Motor pathways
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
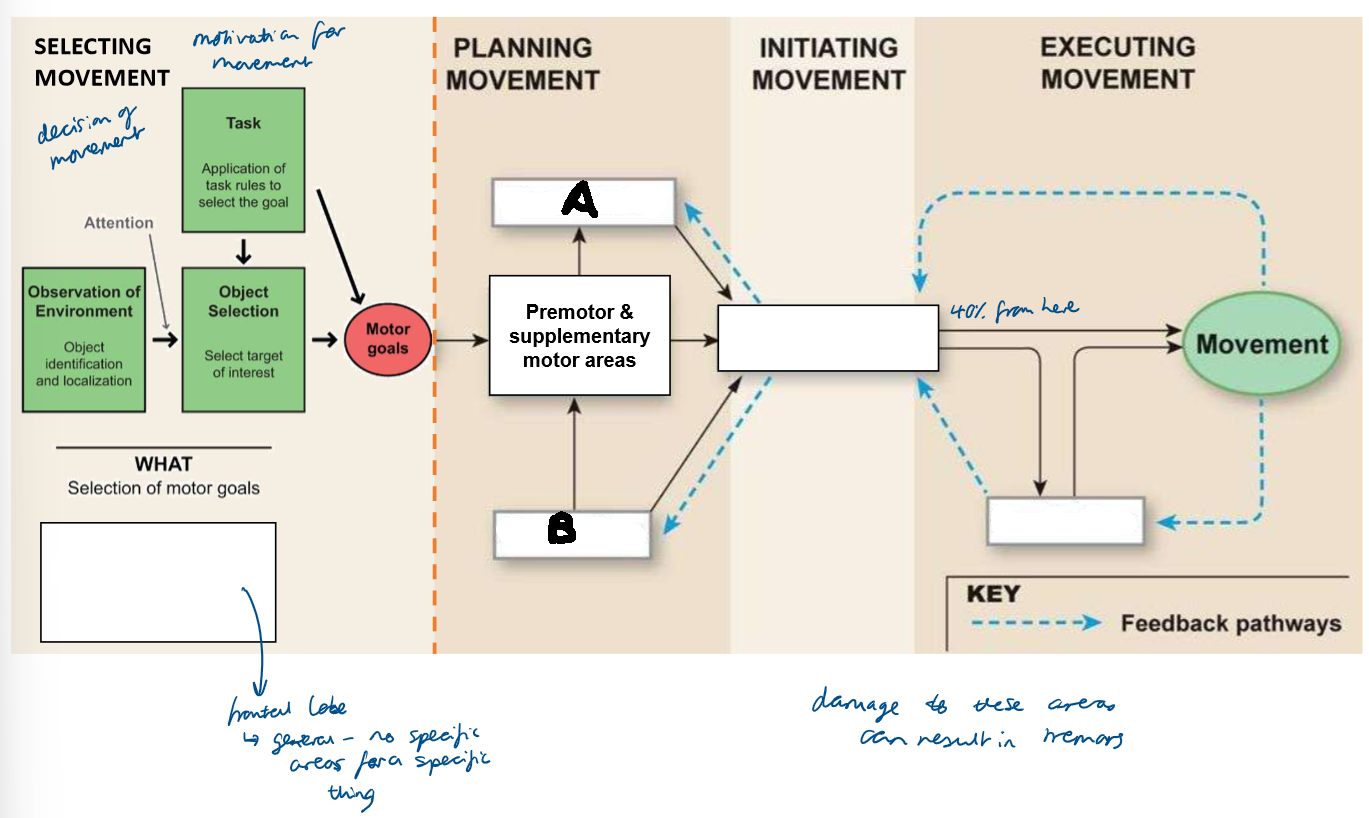
Which part of the brain is responsible for selecting movement?
visual and frontal cortices
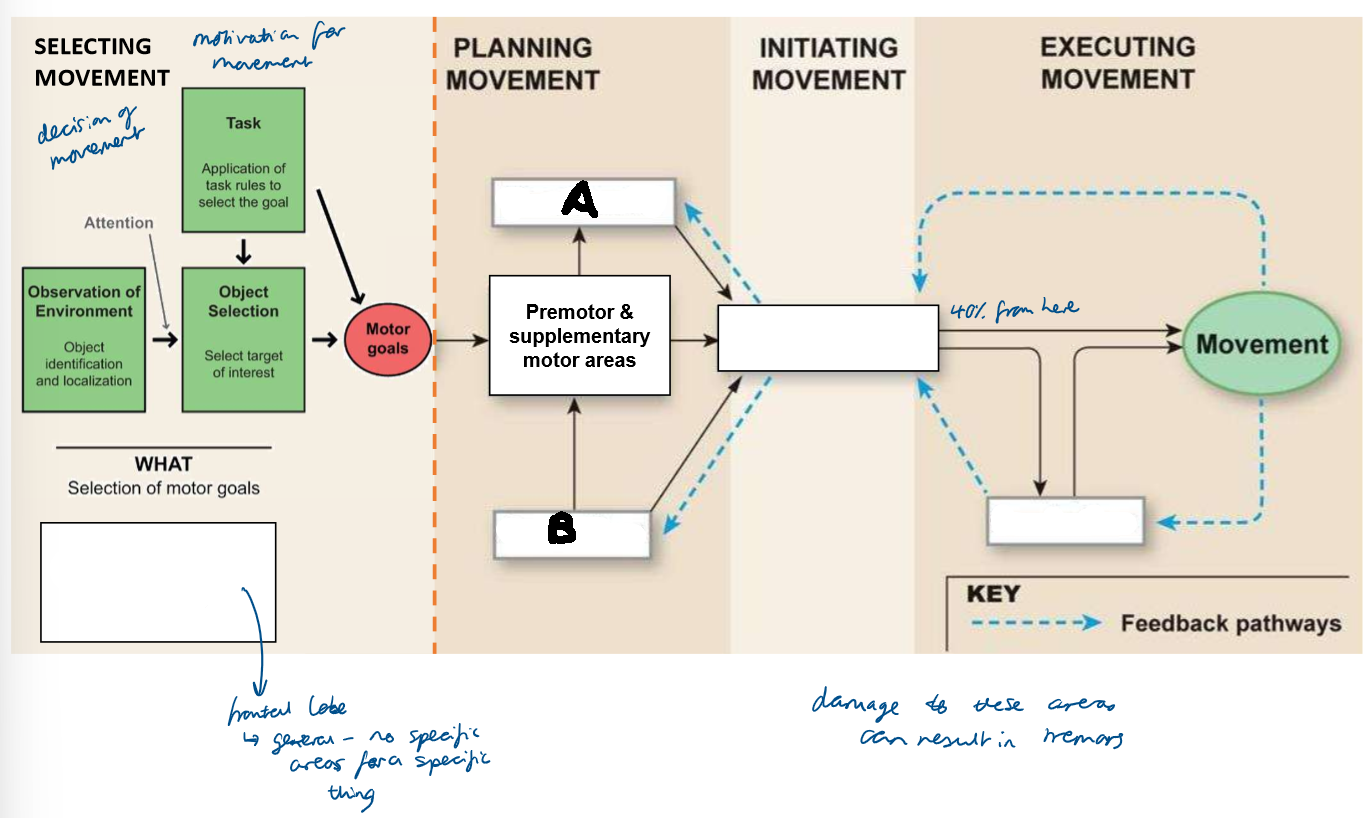
Which part of the brain is responsible for planning movement?
basal nuclei and cerebellum
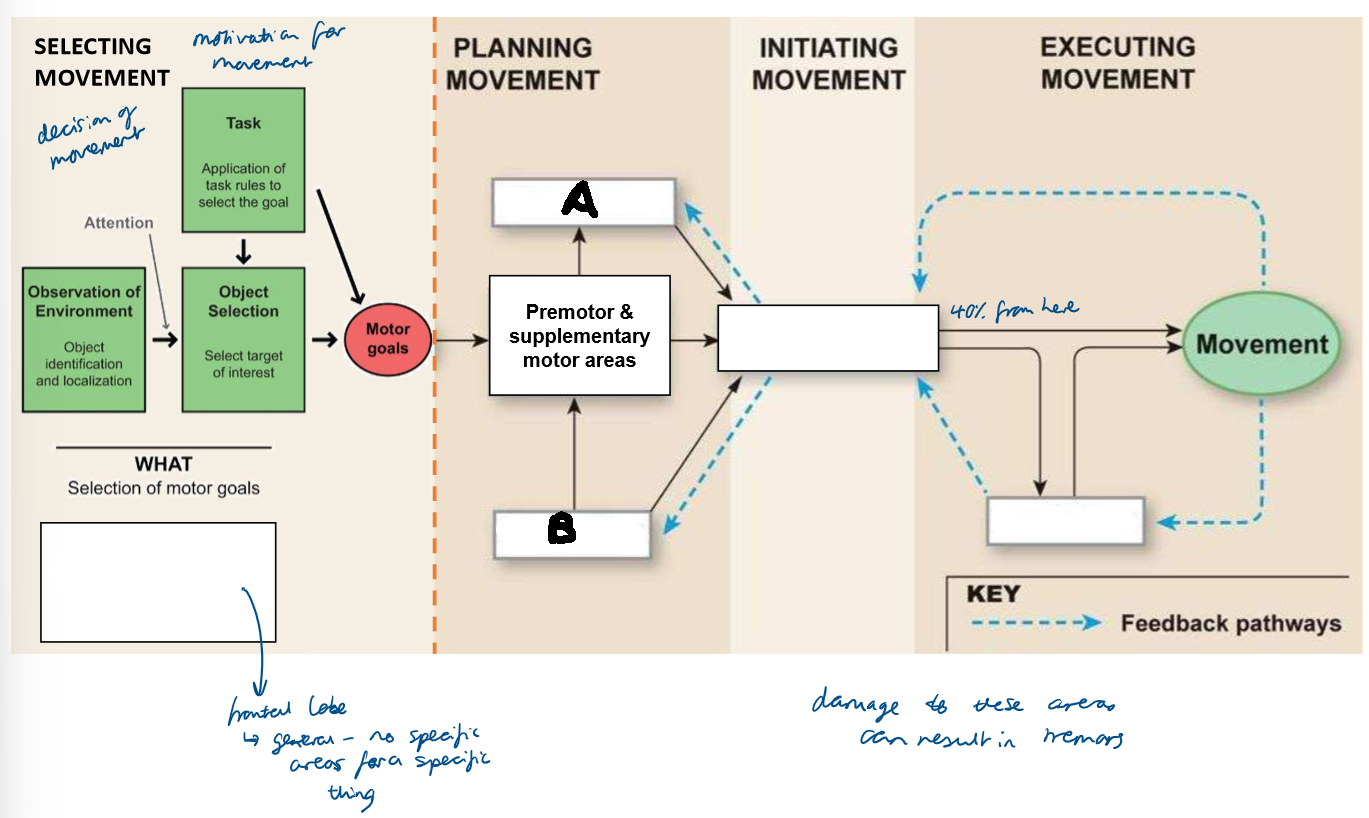
Which part of the brain is responsible for initiating movement?
primary motor cortex
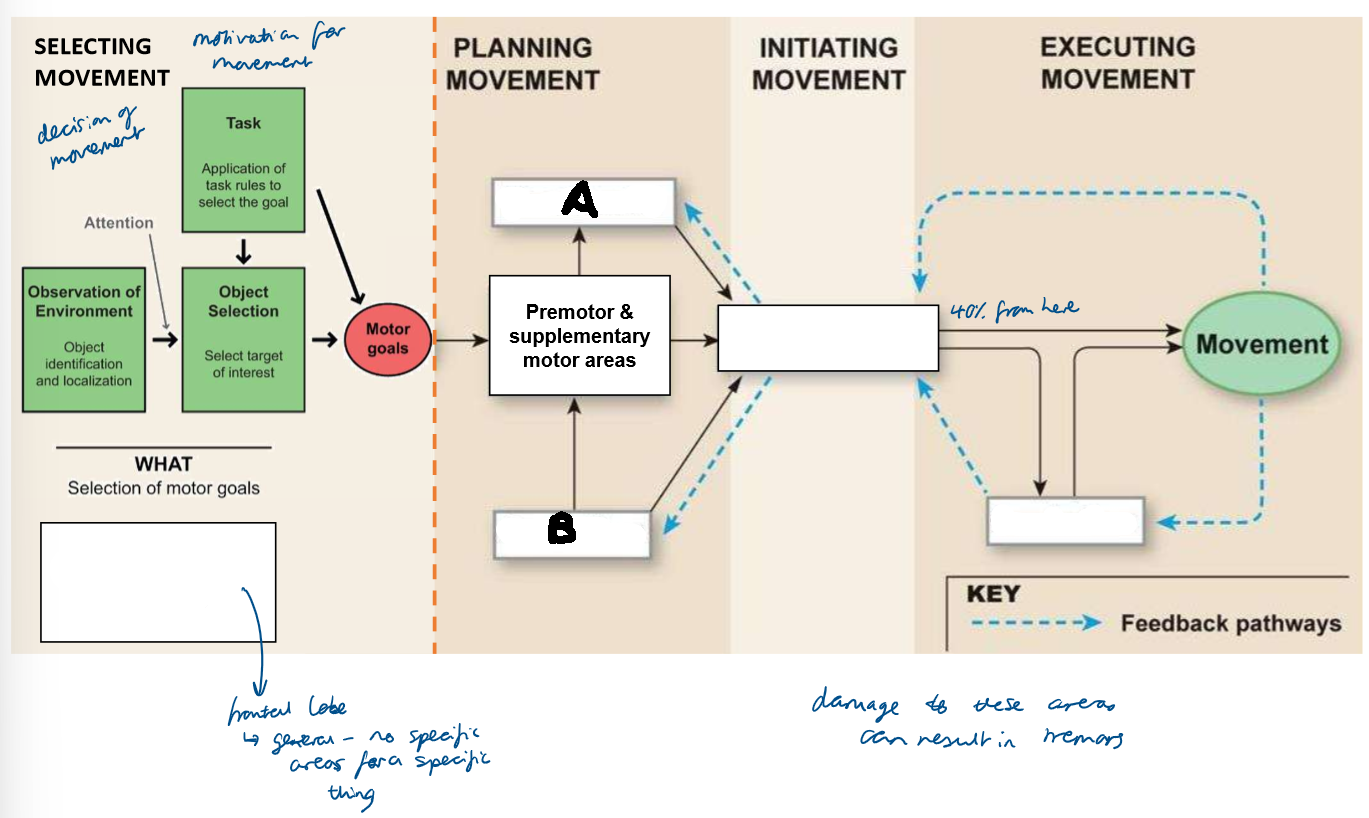
Which part of the brain is responsible for executing movement?
cerebellum
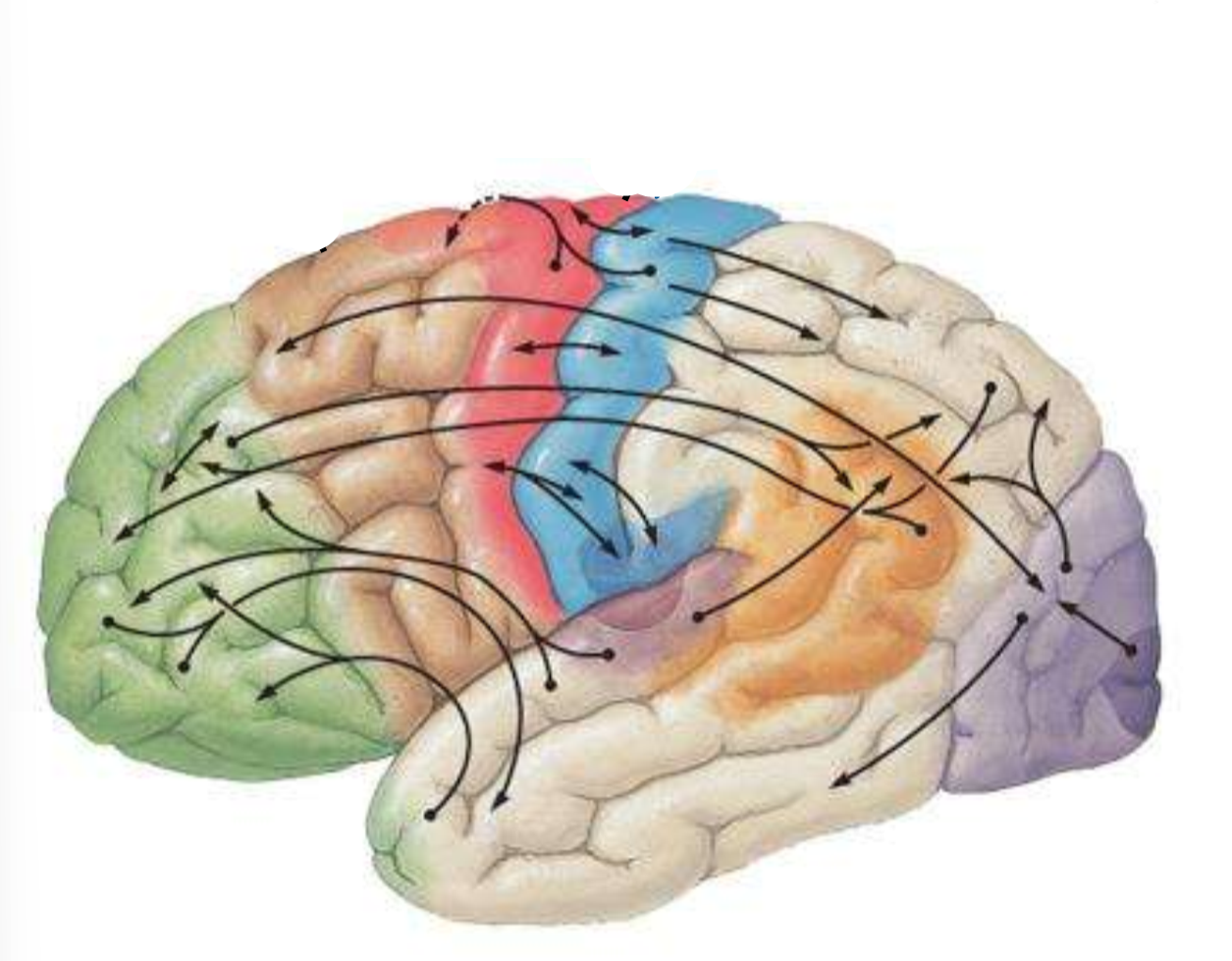
Which is the brown part of the brain?
pre-motor cortex
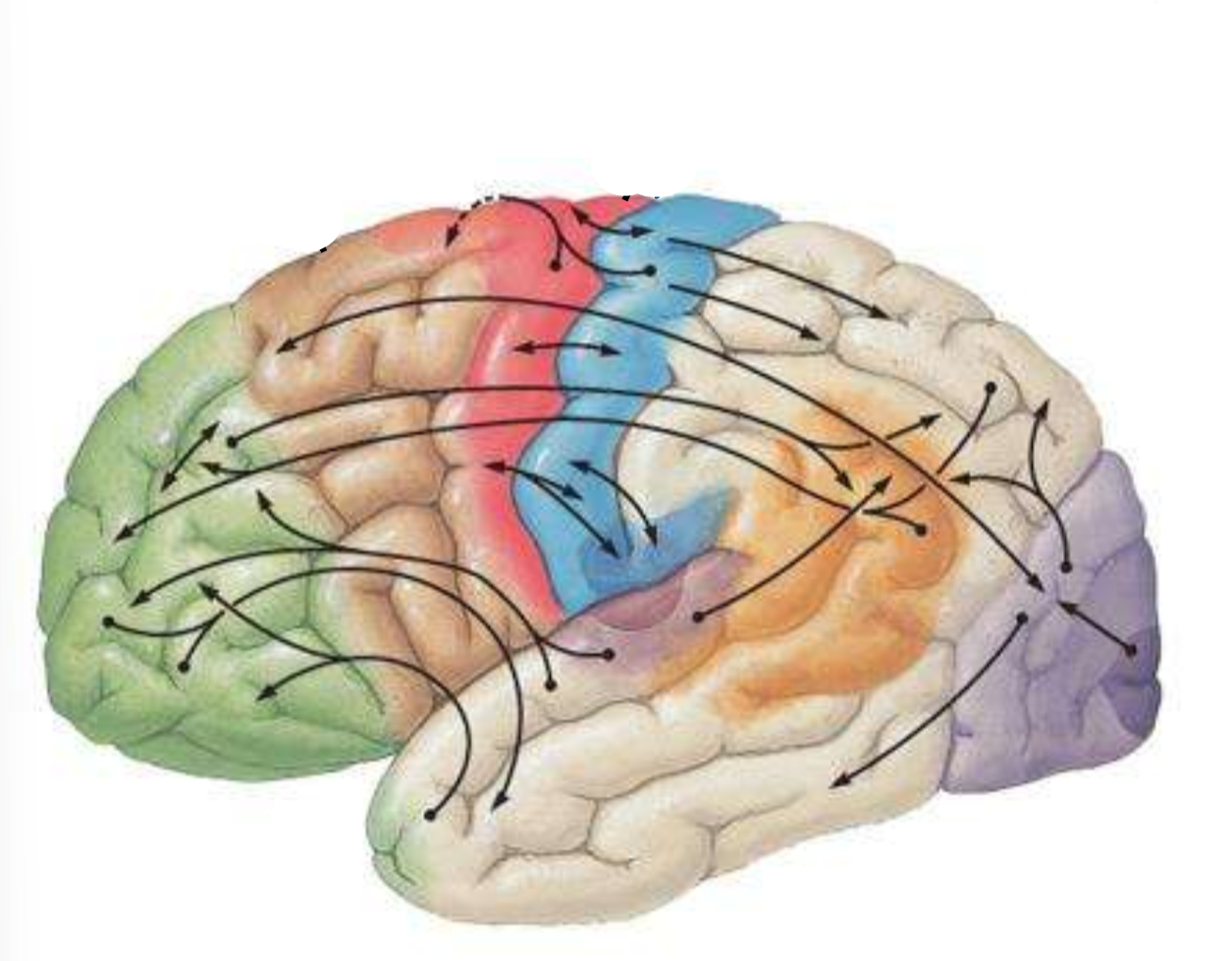
Which is the red part of the brain??
