Dental Instruments (With Pictures VS Definition and Name)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
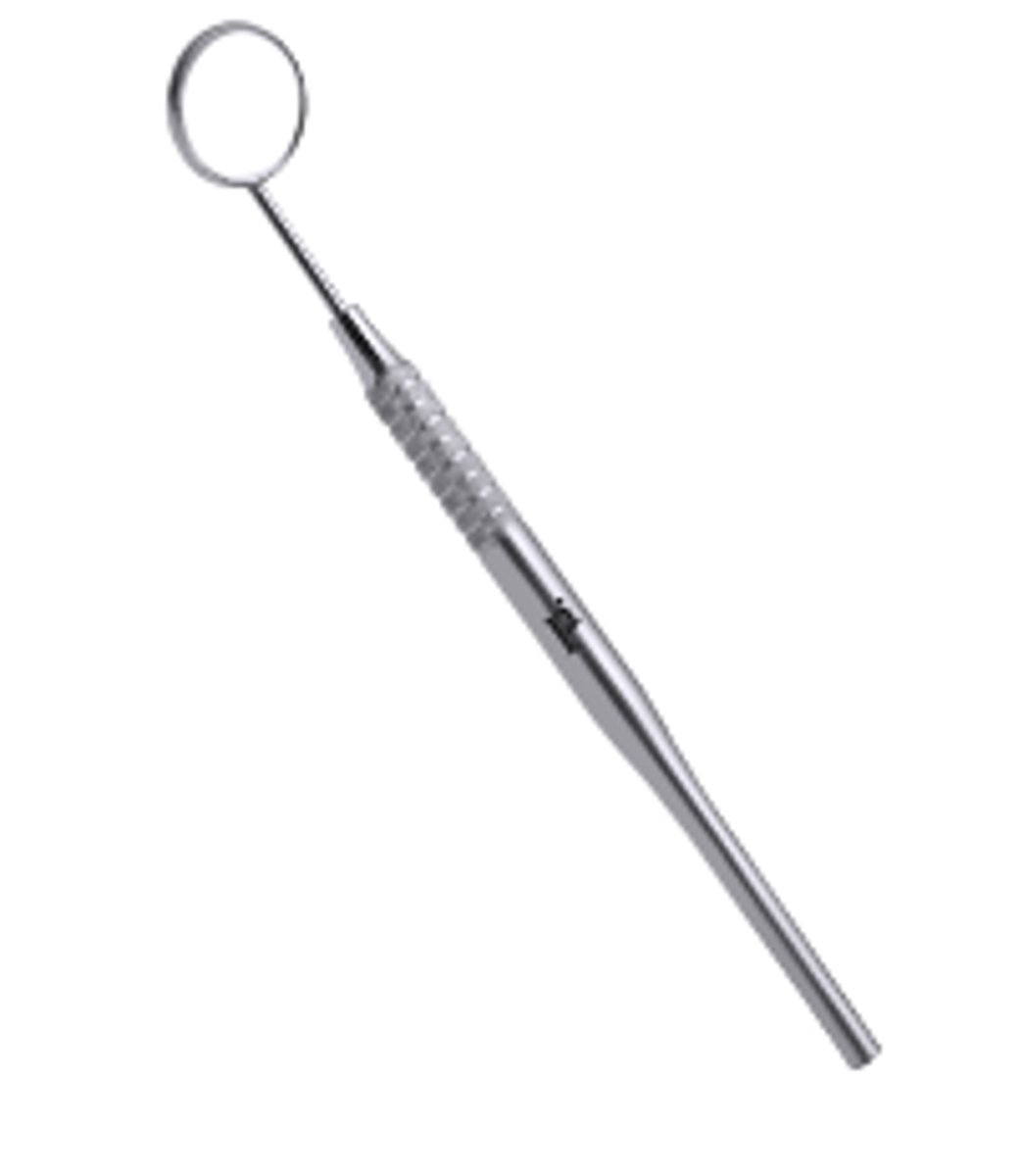
Mouth Mirror (4)
Allows indirect vision
Retraction of soft tissues
Transillumination (Shining A Light Through/On Something)
Reflects light onto desired surfaces

Dental Explorer (1)
To examine teeth for decay (caries), calculus, furcations, or other abnormalities

1. Orban
2. Pigtail
3. Shepherd's Hook
What are the three main dental explorers used?
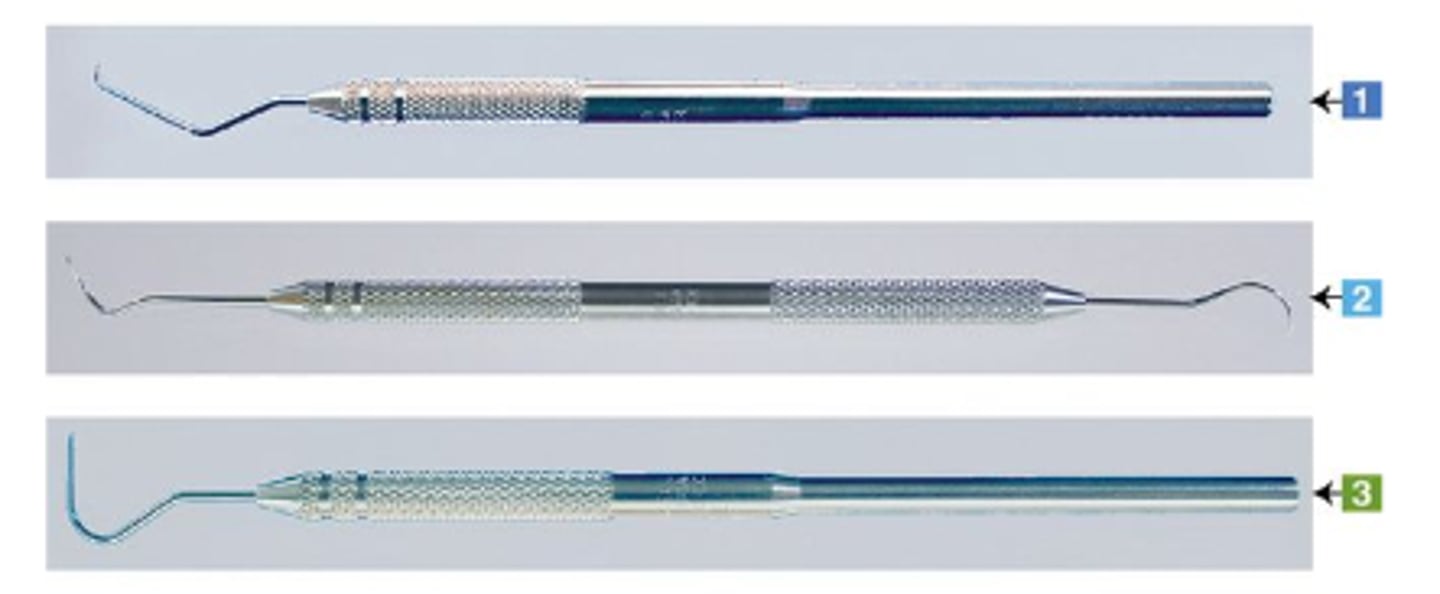
Periodontal Probe (1)
To measure periodontal pocket depth in millimeter increments
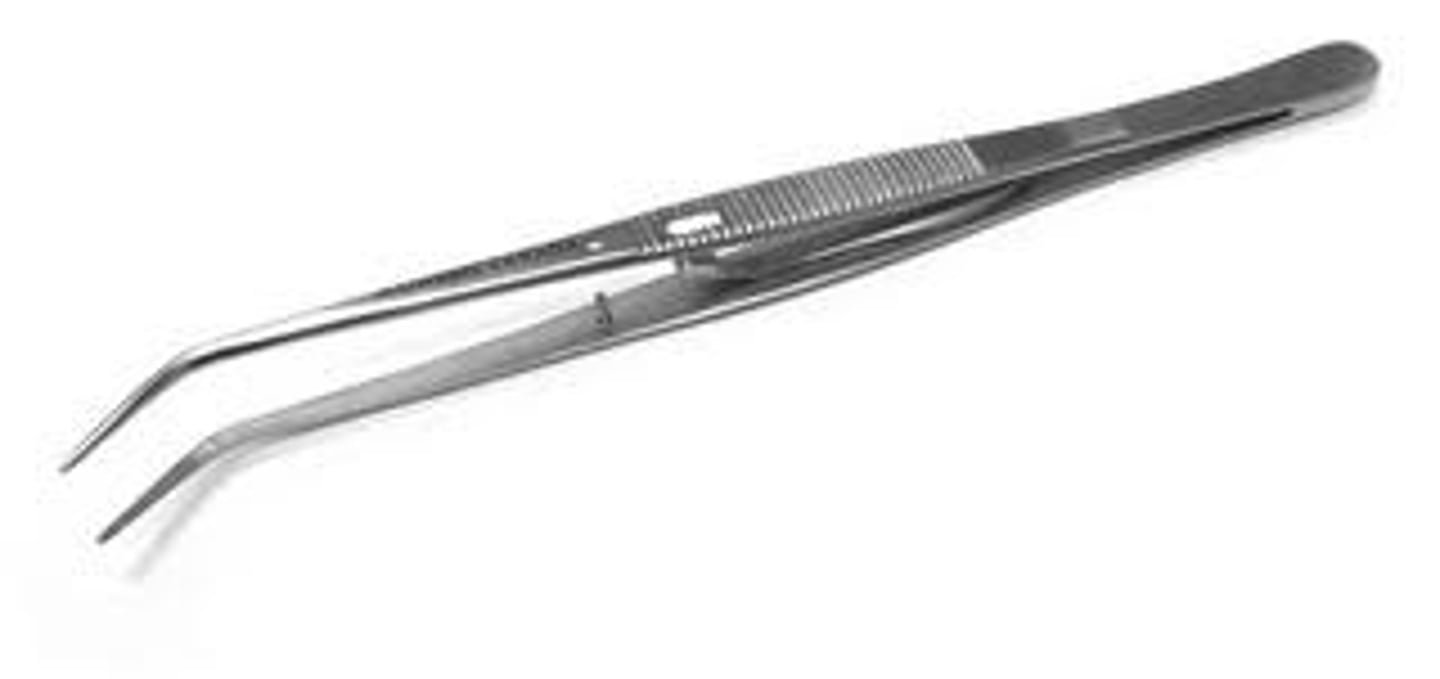
Cotton Pliers / Cotton Forceps (2)
Used for handling cotton pellets, cotton rolls, small instruments, or other small items placed into or withdrawn from the mouth.

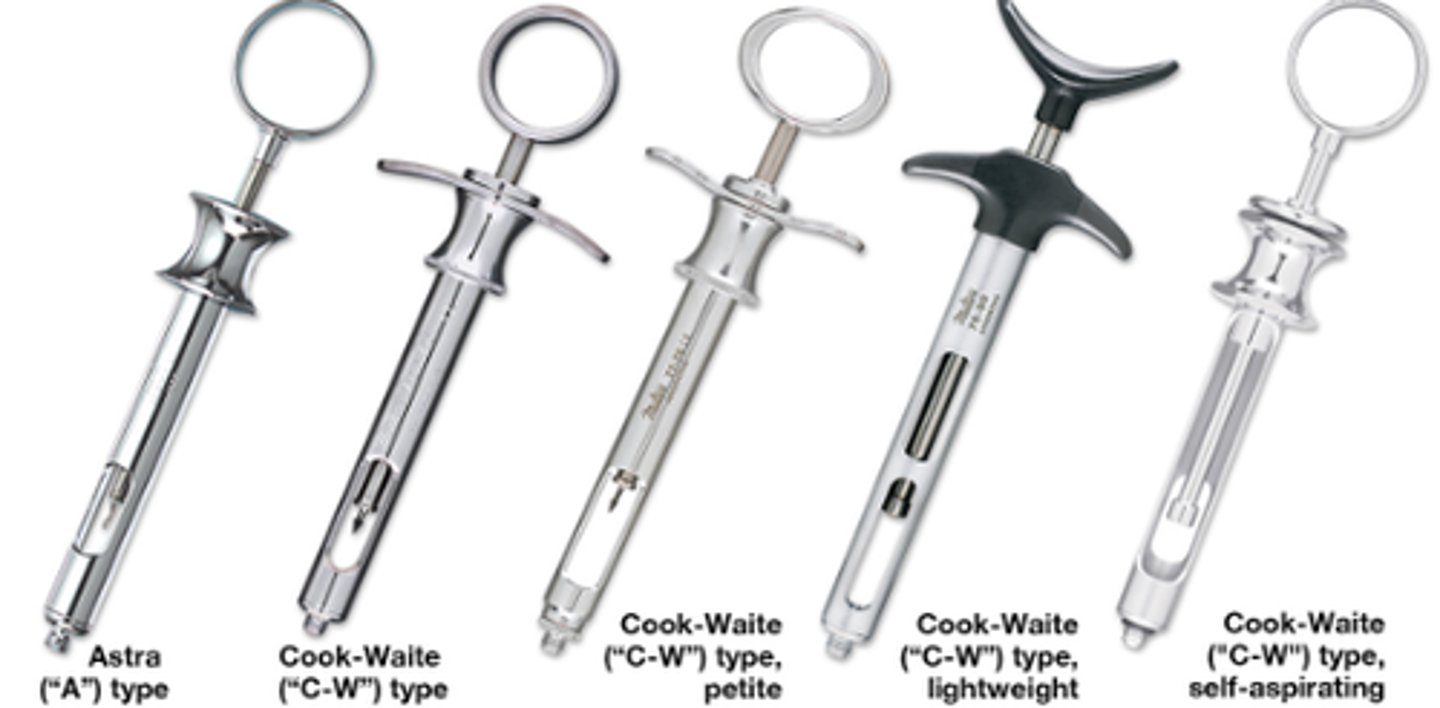
Anesthetic Aspirating Syringe (2)
To administer a local anesthetic
Injects anesthetic from a carpule and allows the dentist to ASPIRATE the injection site by pulling the thumb ring outward.

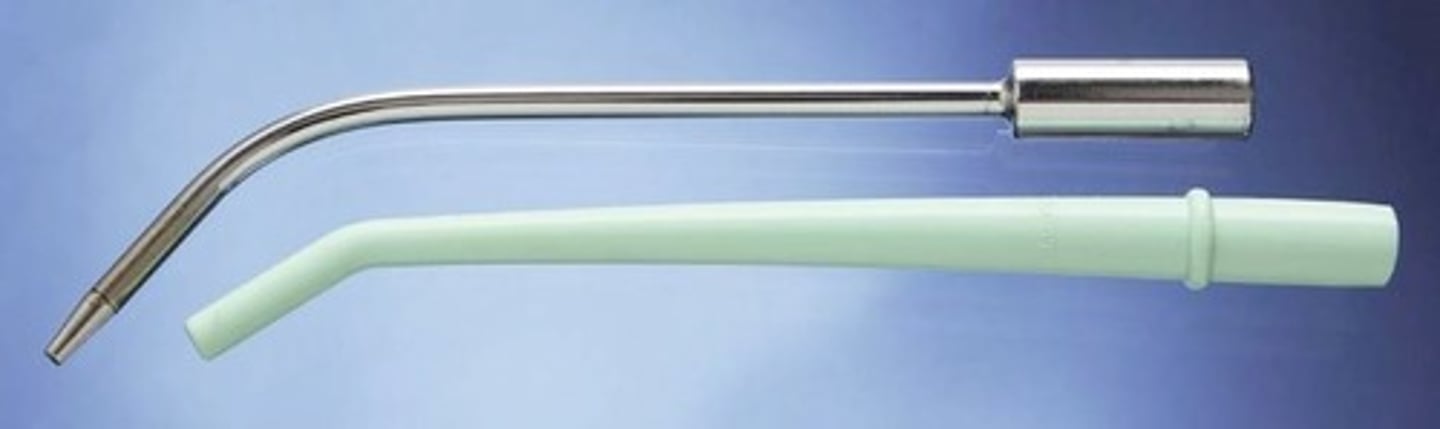
Evacuation Tip High-Volume Velocity (1)
To evacuate large volumes of fluid and debris from the oral cavity

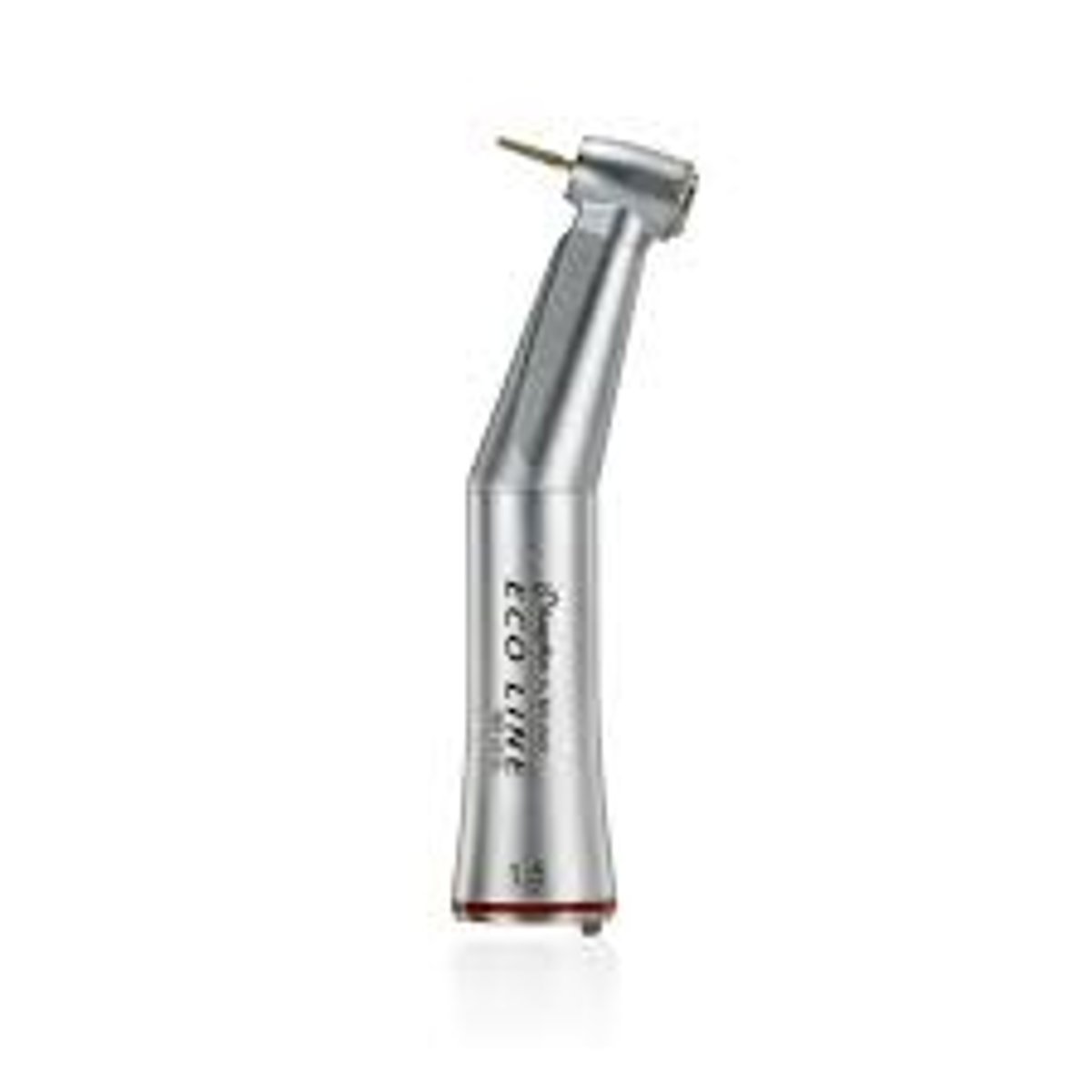
Handpieces (2)
High or low speed tool
To use with bur to cut tooth structure, bone, to remove decay, and to modify or remove restorations.

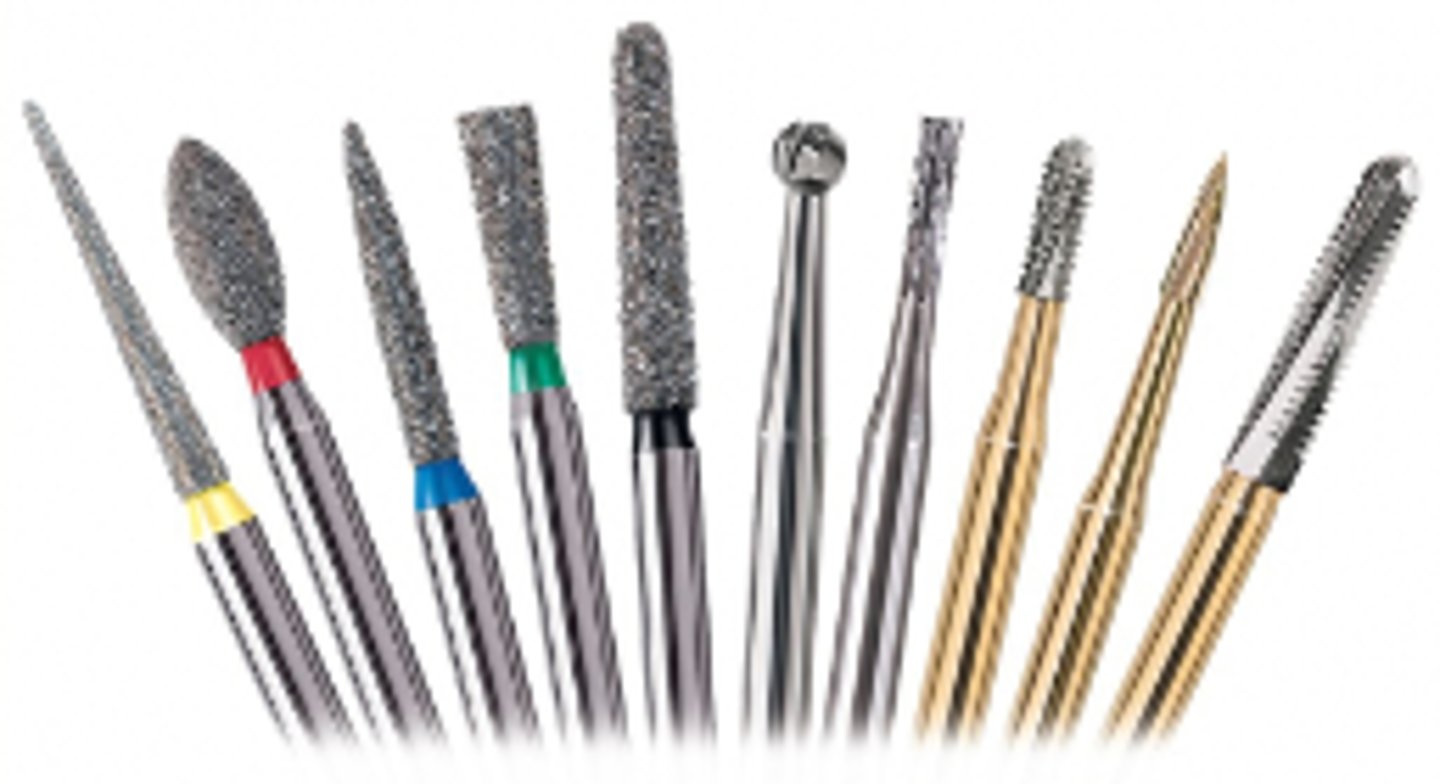
Burs (3)
For cutting hard tissues like tooth or bone
Used to polish restorations
Each type of bur comes in varying degrees of sharpness, lengths, shapes, and sizes

Fiberoptic High-Speed Handpiece (3)
To illuminate tooth during preparation for restoration
To provide light intraorally during use of handpiece
To use with bur to cut tooth structure, to cut bone, to remove decay, and to modify or remove restorations
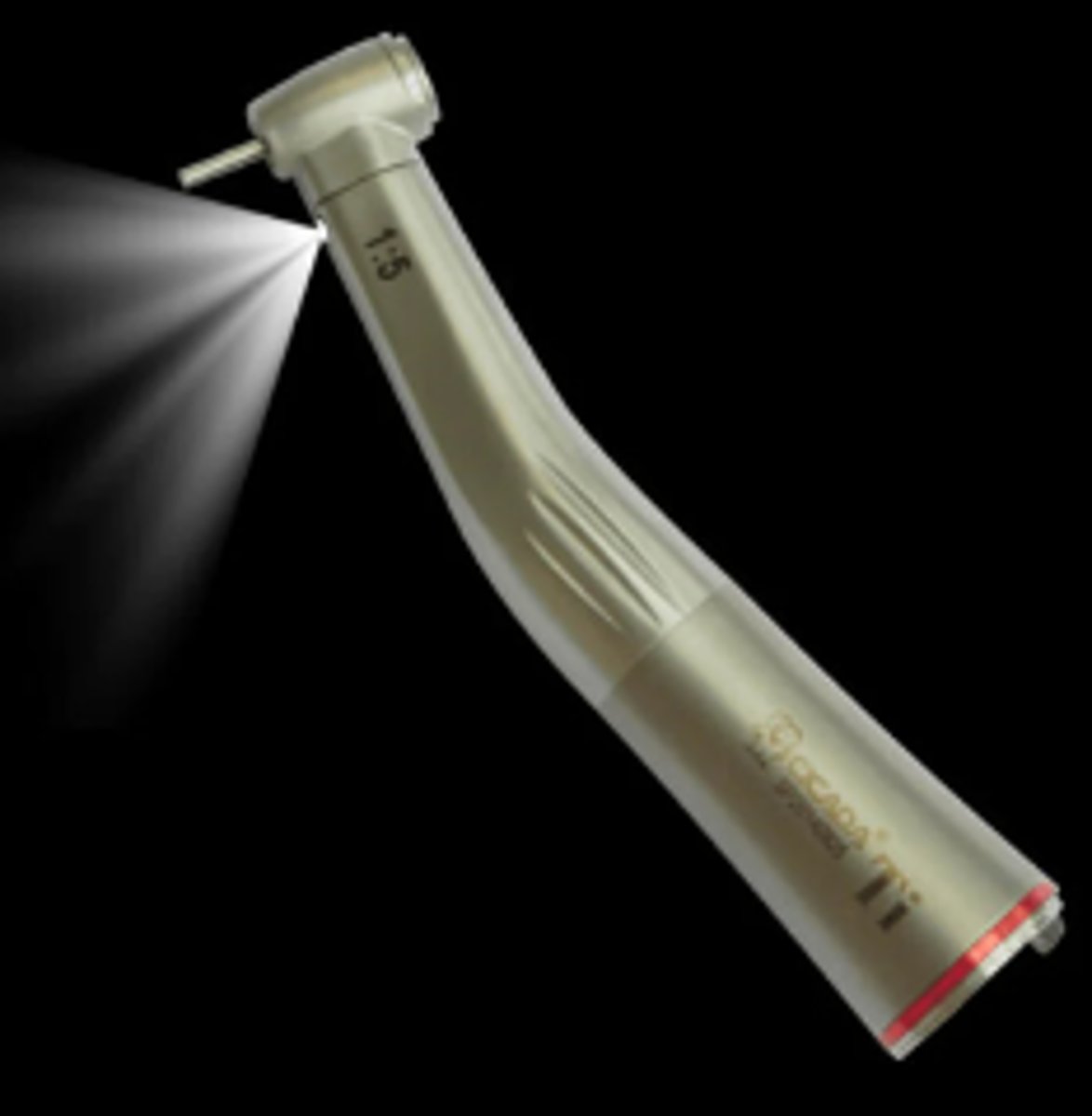
Slow-Speed Handpiece (with Contra Angle Attachment)
To use with burs for intraoral and extraoral procedures
Examples are to remove decay, refine cavity preparation, adjust provisional and permanent crowns and bridges, and many more
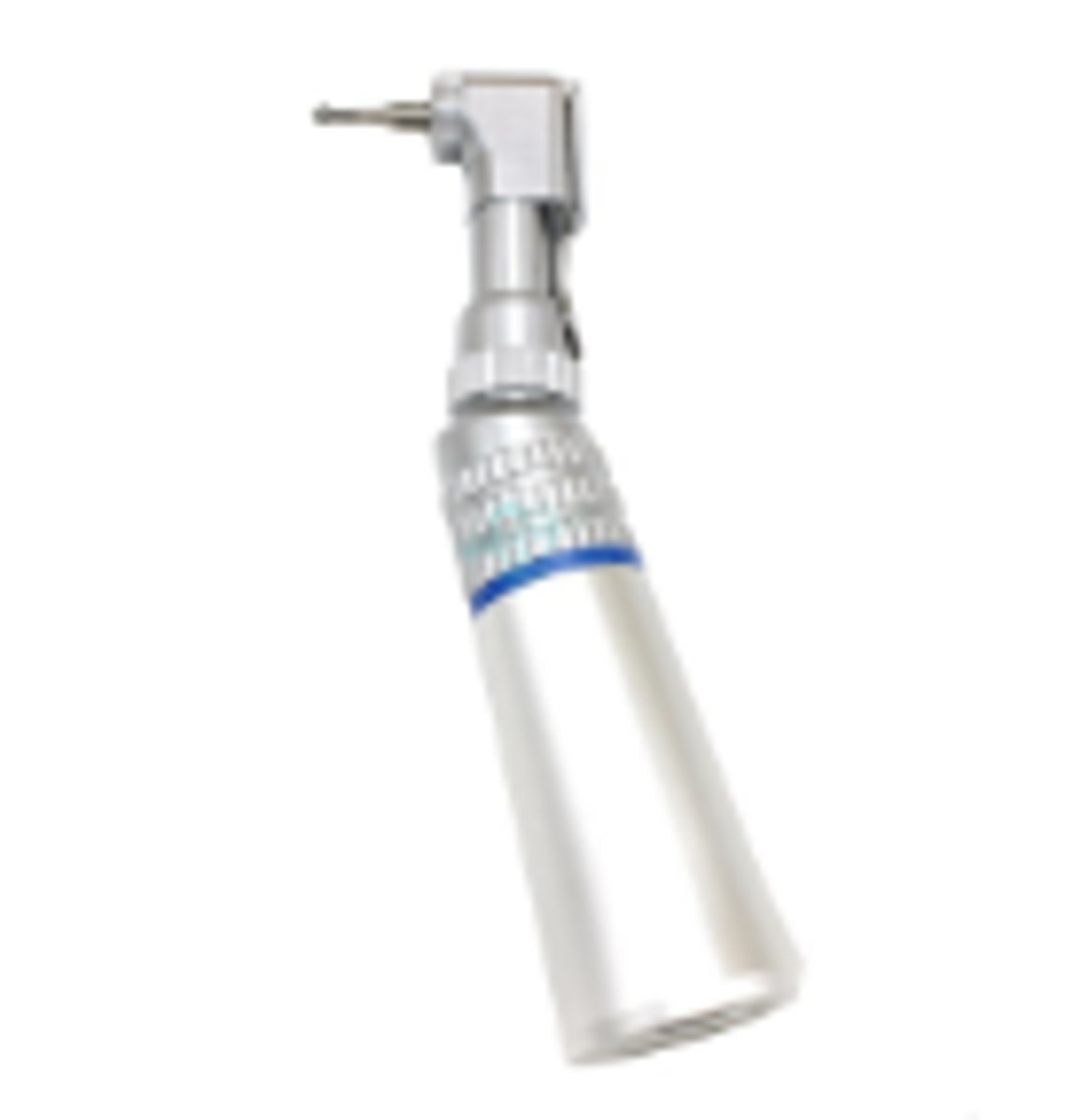

Slow-Speed Handpiece (Prophy Angle Attachment) (1)
To polish teeth with prophylaxis/prophy cup or brush attachment

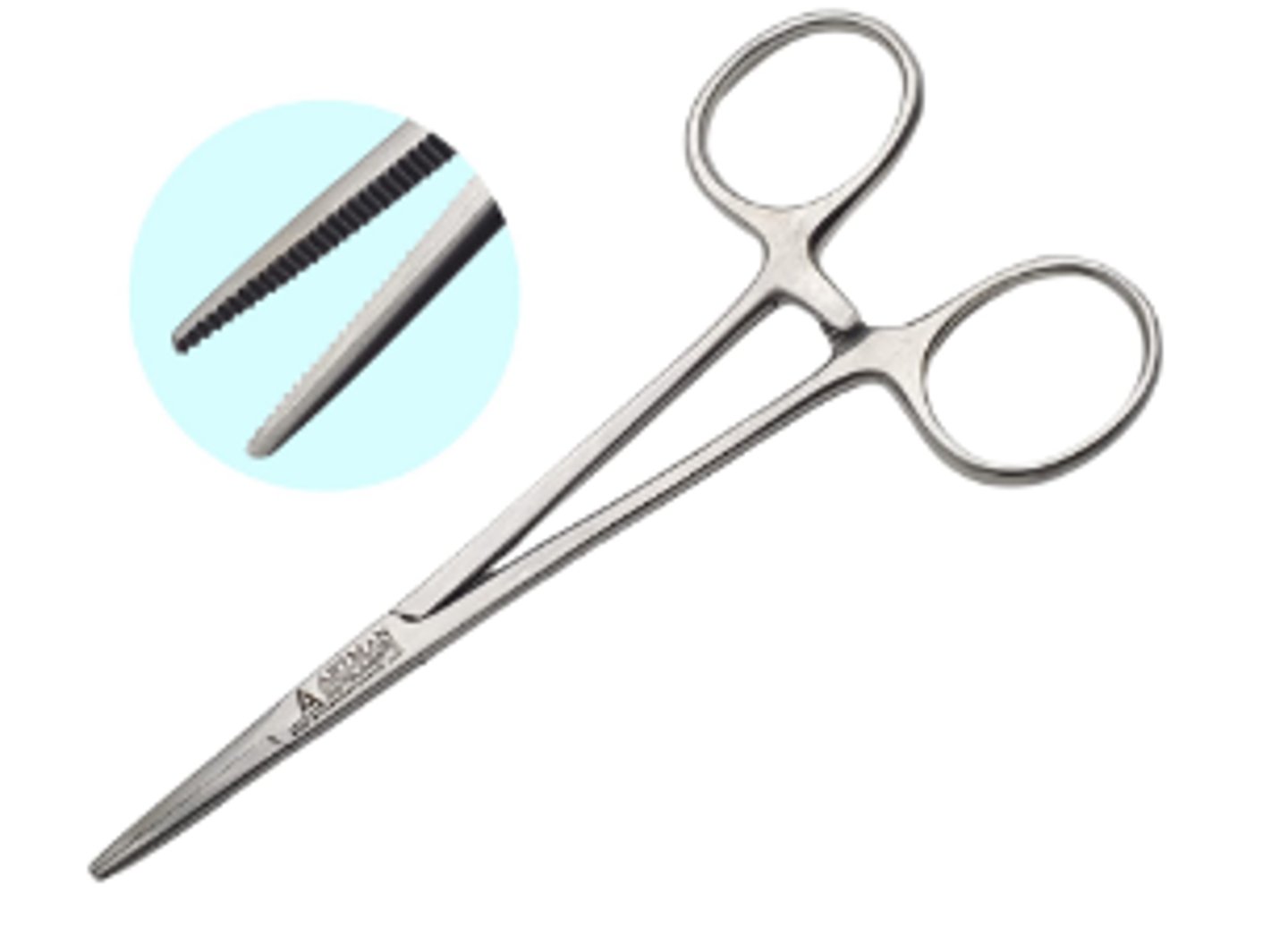
Hemostat (2)
To grasp tissue or bone fragments
To hold and grasp material in and out of the oral cavity

Amalgam Carriers (3)
To carry and dispense the triturated amalgam (silver filling) into the cavity preparation
The amalgam at this point is creamy and pliable
There are 3 main types.

