(COMPLETED) UPPER LIMB - MUSCLE AND FASCIA
1/186
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
- What two main parts make up the skeletal system?
Axial and appendicular skeleton
- Name three examples of long bones.
Humerus, femur, metacarpals
- What type of bones are found in the tarsus and carpus?
Short bones
- Give an example of a sesamoid bone.
Patella
- What bones make up the pectoral girdle?
Clavicle and scapula
- Which end of the clavicle articulates with the sternum?
Sternal end
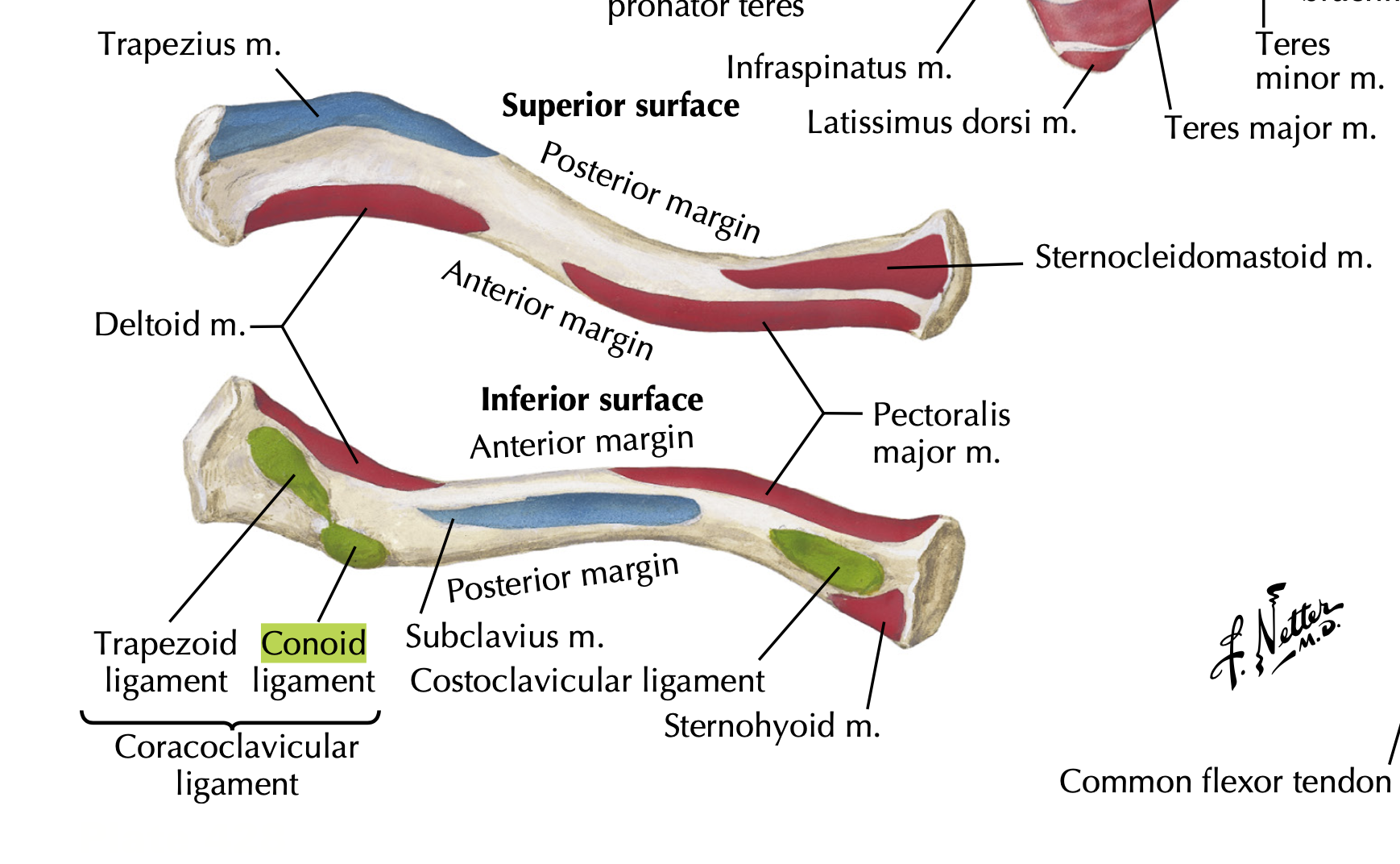
- What ligament attaches to the conoid tubercle?
Conoid ligament
- What are the names of the two fossae located on the posterior surface of the scapula?
Supraspinous and infraspinous fossa
- With which bone does the glenoid fossa articulate?
Humerus
- What is the origin of the long head of the biceps brachii?
