General Chemistry 1 Exam 1 Study Guide
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
pure substance
A sample of matter, either a single element or a single compound, that has definite chemical and physical properties
mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined
elements
A molecule composed of one kind of atom; cannot be broken into simpler units by chemical reactions.
compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
physical property
a characteristic of a substance that does not involve a chemical change, such as density, color, or hardness
chemical property
a property of matter that describes a substance's ability to participate in chemical reactions
states of matter
solid: fixed volume and shape
liquid: fixed volume, no fixed shape
gas: no fixed volume or shape
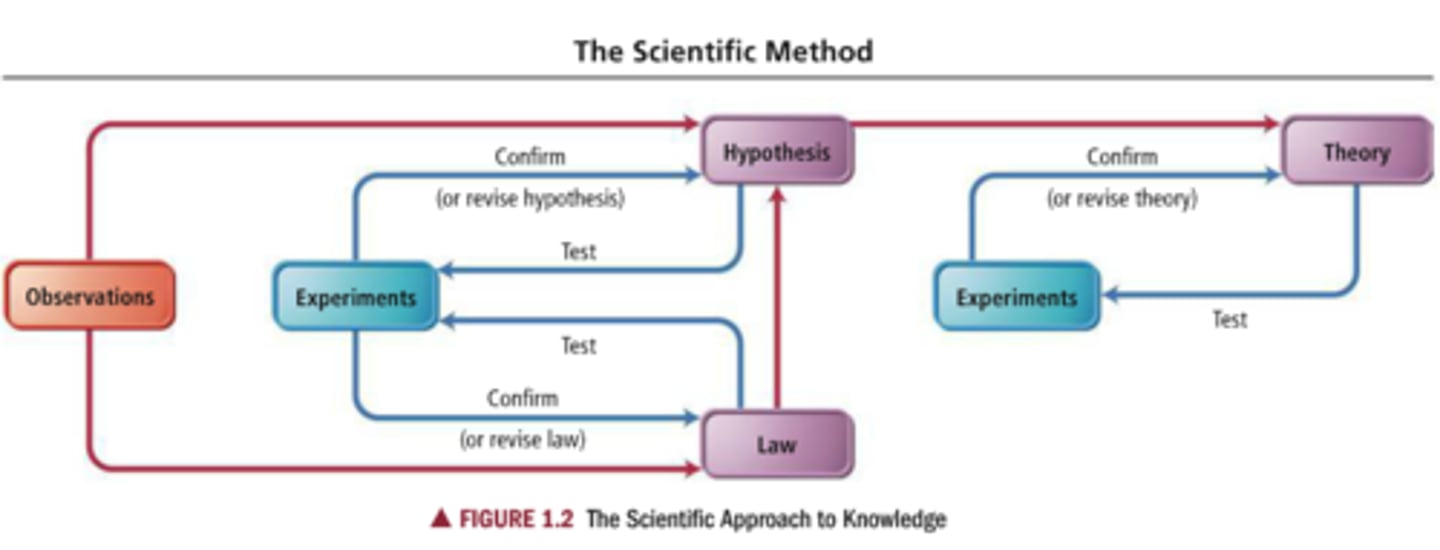
steps of scientific method
observations are made and from those observations hypothesis and laws are made and then are retested by experiments and may be revised, and if enough hypothesis become well established they can form a theory which is then retested and if needed revised
observation
What is seen or measured
hypothesis
A proposed, scientifically testable explanation for an observed phenomenon.
theory
a model for what nature is and why, formed by one or more well established hypothesis
experiment