1. Single Ended
2. Double Ended
3. Amalgam Gun
What are the three main types of Amalgam Carriers?

Amalgam Well (3)
Small bowl-shaped container that holds the mixed (triturated), pliable amalgam PRIOR to its being loaded into the amalgam carrier.
To hold amalgam while loading amalgam carrier

Spoon Excavator (2)
To remove carious dentin
Examples: Carious Crowns, Temporary Cement in Temporary Crowns, Permanent Crowns
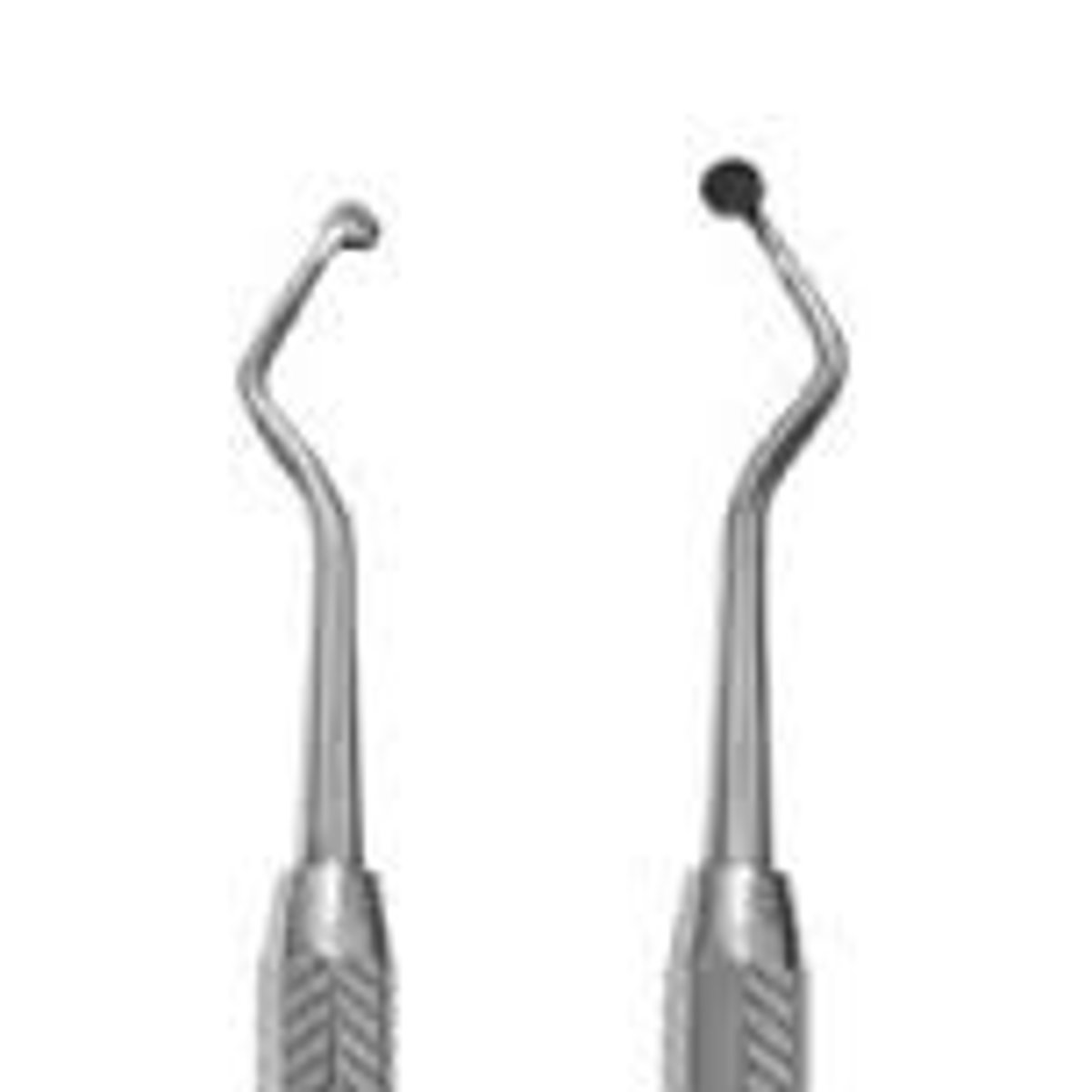

Amalgam Condenser (Plugger) - Smooth and Serrated (3)
To pack and condense the pliable amalgam into the cavity preparation.
To pack and condense other restorative materials.
These instruments are usually double ended with a smaller and larger end.
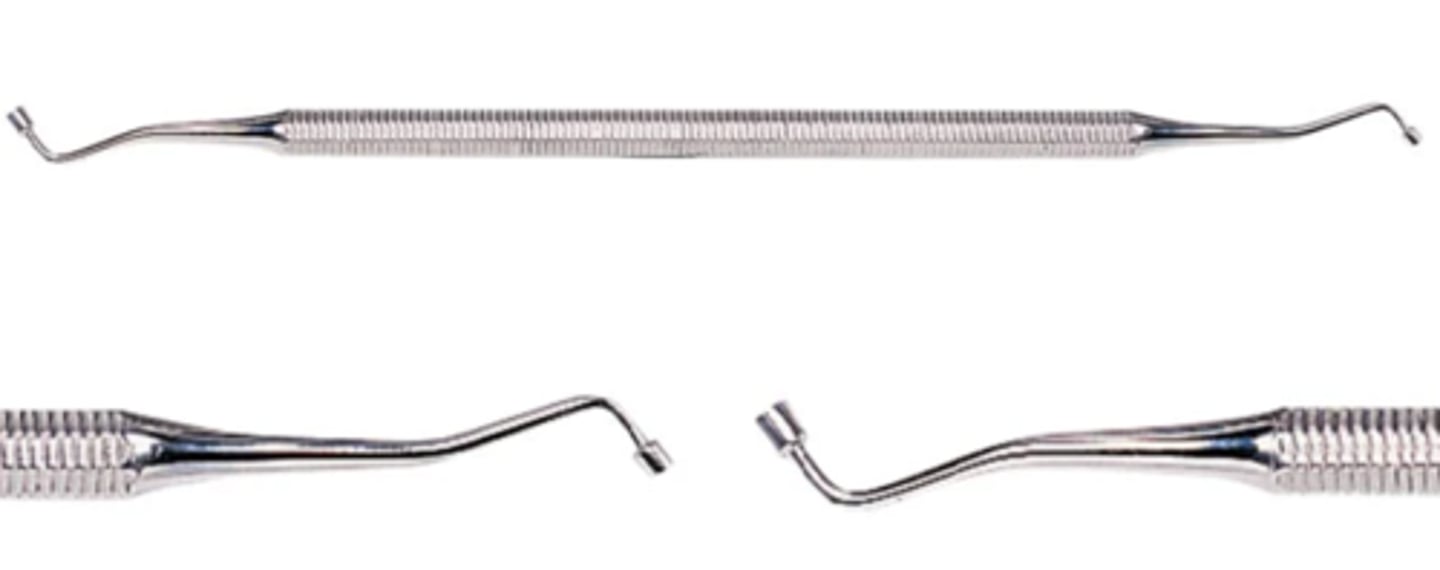

Composite Placement Instrument (2)
To carry composite material to the cavity preparation
To place, condense, and carve composite material in cavity preparation
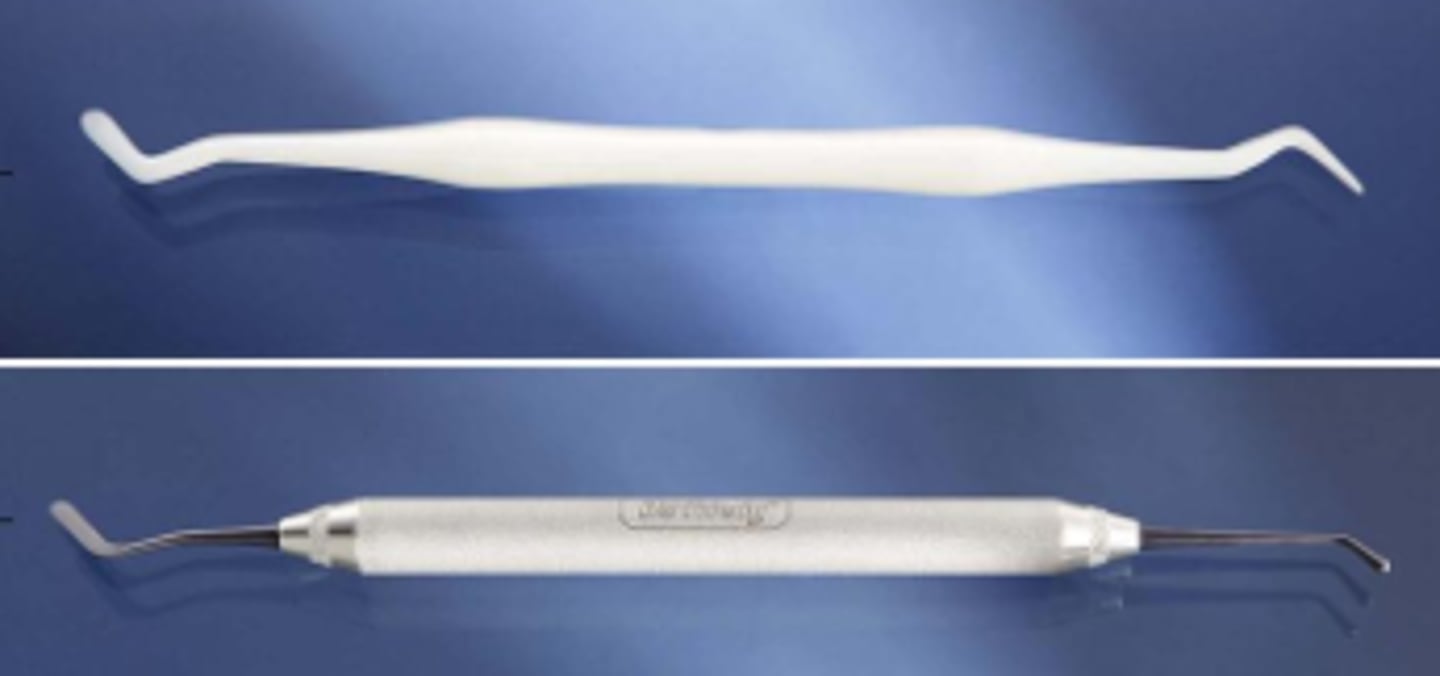
Interproximal Condenser (1)
To pack and condense amalgam into interproximal areas of cavity preparation.

Hollenback Carver (2)
To contour and carve occlusal and interproximal anatomy in amalgam restorations
To contour and carve occlusal and interproximal anatomy in other restorative and temporary filling materials
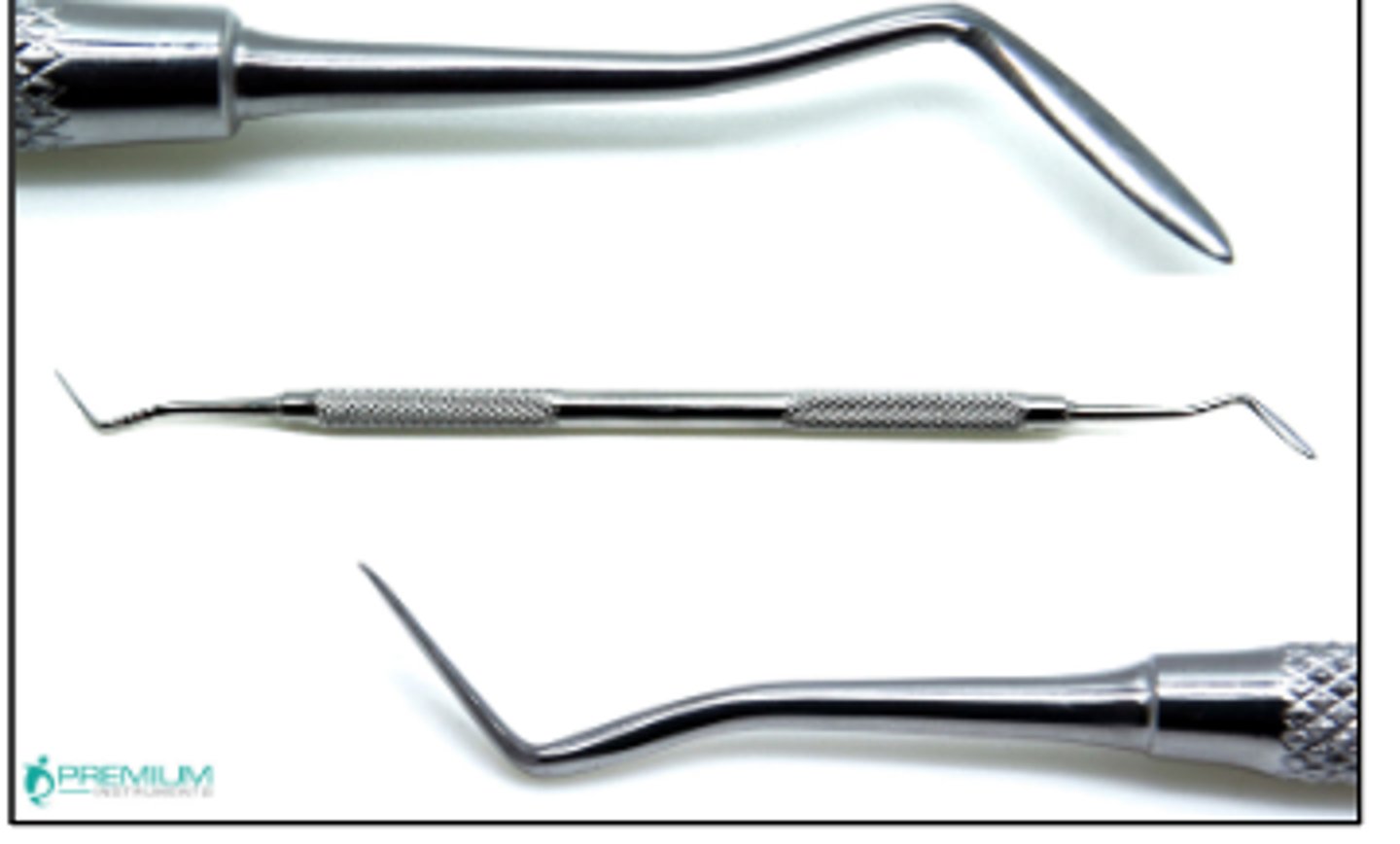
Discoid-Cleoid Carver (2)
To carve occlusal anatomy into amalgam restorations
To carve occlusal anatomy in other restorative and temporary filling materials
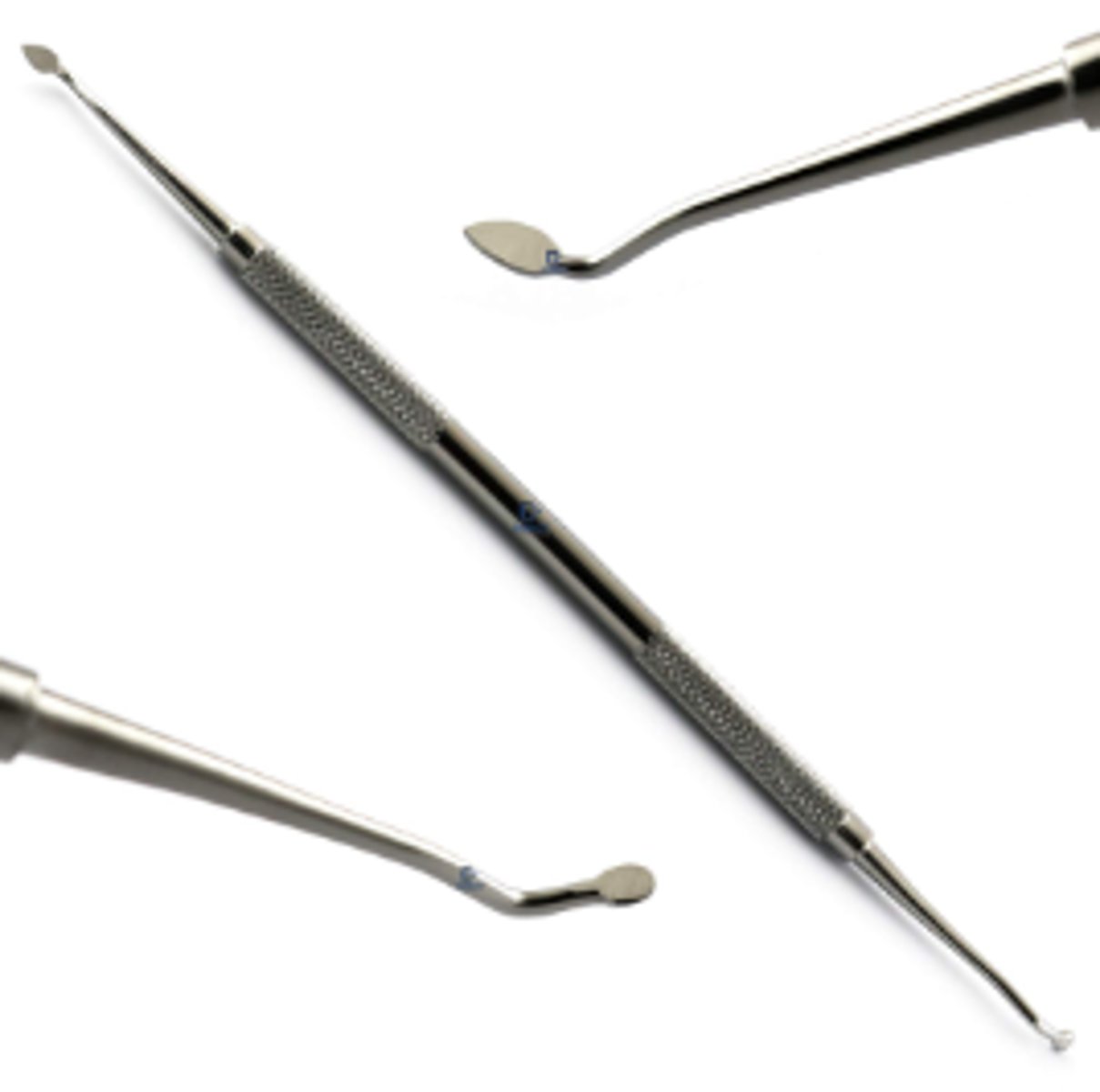

Articulating Paper Holder with Paper (4)
To check centric and lateral occlusion.
Includes: Forceps to hold articulating paper in place. + dark blue and red alternate side of articulating paper
The patient bites down on the paper, grinds side to side to show where the dental restoration is too high
High spots can lead to bruising of the tooth, so it is important to check after a new restoration has been done

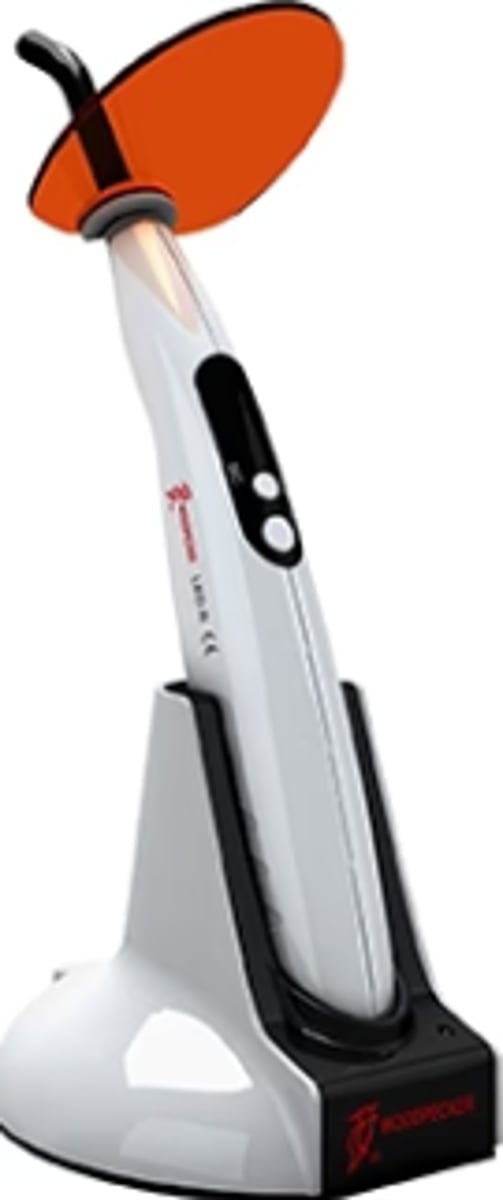
Curing Light (2)
To harden light-cured materials
Examples: Bonding agents, composite, sealants, buildup material

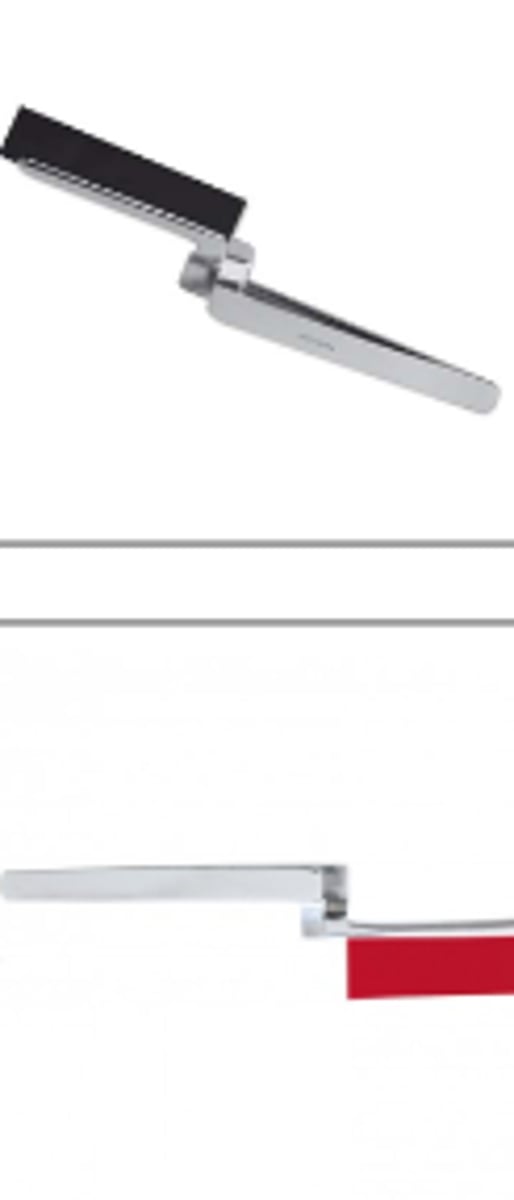
Universal Matrix Band (1)
To replace missing proximal wall or walls of cavity preparation for condensation of restorative material for class II preparations
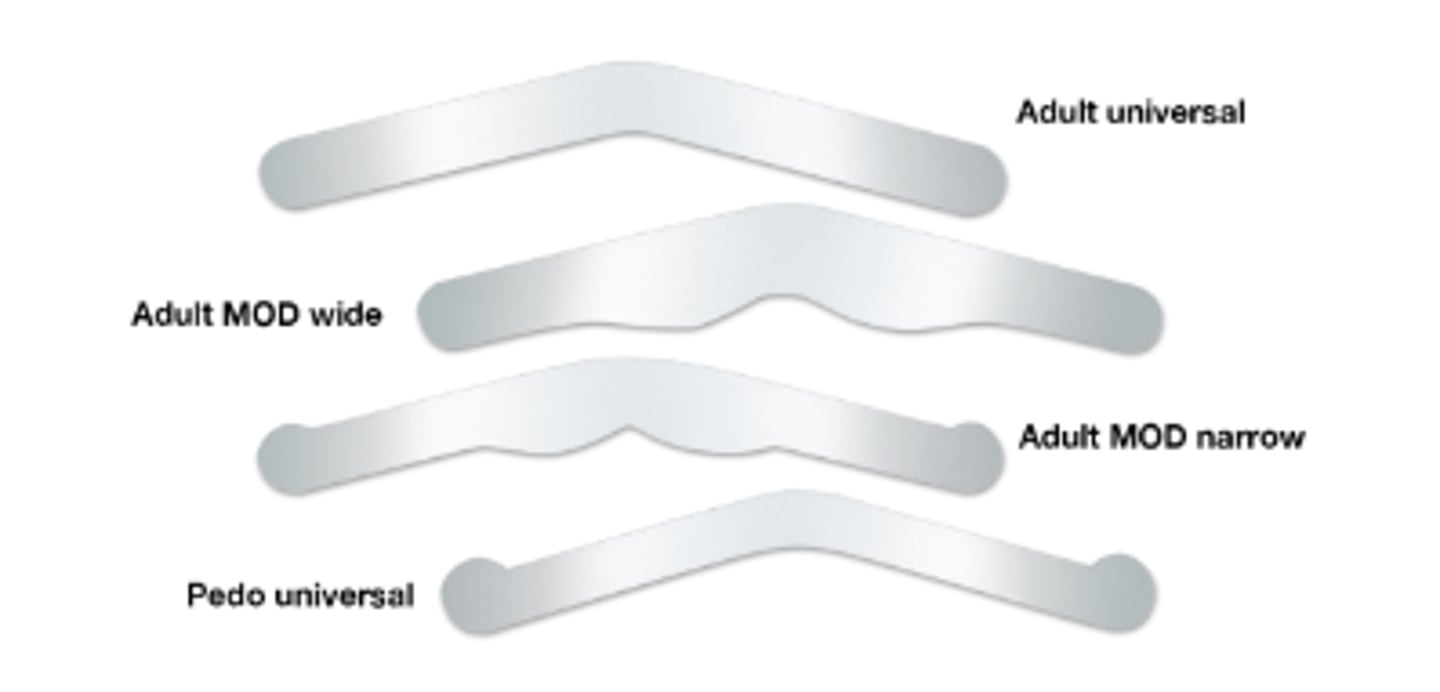
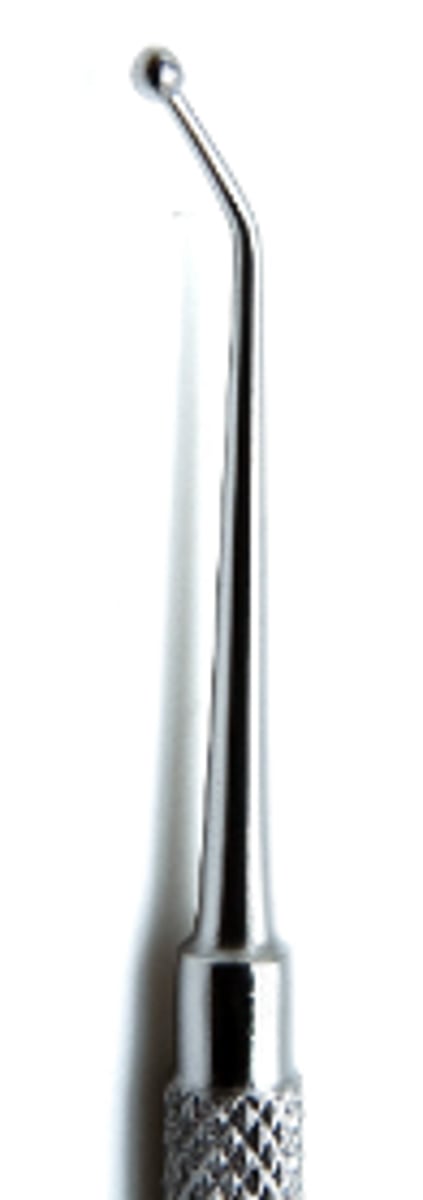
Ball Burnisher (5)
To smooth amalgam after condensing.
To contour matrix band before placement.
To perform initial shaping of amalgam.
To burnish restorative material.
To burnish temporary filling material.

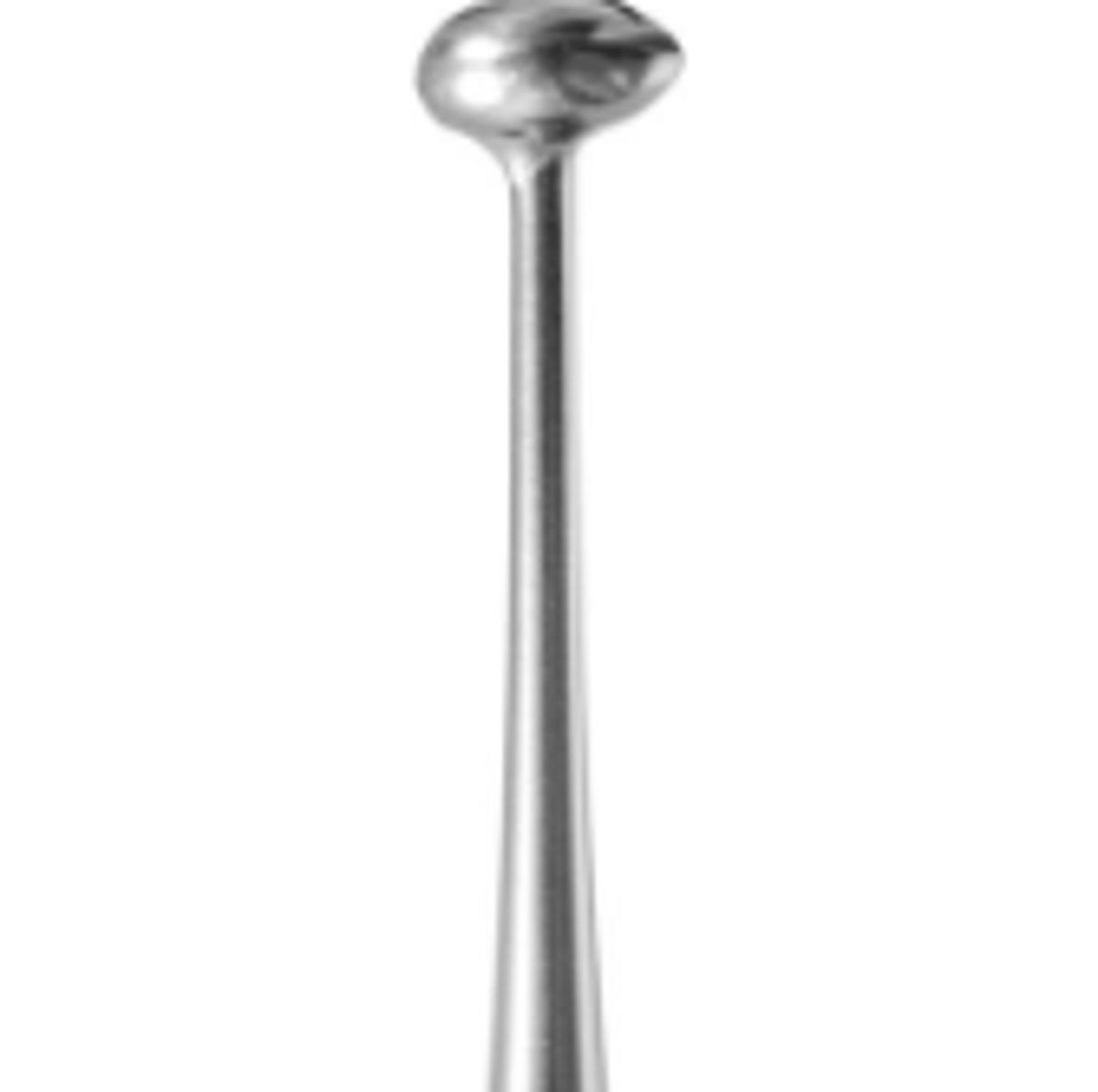
Football Burnisher (5)
To smooth amalgam after condensing.
To contour matrix band before placement.
To perform initial shaping of amalgam.
To burnish restorative material.
To burnish temporary filling material.

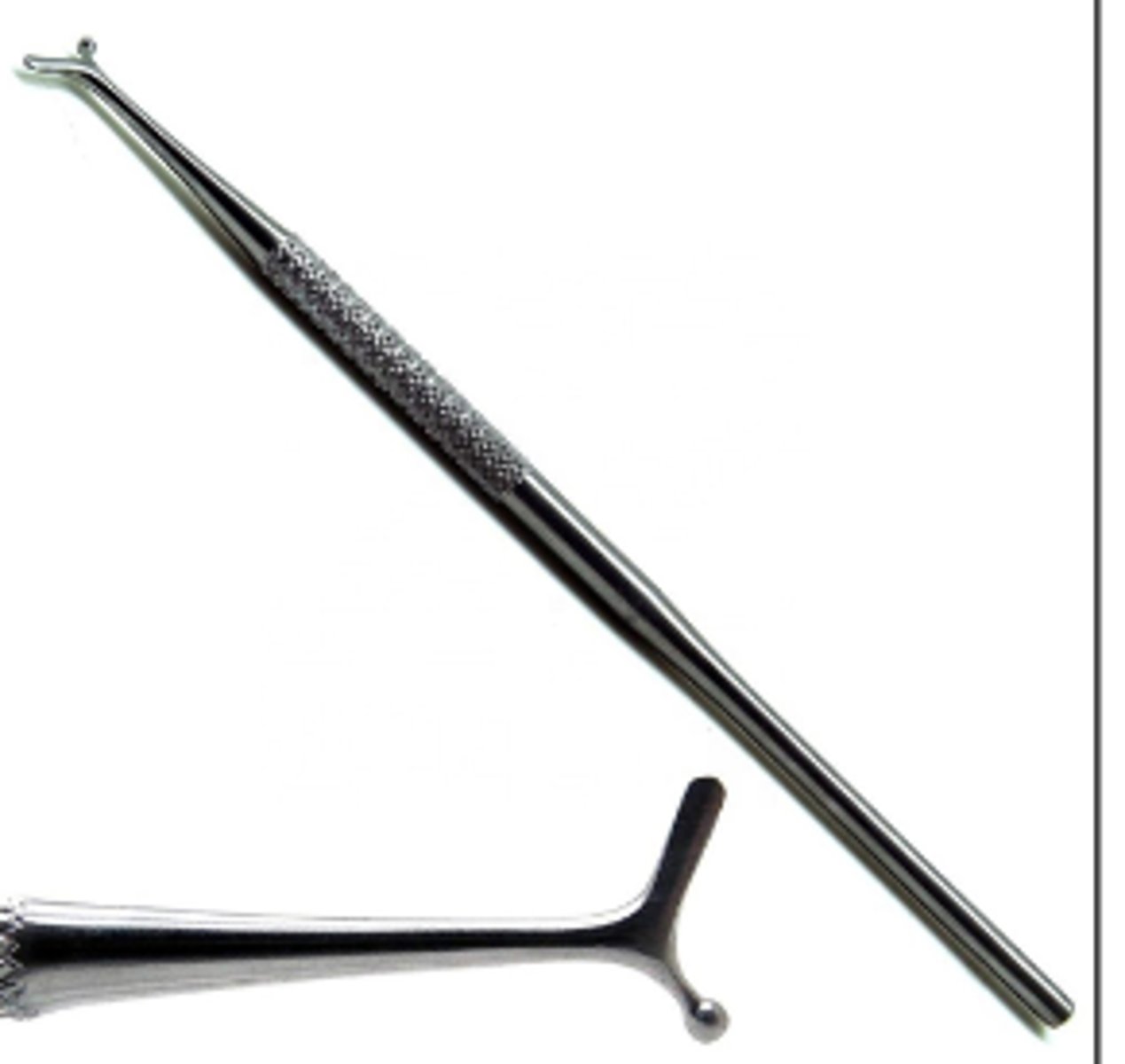
T-Ball Burnisher (5)
To smooth amalgam after condensing.
To contour matrix band before placement.
To perform initial shaping of amalgam.
To burnish restorative material.
To burnish temporary filling material.

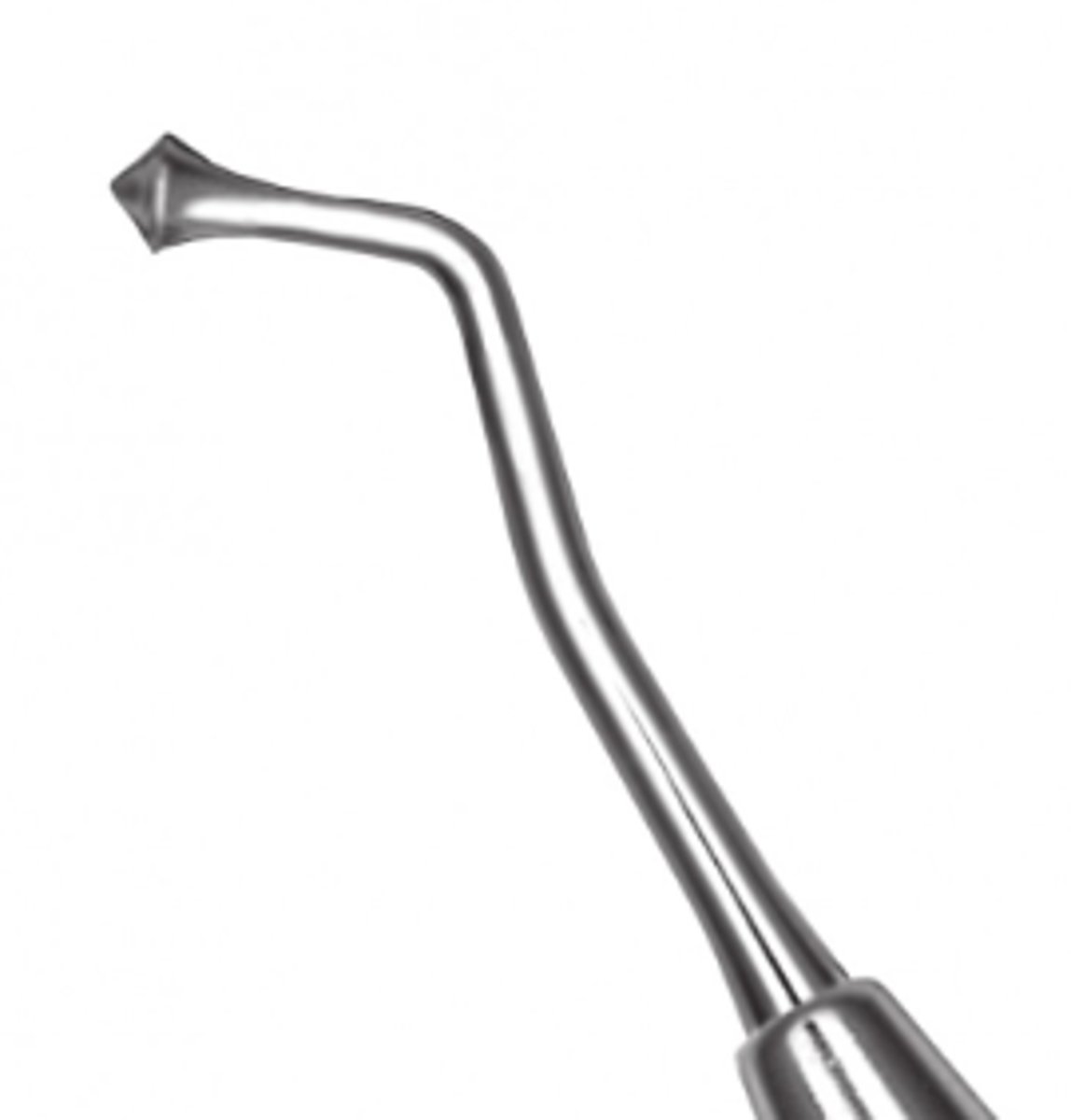
Acorn Burnisher (5)
To smooth amalgam after condensing.
To contour matrix band before placement.
To perform initial shaping of amalgam.
To burnish restorative material.
To burnish temporary filling material.

