A & P Unit 3 Lecture Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/216
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
1
New cards
- requires oxygen
- in mitochondria
- in mitochondria
aerobic respiration
2
New cards
6 second contraction
- produce enough ATP to meet needs
- produce enough ATP to meet needs
stored ATP
3
New cards
15 seconds contraction
- used to convert ADP → ATP
- produce enough ATP to meet needs
- used to convert ADP → ATP
- produce enough ATP to meet needs
creatine phosphate
4
New cards
- in cytoplasm
- without oxygen
- 2.5 X faster than aerobic respir.
- produce enough ATP to meed needs
- without oxygen
- 2.5 X faster than aerobic respir.
- produce enough ATP to meed needs
anaerobic respiration
5
New cards
↑ aerobic respiration
- cell uses oxygen in myoglobin
- cardiovascular + respiratory systems have ↑ O2 delivery to tissues → ↑ ATP production aerobically
- cardiovascular + respiratory systems have ↑ O2 delivery to tissues → ↑ ATP production aerobically
6
New cards
as long as cardiovascular + respiratory systems can deliver sufficient O2 to tissues to make all ATP needed for contraction aerobically →
activity continues
7
New cards
what happens when cardiovascular + respiratory can no longer deliver sufficient O2 to tissues to make all ATP needed for contraction aerobically →
aerobic respiration also kicks in → continues for just a few minutes
8
New cards
what produces enough ATP to meet needs
1. stored ATP
2. creatine phosphate
3. anaerobic respiration
2. creatine phosphate
3. anaerobic respiration
9
New cards
- the amount of O2 needed after exercise to return body to pre-exercise condition
- need O2 to resupply myoglobin w O2
- need O2 to ↑ ATP production aerobically
- need O2 to resupply myoglobin w O2
- need O2 to ↑ ATP production aerobically
excess post-exercise O2 consumption (EPOC)
10
New cards
what is required for:
1. sweat to cool the body
2. adjust pH
3. have ↑ metabolism
4. reapair tissues
1. sweat to cool the body
2. adjust pH
3. have ↑ metabolism
4. reapair tissues
ATP
11
New cards
muscle fiber:
- have lots myoglobin (store O2)
- more capillaries + mitochondria
- smaller diameter
- fewer myofibrils
- adapted for aerobic respiration
- fatigue slow
