Muscular system
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
a-
without
troph
nourishment
-y
process of
a/troph/y
muscle without nourishment; muscles shrink
bi-
two
-ceps
head
bi/ceps
two-headed muscle
fibro
fiber
my
muscle
-algia
pain
fibro/my/algia
pain in the muscle fiber
gastrocnemi
calf or belly of the leg
-us
pertaining to
gastrocnemi/us
pertaining to the calf of the leg
hyper-
excessive
hyper/troph/y
pertaining to excessive nourishment; causes enlargement
intra-
into
muscul
muscle
-ar
pertaining to
intra/muscul/ar
pertaining to inside the muscle
my/algia
muscle pain
my
muscle
-asthenia
weakness
gravis
heavy, grave
my/asthenia gravis
grave muscle weakness; autoimmune disease
neuro
nerve
neuro/muscul/ar
pertaining to the nerve and muscle
physio
nature
physio/therapy
treatment with natural means
sarco
flesh
lemma
husk or covering
sarco/lemma
covering around muscle flesh; cell membrane
plasm
tumor
sarco/plasm
tumor of the flesh; cytoplasm
Skeletal muscles are ____________________________.
attached to bones, striated (striped), and voluntary
Fascia
a band or sheet of fibrous connective tissue that covers, supports, and separates muscle
Smooth muscles are _______________________.
spindle shaped, not attached to bones, are non-striated, and are involuntary; controlled by the autonomic nervous system
Visceral muscles are _________________.