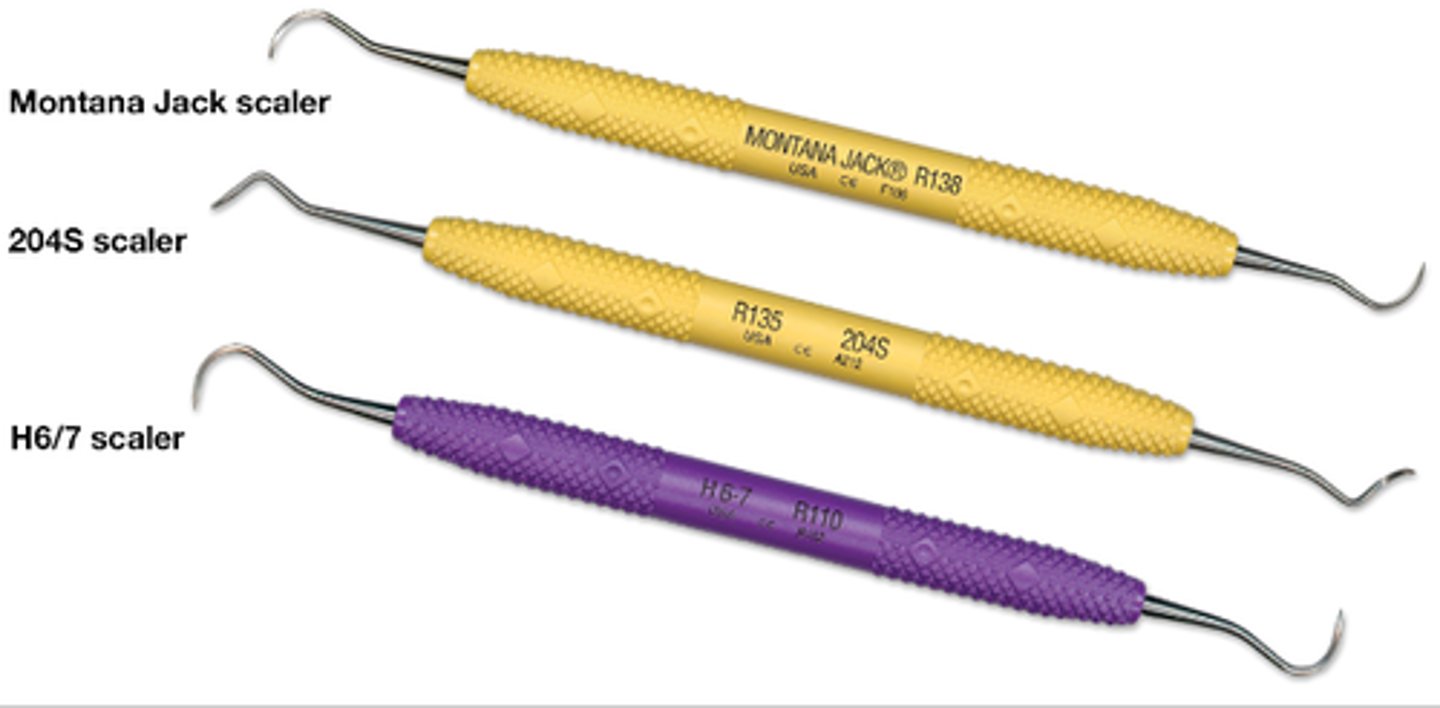
Sickle Scalers (1)
To remove large amounts of deposits from supragingival surfaces.
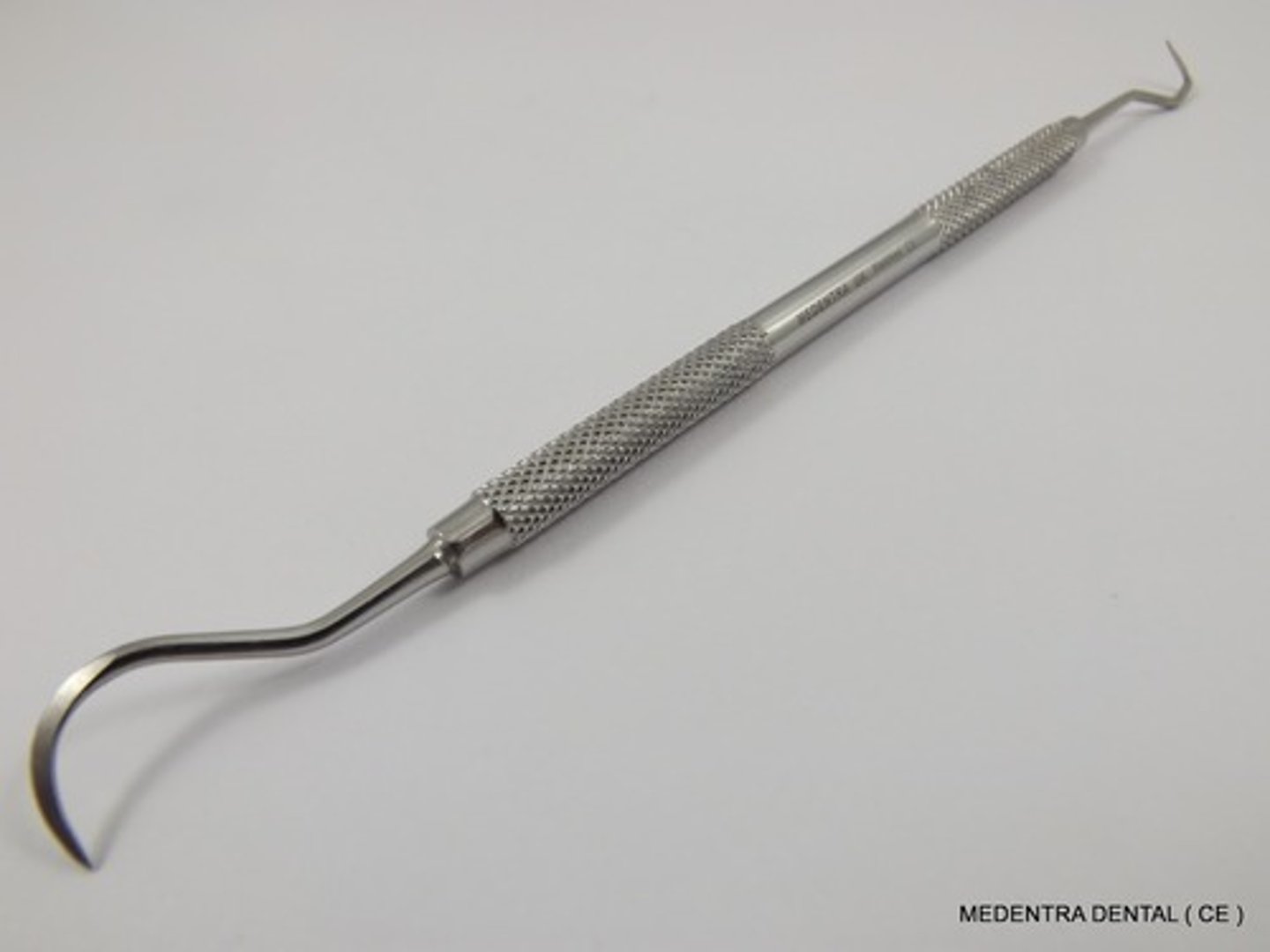
Montana Jack - Sharper, thinner blades with solid resin handle for comfortable grip.
204S - Traditional curved sickle scaler for Posterior teeth.
H6/7 - Traditional curved sickle scaler for Anterior teeth.
What are the three major types of sickle scalers (3)?

Bite-Wing Tabs (1)
To take a bite-wing radiograph projection
Liner Applicator (1)
To place dental liner material (such as calcium hydroxide or glass ionomer) in cavity preparation
Pear Shaped Burs (2)
To open tooth for a restoration
To remove carries
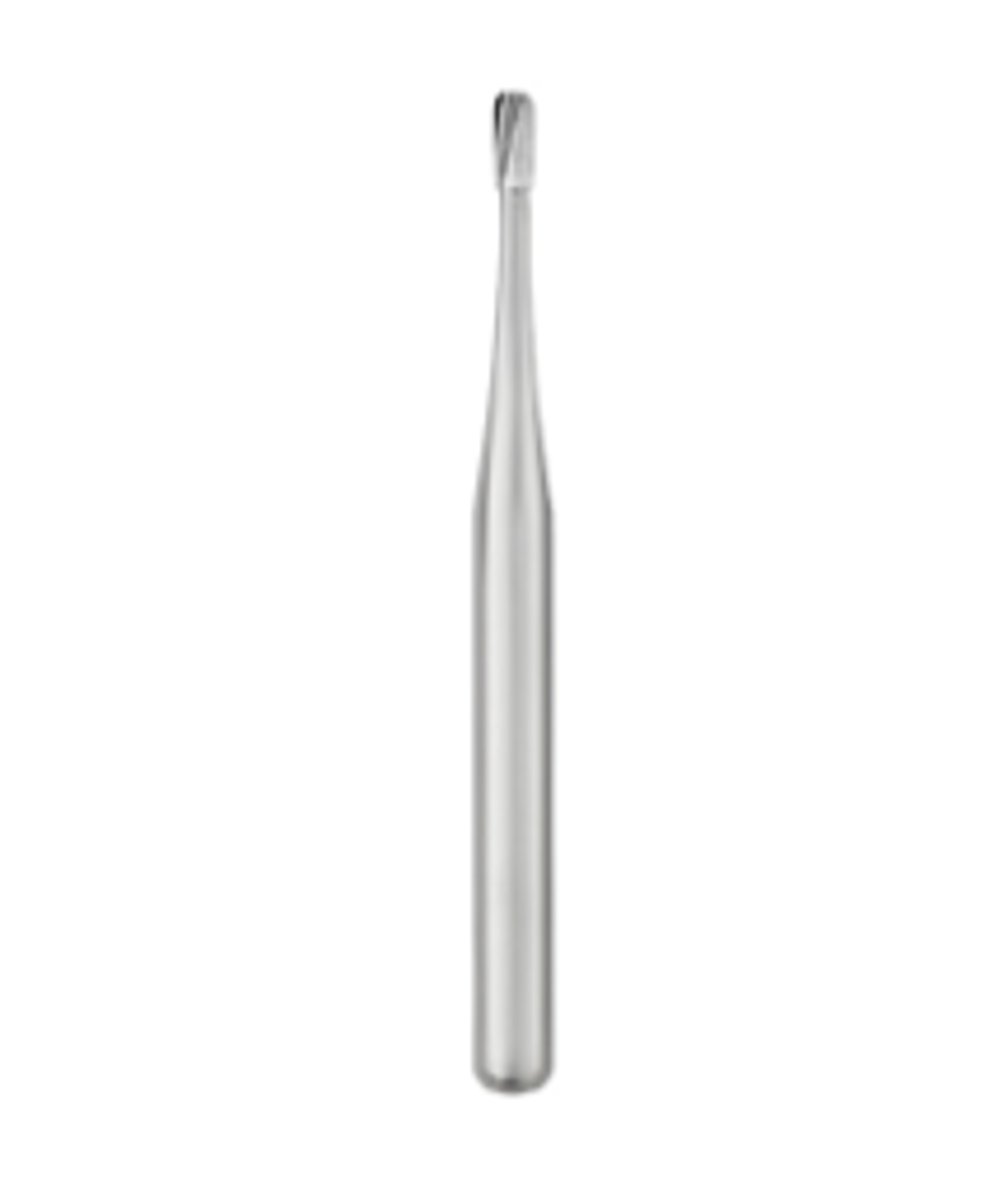

Inverted Cone Burs (2)
To remove caries
To establish retention in tooth for cavity preparation
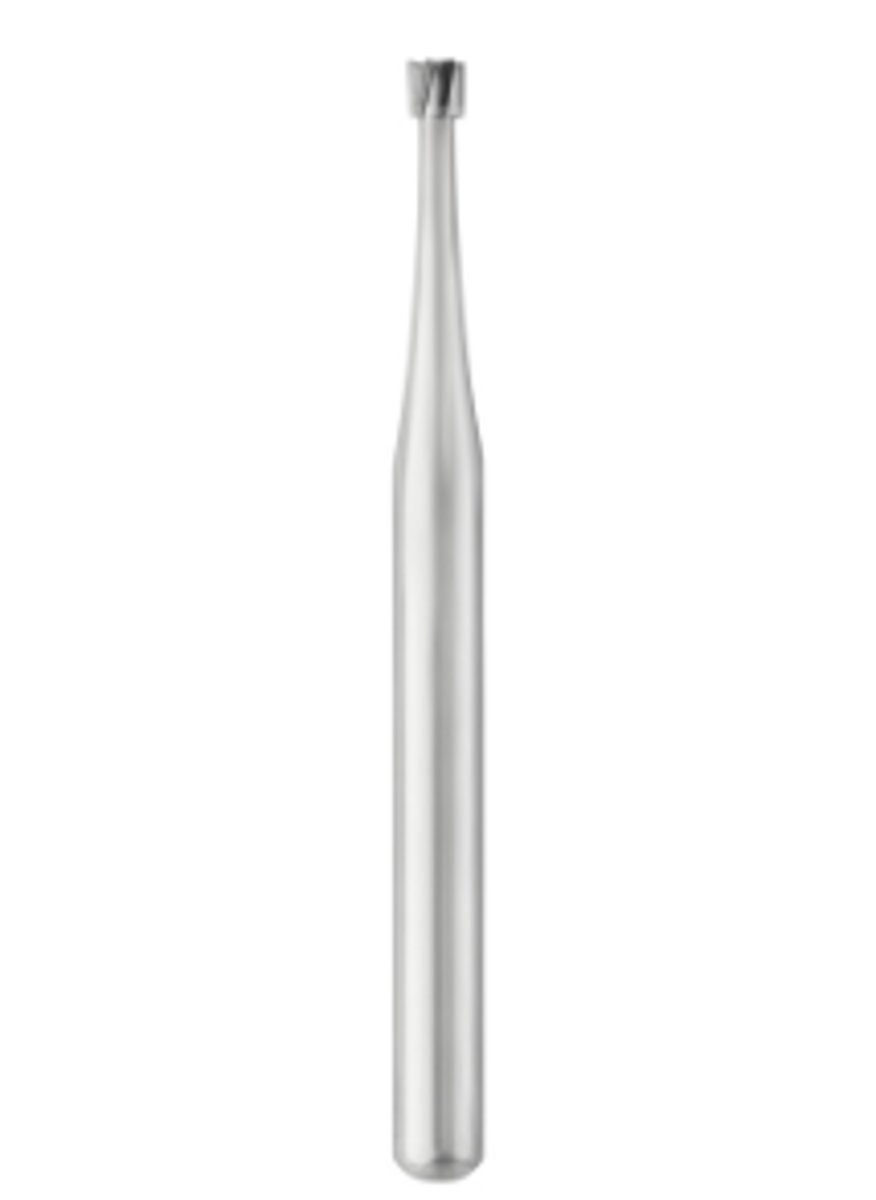

Finishing Burs (3)
To finish composite restorations
To finish restorations by restoring anatomy in tooth
To equilibrate or adjust occlusion
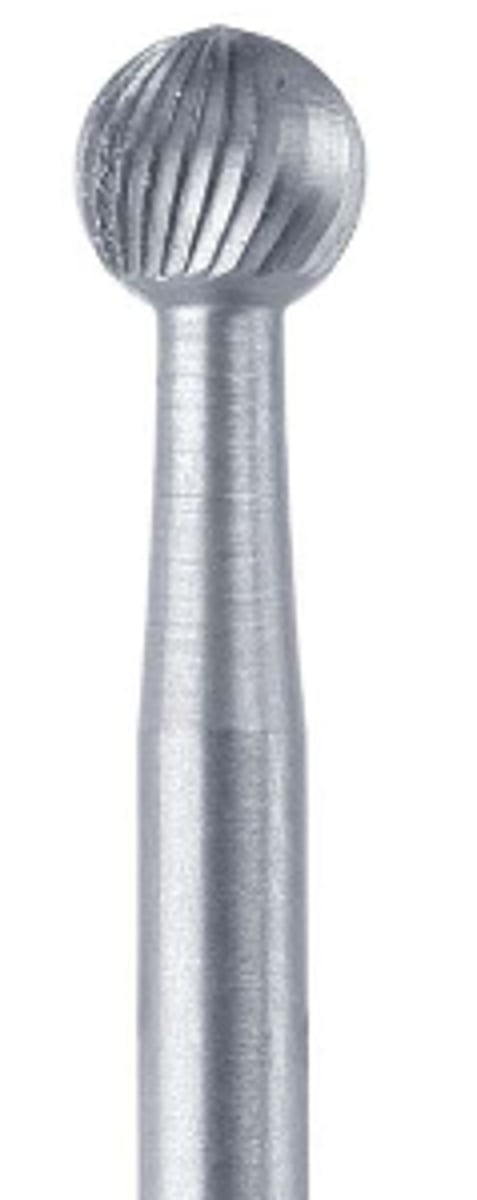

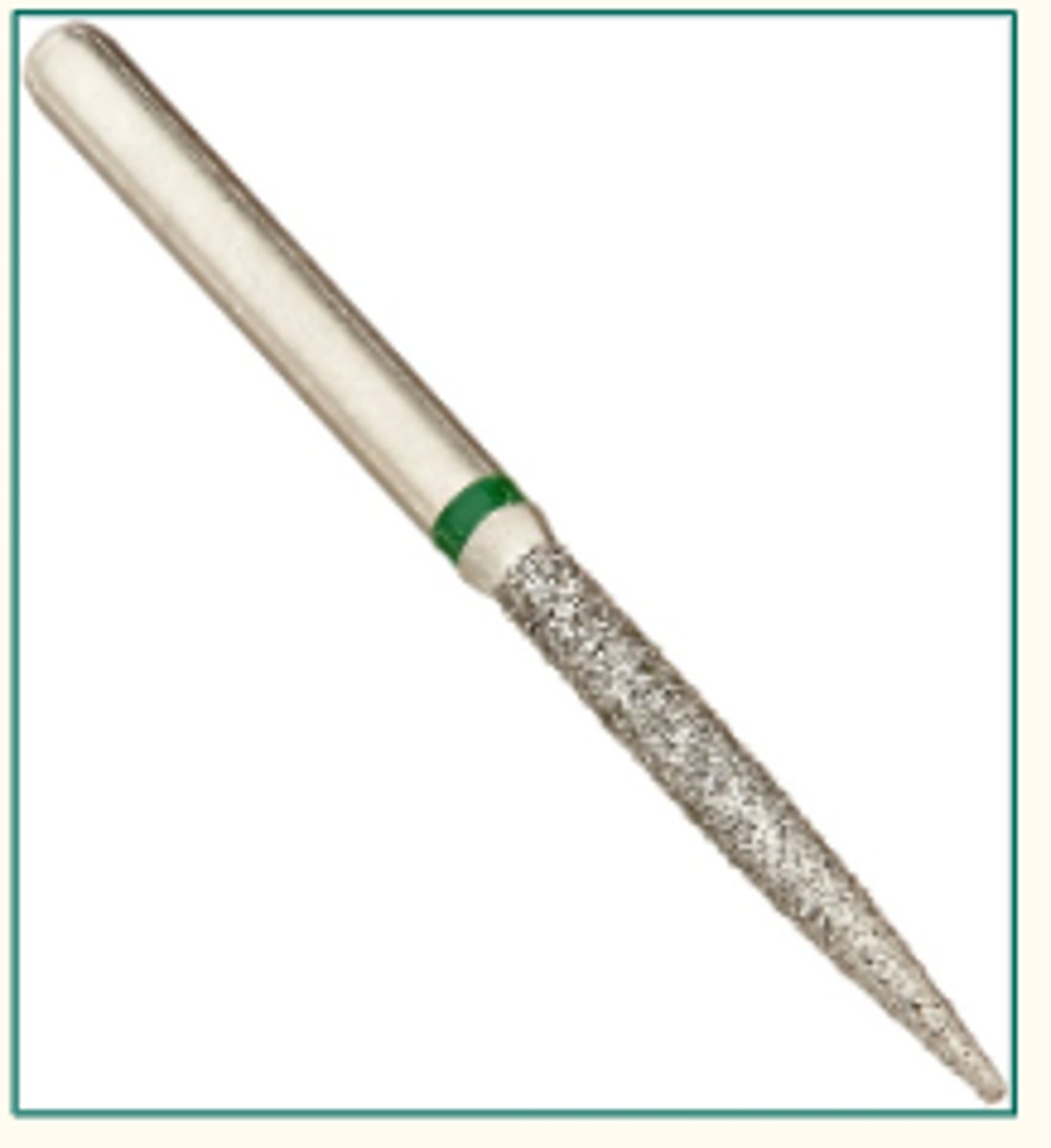
Diamond Bur With Flat End Taper (1)
To reduce a tooth for crown preparation when a square shoulder is needed.
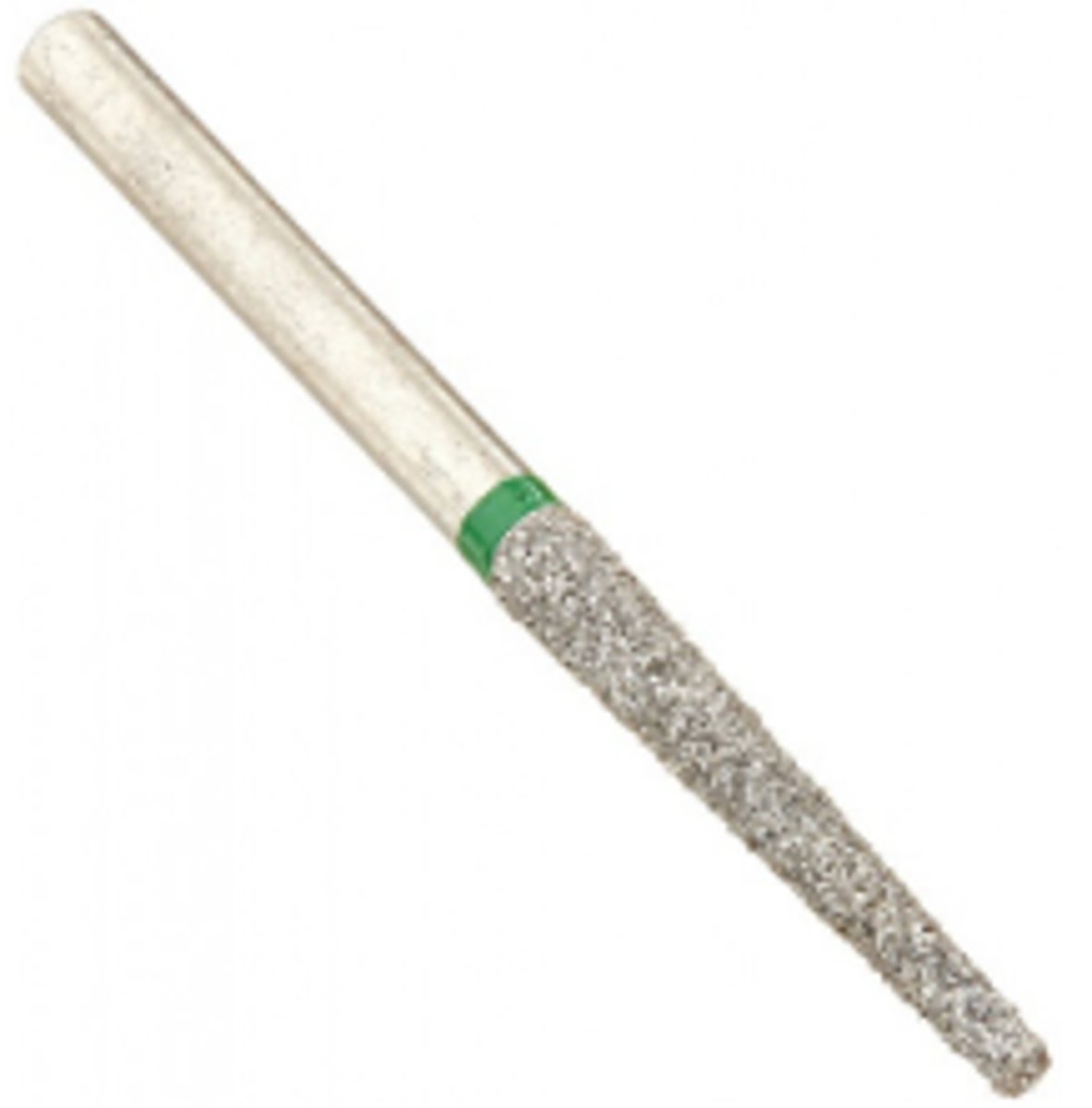

Diamond Bur - Flat-End Cylinder (1)
To reduce a tooth for crown preparation when parallel walls and flat floors are needed.
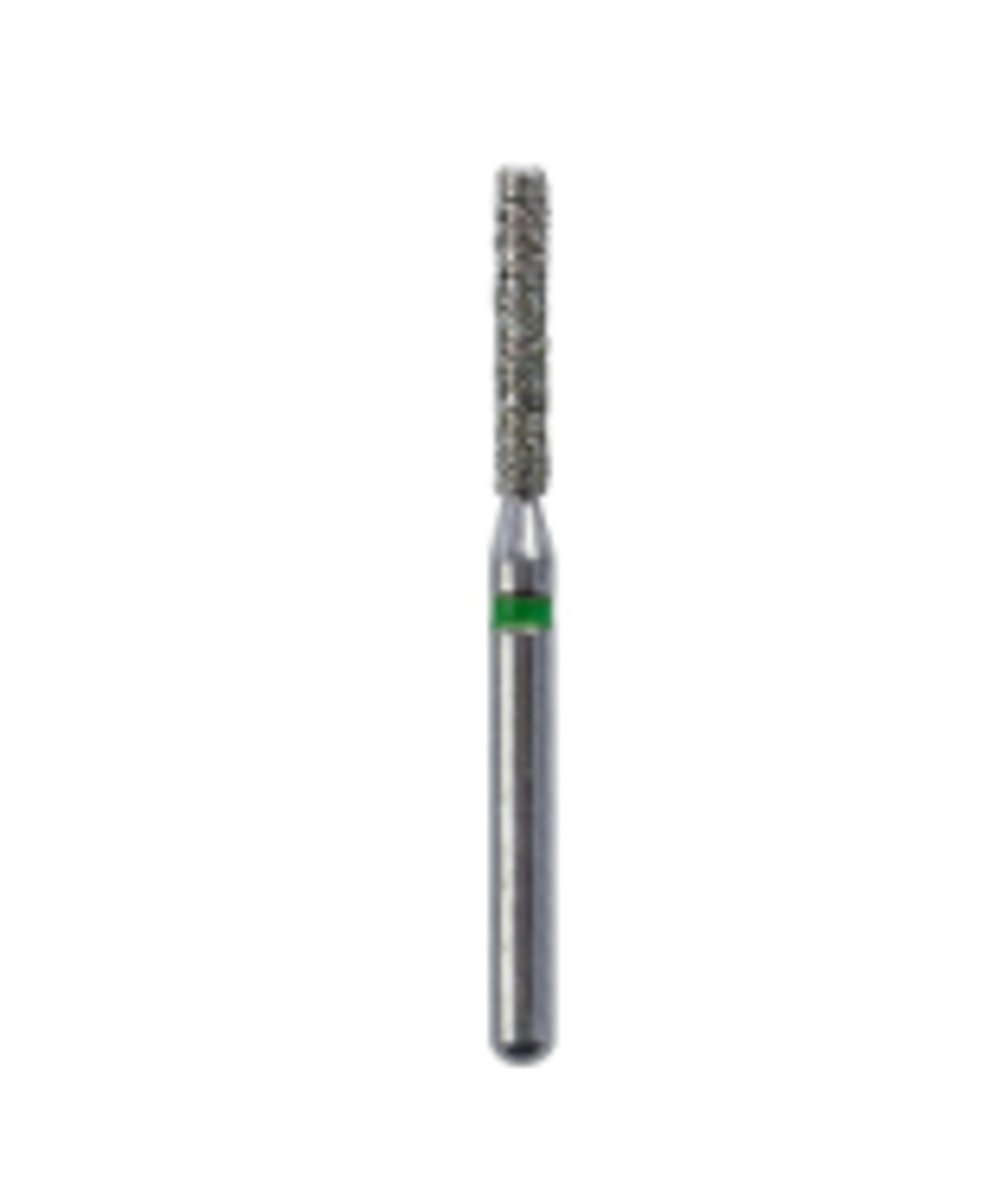

Diamond Bur - Flame (1)
To reduce a tooth for crown preparation for subgingival margins.

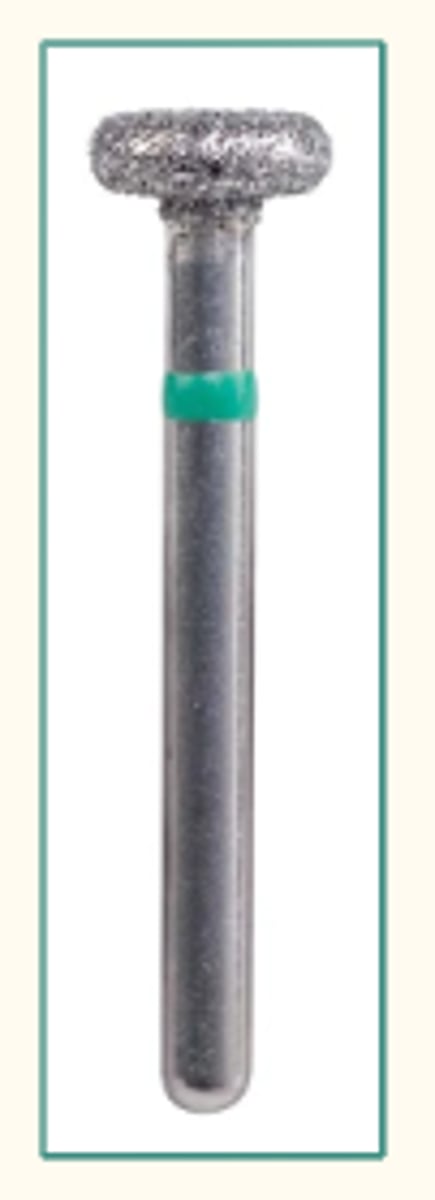
Diamond Bur - Wheel (1)
To reduce a tooth for crown preparation on lingual aspect of anterior teeth and to reduce bulk of incisal edges.

