ANS Lecture 1 - Sympathetic Nervous System
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is the autonomic nervous system
Carries out functions involuntarily (below level of consciousness)
Functions of the ANS
1. Maintains homeostasis or the constancy of the internal environment
2. Fight or flight system - involved in the activation of emergency mechanisms or response to stress
3. Rest or digest (housekeeping functions)
2 anatomical divisions of the nervous system
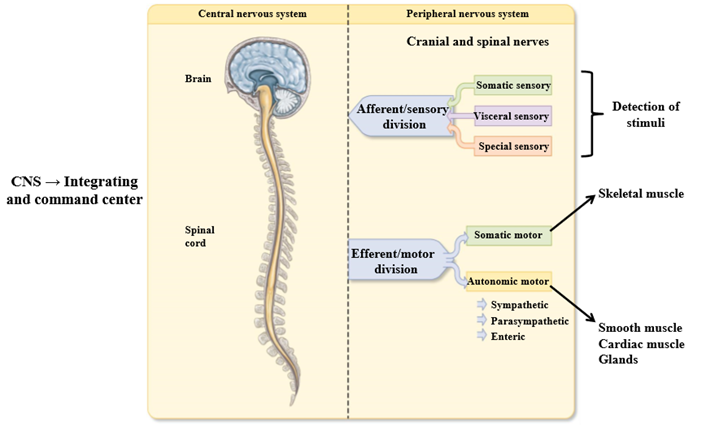
Central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system
CNS
Consists of brain and spinal cord. Neural control center. Revceivings incoming information, analyzes/organizes, and initiates appropriate action
PNS
Found outside the CNS - made of cranial + spinal nerves and the sensory receptors
2 divisions of the PNS
Afferent/sensory division and efferent/motor division

Afferent/Sensory division
Carries information detected by receptors to the CNS. Comprises afferent nerves - carries info from sensory receptors to CNS
