Physiology: Autonomic Nervous system
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Neurons - Sympathetic vs parasympathetic
Sympathetic:
preganglionic nerves are typically short while postganglionic nerves are relatively long
Parasympathetic:
preganglionic nerves are relatively long with short postganglionic nerves
Autonomic neurotransmitters - nerves
Preganglionic nerves: acetylcholine (cholinergic)
Postganglionic sympathetic: noradrenaline (adrenergic)
Postganglionic parasympathetic: acetylcholine (cholinergic)
Somatic Neurotransmitter
Somatic neurons activate skeletal muscle
Activated by a cholinergic pathways
Sympathetic activation: adrenal gland
Exception: No postganglionic neuron
Preganglionic nerve releases acetylcholine
Stimulates chromaffin cell to release noradrenaline (20%) (norepinephrine) and adrenaline (80%) (epinephrine)
Sympathetic activation: sweat glands
sweat glands in the skin use acetylcholine at the ganglion and at the receptor cell.
Sympathetic - Adrenergic receptors: Alpha 1
Tissue: Vascular smooth muscle (most)
Effect: Stimulation - contraction
Affinity: Higher in noradrenaline than adrenaline
Sympathetic - Adrenergic receptor - Alpha 2
Tissue: Endocrine - pancreas
Effect: inhibitory - reduced insulin release
Affinity: Higher noradrenaline than adrenaline
Sympathetic - Adrenergic receptor - Beta 1
Tissue: Heart
Effect: Stimulation - increased force and rate of
Affinity: Equal noradrenaline and adrenaline
Sympathetic - Adrenergic receptor - Beta 2
Tissue: Airway smooth muscle and some vascular
Effect: Inhibitory - relaxation (vasodilation)
Affinity: A lot higher in adrenaline than noradrenaline
Adrenaline
EFFECTS ARE DOES DEPENDANT
At low doses, adrenaline attach to high affinity b2: vasodilation
At high doses, adrenaline will attach to the abundant a1 receptors: vasoconstriction
Acetylcholine
Nicotinic receptors: located on the postgangioliv cell body of autonomic nerves and skeletal muscle in the somatic division
Target cells expression muscarinic receptors
Endocrine vs Exocrine
Endocrine:
No ducts
Hormones
Bloodstream
Exocrine
ducts
Sweat/mucus
Internal or external body surface
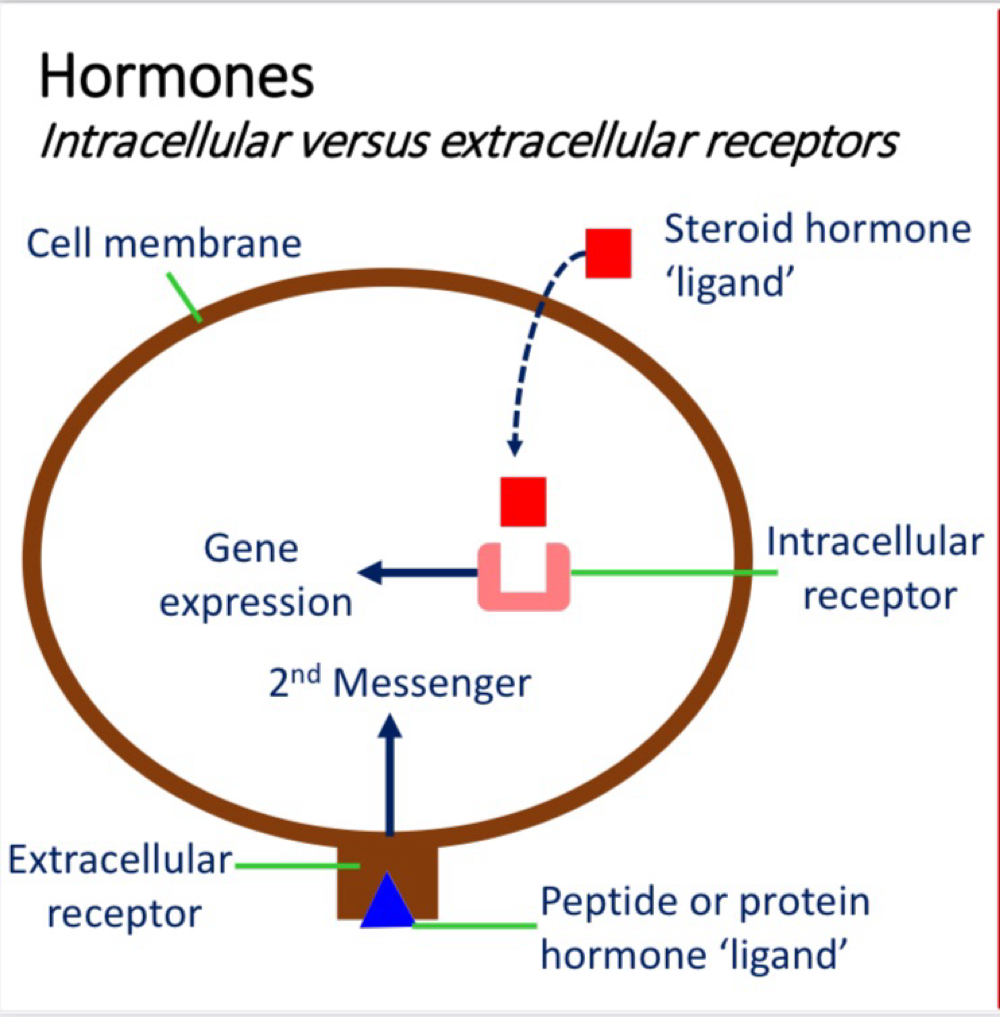
Intercellular receptors vs extracellular receptors
extracellular receptor: Peptide/Protein hormones (lipophobic)
Intracellular receptor: Steroid hormones (pass through the membrane and lipophilic)
Posterior Pituitary
Hormones produced by hypothalamus but stored in posterior pituitary. (Vasopressin or antidiuretic)
Neuron cell bodies originate in the hypothalamus but terminate in a ‘capillary blood supply’
Posteriori Pituitary: Vasopressin and oxytocin
These hormones conserves water in the kidney
Oxytocin acts on the breast and uterus - lactation and uterine contraction during childbirth.
Anterior pituitary
releases (mostly) tropic hormones
No neural connection with the hypothalamus
Synthesises its own hormones
TSH, ACTH, Growth hormone, LH/FSH, Prolactin
Anterior pituitary Hormones: TSH, ACTH, GH and LH/FSH
TSH: Targets thyroid gland, secondary hormone thyroid hormone, effect: Increased metabolic rate
ACTH: Targets adrenal cortex, secondary hormone cortisol, effect: involved in stress response.
GH: Targets skeletal muscle, live and adipose tissue, secondary hormone insulin growth factor 1, effect: growth and metabolism
LH/FSH: Gonads, secondary hormone: sex hormone secretions, effect: Gamete production (ova/sperm)
Negative feedback
Puts a break on the hormone release
Moves a physiological change in the opposite direction
Without negative feedback hormone levels rise above physiological needs leading to complications.
Positive feedback
amplifies a physiological change, eg. change produces more change
Less common than negative feedback
Cortisol
increase in blood glucose
Prevents the uptake of glucose by other tissues, and stimulates glconeogenesis
Stress hormone
ATCH - released by anterior pituitary, which stimulates the release of cortisol by the adrenals cortex