Chapter 5: Observational Learning and Cognitive Factors to Learning
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Learned helplessness (Seligman)
A phenomenon in which exposure to inescapable and uncontrollable aversive events produces passive behavior
ex. In a study on NFL teams over a span of 3 years, researchers found that teams that were badly beaten in one game tended to perform worse than expected the next game. The lack of effort may be due to learned helplessness because the players believed no matter what they did, they could not win the game.
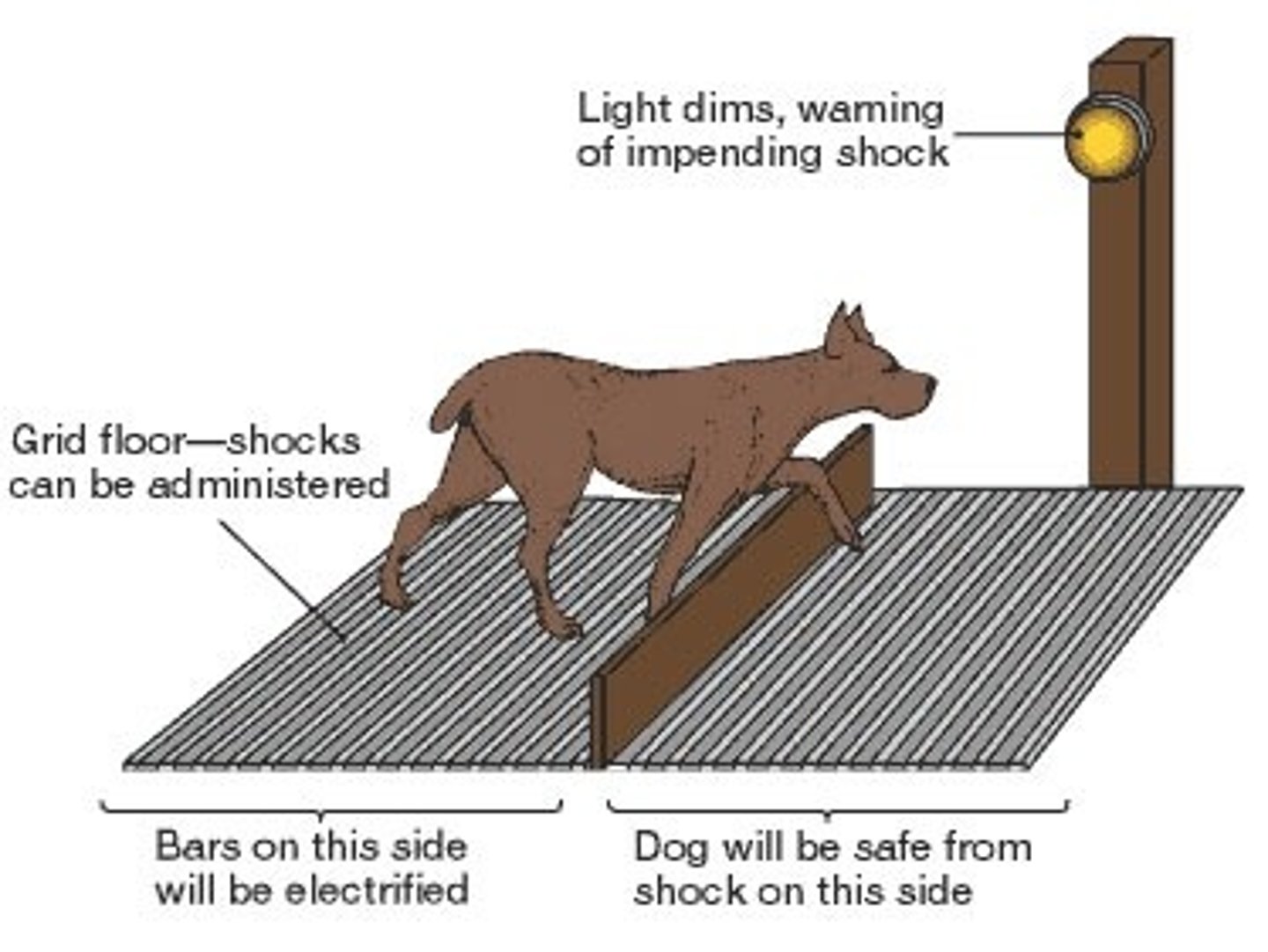
Shuttlebox
The device used by Seligman to test for learned helplessness. Dogs were classically conditioned to associate a tone with a shock. The tone became a CS for the CR of fear in the dogs. The shocks were inescapable by the dogs in the initial setup. Dogs were then moved to the shuttlebox shown in the image. A low barrier divided the area with shocks and an area without shocks. Dogs that had learned to be helpless didn't attempt to step over the barrier and escape the shock.