Supraglenoid tubercle
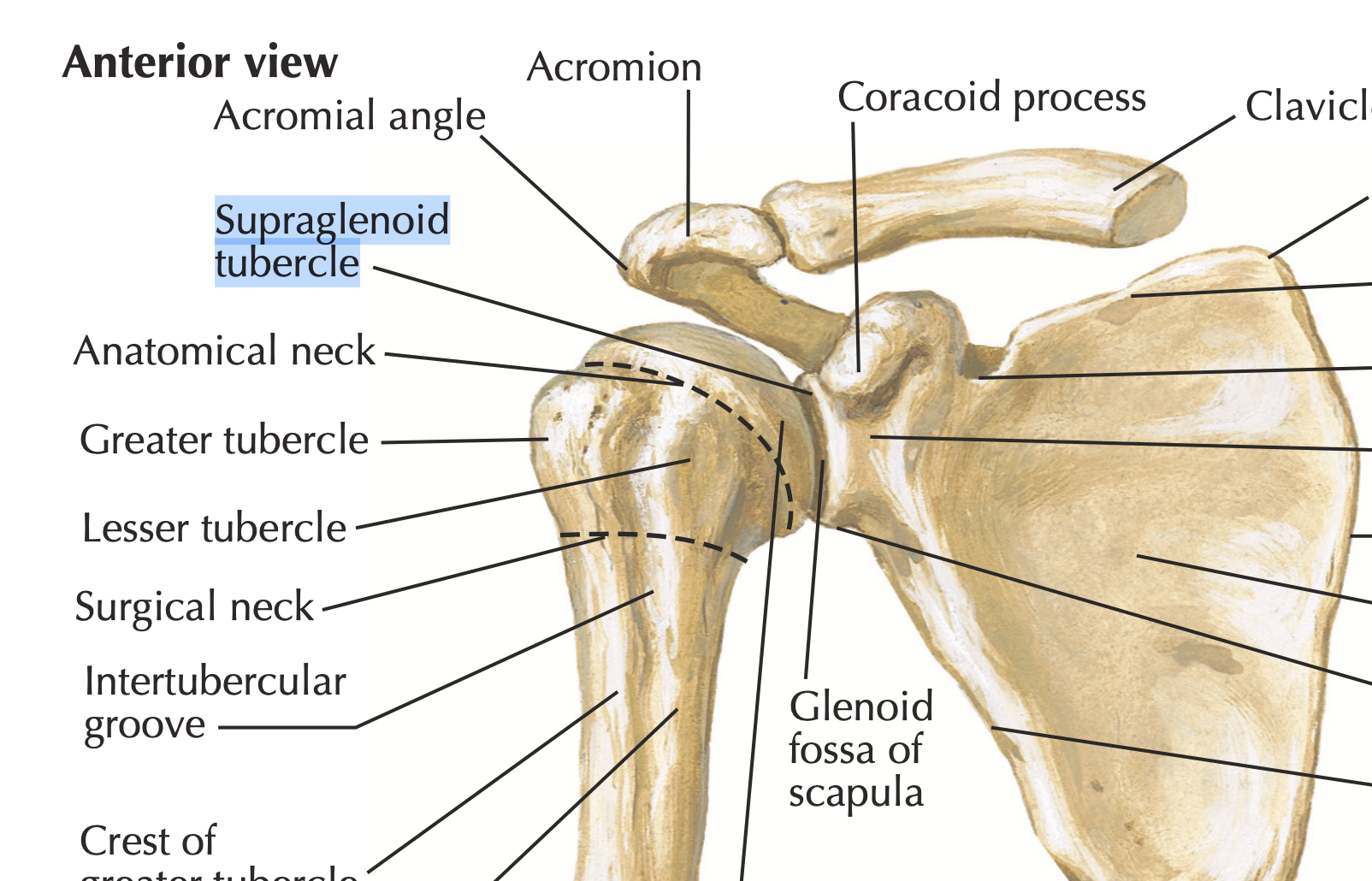
What is the most common site of humeral fracture in the elderly? Surgical or Anatomical Neck?
Surgical neck
- What muscle attaches to the deltoid tuberosity?
Deltoid muscle
- What nerve is housed by the spiral/radial groove?
Radial nerve
- Which bone is lateral and shorter: the radius or the ulna?
Radius
- What part of the ulna articulates with the trochlea of the humerus?
Trochlear notch
- What is the function of the interosseous membrane?
Stabilizes the relationship between the radius and ulna
- Name the eight carpal bones.
Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
- What is the name of the tunnel through which the ulnar nerve and arteries pass in the wrist?
Tunnel of Guyon
- How many metacarpals are in each hand?
Five
- How many phalanges are in each finger?
Three
- Which joint is the only bone-to-bone attachment between the upper limbs and the axial skeleton?
Sternoclavicular joint
- What type of joint is the glenohumeral joint?
Ball and socket joint
- Name the four rotator cuff muscles.
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
- What type of joint is the acromioclavicular joint?
Plane joint
- What type of joint is the elbow joint?
