Ch9 Meiosis; Sex Cell Cycle
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
asexual reproduction
1 parent organism replicates its DNA and splits the contents into 2 genetically identical offspring. Ex. Bacteria, archaea, protists
Sexual reproduction
DNA of the offspring comes from 2 parents. An egg fuses with a sperm producing genetically diverse offspring
Diploid
2n, cells with 2 sets of chromosomes
Haploid
n, cells with 1 set of chromosomes
Humans have how many homologous sets of chromosomes
23
autosomes
numbered chromosomes, 1 to 22
Sex chromosomes
23rd, X or Y for haploid, XX or XY for diploid
germline cell
only cell capable of meiosis; we have 1
somatic cells
Body cells, are diploid
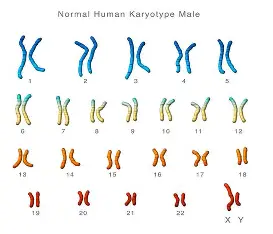
Karyotype
all chromosomes in your nucleus, stained under a microscope to be seen
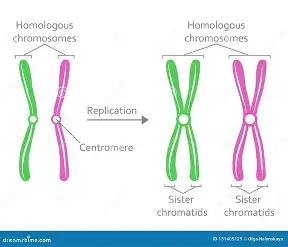
Homologous chromosomes
same size and type and carry the same sets of genes, carry different alleles, DNA sequence is not identical
allele
alternative versions of the same gene
