242: Lab 4 tests and derivatives
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what are the 7 core functional groups?
alcohols, aldehydes, amines, carboxylic acids, esters, ketones, or phenols
what is soluble in pure water?
small, highly polar compounds, alcohol
can you stop solubility tests if your compound is soluble in water? why or why not?
you can stop because changing the pH won’t change the solubility, if it is soluble in water, it will be soluble in acidic or basic H2O
not soluble in H2O, what is soluble in 5% NaHCO3?
carboxylic acids, (5% NaHCO3 is a weak base)
not soluble in NaHCO3, what is soluble in NaOH?
phenols, (NaOH is a strong base)
what is soluble in HCl?
amines (becomes ammonia and dissolves)
what kind of compounds are not soluble in any of the 4 compounds?
aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, esters
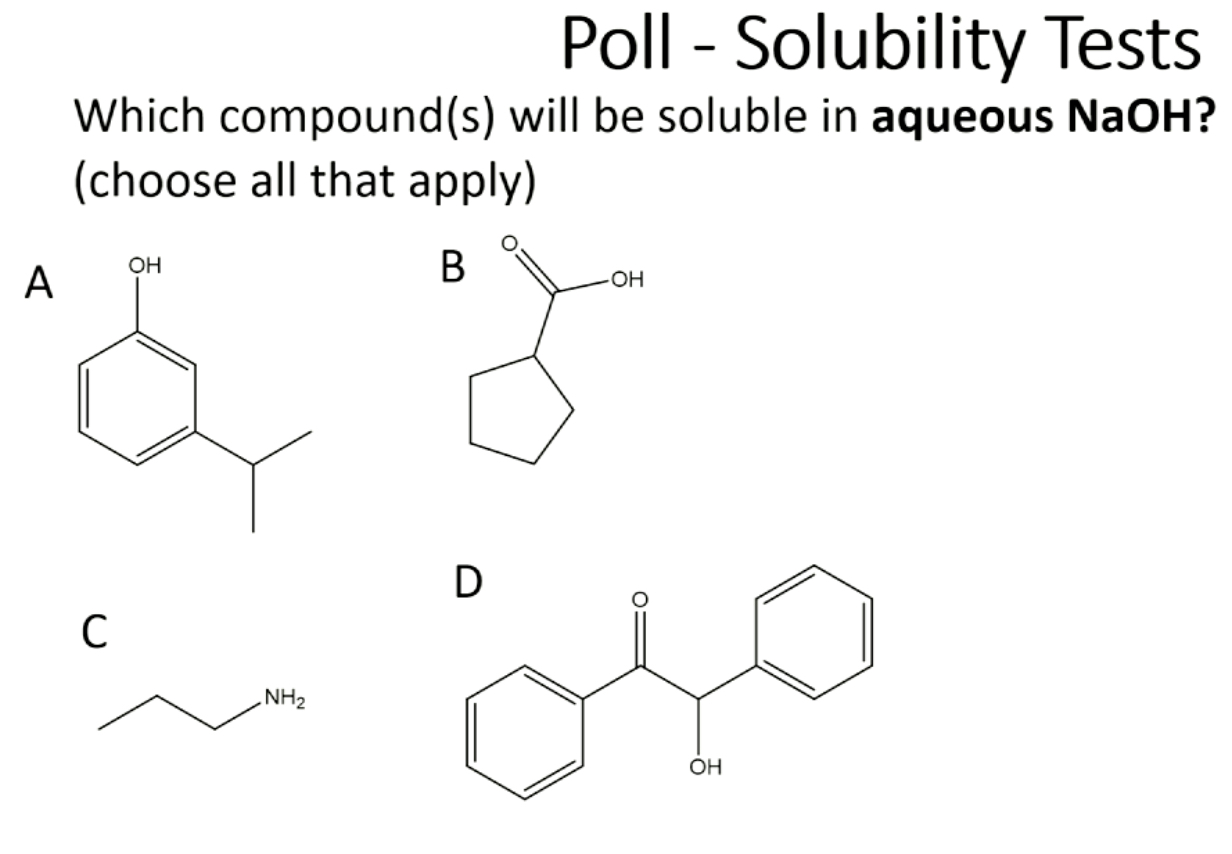
A, B, C (base is soluble in any H2O conditions, small enough), not D because it won’t get deprotonated by hydroxide
what is the ceric nitrate test? (cerium)
alcohols and phenols can form colored complexes with cerium, will confirm OH, but not what kind of alcohol/phenol
what is the ferric chloride test?
tests for phenols and esters, Iron (III) forms strongly-colored complex with phenols and hydroxamic acids, hydroxamic acids formed from esters
parts 1 and 2 of the ferric chloride test?
