Chromosomes and Karyotype
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GO TO TEXTBOOK FOR MORE DETAIL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Acquired Chromosomal Abnormalities
arise during embryogenesis in only a subset of cells (mosaics)
Constitutional Chromosomal Abnormalities
found in each cell of the body
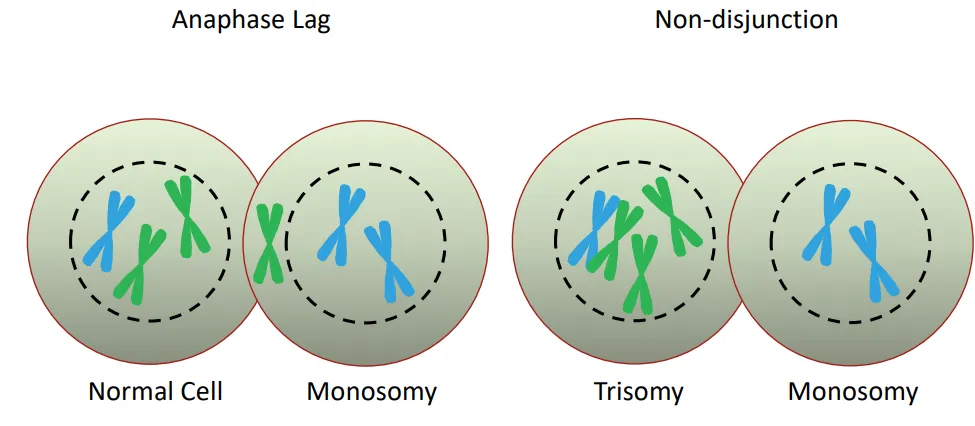
Causes of Chromosome Abnormality | Anaphase Lag
an abnormal division in which one chromosome fails to migrate to the pole of the spindle
the lagging chromosome is often excluded from the nuclei of the daughter cells and forms a micronucleus, which is degraded
Results in → euploidy (normal) and monosomy
Causes of Chromosome Abnormality | Misegregation (Non Disjunction)
failure of homologous chromosomes (meiosis I) or sister chromatids (meiosis II) to separate
Non-disjunction | Meiosis I Errors
all gametes are abnormal
50% carry both copies of the chromosome (trisomy, non-identical)
50% without either copies (monosomy)
Non-disjunction | Meiosis II Errors
50% gametes abnormal
1 with an extra chromosome copy (trisomy, identical) and 1 without (monosomy)
Anaphase vs Non-disjunction
Causes of Chromosome Abnormality | Meiotic Failure (A general Term)
complete nondisjunction
cells fail to separate (failed cytokinesis) in mitosis or meiosis
Causes of Chromosome Abnormality | Dispermy
simultaneous fertilisation of a haploid egg by 2 haploid sperm → triploidy
Causes of Chromosome Abnormality | Incorrect DNA Repair
occurs (typically) when there is a double-stranded break → DNA fragment is easily misplaced
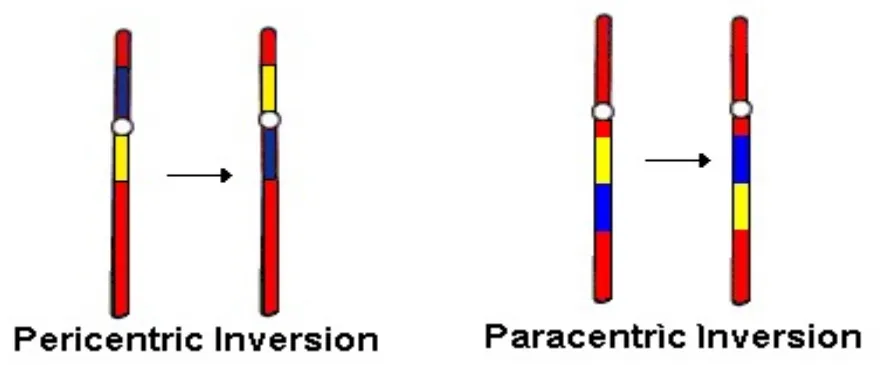
Incorrect DNA Repair | Inversion → Paracentric Inversion
a segment of a single chromosome's arm breaks, flips 180 degrees, and reattaches, but without involving the centromere.