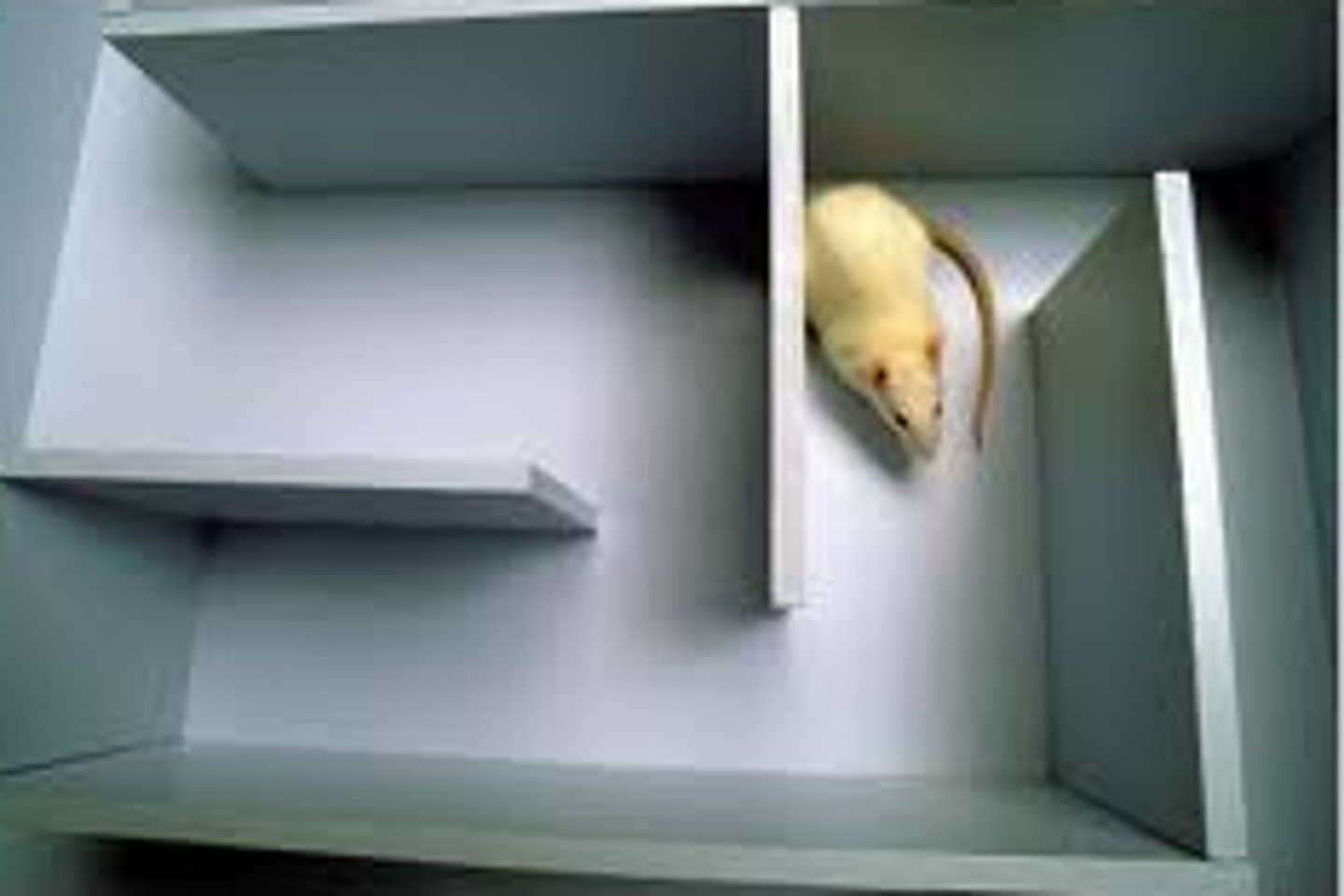
Edward Tolman Experiment
Conducted an experiment with 3 groups of rats in a maze to illustrate the "cognitive aspects" to learning.
Group 1: got a reward every day and steadily improved in running the maze
Group 2: never got a reward and never really improved at running the maze
Group 3: got a reward on the 11th day of running the maze. These rats improved very little, but then dramatically improved as soon as the food reward was introduced on the 11th day.
Why does it matter? Tolman proved that the rats in group 3 had learned the layout of the maze in the absence of classical conditioning, operant conditioning, or observational learning. This proved that there could also be "cognitive aspects" to learning.

cognitive map
a mental representation of the layout of one's environment
ex. Tolman's rats that weren't rewarded until day 11 had formed a cognitive map of the maze
ex. having a mental map of how to get from the high school to the center of Whitman or Hanson.