part 1: test the compound with ferric chloride, if positive: phenol
part 2: mix w/ hydroxylamine, converts esters into hydroxamic acids (hydroxamic acid forms complex with iron chloride
what is the DNP test?
tests for aldehydes/ketones, aldehydes/ketones react w/ hydrazines (or 1° amines) to form hydrazones, precipitates out, (allylic/benzylic alcohols=false positives cuz they’ll oxidize to aldehydes first), doesn’t distinguish between aldehydes/ketones
what is the tollens test?
tests for aldehydes, reagent: AgNO3, NaOH, NH3, redox rxn where aldehyde is oxidized to carboxylic acid
RCHO + Ag(NH3)2+ → RCOOH + Ag(s)
silver precipitates out as “silver mirror”
why do you need to destroy tollens reagent immediately?
tollens reagent can produce explosive silver fulminate, so destroy any unused, and prepare immediately before us
what is the nitrous acid test?
1° alkyl amines form diazonium ions that immediately release N2, even when cold. 1° aryl amines form diazonium ions that only release N2 when warmed. aryl diazonium ions can also be converted into azo dyes, 2° amines form yellow nitroso compounds
what are possible false postives of the nitrous acid test?
ketones, phenols
what is the ferrous hydroxide test?
nitro group present as secondary functional group, redox rxn where nitro group reduced to amine, iron (II) hydroxide oxidized to iron (III) hydroxide