primary motor cortex
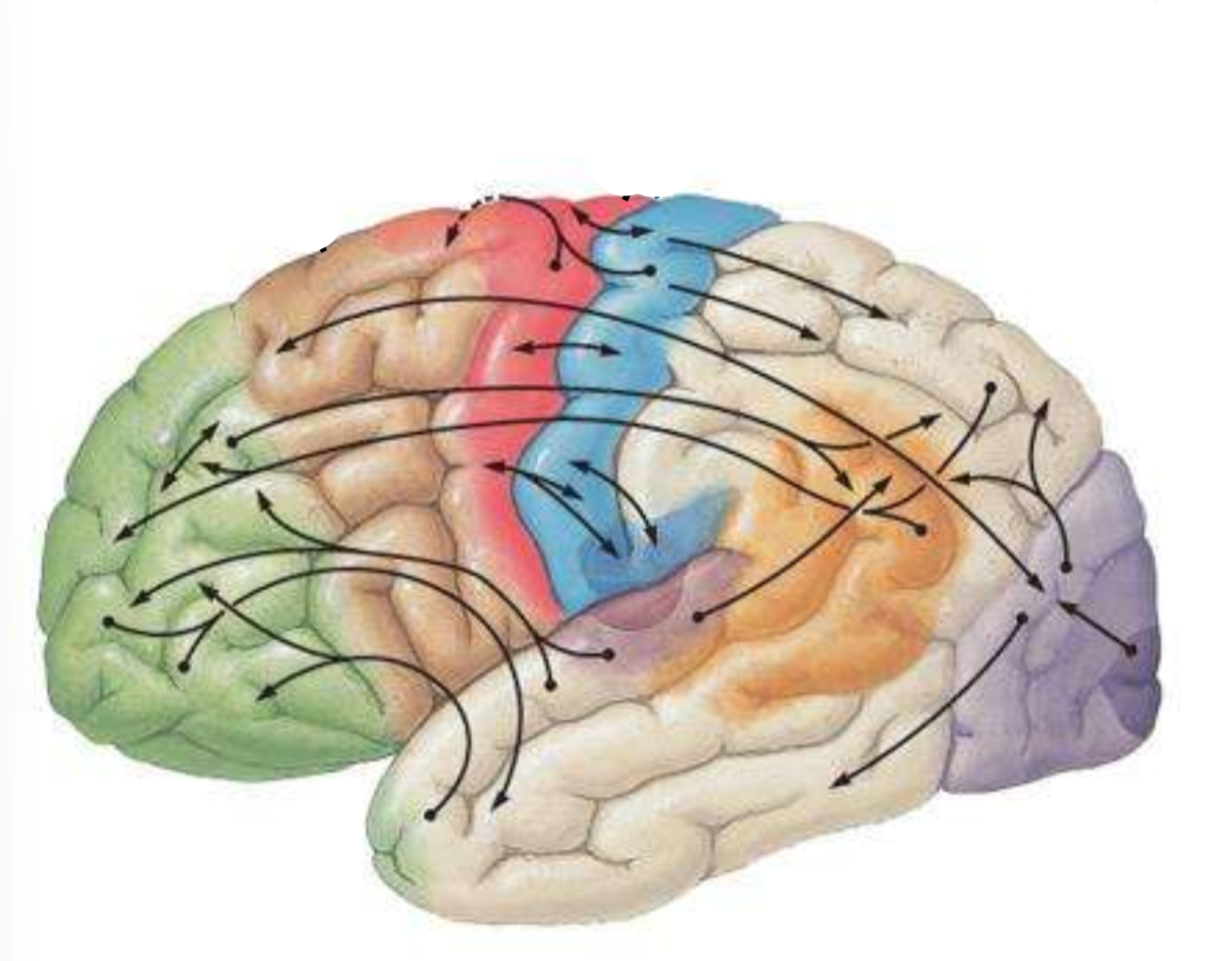
Which is the blue part of the brain?
primary sensory cortex
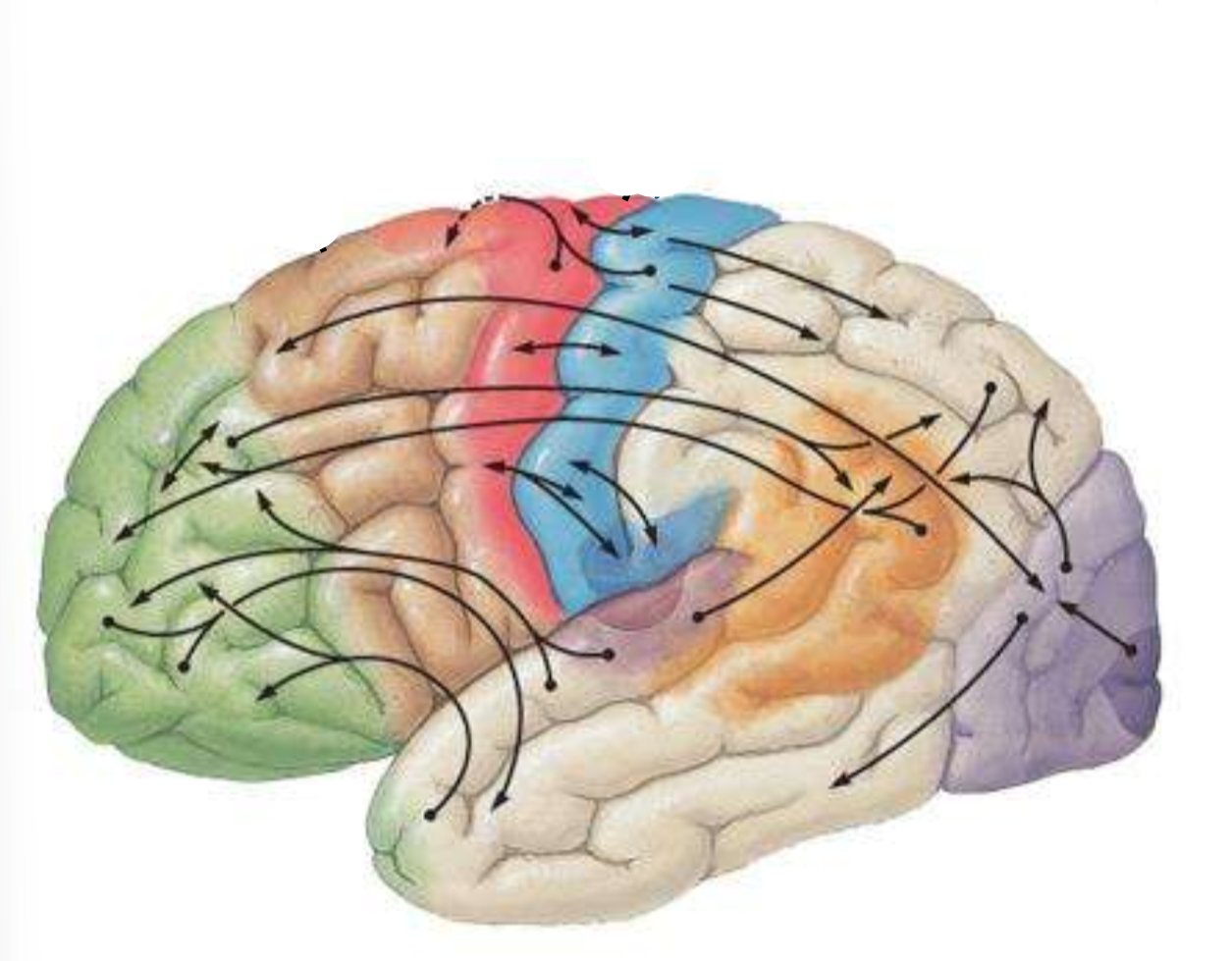
What is the split between the red and blue part of the brain?
central sulcus
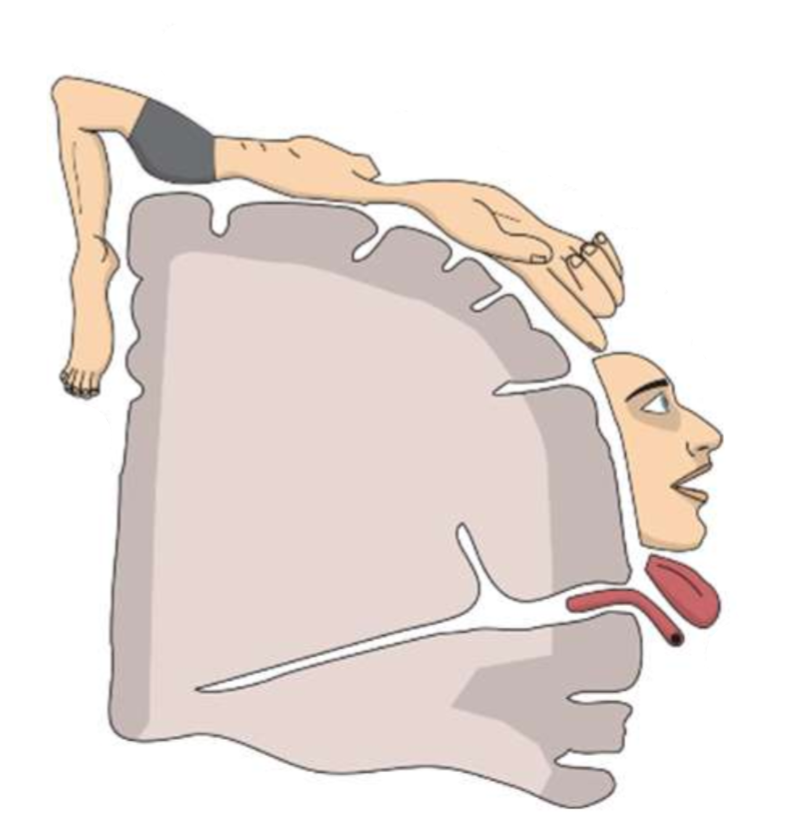
What is the order of body parts in this homunculus?
toes knee hip trunk shoulder arm elbow wrist hand fingers thumb neck brow eye face lips jaw tongue swallowing
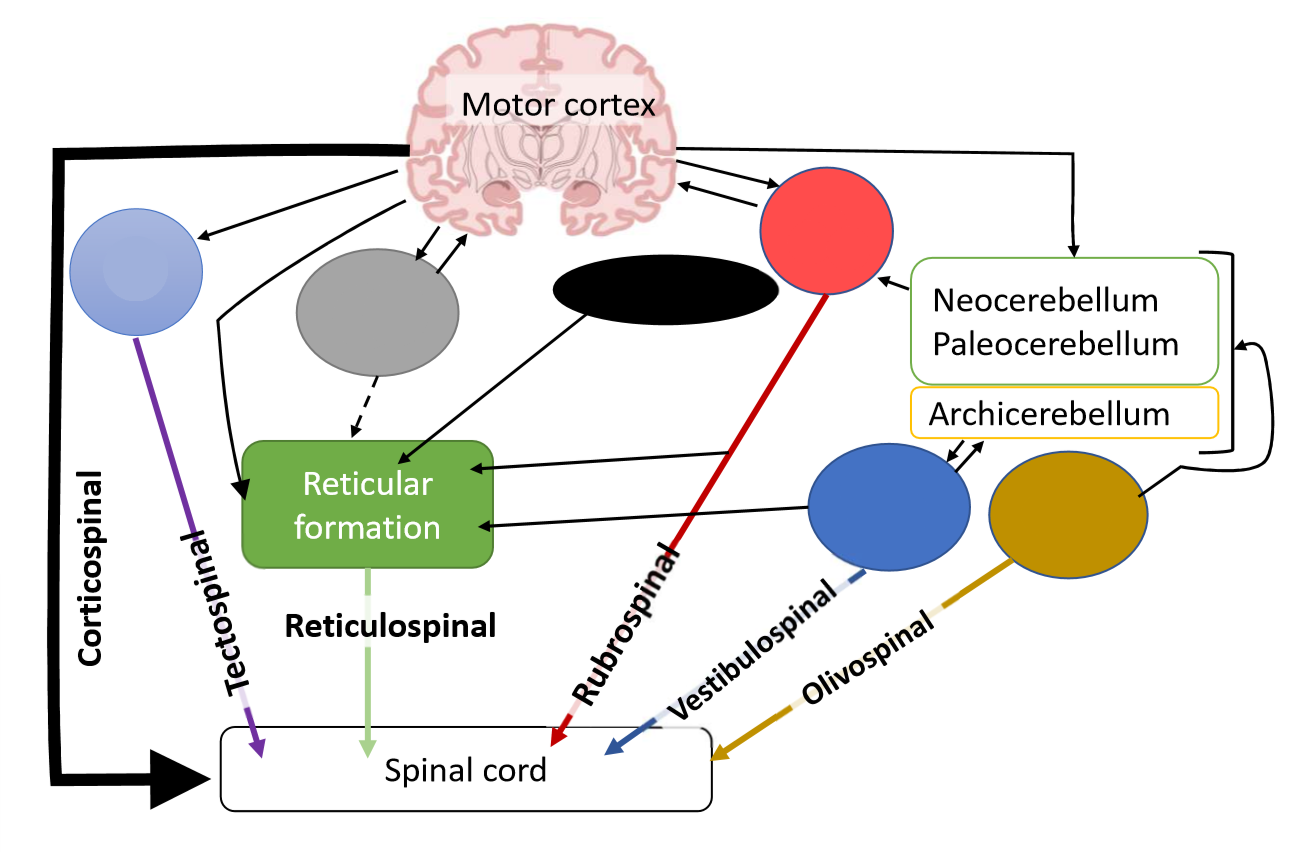
What is the light blue pathway?
