System Design Trade-Offs
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Q&A flashcards to review the main system design trade-offs: polling, database modeling, messaging, concurrency, and performance vs. latency.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What are the main system design trade-offs?
Polling Schemes (Polling, Long Polling, SSE, WebSockets)
Messaging & Queues (Kafka, RabbitMQ, SQS, etc.)
Locking schemes (Conditional Writes, Redis, Status)
Database sharding (latency vs performance sharding)
Hot shards (vertical upsizing, fake mapping, reducing frequency of updates)
Rate Limiting Algorithm
Token Bucket
Refill rate and capacity of the bucket
Explain redis holds last timestamp and total tolens left
every operation updates last time accessed along with tokens left and do this atomicallly using lua scripts
expire keys with more than 1hr of old data.
How do you scale to a lot of users
Consistent hashing along with replication of data
Redis cluster uses hash slots.
Minimize Latency overhead
Connection pooling long lived TCP connections. Avoids TCP handshake
Geographical distribution distribute keys to where the usser is (works for 99% god users)
Aggregated queries and caches.
What does rate limiting teach us about maximizing availiblity
Use Redis shard master slave architecture along with asynchronous writes to maximize availiblity as some data loss is acceptable.
Rate Limiting Diagram
Number of redis key value stores
Asynchronous updates using ___ and stored as
2 redis key val
Queues and stored in memory cache
Rate Limiting extra things
L4 vs L7 loadbalancers.
L4/L7 loadbalancers
What are the 4 polling schemes discussed?
Periodic polling
Long polling
Server-Sent Events (SSE)
WebSockets
What are the 5 concurrency/locking approaches?
Conditional Writes - Dynamo DB feature to ensure atomic writes go through only if certain condition is satisfied.
Database locks — useful when lock duration is short.
Limitation: only valid if the locking period is on the order of seconds.
Status table — a separate table or column tracks the status of operations.
Redis lock (Redlock) — distributed locking using Redis.
Optimistic concurrency control — uses version/timestamp; retries if conflicts occur.
What’s the difference between performance-oriented vs latency-oriented design?
Performance-Oriented: Optimized for throughput, can accept latency.
Latency-Oriented: Optimized for responsiveness, sacrifices throughput.
How do you shard data for latency vs to avoid hot shards?
Same-shard for latency: put related records together in one shard so queries are faster.
Con: this can create hot shards (too much load on one shard).
Uniform/random distribution: spread records evenly across shards.
Pro: avoids hot shards.
Con: queries may need to pull from multiple shards, which can increase latency.
What are different messaging queues and tradeoffs
Amazon SQS: Simple queue with visiblity timeout.
Redis Pub/Sub: Fire and Forget approach useful for chat applications and other notification systems
Kafka: Queue with record history useful for auditability and replayability.
When designing notification system what question to ask interviewer
Clarify what kind of notification, web, sma, email push notification go towards a notification database.
How do you deal with a burst of writes like a lot of likes.
Put a message queue
Apply a streaming aggregator to do a bulk update to db and short circuit to message queue
What clarifying questions to ask for a rate limiting system?
Fixed window Go with this
Sliding window heap discuss the other solution
Clarifying question to ask when the user gives you their social media account
How does authentication happen?
Abstract redis sorted sets.
Dont consider the case when all data cant fill in a single shard.
Worst case assume hashing on score id. Using similar concepts like forst pronciple
Aggregator service and heaps?
Break down aggregation into a smaller component for microservice
Mentipn aggregation using hepas
Database optimizations.
Source of____
Reads
Writes
Make database as source of truth.
Always try to ensure reads are coming from caches and avoid reads from data ase
Always do aggregated bupk writes ok database by having aggregator servicez
Media Optimization Step
1) Initially send everything through ___ REST request
POST request but sizing restrictions.
Media Optimization Part 2:
Pre signed URL
Divide input into chunks
MetadataDB stores S3 link along with status
Media Optimization Part 3:
Transcoding
Transcode into different formats asynchrpnosuly
Traseoff betwen more formats and cost versus doing on the fly transcoding.
Media Optimization Part 4. Old data optimization.
Store old data into S3 glacier
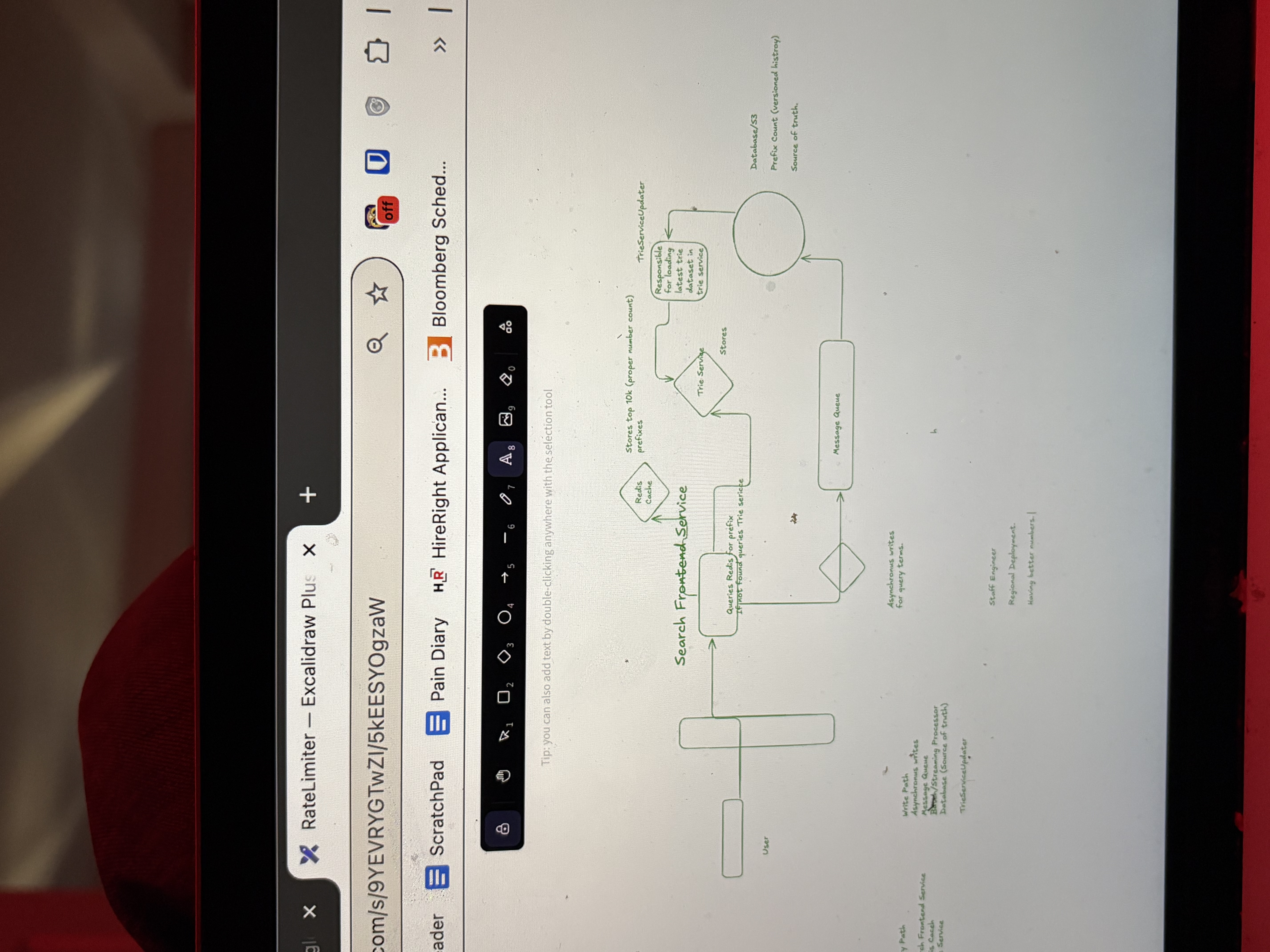
What does typeahead system tell us about numbers and what does that tell is about data layer
Ask the number from the interviewer if it looks right and if it deosnt assume you can always shard.
Always shard the data layer and explain how it is done.
Asynchronous system updates
Always have asynchronous systems creare update with versions into S3 or database as source of truth
Then have an updater service whose job is to replicate this.
What does typeahead system tell us about data schema
For trie service mention the data schema in detail.
Typehaesd system perosnalization
Store the trie (top 1000) and have feature set saved for each user and do a dot product
Typeahead suggestion
Typahead system 2
Web Crawler Major Step
Queue, Hot Path, Processing Path, Controller Logic
Web Crawler: Queue Path
Start with an initial set of URLS and insert into the queue.
Put the elmeents into append only logs, sharded by domain type
Streaming jobs run every k minutes per domain and take one element from the logs and put it into the HotPath Queue(while respecting other nicenes properties)
Web Crawler: Hot Path
Pop elements out from the queue.
Query DNS servers for the IP address (Check first if the element exists in the cache)
HTTP Curl the URL and save it in an S3 bucket indexed on the URL anme
On failure put it back in the queue with exponential backoff.
Web Crawler: Processing Path
Check if the downloaded data is a duplicate or not by comparing it with Redis hashes.
If not duplicate extract it into text, hyperlink and image form and save this in a different S3 bucket.
Web Crawler: Controller Logic
It takes list of new hyperlinks and only adds a new hyperlink if it didn’t exist before.
To miantain niceness and cycles it also tracks the depth of this hyeprlinkand manages the crawl depth to avoid revisiting URLs unnecessarily. The controller logic ensures that the system remains efficient and prevents excessive resource usage.
Web Crawler Number 1B pages
2KB per page 2TB of total memory. IOPS/ seconds x 2TB/x total number of days
Rate Limiting quota types
Consider having different policy enforcement for different user ytypes
Also changes periodically so having pub sub
Time management
10 minute for Requirement + API
Time mangement for High level design
10 minute exactly.
Quantative approach
Always use quantative approach.
Rate Limiting Algorithms
1) Fixed Window - ___
2) Sliding Heap - ___
3) Sliding Counter — ____
4) Refill Window -
– Fixed Window: Easy, but suffers from burst issues.
– Sliding Heap: Accurate, but memory-heavy.
– Sliding Window Counter: Good balance, small memory footprint.
– Token Bucket: Handles bursts and steady rates, an industry standard for distributed systems.
How do you handle idempotenet
Between any two services have a system that is A(idempotent key, input)
Tables for any kind of booking system
Reservation/Payment Details table adn Transaction table
Fault tolerance
Write Ahead Logging
Alternatively break components down into different services with logs in between them.
Real time voitng system
Have options for a question ina. different table so you can link to it.
Numbers
1B users avg qps - 10**4
Peak qps - 10***5
Memory - 1B users 1KB each 1TB * 2 for replicabikity
Nimbers
1Billion users 1KB each data
Peak throughout - 10**5
0.1TB/s
Kafka main blocker is EBS which is around 1GB/s
M5 large
You need 100 such machines along with replicability. Times 3 for quorum.
Different consistency options
AWS global tables
Every region has its master along with replication for eventual consistency
Self consistency is very important so store it in client logic.
POST request limit
Web Servers (2GB) API Gatewy 10(MB)
Whenever there is images, videos Instagram or Dropbox use__
CDN