- postural muscles, leg muscles
- have lots myoglobin (store O2)
- more capillaries + mitochondria
- smaller diameter
- fewer myofibrils
- adapted for aerobic respiration
- fatigue slow
- postural muscles, leg muscles
type I fibers (slow twitch red)
12
New cards
muscle fiber:
- less myoglobin
- fewer mitochondria
- fewer capillaries
- larger diameters → take longer for O2 diffuse through cells
- more myofibrils
- stronger contraction
- adapted for anaerobic respiration
- fatigue quicker, short period of time
- more enzymes in cytoplasm for anaerobic resp.
- store more glycogen
- quick mvmt muscles: eyes, hands, arms
- less myoglobin
- fewer mitochondria
- fewer capillaries
- larger diameters → take longer for O2 diffuse through cells
- more myofibrils
- stronger contraction
- adapted for anaerobic respiration
- fatigue quicker, short period of time
- more enzymes in cytoplasm for anaerobic resp.
- store more glycogen
- quick mvmt muscles: eyes, hands, arms
type II B (fast twitch white fibers)
13
New cards
intermediate between type I and type II B
type II A (fast twitch pink/intermediate)
14
New cards
type of exercise:
- making muscles more "red"
- ↑ myoglobin
- ↑ mitochondria
- ↑ capillaries
- making muscles more "red"
- ↑ myoglobin
- ↑ mitochondria
- ↑ capillaries
aerobic exercise
15
New cards
type of exercise:
- make muscles big + strong
- anaerobic activity
- make muscles more "white"
- ↑ glycogen storage
- ↑ enzymes in cytoplasm for anaerobic resp
- make muscles bigger
- ↑ myofibrils in each muscle cell
- ↑ CT around muscle cells
- make muscles big + strong
- anaerobic activity
- make muscles more "white"
- ↑ glycogen storage
- ↑ enzymes in cytoplasm for anaerobic resp
- make muscles bigger
- ↑ myofibrils in each muscle cell
- ↑ CT around muscle cells
strength training exercise
16
New cards
what makes muscles "bigger"?
↑ myofibrils in each muscle cell
17
New cards
motor units differ in:
1. number of muscle cells in motor unit (10-sev 100s)
2. sensitivity to stimuli (some respond to weak/strong)
2. sensitivity to stimuli (some respond to weak/strong)
18
New cards
only part of neuron that initiates impulses, send info to other neurons, muscle/gland cells
axon
19
New cards
part of neuron that receive info from environment, sensory receptors, other neurons
dendrites
20
New cards
one neuron + all skeletal muscle cells it contacts
motor unit
21
New cards
usually closed, opens in response to stimuli → allow calcium to diffuse in because more calcium outside cell than in
calcium channel
22
New cards
filled with Ach
- type of neurotransmitter
- type of neurotransmitter
synaptic vesicles
23
New cards
Na+ channels, usually closed, open when Ach binds to them
- allow Na+ to enter because more Na+ outside cell than in
- allow Na+ to enter because more Na+ outside cell than in
Ach receptors
24
New cards
single cx in response to single stimulus
muscle twitch
25
New cards
impulse travels along nerve, crosses to muscle at neuromuscular junction
- calcium released, cross bridges form
- calcium released, cross bridges form
lag period
26
New cards
power stroke alternating with recovery stroke
cx phase
27
New cards
pump calcium back into S.R
- 0 cross bridges form
- 0 cx
- 0 cross bridges form
- 0 cx
relaxation
28
New cards
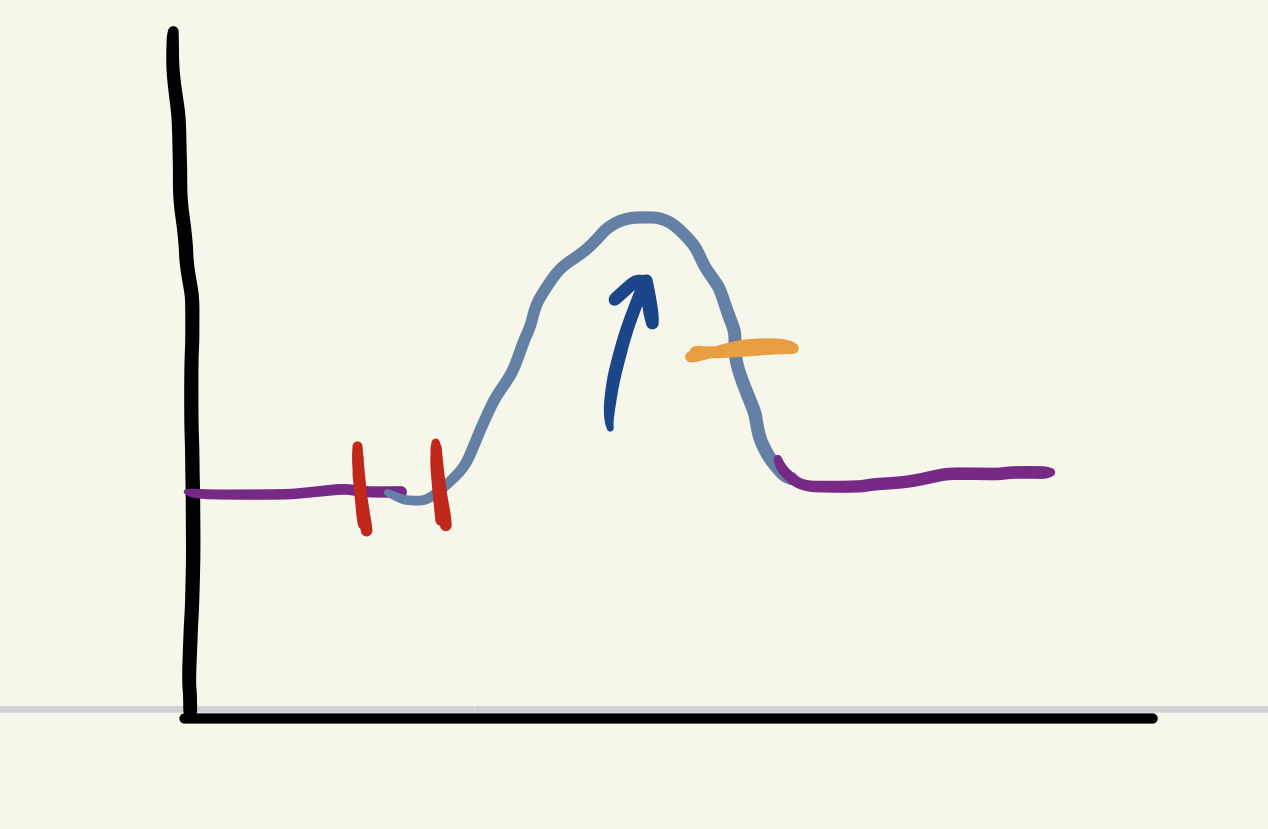
red
stimulus / lag period
29
New cards
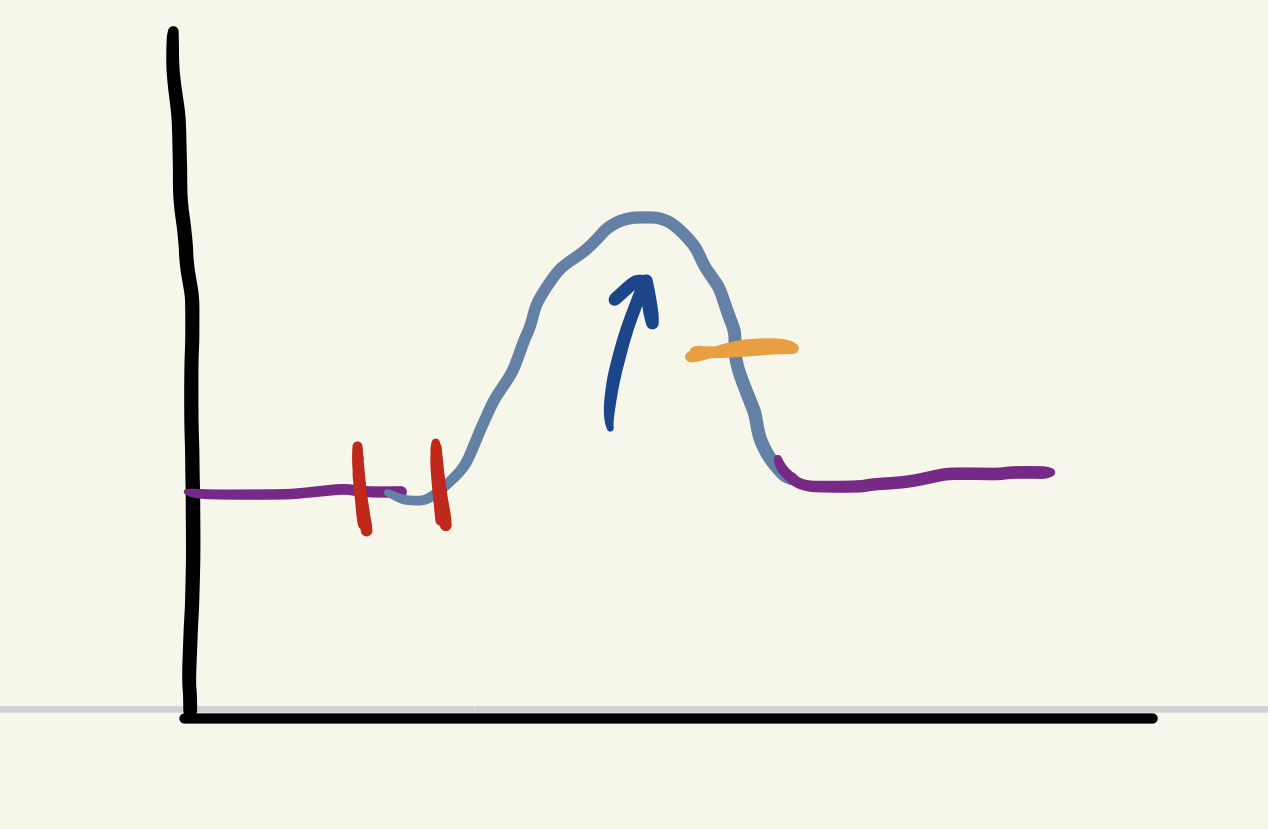
blue arrow
cx phase
30
New cards
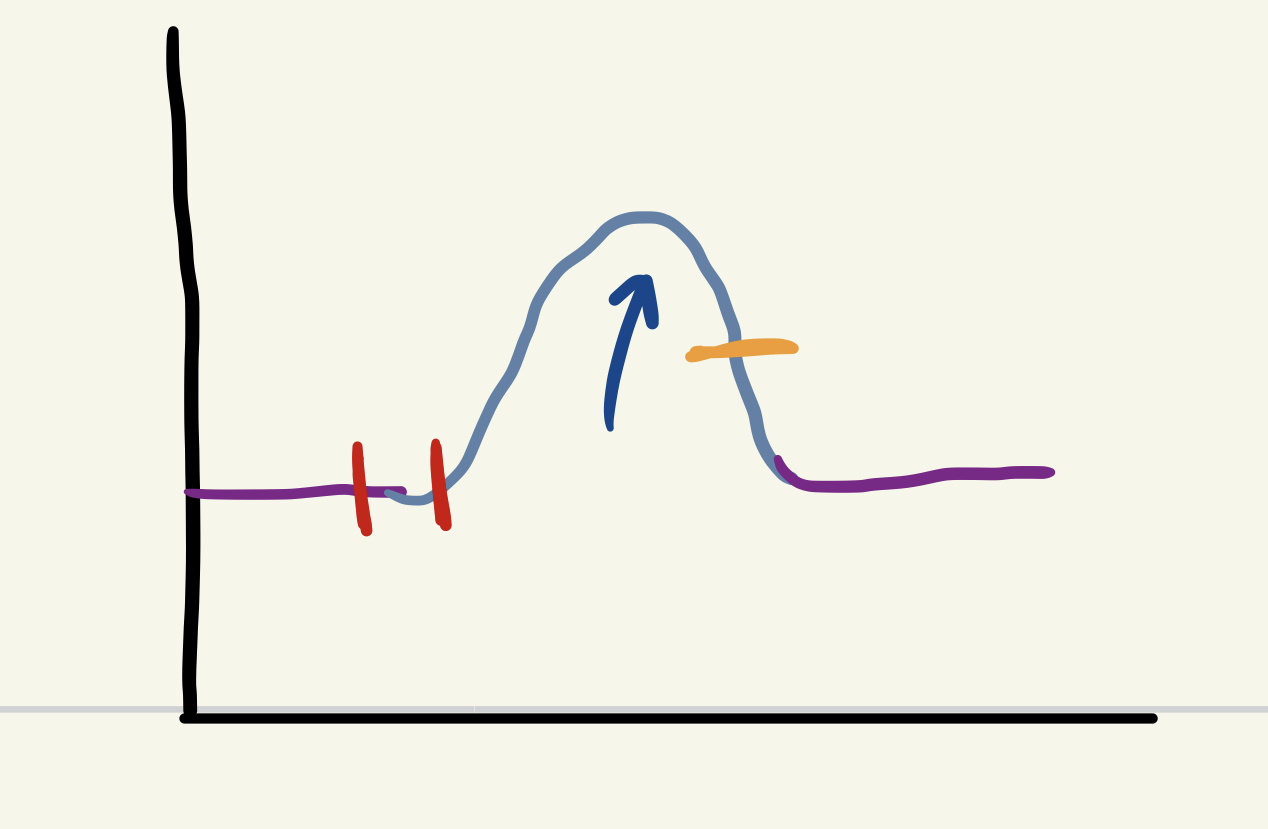
orange
relaxation
31
New cards
stronger stimulus reaches threshold more motor units
- more muscle cells cx
- more muscle cells cx
multiple motor unit summation
32
New cards
lowest stimulus where observational cx occurs
- threshold is just strong enough to reach threshold of motor unit
- threshold is just strong enough to reach threshold of motor unit
threshold stimulus
33
New cards
no ↑ in cx strength after this event
- lowest stimulus strength where all motor units respond
- lowest stimulus strength where all motor units respond
maximal stimulus
34
New cards
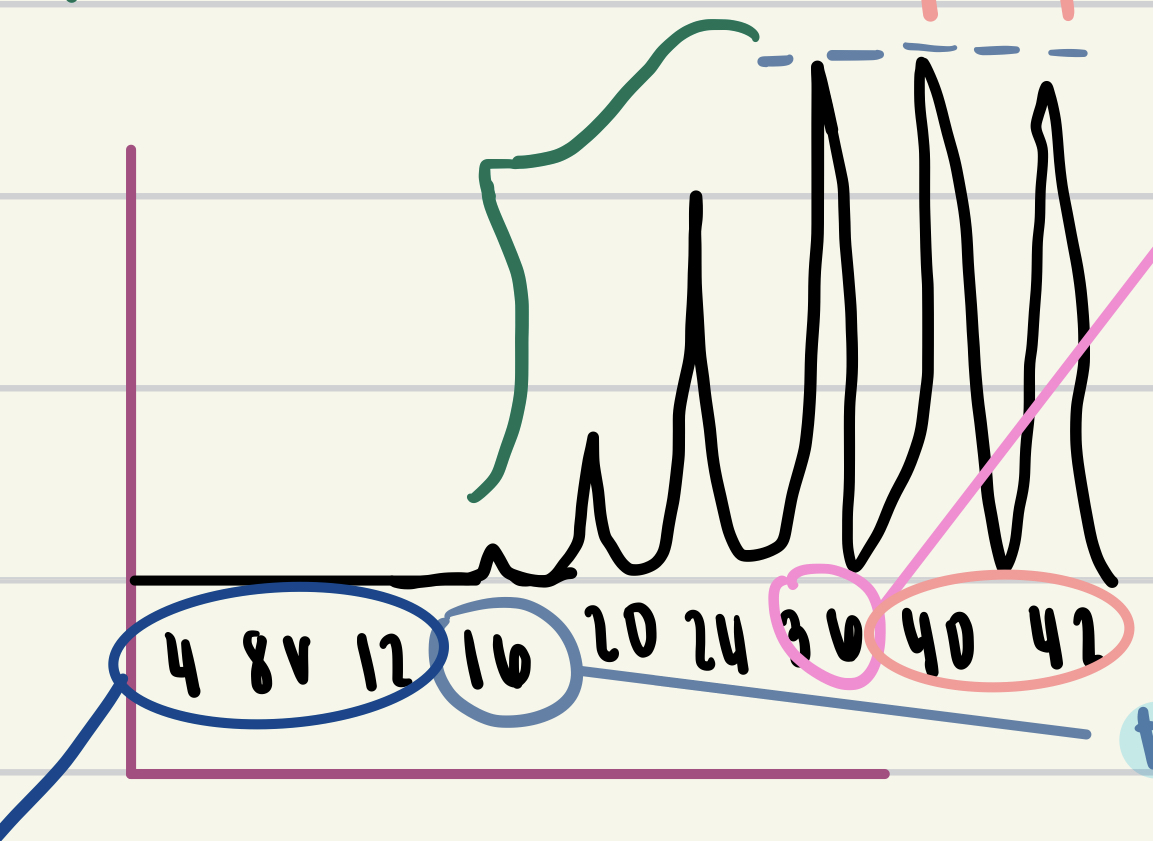
dark blue circle
subthreshold stimuli
35
New cards
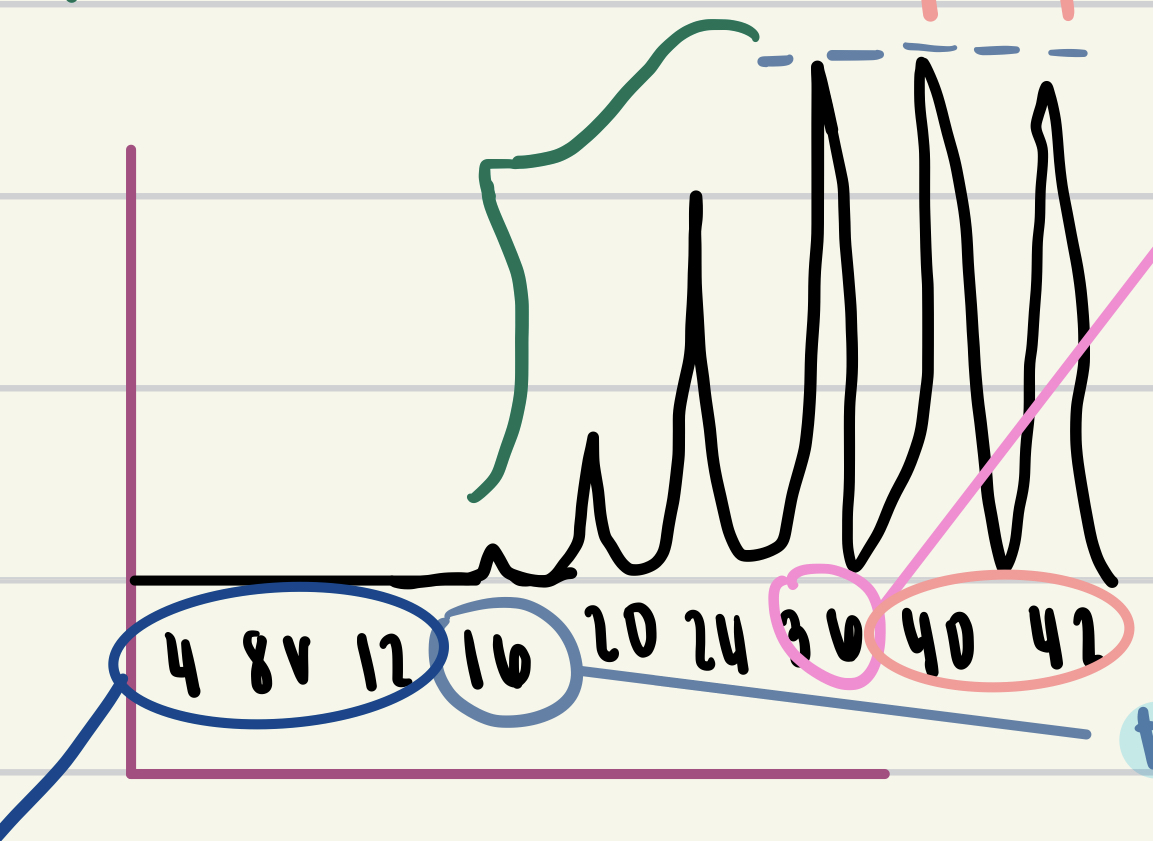
value circled in light blue
threshold stimulus
36
New cards
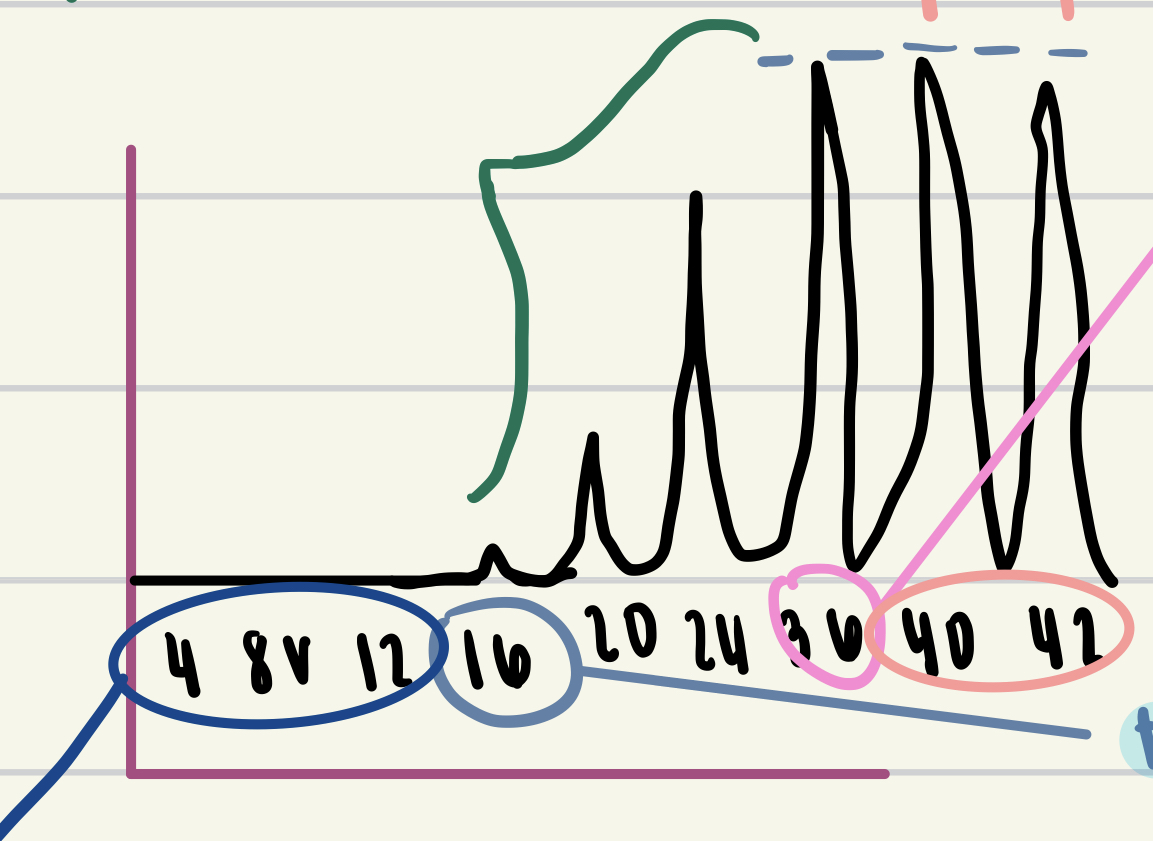
value circled in pink
maximal stimulus
37
New cards
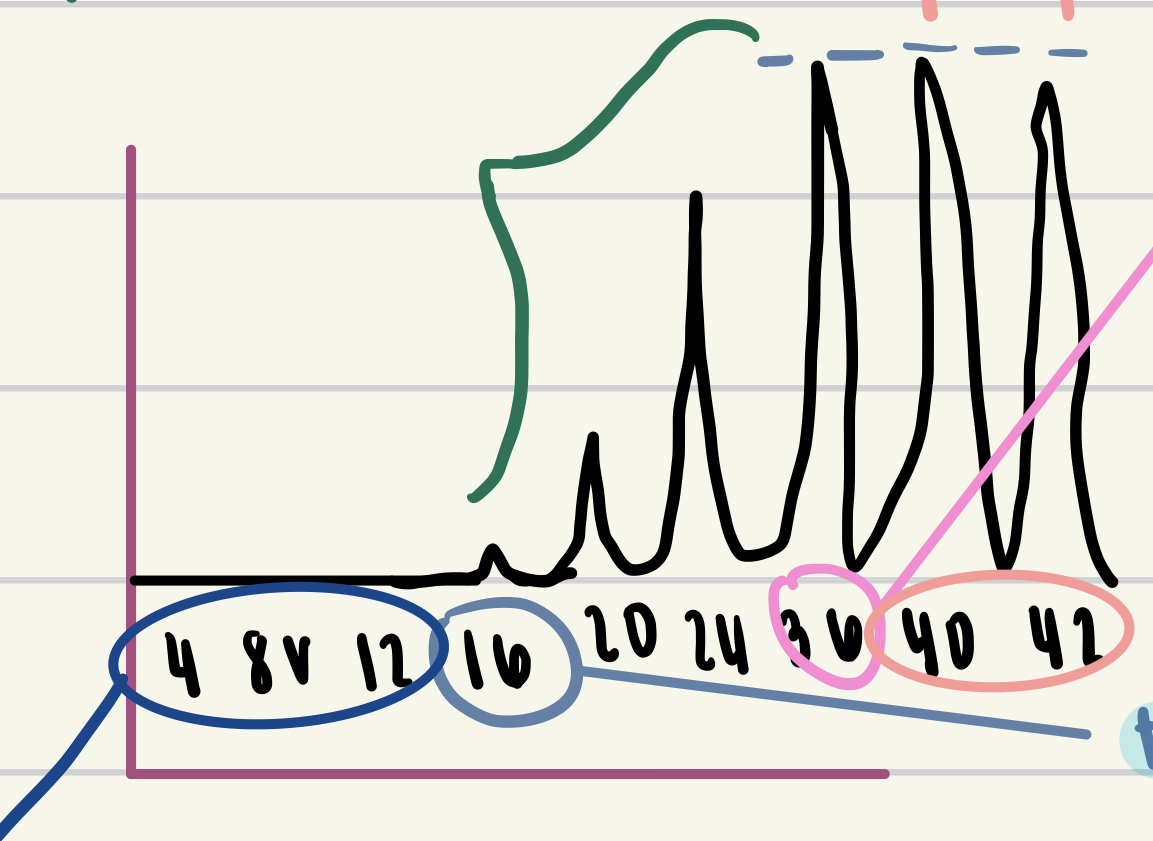
values in green
multiple motor unit summation
38
New cards
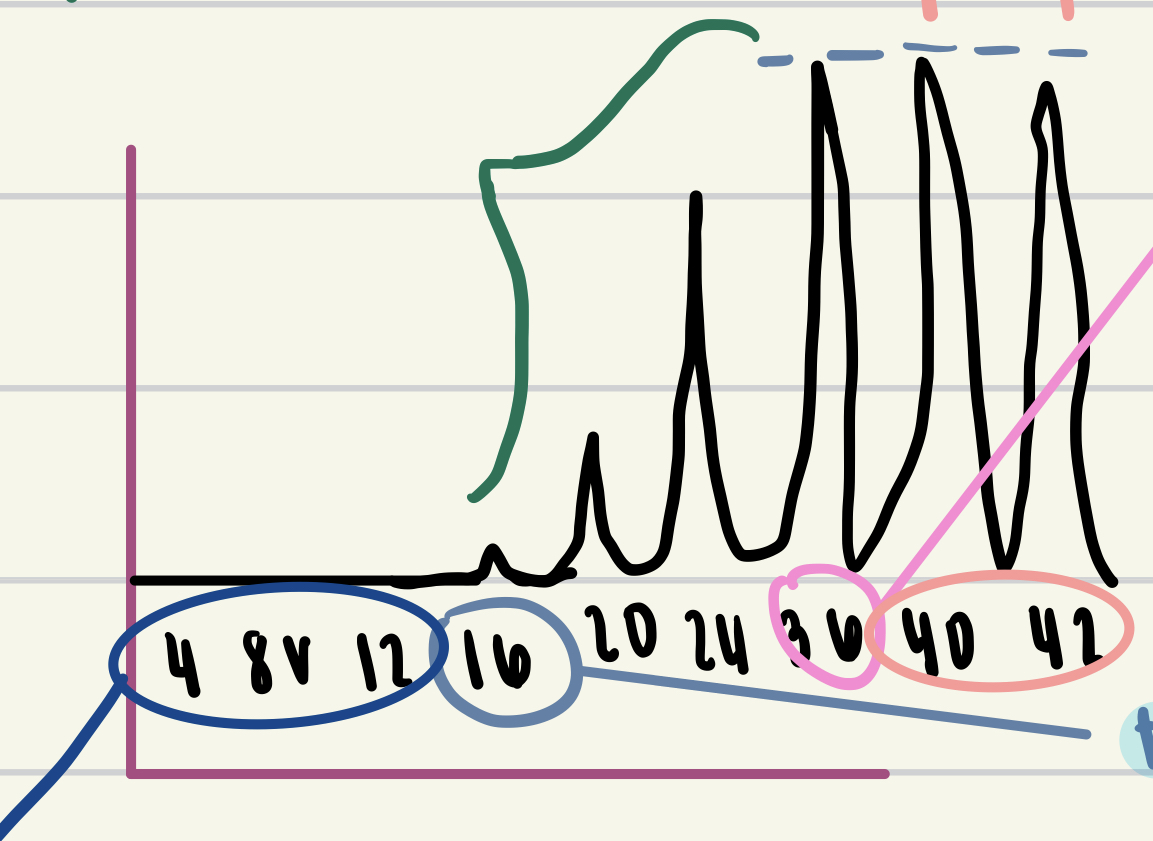
values in peach