Hinge joint
- What movements are allowed by the proximal radioulnar joint?
Pronation and supination
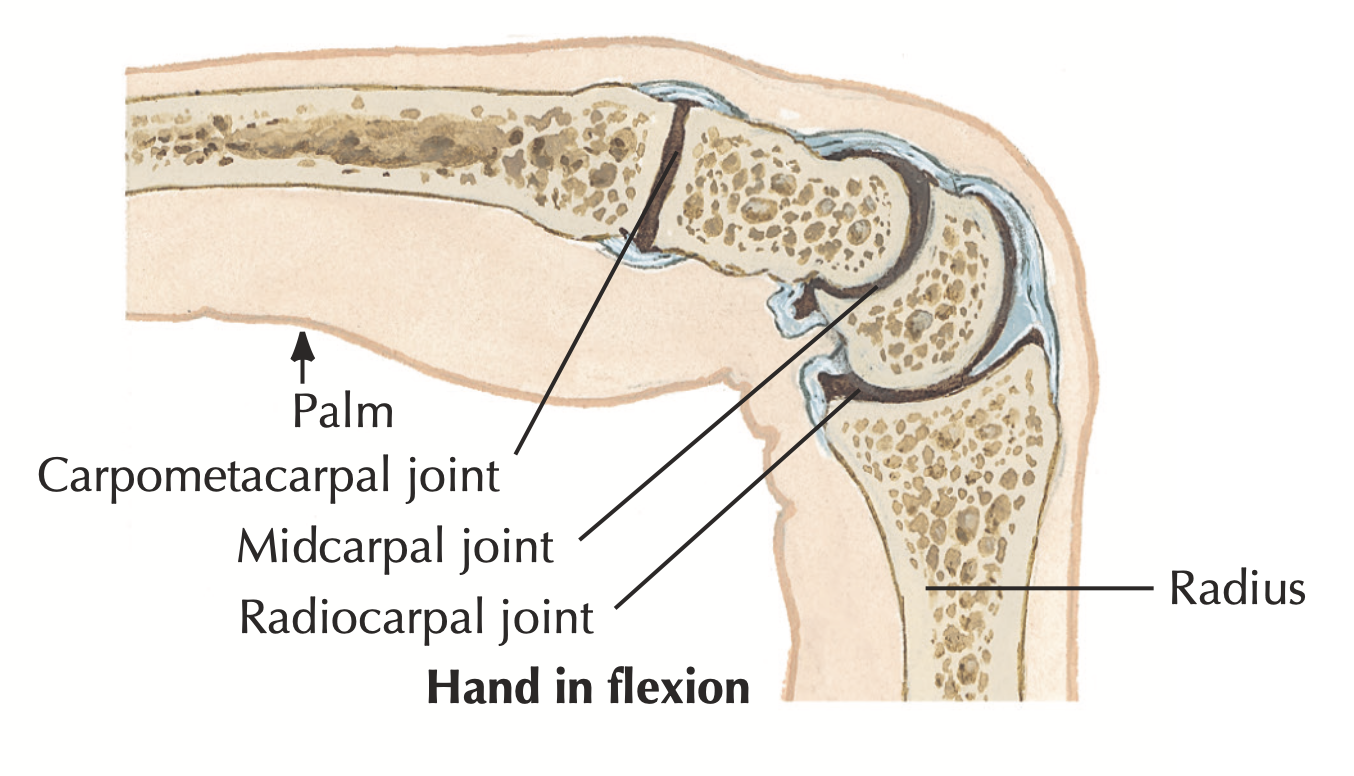
- What type of joint is the radiocarpal joint?