Round Bur (4)
To remove caries from tooth structure
To open tooth for endodontic treatment
To create retention in cavity preparation
To use for many procedures on a tooth

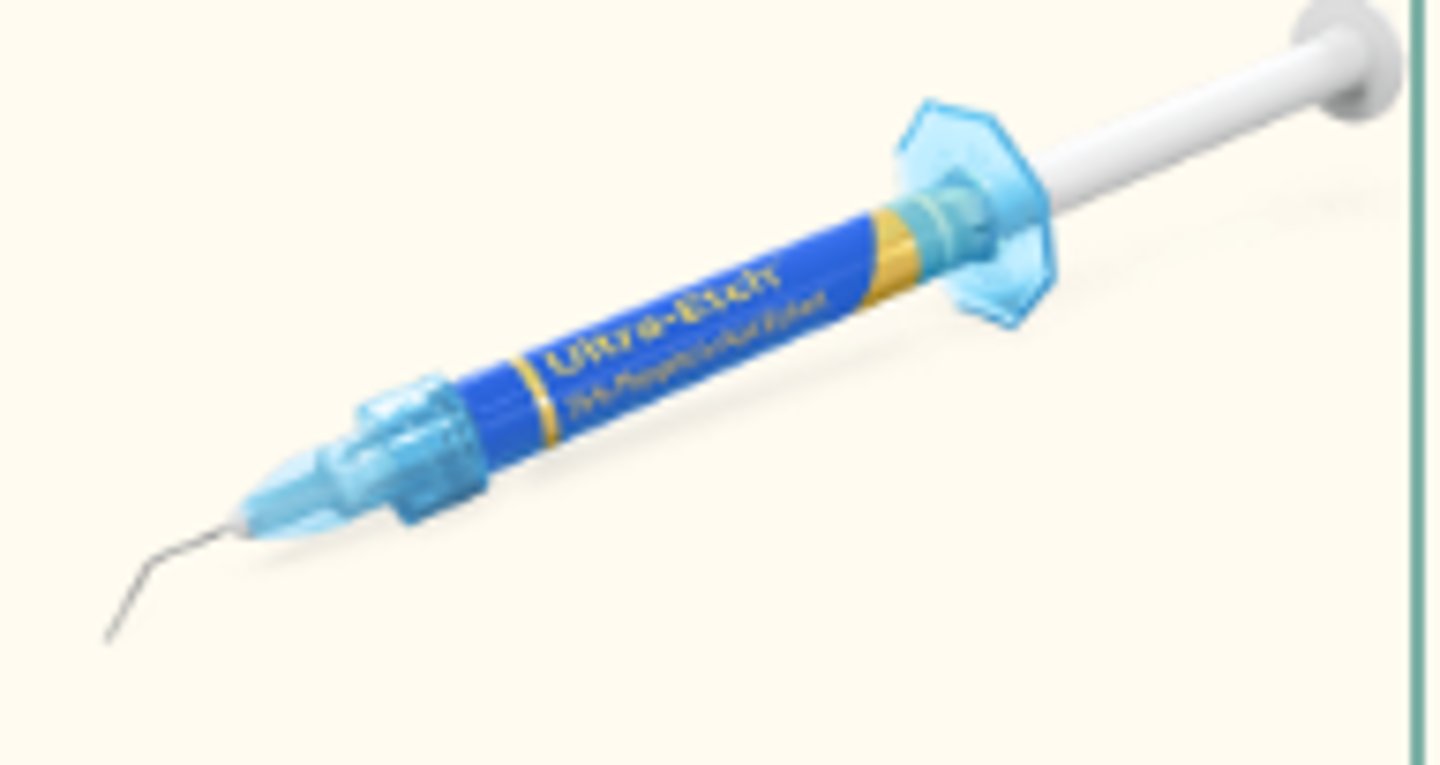
Acid Etchant / Phosphoric Acid (2)
Roughens up the enamel in preparation for the application of adhesive.
Solution/Gel concentrations can be: 15%. 34%, and 37% (most common)

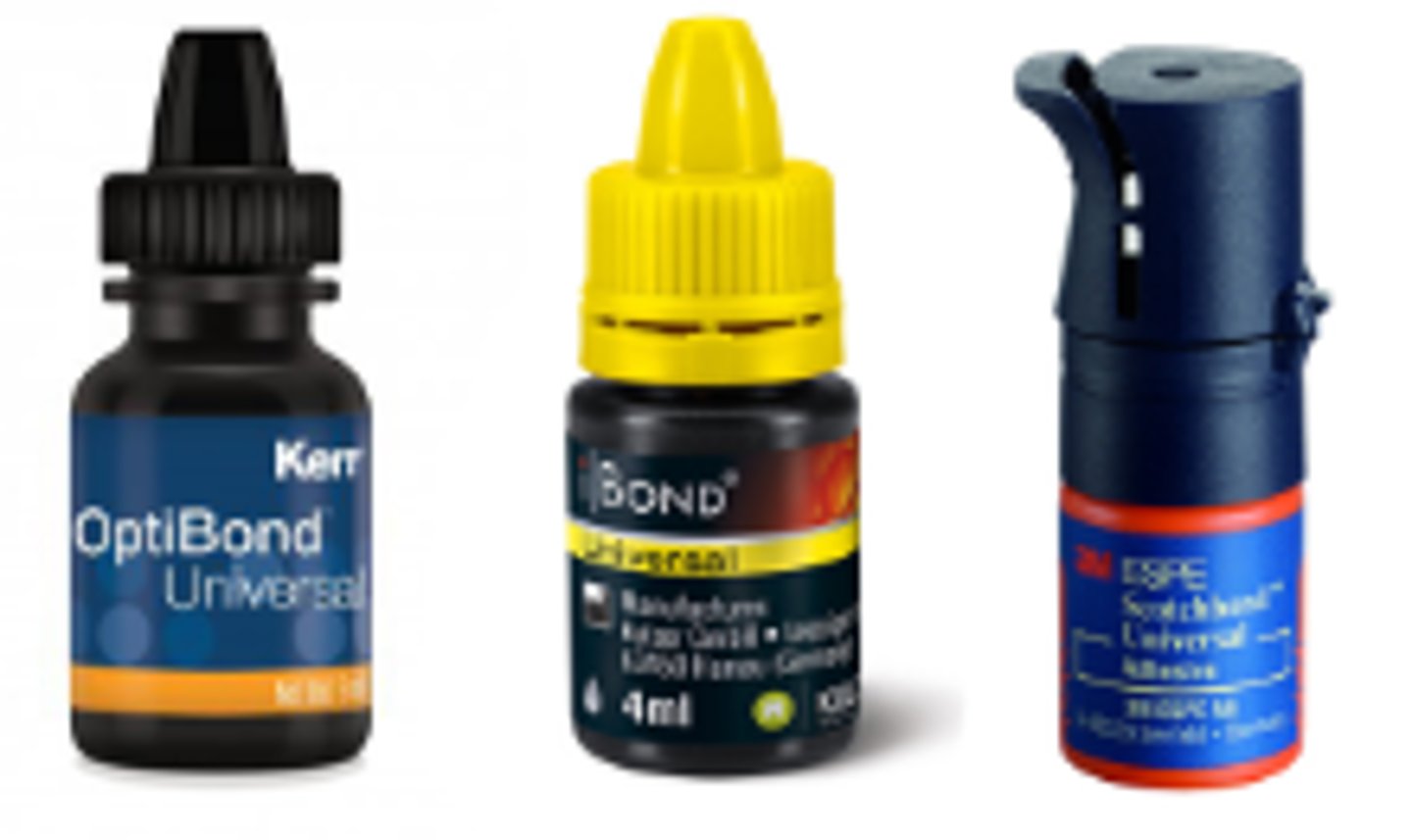
Bonding Agent Adhesive (2)
Resin material that help composite fillings adhere to enamel and dentin
Applied with a microbrush from a mixing well

Composite Resin (2)
Tooth-colored filling made of plastic resin and powdered glass used for filling restoration
Available in syringe or compule / composite gun

Woodson - Plastic Filling Instrument (2)
Used to place and contour pliable materials during restorative procedures
Has Paddle / Plugger end
Finishing and Polishing Burs - Composite Restorations (2)
To correct contours and smooth out any irregularities

Tongue & Cheek Retractor (1)
To hold and retract tongue or cheek during surgery
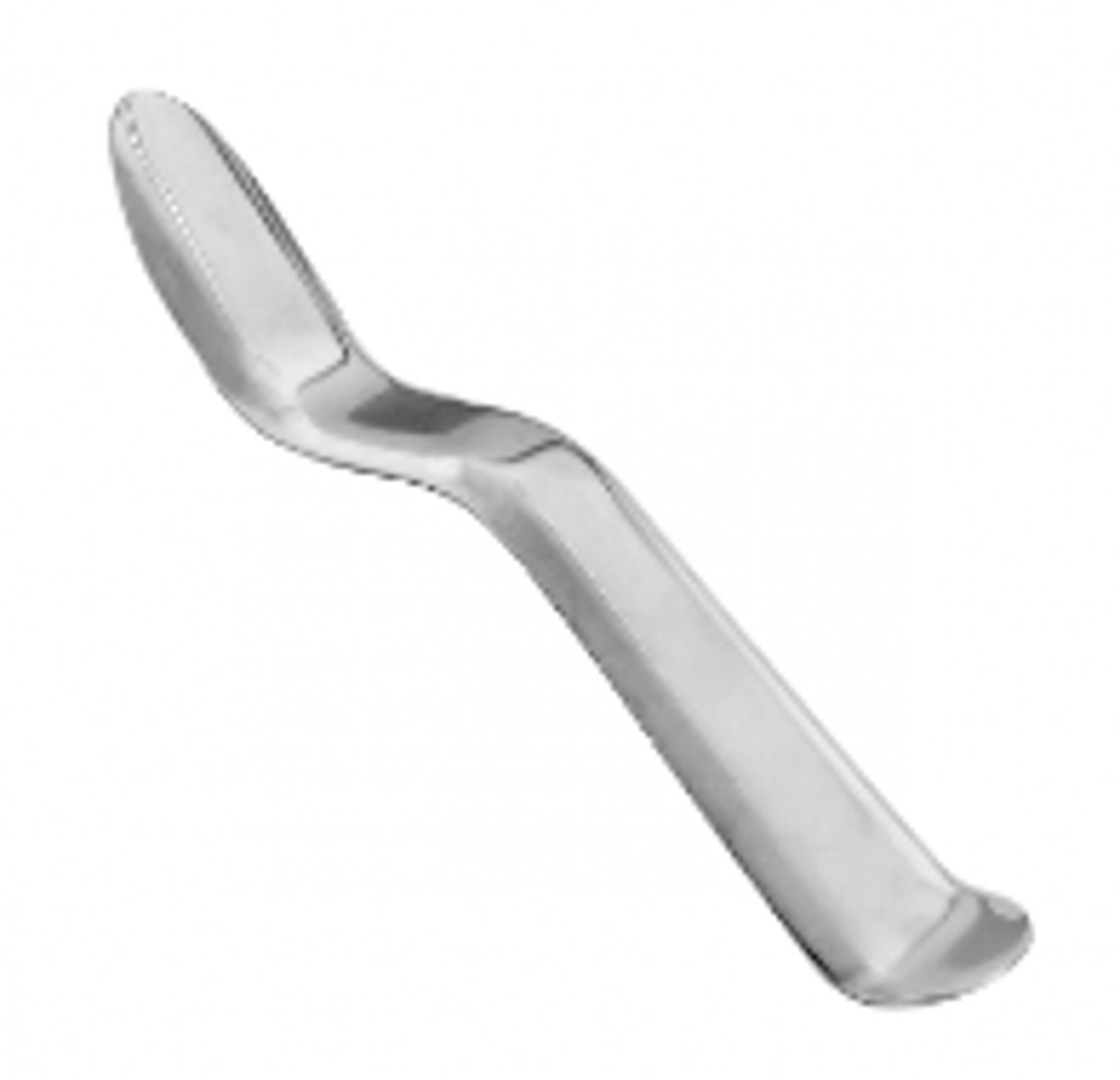

Periosteal Elevator (1)
To separate and retract the periosteum from the bone that is holding the tooth to its socket
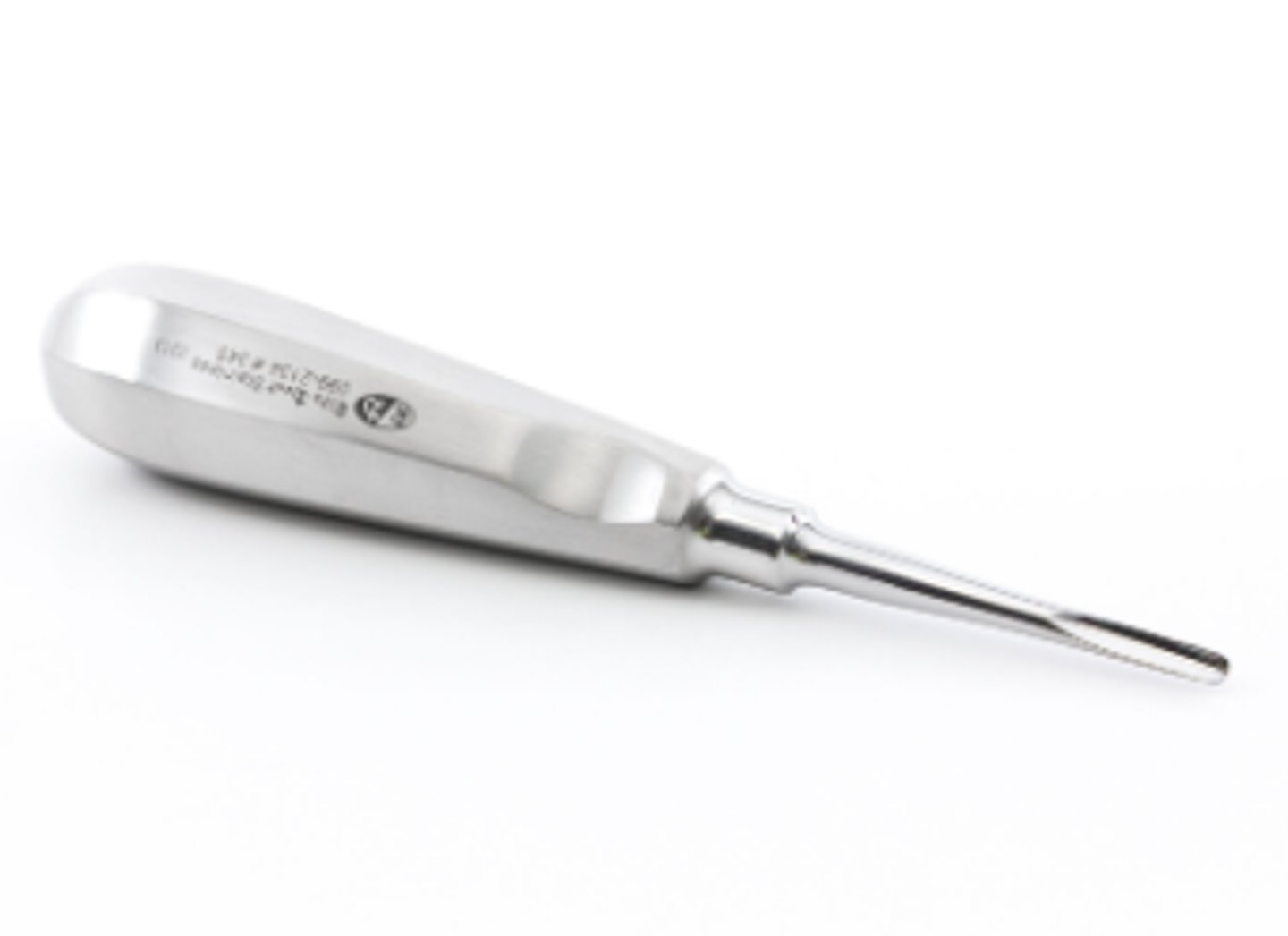
Straight Elevator (2)
To loosen tooth from periodontal ligaments before extraction
To separate and lift tooth from socket
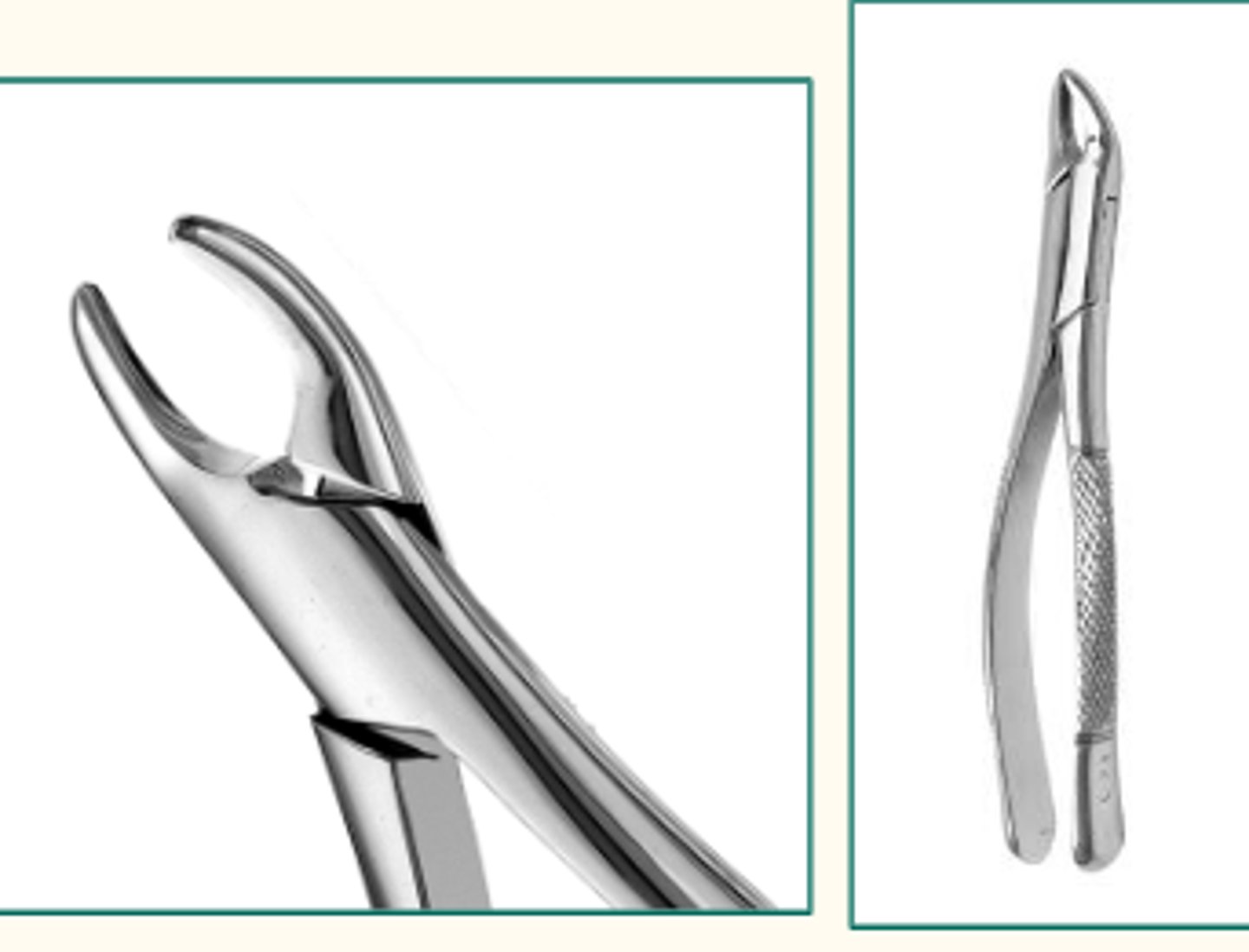
Maxillary Universal Forceps - Cryer 150 (1)
To extract maxillary centrals, laterals, cuspids, premolars, and roots
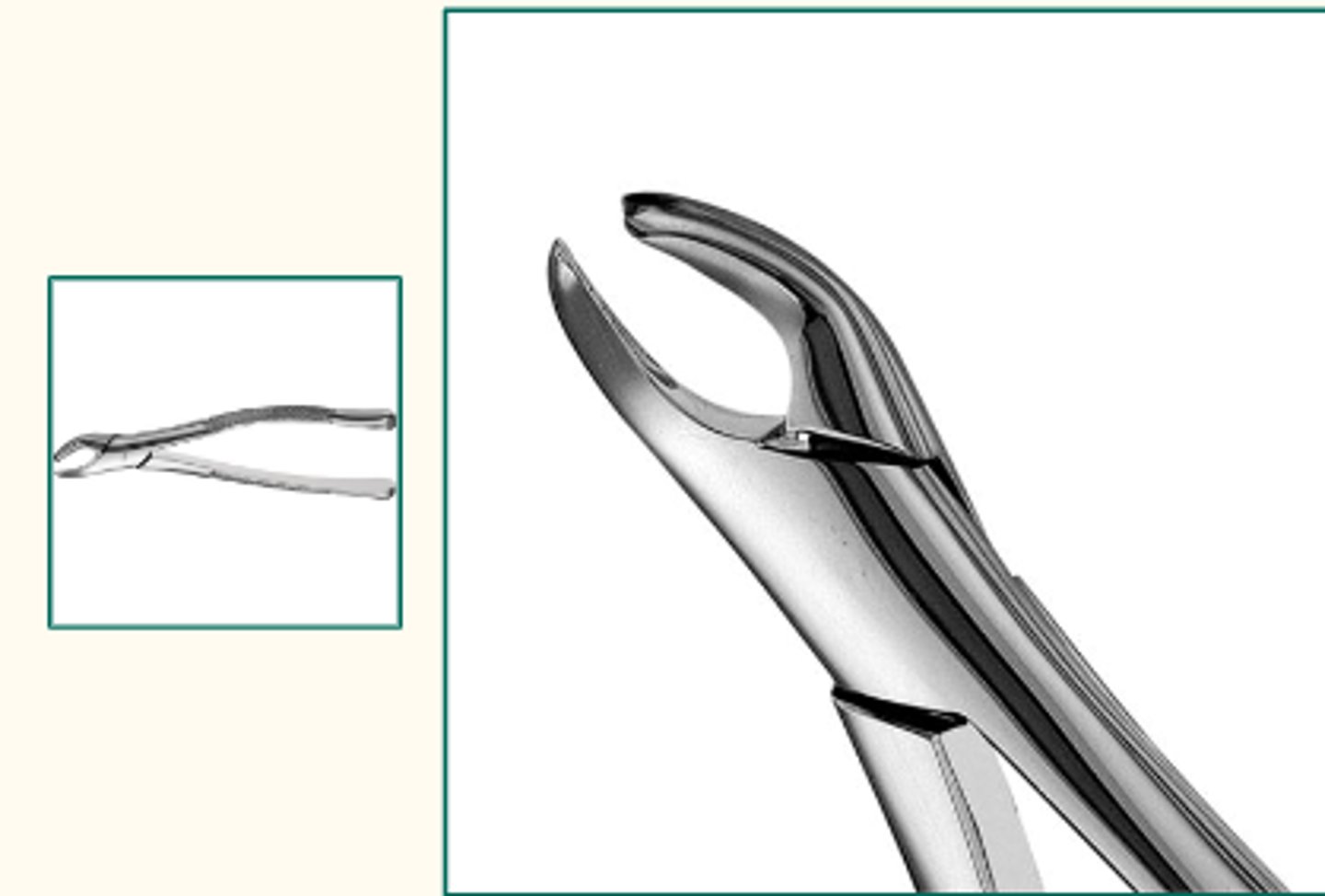
Mandibular Universal Forceps - Cryer 151 (1)
To extract mandibular centrals, laterals, cuspids, premolars, and roots
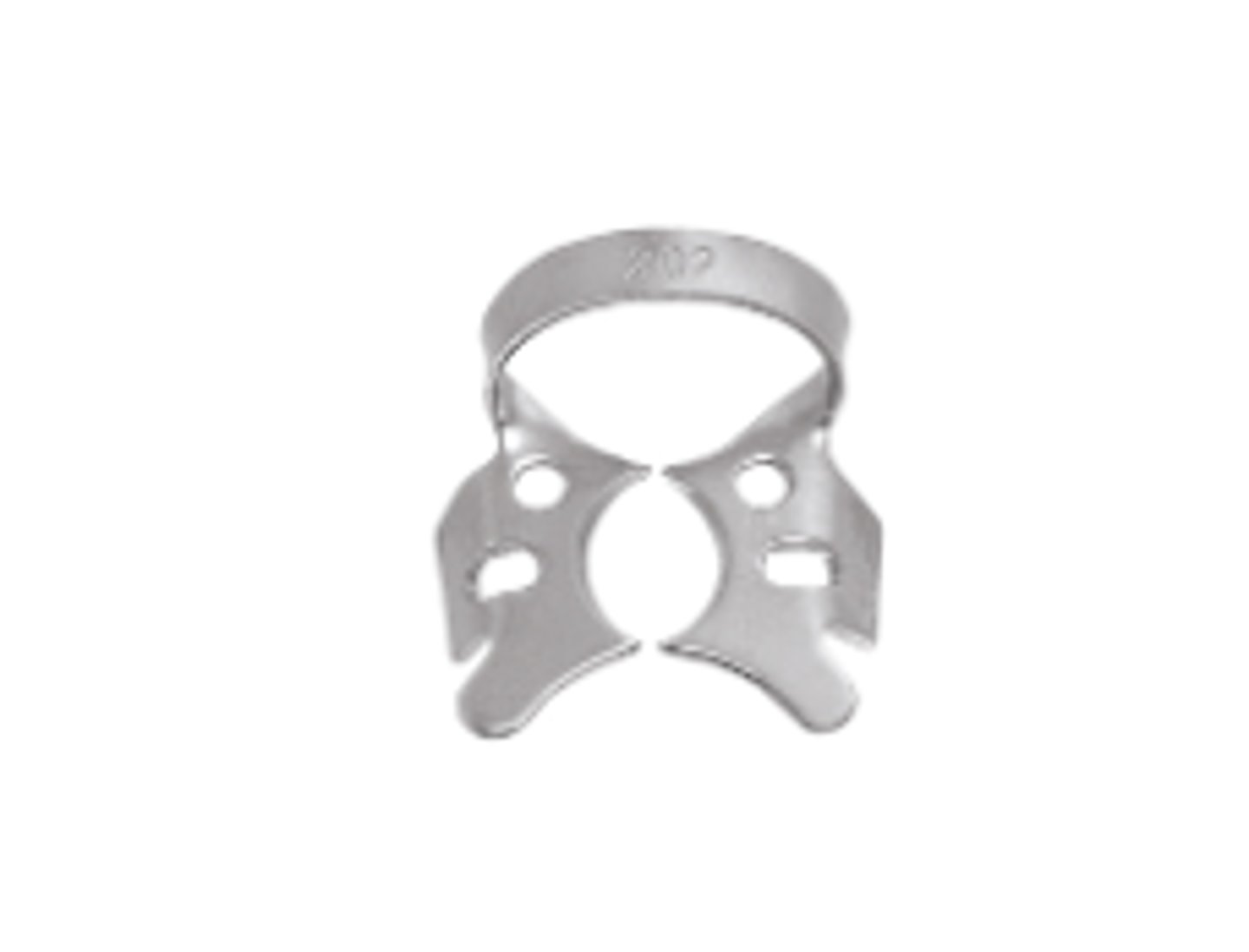
Mandibular Winged Clamp (1)
To anchor and stabilize dental dam

Root Tip Elevators (1)
To lift and remove fragments of root
Straight Nose Corn - Slow Speed Handpiece (2)
Polishing and finishing
Adjusting and contouring
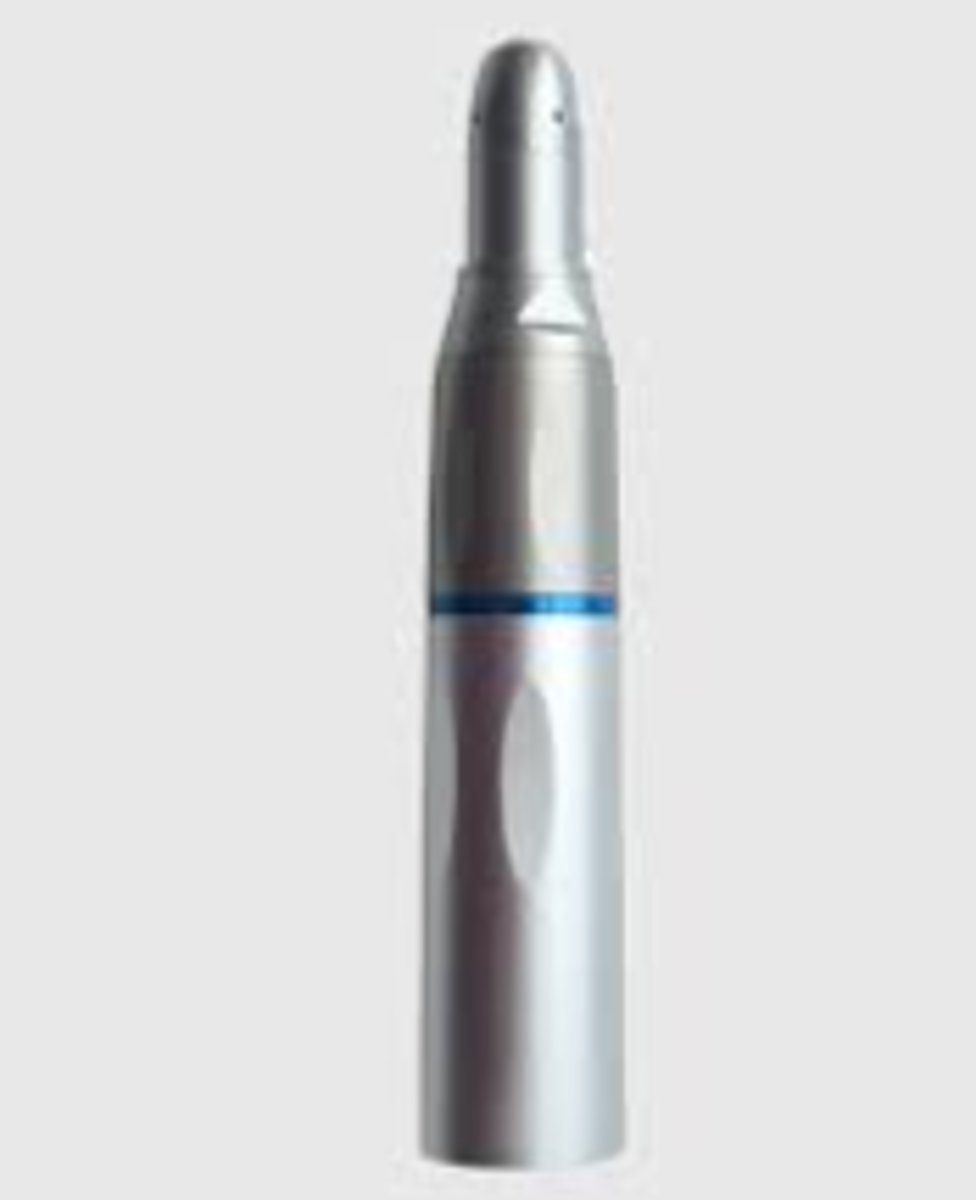

Mandibular (Wingless Clamp)
To anchor and stabilize dental dam
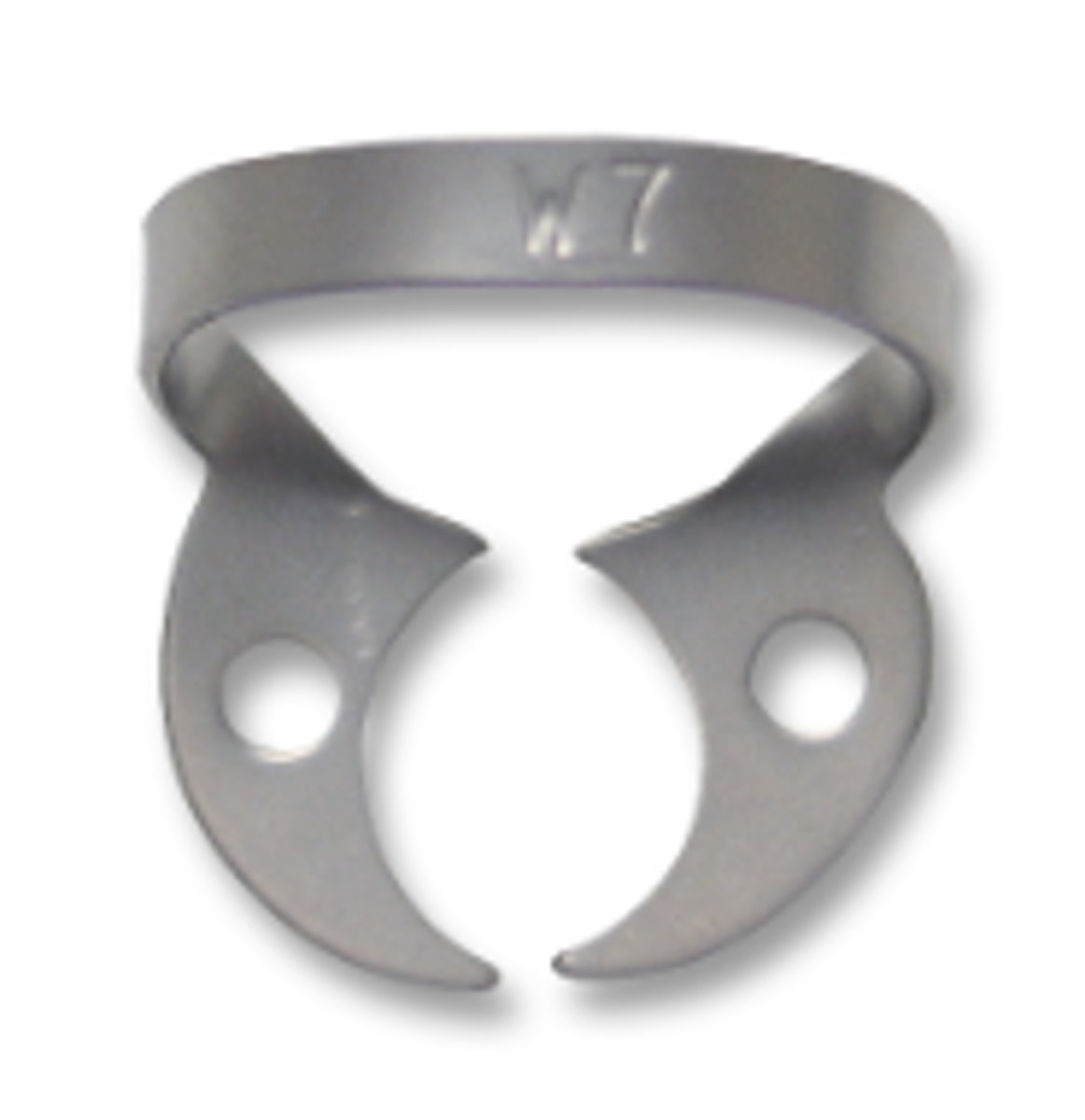

Maxillary (Wingless Clamp) (1)
To anchor and stabilize the dental dam.

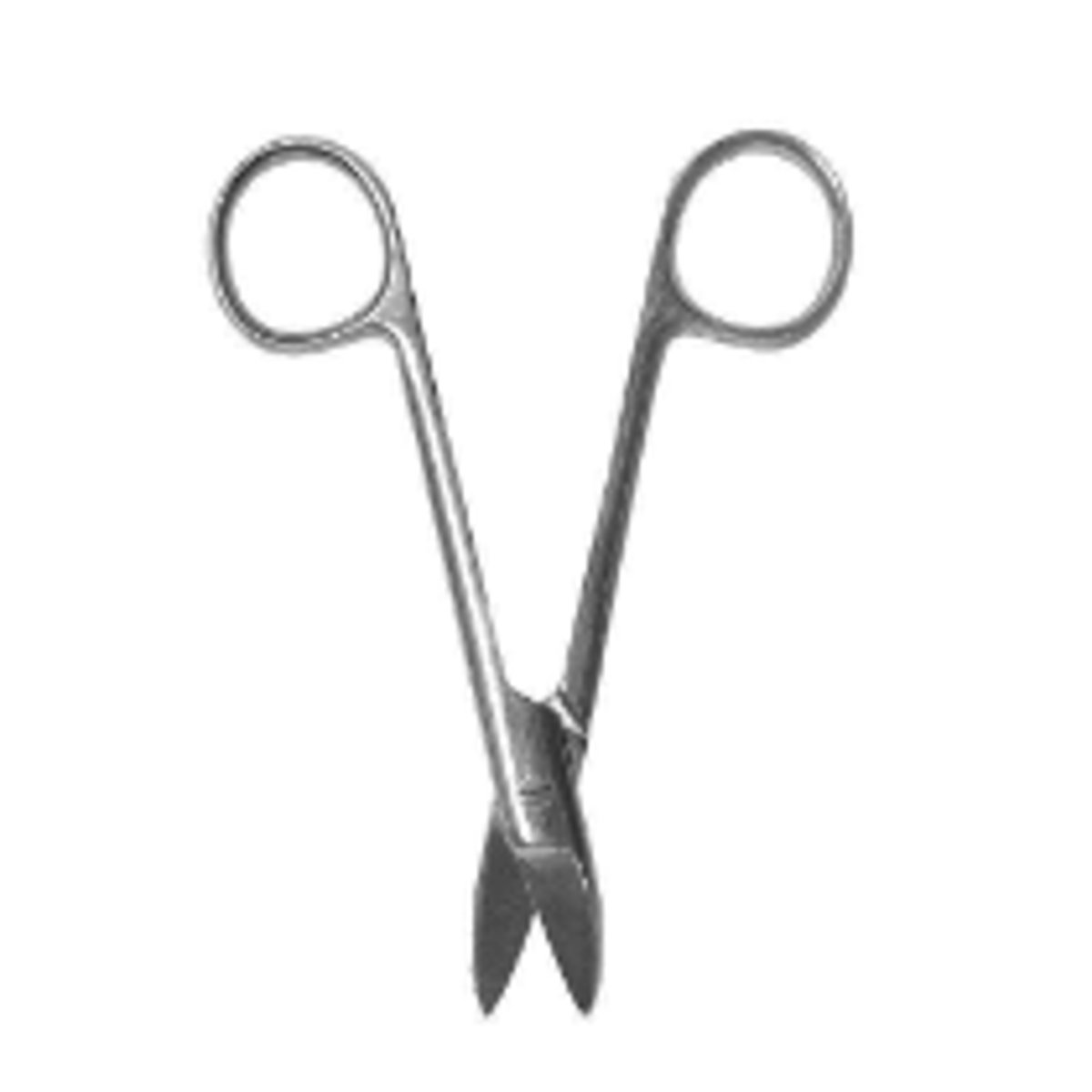
Crown and Bridge Scissors (5)
To trim aluminum temporary crowns on gingival side
To trim custom temporary crowns
To cut gingival retraction cord
To trim matrix bands
To cut dental dam septum

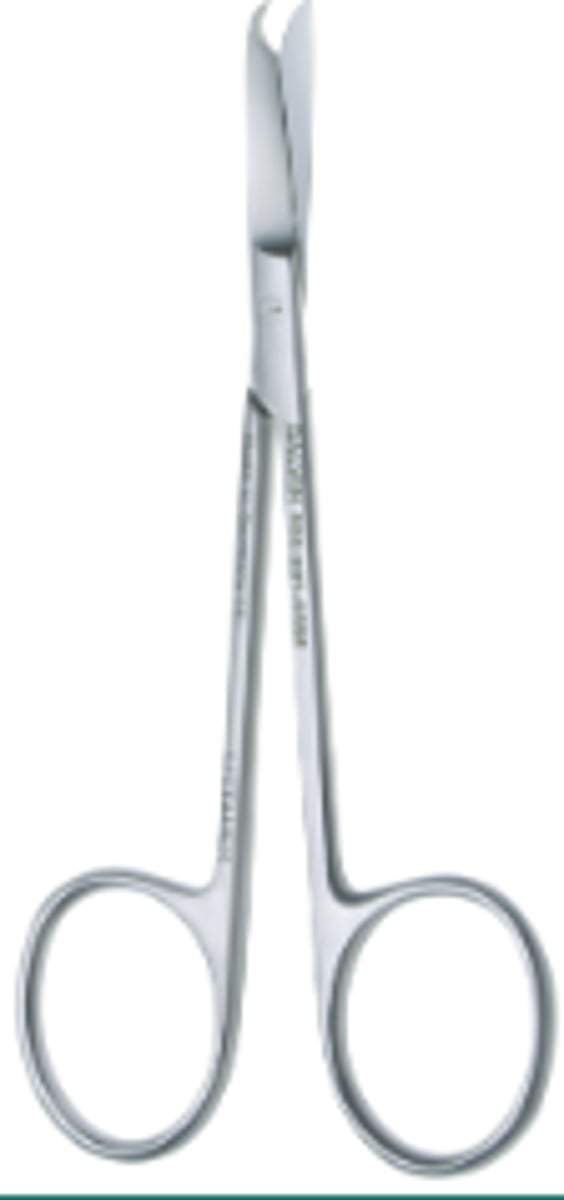
Suture Scissors (1)
To cut sutures
Dental Dam Punch (1)
To punch holes in dental dam for each individual tooth
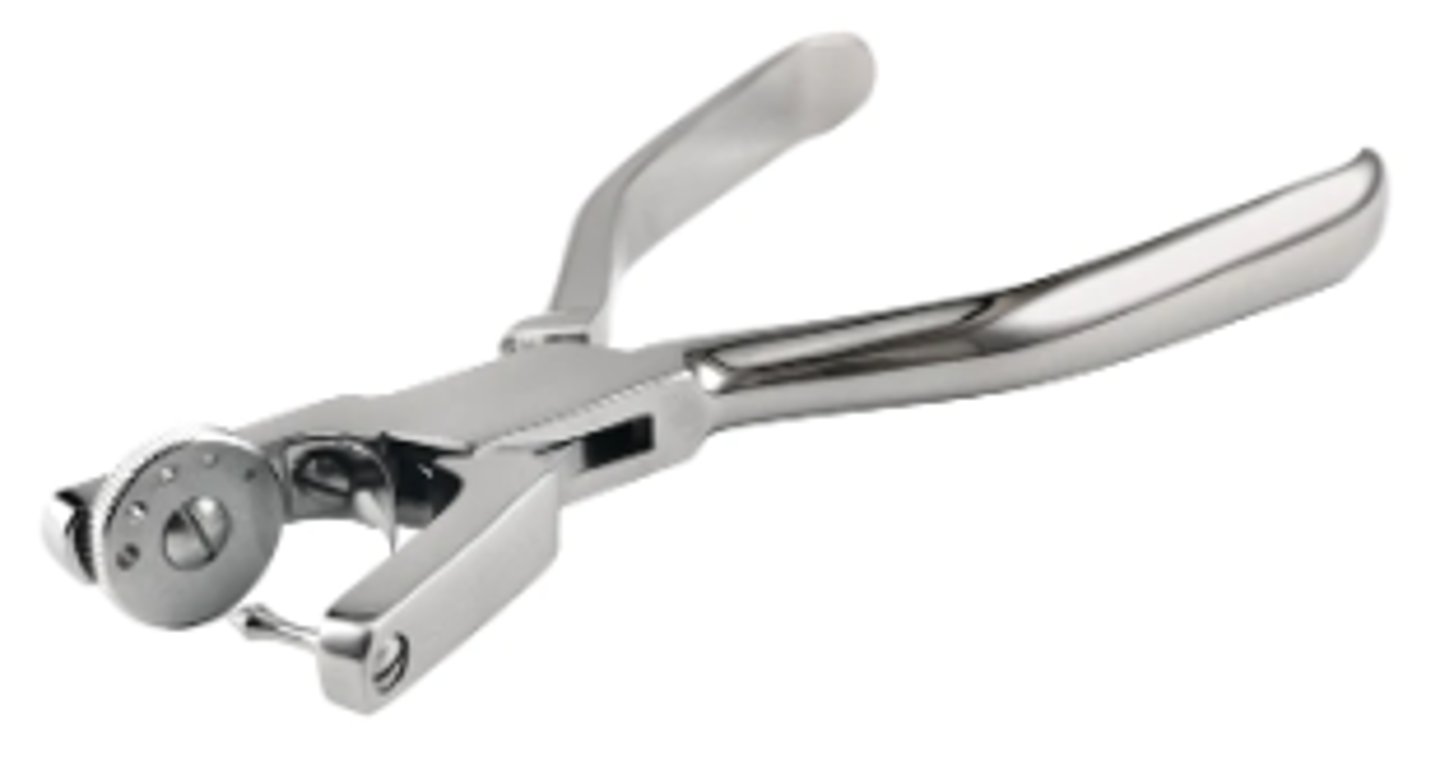

