Superconductivity
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Superconductivity depends on
Magnetic
What is conductivity ?
Flow of electron from one place to another without any resistance and develop current is known as conductivity
Who place an important role in conductivity ?
Temperature
At certain temperature and resistance is 0 and its called
Superconductivity
What are the application of superconductor ?
Magnetic trains
MRI
SQUIDS
High speed supercomputers
Power transmission cables
What is transition temperature ?
The temperature at which a material such as from solid to liquid or from magnetic to non-magnetic or conductor converts in superconductor
What are the properties of super conductor ?
It is a low temperature phenomenon
transition temperature is different for different substance
ferro magnetic and anti fermi magnetic materials are not superoconductors
Those metallic elements having their valence electrons lies between 2 to 8 to exhibit superconductivity
Below the transition temperature the specific heat curve is discontinuous.
Material having high normal resistivity exhibit _______
superconductivity
Which material shows the superconductivity properties ?
zp = 10^6
Superconducting elements in general lie in the _____ columns of the periodic table
inner
Those metallic elements having their valence electrons lies between 2 to 8 to exhibit _______
superconductivity
What is meissner effect ?
The Meissner effect is a cool trick that superconductors can do.
When they become superconducting (very, very cold), they kick out all magnetic fields from inside them.
It's like they create a force field against magnets, making them float and repelling them.
ex - super fast train 😄 .
Diagram of meissner effect ?
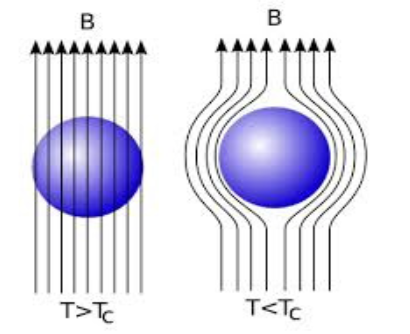
In meissner effect the normal state the magnetic induction inside the specimen is
B = Uo (H+i)
What is H in the magnetic inside the specimen
external applied magnetic field
What is I in the magnetic inside the specimen
Magnetisation produce inside the speicmen
at B = 0 the specimen in semiconductor is ?
0
the value of X = -1
I
H
When will specimen act as a perfectly diamagnetic ?
X = 1 `
the magnetic flux passing through the specimen should not change on cooling to the ————————
Transition temperature
What are the types of semiconductor on the basis of diamagnetic res[onse ?
Type 1 ( Soft superconductor )
Type 2 ( Hard superconductor )
the superconductor which follow the meissner effect is called ?
Type I superconductor
the magnetism is disapper and the converting from superconductor state to normal state is sharp those are known as ____________
superconductors
diagram of Type 1 superconductors
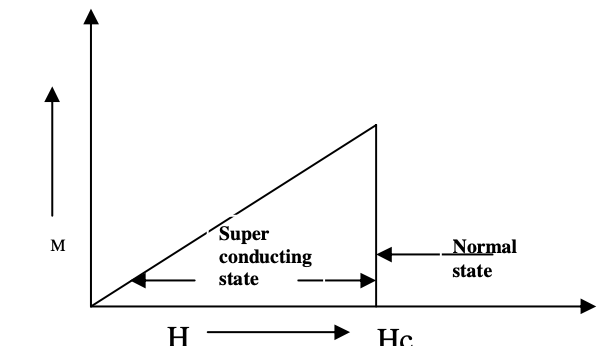
superconductor which doesn’t follow the complete meissner effect is called ________-
Type II superconductor
why there is a tilt in graph of Type ii semiconductors
due to the unequal electron and hole effective masses
Diagram of Type II superconductor ?
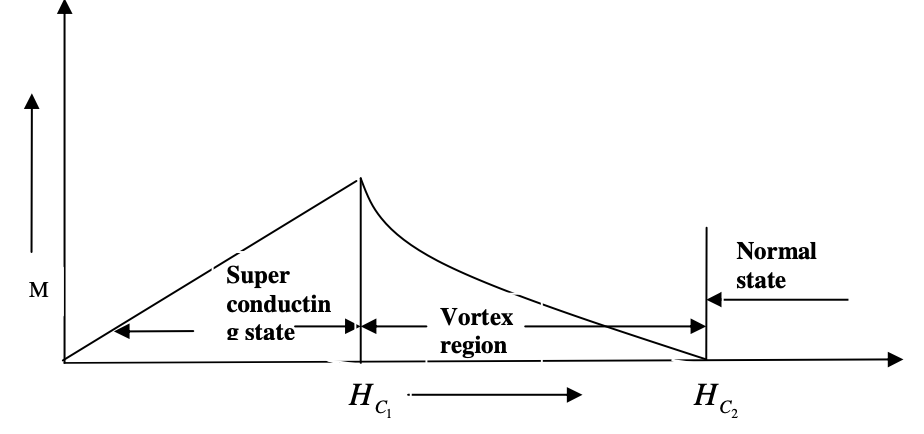
The type 1 semiconductor has ____ critical field value Hc
single
The type 2 semiconductor has ______ critical field Hc1 and Hc2
two
is there any mixed state in Type 1 semiconductor ?