Latent Learning (Tolman)
learning that occurs but is hidden until there is an incentive to demonstrate it
ex. Tolman's rats had formed a cognitive map of the maze but didn't show that they had learned it until a food reward was offered on day 11
observational learning
learning by observing others; also called social learning
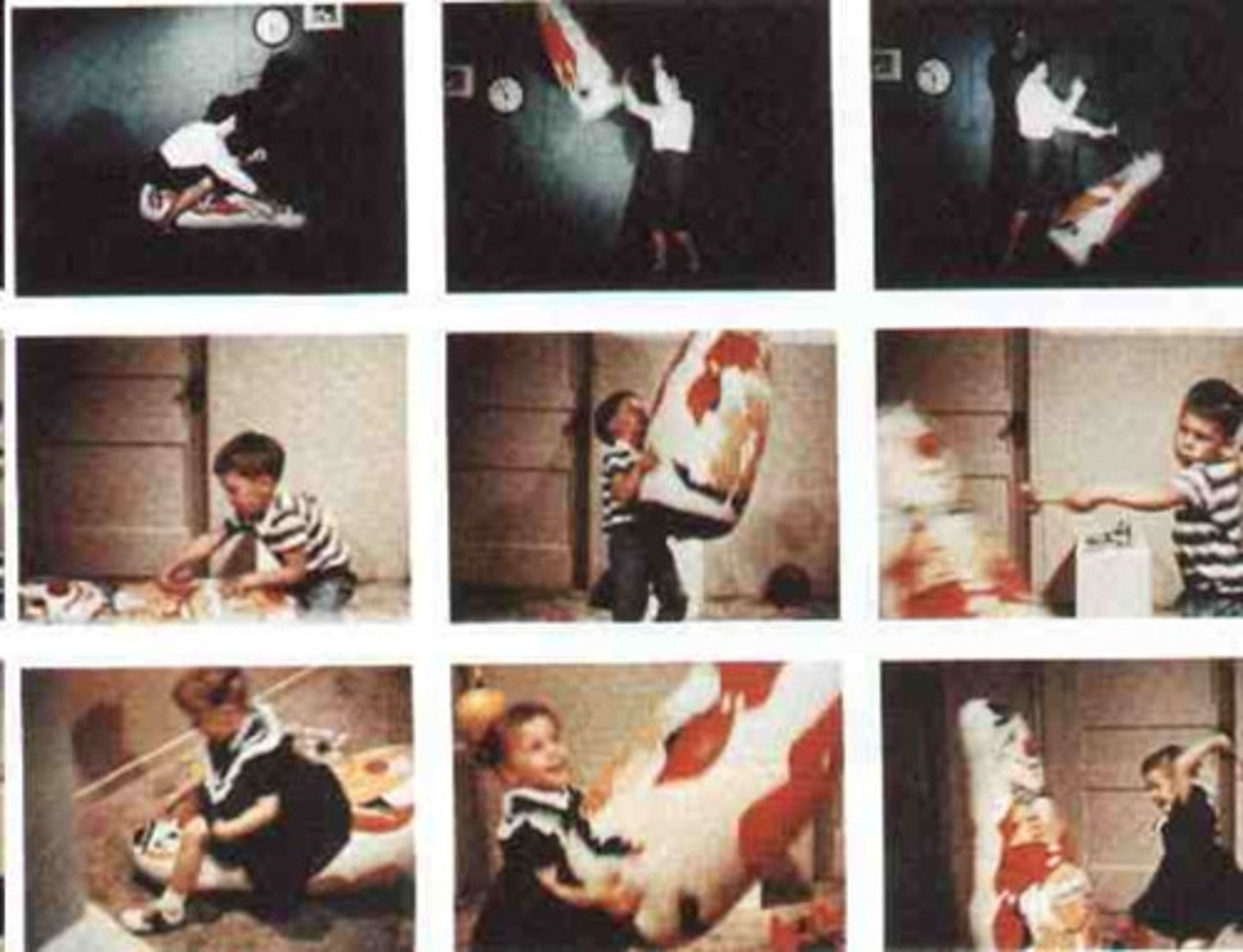
Bobo doll experiment (Albert Bandura Social Learning Theory)
Children that viewed adults playing aggressively with the Bobo Doll toy were likely to imitate the aggressive behavior used by the adults when they played with the toy themselves. The famous study showed the importance or impact of observational learning. This study is often cited when children view and imitate aggressive behavior in television, movies, and video games.
Modeling
the process of observing and imitating a specific behavior
ex. a child engages in modeling by viewing and imitating a parent's mannerisms and gestures when speaking
ex. a child views a television character light a fire and chooses to light a fire themselves
vicarious reinforcement/punishment
By viewing someone else being rewarded or punished for a particular behavior, a person may choose to engage in that behavior (or not) to receive the reward or avoid the punishment in the future.
ex. A student is yelled at for chewing gum in class. A different student opts to not chew gum the next day when offered a piece from someone else.