Somatic sensory information
Sensory info on touch, pain, temperture
Visceral sensory information
Information from internal organs
Special sensory information
Information from special sense organ - visual, olfactory, and auditory sensation
Efferent/motor division
Carries information from the CNS to the effectors, such as glands or muscles that carry out actions directed by CNS
Divisions of the motor system
Somatic nervous system - controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscle and mediation of involuntary reflex arc
Autonomic nervous system - Autonomic motor nerves control smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Is the autonomic system voluntary
No - it is involuntary
Sections of the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic division, parasympathetic division, and the enteric nervous system
Smooth muscle
Muscle tissue that the contractile fibers are not highly ordered. Found in hollow organs (GI tract, bladder, uterus, blood vessels)
Cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart.
Cranial nerves
12 nerves that emerge directly from the brain, including the brain stem
Vagus nerve
Central nerve 10 -important for parasympathetic division of ANS
Spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves (afferent + efferent fibers) from the spinal cord
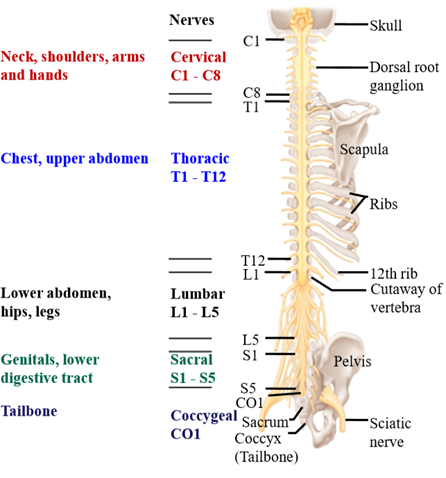
Organization of spinal cord nerves
Cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), lumbar + sacral + coccygeal (lower abdominal and pelvic regions)

Somatic nervous system motor neuron structure
Cell body of neuron found in the CNS. Single axon extends to target organ - the skeletal muscle (1 single synapse between nerve and muscle)
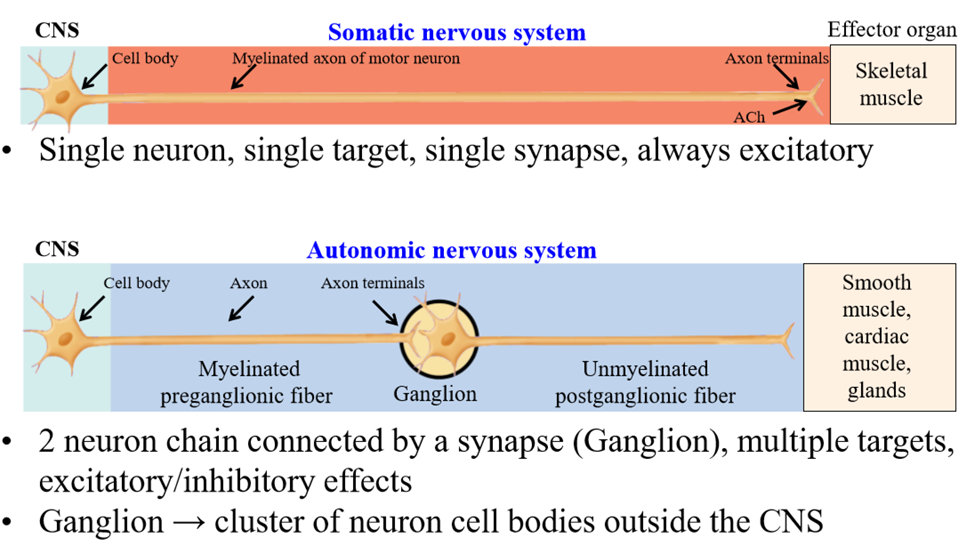
Activation of somatic neuron results in...
Muscle contraction via acetylcholine release
Where does inhibition of muscle contraction occur
In the CNS - efferent neuron is not activated
Somatic nervous system speed of conduction
Faster than autonomic - neurons are large and myelinated