Condyloid joint
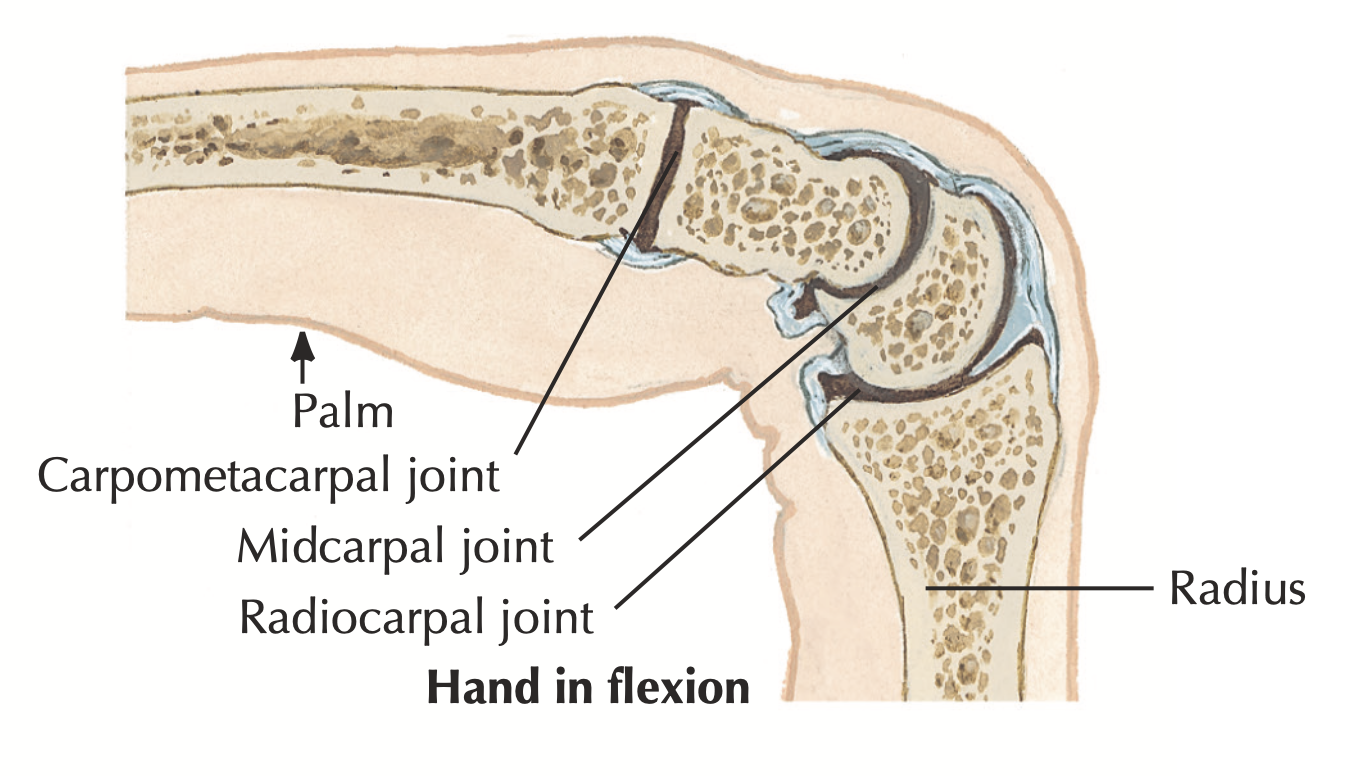
- Give an example of a saddle joint in the hand.
Carpometacarpal joint
- What type of tissue is deep fascia primarily composed of?
Dense connective tissue
- What fascia covers the deltoid muscle?
Deltoid fascia
- What does the pectoralis fascia become laterally?
Axillary fascia
- What is the deep fascia enclosing the arm called?
Brachial fascia
