Biology DAT
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following refers to the minimal amount of air always present in the lungs?
Residual Volume
2
New cards
Which of the following refers to the volume of air moving in the lungs during normal breathing?
Tidal volume
3
New cards
The maximum volume of air that can be expired after a maximum inhalation
Vital Capacity
4
New cards
Which of the following are responsible for the alignment of the chromosomes along the metaphase plate (equatorial plate) during mitosis?
Centrosomes
5
New cards
monosaccharide
a single sugar molecule (glucose and fructose)
6
New cards
Lipids
hydrophobic molecules that function in insulation, energy storage, make up structural components, and participate in endocrine signaling
7
New cards
Triglycerides
Describe structures consisting of three fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol backbone. Can be saturated or unsaturated. Are lipids
8
New cards
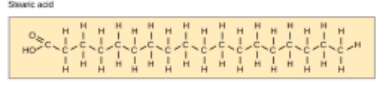
Saturated tryglycerides
contain no double bonds and have straight chains; are bad for health
9
New cards
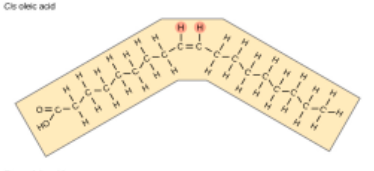
Unsaturated triglycerides
contain double bonds that cause kinks in chains; are better for health
10
New cards
Phospholipids
Are lipids composed of two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone
11
New cards
Amphipathic
Describes a molecule that has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties
12
New cards
Steroids
A lipid; comprised of three 6-membered rings and one 5-membered ring; include hormones and cholesterol; 4 ringed structures
13
New cards
Heterocyclic compound
cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its rings.
14
New cards
Adipocytes
A lipid; specialized fat cells in two categories: **white** and **brown** fat cells
15
New cards
White fat cells (category of adipocytes)
Composed mainly of triglycerides with a thin layer of cytoplasm around it
16
New cards
Brown fat cells (category of adipocytes)
have considerable cytoplasm, lipid droplets scattered throughout, and lots of mitochondria
17
New cards
Glycolipids
similar to phospholipids but have a carbohydrate group instead of a phosphate group
18
New cards
Lipoproteins
Lipids are insoluble so they are transported in the blood via these, which are lipid cores surrounded by phospholipids and apolipoproteins
19
New cards
In cold weather
Cell membranes become more rigid. In order to avoid cell membrane rigidity, cholesterol and mono and polyunsaturated fatty acids are incorporated into the membrane (in fatty acids)
20
New cards
In warm weather
cell membranes become more fluid ad flexible. In order to avoid cell membrane collapse, cholesterol is added to restrict movement. (in fatty acids)
21
New cards
Glycosidic bonds are considered which type of bond?
Covalent
22
New cards
Storage proteins
casein in milk, ovalbumin in egg whites, and zein in corn seeds
23
New cards
transport proteins
hemoglobin carries oxygen, cytochromes carry electrons
24
New cards
Enzymes
catalyze reactions in both forward and reverse directions; almost always considered proteins
25
New cards
Cofactors
non-protein molecules that assist enzymes; the union of this and enzyme is a holoenzyme
26
New cards
Simple Protein classification
Formed entirely of amino acids (ex Albumins & Globulins, Scleroprotein)
27
New cards
Conjugated Protein classification
Simple protein + non-protein (ex. lipoprotein, mucoprotein, chromoprotein, metalloprotein)
28
New cards
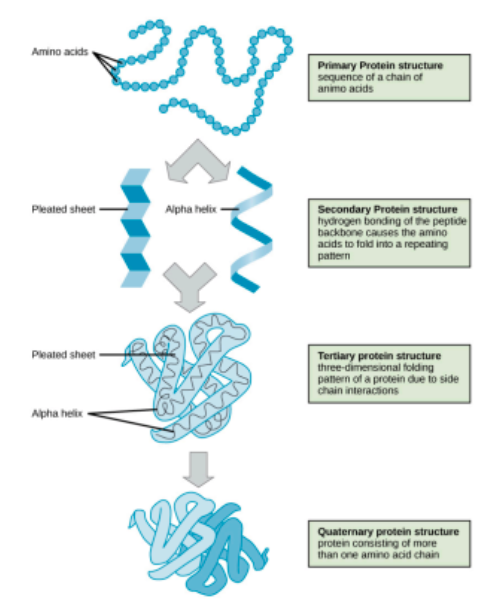
Primary Protein structure
Sequence of amino acids connected by peptide bonds
29
New cards
Secondary Protein structure
3D shape resulting from hydrogen bonding between amino and carboxyl groups of adjacent amino acids (__**alpha helix or beta sheet)**__
30
New cards
Tertiary Protein Structure
3D structure that forms primarily due to non-covalent interactions between amino acid R groups (non-covalent bonds including H-bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic effect)
