progesterone, androgens)
Signs associated with luteal cysts in cattle
Anoestrus
Thick, yellow lutinized wall)
Primarily progesterone production
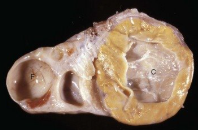
What is this condition?
Cystic corpora lutea = variation of normal luteal structure
animal can be pregnant
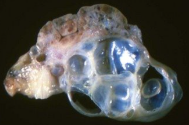
What is this condition? What are associated clinical signs?
Cystic rete ovarii (guineapig)
bilateral non-pruritic alopecia
clitoral hypertrophy
nipple hyperkeratosis
behavioural changes

Describe pathophysiology/pathogenesis of cystic subsurface epithelial structures
Peritoneal cells covering ovary can develop multiple (or a single) cysts
Can undergo papillary hyperplasia and neoplastic transformation
Usually adenomas but can be carcinomas
No hormones produced
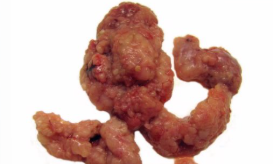
What is this condition? Describe pathogenesis
Papillary cystadenoma/cystadenocarcinoma (surface epithelium and SES tumour)
Neoplasia from surface epithelium covering ovary
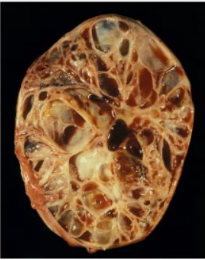
What is this condition and associated clinical signs
Granulosa cell tumour - most common ovarian tumour of the mare (sex cord stromal tumour)
Usually benign
Behavioural/reproductive abnormalities
Inhibin = lack of cycling in opposite ovary
Oestrogen = nymphomania, prolonged oestrus
Progesterone = anoestrus
Testosterone = stallion-like behaviour
Always increased levels of anti-Mullerian hormone
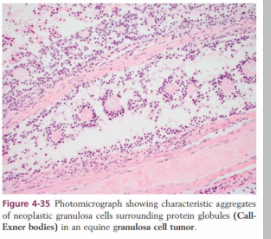
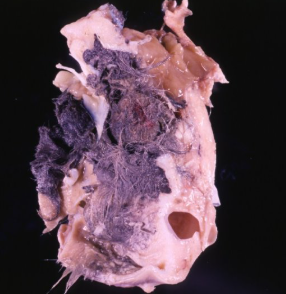
What is this condition?
Teratoma (germ cell tumour)