IMED1001 - Neurotransmission
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Post Synaptic Potential Mechanics
- Opening Na+ channels depolarises the cell (excitatory)
- Opening K+ channels hyperpolarises the cell (inhibitory)
- Opening Cl- channels hyperpolarises the cell (inhibitory)
- Opening Ca2+ channels depolarises the cell (excitatory)
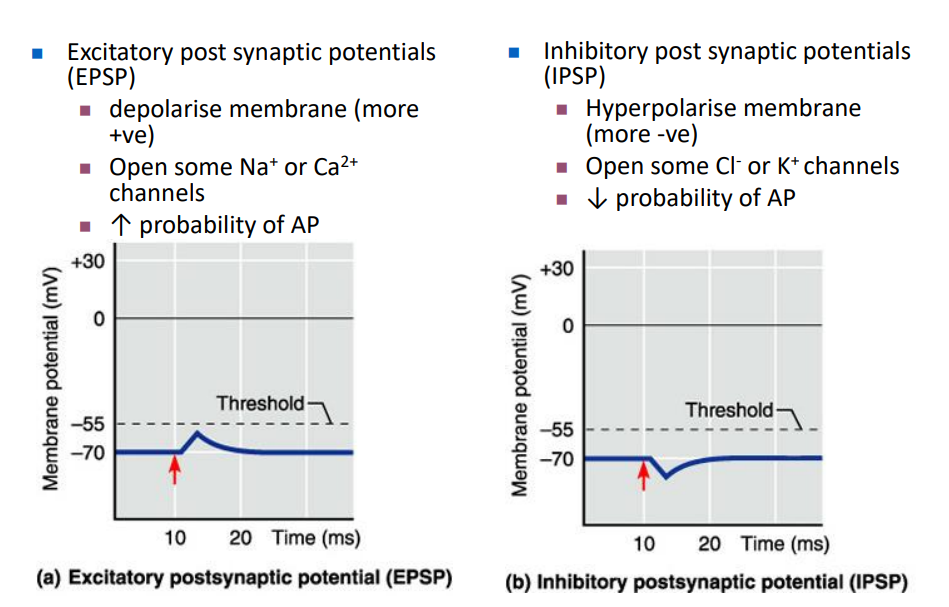
Excitatory Post Synaptic Potentials (EPSP)
- depolarise membrane (more +ve)
- open some Na+ or Ca2+ channels
- increases probability of Action potential
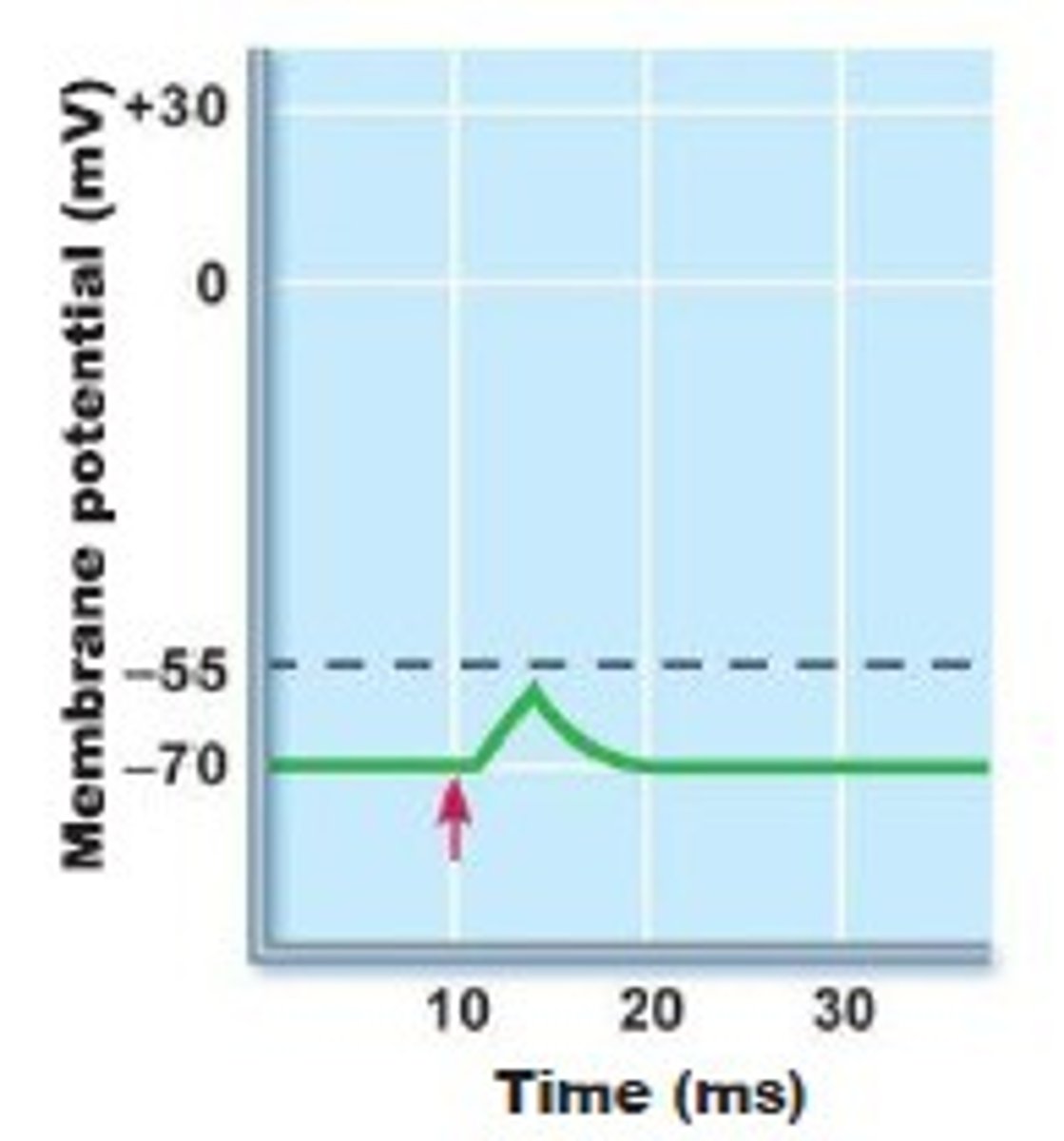
- basically anything that gets closer to the threshold (-55mV) from resting potential is an excitatory post synaptic potential
Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potentials (IPSP)
- hyperpolarise membrane (more -ve)
- open some Cl- or K+ channels
- decreases probability of AP
- basically anything that gets further away from threshold (-55mV) from resting potential is inhibitory post synaptic potential
Post Synaptic Potentials
graded potentials that develop in the postsynaptic membrane in response to a neurotransmitter
- PSPs are not 'all or nothing', they are 'graded'
- EPSP and IPSP are summed (spatially and temporarily) to decide whether the neuron generates an Action potential
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 8
Threshold for Action Potential Generation
- The sum of all IPSPs and EPSPs cause either depolarisation or hyperpolarisation
- If the axon trigger zone exceeds -55mV, all voltage-gated Na+ channels open and Action potential is generated
Axon Trigger Zone
site where action potentials are generated
Sensory Transduction
the process in which a receptor cell converts the energy in a stimulus into a change in the electrical potential across its membrane
Ways impulses pass from cell to cell
- Use of a chemical mediator (e.g neurotransmitters)
- direct electrical transmission (e.g cardiac muscle (rarer))
Gap Junction
A type of intercellular junction that allows the passage of materials between cells.