supermaximal stimuli
39
New cards
more calcium available if partial relaxation → not all calcium returned to SR → more calcium = more cross bridges = stronger cx
wave summation
- partial relaxation between cx
- partial relaxation between cx
40
New cards
muscle stimulated to cx again before it begins to relax
tetany
- sustained cx
- sustained cx
41
New cards
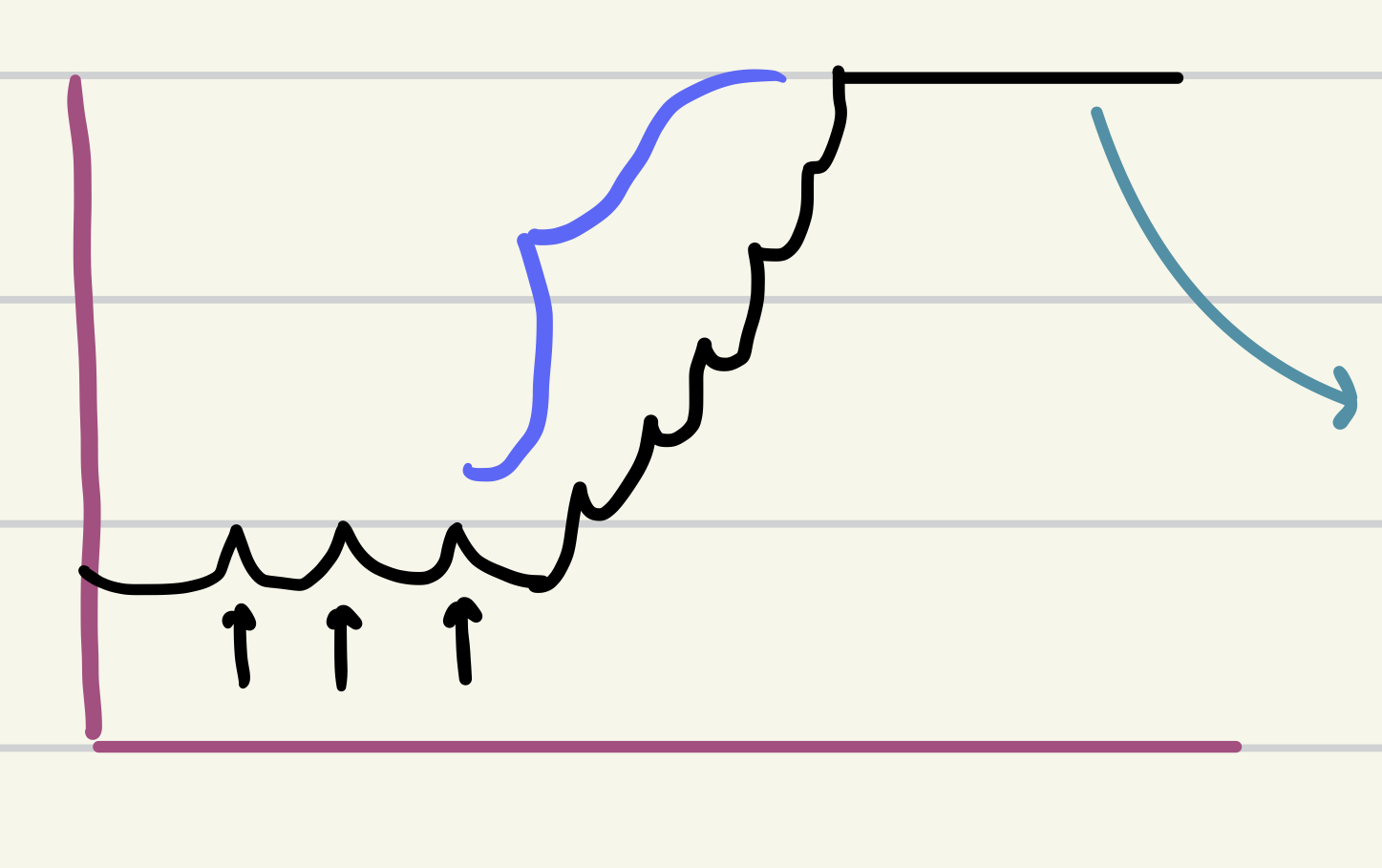
purple
wave summation
- partial relaxation b/t cx
- partial relaxation b/t cx
42
New cards
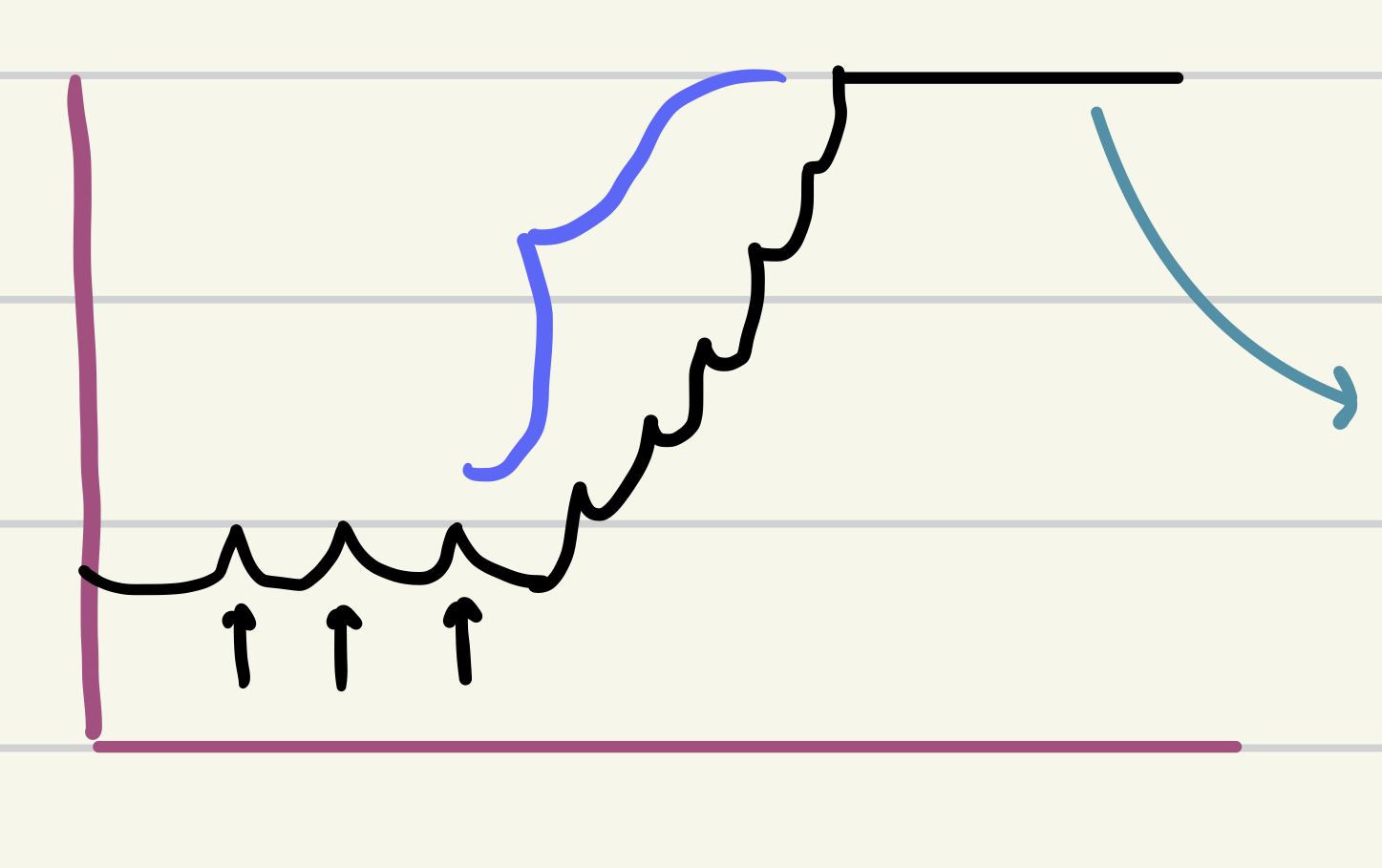
blue
tetany
43
New cards
still some tension on tendon if muscle not completely relaxed → less slack to take up
↑ frequency of stimuli
- tetany
- tetany
44
New cards
change amount of overlap b/t actin + myosin filaments →
changes cx strength
- change length of muscle
- change length of muscle
45
New cards
optimum length for sarcomeres →
provides optimal overlap b/t actin + myosin
- change length of muscle
- change length of muscle
46
New cards
can form cross bridges →
gets lots of sliding of actin over myosin
- change length of muscle
- change length of muscle
47
New cards
overlap just enough so all myosin heads can bind to actin
change length of muscle
48
New cards
muscle too stretched = little overlap b/t actin + myosin
→ few cross bridges can from
→weaker cx
- change length of muscle
→weaker cx
- change length of muscle
49
New cards
muscle too short = so much overlap, sarcomere so short
→ little sliding of actin over myosin
→ weaker cx
- change length of muscle
→ weaker cx
- change length of muscle
50
New cards
type of muscle:
- striated: has actin + myosin arranged into sarcomeres → alternating arrangement
- involuntary: can initiate its own impulse to cause heartbeat
- intercalated discs b/t cells
- less SR than skeletal muscle
- striated: has actin + myosin arranged into sarcomeres → alternating arrangement
- involuntary: can initiate its own impulse to cause heartbeat
- intercalated discs b/t cells
- less SR than skeletal muscle
cardiac muscle
51
New cards
highly folded PM b/t cells
↑ surface area
lots of desmosomes (hold cells together)
↑ surface area
lots of desmosomes (hold cells together)
intercalated discs
52
New cards