An investigation done in order to make a discovery or test a hypothesis
scientific law
a brief statement that summarizes past observations and predicts future ones
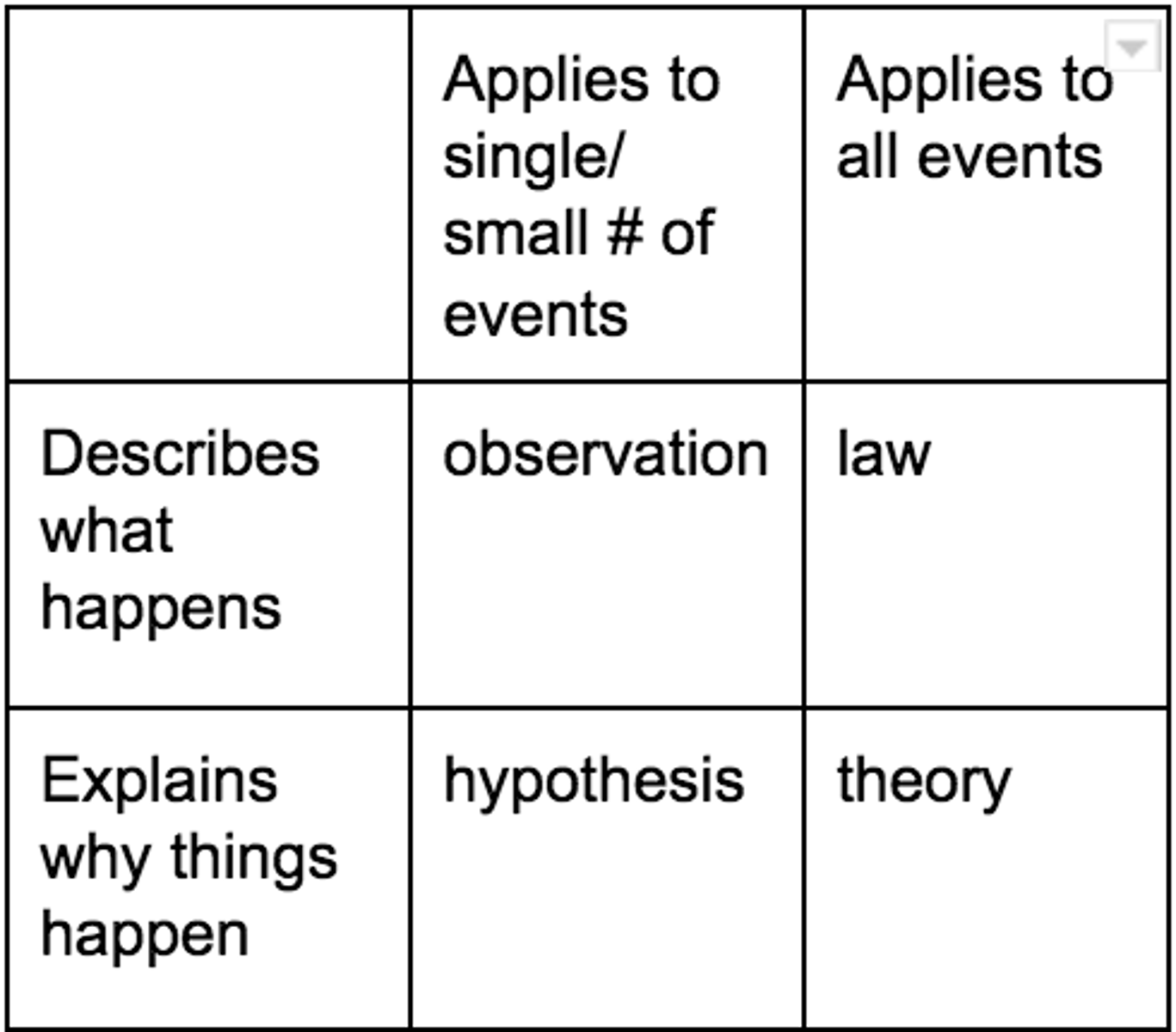
hypothesis vs law vs observation vs theory
Describes what happens: observation, law
Describes why things happen: hypothesis, theory
Applies to single/small # of events: observation, hypothesis
Applies to al events: law, theory
SI unit for mass
kilogram (kg)
SI unit for length
meter (m)
SI unit for time
second (s)
SI unit for temperature
Kelvin (K)
SI unit for amount of substance
mole (mol)
pico-
10^-12
nano-
10^-9
micro-
10^-6
milli-
10^-3
centi-
10^-2
deci-
10^-1
kilo-
10^3
macro-
10^6