when members of a homologous pair are replicated
identical alleles are on sister chromatids
gametes are produced by
meiosis
gamete
haploid sex cells, ex sperm and egg
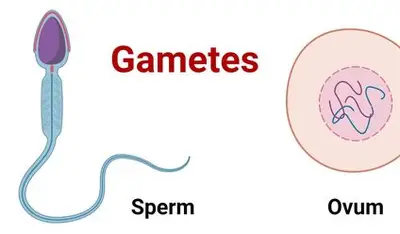
fertilization
2 haploid sex cells fuse, 1 diploid zygote is formed
zygote
1st cell of a new organism
tetrad
homologous pair
germ cells
specialized diploid cells that divide by meiosis to form haploid gametes; male is spermatogonia, female oocytes
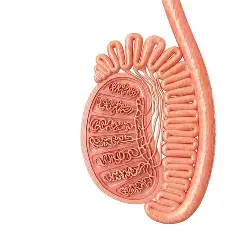
sperm cells form in
testes
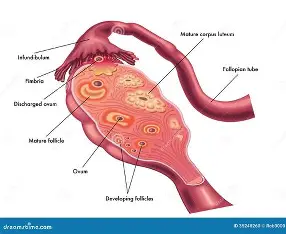
egg cells form in
ovaries
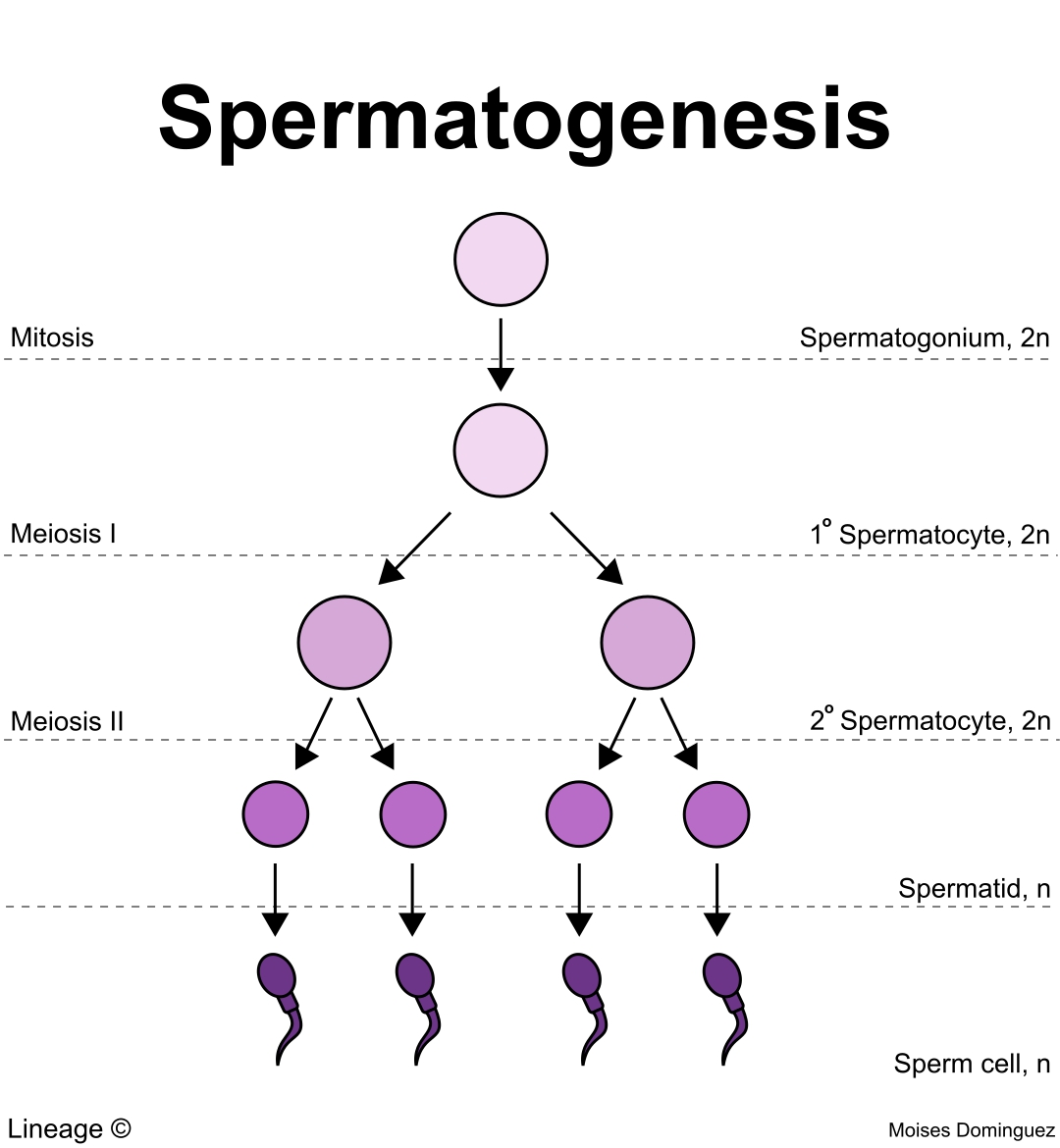
Spermatogenesis
1 spermatogonium produces 4 sperms
spermatogonia
male germ cells
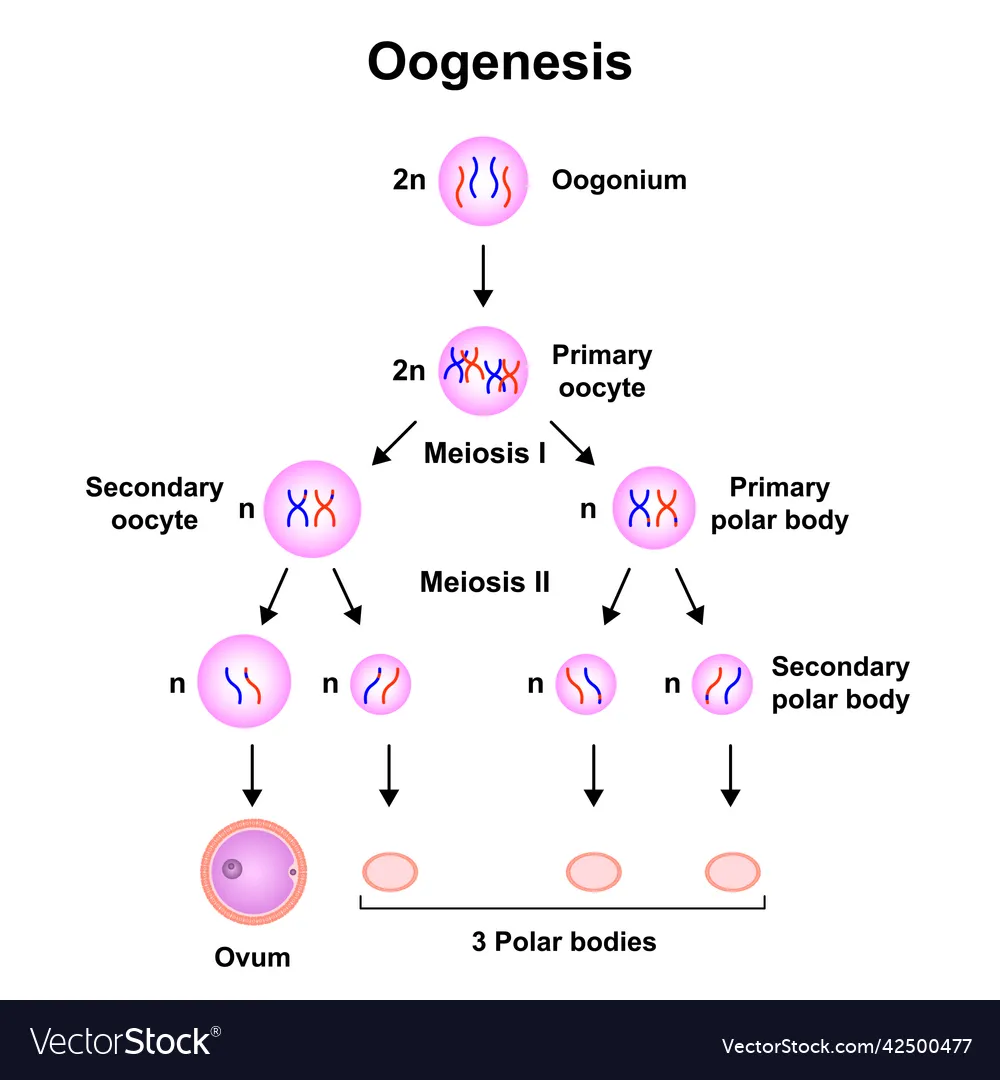
Oogenesis
1 oogonium produces 1 egg and 3 polar bodies
Spermatogenesis step 1
1 spermatogonium splits by mitosis into a spermatogonium and a primary spermatocyte
Spermatogenesis step 2
the primary spermatocyte splits by meiosis 1 into 2 haploid secondary spermatocytes
Spermatogenesis step 3