calcium entering cell from extracellular fluid → release more calcium from SR
calcium induced calcium release
53
New cards
type of muscle:
- involuntary
- walls hallow muscular organs
- smooth, no striations
- actin + myosin filaments present, but not arranged into sarcomeres
→ arranged diagonally
- myosin filaments have heads along entire length
- no Z discs, has dense bodies instead that actin filaments attach to
- involuntary
- walls hallow muscular organs
- smooth, no striations
- actin + myosin filaments present, but not arranged into sarcomeres
→ arranged diagonally
- myosin filaments have heads along entire length
- no Z discs, has dense bodies instead that actin filaments attach to
smooth muscle
54
New cards
- actin + myosin present, not arranged into sarcomeres
- myosin filaments have heads along entire length
- myosin filaments have heads along entire length
allow cx of very stretched muscle
55
New cards
type of muscle:
- has intermediate filaments
- no troponin
- little SR
can cx from impulse, hormones, stretching, local tissue conditions
- has intermediate filaments
- no troponin
- little SR
can cx from impulse, hormones, stretching, local tissue conditions
smooth muscle
56
New cards
each cell must get its own impulse from neuron to cx
- each cell acts individually
- bronchi, walls of larger arteries, arrector pili muscles
- each cell acts individually
- bronchi, walls of larger arteries, arrector pili muscles
multi-unit smooth muscle
57
New cards
cells joined by gap junctions
impulse travels cell to cell thru gap junctions
wave-like pattern of cx
most viscera
move something thru particular organ
impulse travels cell to cell thru gap junctions
wave-like pattern of cx
most viscera
move something thru particular organ
single unit (visceral) smooth muscle
58
New cards
decrease in size of muscle b/c disuse or denervation
- < 1 year: muscle cells lose myofibrils, REVERSIBLE
- > 1 year: muscle cells die, replaced by scar tissue
- < 1 year: muscle cells lose myofibrils, REVERSIBLE
- > 1 year: muscle cells die, replaced by scar tissue
atrophy
59
New cards
followed prolonged atrophy
- scar tissue shrinks, cause permanent flexing at the joints
- scar tissue shrinks, cause permanent flexing at the joints
contractures
60
New cards