R-NO2 + Fe(OH)2 → R-NH2 + Fe(OH)3 (precipitate)
what is the silver nitrate test?
tests for alkyl halides (secondary functional group), halide that can leave readily will react with H2O soluble silver nitrate to form H2O insoluble silver halide (silver halide salt precipitate), halides that can’t act as LGs will not react, false positive: carboxylic acids
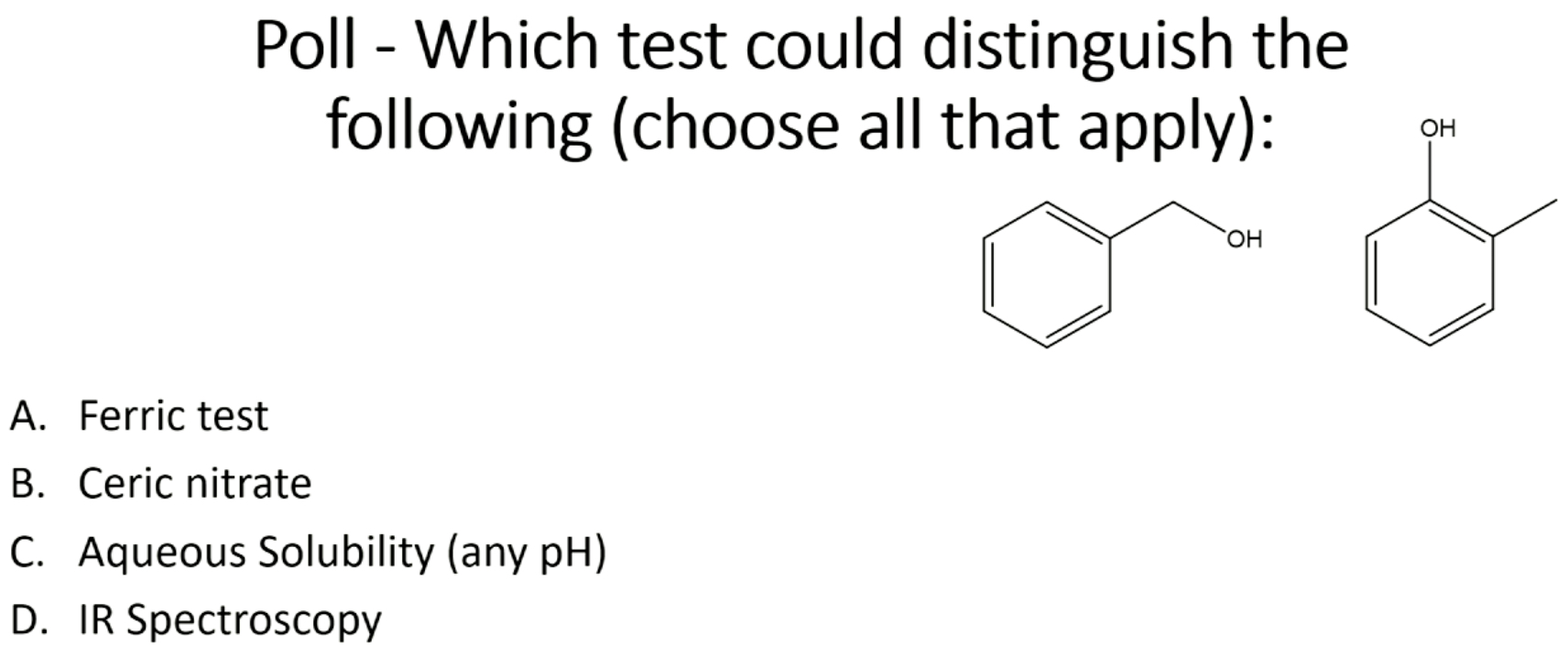
A, C

C, D, E, F, G

F
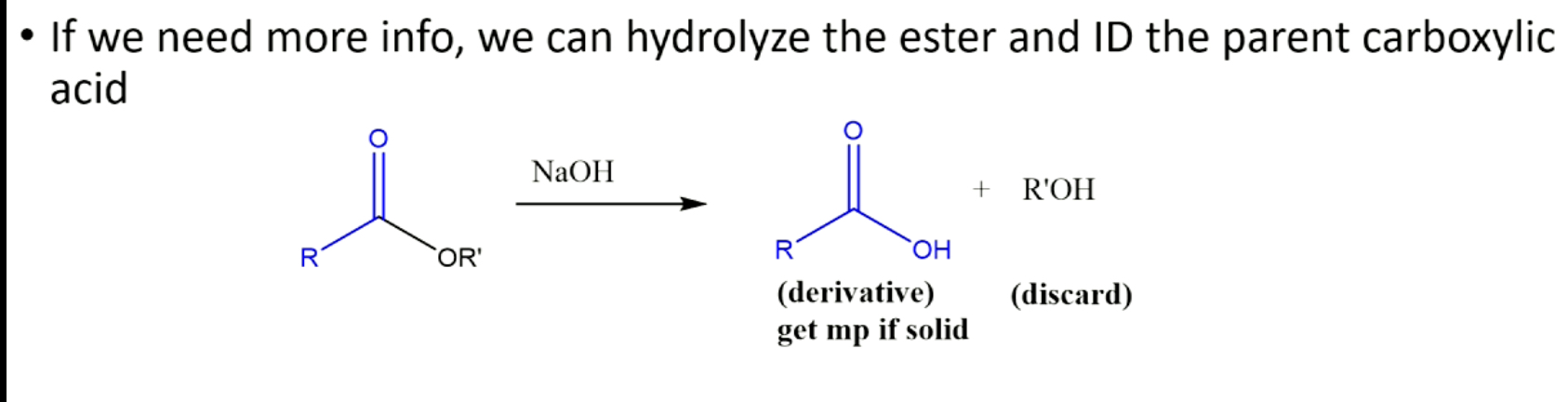
carboxylic acid derivative
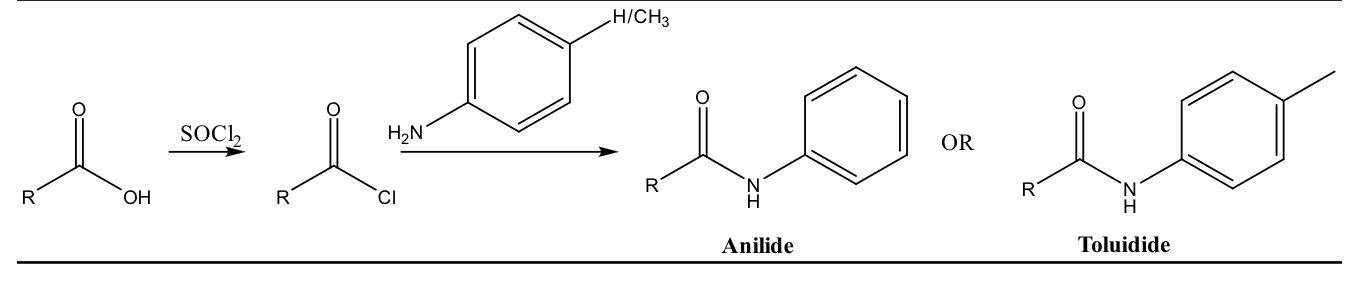
form anilides and toluidides: amides from carboxylic acids turned into aromatic acid chlorides
alcohol/phenol derivative
urethanes (½ amides, ½ ester)
phenylurethane/naphthylurethane= ester formation (either alcohols or phenols)
3,5-dinitrobenzoate ester: alcohols only= ester formation
aldehyde/ketone derivative
semicarbazone derivative= imine formation (semicarbazone)
oxime derivative= imine formation (oxime)
both react with aldehydes/ketones
amine derivative
acetamides and benzamides, tertiary amines will not work (only 1° & 2° alkyl & arylamines)

B, C
ester derivative
esters have 2 unknowns, carboxylic acid half and alcohol half (esters formed from carboxylic acid and alcohol), in theory make derivatives of both
what to do if need more info after forming derivative from ester?