smooth muscles
Cardiac muscle is ____________________.
Involuntary, striated and branched muscle tissue found only in the heart.
Sphincter muscles are _________________________________.
Special circular muscles that control an opening, found in the walls of the anus, urethra, mouth, and intestines.
contractility
ability to shorten forcibly when stimulated
excitability
ability to respond to stimuli by producing electrical signals called action potentials (impulses)
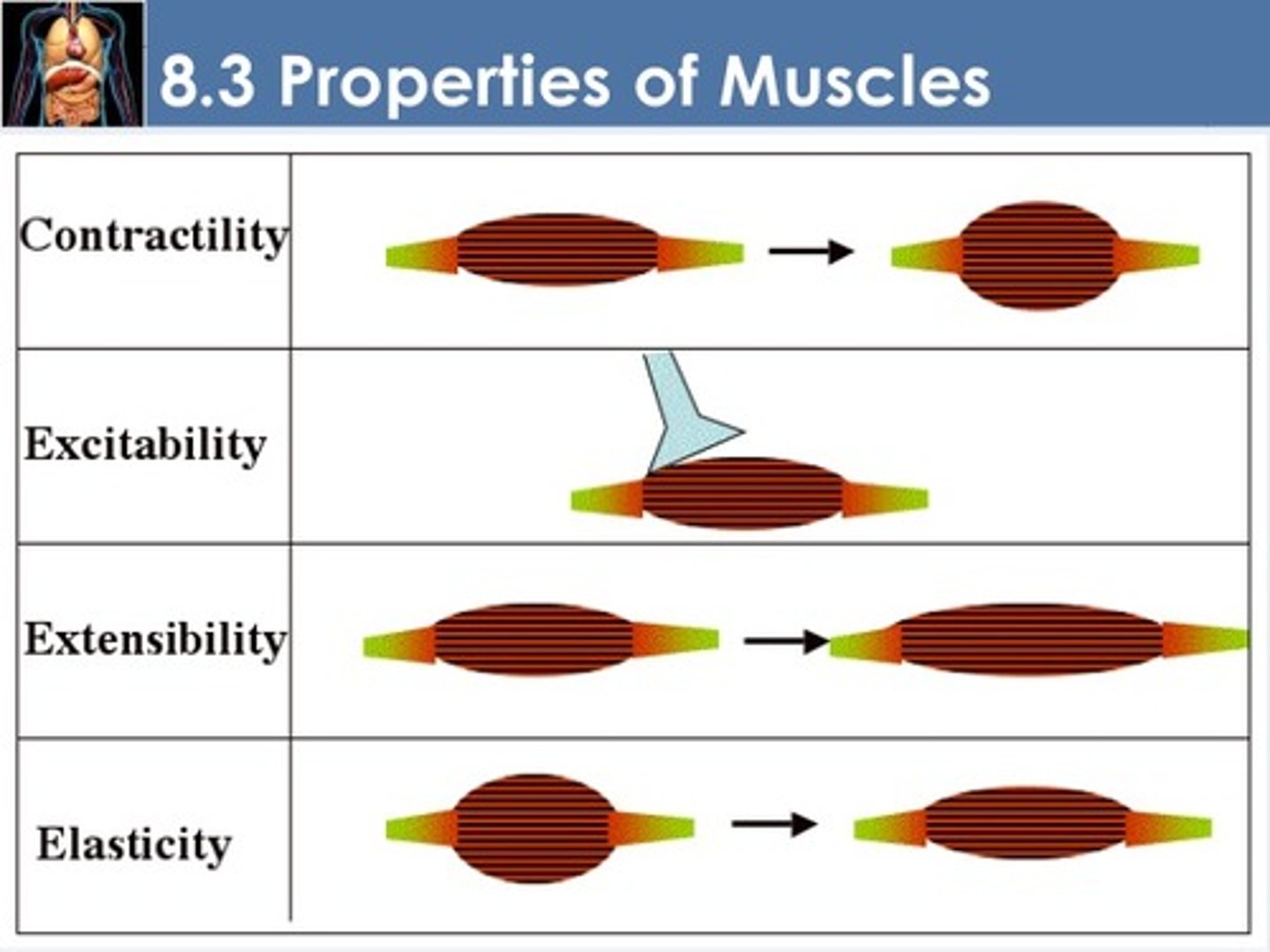
Extensibility
ability to be stretched
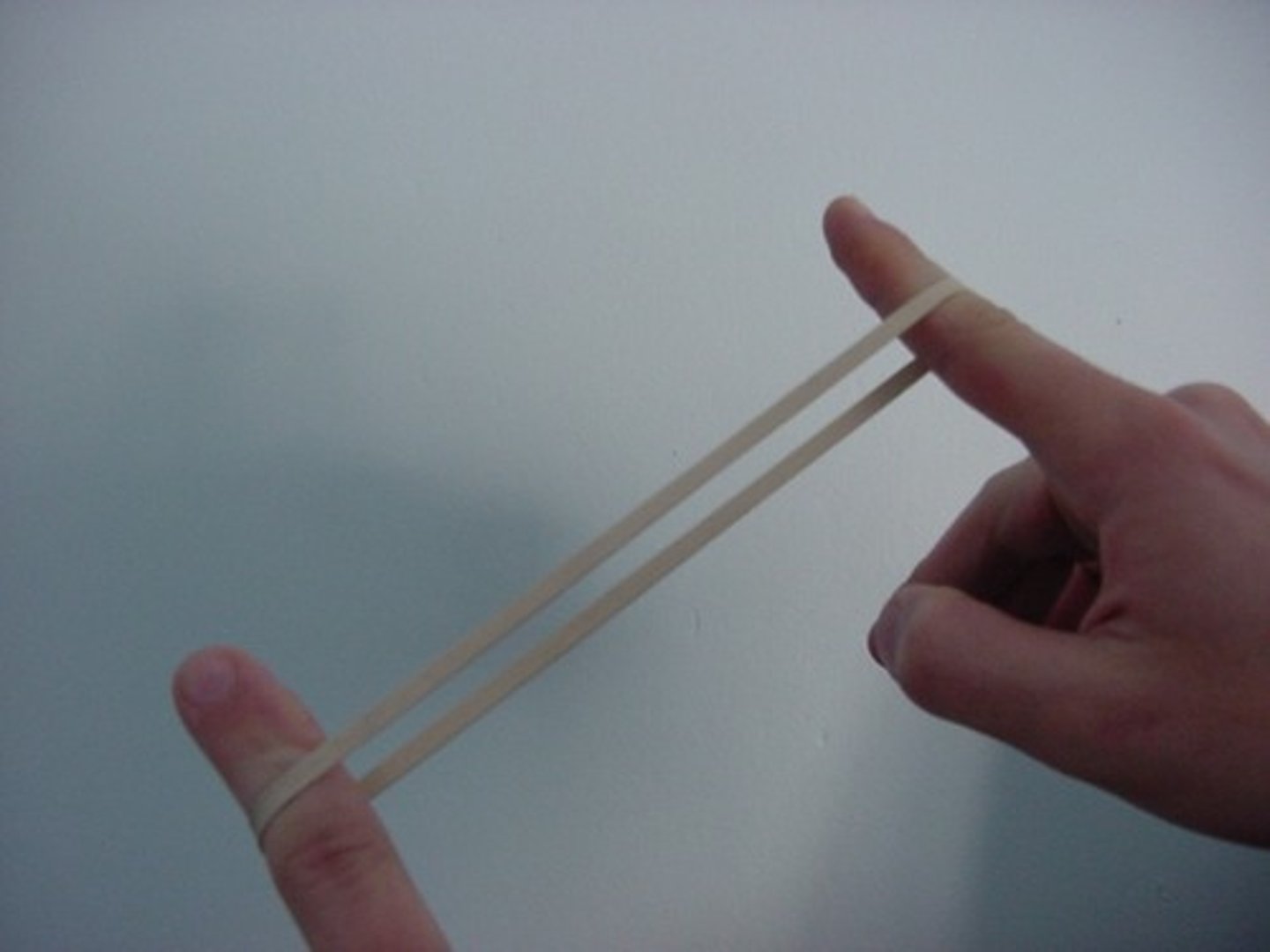
Elasticity
Ability of a material to return to its original shape after being stretched.

tendon
Connects muscle to bone
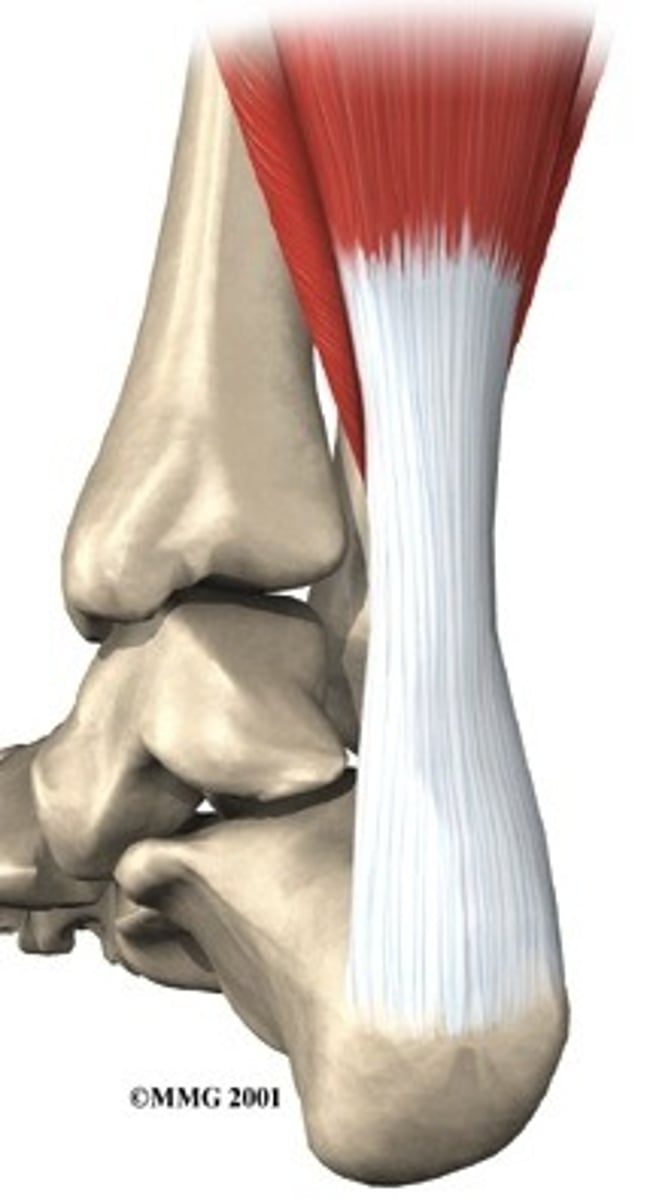
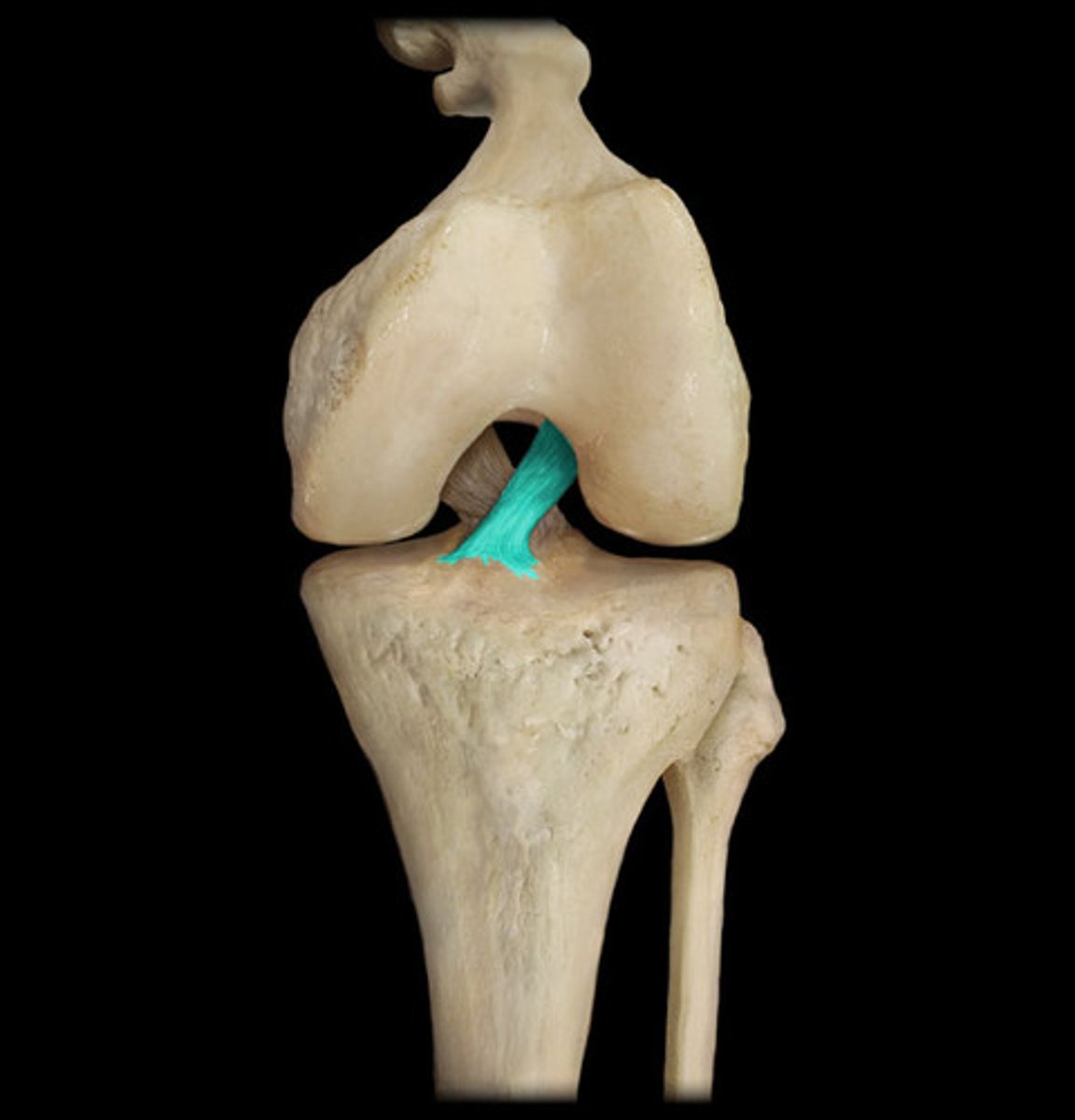
ligaments
Connect bone to bone
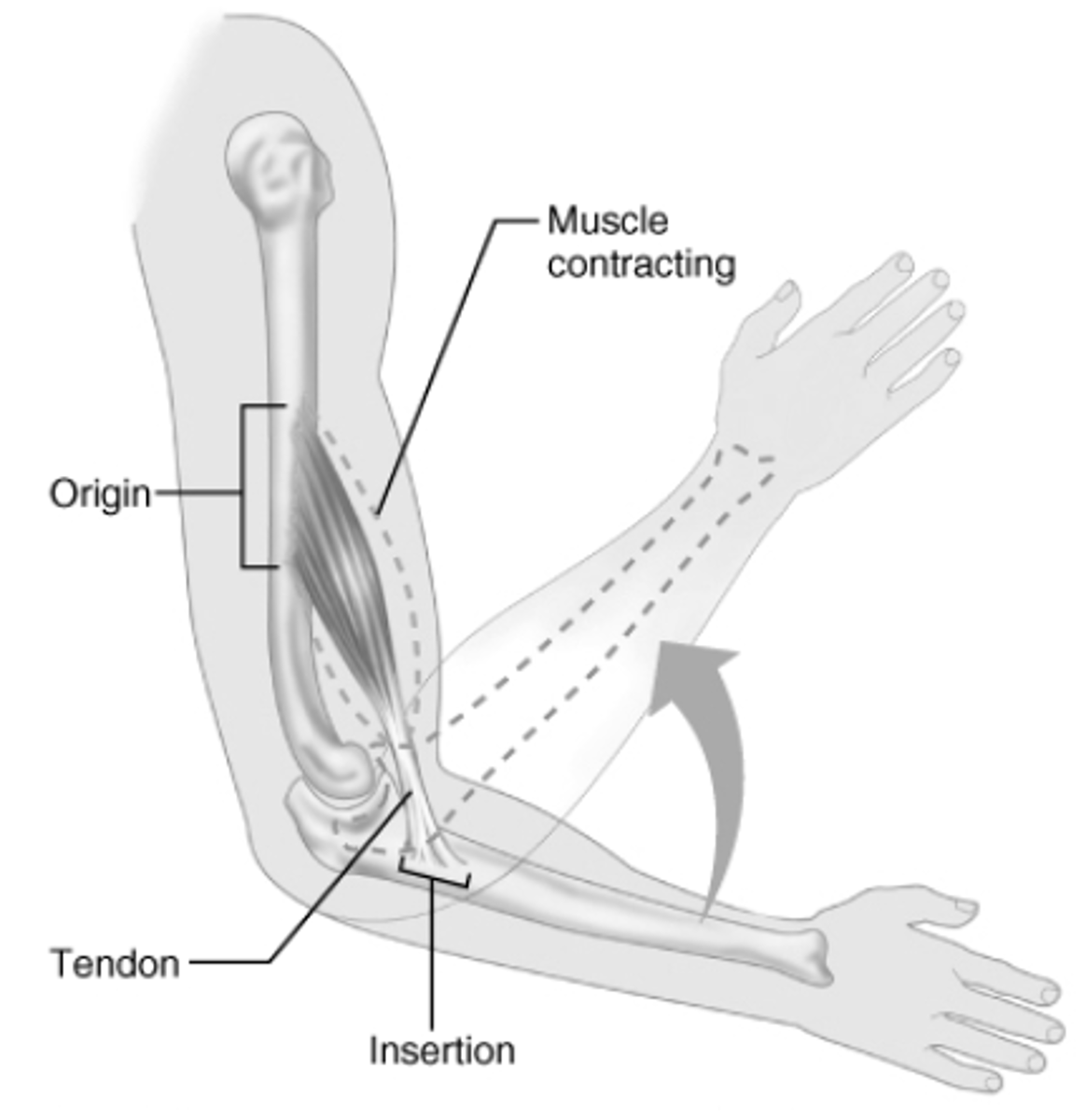
the origin of a muscle
the part of a skeletal muscle that is attached to a fixed structure or bone; moves the least during muscle contraction
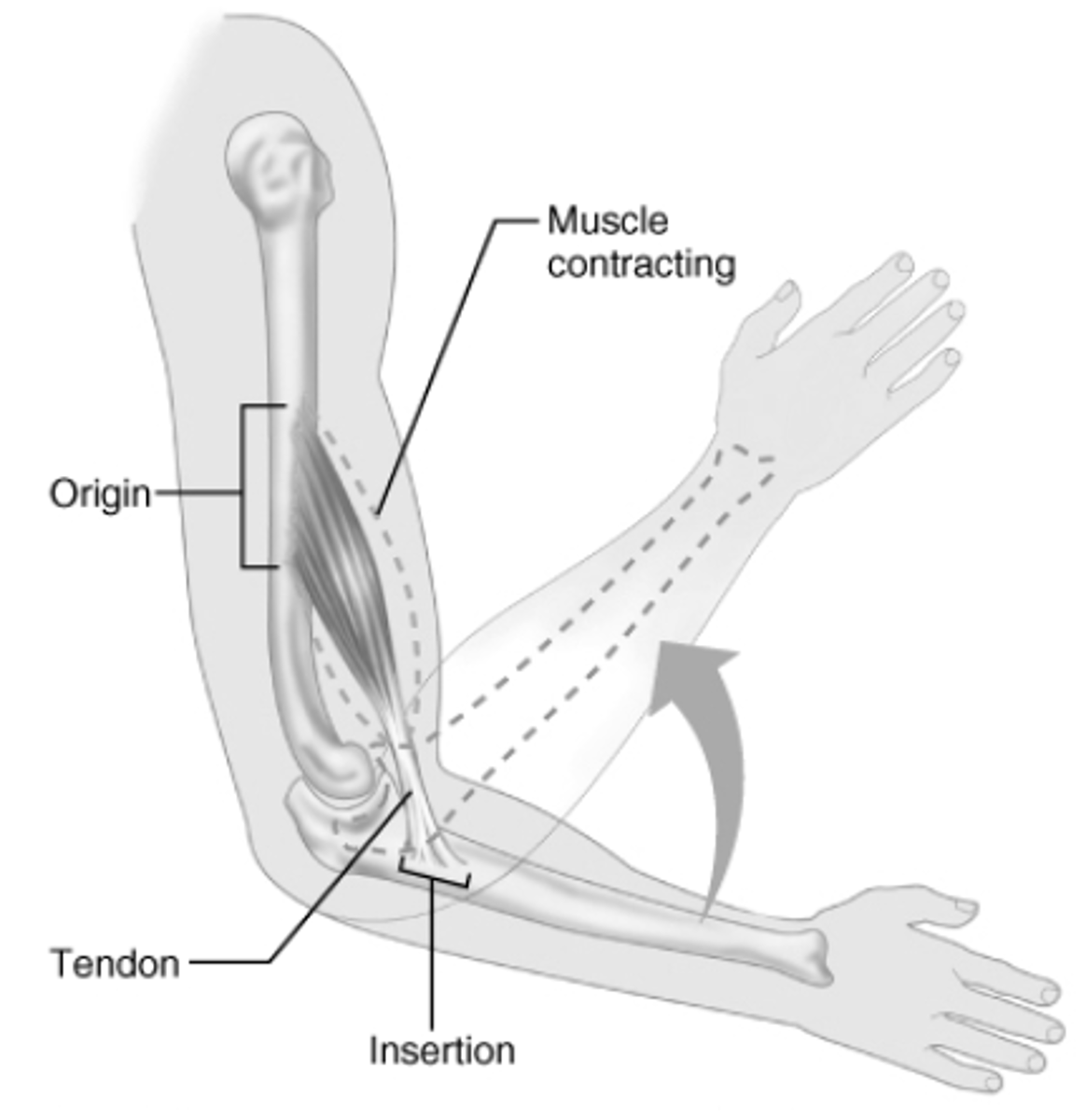
the insertion of a muscle
connection of the muscle to a bone that moves
Origin and insertion of sternocleidomastoid?
Origin: sternum and clavicle.
Insertion: mastoid process
Location: side of neck
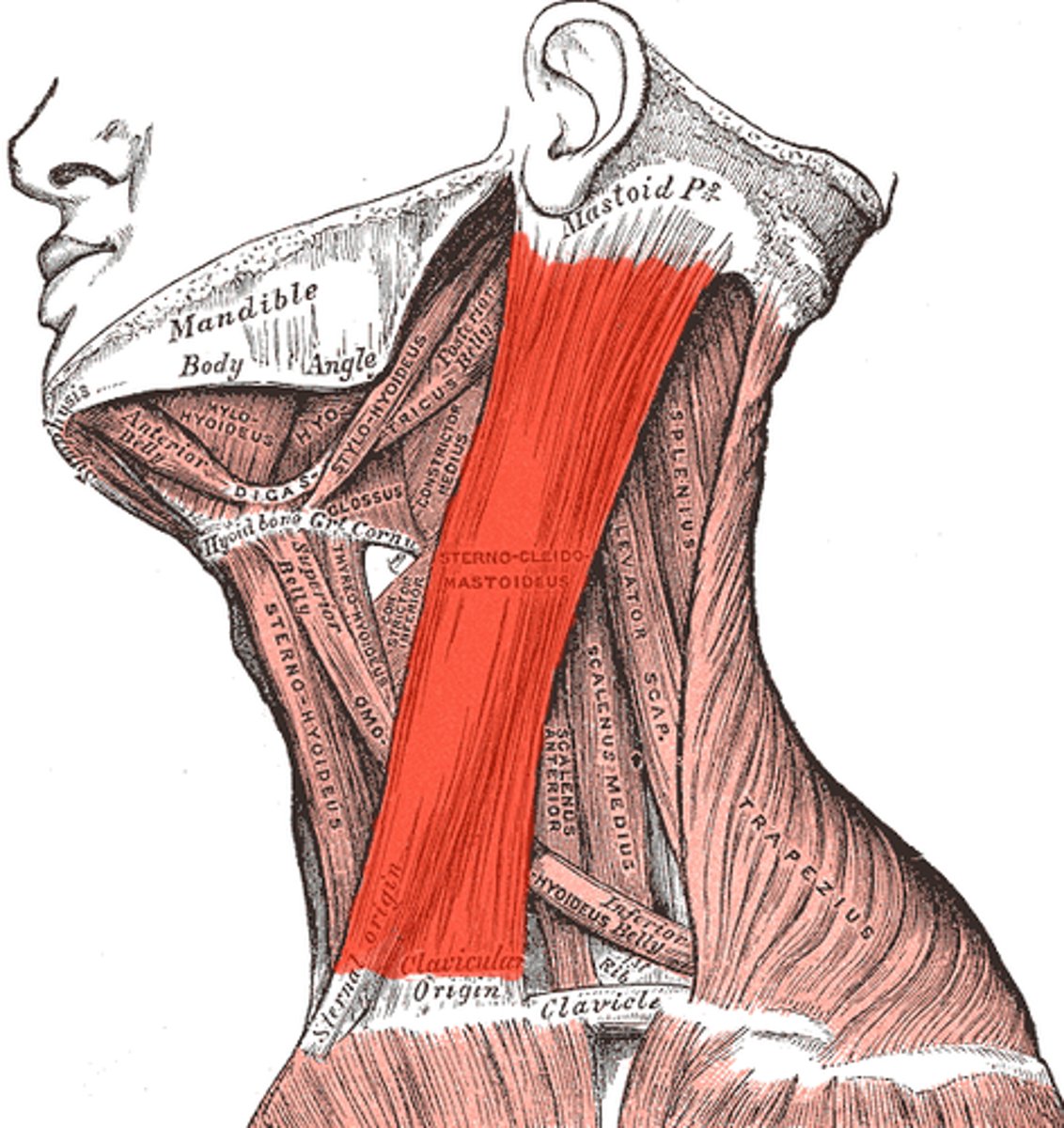
Belly of the muscle
The middle part of the muscle
Muscles are arranged in ___________.