- genetic disease
- mother → son
- lack of dystrophin protein
- smooth muscle affected
- contractures
- no cure
- no dystrophin: muscle cells tear to point they can't be replaced/repaired
→ muscle cells start to die, replaced by scar tissue
- mother → son
- lack of dystrophin protein
- smooth muscle affected
- contractures
- no cure
- no dystrophin: muscle cells tear to point they can't be replaced/repaired
→ muscle cells start to die, replaced by scar tissue
duchenne muscular dystrophy
61
New cards
- autoimmune disease
- women>men
- antibodies produced, block some Ach receptors on sarcolemma
- fewer Ach receptors produced → ↓ Ach binding to receptors
↓ muscle cx
- facial muscles affected first
- problems speaking, swallowing, control eye mvmts
- women>men
- antibodies produced, block some Ach receptors on sarcolemma
- fewer Ach receptors produced → ↓ Ach binding to receptors
↓ muscle cx
- facial muscles affected first
- problems speaking, swallowing, control eye mvmts
myesthenia gravis
62
New cards
TX duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PT
- bracing
- walking + breathing assistance
- steroids to slow the progression
- bracing
- walking + breathing assistance
- steroids to slow the progression
63
New cards
TX myesthenia gravis
- immune suppressing drugs, steroids
Ach-E inhibitors → inhibit breakdown Ach →more Ach binding to receptors
Ach-E inhibitors → inhibit breakdown Ach →more Ach binding to receptors
64
New cards
tear/stretch of muscle tissue
TX = RICE
TX = RICE
strain
65
New cards
- weakness in organ wall, organ can protrude
hernia
66
New cards
most common hernia, in inguinal canal
- men>women due to larger inguinal canal
- men>women due to larger inguinal canal
inguinal hernia
67
New cards
hernia in umbilical region
- second most common
- second most common
umbilical hernia
68
New cards
hernia where small intestine returned to abdomen cavity manually
reducible hernia
69
New cards
hernia that is not reducible
- may become strangulated
- vessels of small int compressed → no blood supply to tissue → tissue dies
- may become strangulated
- vessels of small int compressed → no blood supply to tissue → tissue dies
irreducible hernia
70
New cards
multiple layers of PM wrapped around axon