- What fascia forms the floor of the axilla?
Axillary fascia
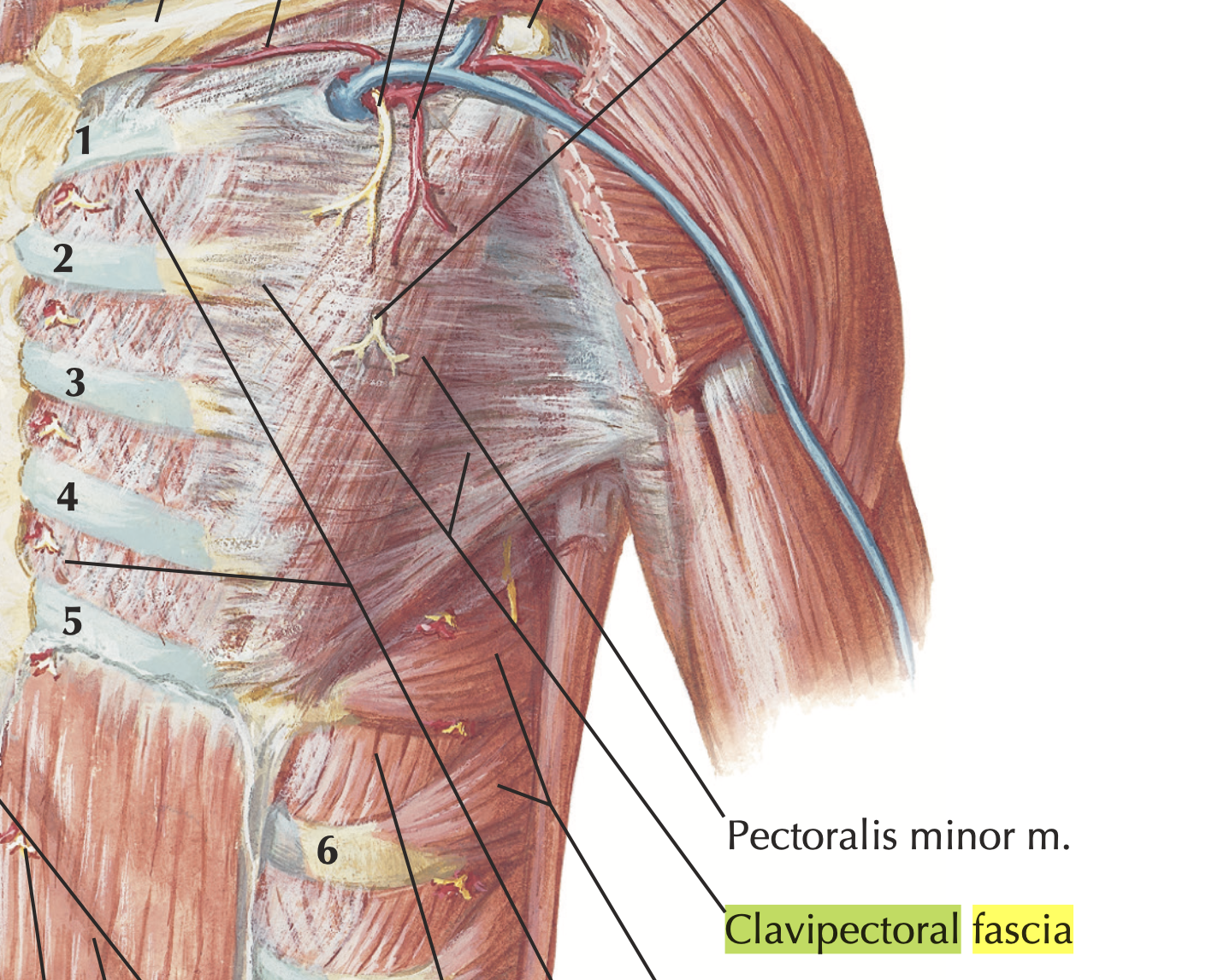
- What two muscles are enclosed by the clavipectoral fascia?
Subclavius and pectoralis minor
- What three structures pass through the costocoracoid membrane?
Cephalic vein, thoracoacromial artery, lateral pectoral nerve
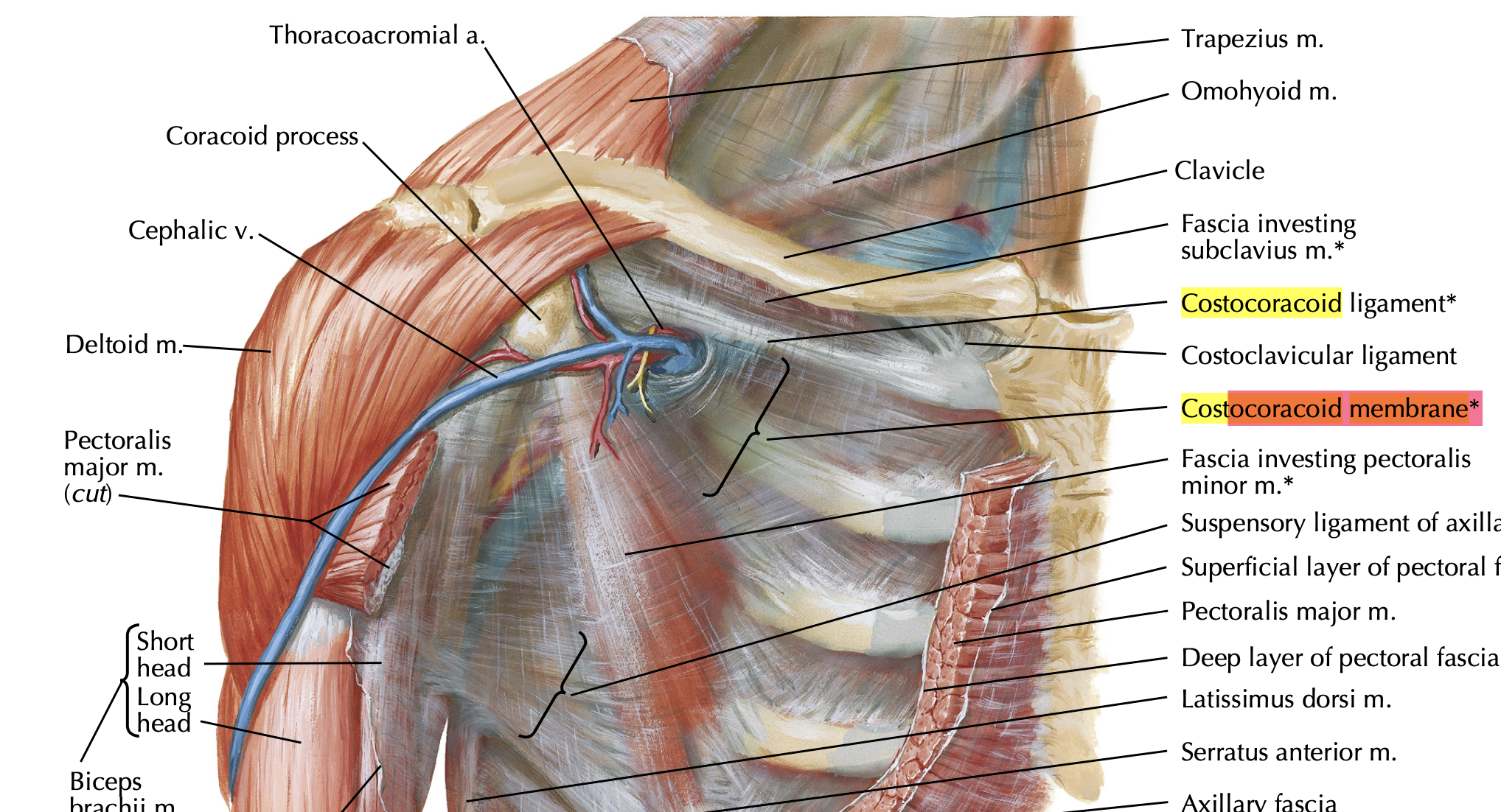
- What is the function of the suspensory ligament of the axilla?