The secondary spermatocytes both split into 2 spermatids using meiosis 2.
Spermatogenesis step 4
The 4 spermatids mature into 4 sperm
Oogenesis step 1
a diploid oogonium splits by mitosis into an oogonium and a primary oocyte.
Oogenesis step 2
The primary oocyte splits by meiosis 1 into a haploid polar body and a haploid secondary oocyte.
Oogenesis step 3
The polar body haploid splits by meiosis 2 into 2 polar bodies. The Haploid secondary oocyte splits by meiosis 2 into an Ovum and a polar body
ovum
egg
meiosis halves the
chromosome number
meiosis produces
4 genetically distinct gametes
in meiosis
DNA replicates once, the nucleus divides twice
Meiosis generates variability because of
crossing over, independent assortment, random fertilization, mutations, and nondisjunction’s
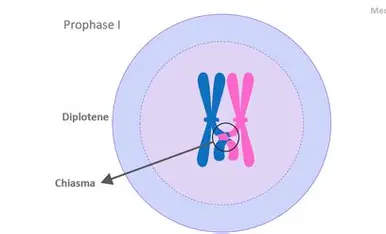
Prophase I
homologous chromosomes pair up and attach to the spindle, condensing. Crossing over shuffles genes. Results in 4 different sister chromatids
metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up in 2 rows. Independent assortment occurs.
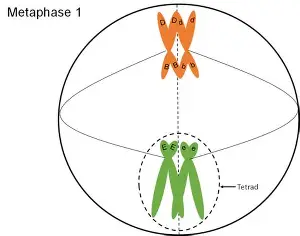
independent assortment
chromosome pairs align randomly, scrambling the combination of chromosomes for every gamete
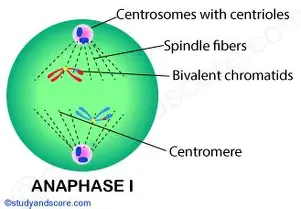
anaphase I
homologous chromosomes separate haploid daughter cells
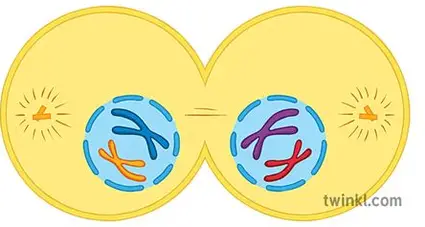
Telophase I
sister Chromatids remain together
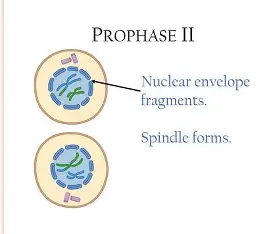
Prophase II
chromosomes attach to a spindle
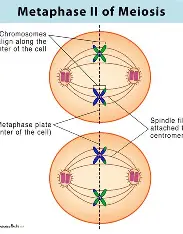
Metaphase II
chromosomes line up in a row single file
Chiasmata
site of crossing over
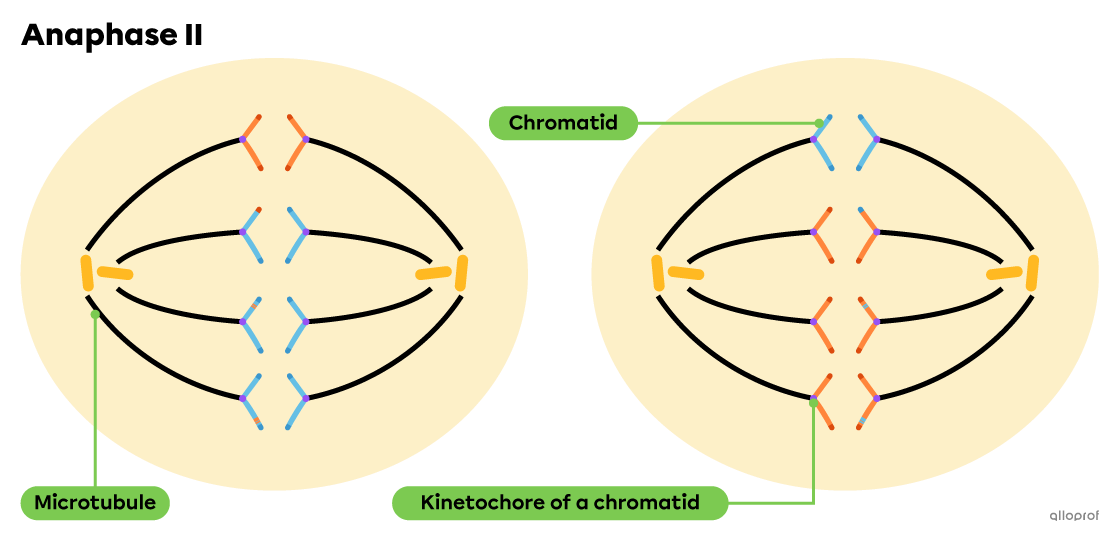
Anaphase II
sister chromatids separate into nonidentical haploid cells
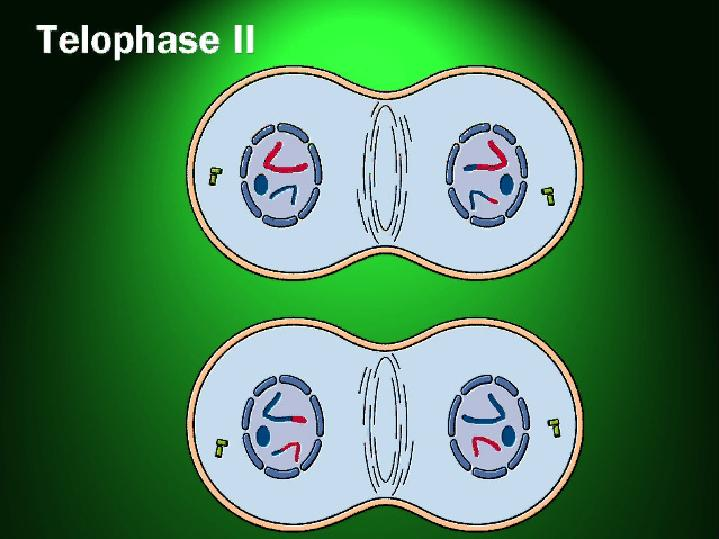
Telophase II
4 new cells have 1 set of chromosomes
Monozygotic
an embryo split in 2, each embryo develops independently. 1 zygote develops into 2 individuals. Identical twins.
Dizygotic
2 sperm cells fertilize 2 separate egg cells. Fraternal twins.
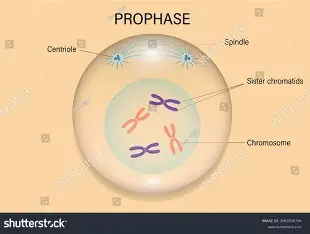
Mitosis prophase
chromosomes condense
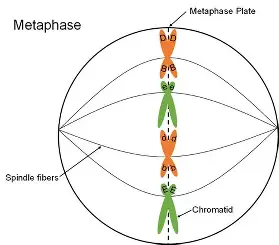
mitosis metaphase
chromosomes line up single file
Mitosis anaphase/telophase
centromeres dissolve, sister chromatids separate into identical daughter cells
requires 2 nuclear divisions
Meiosis
requires 1 nuclear division
mitosis
chromosomes synapse and cross over
meiosis
centromeres survive anaphase I
meiosis
centromeres dissolve in anaphase
mitosis
halves chromosome number
meiosis
preserves the chromosome number
mitosis
produces 4 daughter nuclei
meiosis
produces 2 daughter nuclei
mitosis
produces daughter cells genetically different from parent and each other
meiosis
produces genetically identical daughter cells
mitosis
used only for sexual reproduction
meiosis
used for asexual reproduction and growth
mitosis
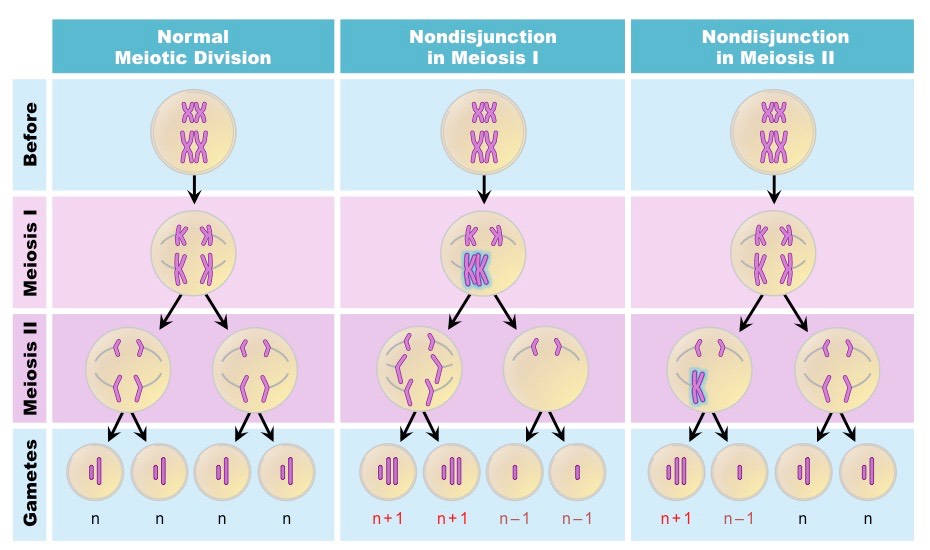
nondisjunction
when chromosomes fail to separate properly; forms abnormal games leading to zygotes with too many or too little chromosomes
nondisjunction can occur in anaphase I
all 4 zygotes have too many or too little chromosomes
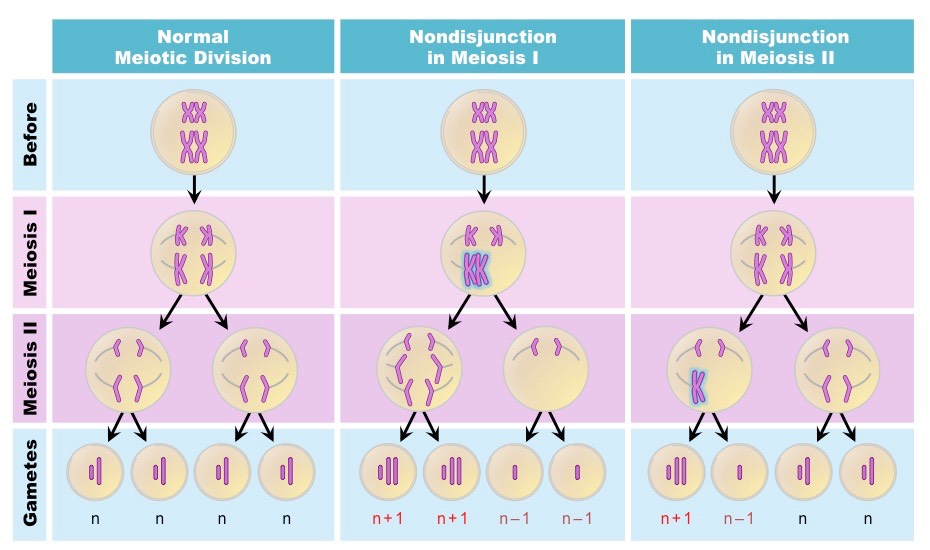
nondisjunction can occur in anaphase II
only 2 zygotes will be normal
down syndrome
3 copies of chromosome 21 instead of 2; caused by nondisjunction
nondisjunction of sex chromosomes
sex disorders; XXX, XXY, XYY, XO
trisomy
extra copy of a chromosome, causes genetic disorders
mutation in chromosome structure effects
the organism
Meiosis also produces
spores
fungi, some protists, and some plants produce haploid spores using meiosis
the spores undergo mitosis to form haploid gametophytes which produce sperm and eggs
Step 1 of spore life
Mature Sporophyte produces spores using meiosis
Step 2 of spore life
the spores undergo mitosis becoming male and female gametophytes
Step 3 of spore life
the gametophyte undergoes mitosis becoming gametes
Step 4 of spore life
the gametes fertilize producing a zygote
Step 5 of spore life
The zyogtye undergoes mitosis becoming a sporophyte
interphase
DNA replicates, cell produces proteins needed for cell division
early prophase comes after interphase
chromosomes condense and become visible 2n=4
Late prophase
crossing over occurs, spindle forms, nuclear envelope breaks up
metaphase 1 is after
prophase
anaphase 1 is after
metaphase 1
telophase and cytokinesis is after
anaphase
Sex cell cycle
interphase, Meiosis I, Interkinesis, Meiosis II
Interphase consists of
G0, G1, S, G2
Interkinesis consists of
G1, G2
Sex cell cycle detailed
G0, G1, S, G2, Prophase I, Metaphase I, anaphase I, Telophase I, cytokinesis I, G1, G2, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II, cytokinesis II