myelin sheath
71
New cards
- surrounded by myelin sheath
- insulates + protects axon
- ↑ speed impulse conduction
- insulates + protects axon
- ↑ speed impulse conduction
myelination of axons
72
New cards
type of cell that forms myelin sheath in peripheral nervous system
- line up along axon → wrap around axon many times → multiple layers PM wrapped around axon
- line up along axon → wrap around axon many times → multiple layers PM wrapped around axon
schwann cells
73
New cards
all cytoplasm + organelles get squeezed to outer margins of schwann cells
neurilemma
74
New cards
areas of axon with no myelin (b/t myelinated areas)
nodes of ranvier
75
New cards
provide white color (white matter)
myelin/myelinated fibers (axon)
76
New cards
form myelin sheath in central nervous system
- has multiple flat extensions
- each wrap around part of axon many times → form myelin sheath
- has multiple flat extensions
- each wrap around part of axon many times → form myelin sheath
oligodendrocytes
77
New cards
when does myelin sheath begin forming?
before birth, not complete until adulthood
78
New cards
- autoimmune disease
- women>men
- destruction of myelin sheath in CNS
- immune system cells damage myelin in CNS
- replaced scar tissue
- interfere with impulse conduction
- ↓ muscle activity
- cognitive/balance impaired
- ↓ sensation
- burn/tingle sensation
- facial muscles affected first (slurred speech, difficult swallowing)
- women>men
- destruction of myelin sheath in CNS
- immune system cells damage myelin in CNS
- replaced scar tissue
- interfere with impulse conduction
- ↓ muscle activity
- cognitive/balance impaired
- ↓ sensation
- burn/tingle sensation
- facial muscles affected first (slurred speech, difficult swallowing)
multiple sclerosis
79
New cards
TX multiple sclerosis
immune suppressing drugs
plasma phoresis
plasma phoresis
80
New cards
classification of neurons
1. structure
2. function
2. function
81
New cards
type of neuron classified by structure:
- 99% neurons
- many dendrites, one axon
- all motor neurons
- all association neurons (interneurons)
- 99% neurons
- many dendrites, one axon
- all motor neurons
- all association neurons (interneurons)
multipolar neurons
82
New cards