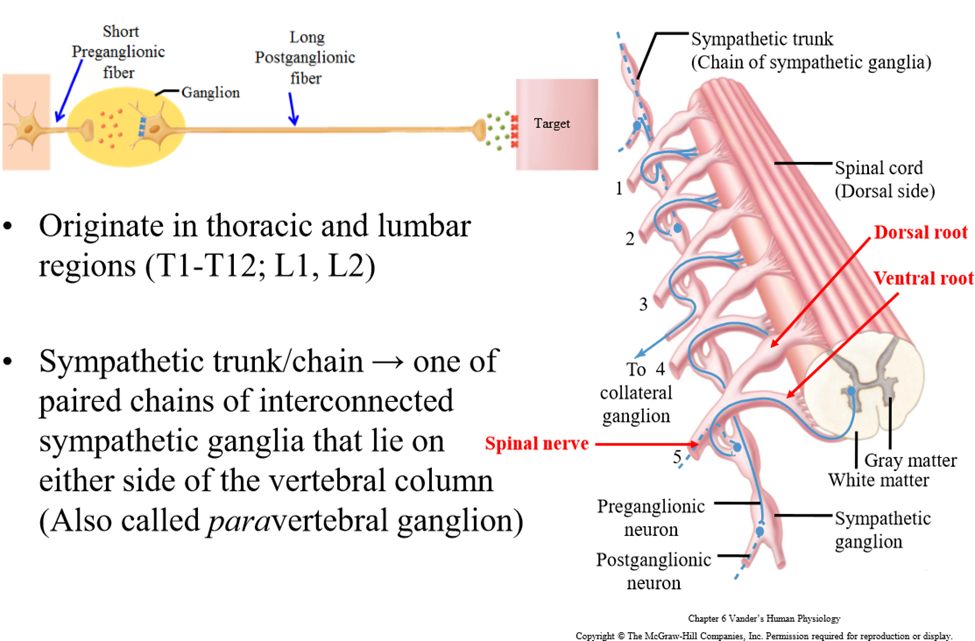
Autonomic nervous system structure
Organized into a chain of 2 neurons - connect the CNS and target tissue organ via a ganglion
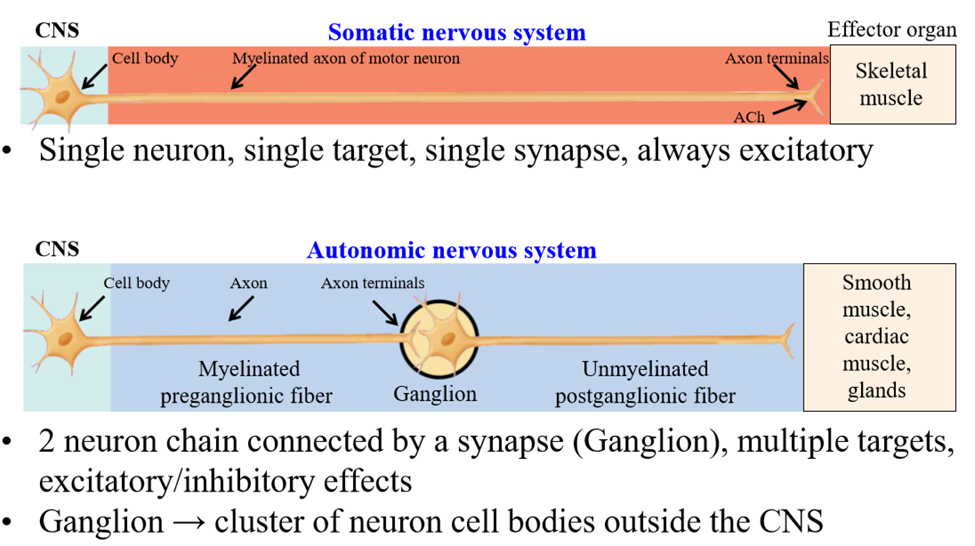
Ganglion
Where the preganglionic neuron synapes with the postganglionic neuron. It is a cluster of cell bodies outside the CNS
Preganglionic neuron
First neuron of the chain - cell body is isnide of the CNS - extends from CNS to ganglia
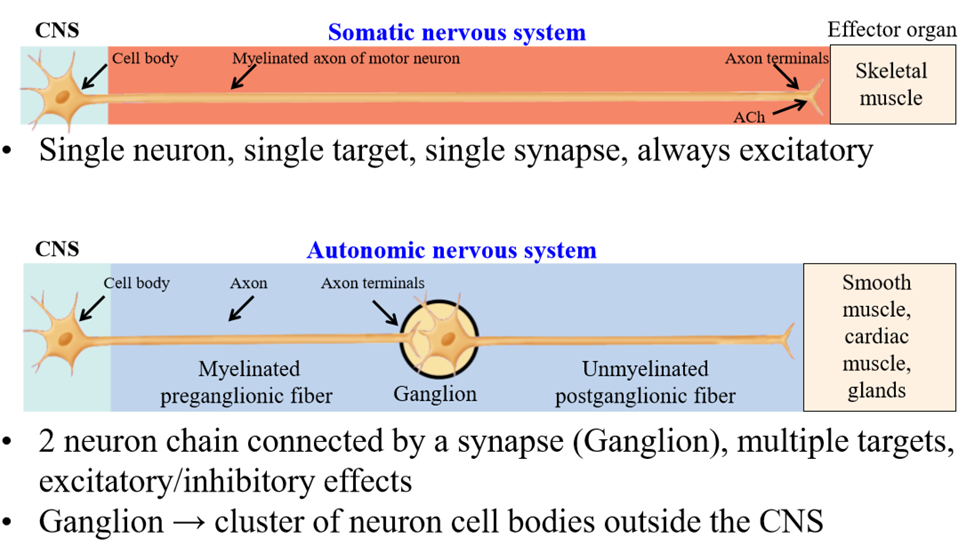
Postganglionic neuron
Second neuron of the chain - cell bodies are inside the ganglia, outside the CNS. Axon leaves ganglia and travels to tissue
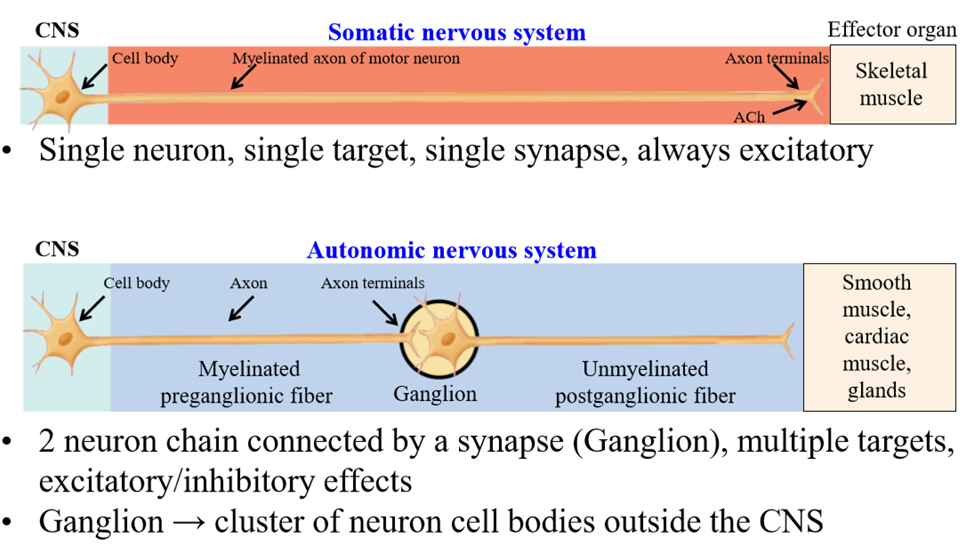
Speed of autonomic nervous system
Slower than somatic nervous system - preganglionic neurons are lightly myelinated and postganglionic neurons are unmyelinated
Comparison of somatic and autonomic control
Somatic = voluntary
Autonomic = involuntary
Comparison of somatic and autonomic response
Somatic = skeletal muscle
Autonomic = smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands
Comparison of somatic and autonomic efferent (motor) pathway
Somatic - one neuron
Autonomic - 2 neuron chain connected by ganglion
Comparison of somatic and autonomic neurotransmitter
Somatic = Acetylcholine
Autonomic = ACh, norepinephrine, epinephrine, many others
Comparison of somatic and autonomic myelination
Somatic = myelinated
Autonomic = myelinated preganglionic fiber, unmyelinated postganglionic fiber
Subdivision of the autonomic nervous sytem
Sympathetic (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)
Ganglion location in PSNS
Ganglion is very closer to or even within the walls of target organ. Preganglionic neuron is long, post is short (more isolated signal)
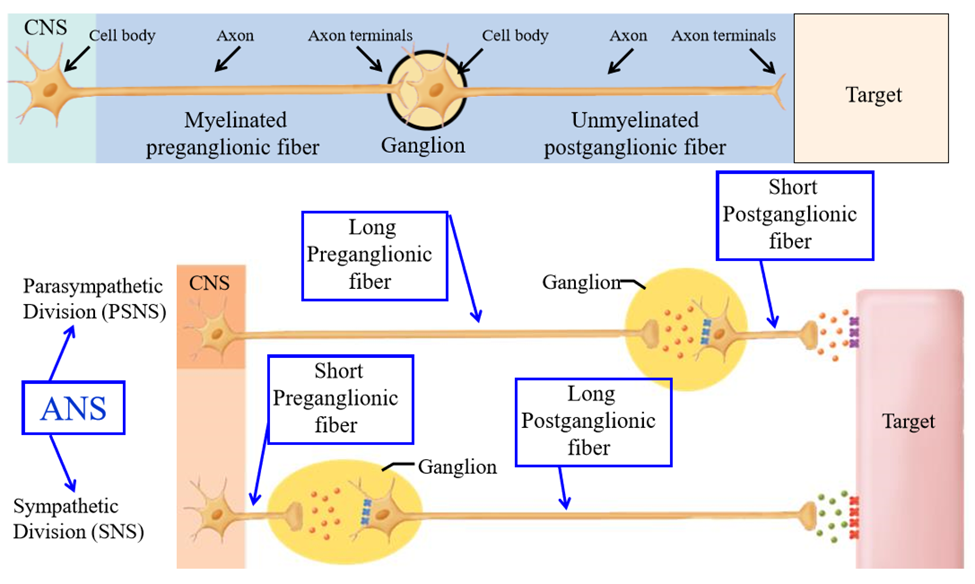
Ganglion location in SNS
Ganglion is located close to spinal cord. Preganglionic neuron is short, post is long (allows for branching and mass discharge)
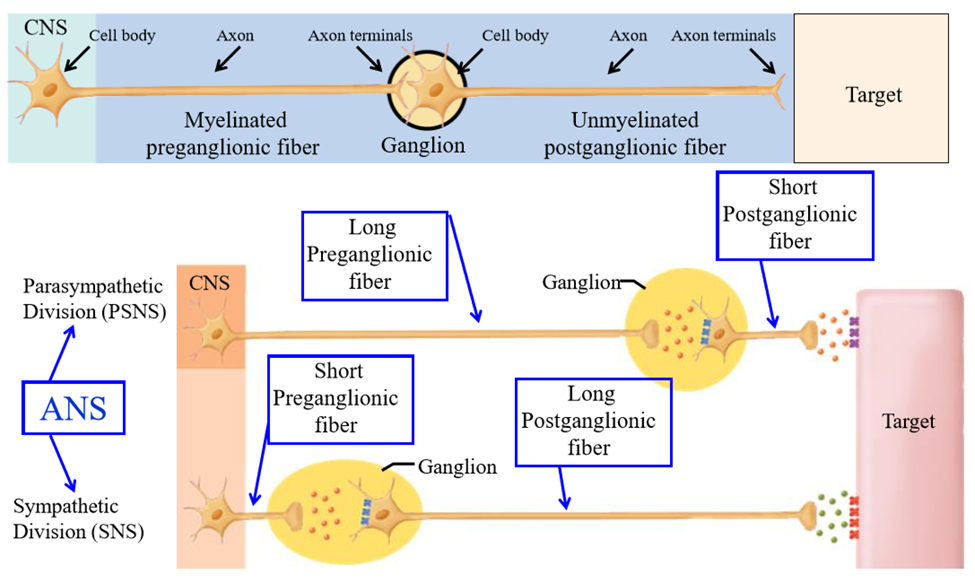
Mass discharge of SNS
Many organs and tissues are activated following SNS activation