Pairs
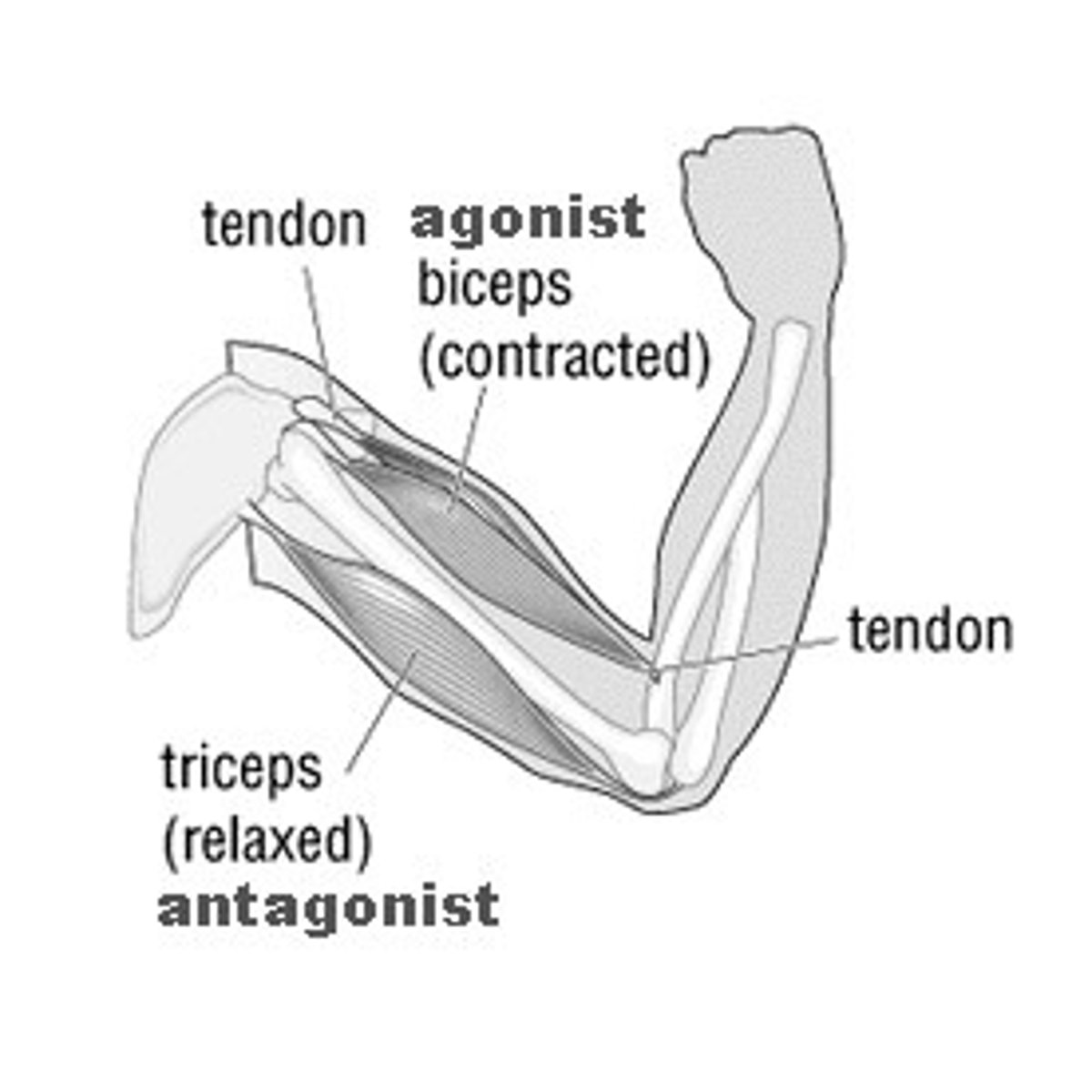
Prime mover
A muscle that produces movement in a single direction.

Antagonist
Allows movement in opposite direction from muscle
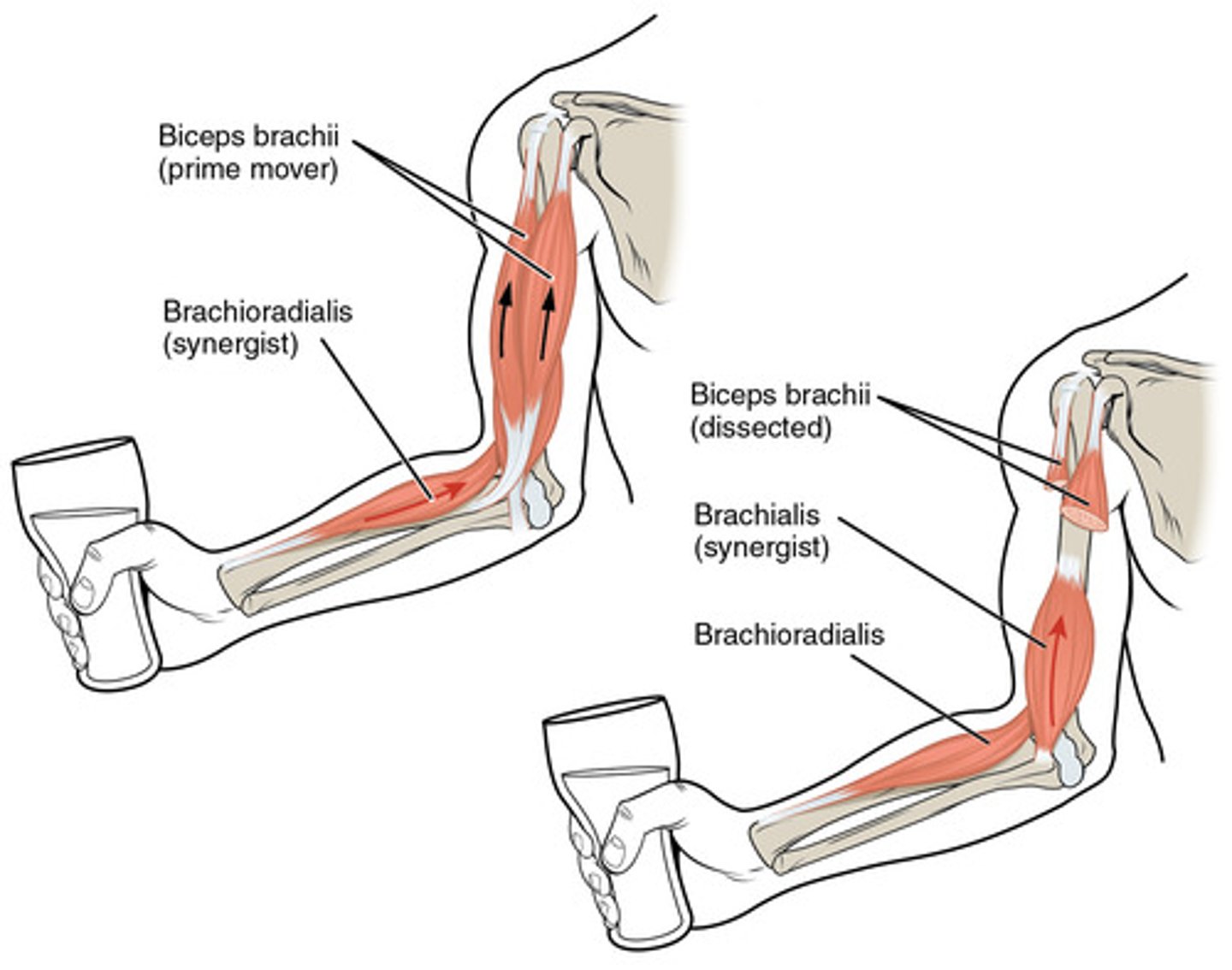
synergists (agonists)
muscles that contract and assist the prime mover by keeping the movement steady or stabilizing the joint activity
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
compound used by cells to store and release energy
Muscle twitch
a single momentary muscle contraction, and is the response to a single stimulus.
motor unit
a motor neuron and all the muscle cells it stimulates
neuromuscular junction
the junction between a nerve fiber and the muscle it supplies
The basic source of energy is ________________.