Supports and pulls axillary fascia upward during arm abduction
- Name the two compartments of the arm.
Anterior and posterior
- What membrane is found between the radius and ulna?
Interosseous membrane
- Name the five compartments of the palm.
Hypothenar, thenar, central, adductor, interosseous
- What is the function of extrinsic muscles in the pectoral girdle?
Act on the shoulder girdle but are not located within it
- What is the general action of muscles in the anterior portion of the arm?
Flexion
- What is the general action of muscles in the posterior portion of the arm?
Extension
- What type of muscle is the pectoralis major?
Convergent
- What is the main action of the pectoralis major?
Adducts and medially rotates the humerus
- What nerve innervates the pectoralis minor?
Medial pectoral nerve
- What process of the scapula does the pectoralis minor attach to?
Coracoid process
- What is the main action of the pectoralis minor?
Stabilizes the scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly
- Where is the subclavius muscle located?
Inferior to the clavicle
- What nerve innervates the subclavius?
Nerve to subclavius
- What is the main action of the subclavius?
Anchors and depresses the clavicle
- What is another name for the serratus anterior?
Boxer’s muscle
- What nerve innervates the serratus anterior?
Long thoracic nerve
- What is the main action of the serratus anterior?
Protracts the scapula and holds it against the thoracic wall
- What condition results from paralysis of the serratus anterior?
Winging of the scapula
- Name the superficial muscles of the posterior axio-appendicular group.
Trapezius and latissimus dorsi
- Name the deep muscles of the posterior axio-appendicular group.
Levator scapulae and rhomboids
- What shape is the trapezius muscle?
Diamond or trapezoid
- What are the three different fiber directions of the trapezius?
Descending, middle, and ascending
- What is the main action of the middle fibers of the trapezius?