tectum
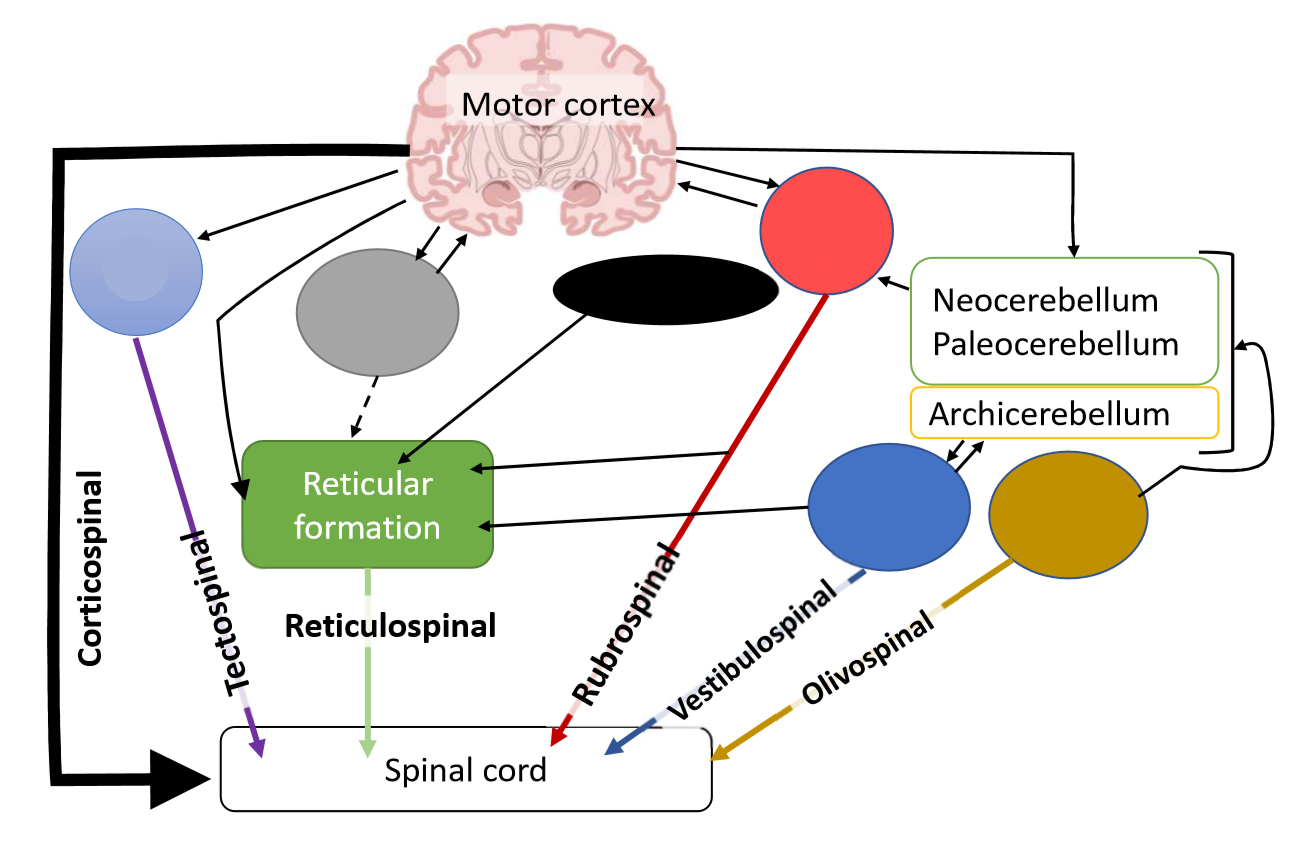
What is the function of the tectospinal tract?
reflex head movements in response to visual, auditory and painful stimuli
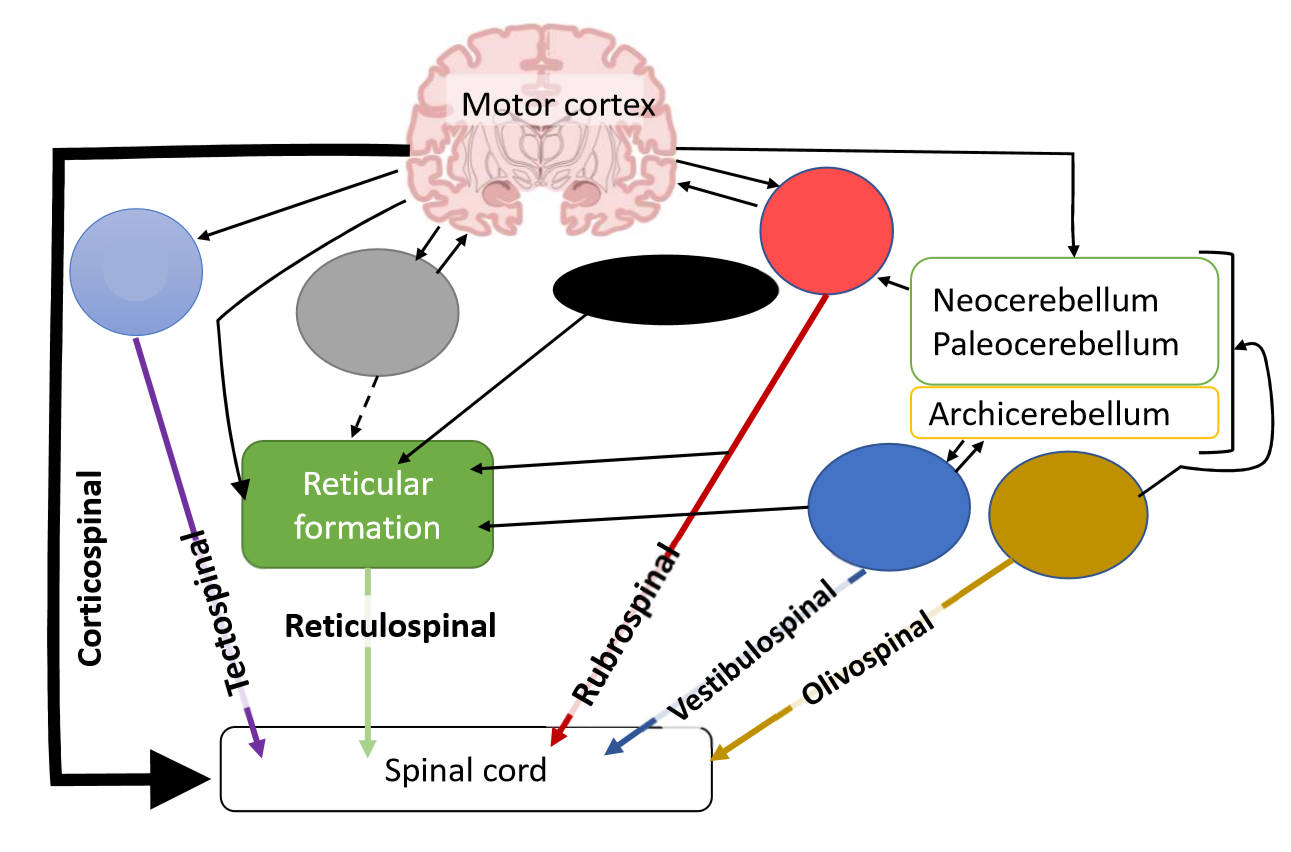
What is the grey pathway?
basal ganglia
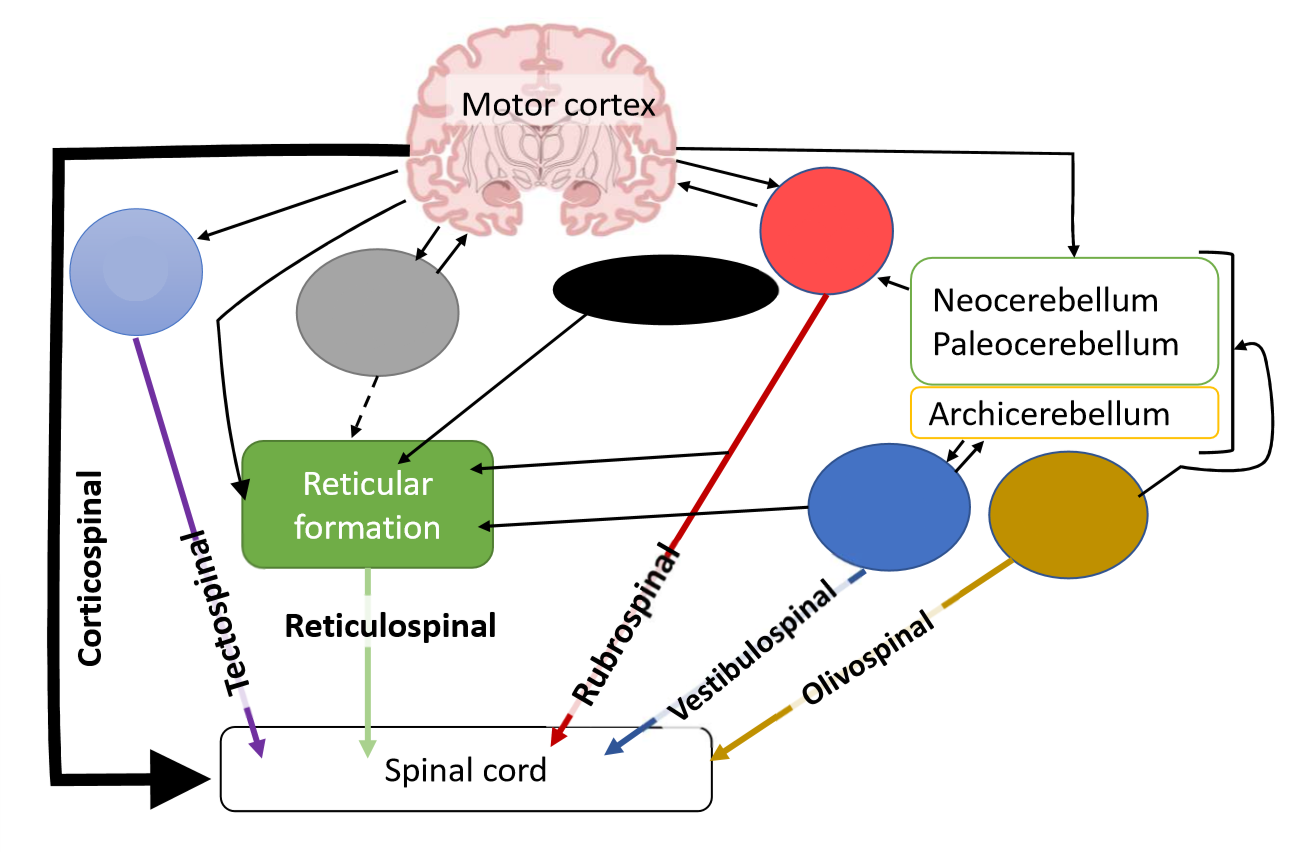
What is the black pathway?
hypothalamus
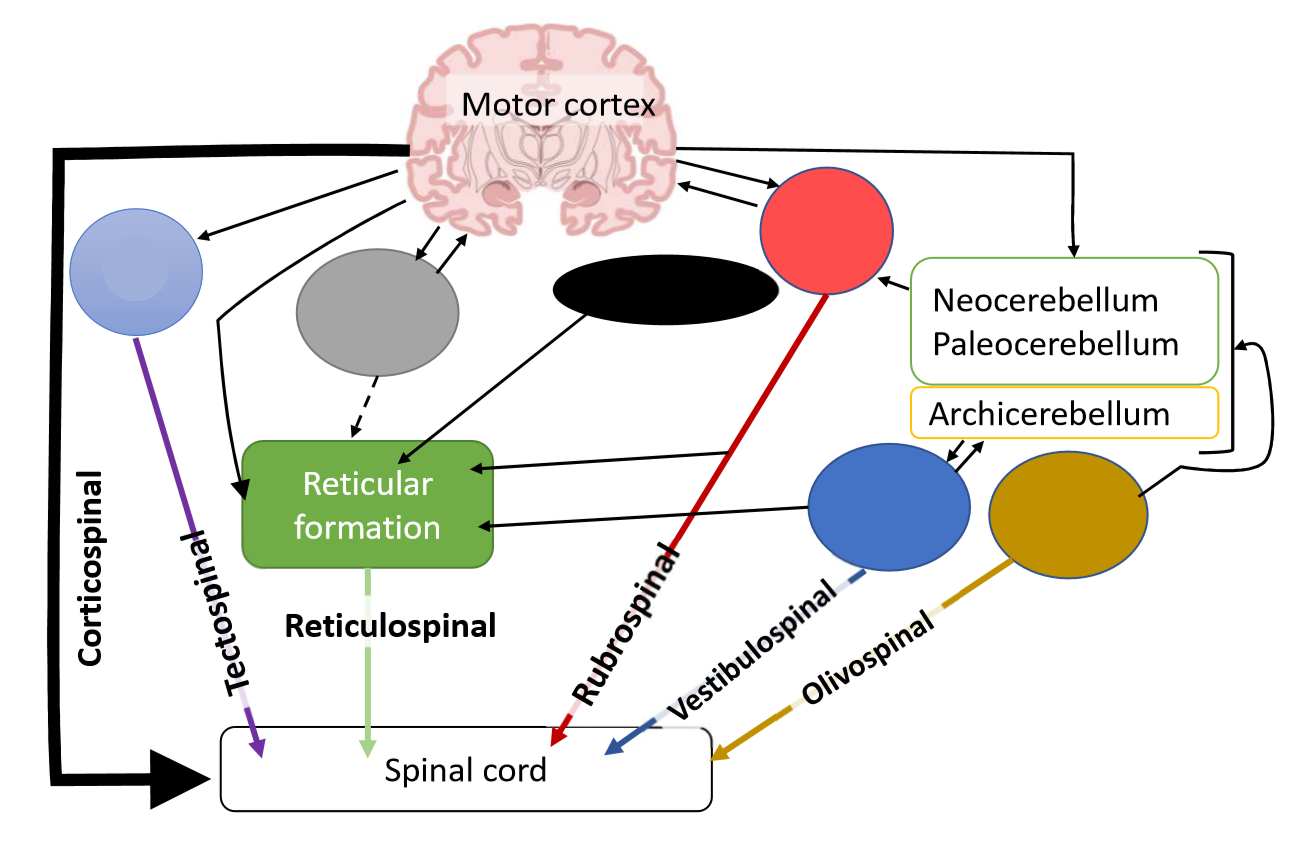
What is the reticulospinal tract?
control of muscle tone, posture and locomotion
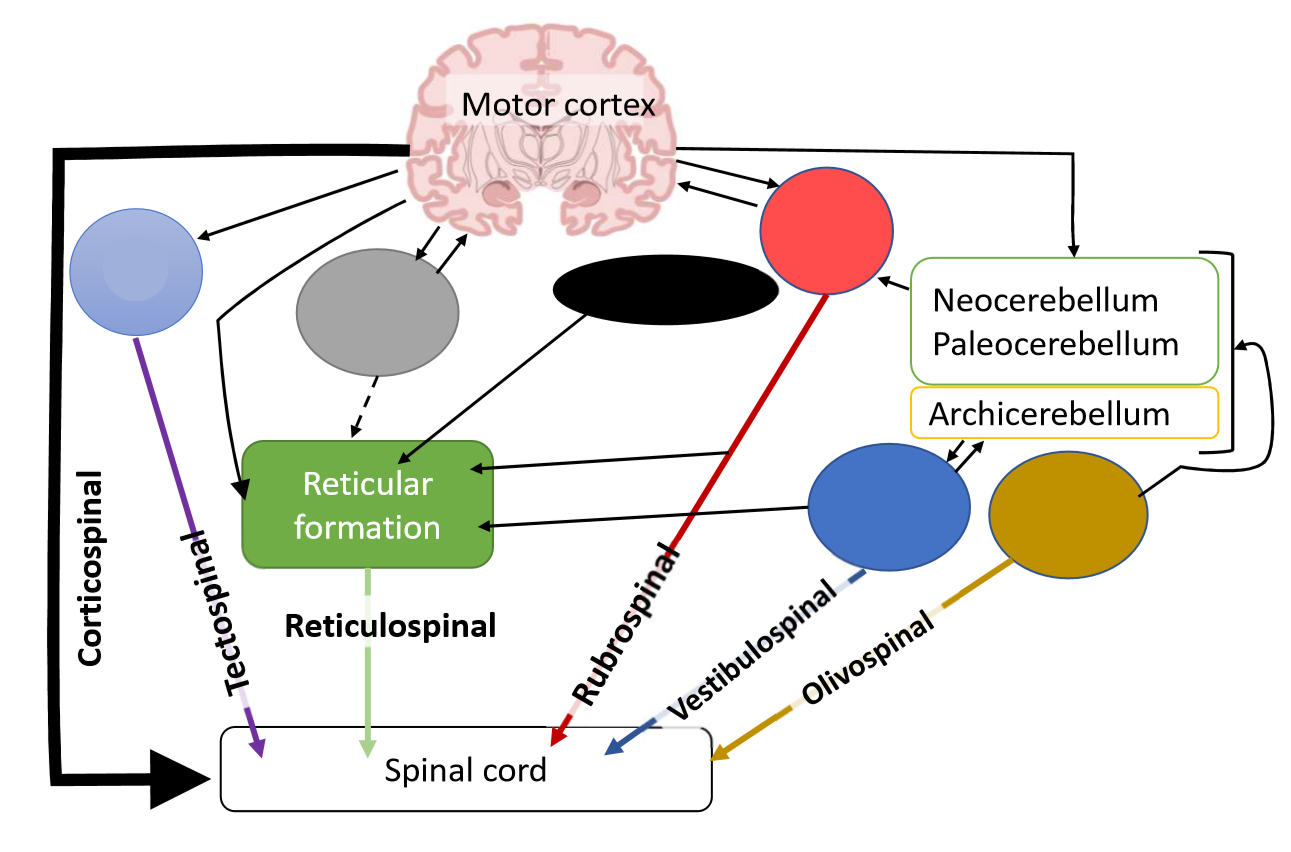
What is the red pathway?
red nucleus
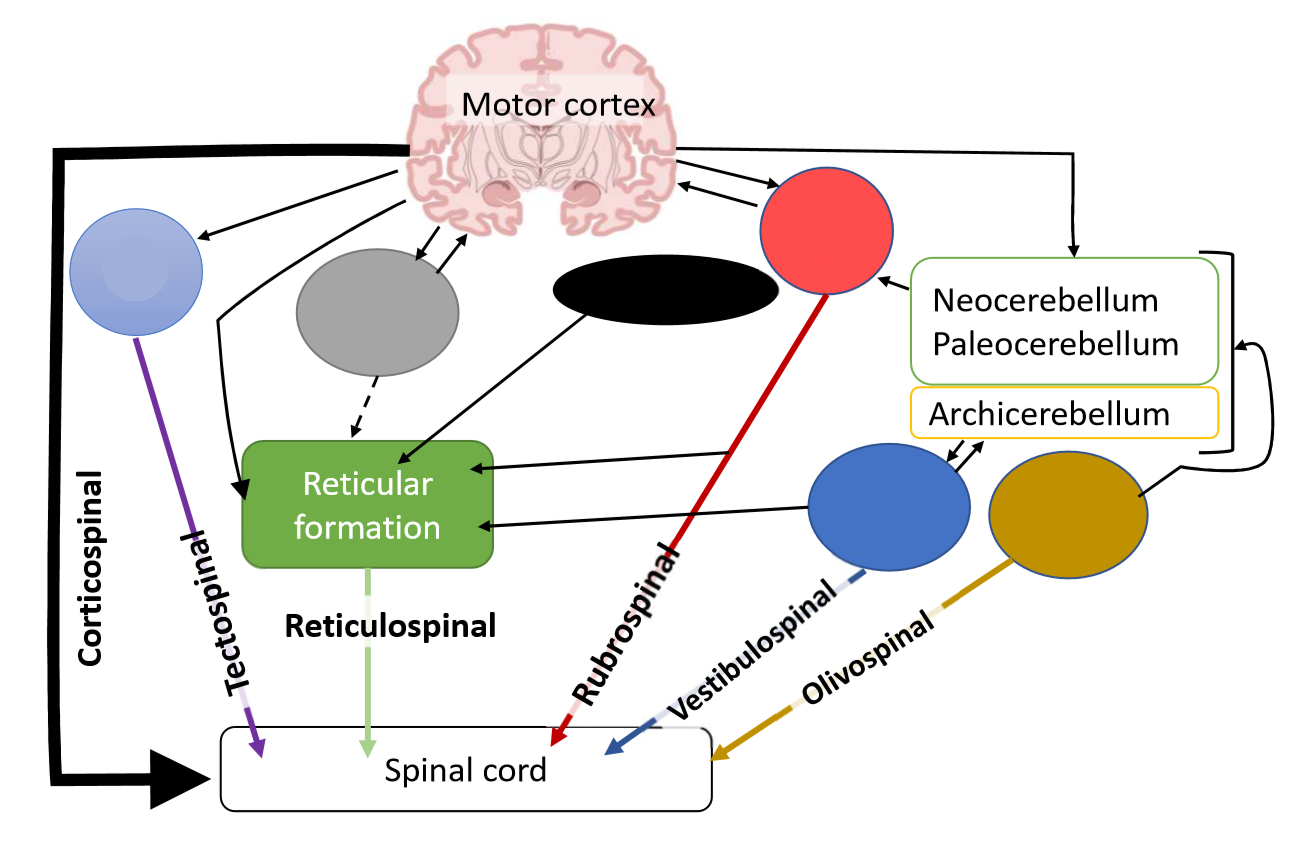
What is the function of the rubrospinal tract?
carries signals
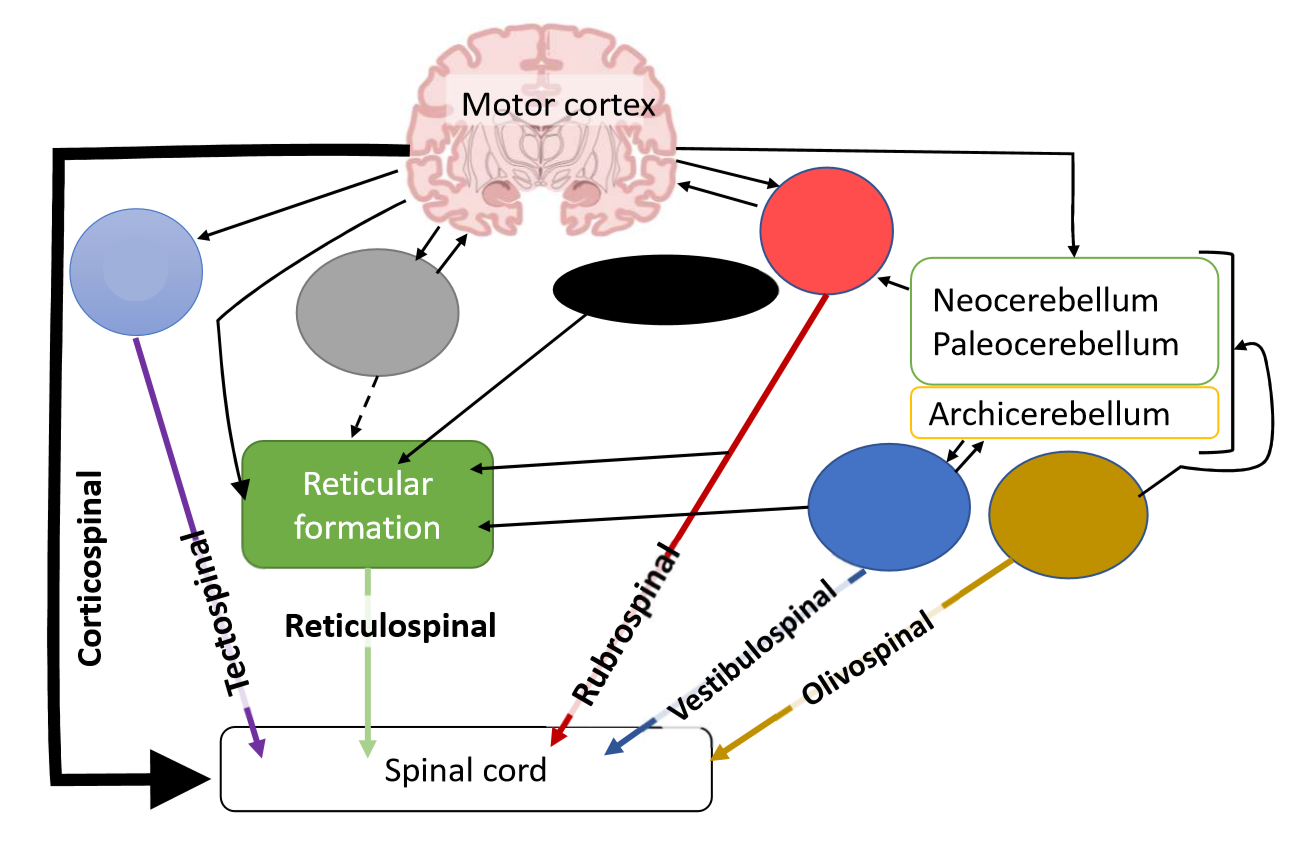
What is the dark blue pathway?
vestibular nuclei
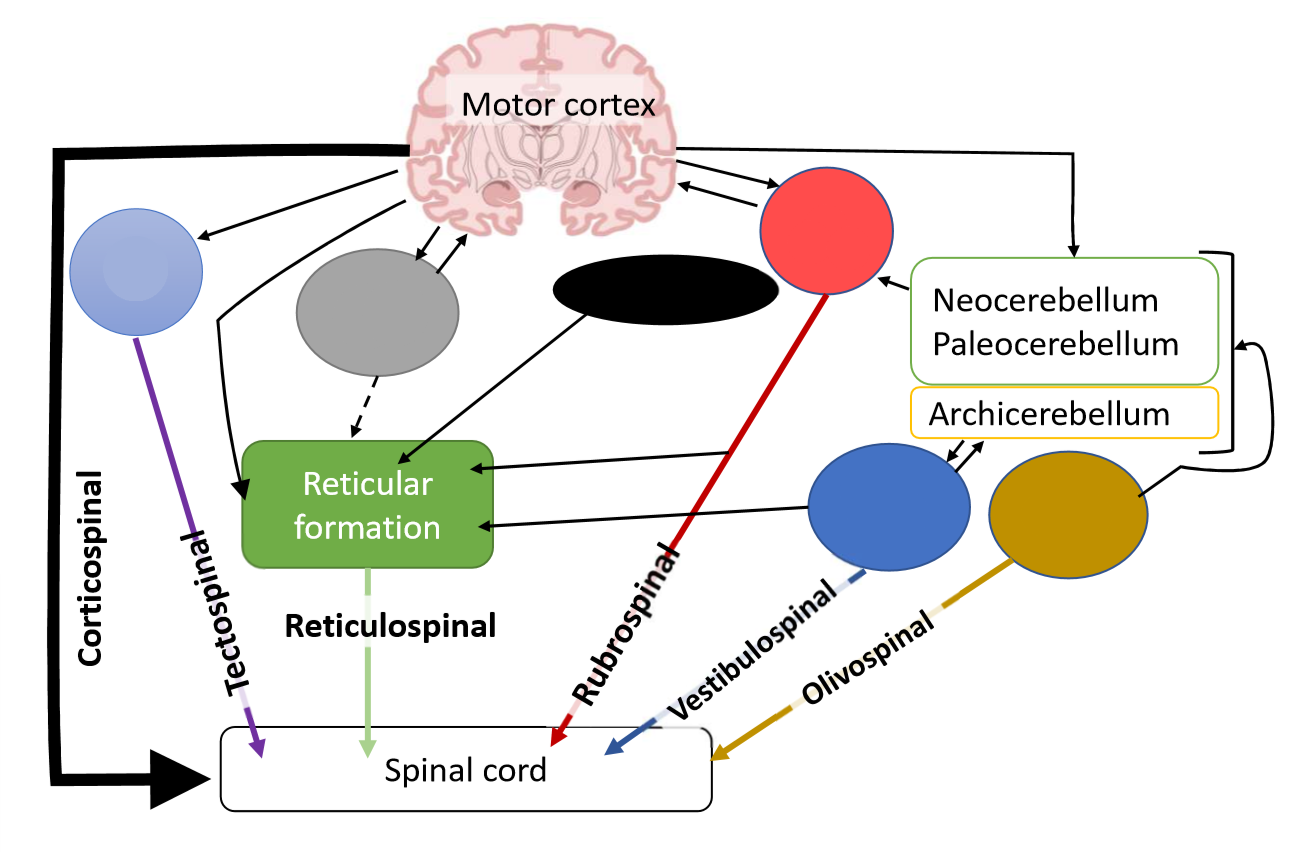
What is the function of the vestibulospinal tract?
adjustments of posture to maintain balance during locomotion in response to vestibular signals
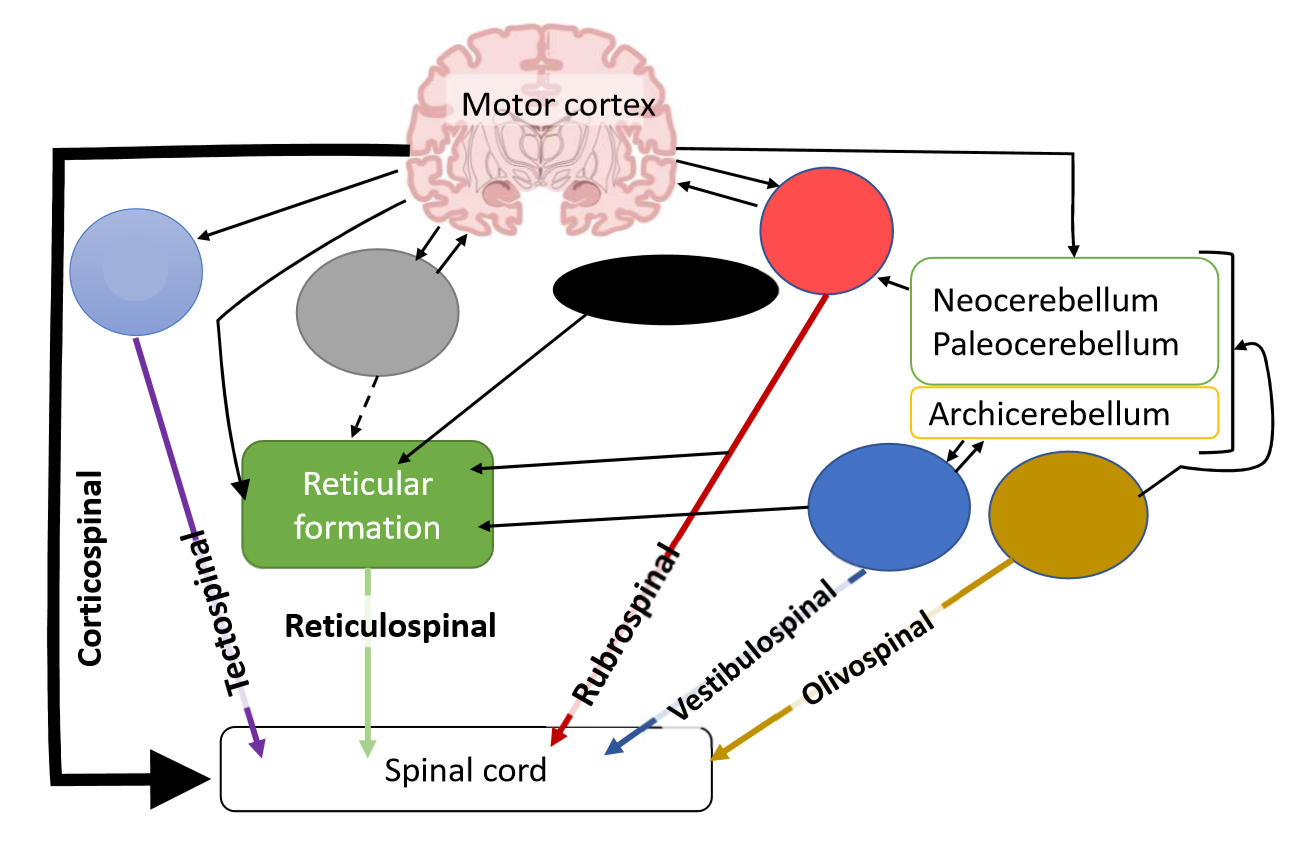
What is the brown pathway?
olive
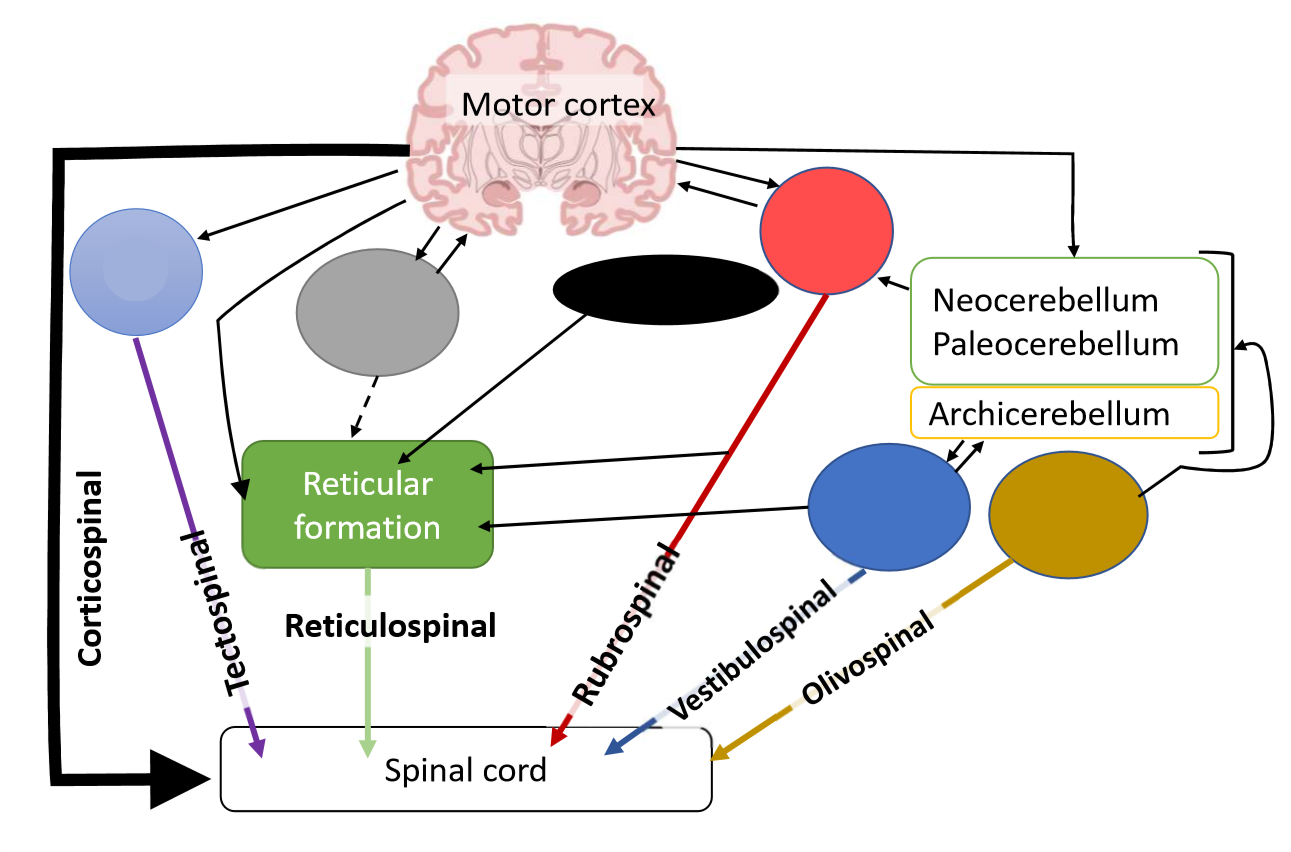
What is the function of the olivospinal tract?
influences spinal reflexes
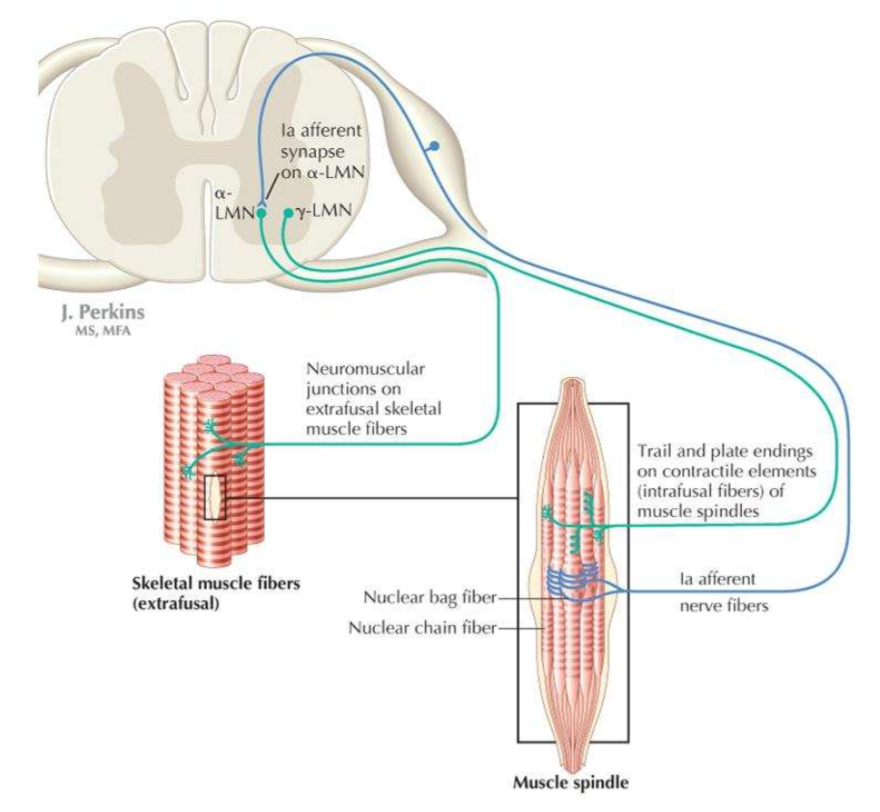
What are the two types of somatic efferent nerves supplying skeletal muscles?
alpha motor neurons, gamma motor neurons
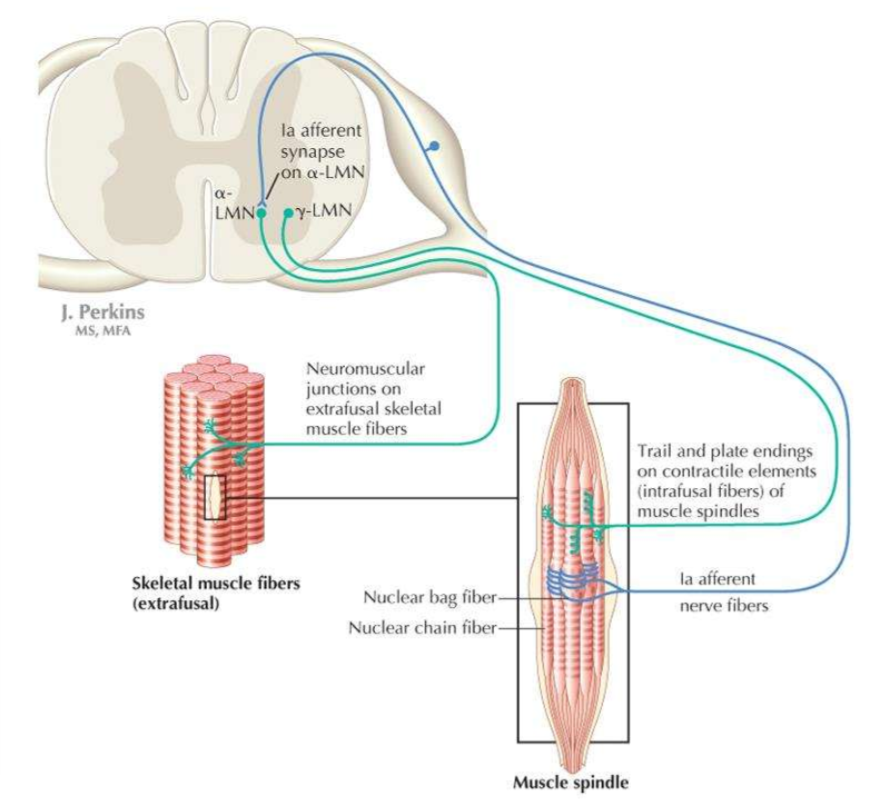
What are the characteristics of alpha motor neurons?
thick axons, fast conduction, innervates extrafusal muscle fibres, drives muscle contraction
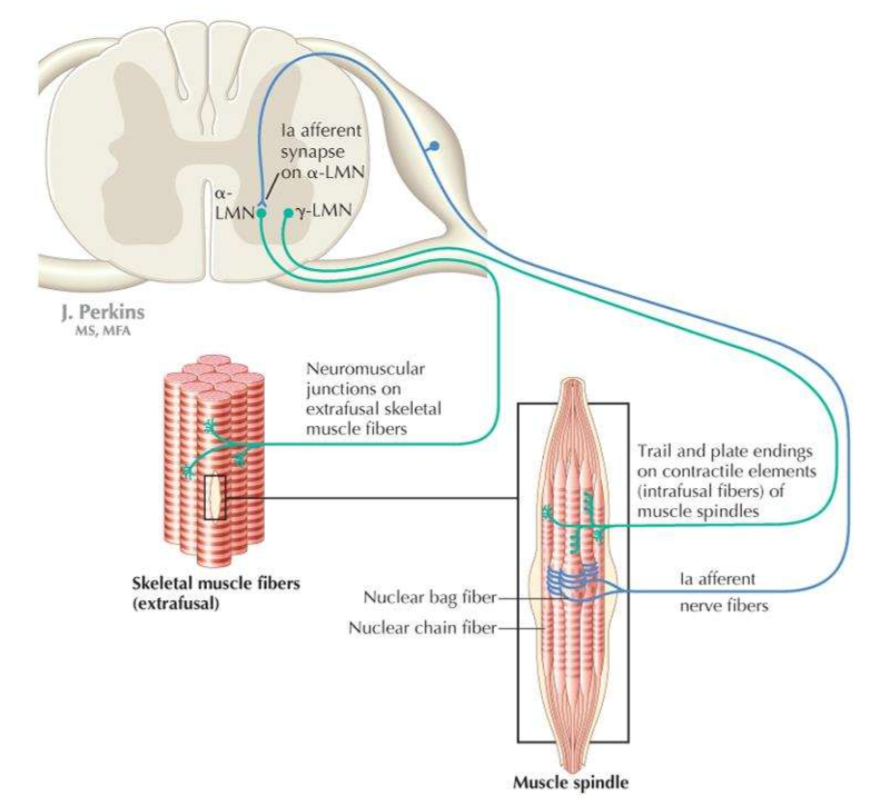
What are the characteristics of gamma motor neurons?
thin axons, slow conduction, innervates intrafusal muscle spindles, innervates tension spindle as muscle contracts to maintain proprioceptive feedback
Which neurotransmitter is used at the neuromuscular junction?
acetylcholine
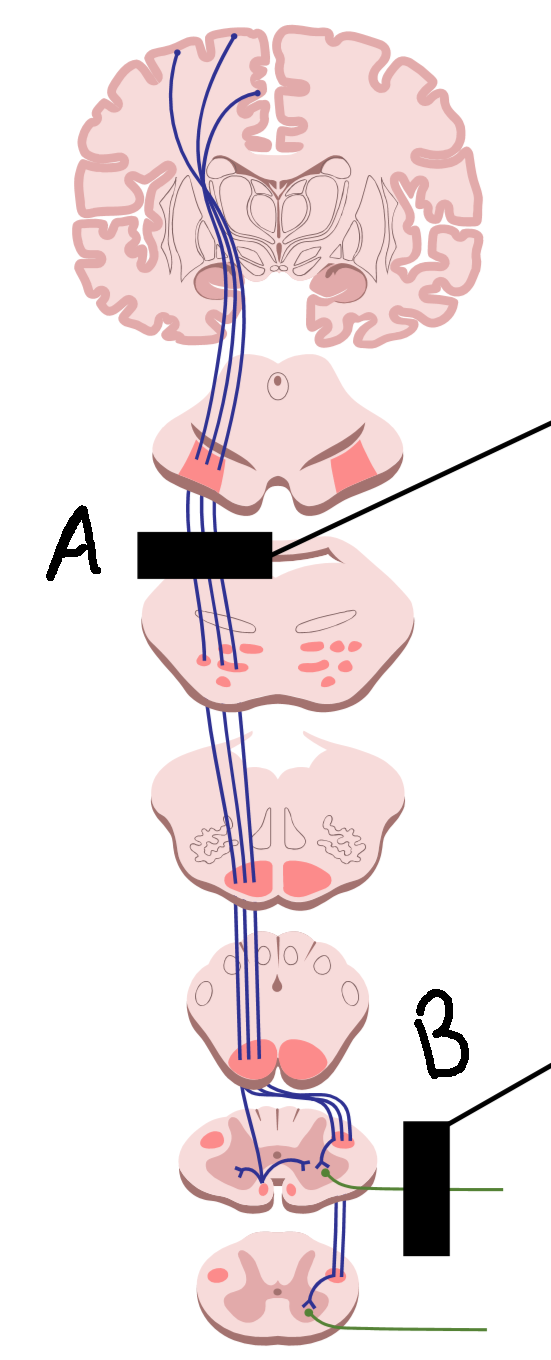
What is it called when there is degeneration at A?
upper motor neuron disease
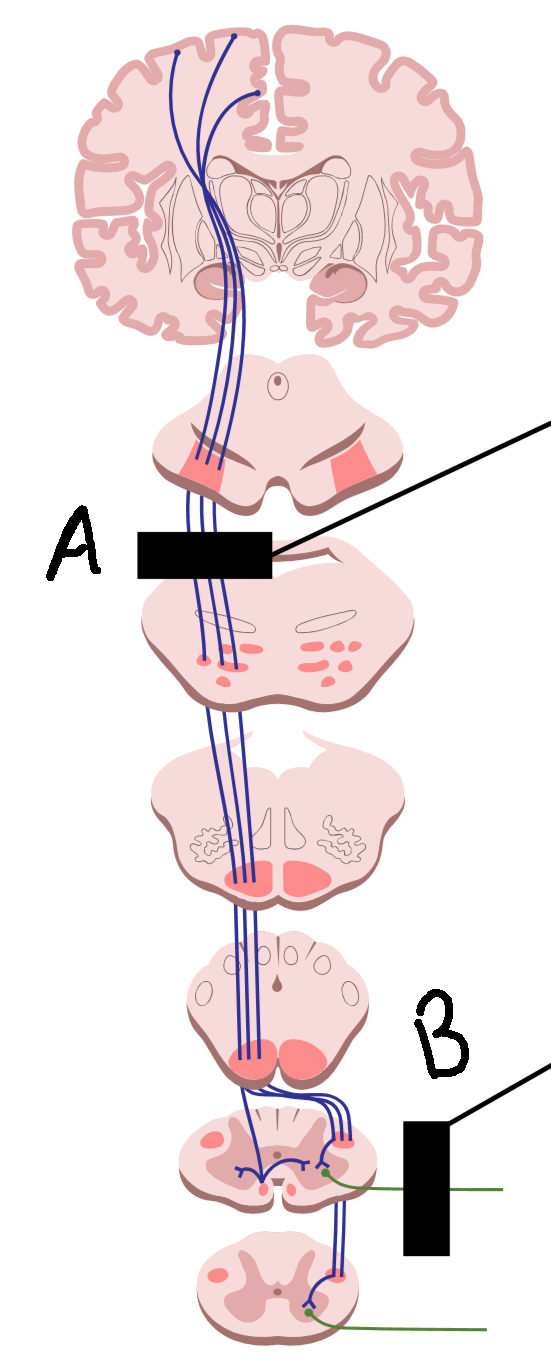
What is it called when there is degeneration at B?
lower motor neuron disease
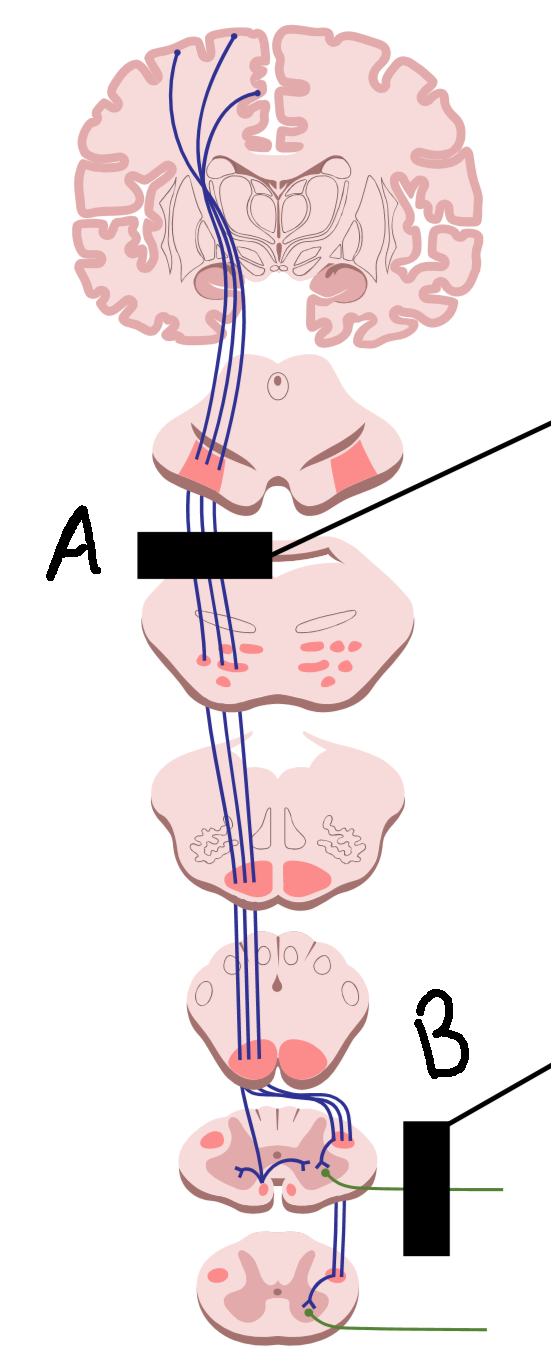
What are symptoms of A?
muscle rigidity and spasm, hyperreflexia, hypertonia
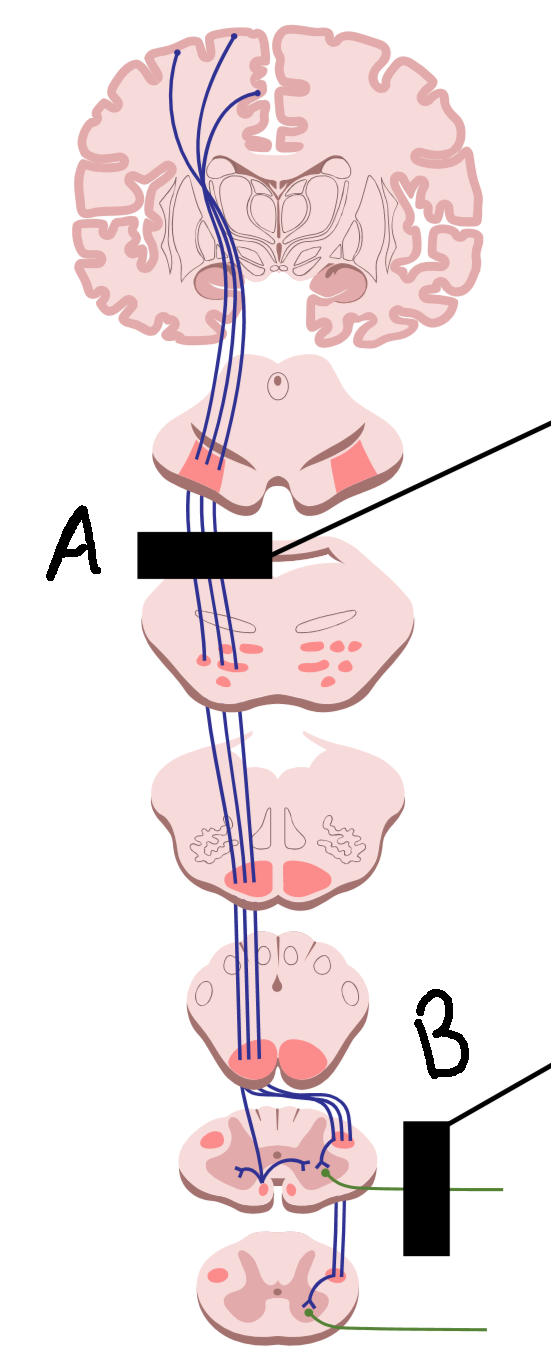
What are symptoms of B?
no reflexes, wasting and weakness, hyporeflexia, hypotonia, flaccid paralysis
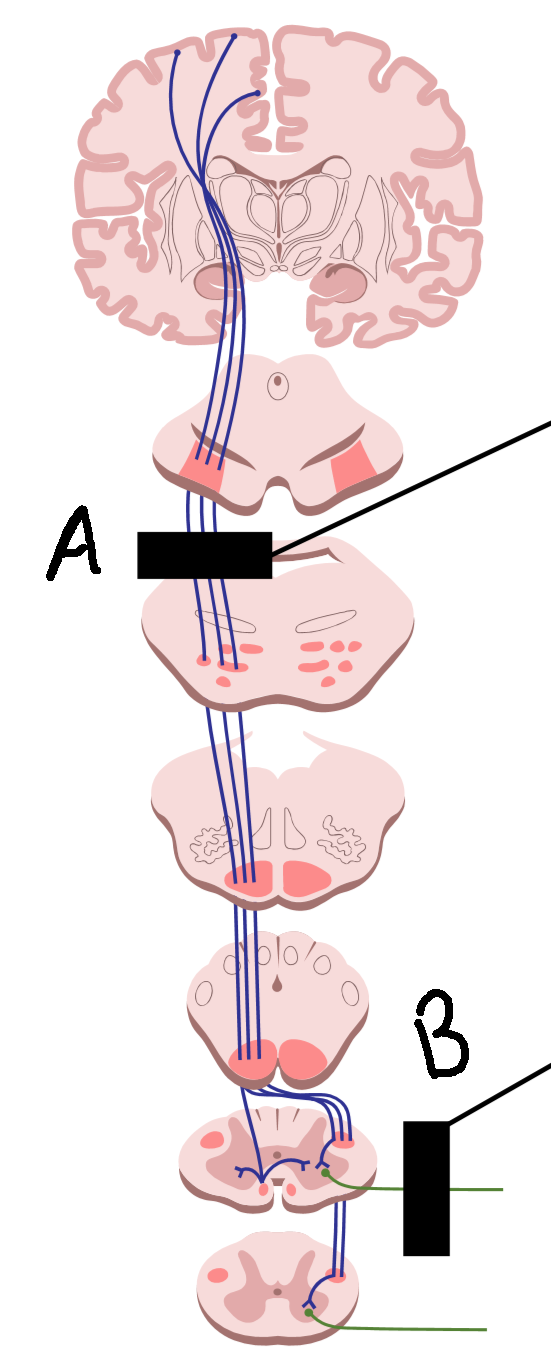
What causes A?
stroke, head injury, brain tumor, spinal cord injury
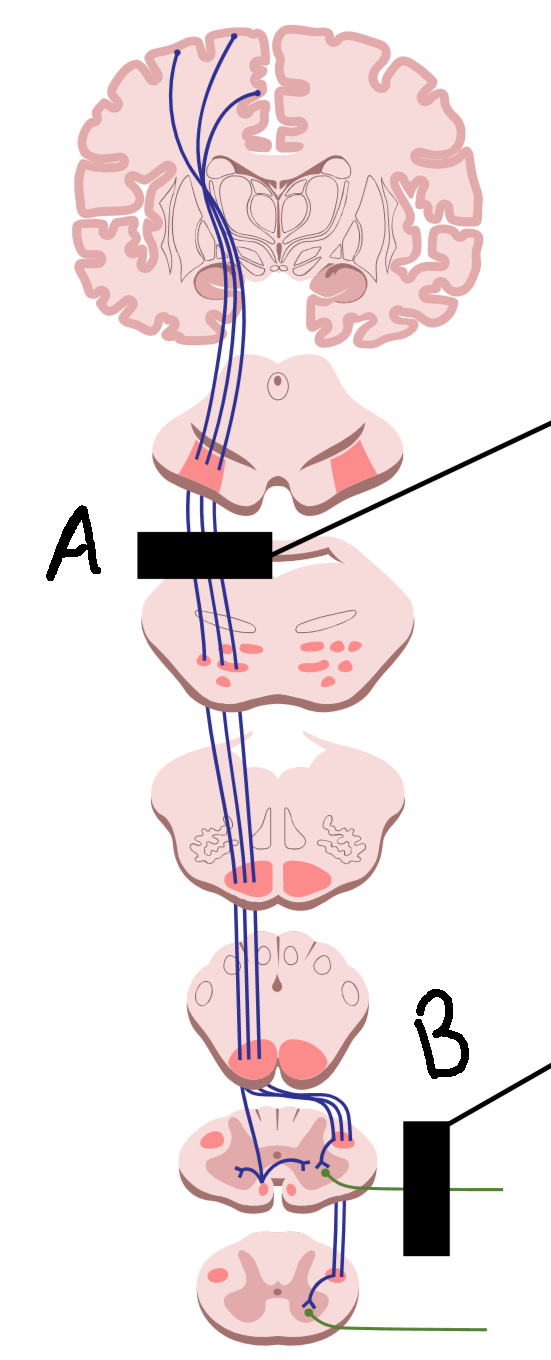
What causes B?
trauma to PNS, environmental toxins and viruses