no
is ther any mixed state in type II Semiconductor ?
yeah !
Which are known as soft superconductor ?
Type I semiconductor !
Which are known as hard superconductor ?
Type II semiconductor !
Material with pure form are type _____ superconductor
I
Material with impurities or alloy are type _____ superconductor
II
What are the example of Type I semiconductor ?
Zn , Al , Hg
What are the example of Type II semiconductor ?
Zr , Nb
According to london’s equation the magnetic flux doesnot suddenly drop to zero at the surface of the type I semiconductor , but decrease ________
exponentially
types of josephon effect ?
DC josephson effect
AC josephson effect
what is DC josephson effect ?
The DC Josephson effect is the phenomenon where a supercurrent flows between two superconductors separated by a thin insulating barrier without the potential difference
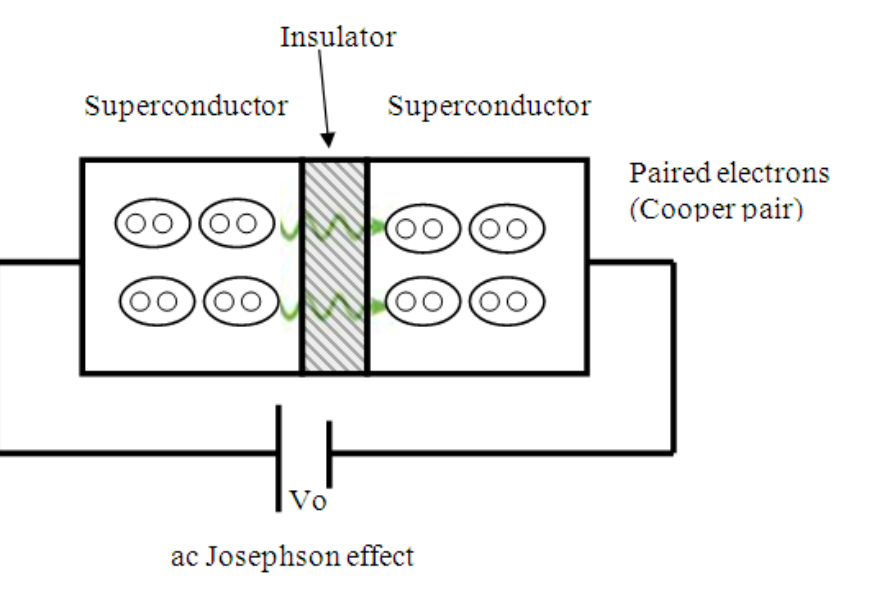
What is AC josephson effect ?
AC Josephson effect is a phenomenon in supercurrent flows between two superconductors separated by thin insulating barrier with the potential difference
What are the application of josephson effect ?
Josephson effect is use to generate micro waves
AC josephson effect is use to define standard volt
AC josephson effect is used to measure very low temprature
AC josephson effect is use for switching of signals from one circuit to another
BCS theory of superconductor was put forward by ———
bardeen , cooper
the BCS theory is introduced in which year ?
1957
the BCD theory can explain ?
Mesinner effect
Zero resistivity
Why we use BCS theory ?
To replace the phenomenon of superconductivity
What is the principle of nanomaterial ?
Size Matters
Quantum Effects
Enhanced Properties
Increased Surface Area
what is nano technology ?
Technology that works with materials and devices at the nanoscale, typically 1 to 100 nanometers.
What are the application of nano technology ?
Healthcare and Medicine : early detect of disease
Cosmetic - sunscreen
Space Exploration - light weight
Properties of nano technology ?
Thermal Properties
Electrical Properties
Optical Properties
Magnetic Properties