Dental Dam Forceps (1)
To place dental dam clamp on tooth and to remove clamp after procedure
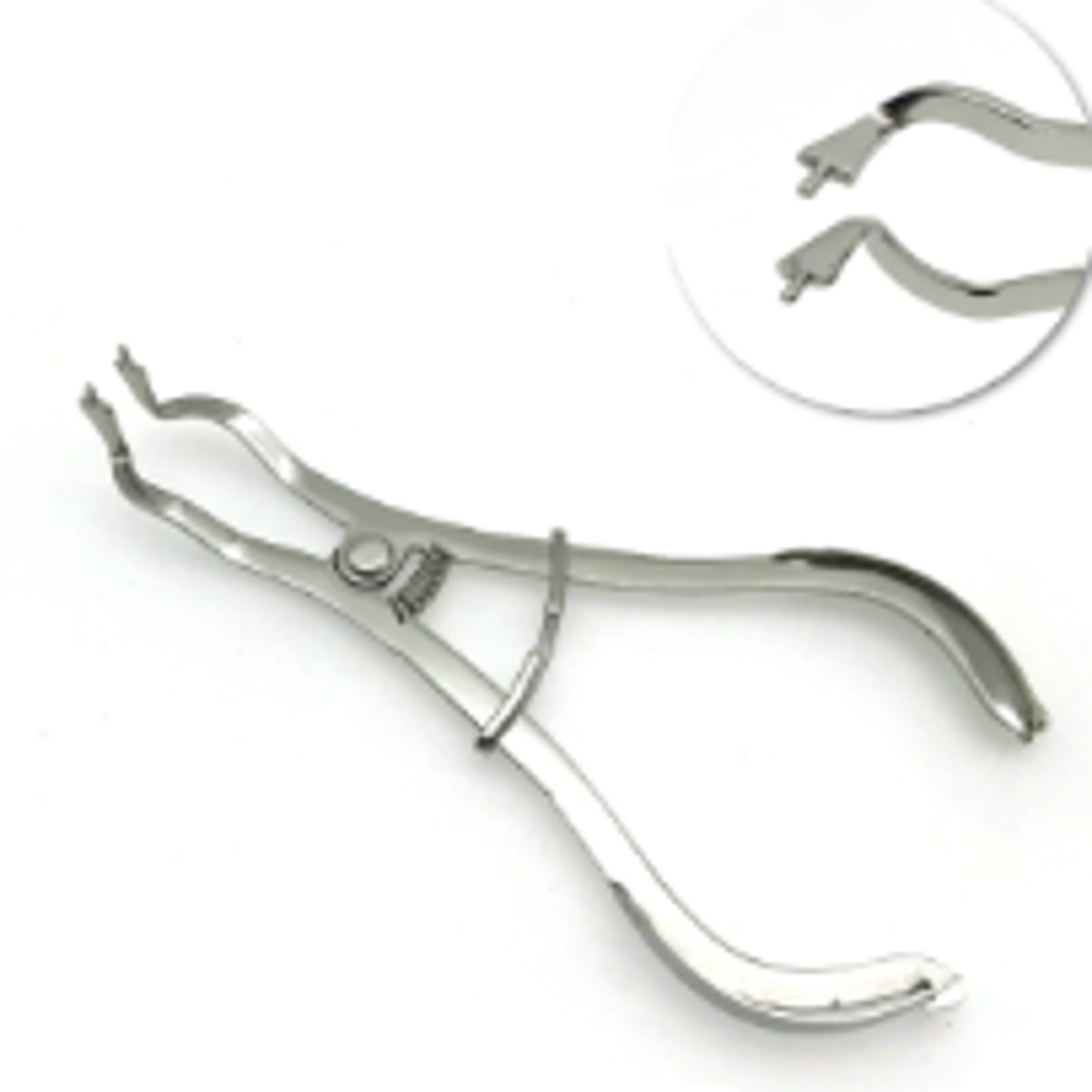
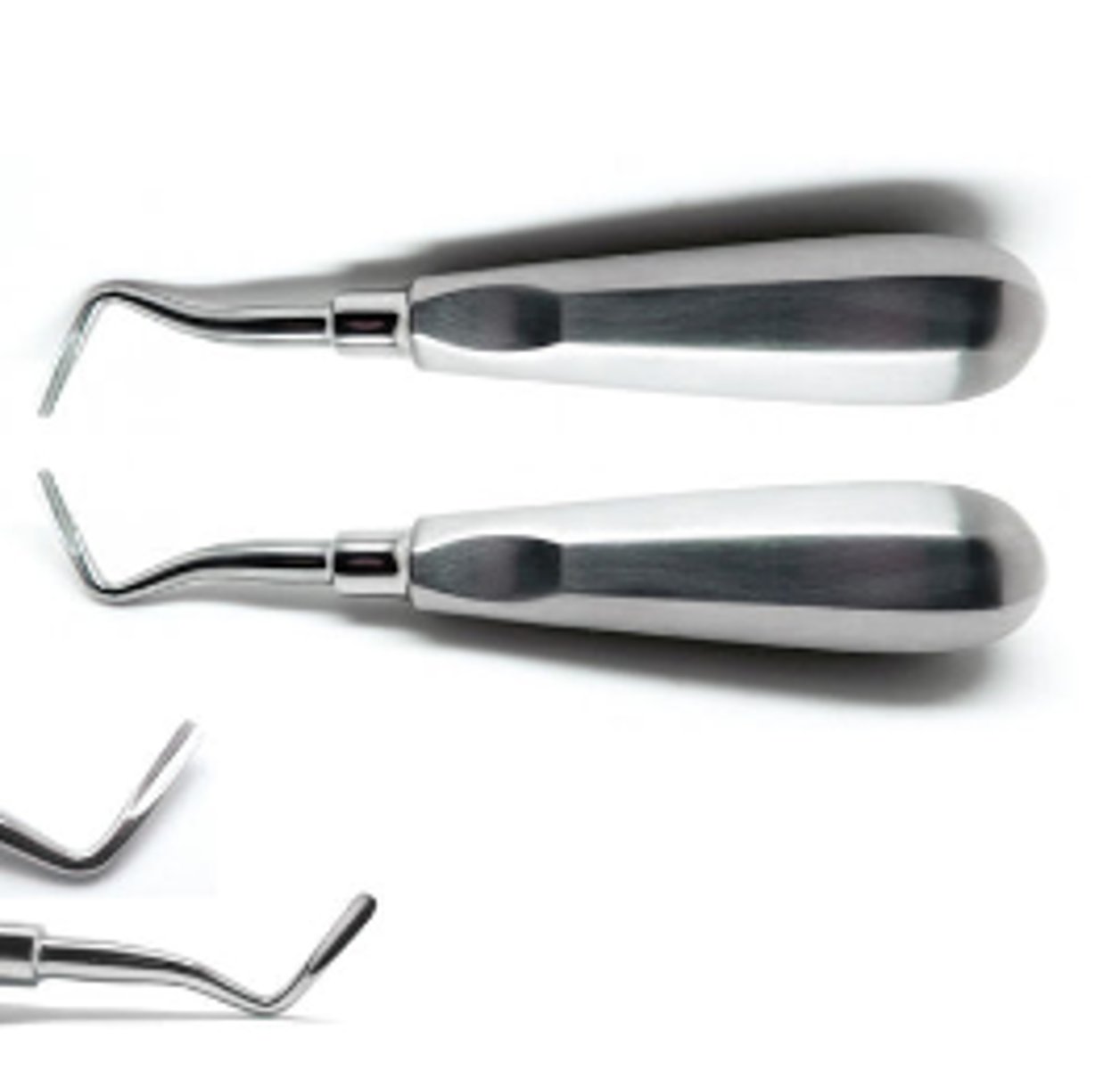
Endodontic Explorer (1)
To locate opening of small canal orifices for endodontic procedure
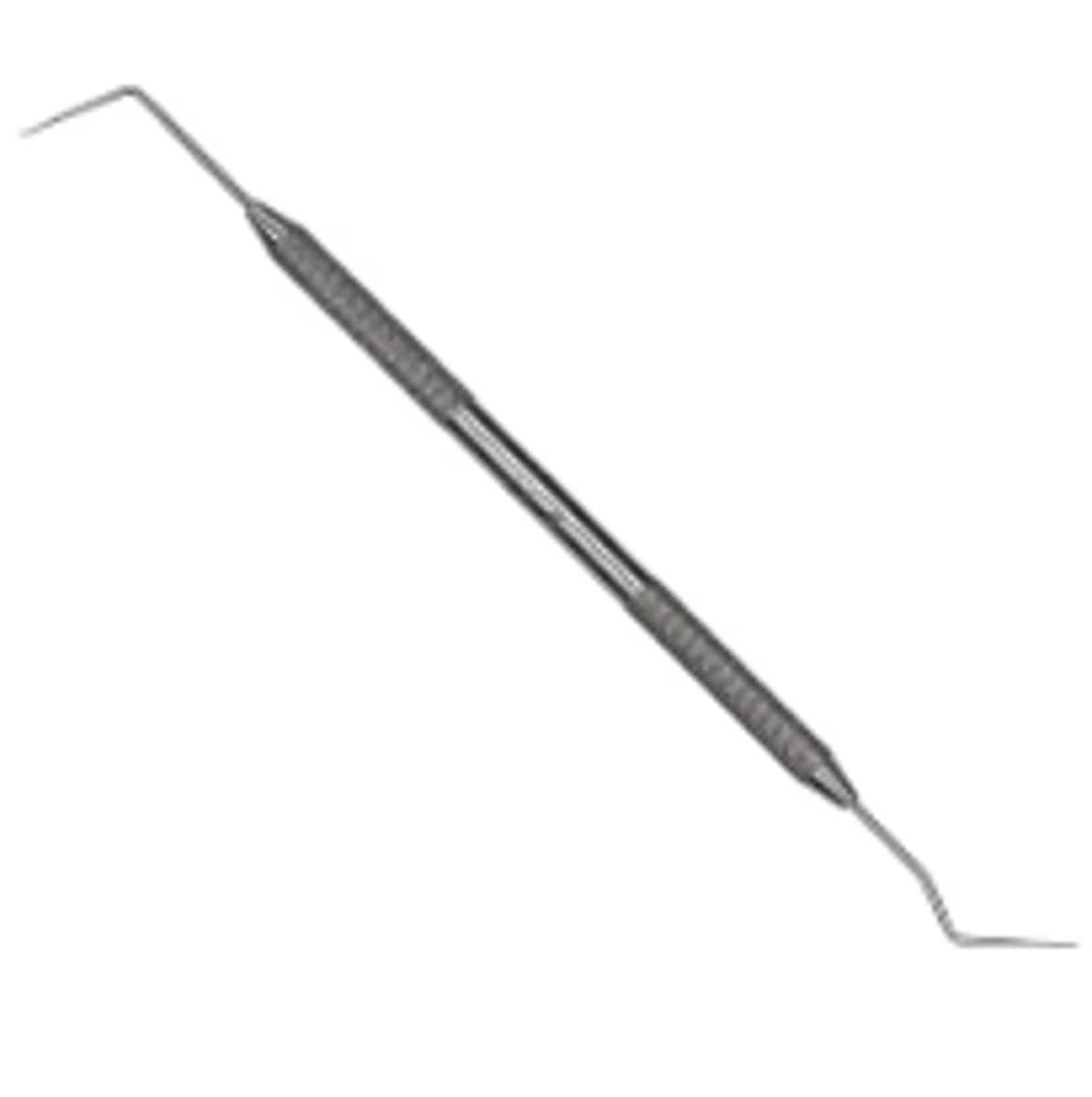

Bird Beak Pliers (2)
To bend and form orthodontic wire
To remove bonded bracket by squeezing bracket
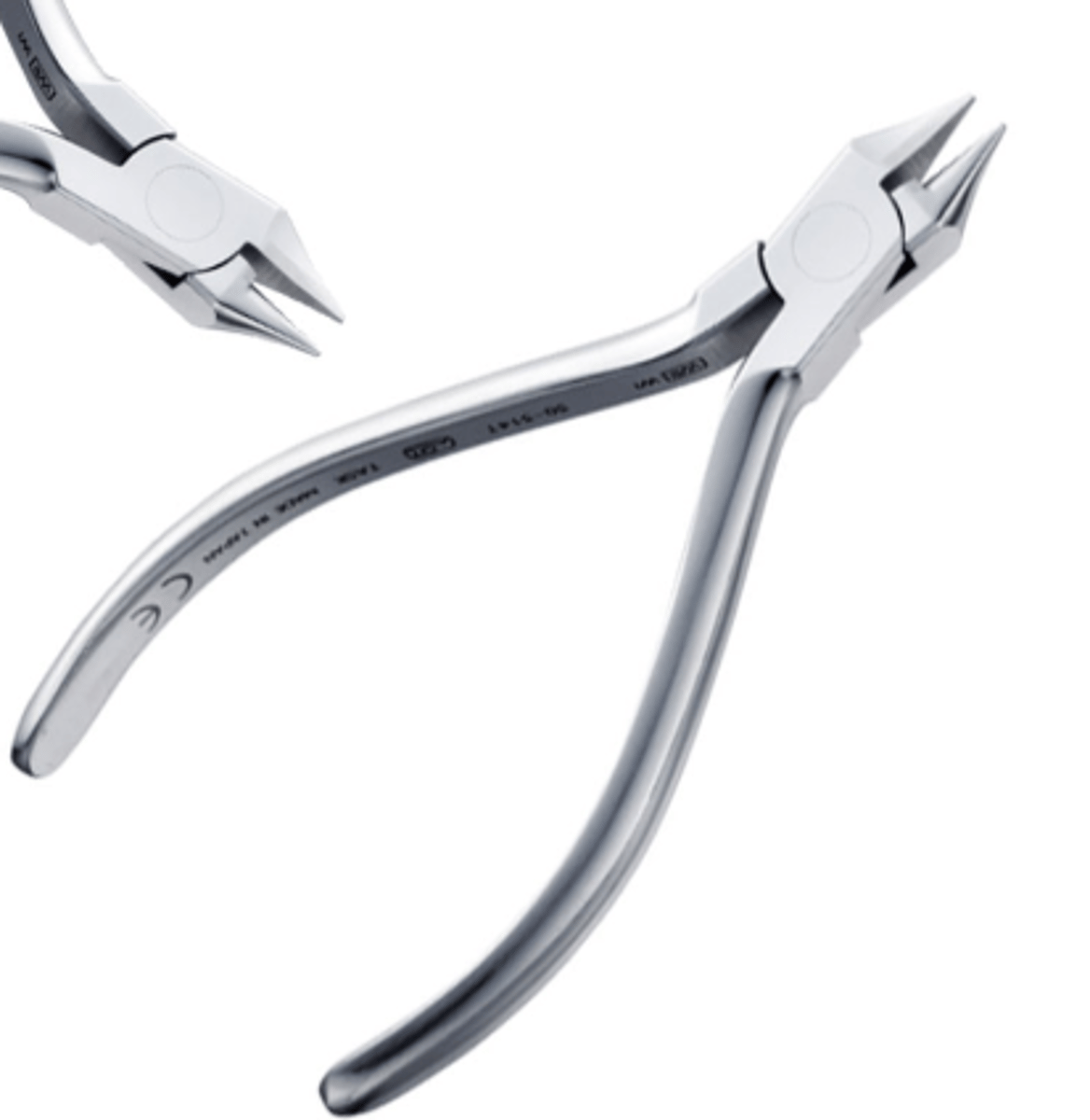

Howe (or How) Pliers (2)
To place and remove arch wires
To check for loose bands
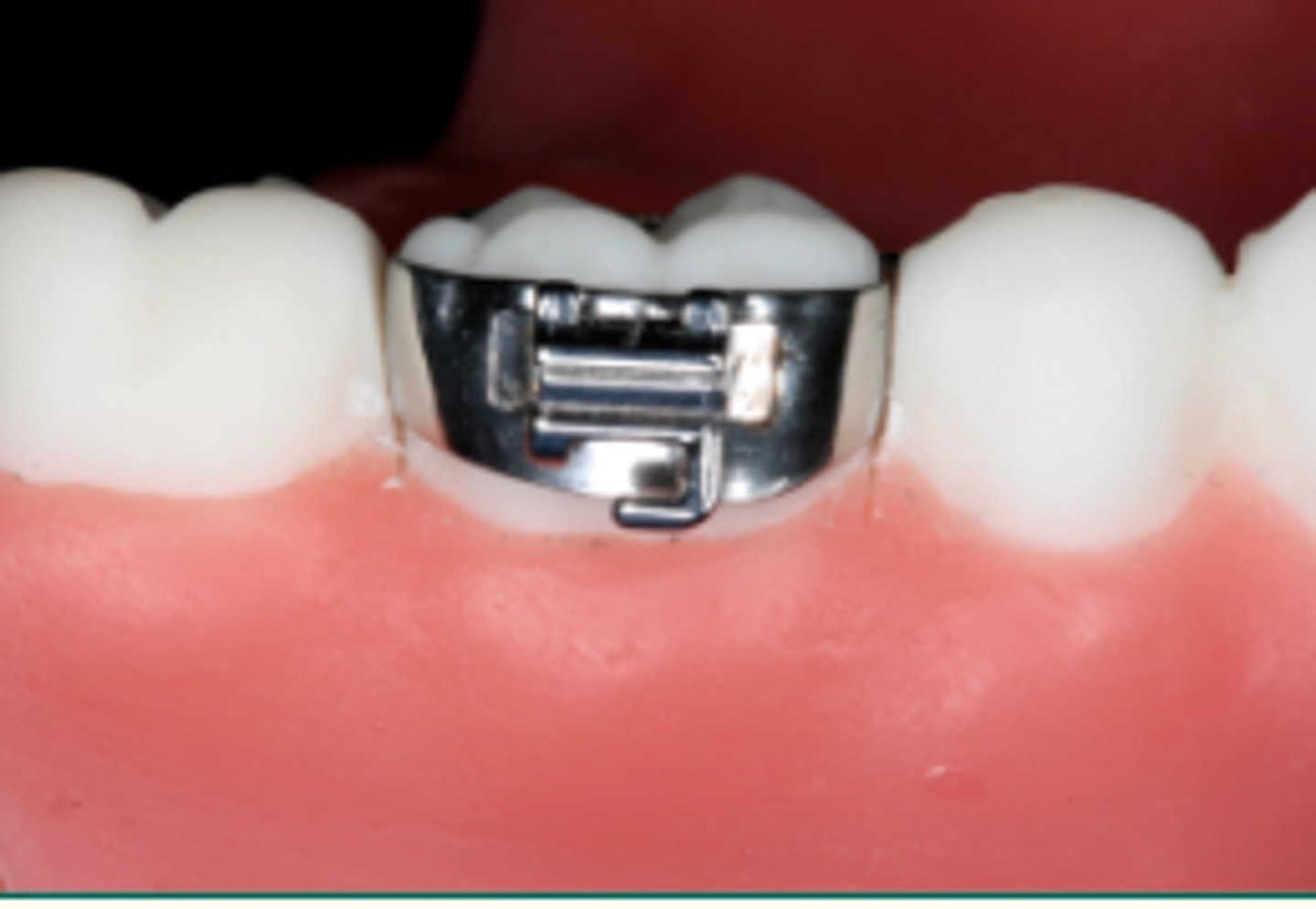
Orthodontic Band (1)
Used to secure auxiliary devices to aid in tooth positioning
Orthodontic Separators (1)
Small elastic bands placed between teeth to make room for orthodontic appliances
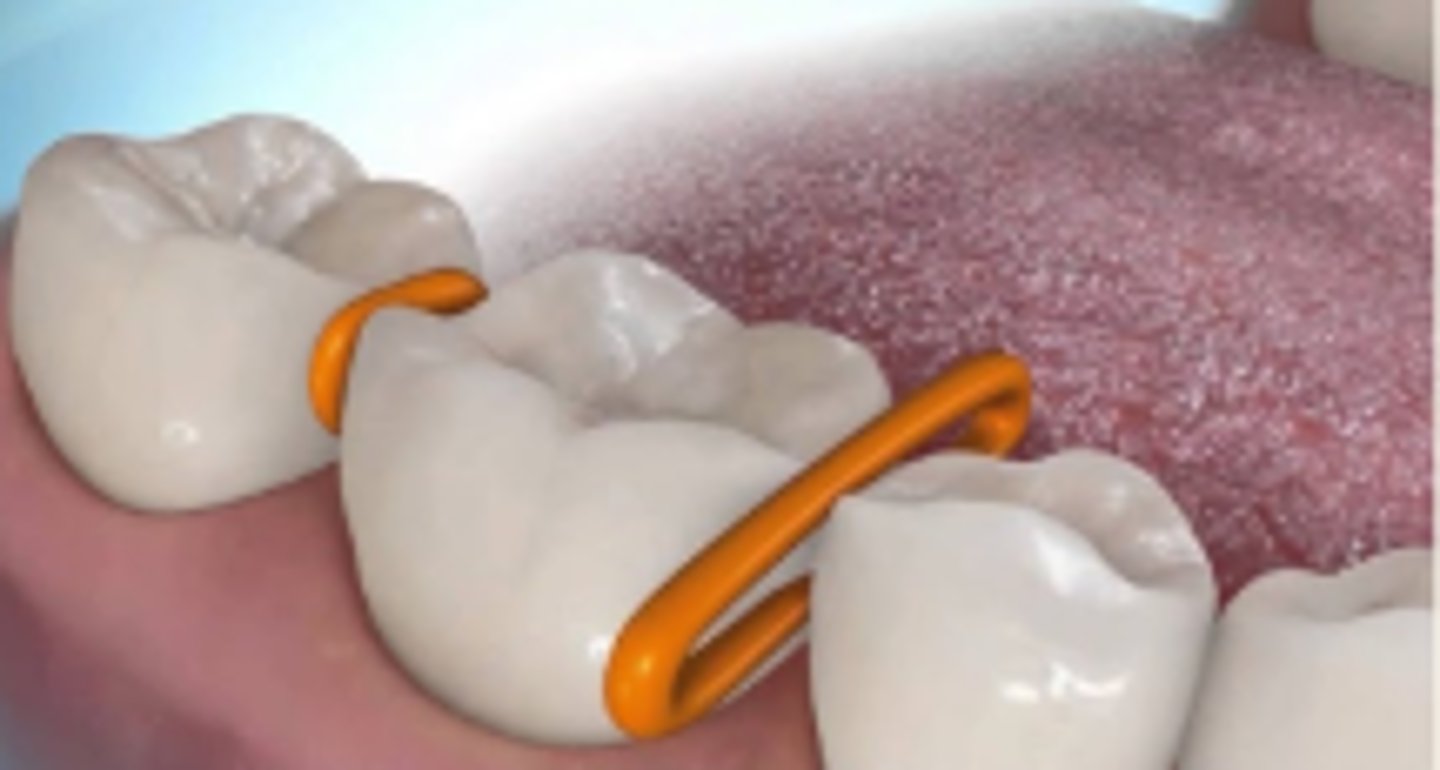
Orthodontic Separator Placing Instrument (1)
Used for placing elastic separators interproximally

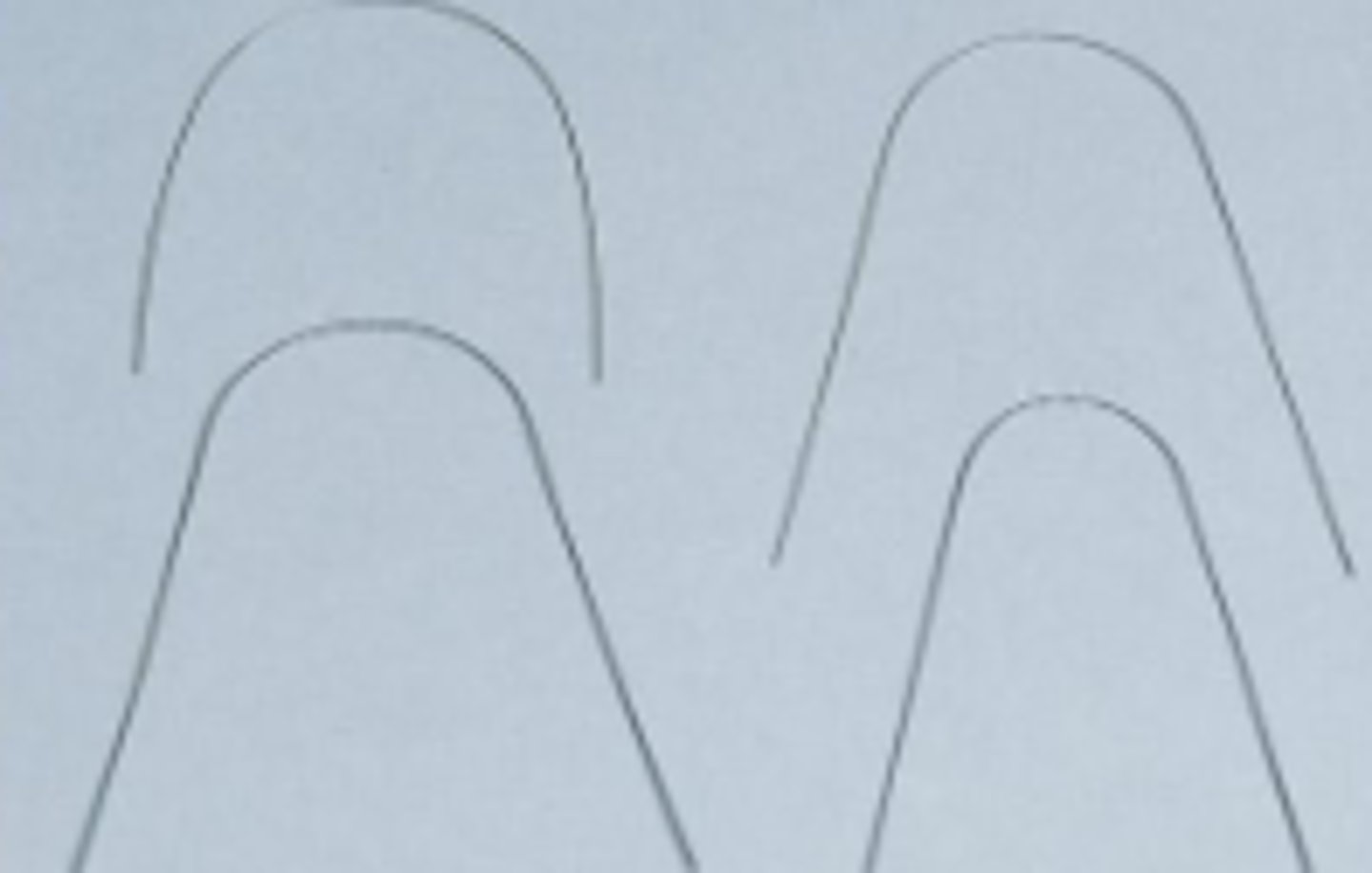
Arch Wire (1)
Move teeth into their correct positions by applying gentle, constant pressure

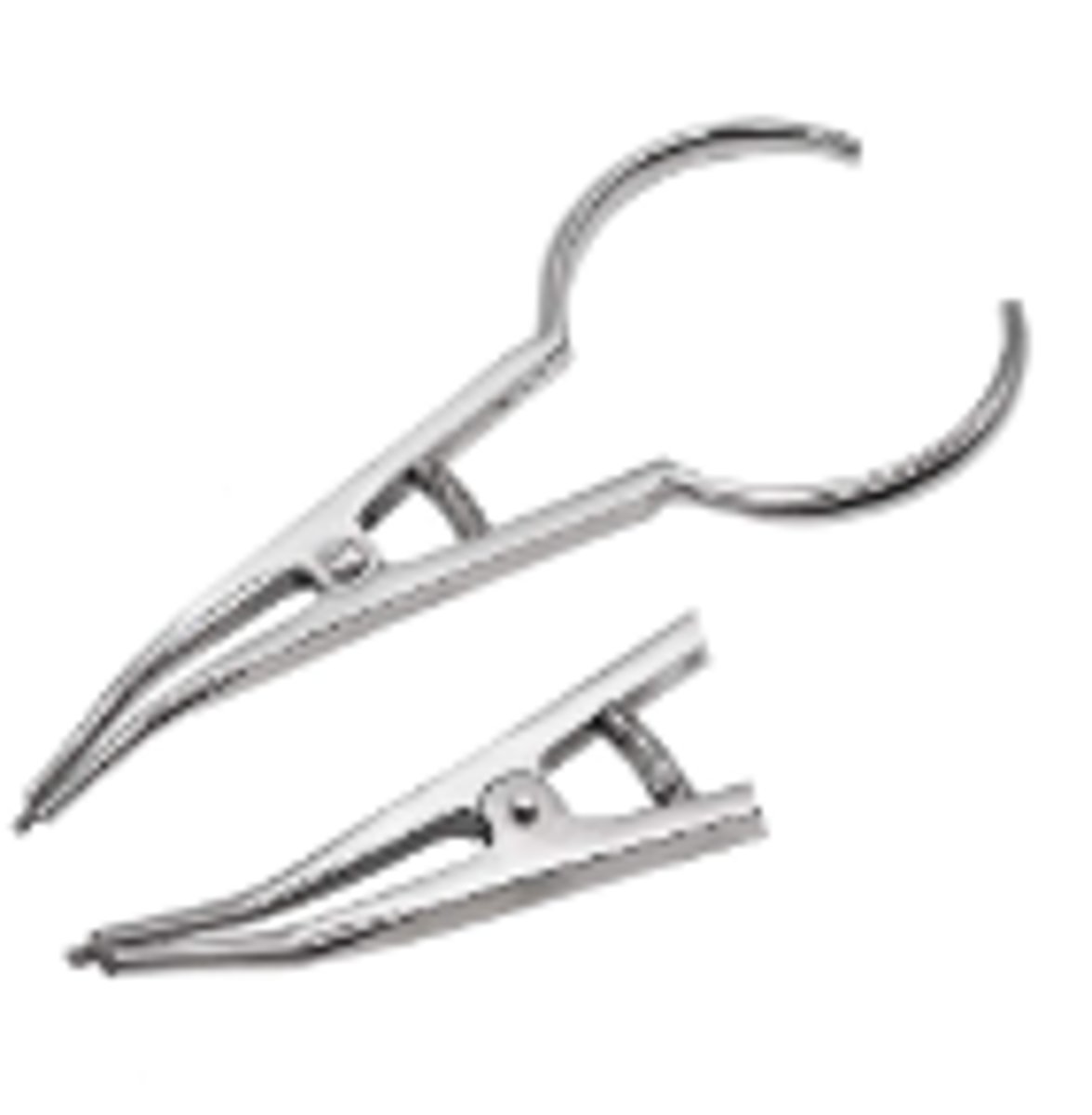
Mathieu Ligature Pliers (1)
Gripping and placing elastic auxiliaries
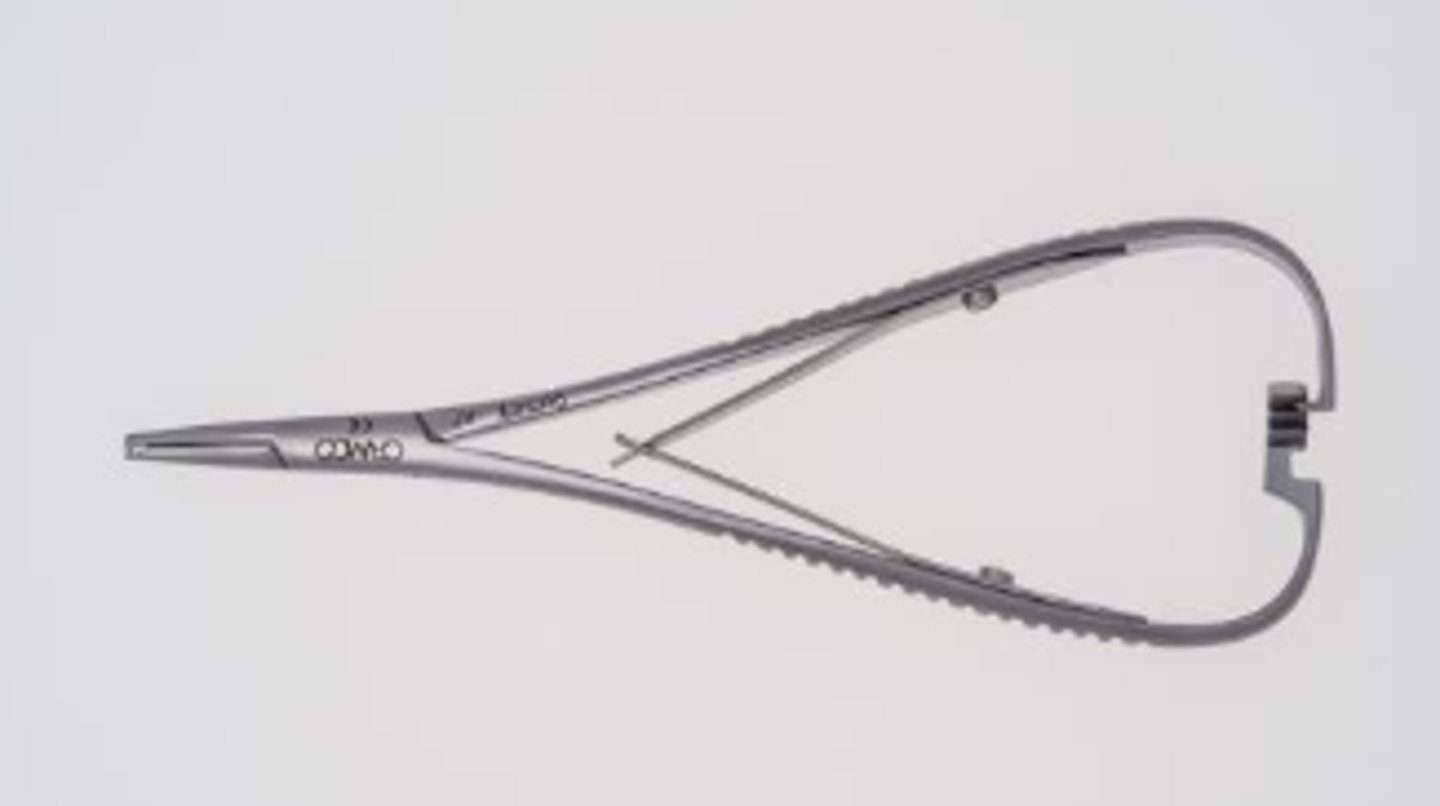
Distal End Cutter (1)
Plier used to cut off the ends of the ends of the arch wire.
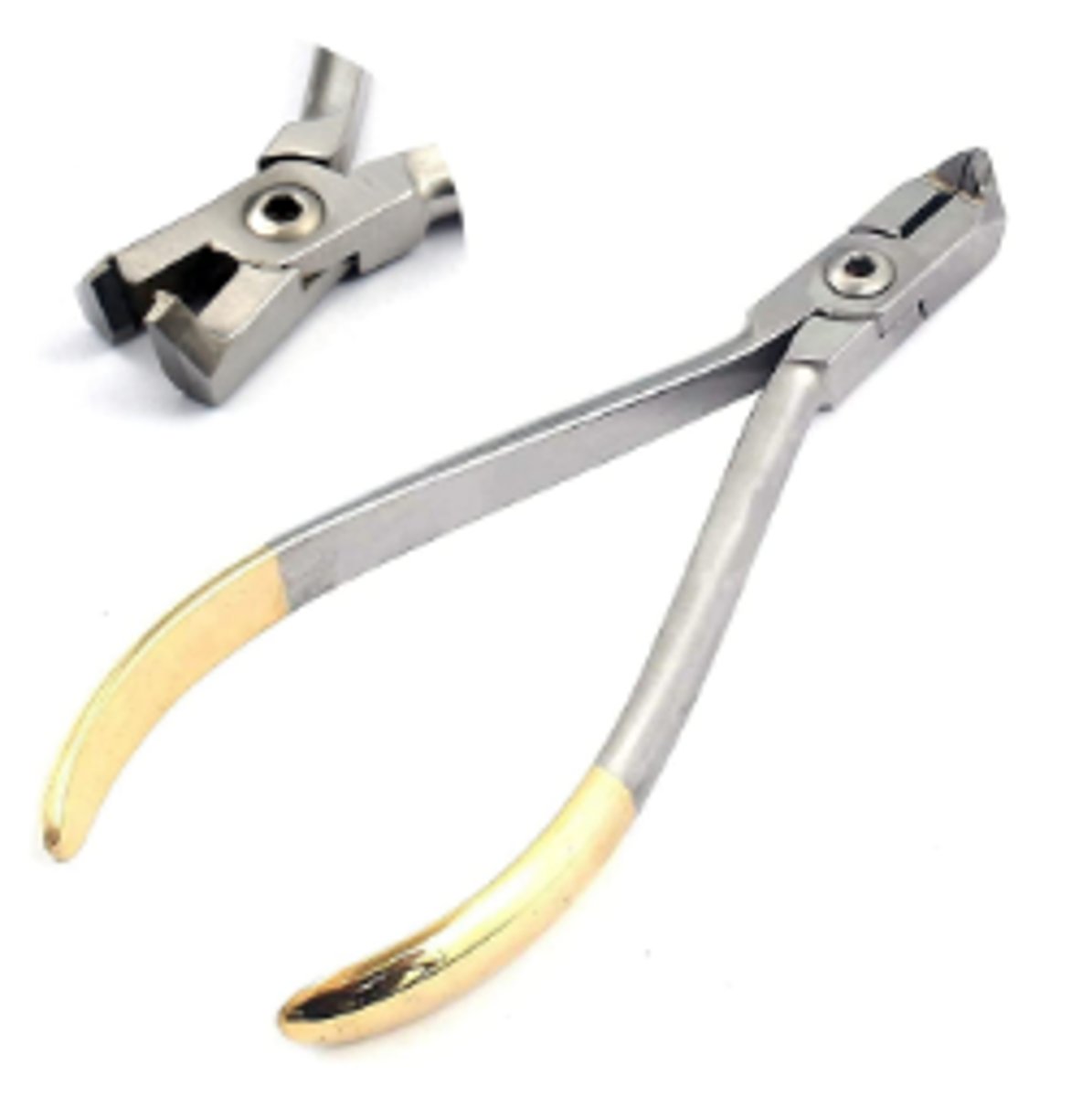