May not involve → loss or gain of chromosomal information
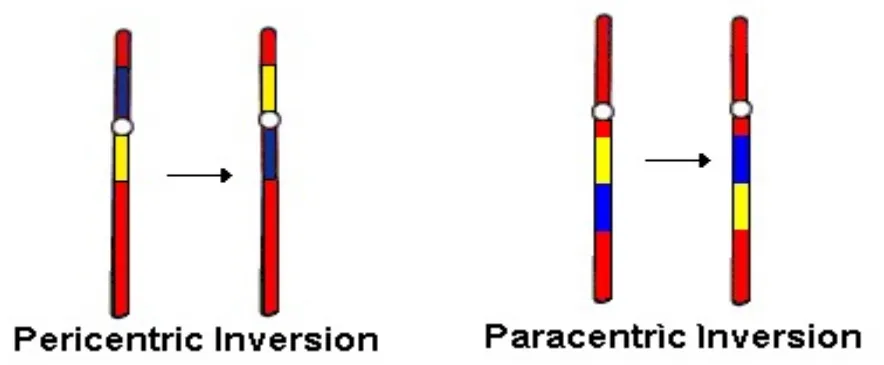
Incorrect DNA Repair | Inversion → Pericentric Inversion
a segment of a chromosome breaks on either side of the centromere, flips 180 degrees, and then reattaches in reverse order, including the centromere itself
Do inversion always cause abnormality?
no, if the breakpoints of the inversion do not disrupt genes
How does the replication of inverted gene cause inversions?
chromosomes form a hairpin loop for crossing over of prophase → may lose or gain genes
Incorrect DNA Repair | Translocation
movement of genetic material to another nonhomologous chromosome
may not include → loss or gain chromosomal material
Incorrect DNA Repair | Translocation → Insertional Translocation
Where gene segments from one nonhomologus chromosome is insert to another nonhomologus with no reciprocation. Only one chromosome exchanges a gene segment.
Incorrect DNA Repair | Translocation → Reciprocal Inversion
Where gene segment is exchanged between nonhomologous chromosomes. They both exchanged gene segments with each other.
Robertsonian Translocation
centric fusions of acrocentric chromosomes → 2 acentric + 1 dicentric
no net gain or loss of genetic material ∴ normal phenotype (balanced)
increased risk for fetal abnormalities or miscarriage
Robertsonian Translocation | 2 normal split from qq and pp
DRAW IT
Robertsonian Translocation | normal + qq split from normal and pp?
DRAW IT
Incorrect DNA Repair | Deletion
can be large or small
size roughly correlates with the severity of the abnormality
Incorrect DNA Repair | Duplication
fragment of one deletion can bind with homologous partner → duplication
Ring Chromosomes
when telomeres are lost, and sticky chromosome ends fuse
What determines how affected an individual is?
the genes lost (symptomatic if genes are lost or disrupted)
What Each Abnormality Results in
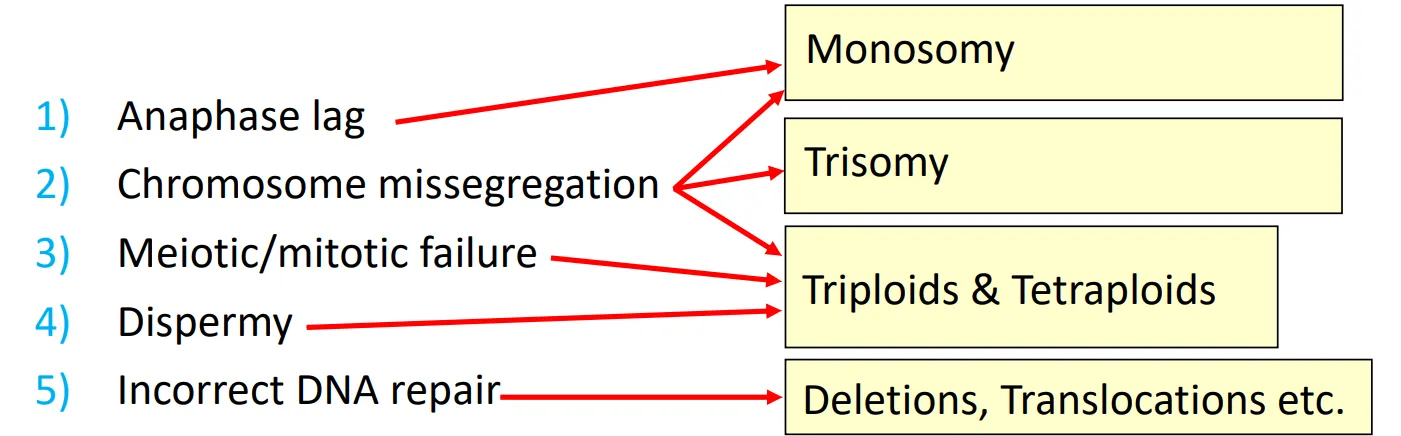
Karyotype Disorders | Can Arise via Non-disjunction and Robertsonians
trisomy 13
trisomy 18
trisomy 21
monosomy X
Aneuploidy
addition/ loss of chromosomes (or parts) from the normal (euploid) set of 23
→ Inherited via meiotic errors furing gametogenesis
caused via non-disjunciton
commonly as a trisonomy, rarely a monosomy
Embryonically lethal in chromosomes → 10, 15, 16
Suriviable in chromosomes → 13, 18, 21 → because these are small chromosomes with less genes
Possessing One chromosome is lethal but why can males have XY
all females are mosaic
normal cell development and function only require 1 X chromosome
early in development, XX cells randomly deactivate one X (by XIST gene)
the inactive X becomes hyper-condensed → Barr-body (heterochromatin)
Polyploidy
presence of whole sets of chromosomes in excess of the normal (euploid) set of 23
complete nondisjunction
cells fail to separate (failed cytokinesis) in mitosis or meiosis
dispermy
what % of early miscarriages show an abnormal karyotype

what is parent-of-origin imprinting?