type of neuron classified by structure:
- 2 cytoplasmic extensions with cell body b/t
- 1 axon, 1 serves as dendrite
- some sensory neurons (eyes, nose)
- 2 cytoplasmic extensions with cell body b/t
- 1 axon, 1 serves as dendrite
- some sensory neurons (eyes, nose)
bipolar neurons
83
New cards
type of neuron classified by structure:
- one long cytoplasmic extension, neuron cell body to side
- distal, unmyelinate = dendrites
- myelinated = axon
- one long cytoplasmic extension, neuron cell body to side
- distal, unmyelinate = dendrites
- myelinated = axon
unipolar neurons
84
New cards
type of neuron:
- most unipolar, some bipolar
- body → CNS
- most unipolar, some bipolar
- body → CNS
sensory neuron
85
New cards
type of neuron:
- CNS → body
- muscles/glands
- all multipolar
- CNS → body
- muscles/glands
- all multipolar
motor neurons
86
New cards
type of neuron:
- interconnecting neurons/association
- carry info neuron to neuron in CNS
- all multipolar
- interconnecting neurons/association
- carry info neuron to neuron in CNS
- all multipolar
interneurons
87
New cards
- gray matter
- info integrated, processed, decisions made
- most in CNS
- info integrated, processed, decisions made
- most in CNS
clusters neurons cell bodies
88
New cards
where is gray matter located in CNS
- outer surface brain "cortex"
- inner regions spinal cord
- nuclei : other clusters neuron cell bodies
- inner regions spinal cord
- nuclei : other clusters neuron cell bodies
89
New cards
where is gray matter in peripheral NS
ganglion
90
New cards
clusters neuron cell bodies (gray matter) in peripheral NS
ganglion
91
New cards
white matter
myelinated axons
92
New cards
- carry info place to place
white matter - myelinated disc
93
New cards
bundles of white matter in CNS
tracts
94
New cards
carry info place to place in brain or b/t brain + spinal cord
tracts
95
New cards
bundles of white fibers in peripheral NS
nerves
96
New cards
carry info back and forth from body to CNS
nerves
97
New cards
make up the control system
nervous + endocrine
98
New cards
nerve impulses + neurotransmitters
nervous system
99
New cards
communicate with hormones
endocrine system
100
New cards
part of NS that includes brain + spinal cord only
CNS