Gingival Retraction Cord Instrument / Cord Packer (1)
To place gingival retraction cord in sulcus after tooth is prepared for a crown and before final impressions are taken
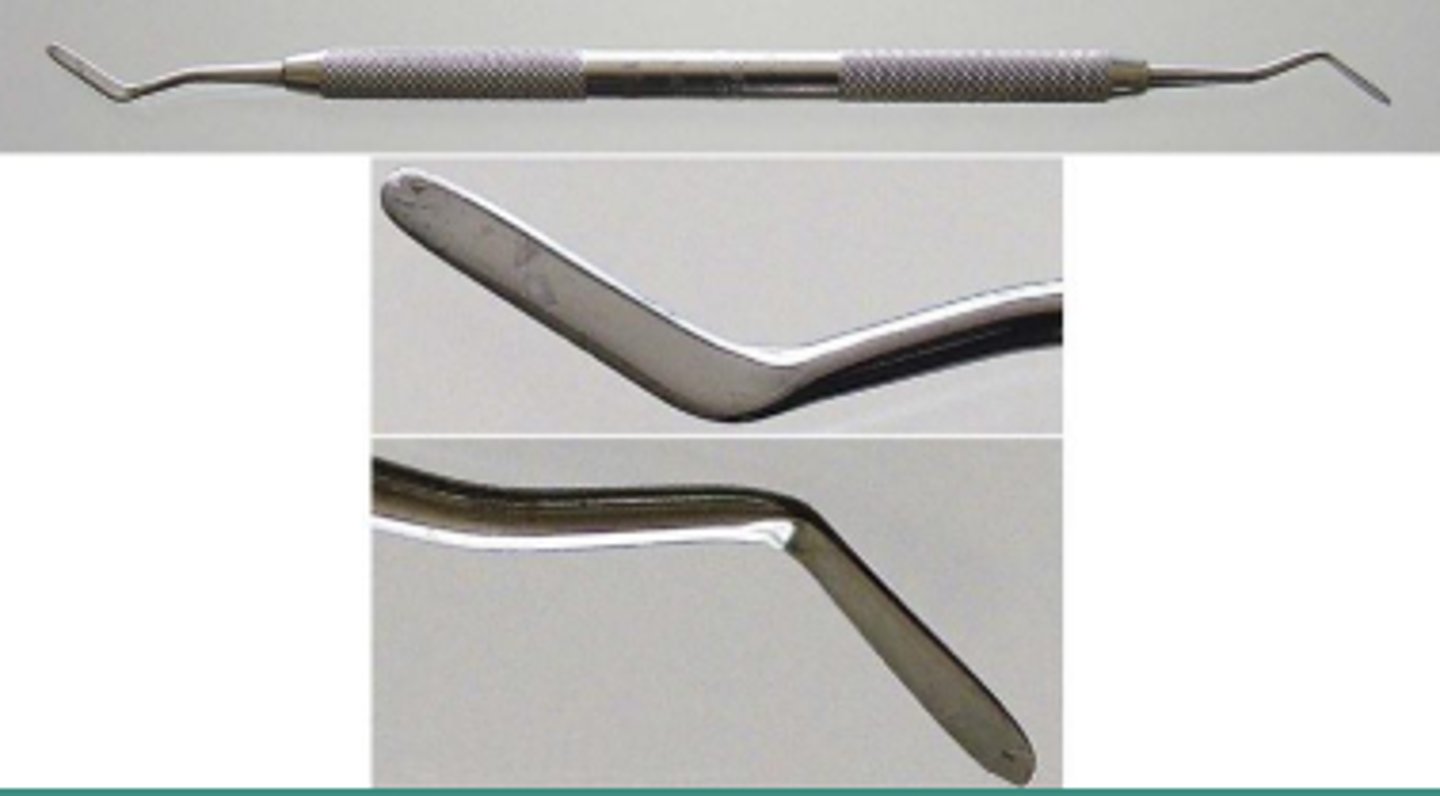
Contouring Pliers (1)
To crimp and contour marginal edge of temporary crown or stainless steel crown.
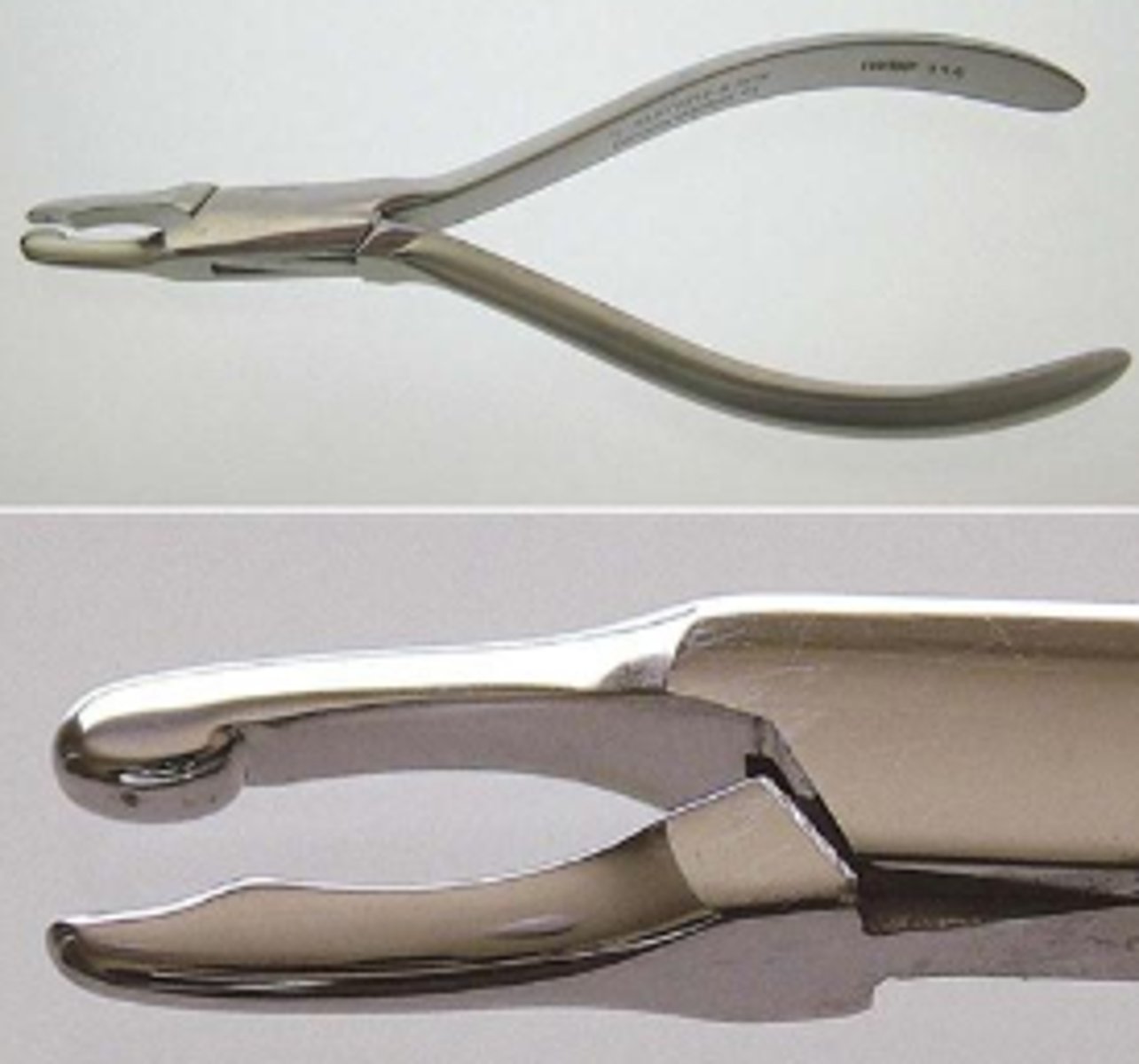
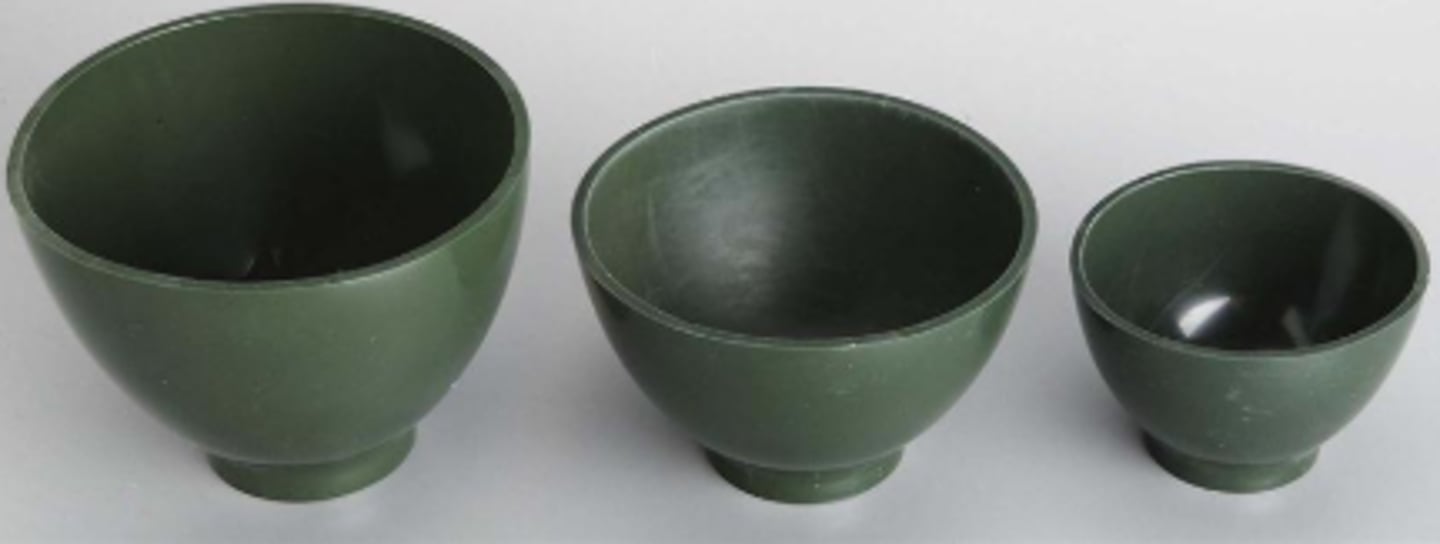
Flexible Rubber Bowl (1)
To mix material, usually a powder and a liquid

Flexible Alginate Spatula (1)
To mix powder and a liquid in a flexible bowl.

Alginate (1)
A powder impression material used to create NEGATIVE molds (impressions) of teeth and surrounding oral tissues
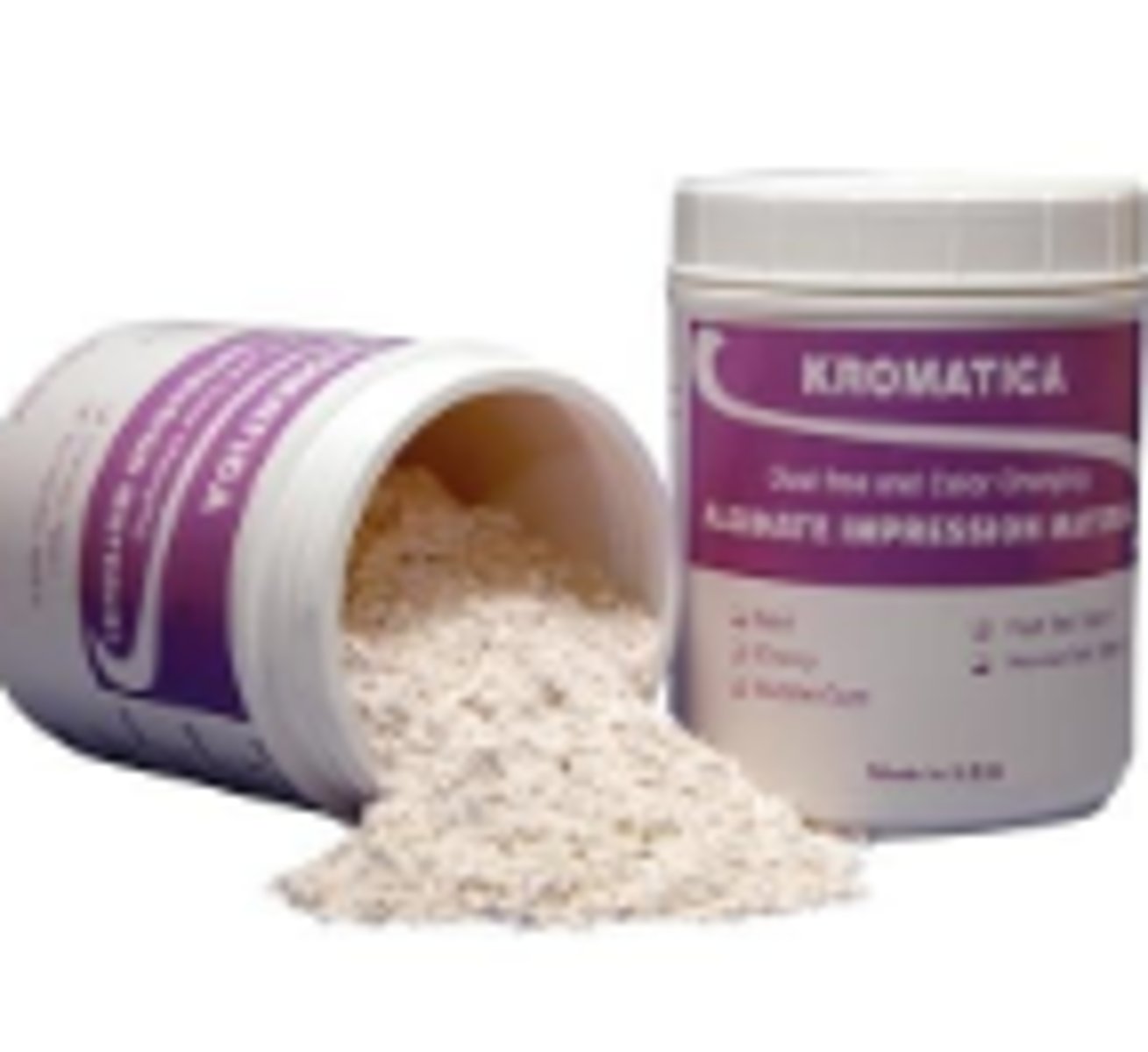

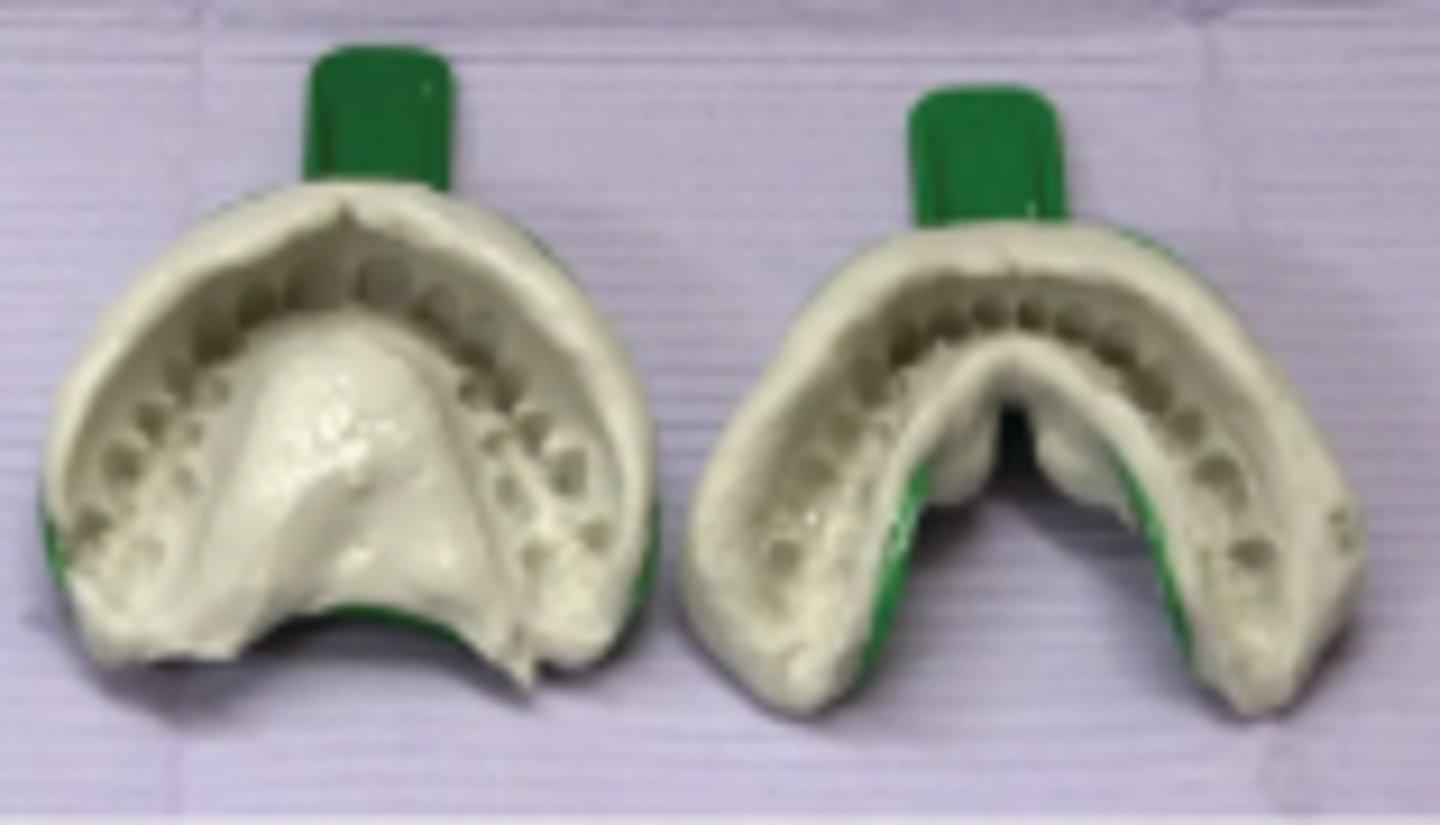
Dental Lab Stone (1)
A gypsum product used in dental laboratories for creating study models, working models, and casts, offering greater strength and accuracy than plaster.
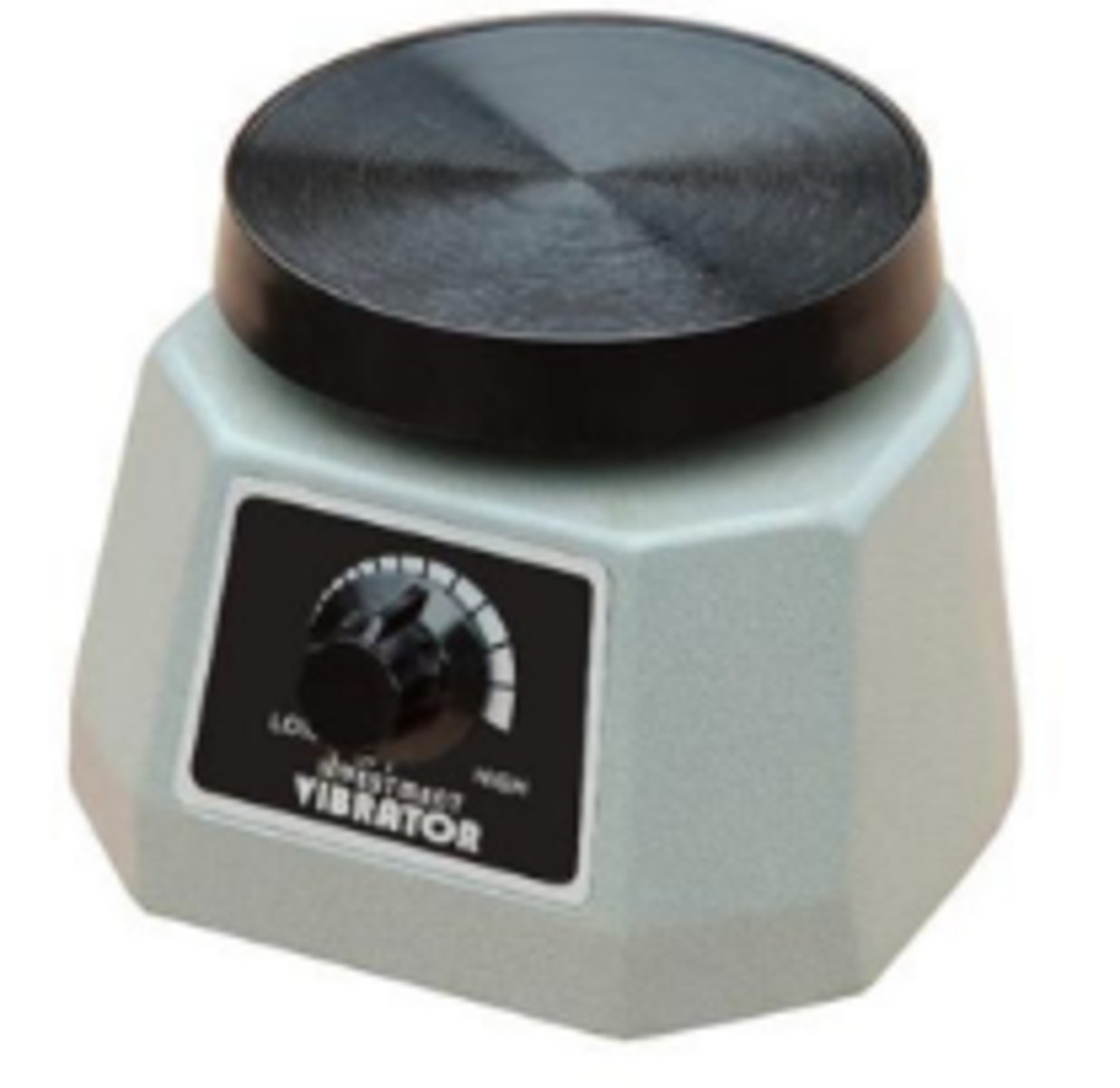
Dental Lab Vibrator (1)
A device used in dental laboratories to remove air bubbles from mixed materials like plaster, gypsum, and dental stones.

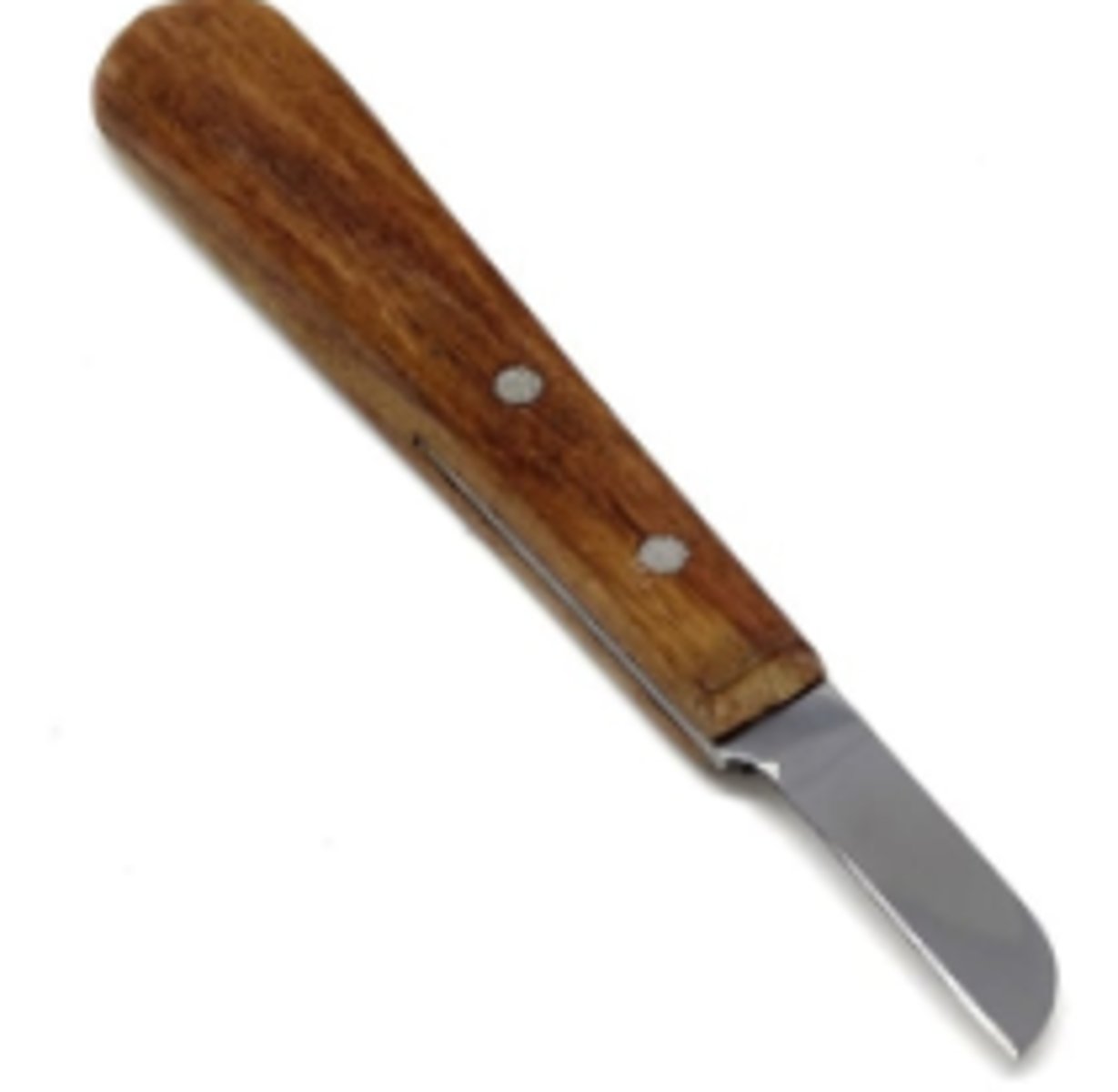
Dental Lab Knife (1)
A sharp-edged, stainless steel instrument with a wooden handle, used in dental labs for cutting, mixing, and manipulating dental materials like plaster, alginate, and stone.

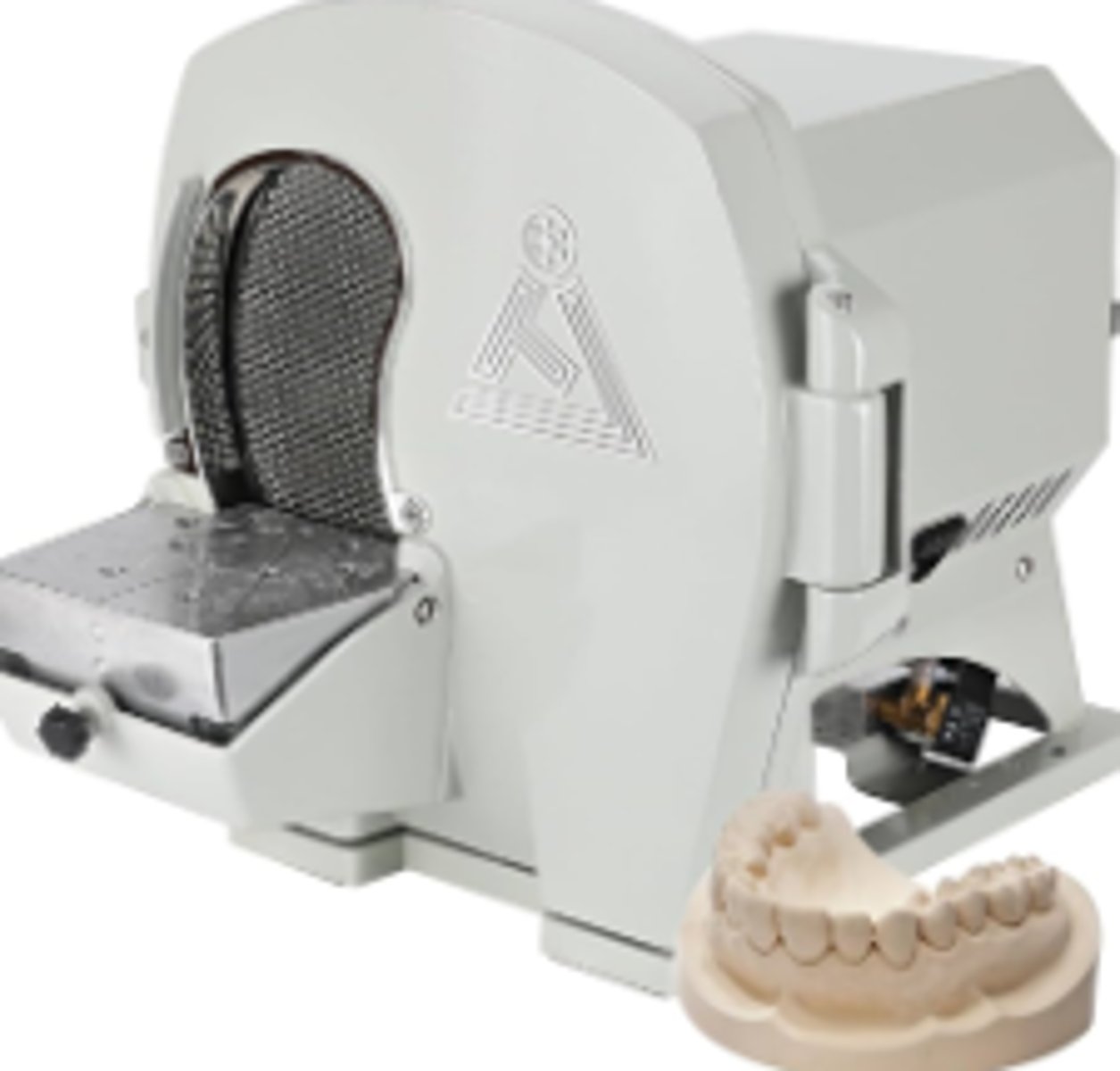
Dental Wet Model Trimmer (1)
A laboratory machine used to shape and trim dental models (casts made from impressions) using a wet abrasive wheel.
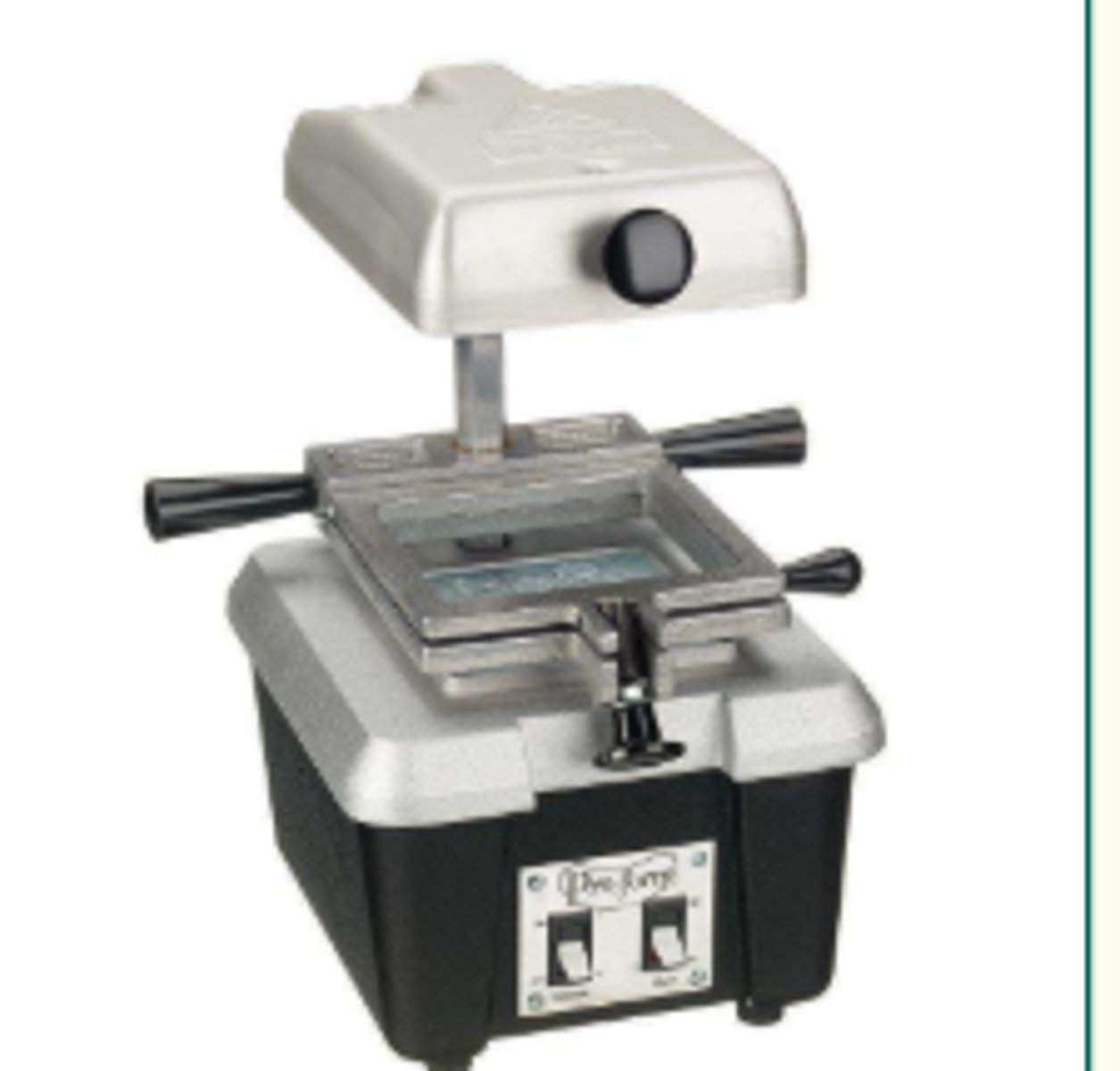
Dental Vacuum Forming Machine (1)
A device that uses vacuum pressure to shape a heated plastic sheet onto a mold, creating various dental appliances like mouthguards, bleaching trays, and custom trays.