Glucose
The energy derived from glucose is store in the form of ________________________.
ATP and phosphocreatine
Muscle fatigue
the inability of a muscle to contract, caused by an accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles
muscle tone
the state of balanced muscle tension that makes normal posture, coordination, and movement possible
isotonic contraction
when muscles contract and shorten; ex: talking, walking.
isometric contraction
when a muscle tenses but does not shorten
ex: tensing abdominal muscles during exercise
There are _____ skeletal muscles in the human body.
656
There are 327 antagonist muscles and ____ unpaired muscles
2
The unpaired muscles are:
the orbicularis oris (mouth) and the diaphragm
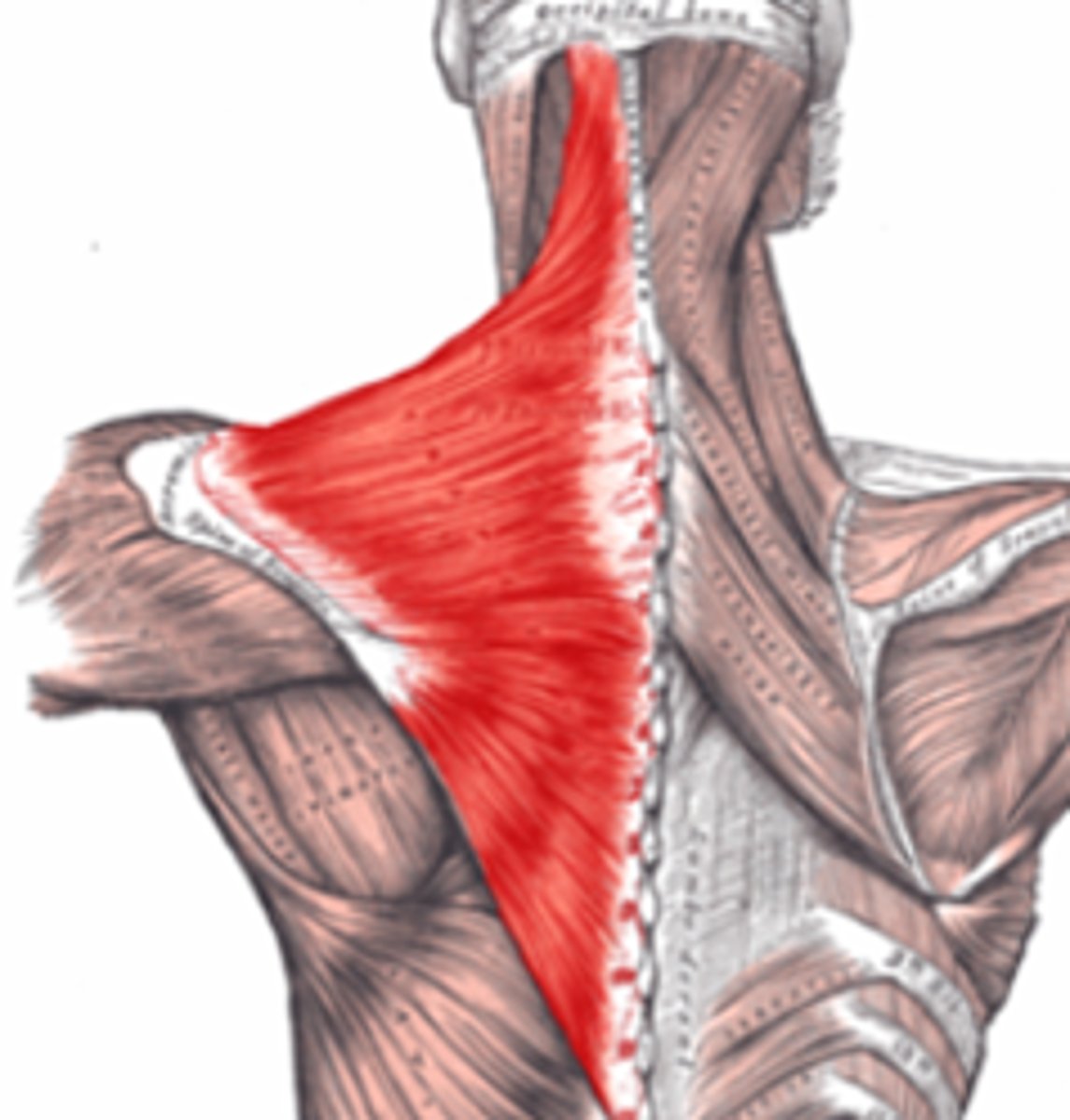
Trapezius
Back of neck and upper back
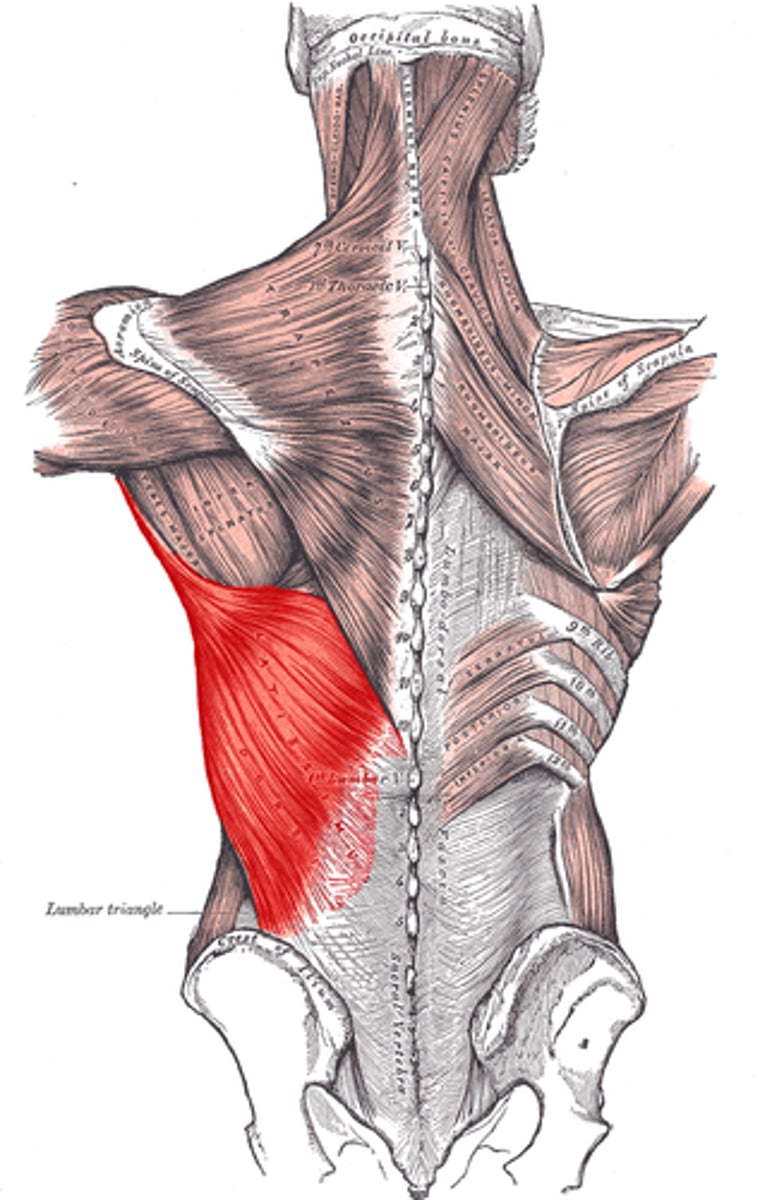
Latissimus dorsi
Lower back
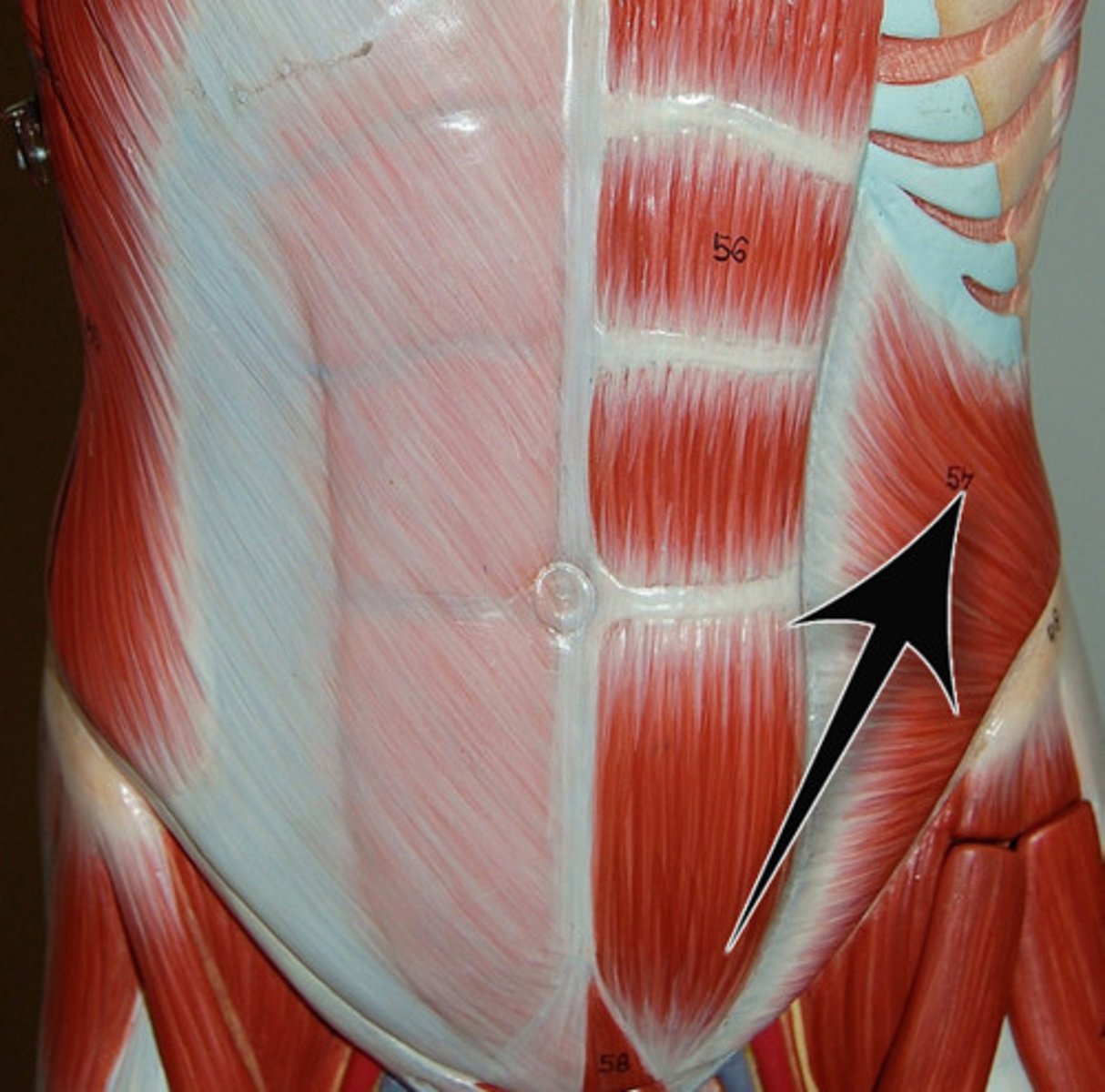
External oblique
anterior and lateral abdomen
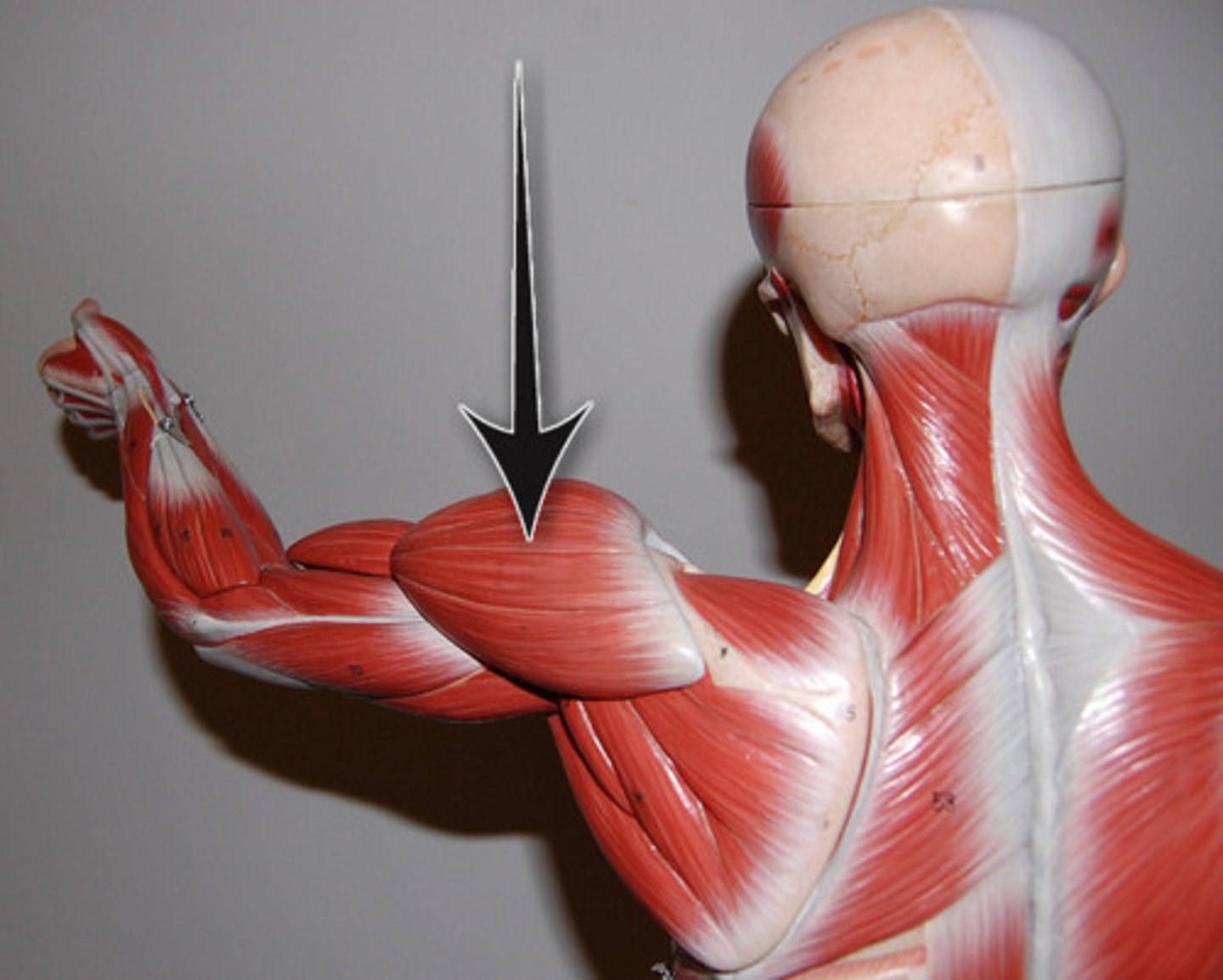
Deltoid
shoulder
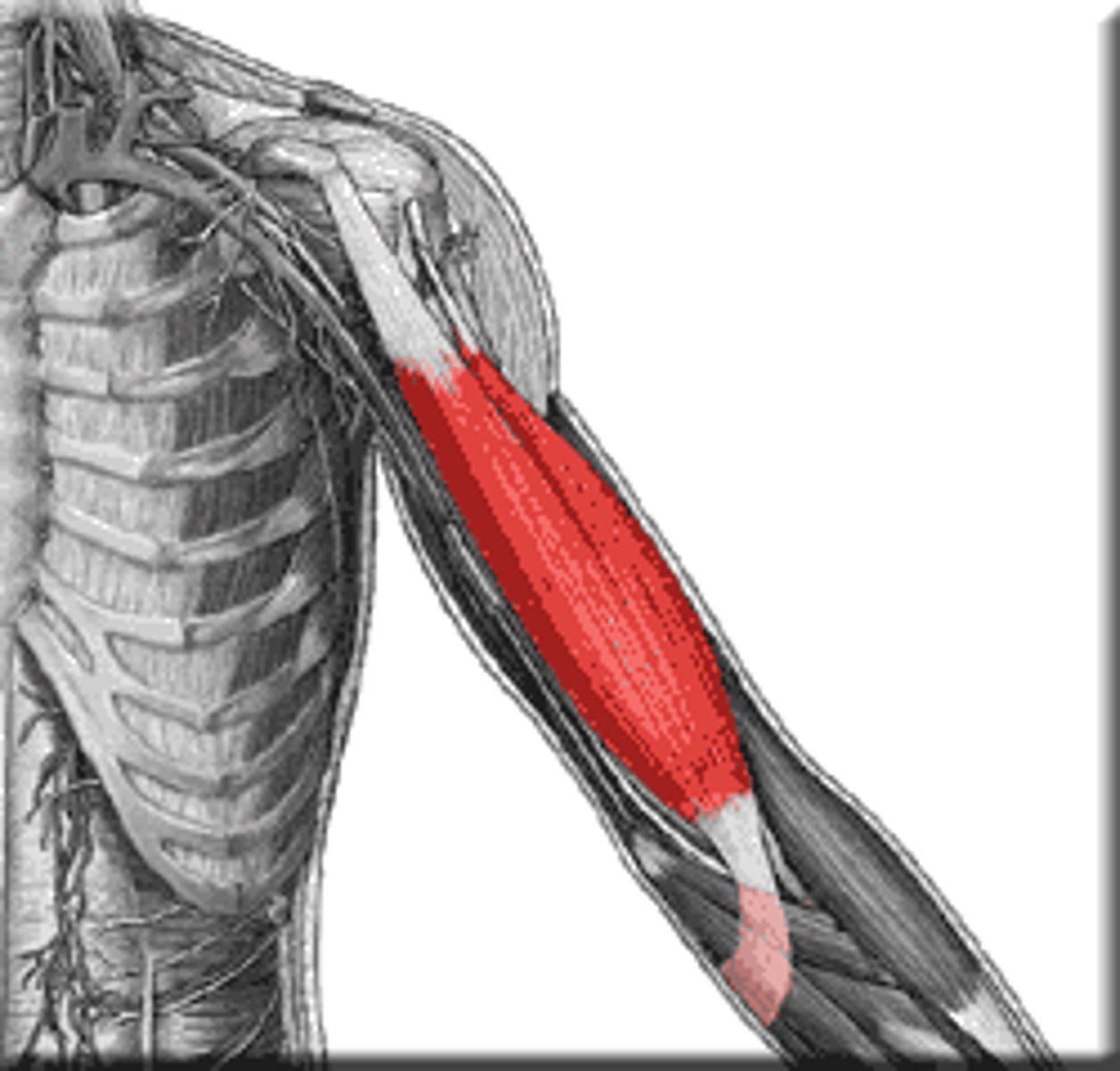
Biceps brachii
Anterior aspect of arm
Triceps brachii
posterior aspect of arm
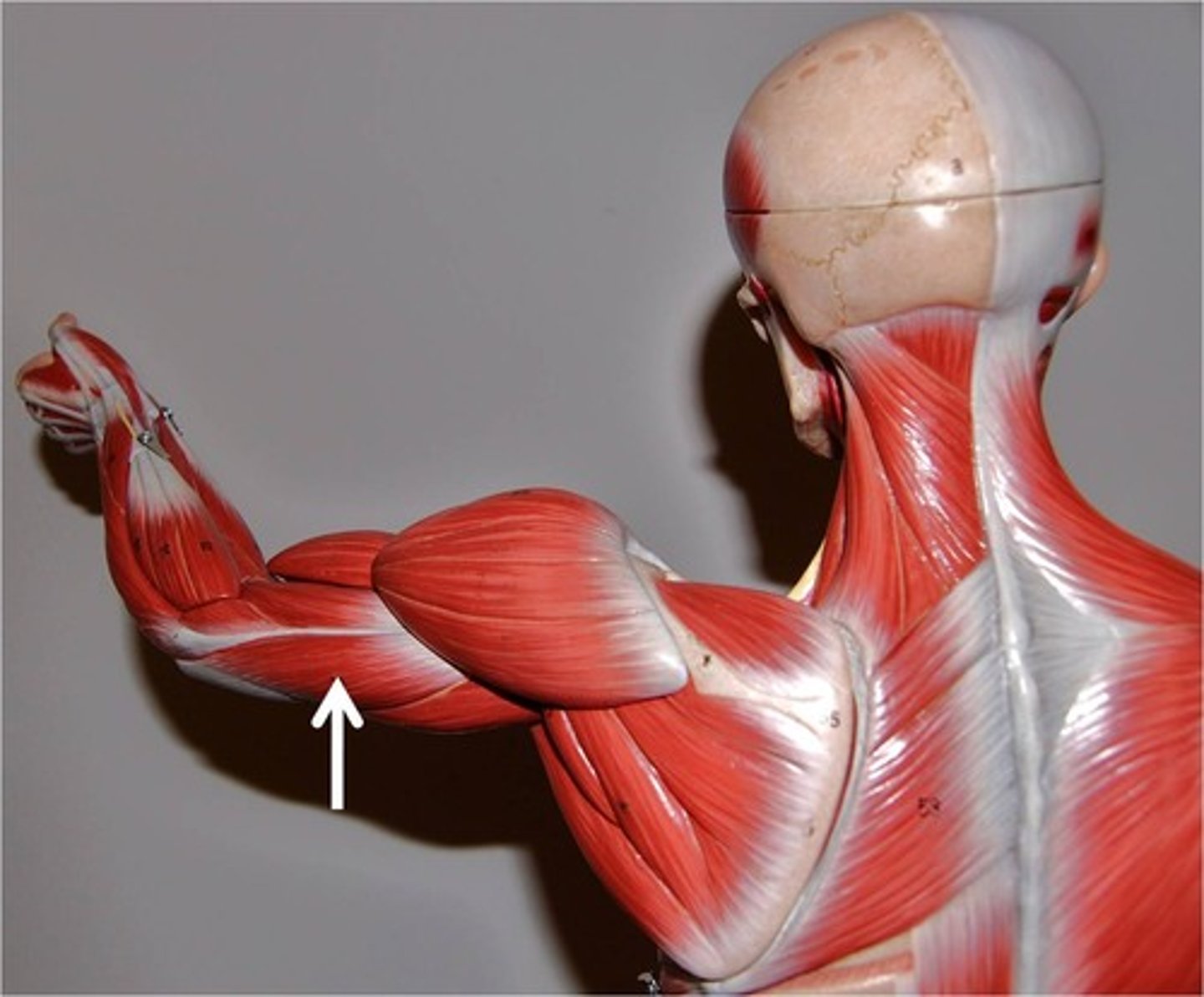
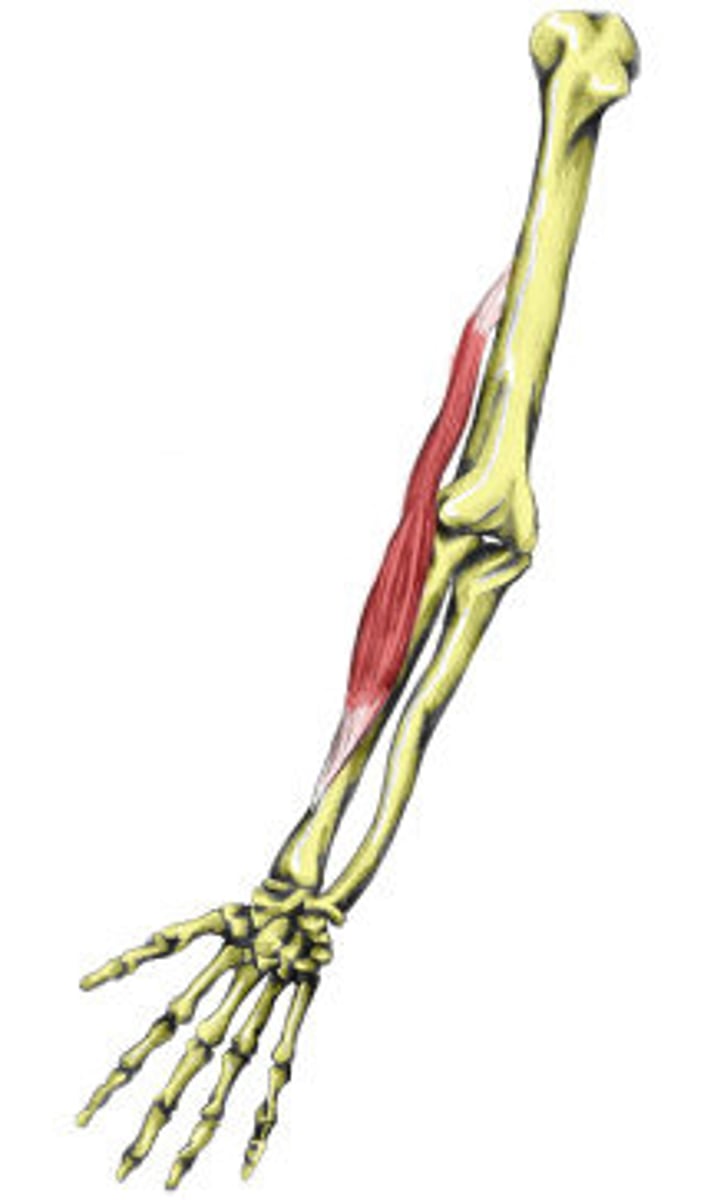
Brachioradialis
Anterior and proximal forearm
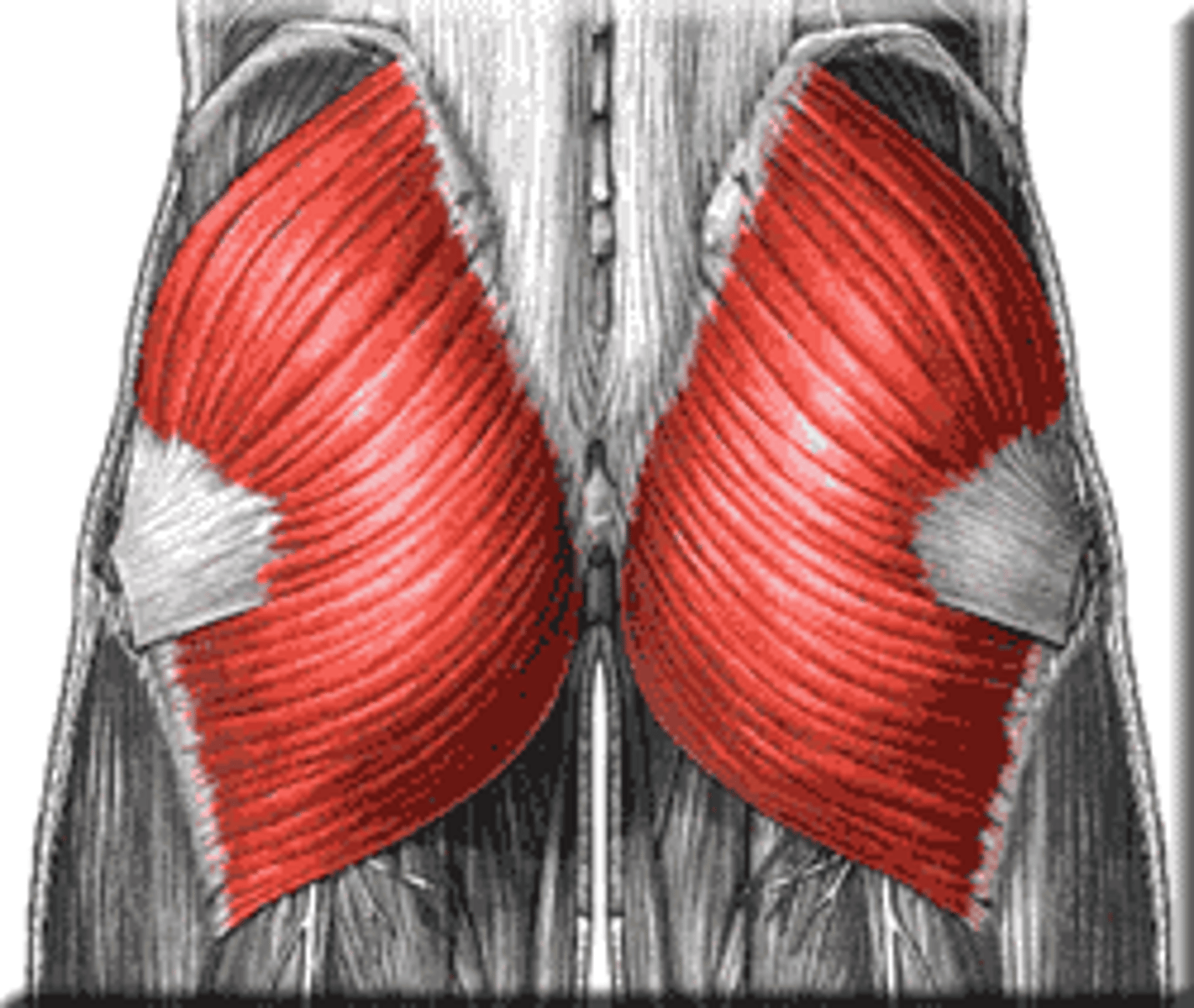
Gluteus maximus
Buttock
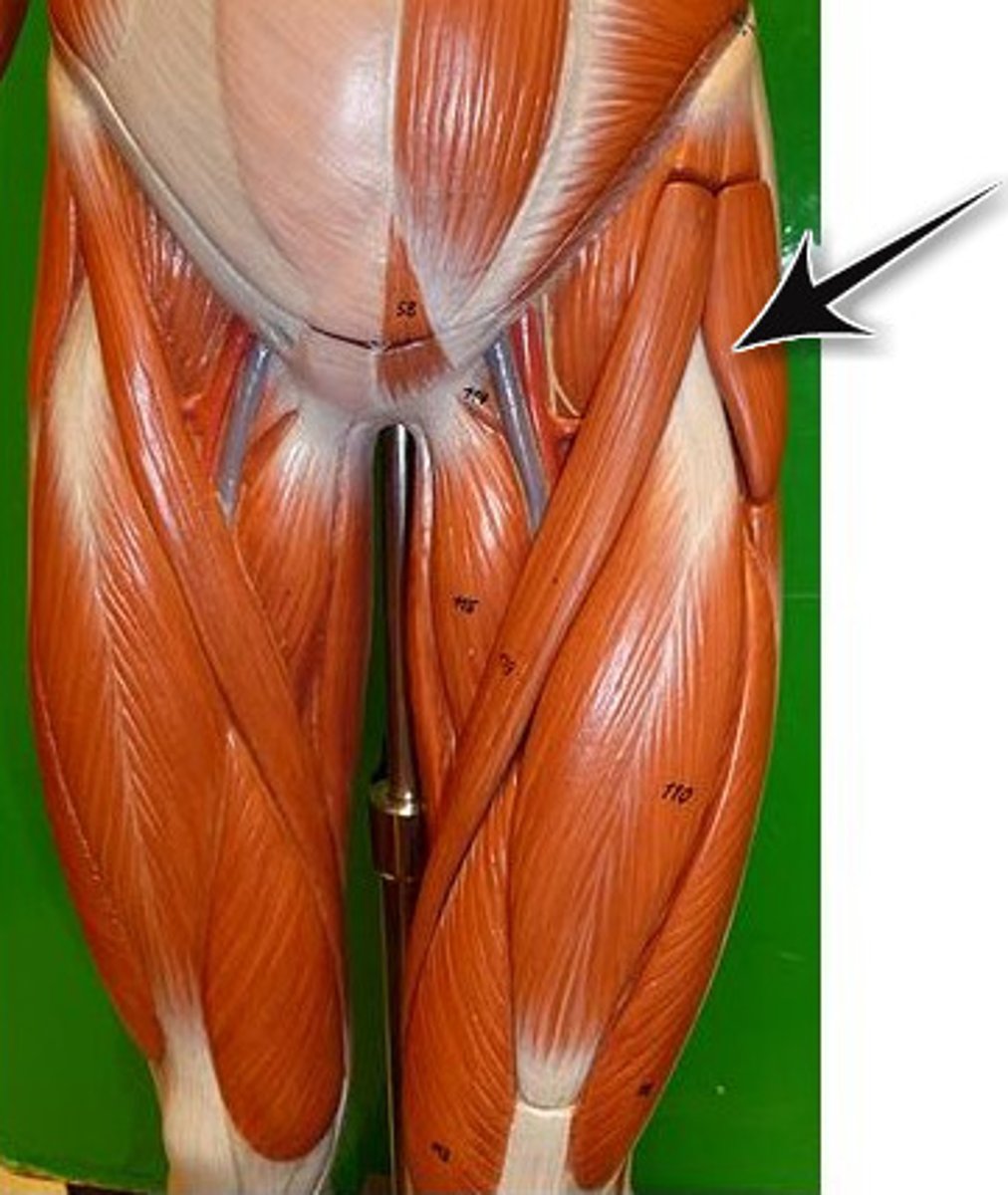
Tensor fasciae latae
lateral and proximal thigh
Sartorius
Anterior thigh
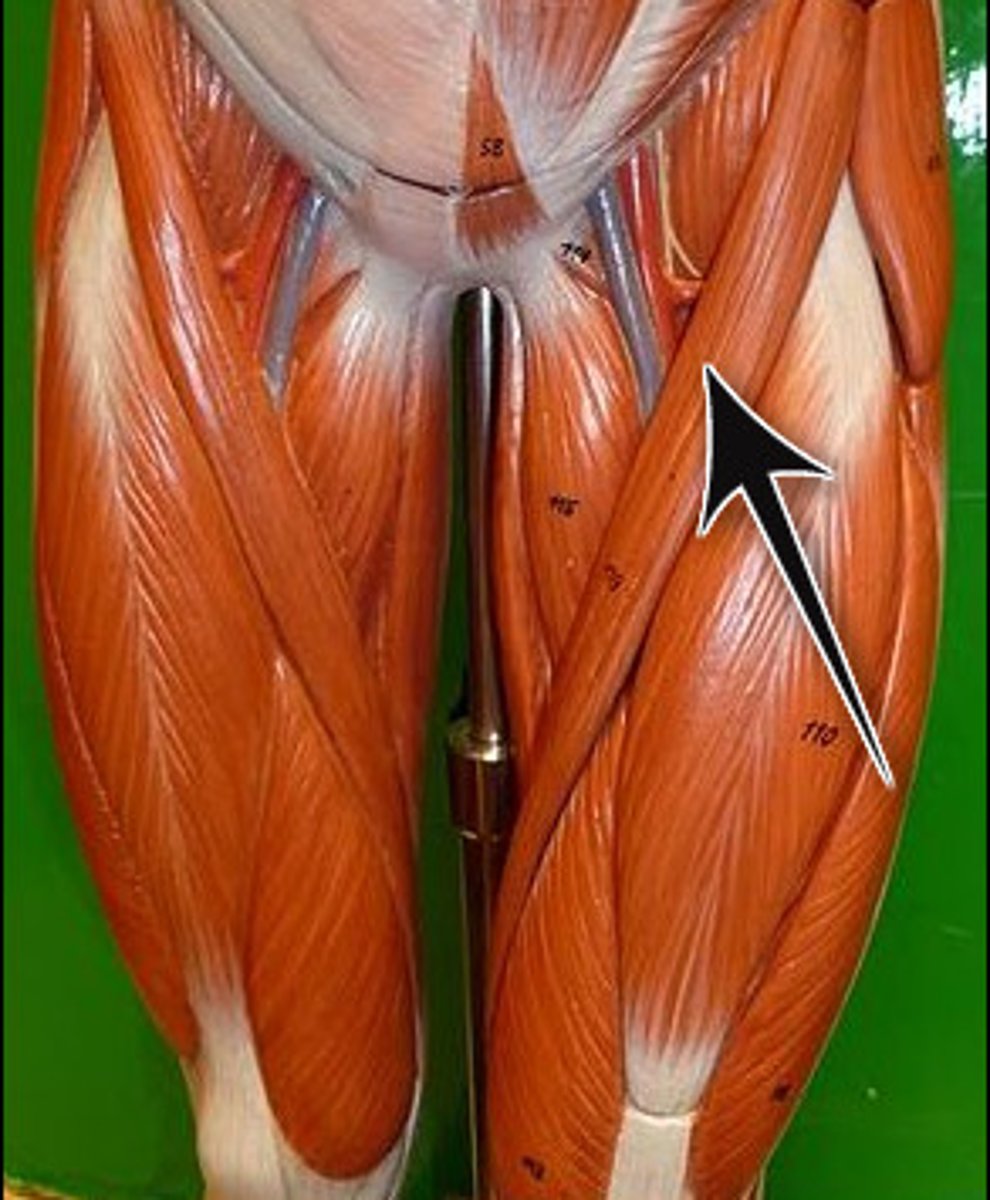