1L=Xgal
0.264
1kg=Xlbs
2.2046
1km=Xmil
0.622
1in=Xcm
2.54
1cm^3=Xml
1
SI unit for volume
cubic meter (m^3)
SI unit for density
kilogram per meter cuber (kg/m^3)
density formula
D=m/v
1 celsius= X kelvin
274.15 (C+273.15)
32 Fahrenheit= X celsius
0 (C=(F-32)*5/9)
percision
how close measurements are to the mean
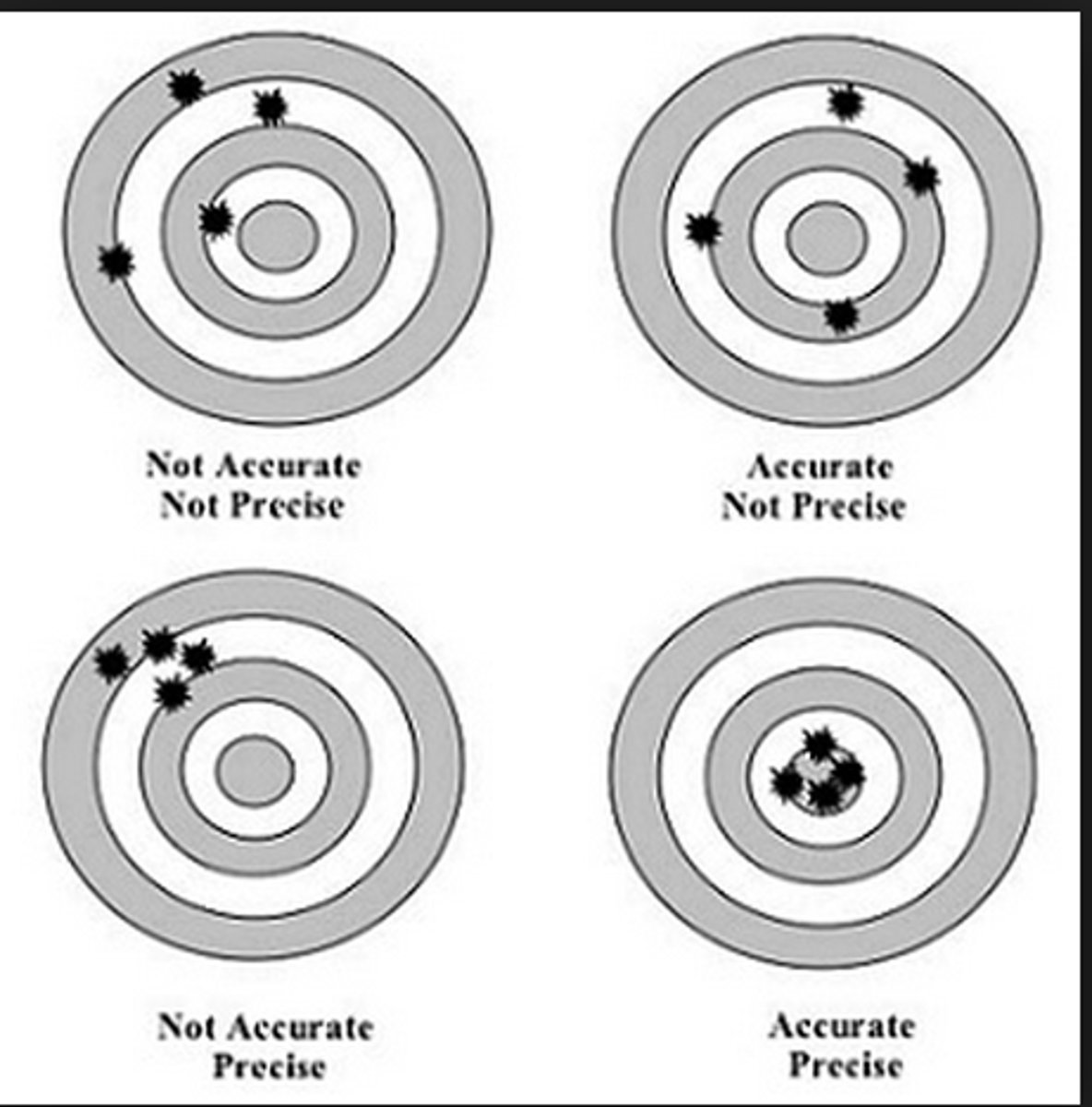
accuracy
how close measurements are to the actual value or target
formula for cylinder volume
(2πr)H
formula for sphere volume
3/4πr^3
formula for cube volume
L^3
formula for rectangular prism
LWH
law of conservation of mass
the mass of the reactants will be the same as the mass of the products
law of definite proportions