Retract the scapula
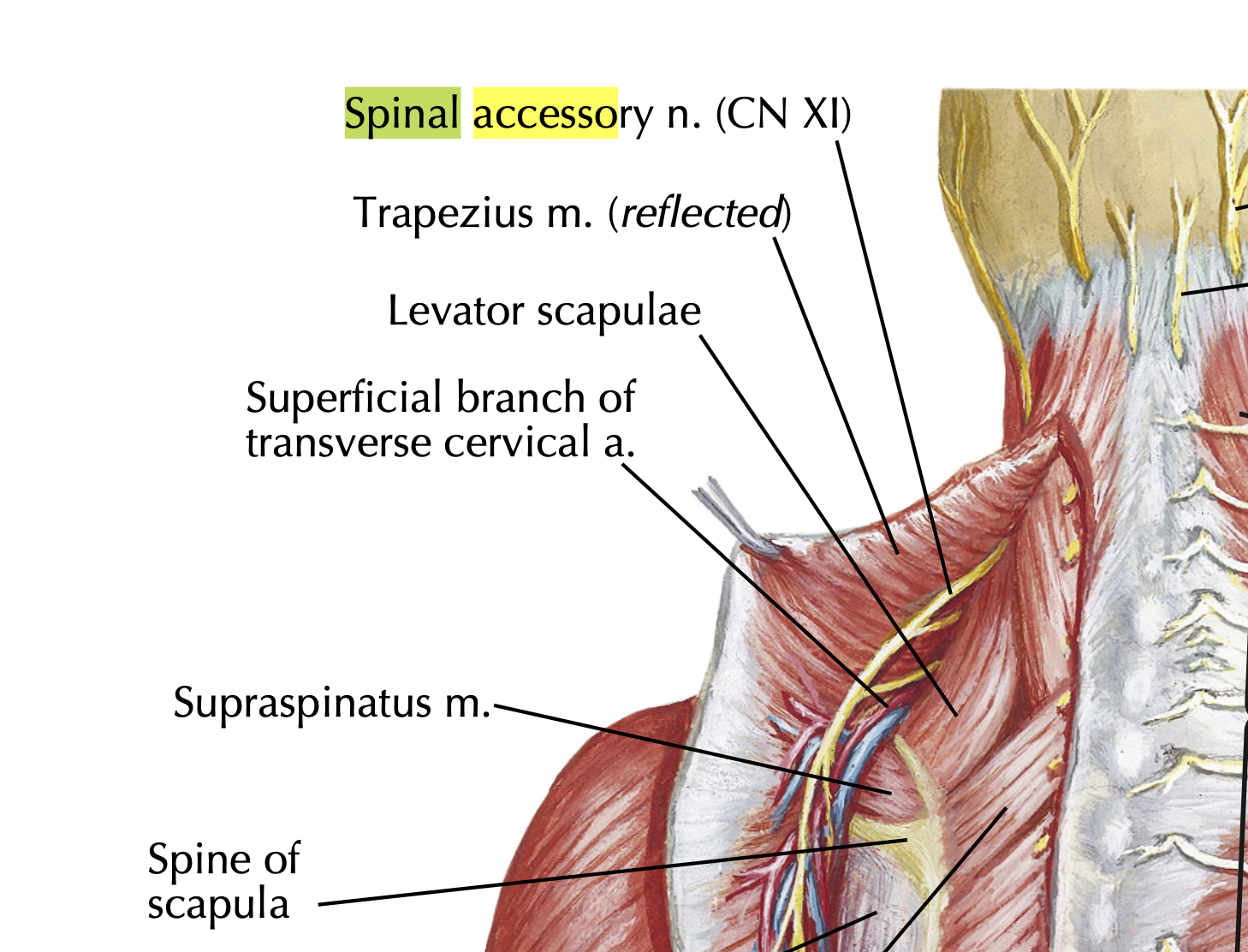
- What nerve innervates the trapezius?
Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- What is the shape of the latissimus dorsi muscle?
Large, fan-shaped
- What is the insertion point of the latissimus dorsi?
Floor of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
- What nerve innervates the latissimus dorsi?
Thoracodorsal nerve
- What are the main actions of the latissimus dorsi?
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the humerus
- Where does the levator scapulae lie relative to the sternocleidomastoid?
Deep
- What is the main action of the levator scapulae?
Elevates the scapula
- What nerves innervate the levator scapulae?
Dorsal scapular and cervical nerves
- What shape are the rhomboid muscles?
Rhomboid
- What action do the rhomboids perform against the serratus anterior?
Retraction of the scapula
- Which rhomboid muscle is located superior to the other?
Rhomboid minor
- What is another name for the nuchal ligament?
Paddywhack
- What type of muscles are the posterior scapulohumeral muscles?
Intrinsic shoulder muscles
- How many muscles are in the posterior scapulohumeral group?
Six
- Which muscle is not part of the rotator cuff: teres major or teres minor?
Teres major
- What are the three parts of the deltoid muscle?
Clavicular, acromial, and spinal
- What is the action of the acromial part of the deltoid?
Abduction of the arm
- What nerve innervates the deltoid?
Axillary nerve
- What is the main action of the teres major?
Adducts and medially rotates the arm
- What is the main action of the rotator cuff muscles?
Stabilize the glenohumeral joint
- What is the only attachment of the scapula to the axial skeleton?
Acromioclavicular joint (False: The scapula is not attached to the axial skeleton. Only the clavicle is attached via the sternoclavicular joint.)
- What is the main action of the supraspinatus?