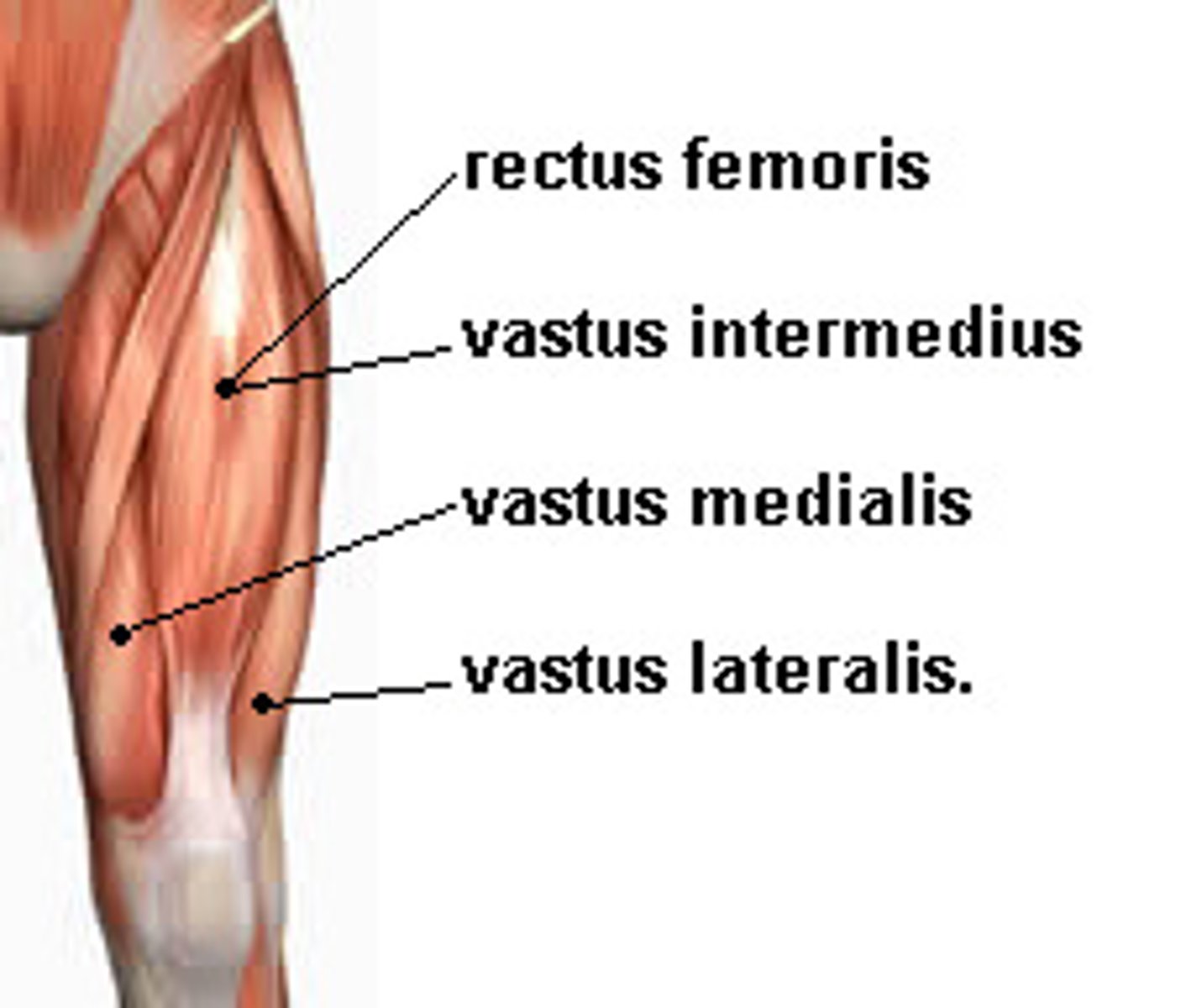
Quadriceps femoris group
Anterior thigh
Consists of rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius)
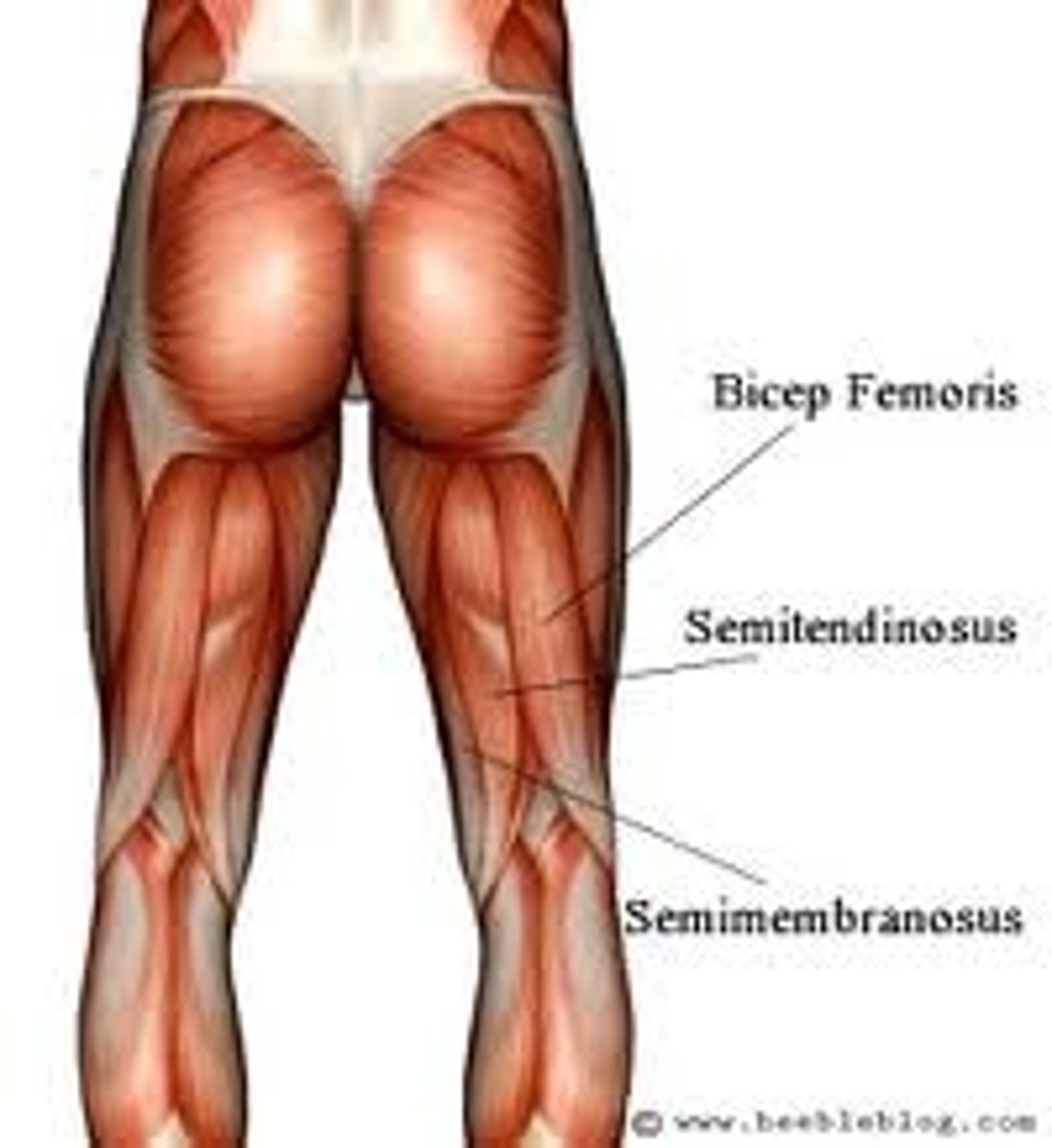
Hamstring group
Posterior thigh
Consists of bicep femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus
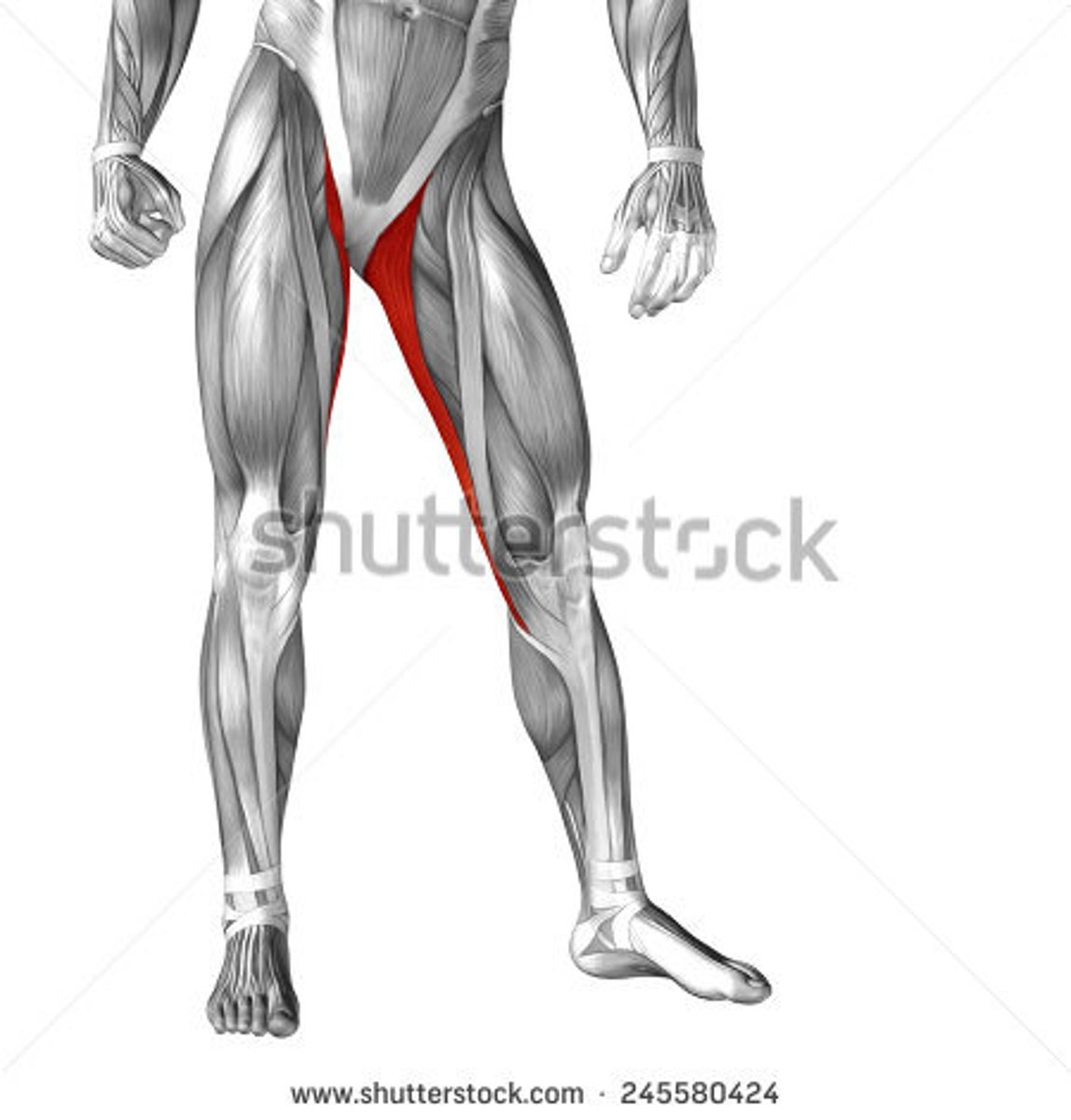
Gracilis
Medial thigh
Tibialias anterior
Anterior leg
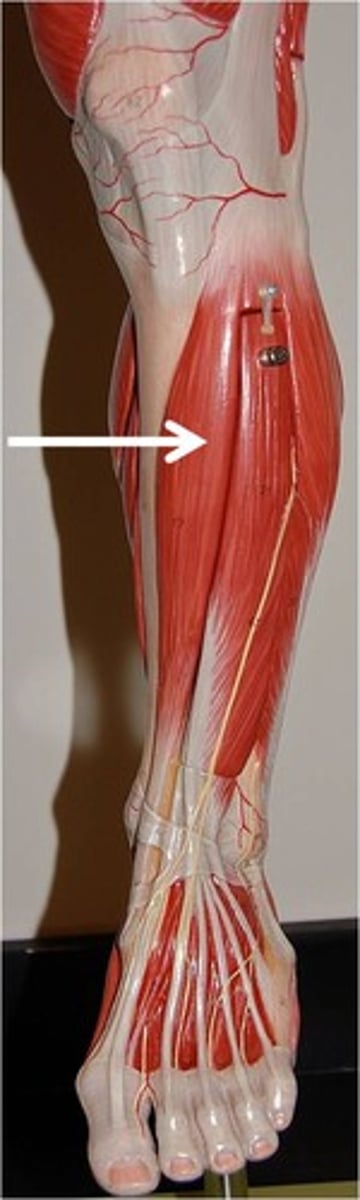
Gastrocnemius
Posterior leg (calf)
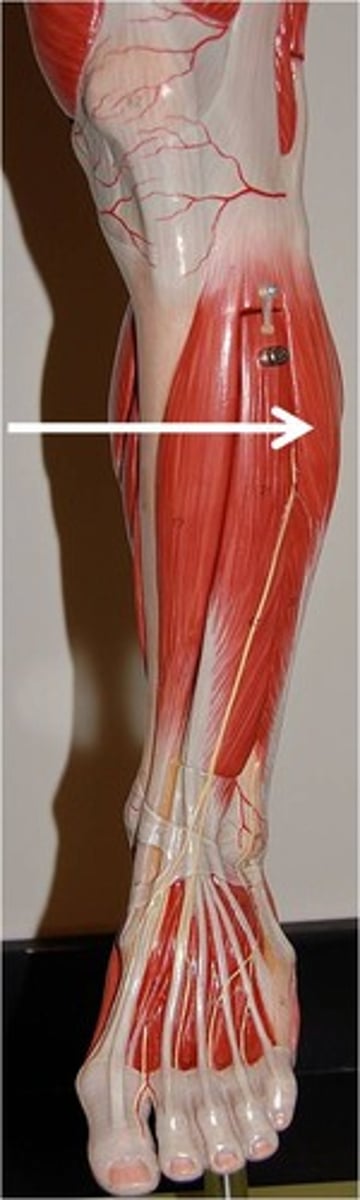
Soleus
Posterior (deep) leg
Peroneus Longus
Lateral leg
muscles of mastication (chewing)
masseter and temporalis
Medications that are administered intramuscularly, go:
into the muscle
Muscle strain
