Scholarship in OT & Research as Foundation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
scholarly knowledge
− Using the knowledge base of the profession
− Evidence-based practice
− Reflective practuce
scholarship
Systematic
• Public, subject to review, part of (professional/discipline) knowledge base
− Develop/contribute to generalizable knowledge
importance of scholarship
growth, development, & vitality of the profession
Vitally important contributon to profession, academy, & society
scholarship of discovery
‒ The engagement in activity that leads to the development of “knowledge for its own sake”
‒ Original research to expand knowledge base of a discipline
‒ Generating new knowledge
‒ Qualitative research
ex. ethnographic study
scholarship of integration
Making creative connectons both within & across disciplines to integrate, synthesize, interpret, & create new perspectves & theories
‒ Aim is to find the meaning of research findings & interpret the fndings in ways that synthesize isolated facts from within & outside the discipline
• & integrate them to provide a richer & more thorough understanding of the issues
ex. meta-analysis
scholaship of application
Apply the knowledge generated by the Scholarship of Discovery or Integraton to address
real problems at all levels of society— Randomized Control Trial
‒ Focuses on program development and occupatonal therapy interventon
‒ Using knowledge about the value of occupaton as a health determinant to address
health disparites of populations
‒ Often viewed synonymously with knowledge translation
ex. applicaton of theoretical knowledge to practce interventions or to teaching in the classroom
scholarsip of teaching and learning
Involves the systematic study of teaching and/or learning and the public sharing and
review of such work through presentations, publications, and performances
randomized controlled trial (RCT)
a scientific study where participants are randomly assigned to groups to compare different treatments or interventions, with one group receiving the experimental treatment and the other serving as a control
role of research
Supports the theories & conceptual models that are foundations for practice
− Justfies the occupatonal therapy interventons for desirable outcomes
• Assessment
importance of research
− profession’s identity, standing, & social obligation
− Fulflling the economic imperative & the vital role of research to sustain the viability & vitality of the profession
−Health care culture
evidence based practice
best research evidence
patient values and preferences
clincial expertise
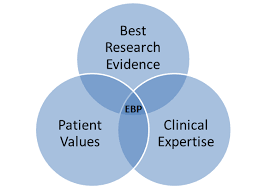
sequence of evidence-based practice
ask the cinical question
search the research literature for the best evidence
critically appraise the evidence
integrate evidence into the clinical reasoning process along with client preferences & values
document & evaluate outcomes or changes observed based on evidence
dissemenate the findings to stakeholders
key areas of research
− Efficacy
− Effectiveness
− Practice
− Services
knowledge translation
the synthesis, disseminaton, and applicaton of knowledge and evidence to improve the health of clients and strengthen the greater health system
implementation science
the scientific study of methods to promote the systematic uptake of research findings and other evidence-baased practices into routine practice, and, hence to improve the quality and effectiveness of health services and care
classicism
Reasoning that if pure logic was used to connect the natural world to scientific knowledge,then scientific knowledge could be demonstrated to be true (absolute truth)
inductive
generating explanations & theory from specific observations of the natural world
explanatons & theories are generated from specifc observatons of the natural world
deductive
deriving predictions from existing theory to see if those predictions hold in the natural world
predictons are derived from existng theory to see if those predictons hold in the natural world
modernism (logical positivism)
Replaced the concern for absolute truth with concern for how to correct errors in knowledge (revisions)
‒ Science as a process of testing & verification of the theory created through inductive reasoning
Relevance to OT: Quantitative research approaches (i.e., testing hypotheses that are rooted in theory)
critical modernism
Argues that theories progress by becoming better at the particular way they make sense of the world
‒ Logic is necessary, not sufficient in and of itself: role of intuition in induction
‒ Research does not prove or disprove theory; it does improve theory
‒ Relevance to OT: Qualitative research approaches (i.e., theories evolve by providing increasingly accurate estmates of the subjective world; perspectives based on observations of people interacting in natural contexts & the perspectives / experiences of those people)
postmodernism
Set of ideas in which scientific knowledge is no more privileged than any other source of knowledge
‒ All knowledge, including scientfic knowledge, is socially constructed
‒ Particular perspective of a particular group of people who have a particular purpose in mind
‒Relevance to OT: Disabilites studies
postmodern perspectives
evident in qualitative research & descriptive quantitative research
purpose of theories
To explain relatonships between concepts & predict how to create change
− In research, it is what makes sense of the phenomena examined, the questons asked, & the mechanisms for addressing problems
contemporary approaches
understand theory in terms of shared knowledge rather than fact