Initiates and assists deltoid in abduction of the arm
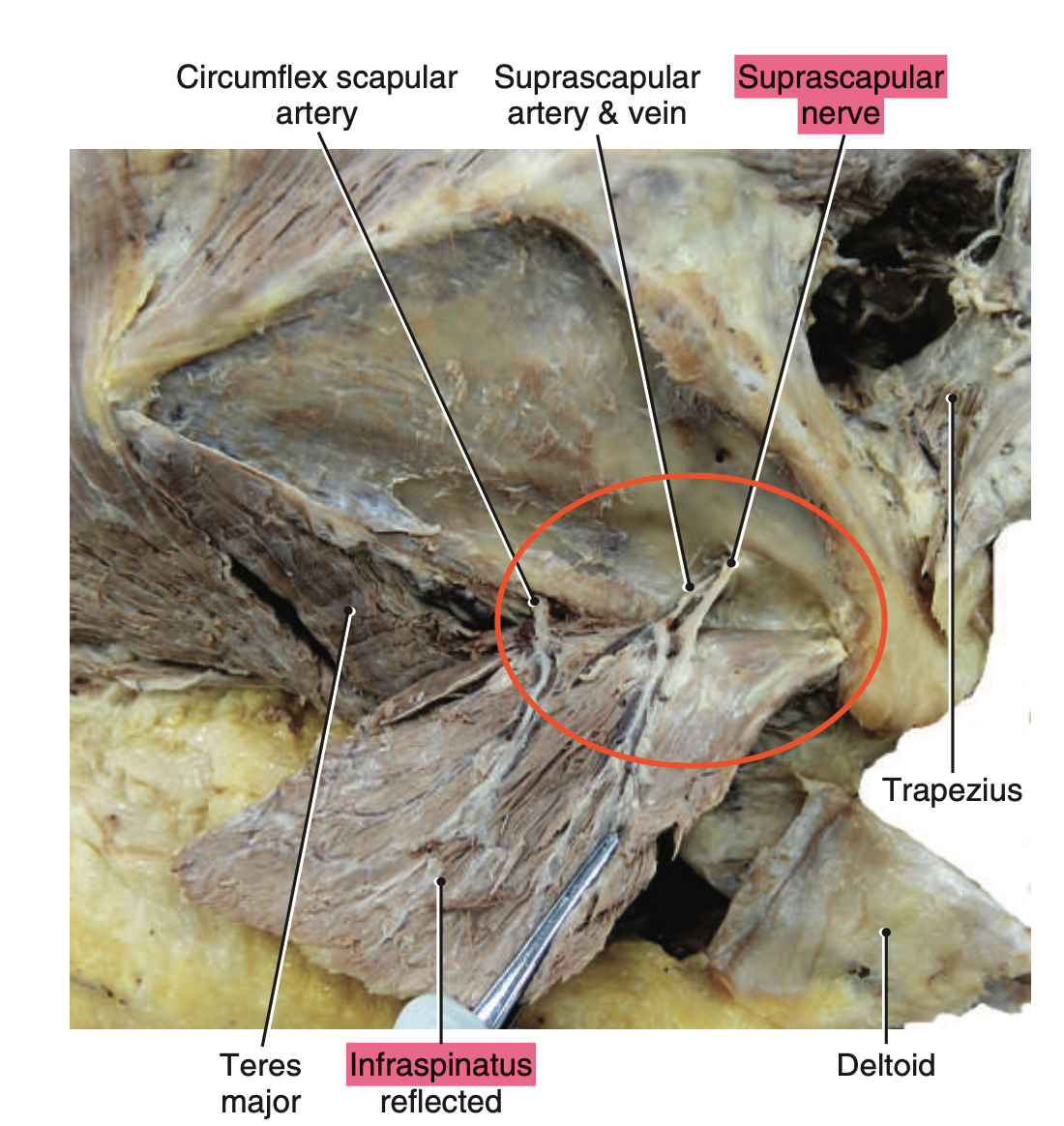
- What nerve innervates the supraspinatus?
Suprascapular nerve
- What is the main action of the infraspinatus?
Powerful lateral rotator of the arm
- What nerve innervates the infraspinatus?
Suprascapular nerve
- What two spaces does the teres minor form a border of?
The Superior Border of:
Upper triangular space & Quadrangular space
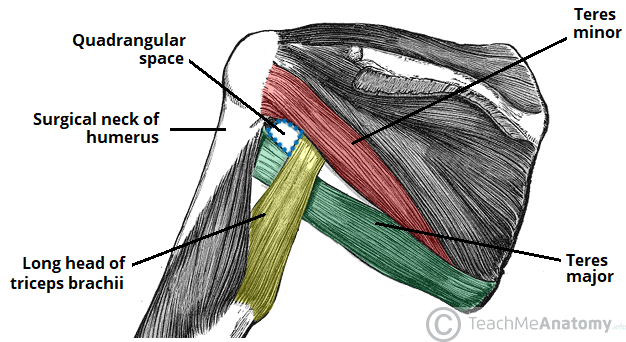
- What nerve innervates the teres minor?
Axillary nerve
- What is the main action of the subscapularis?
Medial rotator of the humerus, adducts humerus
- What nerves innervate the subscapularis?
Upper and lower subscapular nerves
- What type of injury may damage the rotator cuff?
Musculotendinous injury
- What groove contains the cephalic vein?
Deltopectoral groove
- What lies underneath the skin?
Superficial fascia
- What is another name for subcutaneous tissue?
Superficial fascia
- What do intermuscular septa do?
Compartmentalize and invest the muscles
- What does the pectoralis fascia enclose?
Entire pectoralis major muscle
- What is the axillary fascia?
Deep fascia underneath the fat pad in the armpit
- What vein drains into the axillary vein?
Cephalic vein
- What artery gives rise to the clavicular, acromial, deltoid, and pectoral arteries?
Thoracoacromial artery
- What nerve innervates the pectoralis major?
Lateral pectoral nerve
- What does the clavipectoral fascia become inferiorly?
Suspensory ligament of axilla
- What fascia does the suspensory ligament of the axilla converge with?
Pectoralis fascia