all samples of a given compound have the same ratio of components
law of constant composition
mass % of each element in a compound is fixed
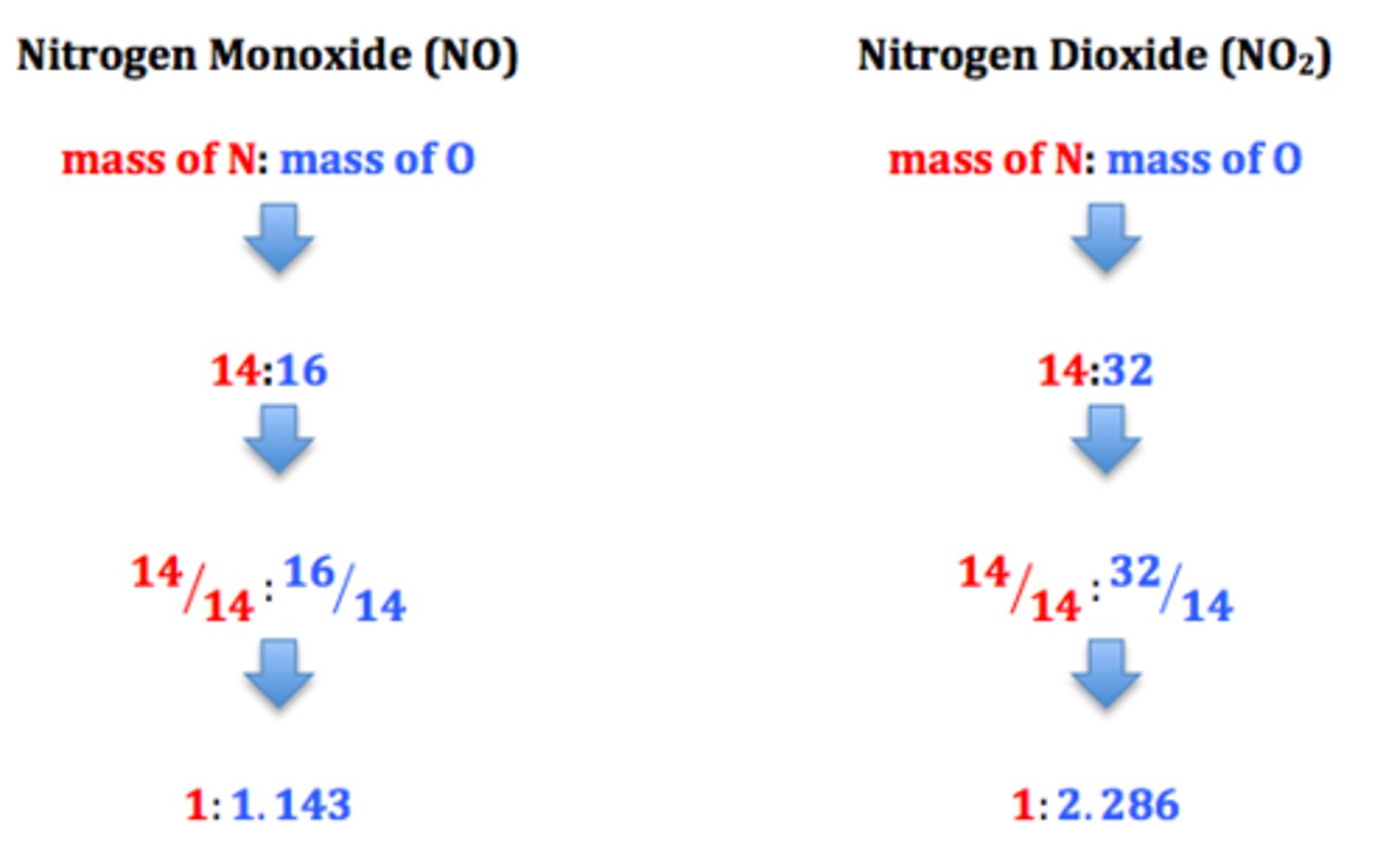
law of multiple proportions
when two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small, whole numbers
mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
atomic mass
(chemistry) the mass (in atomic mass units) of an isotope of an element
average atomic mass
weighted average of the atomic masses for the isotopes of an element
atomic number
Number of protons
average atomic mass formula
atomic mass=(percent abundance)*(amu)+ percent abundance and masses of other isotopoes