Overstretching or tearing of a muscle
Muscle spasm
involuntary muscle contraction; cramp
Dystonia
a condition of abnormal muscle tone that causes the involuntary muscle contractions seen as repetitive movements or abnormal postures
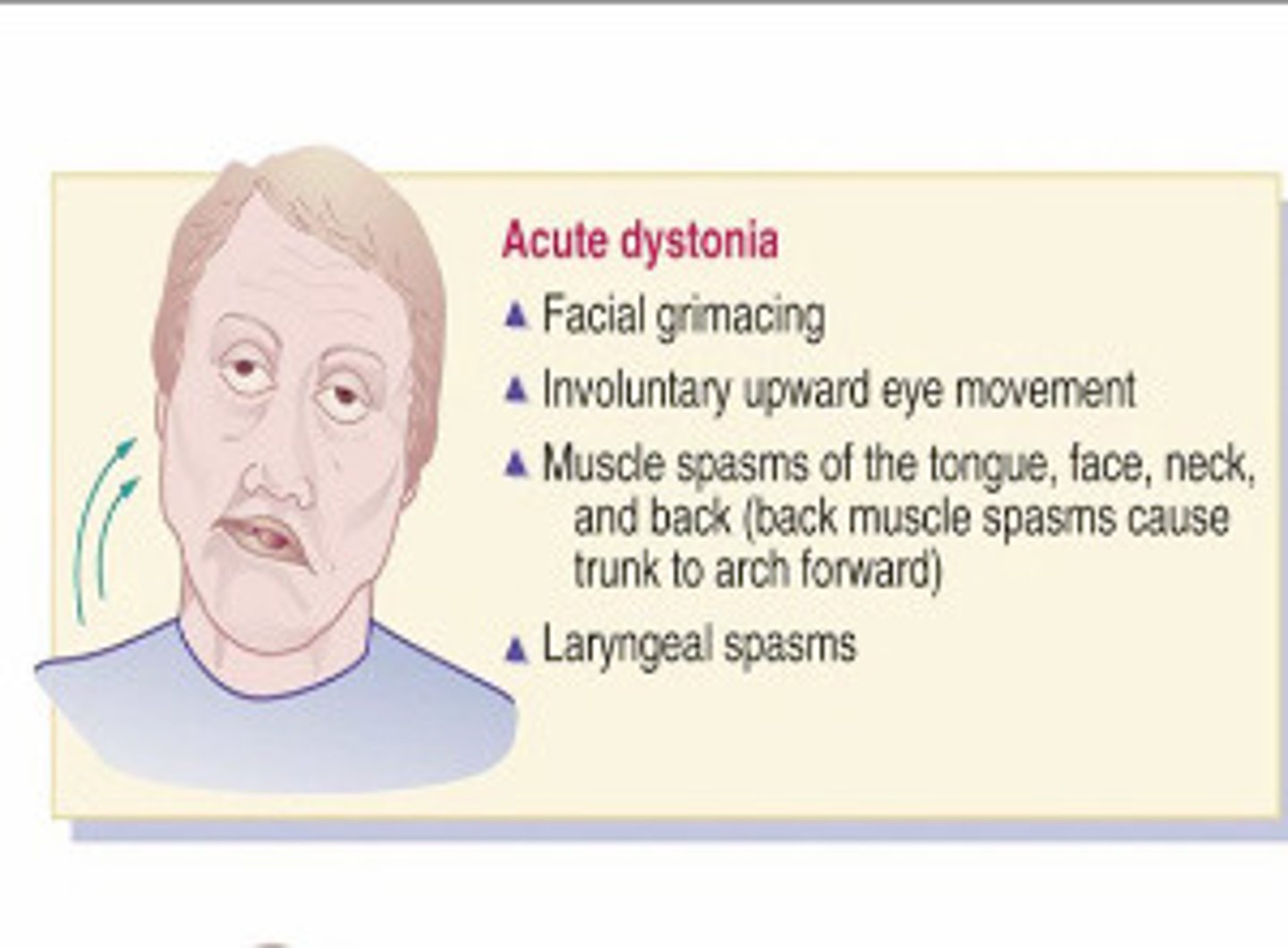
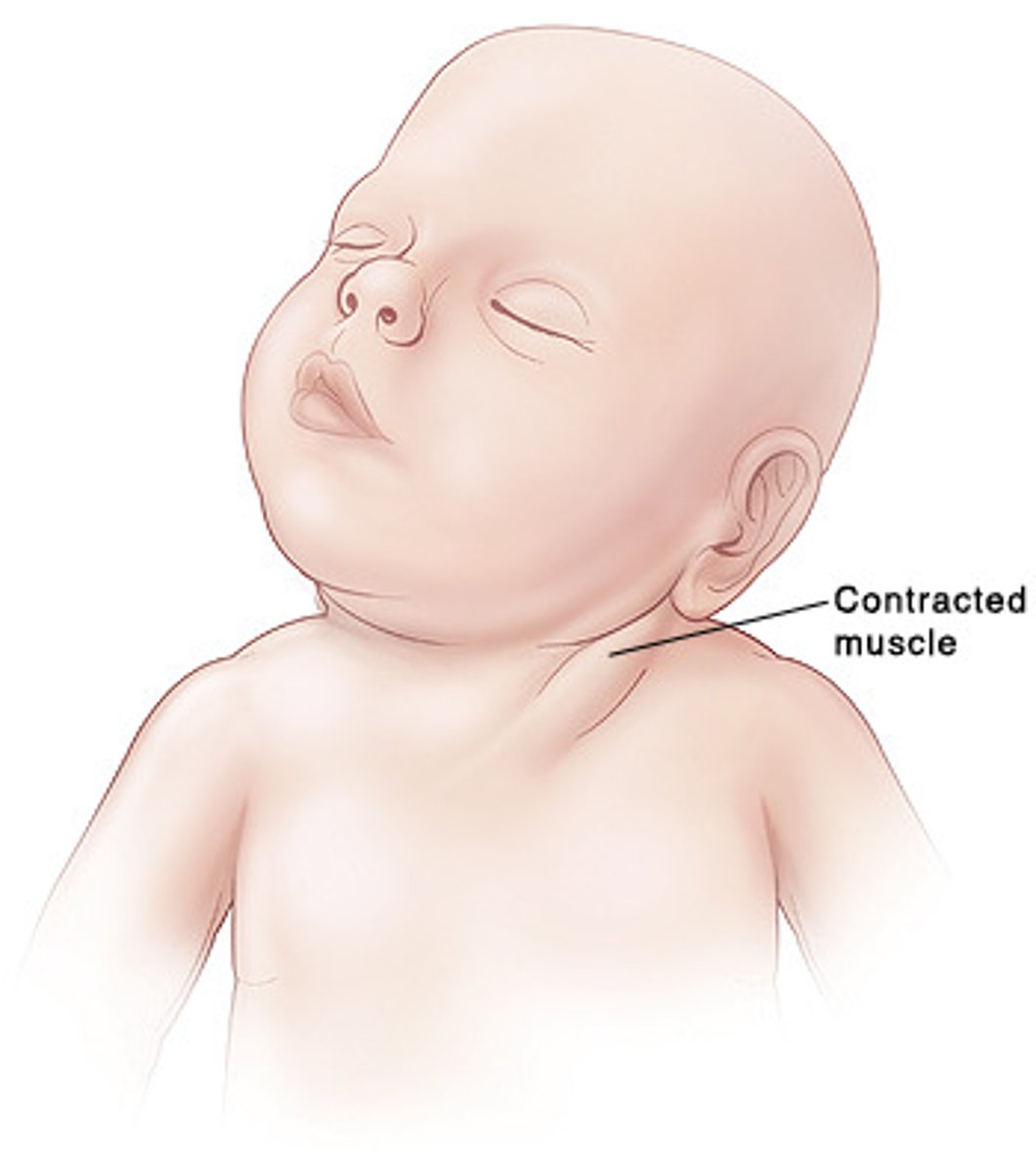
Torticollis
"wryneck"; head turns to one side or is pulled backwards or forwards
Blepharospasm
involuntary twitching of the eyelid
Craniofacial dystonia
Affects the muscles of the head, face, and neck; the jaws, lips, and tongue may also be affected
Hernia
Protrusion of an organ through a weak muscle
Tetanus
"Lockjaw": infectious disease characterized by continuous spasms of voluntary muscles
Muscular dystrophy