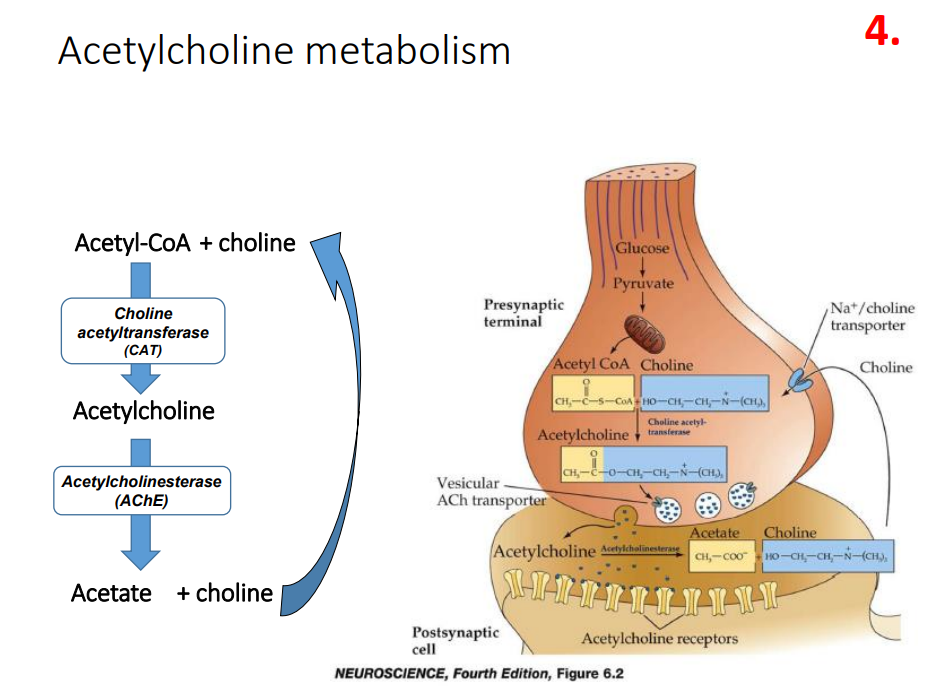
Production of Acetylcholine
- most neurotransmitters are derivatives of amino acids, produced by enzymes
- Reaction to produce acetylcholine:
Acetyl CoA + Choline --(Choline Acetyltransferase)--> Acetylcholine
ADD DIAGRAM FROM slide 17
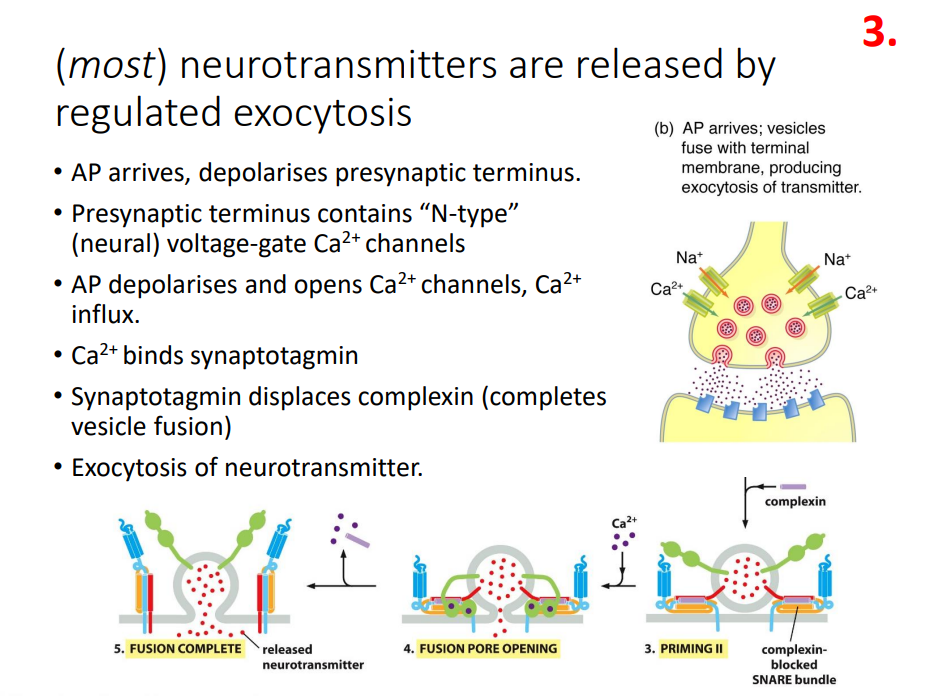
How Neurotransmitters are released
regulated exocytosis
SNARES
- mediate vesicle fusion (v-SNAREs on vesicle, t-SNAREs on target membrane)
- vSNARE and tSNARE only partially assemble
- need help from synaptotagmin to fuse
- Synaptotagmin is activated by Ca2+ binding
First part of transmission at the synapse (what happens at the pre-synaptic neuron)
- AP arrives, depolarises presynaptic terminus
- Presynaptic terminus contains "N-type" (neural) voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
- AP depolarises and opens Ca2+ channels, Ca2+ influx
- Ca2+ binds synaptotagmin (calcium sensors)
- Synaptotagmin displaces complexin (completes vesicle fusion)
- Exocytosis of neurotransmitter
What has the effect, the neurotransmitter or the receptor?
- neurotransmitter has no effect on post-synaptic effects
- its the receptor that has the effect
Receptors that transduce (convert) the neurotransmitter signal (NAMING ONLY)
- Ionotropic receptors
- Metabotropic receptors
Ionotropic Receptors
- open/close an ion channel
- ligand-gated ion channels (e.g many synpatic Rs)
Metabotropic Receptors
- activate an enzyme
- ligand binding outside cell activates enzyme inside cell
- e.g receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs)
The same neurotransmitter can be
excitatory or inhibitory by just acting through different receptors
Two dominant neurotransmitters of CNS (NAMING ONLY)
- Glutamate
- GABA
- have opposite effects
Glutamate