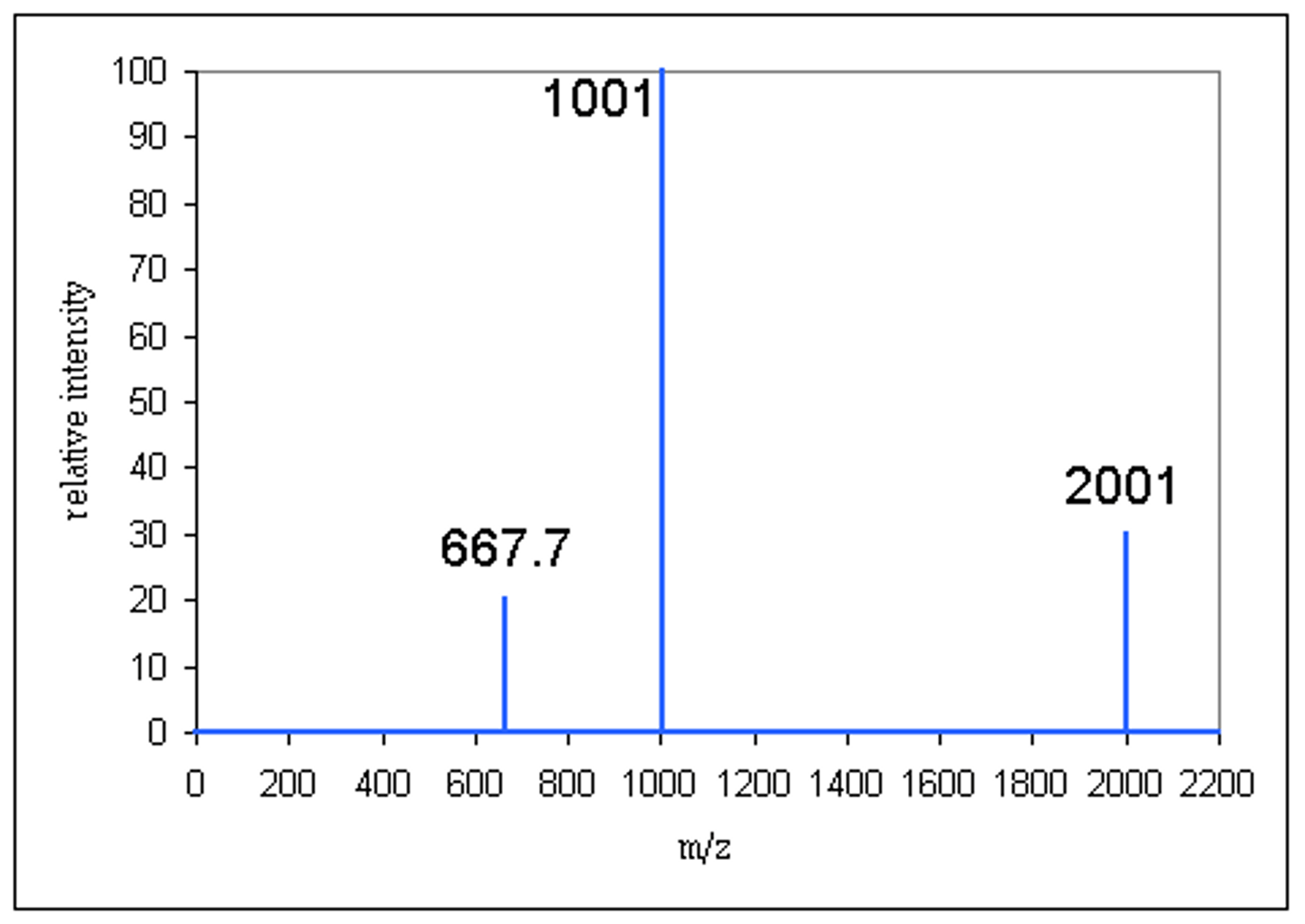
how to solve for % abundance on a mass spectrometer relative scale
(% intensity you wish to find the percent abundance of/ sum of all percent intensities on spectrum) * 100
practice for identifying elements
(https://quizlet.com/64089/elements-of-the-periodic-table-and-their-symbols-flash-cards/)
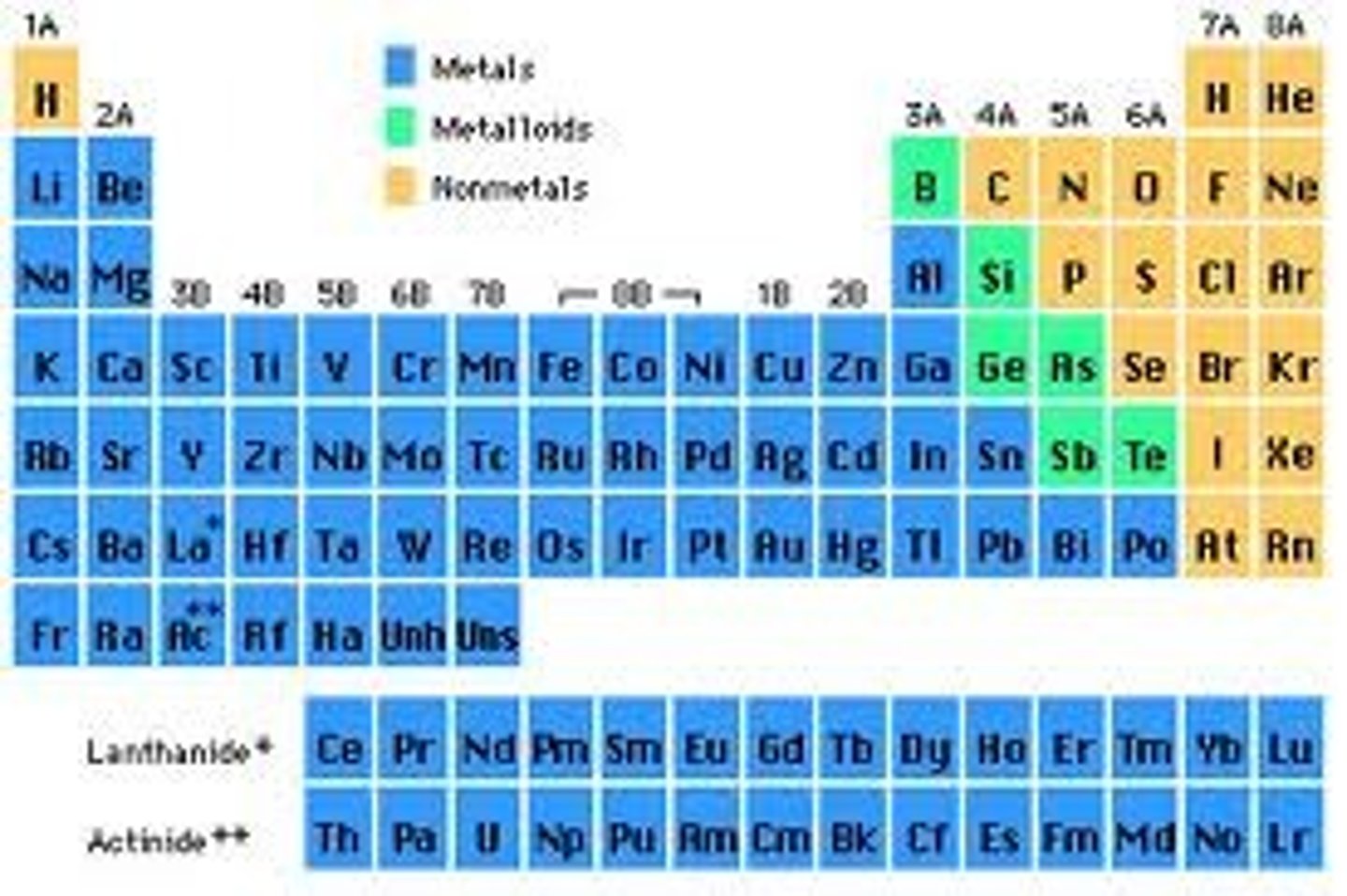
metals on periodic table
(i will have a periodic table and show you were i think the metals are and you tell me if I am correct from the answer key)(hydrogen is not a metal)
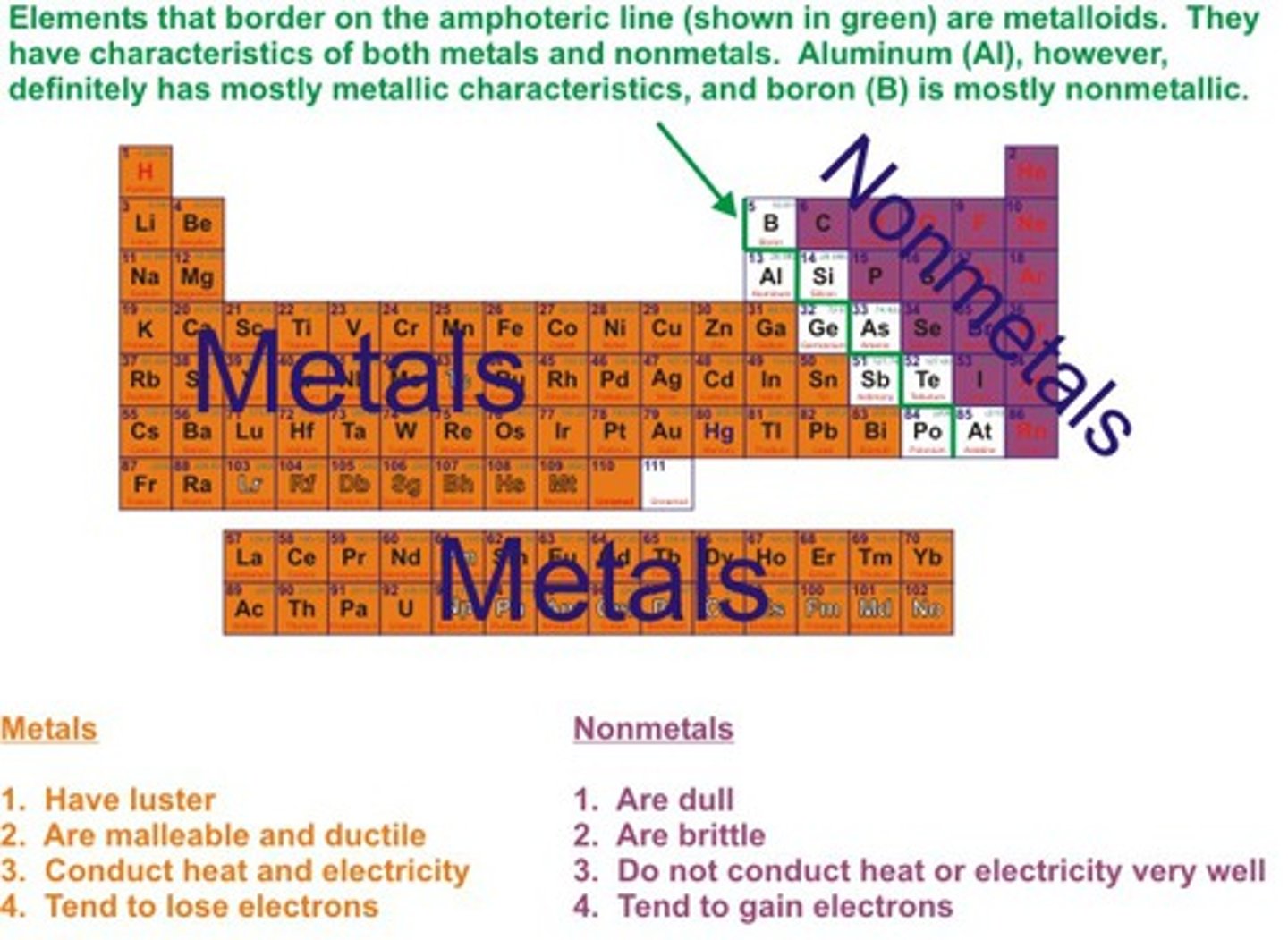
nonmetals on the periodic table
(orange ones are nonmetals)
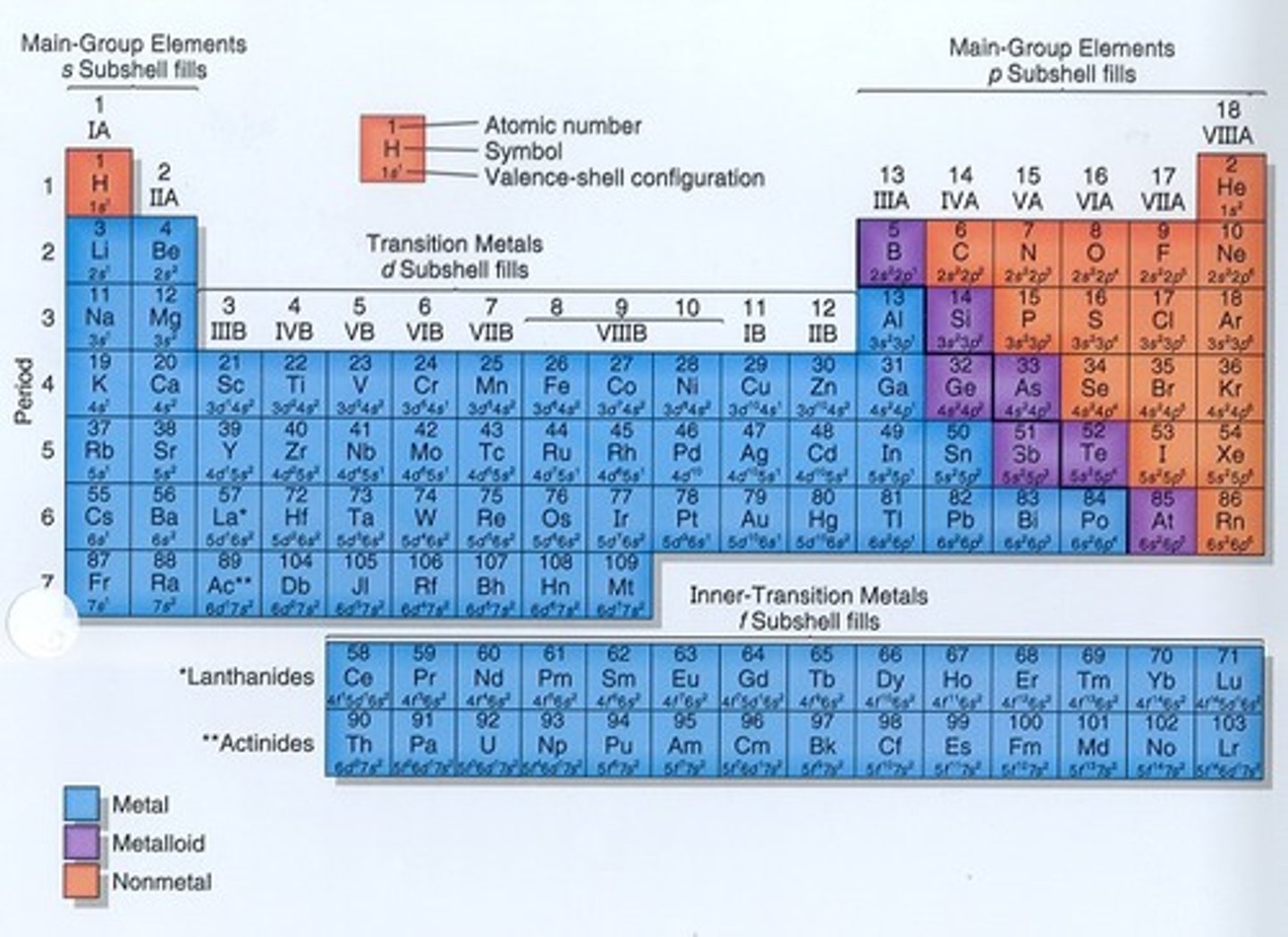