31
New cards
Disulfide bonds
Strong type of covalent bond between cysteines
32
New cards
Cysteine
a sulfur containing amino acid
33
New cards
Quaternary Protein structure
3D shape of a protein that is a grouping of two or more separate peptide chains
34
New cards
Protein Structures
35
New cards
3 main protein categories
Globular proteins, Fibrous/structural proteins, Membrane proteins
36
New cards
Globular proteins
somewhat water soluble, mostly dominated by tertiary structure, have a diverse range of functions
37
New cards
Fibrous/structural proteins
not water soluble, mostly dominated by secondary structure, are made of long polymers, function to maintain and add strength to cellular and matrix structure
38
New cards
Membrane proteins
Includes proteins that function as membrane pumps, channels, or receptors
39
New cards
Protein Denaturation
the protein is reversed back to its primary structure; usually irreversible
40
New cards
Protein digestion
Eliminates all protein structure, including primary structure
41
New cards
Nucleotides
Monomers that make up nucleic acids. Consists of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group
42
New cards
Nucleosides
sugar+nitrogenous base
43
New cards
Purines (nitrogenous bases)
consist of 2 rings; include adenine and guanine
44
New cards
Pyrimidines (nitrogenous bases)
consists of 1 ring, and include cytosine, uracil, and thymine
45
New cards
Cell theory
states that
1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure, function, and organization in all organisms
3. All cells come from preexisting, living cells
4. Cells carry hereditary information
1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure, function, and organization in all organisms
3. All cells come from preexisting, living cells
4. Cells carry hereditary information
46
New cards
RNA World Hypothesis
proposes that self-replicating RNA molecules were precursors to current life. Also states that RNA stores genetic information like DNA and catalyzes chemical reactions
47
New cards
Central Dogma of Genetics
states that biological information cannot be transferred backwards from protein to either protein or nucleic acid. Information must travel DNA → RNA→proteins
48
New cards
Stereomicroscope
Uses visible light to view the surface of a sample
49
New cards
Compound microscope
Uses visible light to view a thin section of a sample
50
New cards
Phase Contrast Microscope
Uses light phases and contrast for a detailed observation of living organisms, including internal structures if thin
51
New cards
Anabolic
Small molecules are assembled into large ones. Energy is required
52
New cards
Catabolic
Large molecules are broken down into small ones. Energy is released
53
New cards
enzymes are…
Globular proteins that act as catalysts
54
New cards
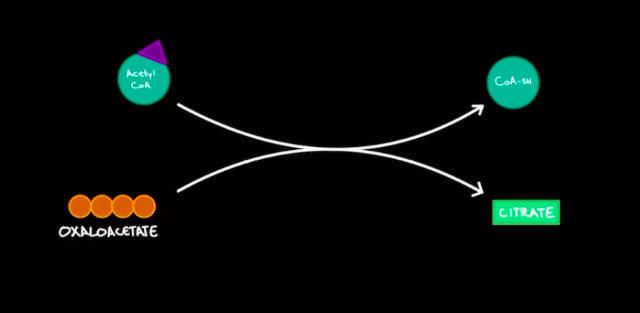
Krebs Cycle
* Occurs in mitochondrial matrix
* aerobic process
* A step in cellular respiration
* aerobic process
* A step in cellular respiration
55
New cards
Pyruvate decarboxylation
* Occurs in mitochondrial matrix
* A step in cellular respiration
* A step in cellular respiration
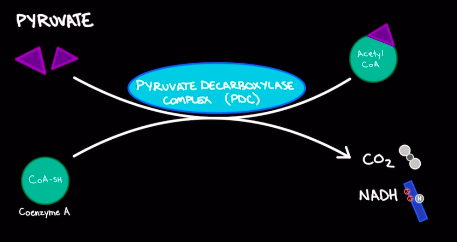
56
New cards
Membrane proteins
* Channel Proteins
* Recognition Proteins
* Ion channels
* Porins
* Carrier proteins
* Transport proteins
* Adhesion proteins
* Receptor proteins
\
* Recognition Proteins
* Ion channels
* Porins
* Carrier proteins
* Transport proteins
* Adhesion proteins
* Receptor proteins
\
57
New cards
Channel proteins
provide a passageway through the membrane for hydrophilic, polar, and charged substances
58
New cards
Recognition proteins
type of glycoprotein that is used to distinguish between self and foreign
59
New cards
Ion channels
used to pass ions across the membrane and referred to as gated channels in nerve and muscle cells
60
New cards
Porins
allow the passage of certain ions and small polar molecules
61
New cards
Which membrane protein increases the rate of water passing in kidney and plant root cells?