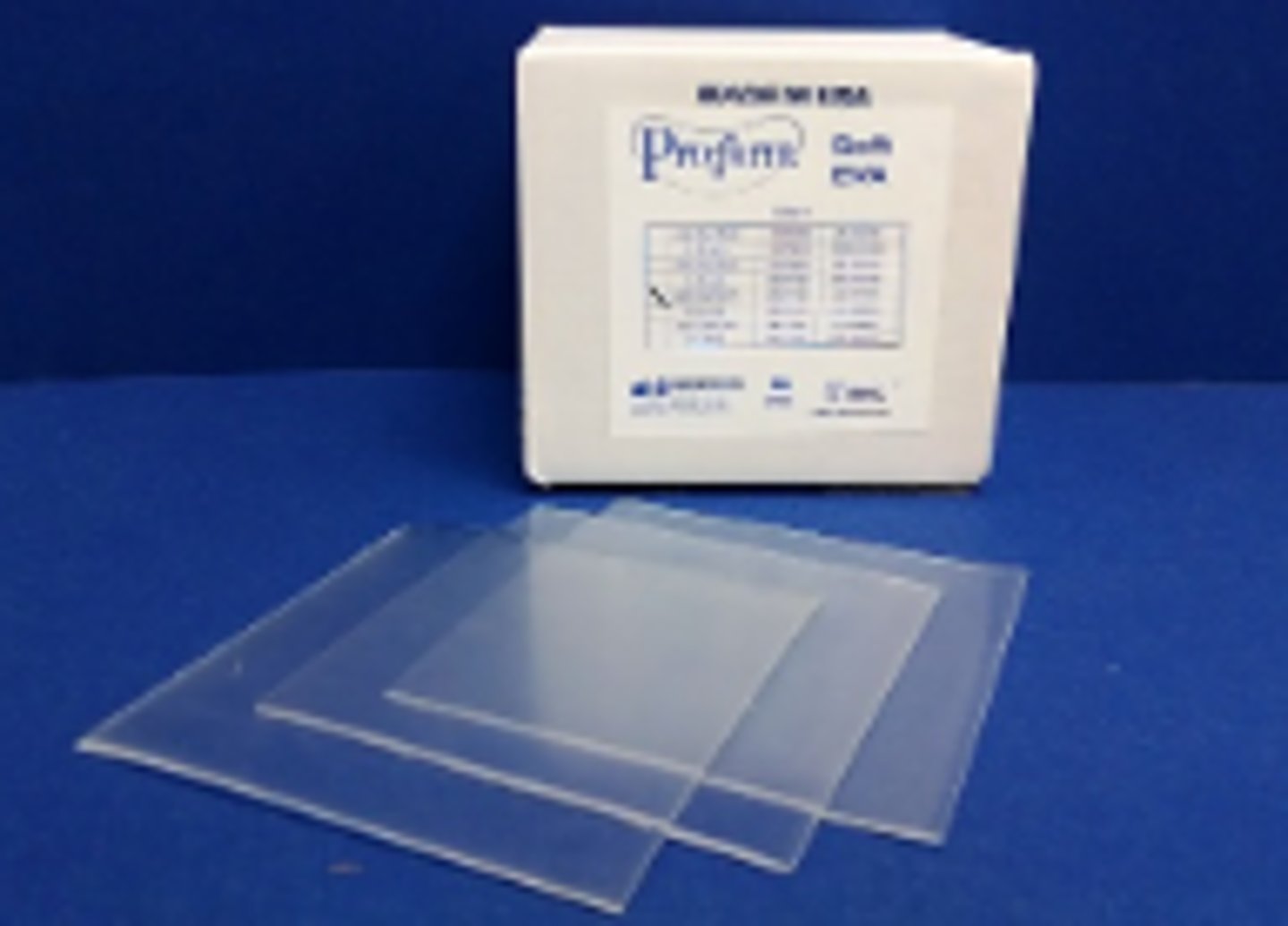
Bleaching Tray Material (1)
The flexible, often clear plastic material used to fabricate trays that old whitening gel during tooth whitening procedures.

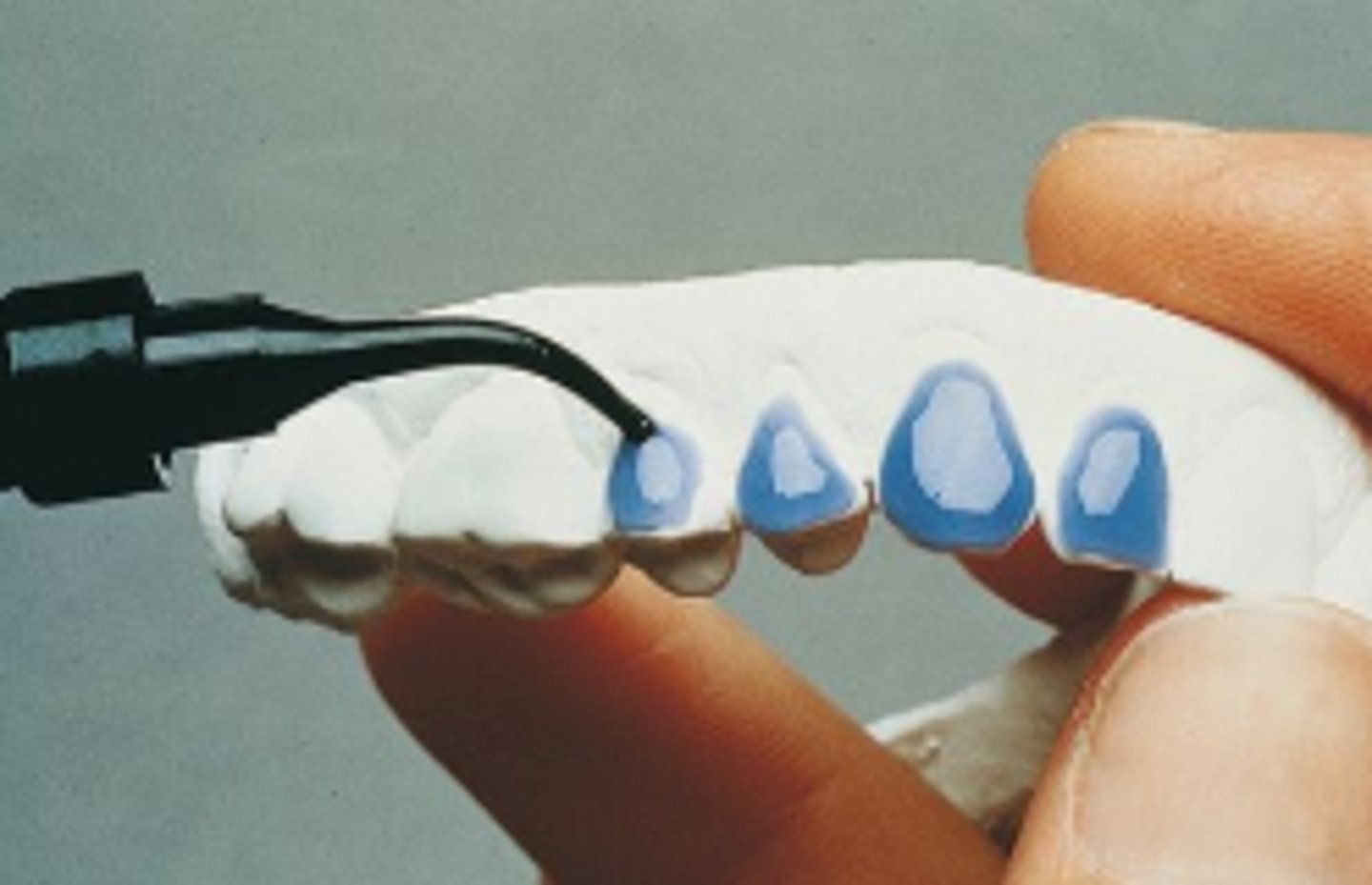
Block-Out Resin
- A viscous material used to create reservoir spaces in custom bleaching/whitening trays
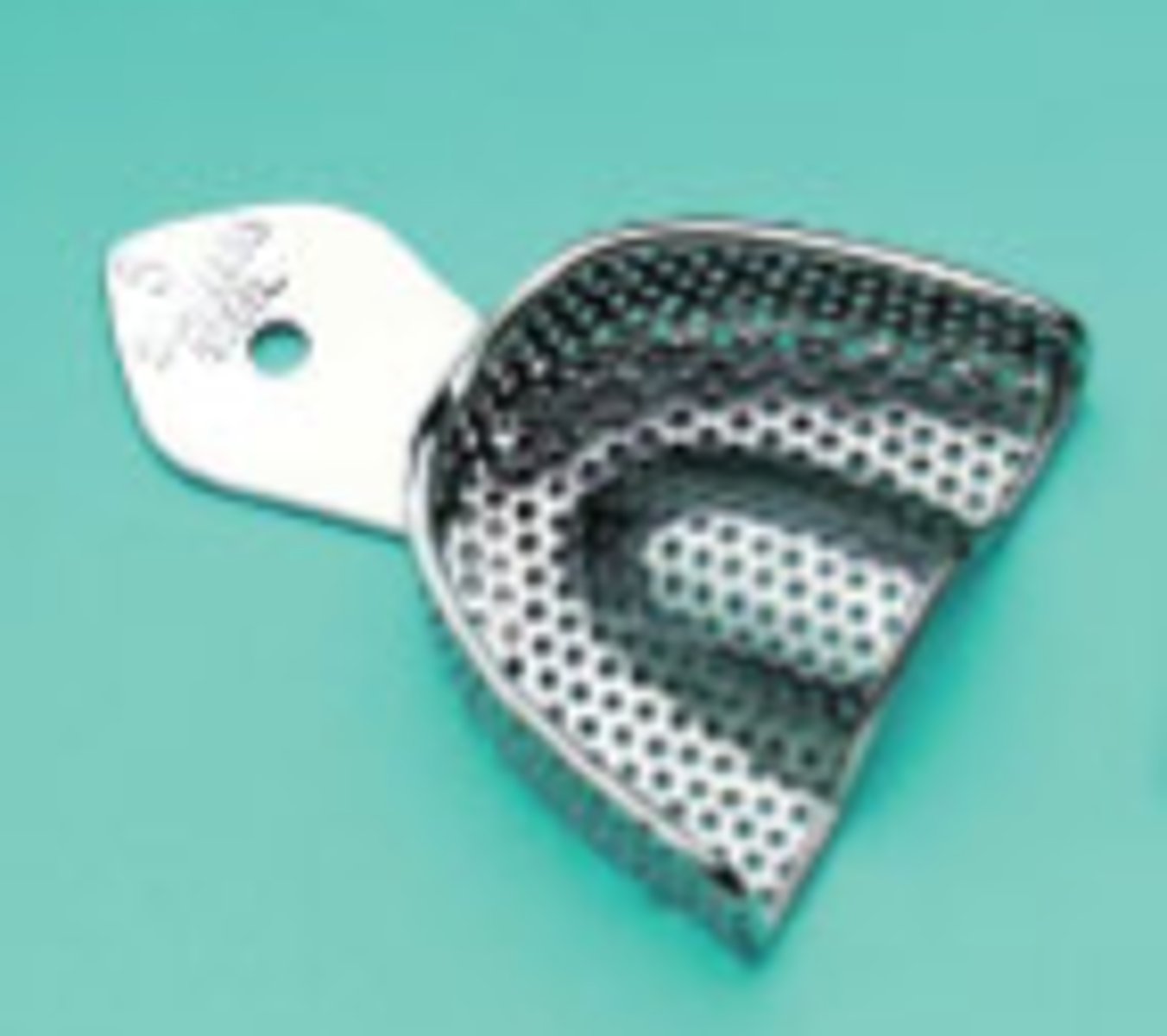
Metal Perforated Impression Tray
- A reusable dental tray made of metal with small holes
- Holds and supports impression material while making accurate molds of a patient's teeth and gums

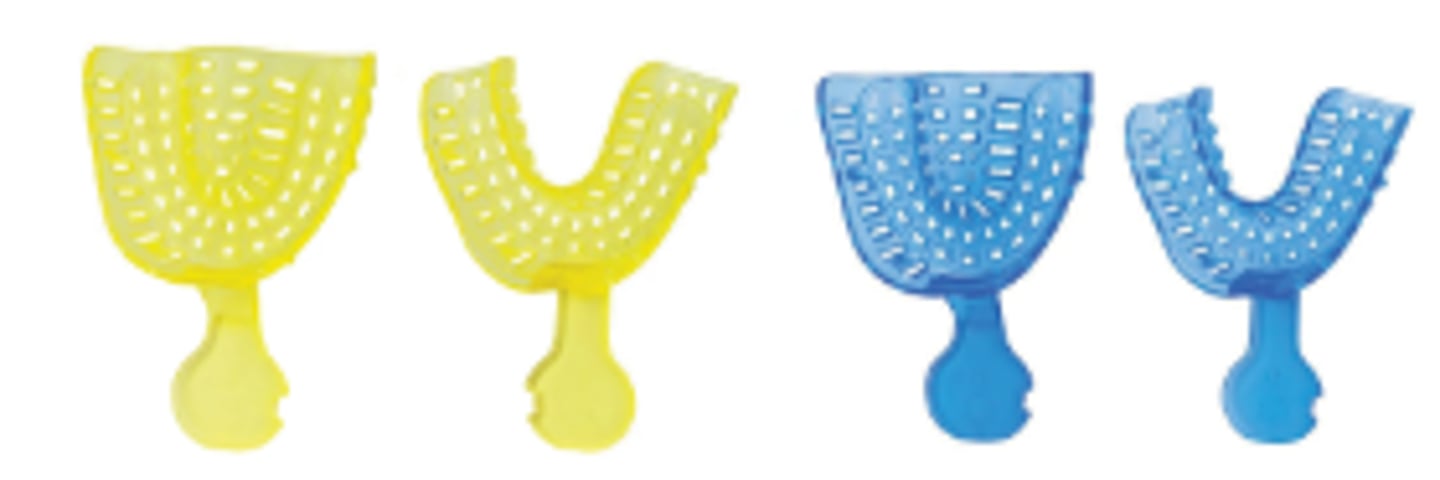
Plastic Perforated Impression Tray
- A lightweight, disposable dental tray made of plastic with small holes
- Holds impression material to create accurate molds of a patient's teeth and gums

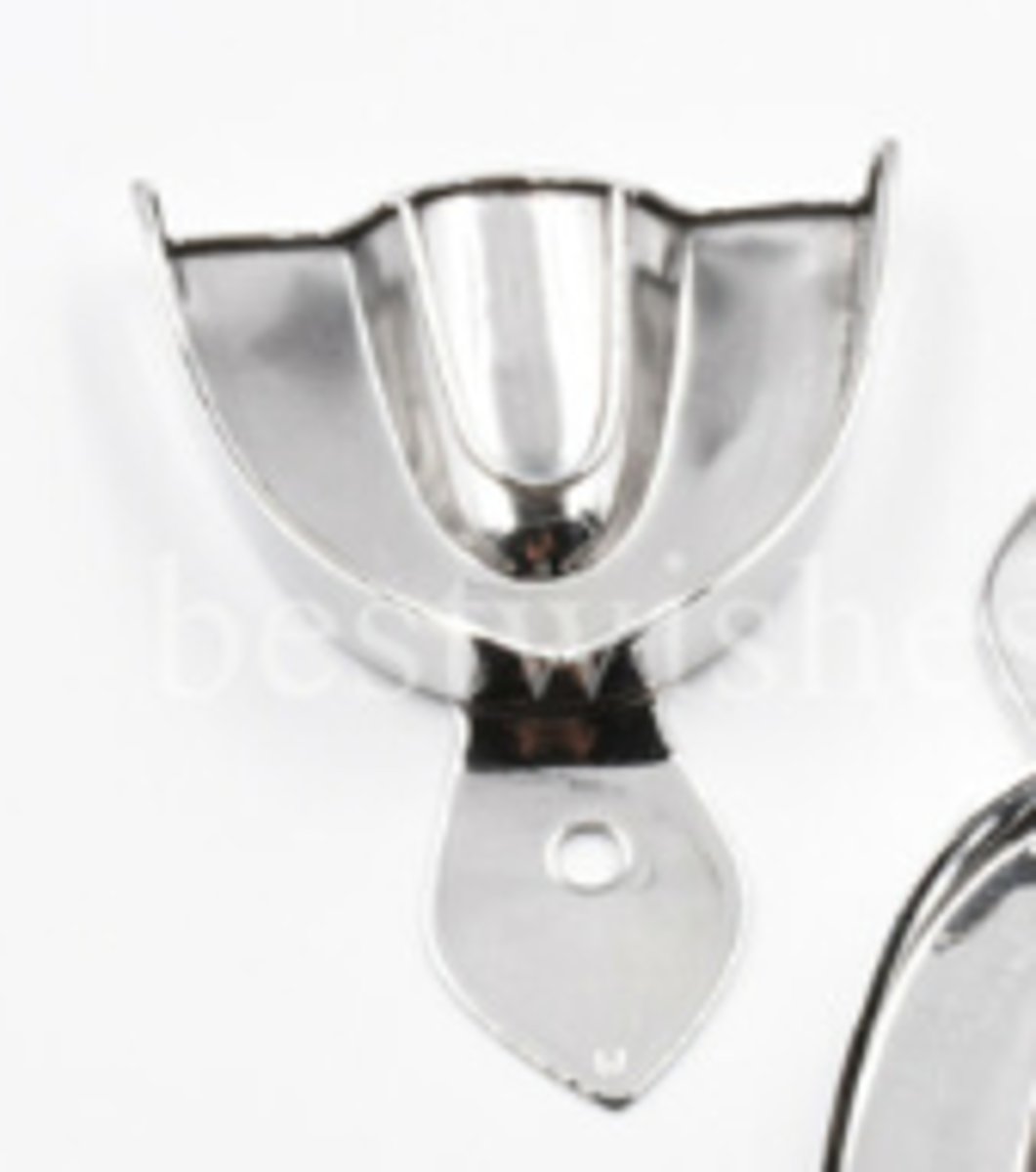
Metal Non-Perforated Impression Trays
- A reusable dental tray made of solid metal without holes
- Holds impression material for taking molds of teeth and gums;

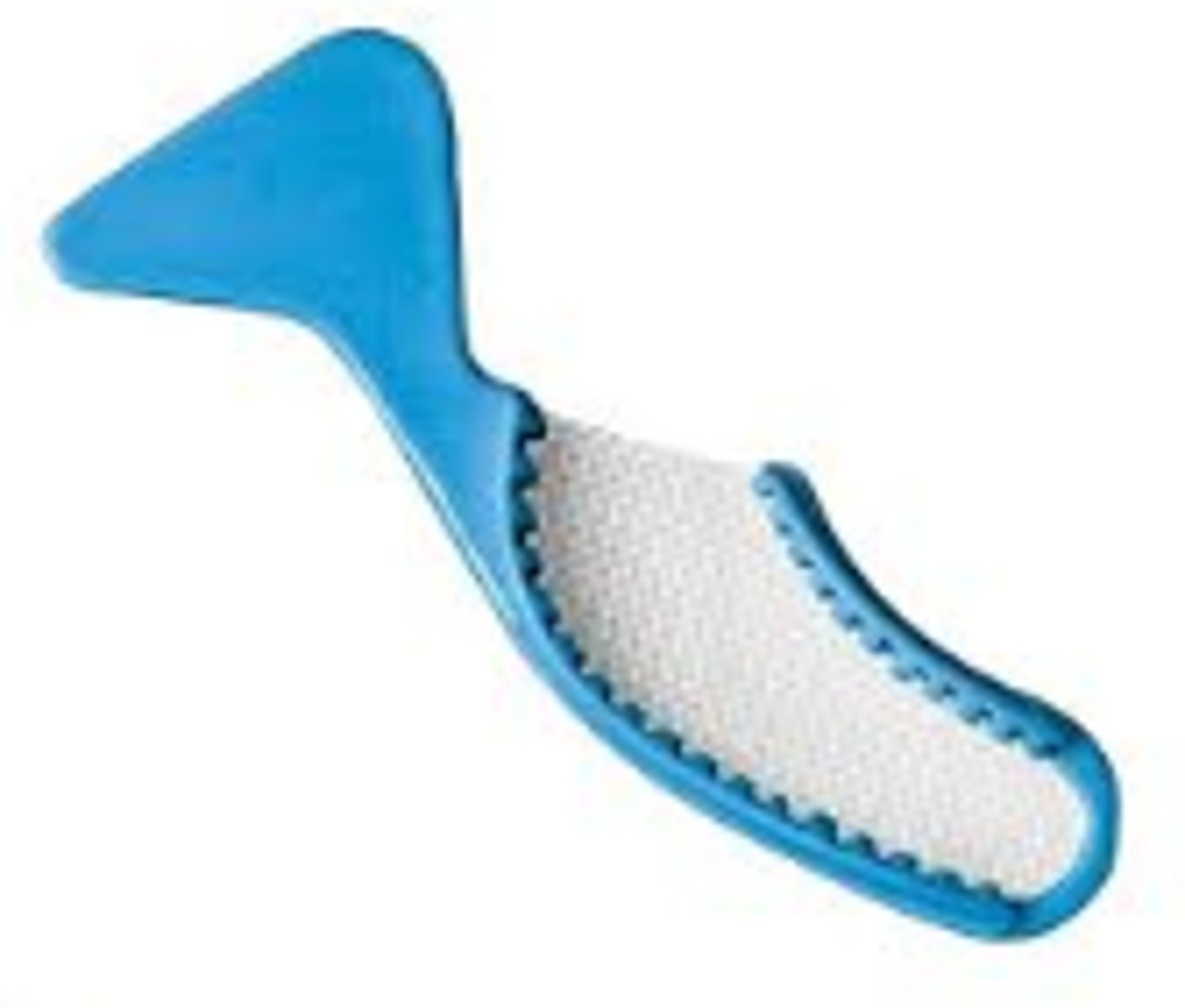
Disposable Quadrant Tray
- Holds impression material to capture an accurate mold of one quadrant

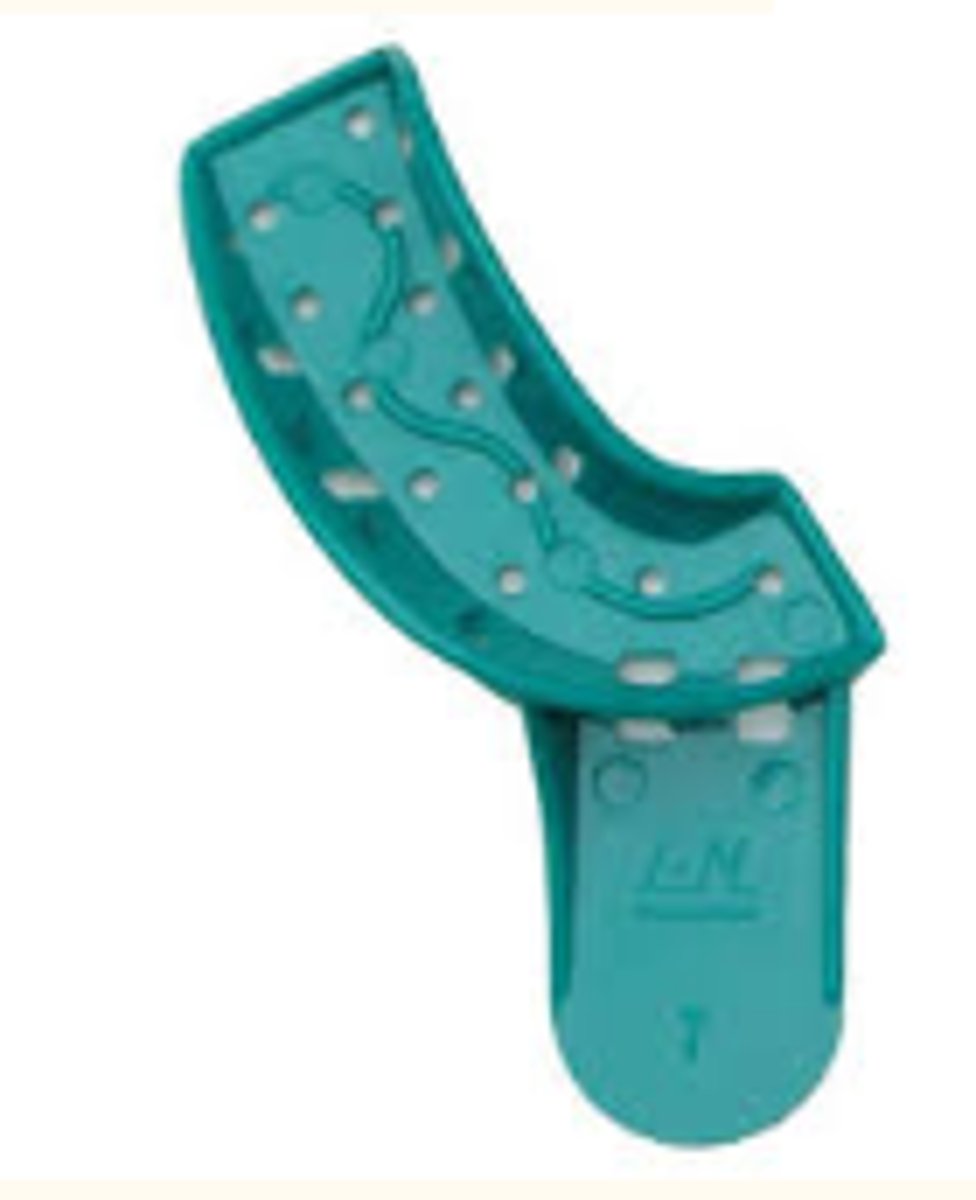
Plastic Quadrant Tray
- Used to hold impression material when capturing a mold of a quadrant

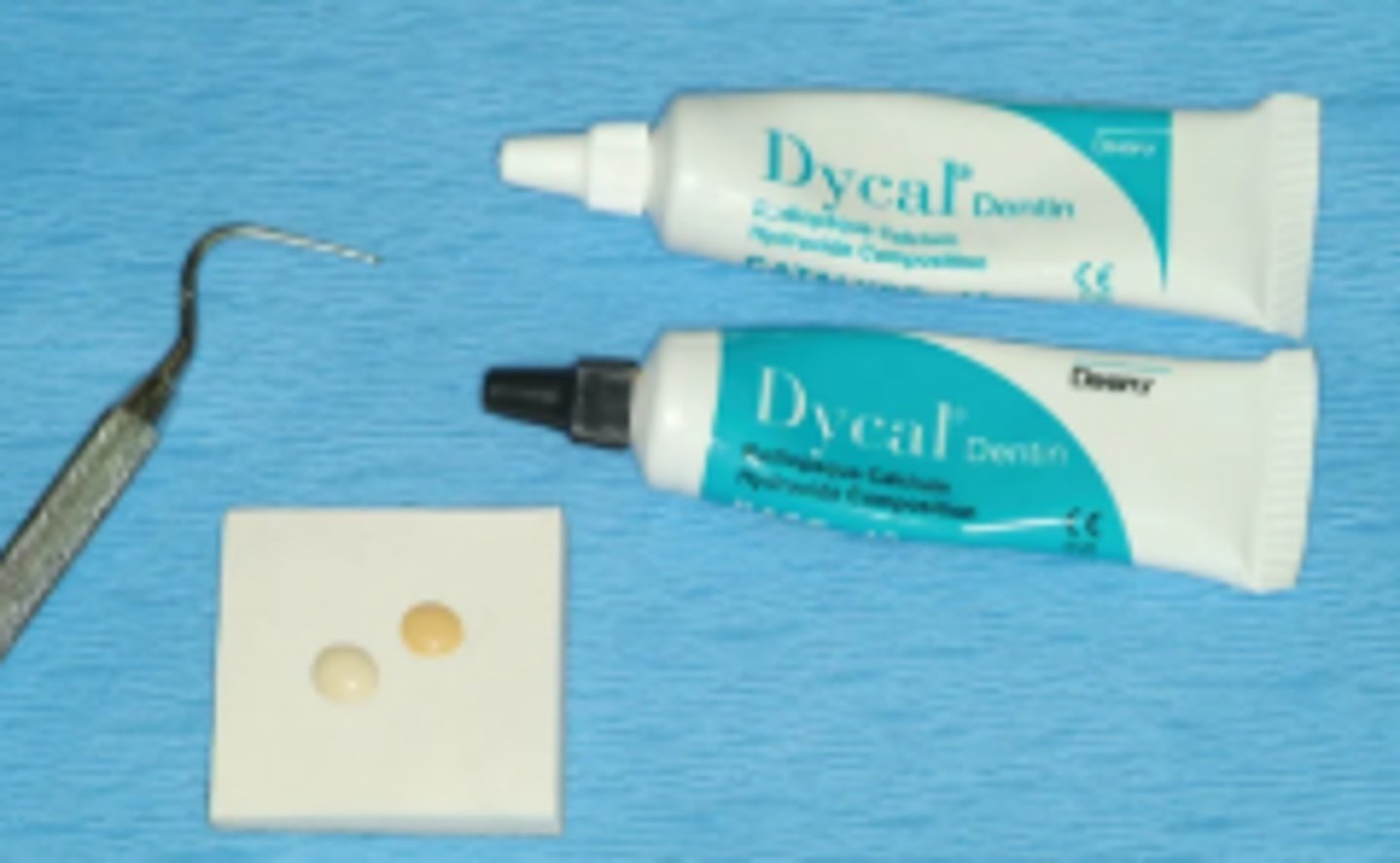
Calcium Hydroxide Base/Liner Material
- Placed as thin layer inside of prepped tooth
- : Protects the pulp, promotes dentin repair
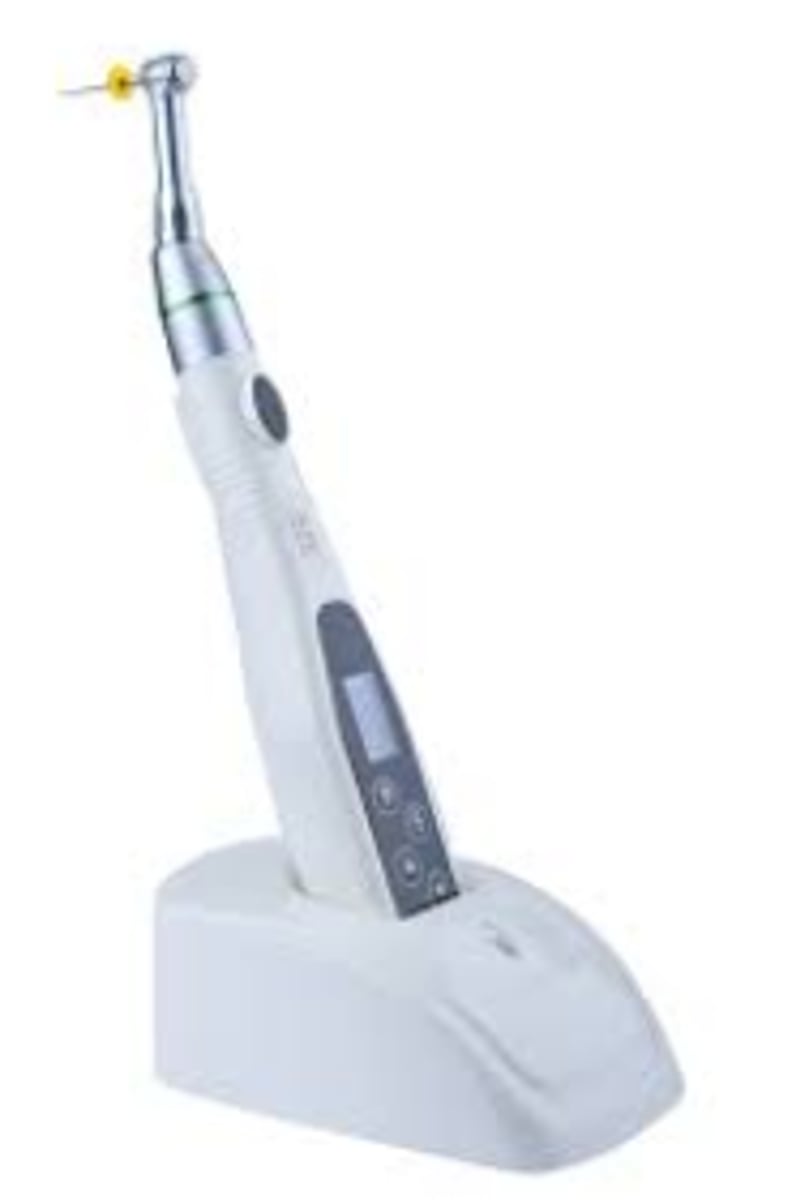
Endodontic Handpiece
- Automates the cleaning and shaping of root canals

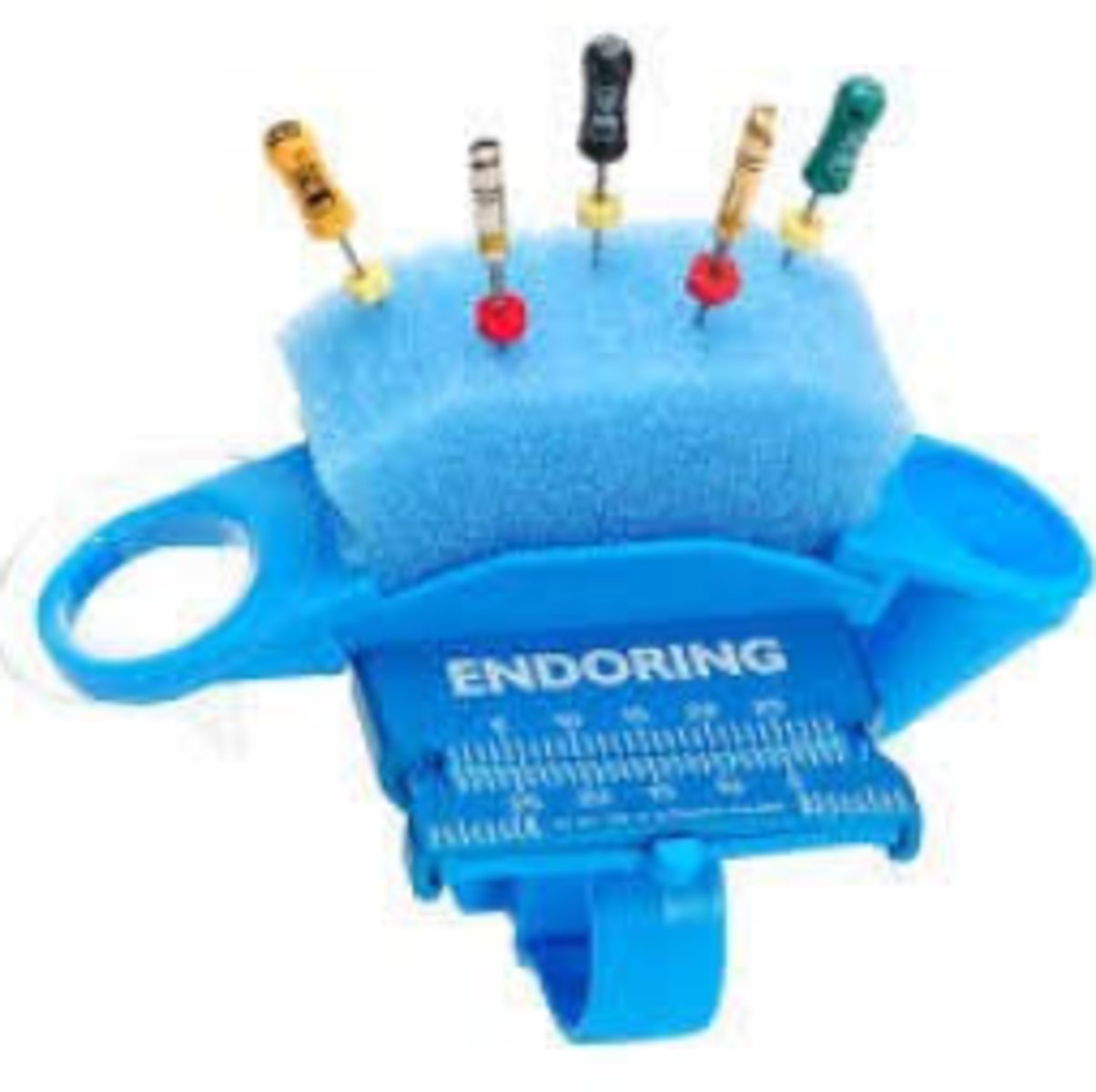
Endo Ring
- A chairside dental accessory that holds and organizes endodontic paper points and files