metalloids on the periodic table
(greens are metalloids)
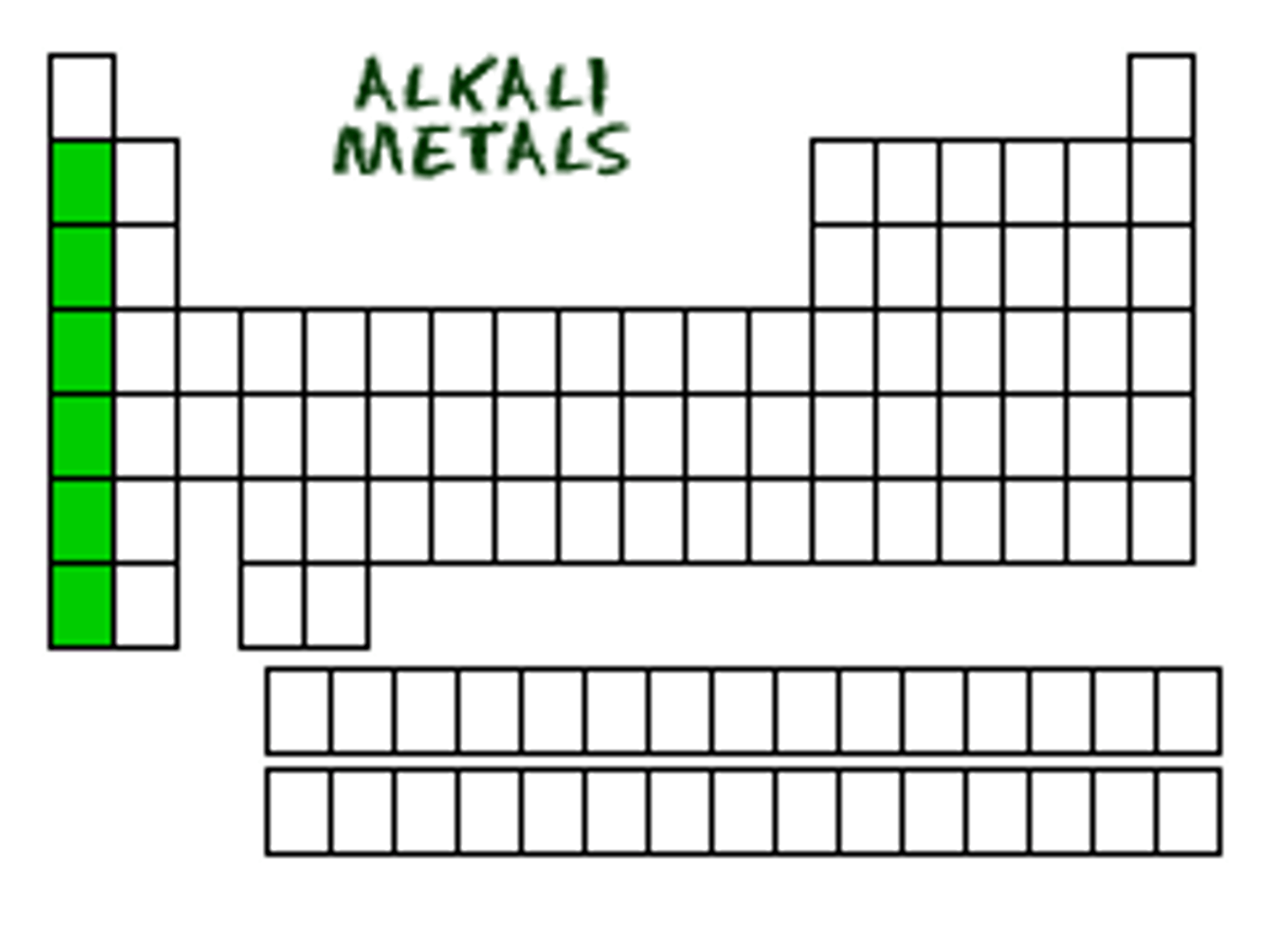
alkali metals
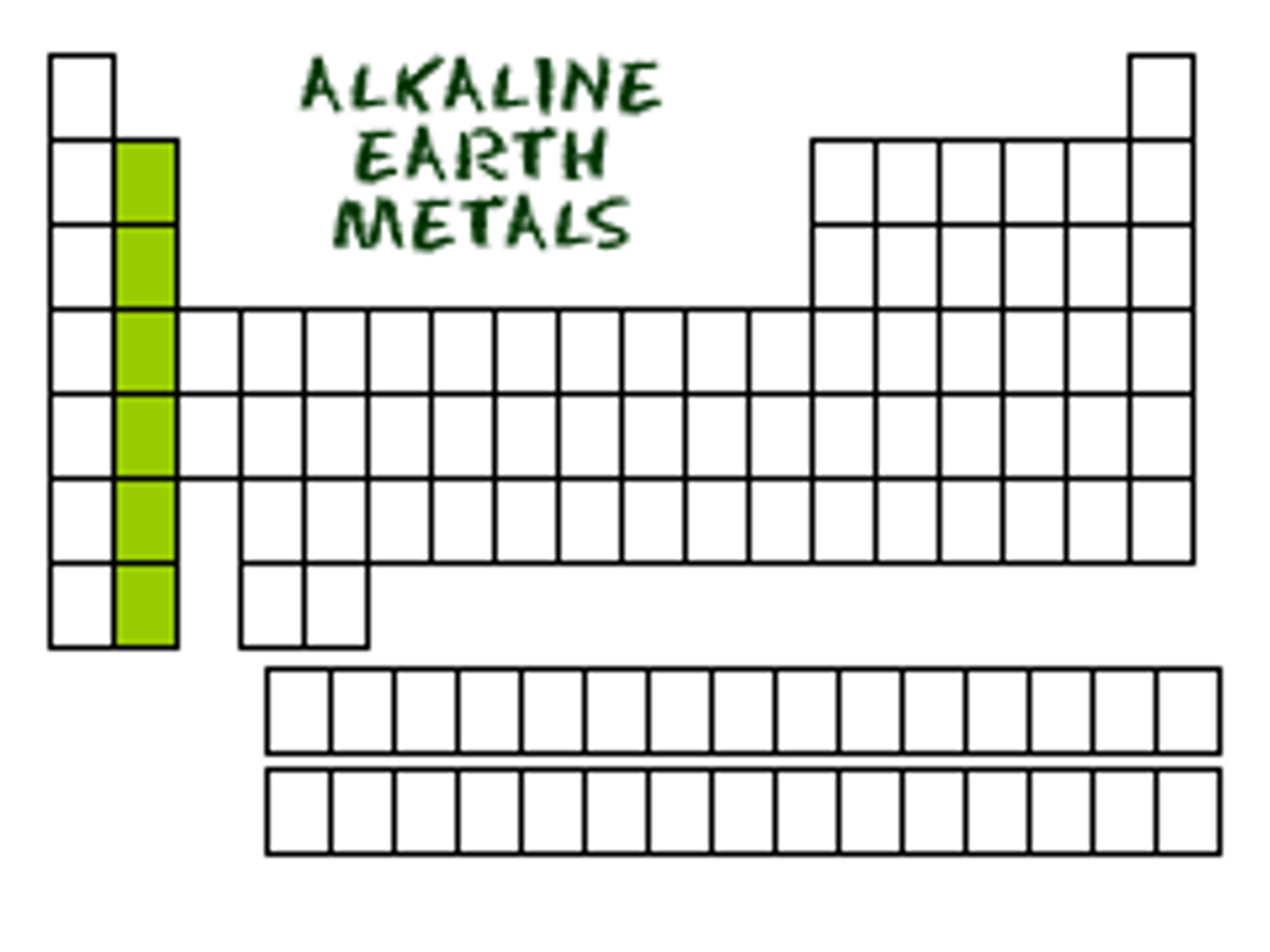
alkaline earth metals
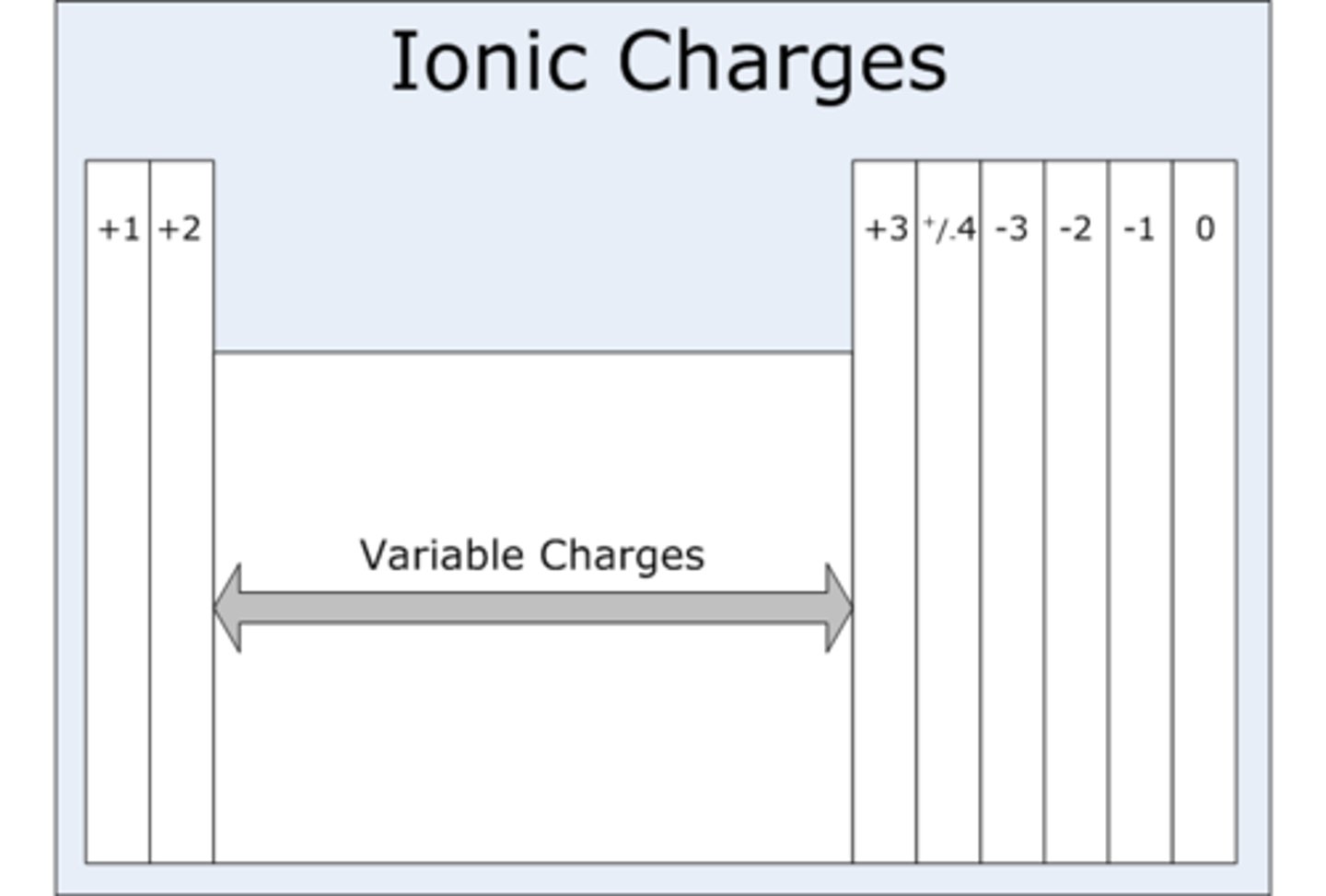
charge of ions on periodic table
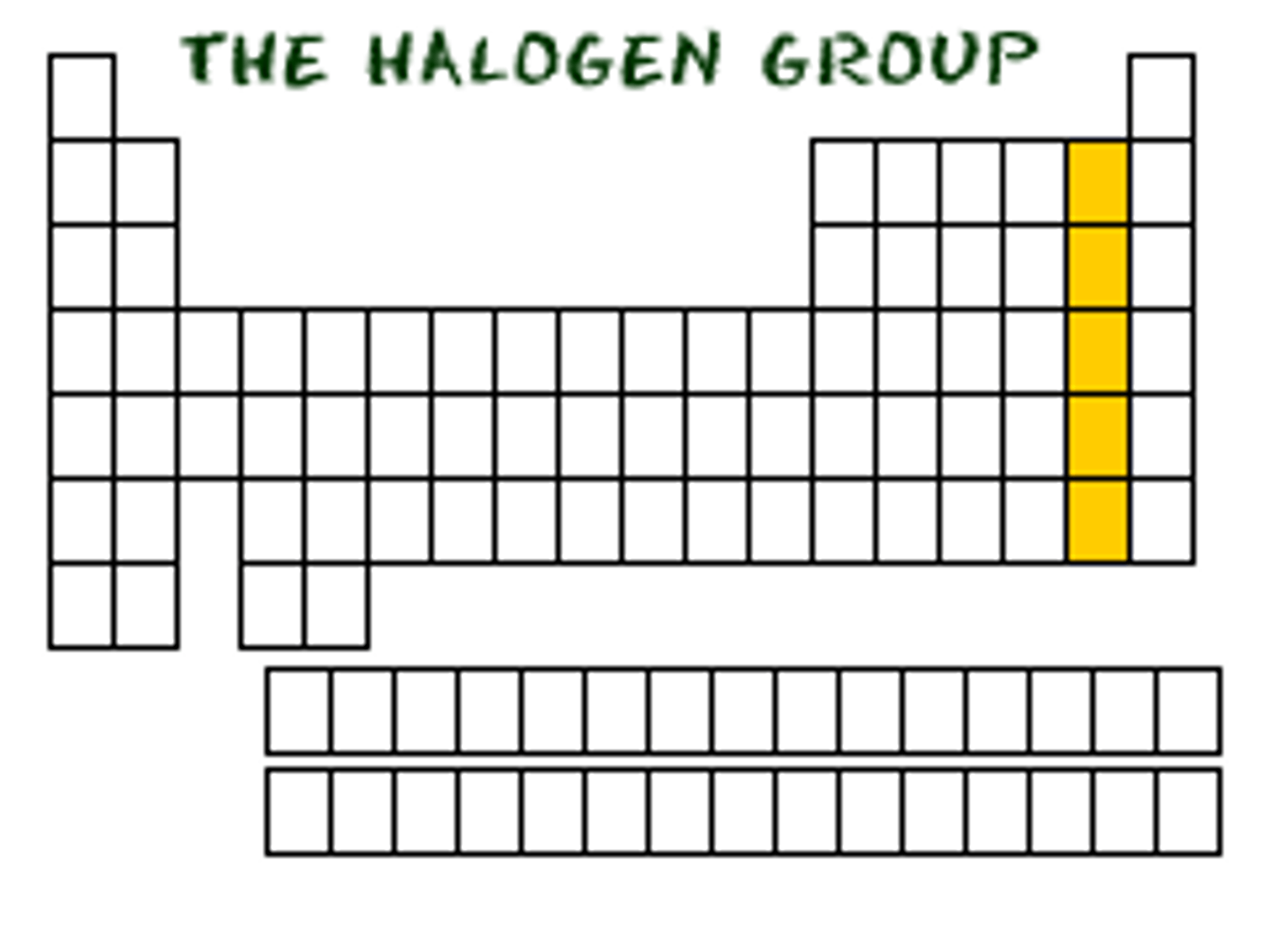
halogens
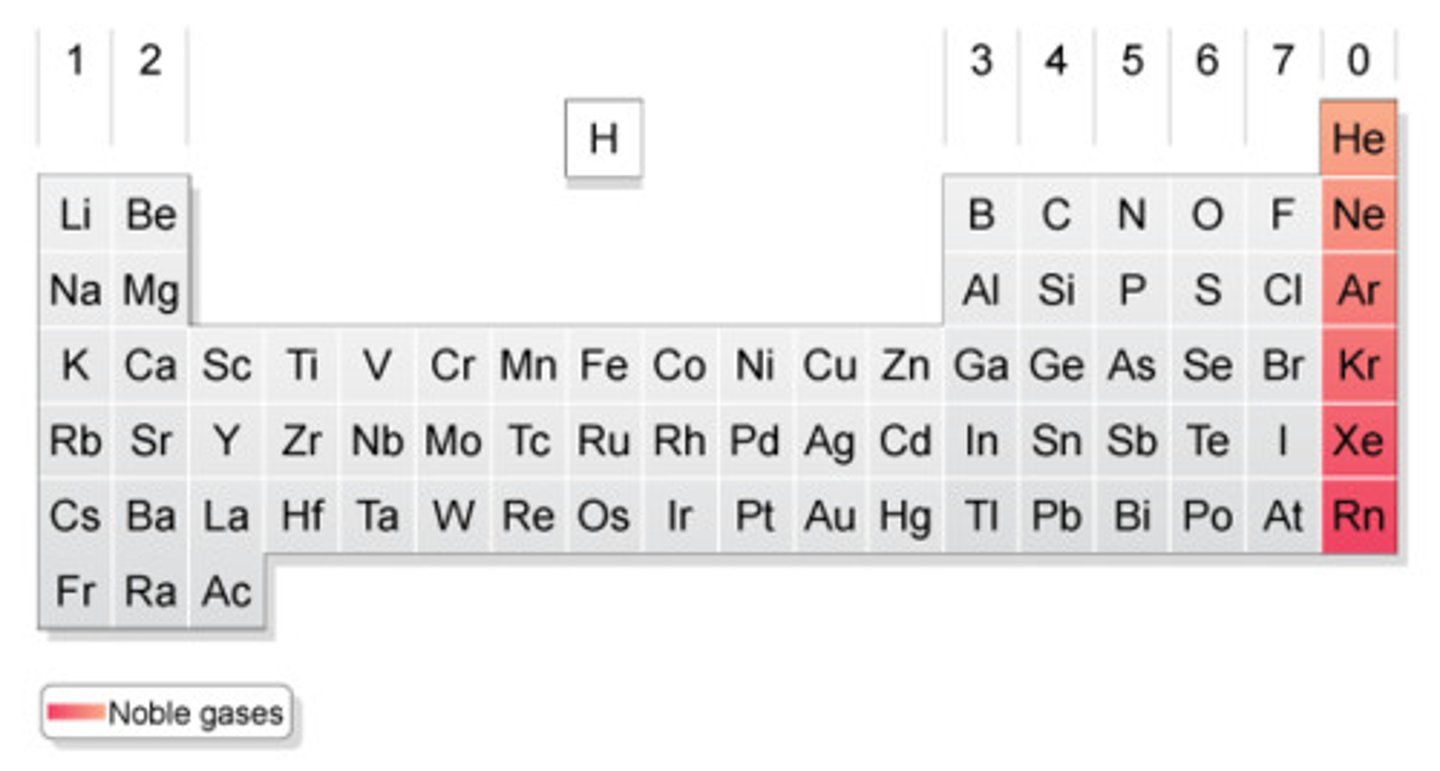
nobles gases
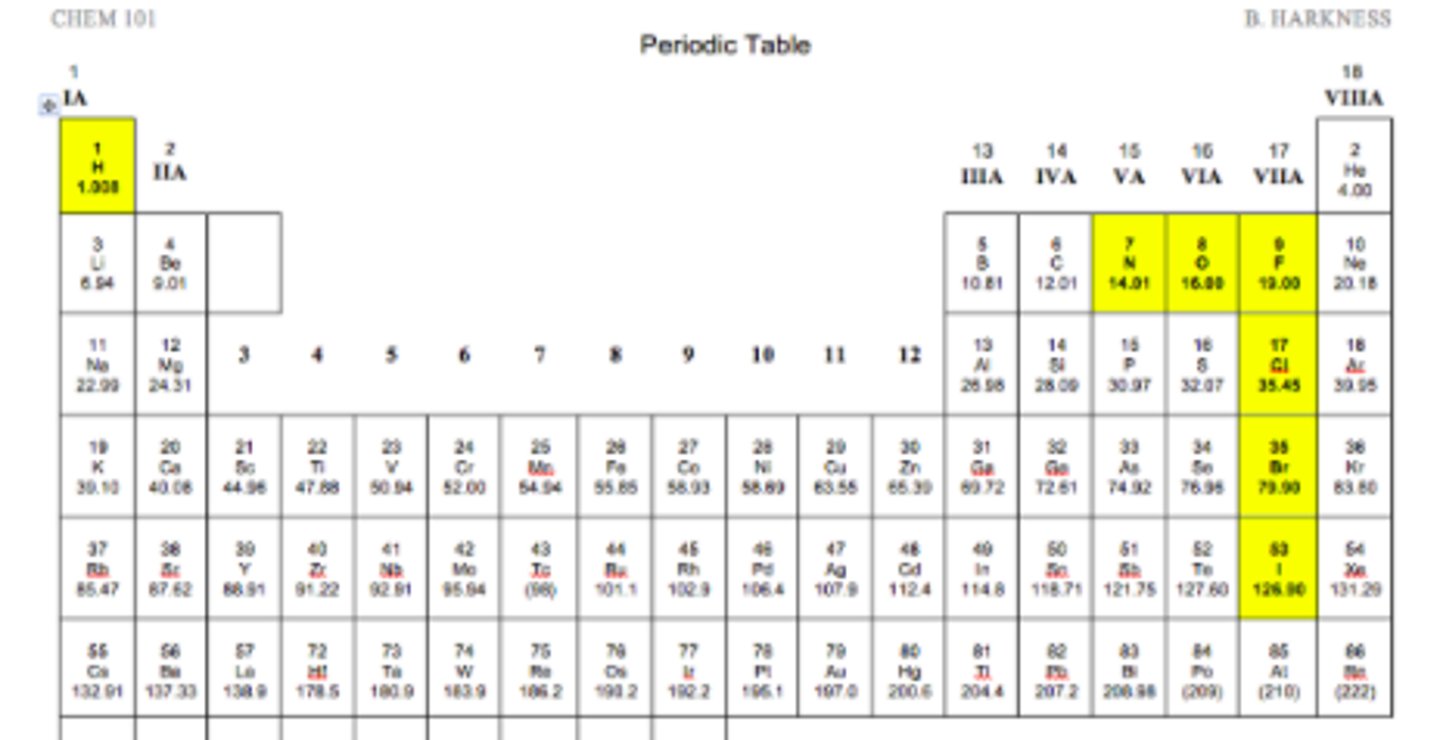
diatomic gases
(rules of sevens starting from flourine 3 left and 4 down) ( also hydrogen is diatomic)
1 mole
6.022*10^23 things (in this case atoms of an element)
molar mass
the mass of one mole of a pure substance, also the atomic mass in grams
ionic bonds occur between what types of elements?