group of hereditary diseases characterized by degeneration of muscle and weakness
Ex: Duchenne's muscular dystrophy
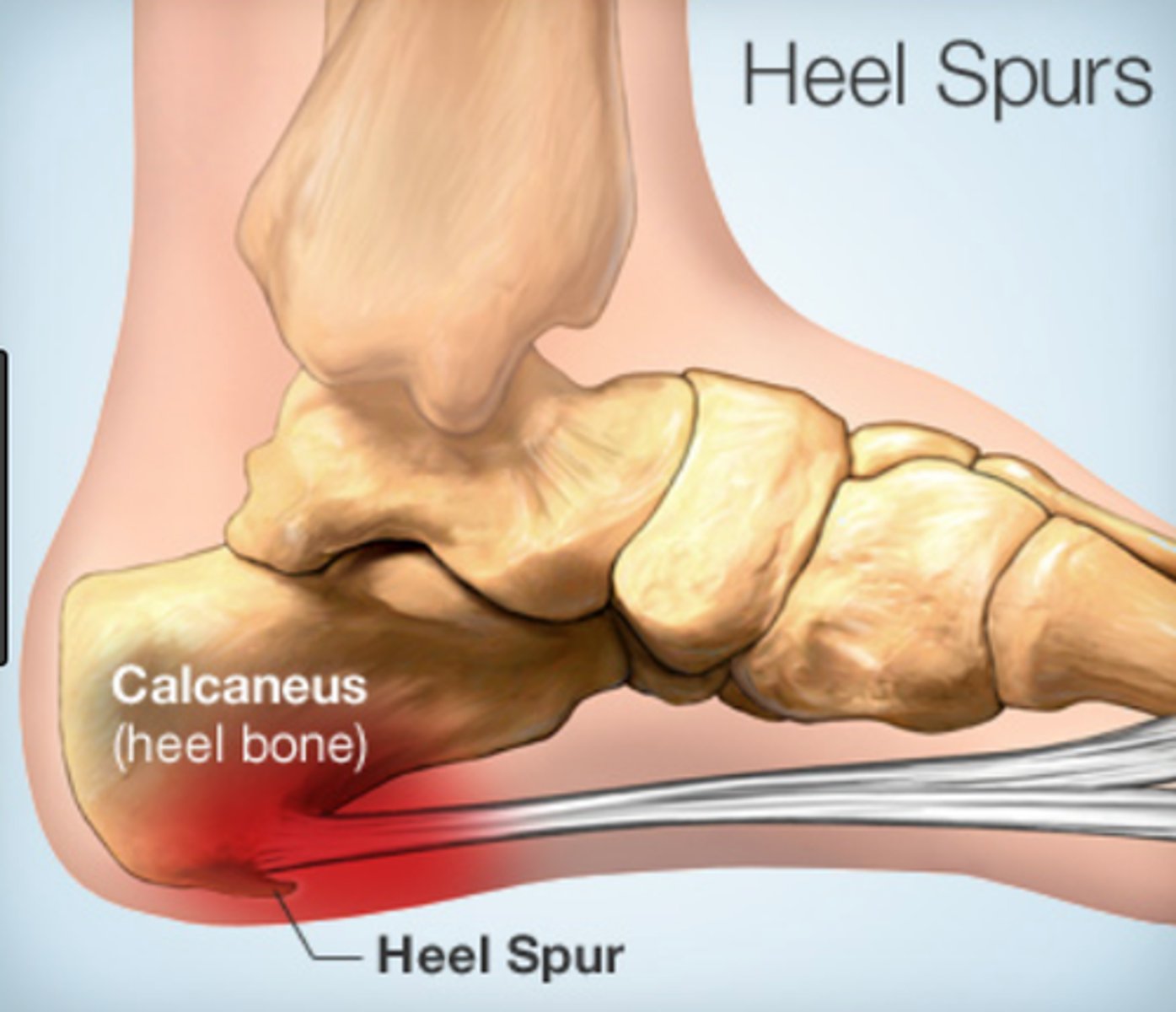
Heel spur
calcium deposit in the plantar fascia
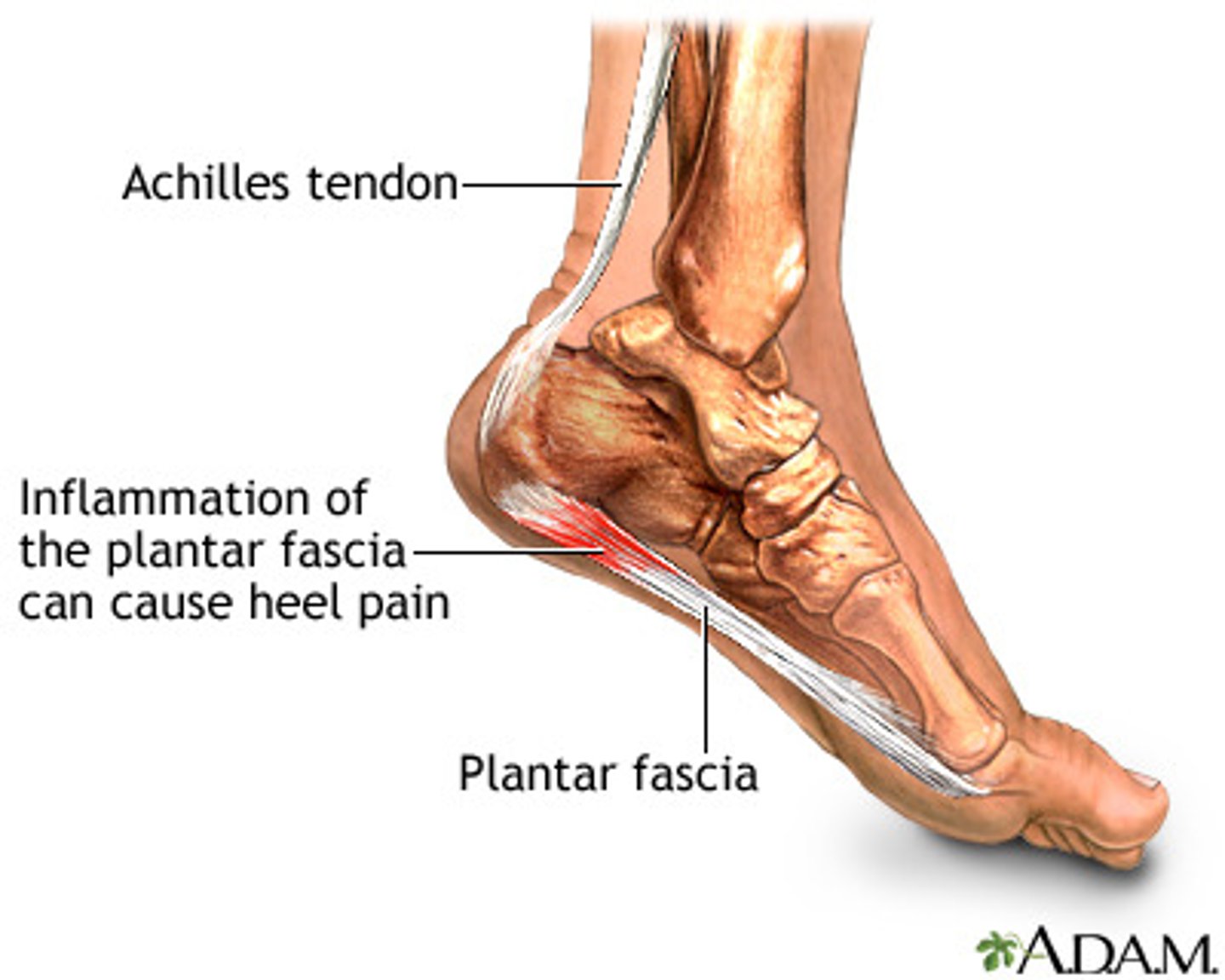
Plantar fasciitis
inflammation of the plantar fascia on the sole of the foot
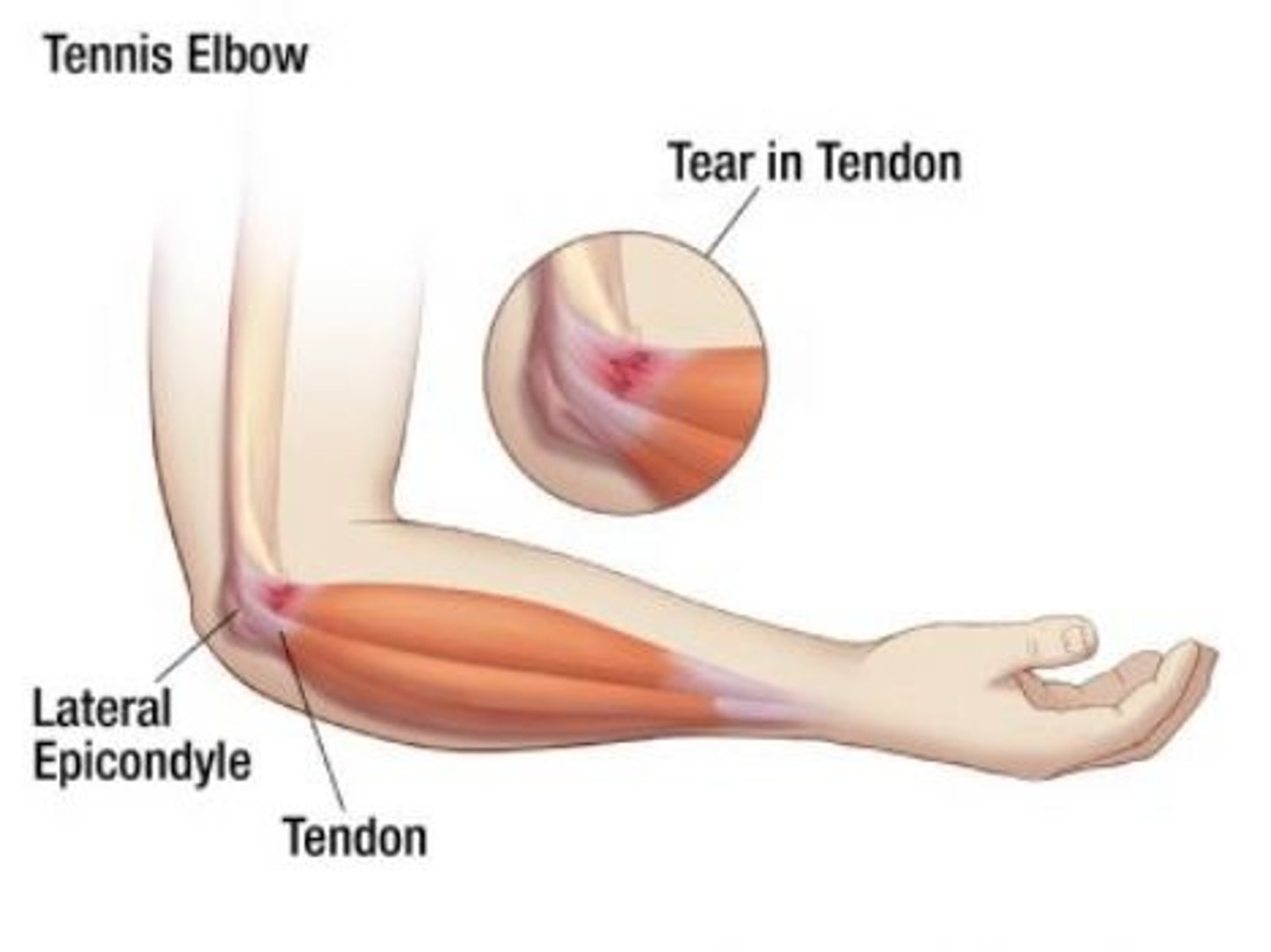
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
Inflammation of the extensor muscles of the forearm, caused by overuse or trauma
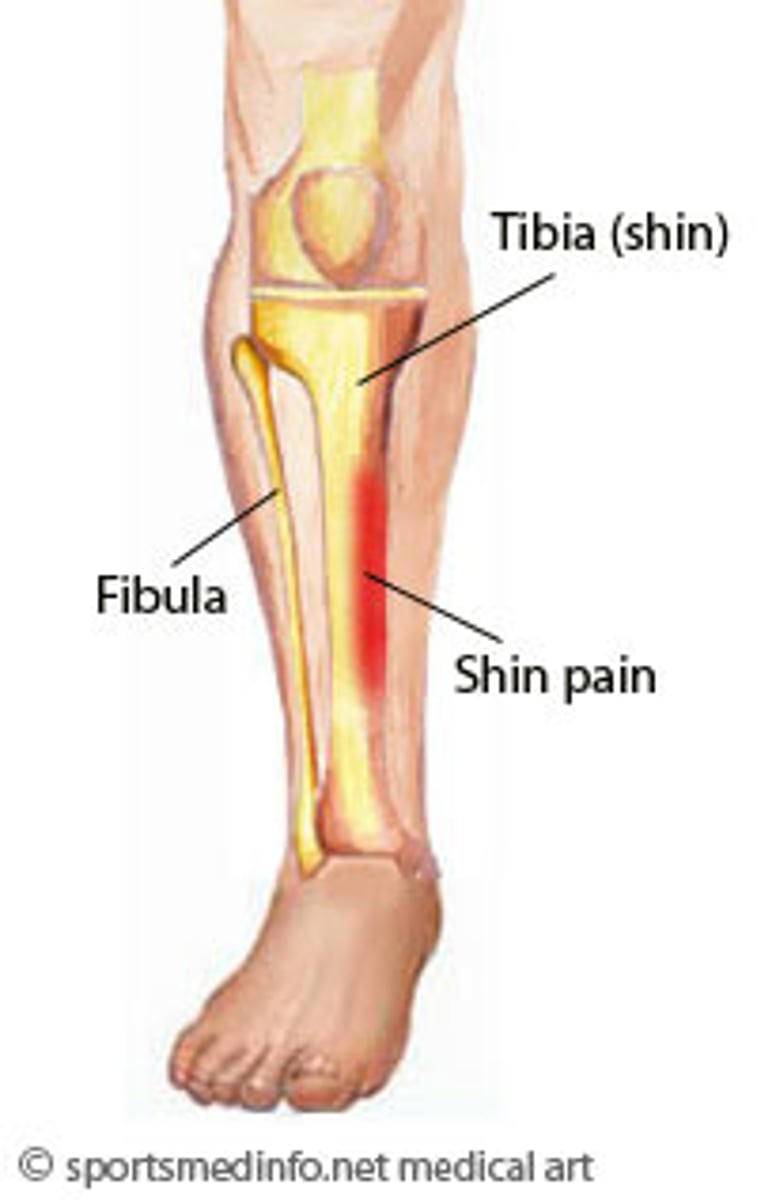
Shin splints
acute pain in the shin (tibia) caused by prolonged running, typically on hard surfaces.
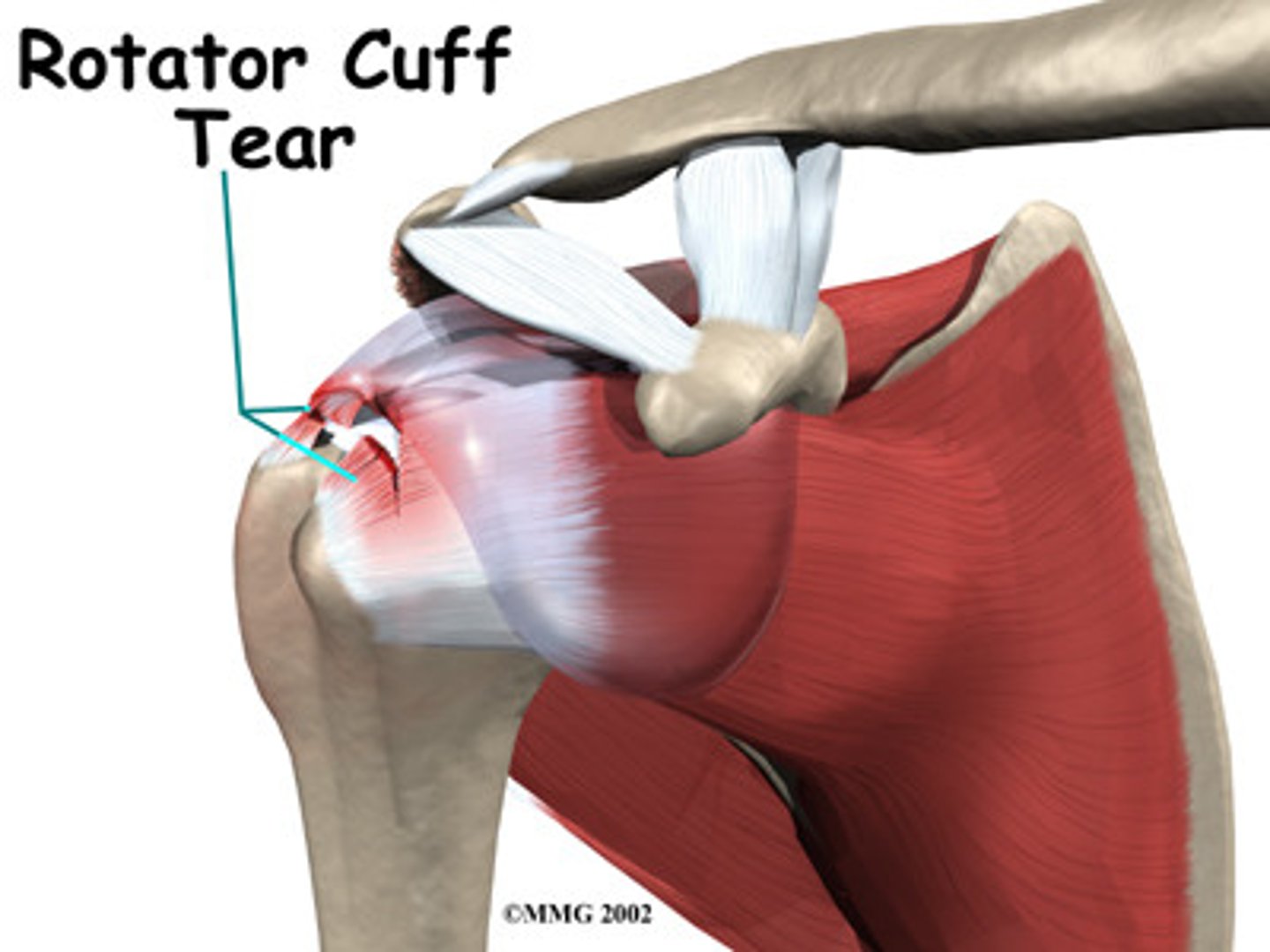
Rotator cuff injury
inflammation of the rotator cuff in the shoulder caused by overuse