Porins
62
New cards
Which membrane protein is specific to movement across the membrane via integral membrane protein?
Carrier Proteins
63
New cards
Active transport requires…
ATP
64
New cards
facilitated diffusion does not…
require ATP
65
New cards
Receptor proteins
serve as binding sites for hormones and other trigger molecules
66
New cards
Glycocalyx
a carbohydrate coat that covers the outer face of the cell wall of some bacteria and the outer face of the plasma membrane in some animal cells
67
New cards
The nucleoid is found only in…
prokaryote cells
68
New cards
Peroxisomes
Organelles common in the liver and kidney that function to breakdown substances
69
New cards
phospholipid membrane is made of…
phosphate head and two fatty acids
70
New cards
The phospholipid membrane is…
amphipathic
71
New cards
Amphipathic
having both a polar and non-polar portion
72
New cards
The phosphate head in phospholipid membranes is ____ __while the fatty acid tails are______
hydrophilic, hydrophobic
73
New cards
What most easily diffuses through the phospholipid bilayer?
hydrophobic molecules
74
New cards
Cholesterol is used for what in the animal cell membrane?
Structural support
75
New cards
What is used for structural support in prokaryote cell membranes?
Hopanoids
76
New cards
What is used for structural support in the cell membrane of plant cells?
Sterols
77
New cards
What is the purpose of MHC I molecules?
to distinguish self from foreign cells
78
New cards
How do Rhizopoda move in their environment?
Pseudopodia
79
New cards
Organisms that can be classified as slime or water molds fall under which kingdom?
Protista
80
New cards
similarity between fungus-like protists and fungus?
Both reproduce by forming spores
81
New cards
Saprobes
Obtain energy from dead, decaying matter
82
New cards
When slime molds experience food deprivation what is excreted?
cAMP
83
New cards
When cellular slime molds are in harsh conditions, what do individuals do?
aggregate to form a moving slug
84
New cards
The 3 main modes of transportation across a cell membrane
simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport
85
New cards
The order of stages in interphase
G1→ G0 → S → G2
86
New cards
Vegetative Propagation
A form of asexual reproduction in plants that produces genetically identical offspring
87
New cards
Fern
Vascular, seedless plant. Phylum pterophyta
88
New cards
Dicot angiosperms have
two cotyledon, broad leaf, network of veins, vascular bundles in a ring, flowers in multiples of 4 or 5, taproots
89
New cards
monocot angiosperms have
single cotyledon, long narrow leaf, parallel veins, vascular bundles scattered, flowers in multiples of 3, fibrous root system
90
New cards
What plant tissue type makes up majority of the plants mass?
Ground tissue
91
New cards
What is the most prominent ground tissue in plants?
Parenchyma
92
New cards
The left lung is ____ and consists of..
smaller, 2 lobes
93
New cards
The right lung is ____ and consists of …
larger, 3 lobes
94
New cards
Pleurae
membranous cover surrounding lungs; has two layers
95
New cards
Two layers of the pleurae
Visceral and parietal
96
New cards
The space in between the visceral and parietal is called
the intrapleural space
97
New cards
Visceral pleura
Lines the surface of the lungs
98
New cards
Parietal pleura
lines the inside of the chest cavity
99
New cards
Circulatory system
Responsible for circulating and transporting nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and red blood cells throughout the body
100
New cards
Protozoans
Unicellular animal-like protists