phenomenon where gene expression depends on inheritance from biological father or mother
what is uniparental disomy?
inheritance of 2 chromosomes or chromosome parts from the same parent
Requires
simultaneous non-disjunction in the same chromosomes in both egg and sperm
OR
Trisomy followed by chromosome loss
how can you tell how early an error occurred in an mosaic?
one with more cells (an earlier cell was affected so it has duplicated more)
what technology is used to detect many micro-deletions?
FISH (detects the presence or absence of specific genes on chromosomes by hybridisation)
why does ectodermal dysplasia present with patterned skin?
gene controlling ectodermal dysplasia are located on the X chromosome and turned off in some areas by X chromosome inactivation
Ectoderm Dysplasia | where is skin normal vs pink with no sweat glands?
Normal → where the X chromosome bearing the defective gene has been deactivated
Pink → where the X chromosome bearing the normal gene has been deactivated
what defect causes Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathy?
duplication of 17p11.2 gene
what defect causes Charcot-Marie Tooth disease?
duplication of PMP22 gene
what defect causes William's Syndrome? consequence?
DNA loss around the 7q11.23 region
Consequences → vasculature disorder due to the loss of the elastin gene
Ring Chromosome 22 |
cognitive impairment
hypotonia (muscle weakness)
lack of coordination
what causes Prader-Willi syndrome?
loss of paternal 15q11-13 region
Prader-Willi Syndrome | Clinical Features
chronic feeling of hunger → hyperphagia
life-threatening obesity
Prader-Willi Syndrome | Clinical Features
chronic feeling of hunger → hyperphagia
life-threatening obesity
Prader-Willi and Angelman’s Syndrome
Prader-Willi
deletion of paternal gene
maternal uniparental disomy
methylation defect (paternal gene switched off)
Angelman’s
deletion of maternal gene
paternal uniparental disomy
methylation defect (maternal gene switched off)
Balanced Translocation
Common Features (#8)
Robertsonian translocation
Increased risk of Down’s
syndrome
45,X_ der(14;21)(q10;q10)
Classic Down Syndrome | Trisomy 21
Flat Facial Features
Increased gap between 1st and 2nd toe
Increased nuchal fold
47,X_,+21
Cri Du Chat
Cat-like cry
Down-slanted palpebral fissures
46,X_,del(5)(p15.3)
Diplo-Y
Poor Coordination
Prominent glabella
Increased length vs breadth
→ Ears
→ Hands
→ Fingers
→ Feet
→ Toes
47,XYY
Edward Syndrome | Trisomy 18
Short Sternum
Clenched hands with overlapping fingers
rocker-bottom-feet
47,X_,+18
Klinefelter Syndrome
gynecomastia
Hypogonadism
Hypospadias
Hypogenitalism
47,XXY
Affected Sex | male
Patau Syndrome | Trisomy 13
Microphthalmia
Cutis aplasia of the scalp
holoprosencephaly
Polydactyly
47,X_,+13
Translocation Down Syndrome
Flat facial profile
Increased nuchal fold.
Increased gap between 1st
& 2nd toe.
Single Palmar Crease
Triple X
Development is almost
normal.
Clinodactyly
Tendency for back
problems
47,XXX
Triploidy
Large placenta w/
hydatidiform changes
Low nasal bridge
Syndactyly of the 3rd & 4th
fingers
69,X_ _
Turners Syndrome
Pterygium colli deformity
Low posterior hairline
Broad chest w/ widely
spaced nipples
affected sex = females
45,X
Wolf-Hirschorn Syndrome
Broad or beaked nose
Preauricular tag/pit → small hole in front of the upper ear, located just between the face and the cartilage of the ear rim
46, X_, del(4)(p16.3)
Jacobsen Syndrome
Broad nasal bridge
Macrocephaly
Trigonocephaly
Paris-Trousseau syndrome → which is a disorder of
platelets, which are
necessary for blood
clotting.
46,X_,del(11q)
Fragile X Syndrome
Prominent jaw and
forehead
Unusually flexible fingers
Flat feet
Males can display
macroorchidism after
puberty.
46,X_, fra(X)(q27.3)
Klinefelter Syndrome | Aneuploidy is usually fatal why no death here?…
X-chromosome inactivation, turns off all but one X chromosome per cell ∴ the ill effects of any extra chromosomes are reduced