- the dominant excitatory CNS neurotransmitter
- binds/opens iGluRs (ionotropic glutamate receptors)
- AMPA receptor is a Na+ channel (EPSP)
- NMDA receptor is a Na+ and Ca2+ channel (EPSP)
- Also mGluRs (metabotropic glutamate receptors)
GABA
- the dominant inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter (antagonist to glutamate)
- Binds/opens GABA Rs: Cl- channels (Cl- influx causing hyperpolarisation, inhibits post synpatic neuron (IPSP)
- has a metabotropic receptor
Two dominant neurotransmitters in PNS (NAMING ONLY)
- Acetylcholine (ACh)
- Noradrenaline (NA)
Acetylcholine (Nicotinic, Muscarinic)
- excitatory or inhibitory
- Nicotinic (ionotropic - ligand gated Na+ channel, always excitatory)
- Muscarinic (metabotropic - activates enzymes. Often inhibitory (can be excitatory))
has both ionotropic and metabotropic receptors
Noradrenaline (Adrenergic)
- excitatory or inhibitory
- Alpha-adrenergic receptors: metabotropic - activates enzymes. Excitatory of inhibitory
- Beta-adrenergic receptors: Metabotropic - activates enzymes. Excitatory or inhibitory
only has metabotropic receptors
Which neurotransmitters control heart rate
Acetylcholine (ACh) and Noradrenaline (NA) (antagonistic effects. If you want to increase heart rate, noradrenaline used, if you want to decrease heart rate, acetylcholine is used
How to make neurotransmitters stop
- Neurotransmitter re-uptake: Uptake by presynaptic neuron or local glial cells. Most neurotransmitters: serotonin, glutamate, dopamine, noradrenaline, GABA
- Neurotransmitter degredation: Enzymes in the synapse chew up neurotransmitter molecules. Acetylcholine, also dopamine and noradrenaline
Acetylcholine Metabolism
SLIDE 30 of Lecture on Neurotransmission
Glial Cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons