Muscle Physiology Review
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential vocabulary and definitions related to muscle anatomy and physiology, including muscle types, properties, functions, and the processes involved in muscle contraction and relaxation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
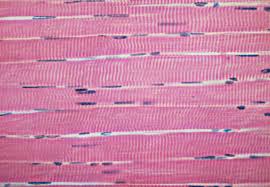
Skeletal Muscle
Attached to bones, striated, voluntary, and contracts rapidly but tires easily.
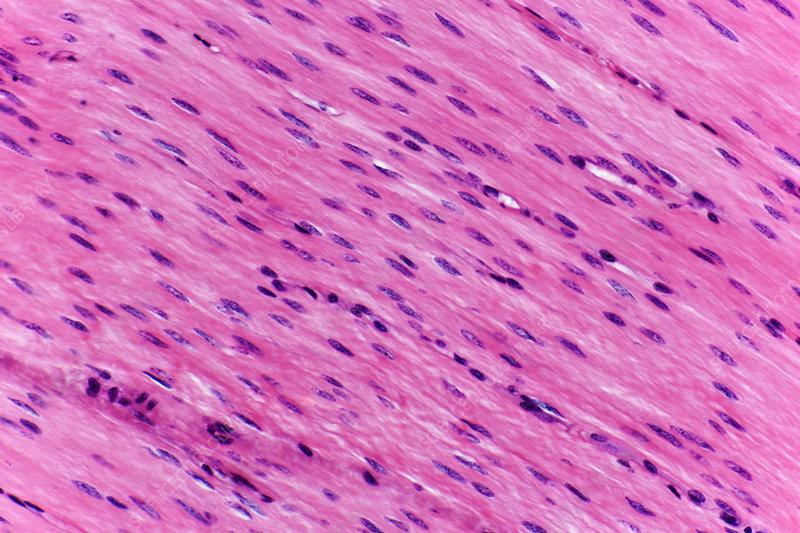
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary muscle found in the walls of hollow organs, non-striated, and has slow, sustained contractions.
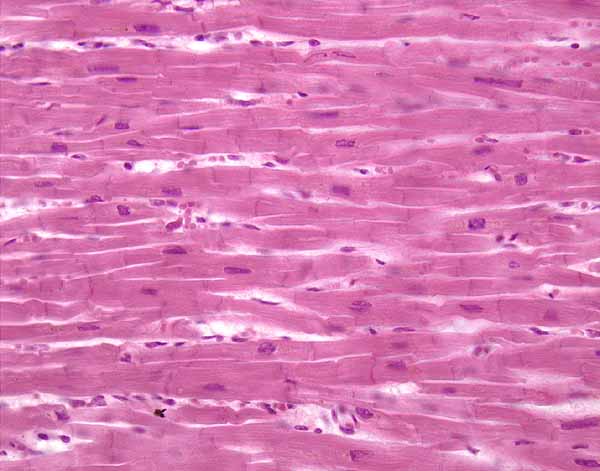
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary muscle that makes up the heart, branching, striated, and has intercalated discs.
Irritability
The ability of muscle fibers to receive and respond to a stimulus.
Contractility
The ability of muscle fibers to forcibly shorten when stimulated.
Extensibility
The ability of muscle fibers to stretch.
Elasticity
The ability of muscles to recoil and return to their resting length after being stretched.
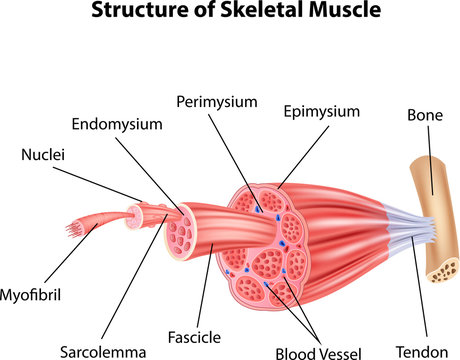
Endomysium
Connective tissue layer that covers each muscle fiber.