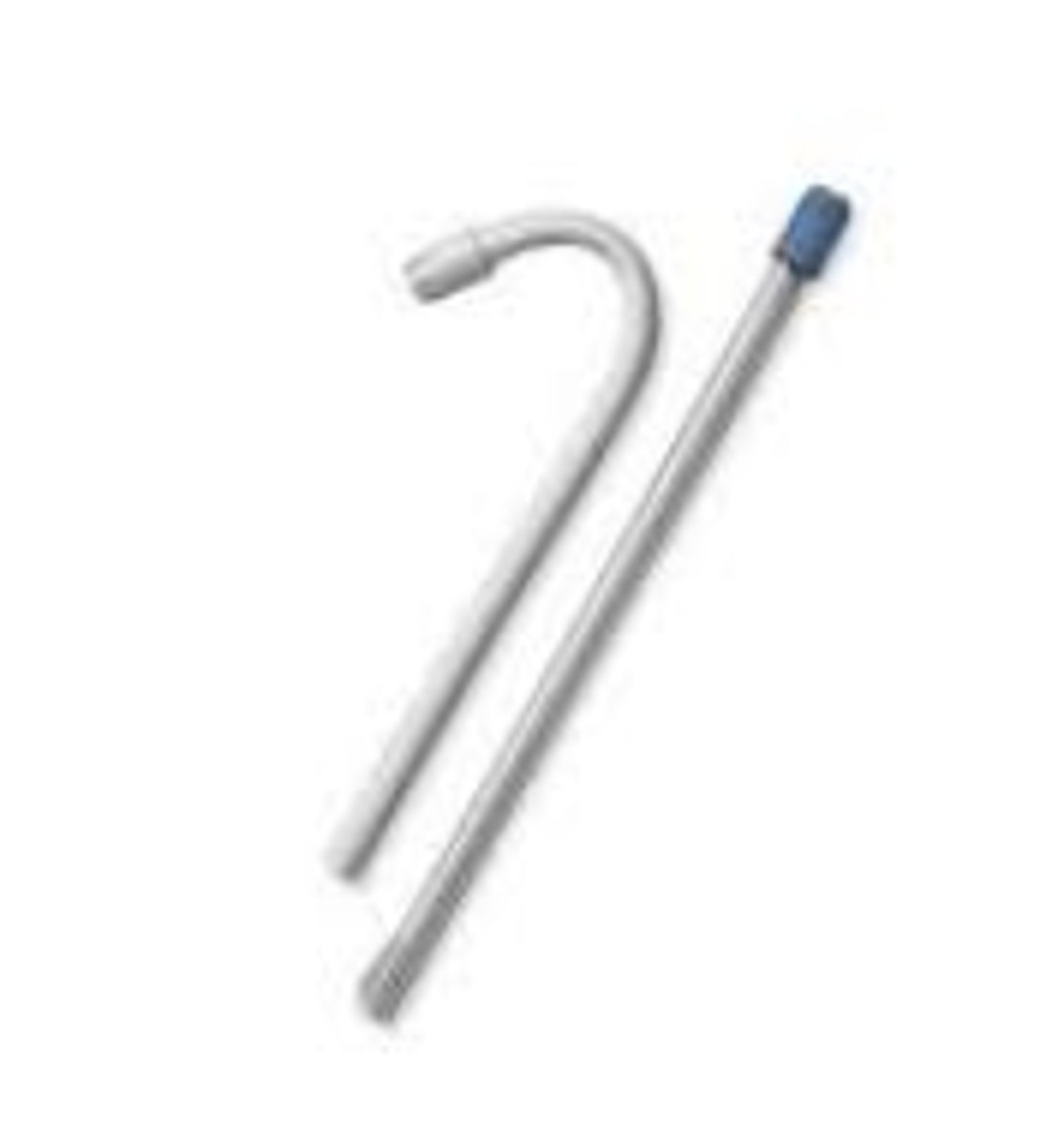
Low-Speed Suction Tip - Saliva Ejector
- Used to remove saliva, water, and light debris from the patient's mouth

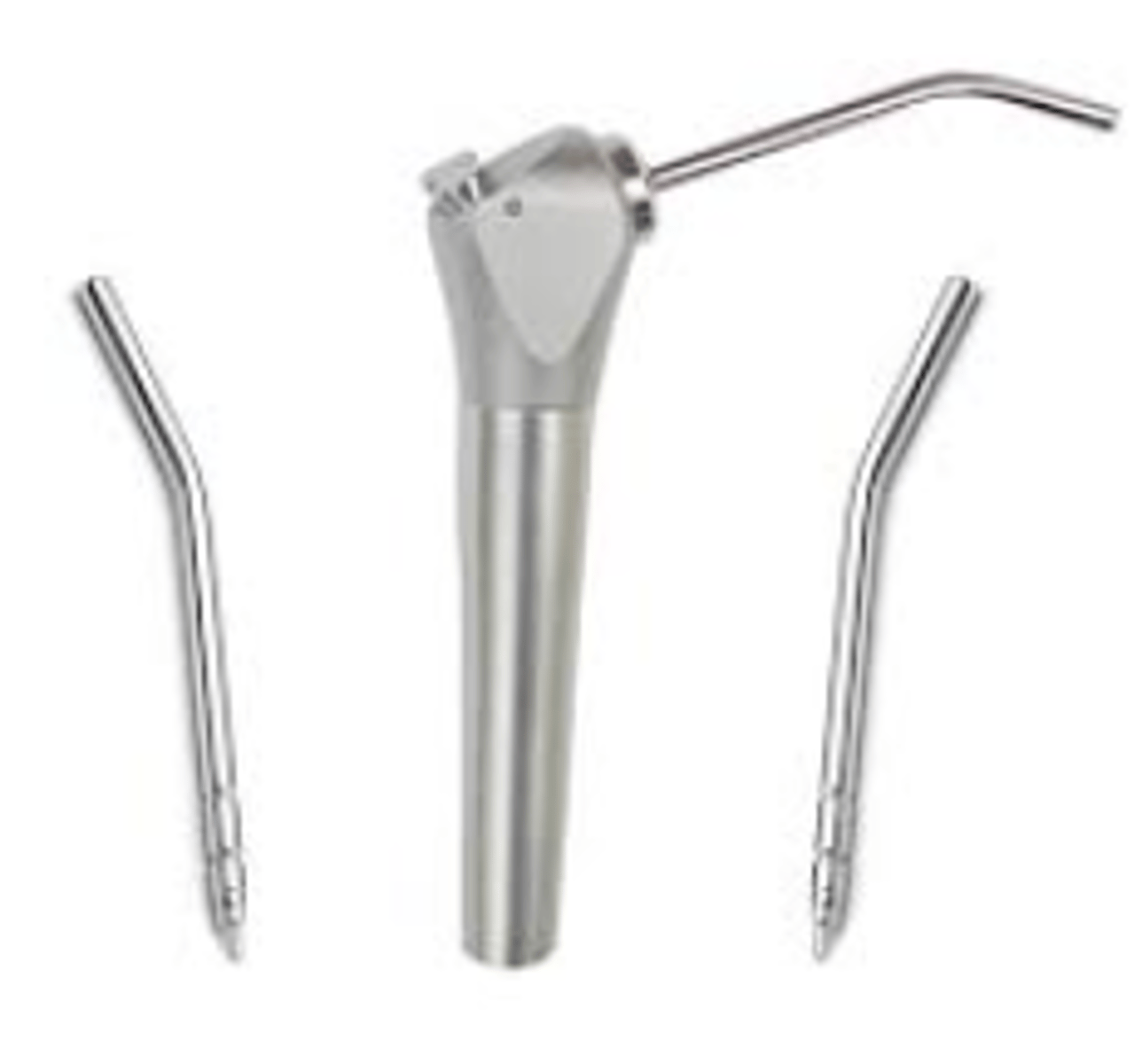
Air/Water Syringe Tip
- Used to deliver a stream of air, water, or a combination of both to the oral cavity

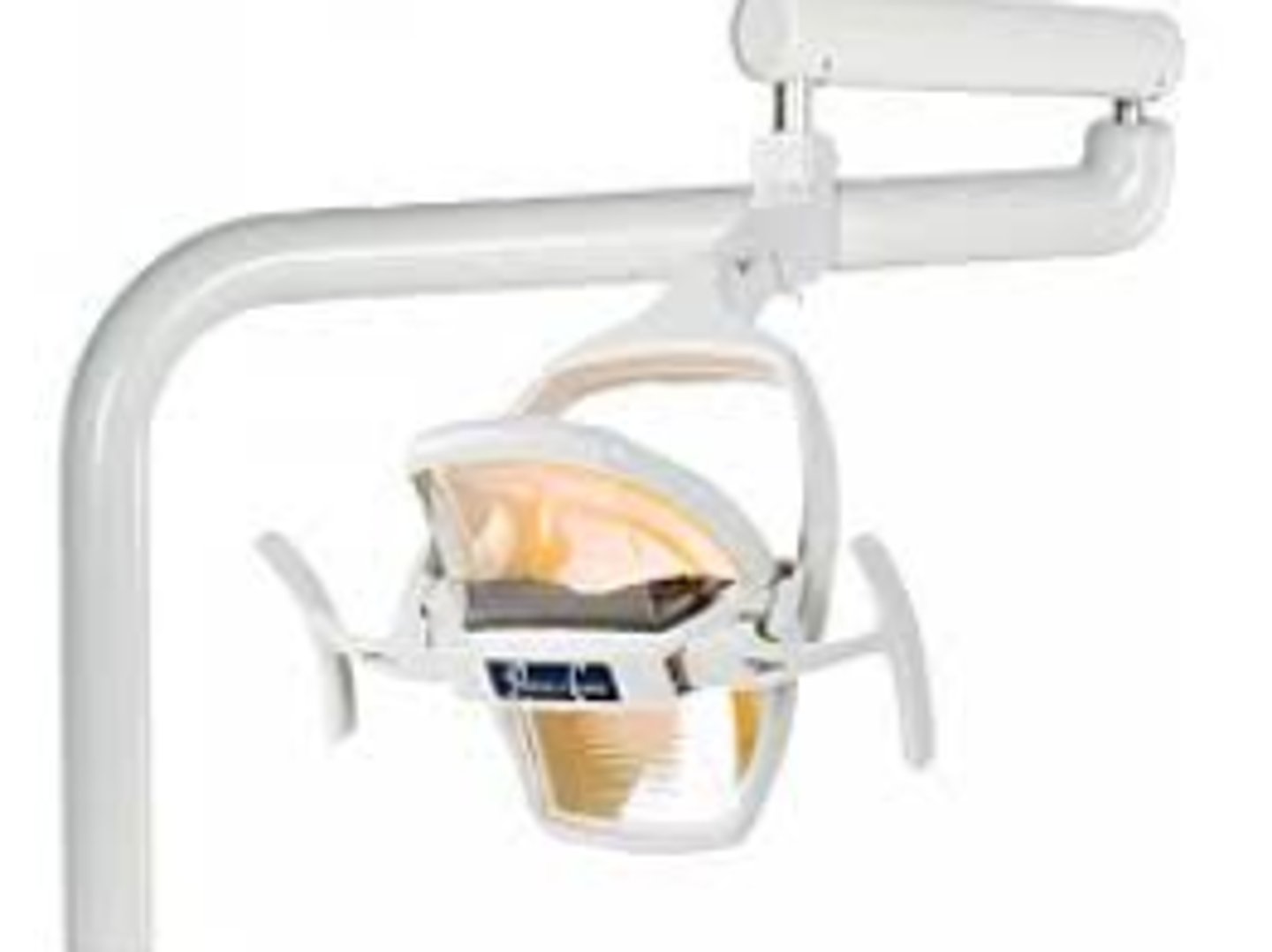
Overhead Light
- Helps the dental team clearly see the teeth, gums, and surrounding tissues during procedures

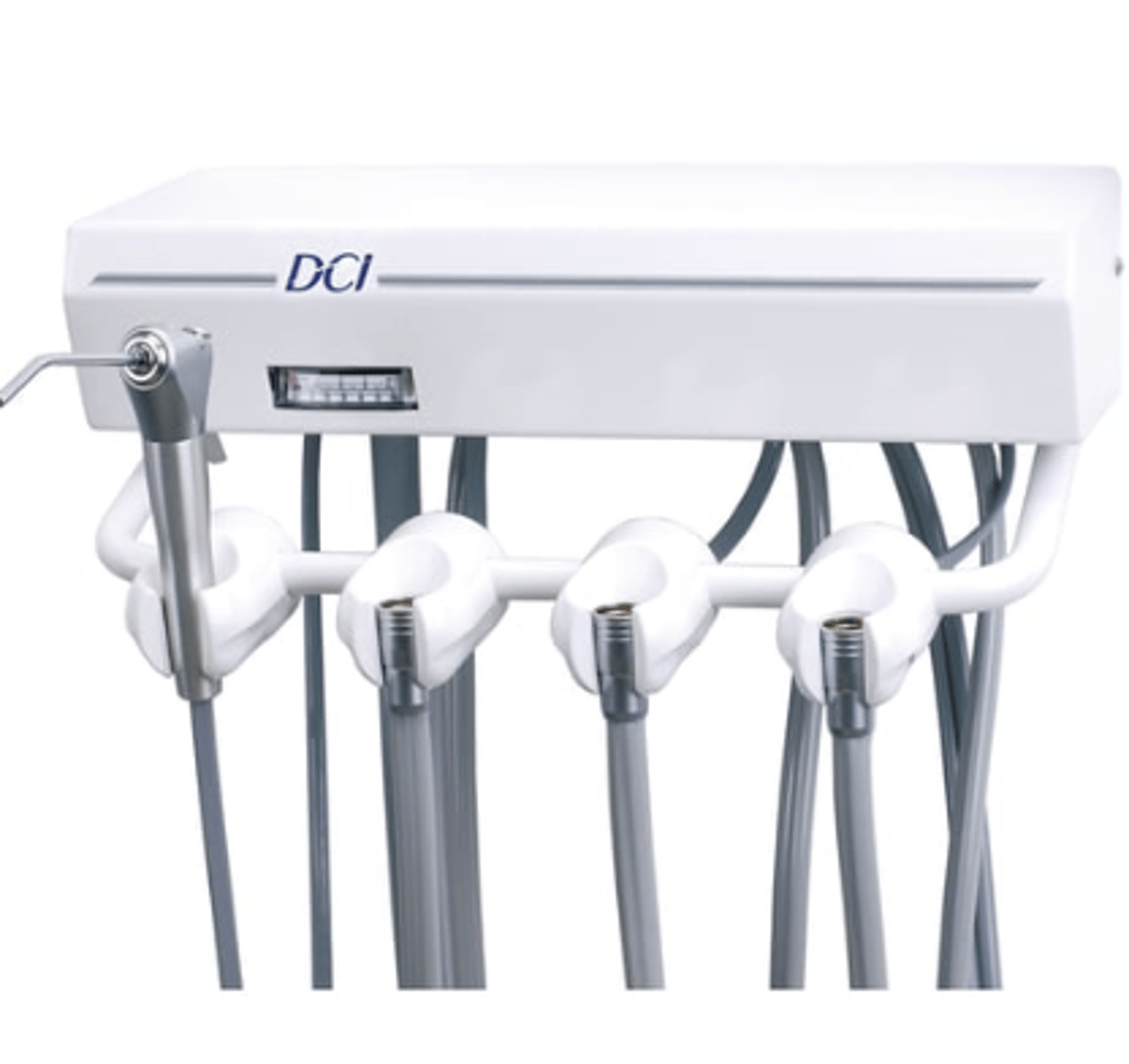
Dental Unit
- Central piece of dental equipment
- Provides power and delivery for dental instruments

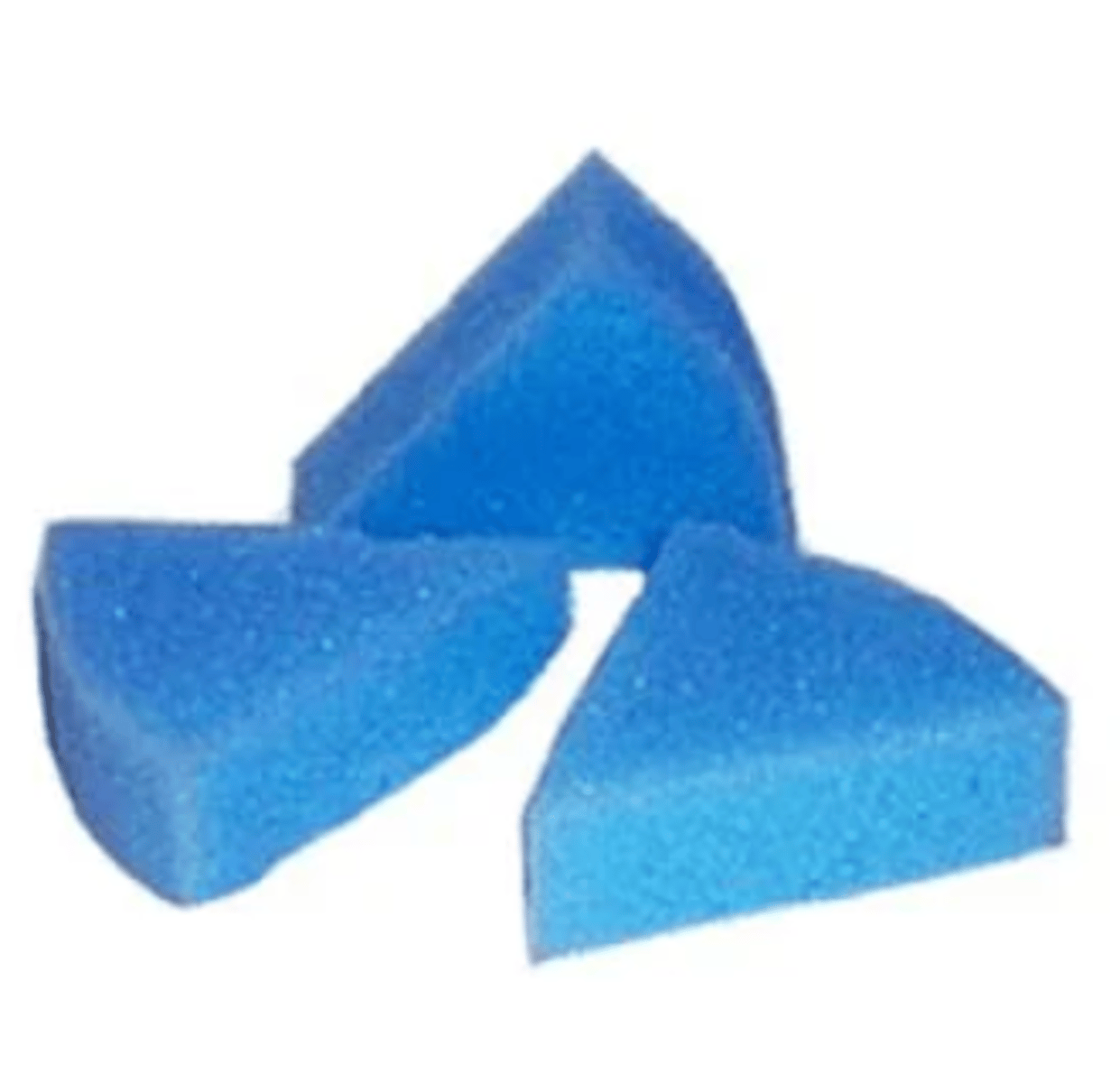
Endo Triangle Foam
- Provides a clean and secure place to stick endodontic instruments between use

Luer Lock Irrigation Syringe
- Safely delivers sodium hypochlorite or other irrigating solutions into the root canal to flush out debris
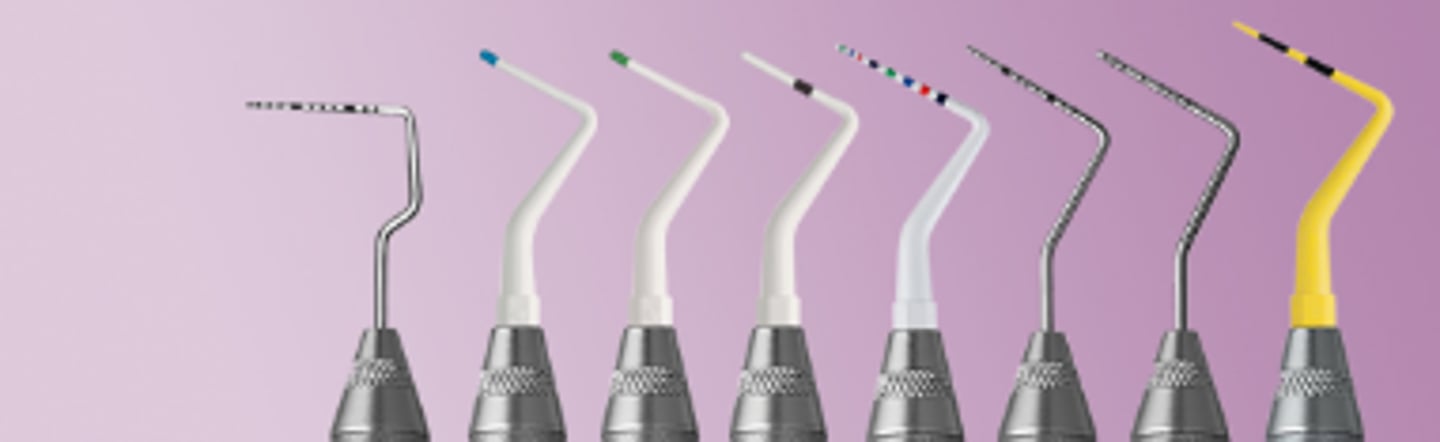
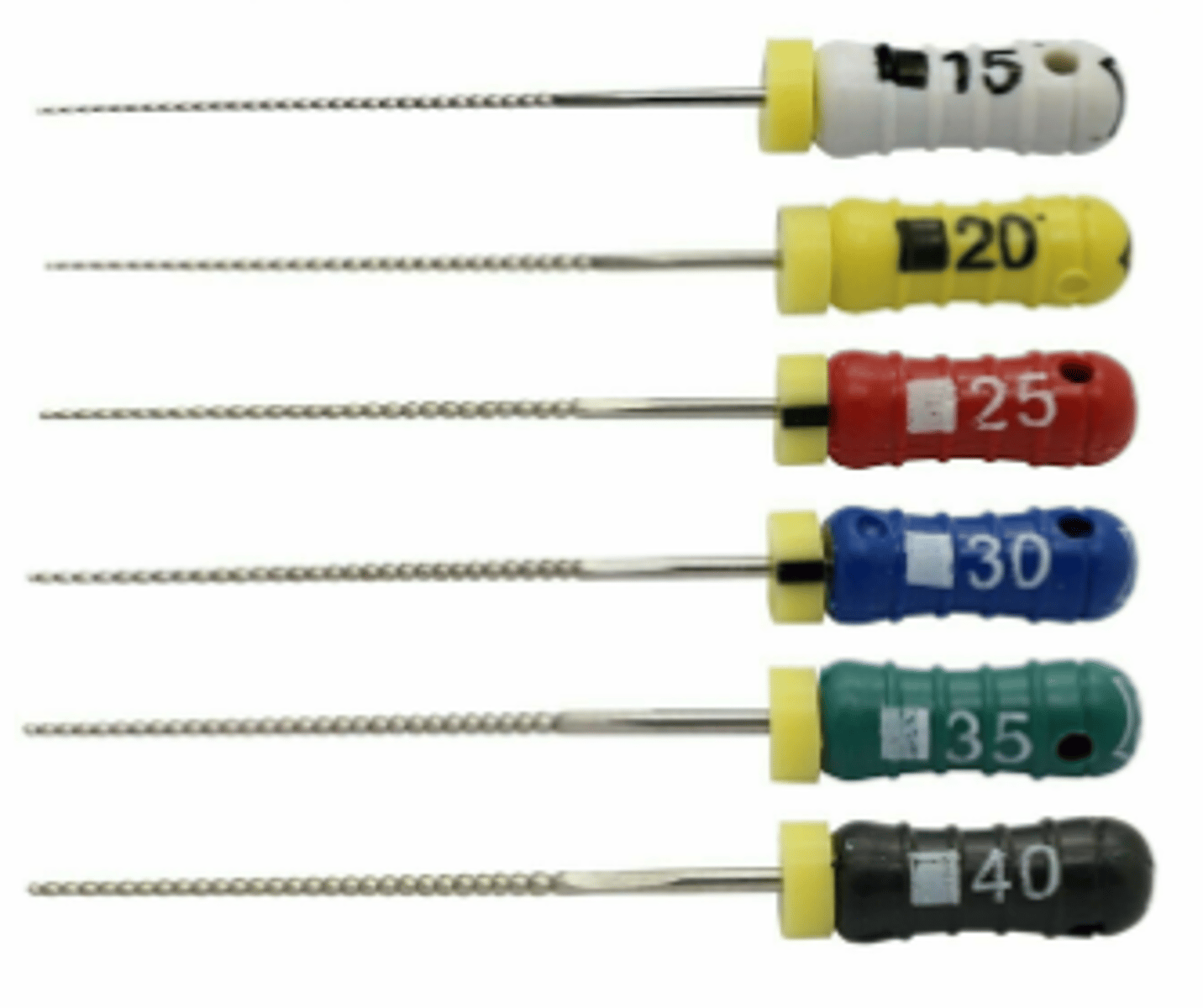
K Files
- Used during root canal treatment to clean and shape the root canals

Sodium Hypoclorite
- Disinfects the root canal by killing bacteria, dissolving organic tissue

Endodontic Spreader
- Designed to laterally compress gutta-percha points against the canal walls during the fiilling process.
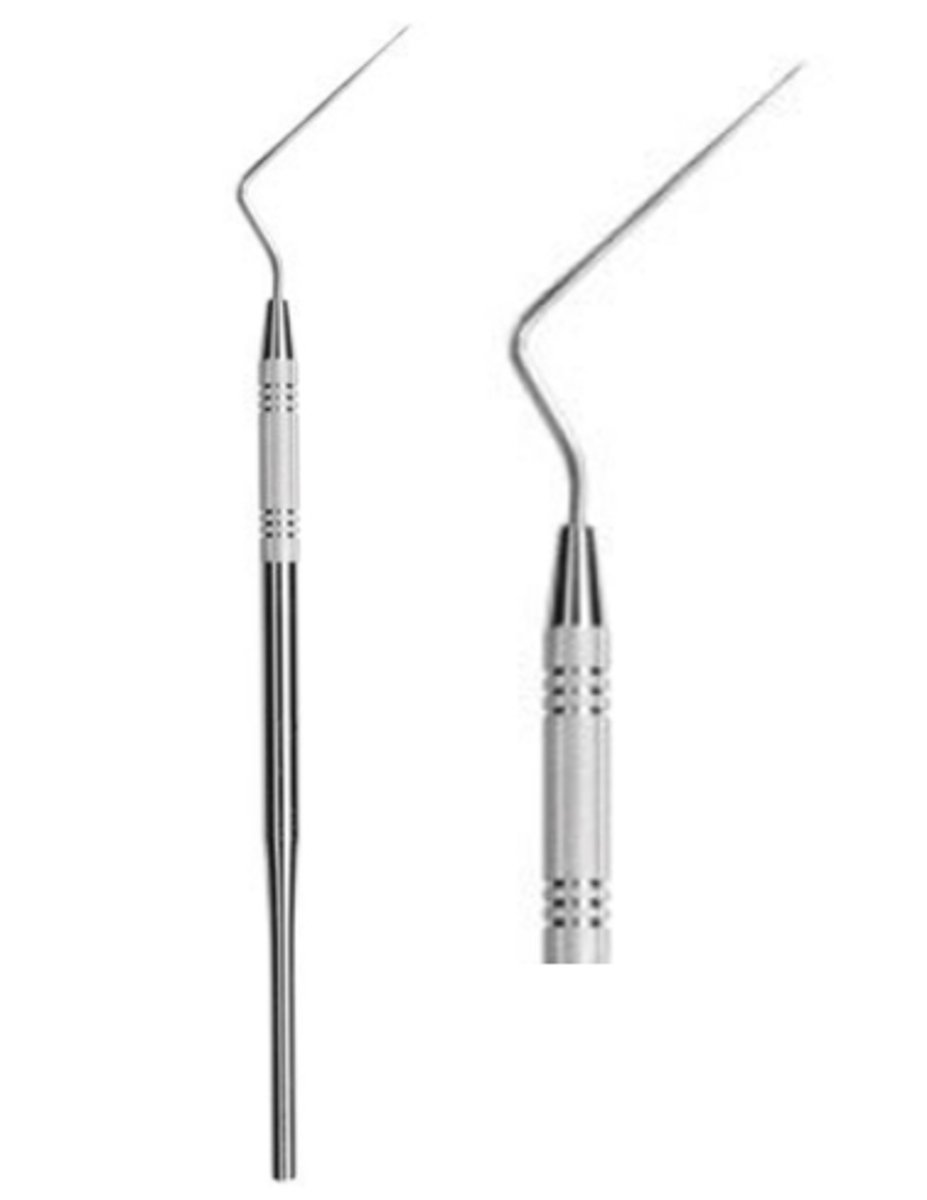
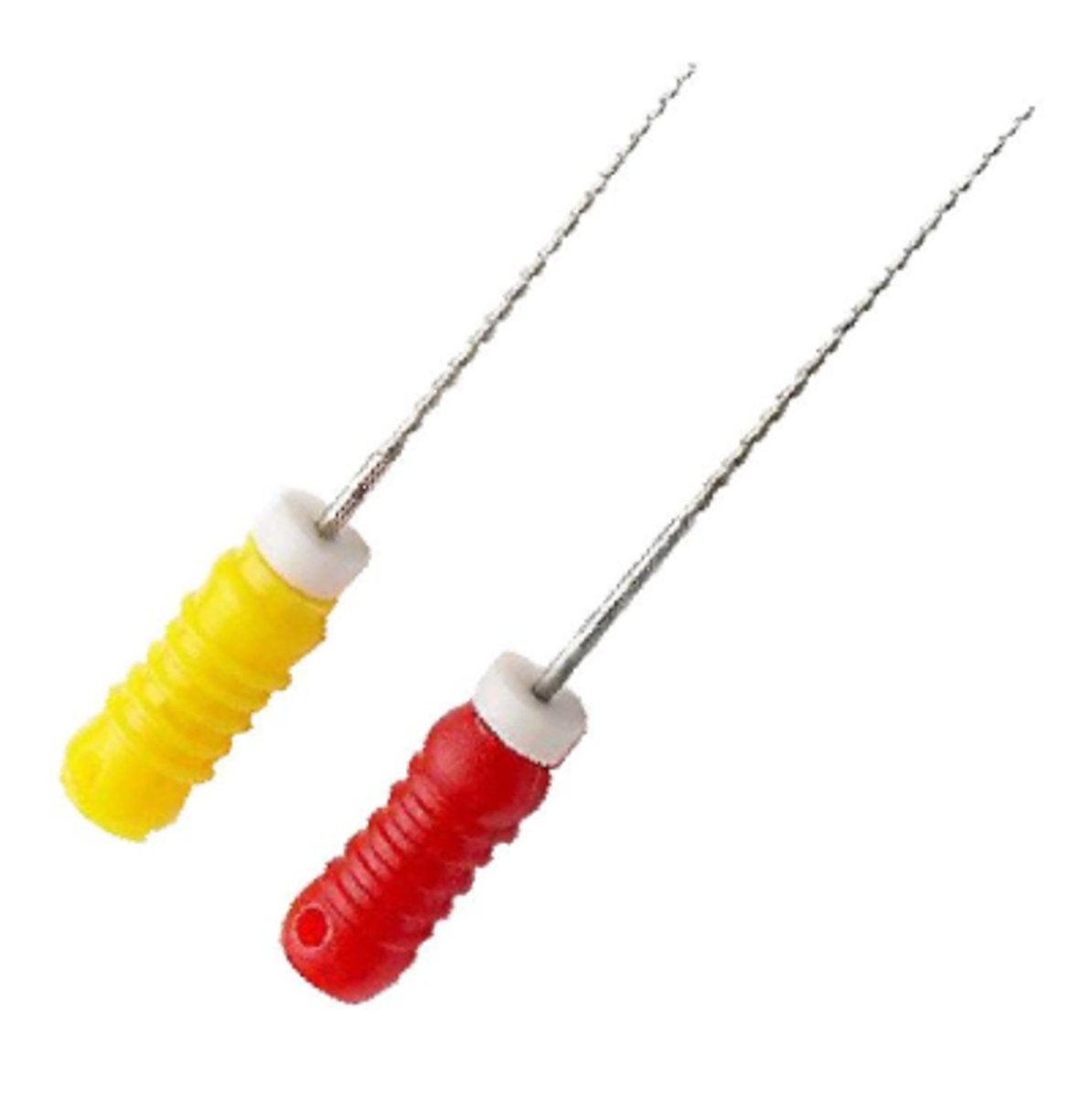
Endo Reamer
- Used during root canal therapy to enlarge and smooth the canal walls by a twisting, filing motio

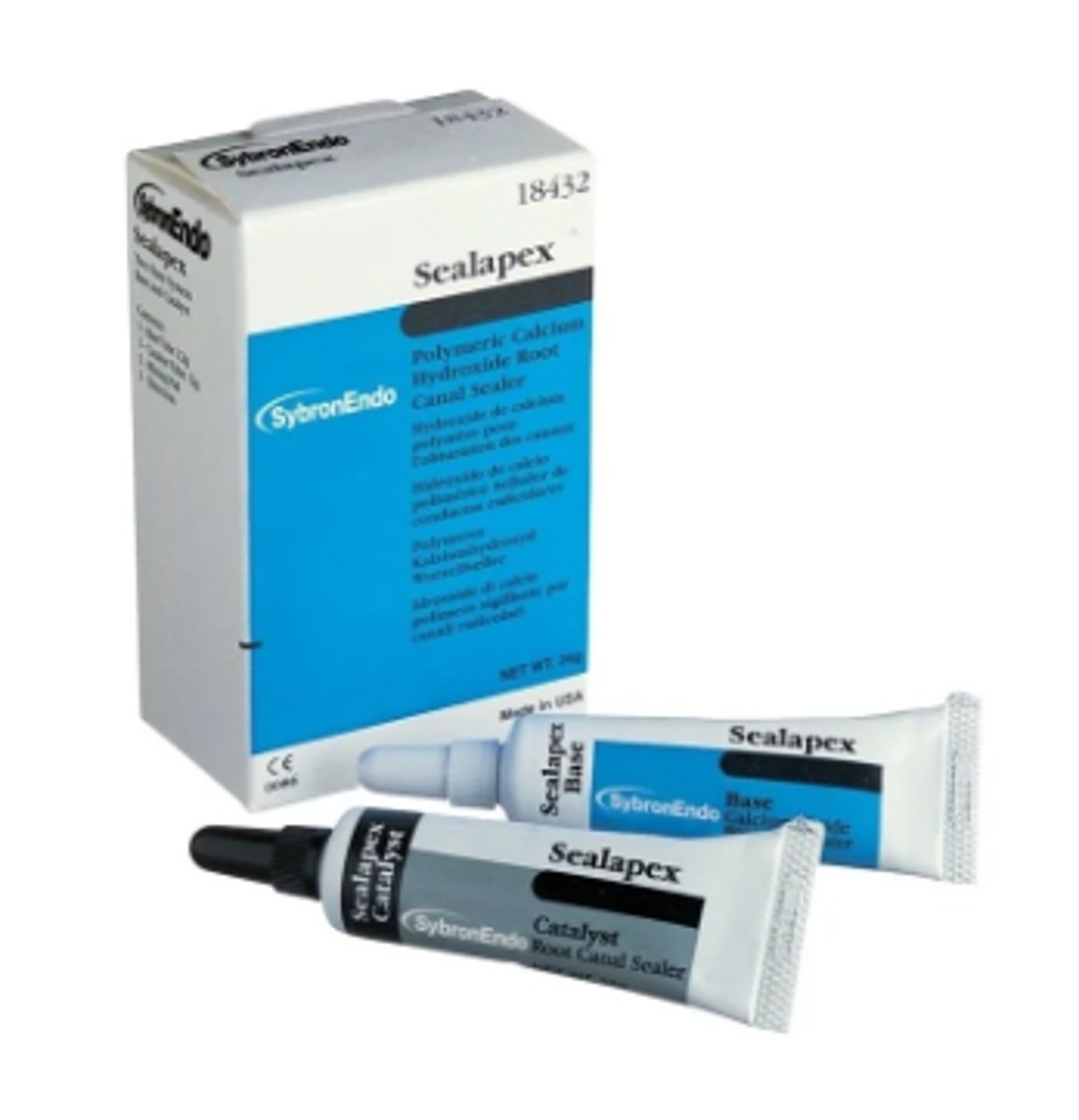
Root Canal Sealer / Cement
- Seals microscopic spaces and irregularities inside the canal, preventing bacteria and fluids from re-entering