metals and nonmetals
covalent bonds occur between what kinds of elements
nonmetals and nonmetals
polyatomic ion
several atoms attached together by covalent bonds into one ion, so basically a covalently bound compound with a charge
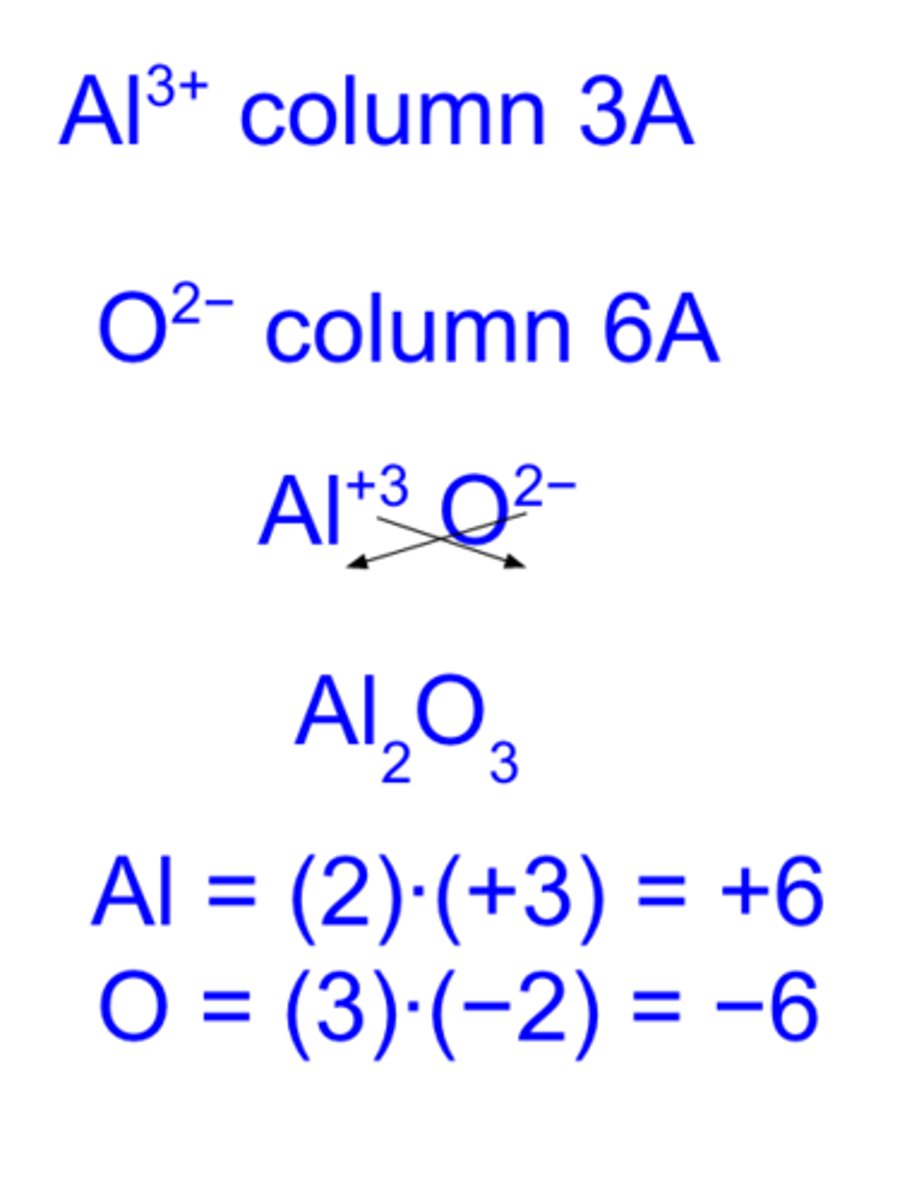
writing formulas for ionic compounds
1. write metal cation with charge
2. write nonmetal anion with charge
3. charge (without -/+ sign) becomes subscript fro other ion
4. reduce subscripts to smallest whole number ratio
5. check that sum of charges of anions and cations cancel eachother out
how would you name a metal with an invariant charge in a ionic compound
just use the metal name
how would you name a metal with a variable charge in an ionic compound
use the metal name then put the charge in roman numerals in parenthesis next to it
iron(III)
how would you name a nonmetal in an ionic compound
use the stem of the nonmetal name with the suffix -ide
carbon=carbide
when naming a polyatomic ion what would you do if the ion starts with hydrogen
add the hydrogen- perefix and add 1 to the charge
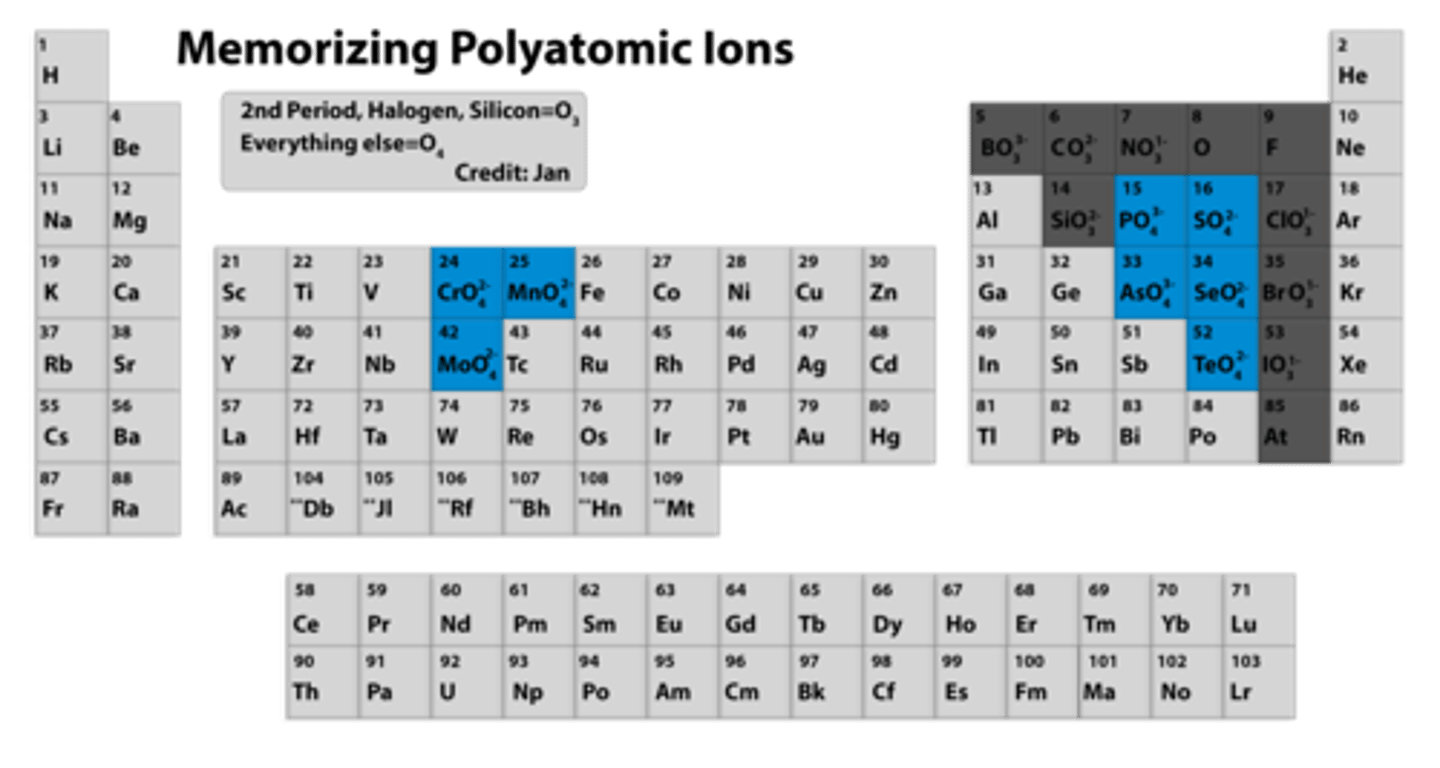
the -ate prefix goes on which polyatomic ions?
oxoanions
what do you do to an -ate ion with one extra oxygen
give in a per- prefix
what do you do to an -ate ion with one less oxygen
change the -ate suffix to -ite
what do you do to an -ate ion with 2 less oxygens
replace the -ate with -ite and give it a hypo- prefix
how do you determine the max number of oxygens in an oxoanion
the center 4 oxoanions and tellurate have a max of 4 oxygens
charge of an oxoanion is
=(x(-2))+main group column number
with x being the number of oxygens
NH4(+)
ammonium
hydrates
ionic compounds with a sepcific number of waters

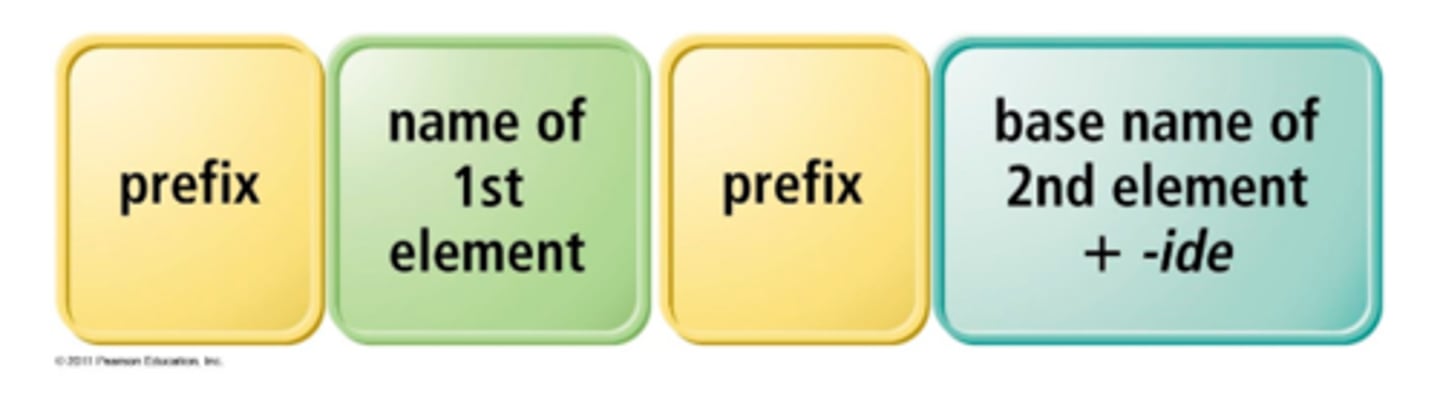
when writing the name of formulas for covalently bound compounds what would you do
(never use mon- for the first element) (drop last a if name begins with a vowel