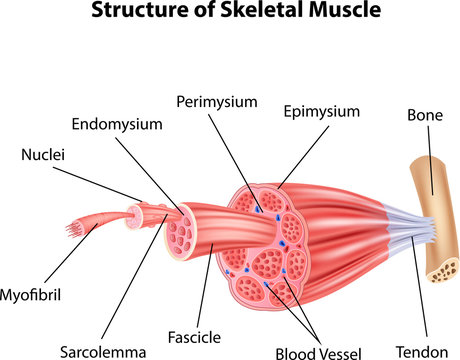
Perimysium
Stronger connective tissue layer that wraps around fascicles of muscle fibers.
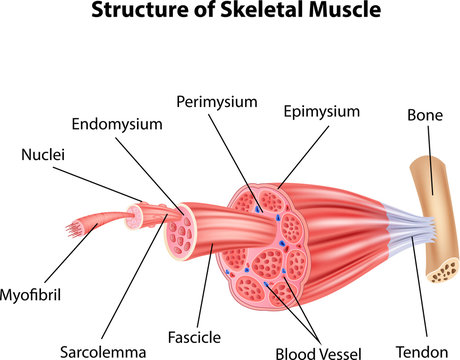
Epimysium
Connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle.
Tendons
Connective tissues that attach muscle to bone.
Sarcolemma
The cell membrane of muscle cells.
Sarcoplasma
The cytoplasm of muscle cells, containing myofibrils and organelles.
Myofibrils
Contractile organelles found in muscle cells that run the length of the cell.
Z-line
Defines the boundaries of each sarcomere in muscle fibers.
A-band
Region of the sarcomere that contains both thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments.
I-band
Region of the sarcomere that contains only thin (actin) filaments.
H-zone
The region in the center of the A-band that contains thick filaments only.
Sliding Filament Theory
The process by which myosin heads bind to actin to pull actin filaments, shortening the sarcomere.
Troponin
A protein that, when bound to calcium, shifts tropomyosin to expose active sites on actin.
Tropomyosin
A protein that blocks the binding sites on actin, preventing contraction.
Calcium Ions
Essential for muscle contraction; bind to troponin to initiate cross-bridge formation.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter released at the neuromuscular junction to stimulate muscle contraction.
Neuromuscular Junction
The site where a motor neuron connects with a muscle fiber to initiate contraction.
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
The energy currency required for muscle contractions; releases myosin head from actin after muscle contraction
Rigor Mortis
Postmortem stiffness of muscles caused by the lack of ATP which prevents cross-bridges from detaching.
Muscle Atrophy
The wasting away or decrease in size of muscle fibers due to disuse.
Muscle Hypertrophy
The increase in size of muscle fibers due to forceful, repetitive activity.
Creatine Phosphate
A compound that helps produce ATP quickly during short bursts of intense activity.
Oxygen Debt
The extra oxygen needed after exercise to restore metabolic conditions to resting levels.
Cellular Respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into ATP
Krebs Cycle
Generates ATP in the presence of oxygen
Glycolysis
The breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid; does not require oxygen
Lactic Acid
A byproduct of anaerobic respiration (without oxygen) that can accumulate and lead to muscle fatigue.
Flexion
A movement that decreases the angle between bones.
Extension
A movement that increases the angle between bones.
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body.
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body.
Circumduction
Circular movement that combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
Rotation
Movement around a central axis of a joint.
Dorsiflexion
Movement that brings the toes closer to the shin.
Plantar Flexion
Movement that decreases the angle between the foot and the leg, pointing the toes downwards.
Inversion
Movement that tilts the sole of the foot inward, toward the midline of the body.
Eversion
Movement that tilts the sole of the foot outward, away from the midline of the body.
Supination
Rotational movement of the forearm that turns the palm upward.
Pronation
Rotational movement of the forearm that turns the palm downward.
Retraction
Movement of a body part backward, typically involving the shoulder blade or jaw.
Protraction
Movement of a body part forward, such as the shoulder blade or jaw.
Elevation
Movement of a body part upward, such as raising the shoulders.
Depression
Movement of a body part downward, such as lowering the shoulders.