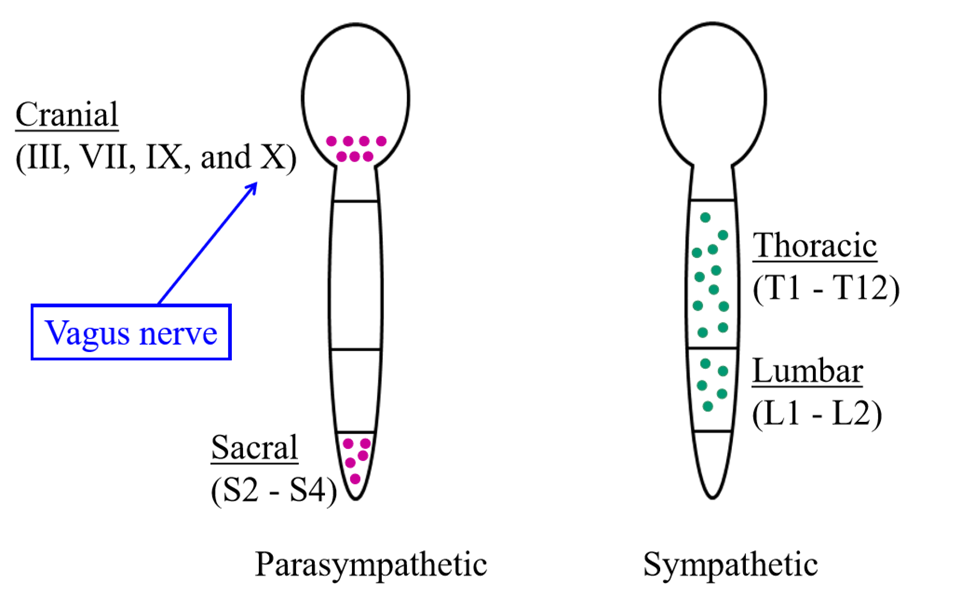
Where the cell bodies of the SNS located
Thoracic (T1-T12) and lumbar (L1-L2) regions of spinal cord
Where are the cell bodies of the PSNS located
In the brainstem and sacral region of the spinal cord
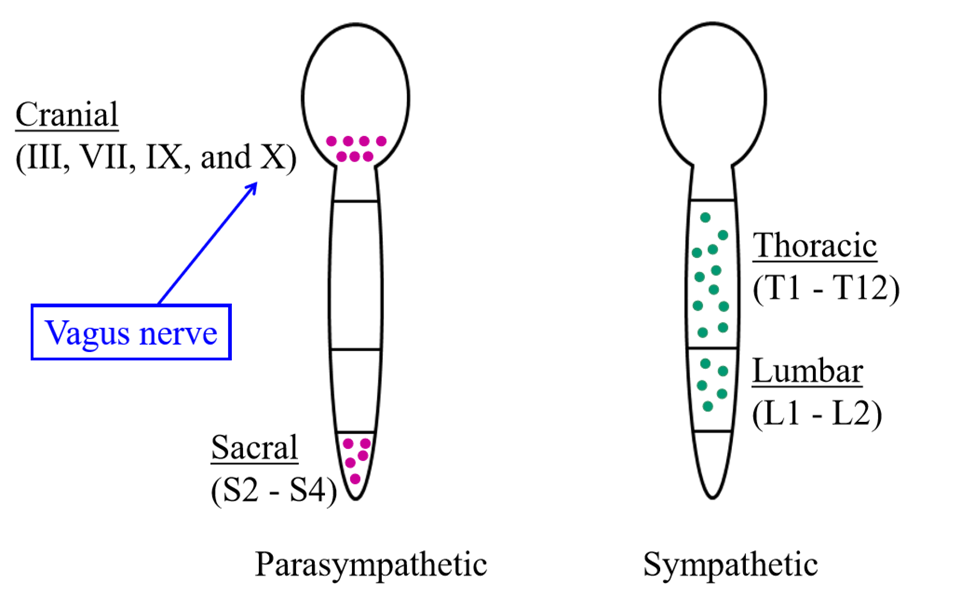
Why is the sympathetic nervous system also called the thoracolumbar division
Cell bodies of preganglionic neurons are found in thoracic or lumbar region of spinal cord
Sympathetic ganglia
Paravertebral ganglia - run parallel to spinal cord on each side
Dorsal root of spinal crod
Pathway into spinal cord - carries sensory information. Contains axons of afferent/sensory pathway
Ventral root of spinal cord
Pathway leaving spinal cord - carries motor information. Contains axons of motor/efferent pathway
Sympathetic trunk/chain
Paired chains of interconnected sympathetic ganglion that lie on either side of vertebral colum. Signals can leave the ventral root into the sympathetic trunk, and can enter the nearest ganglion or travel up and down the trunk
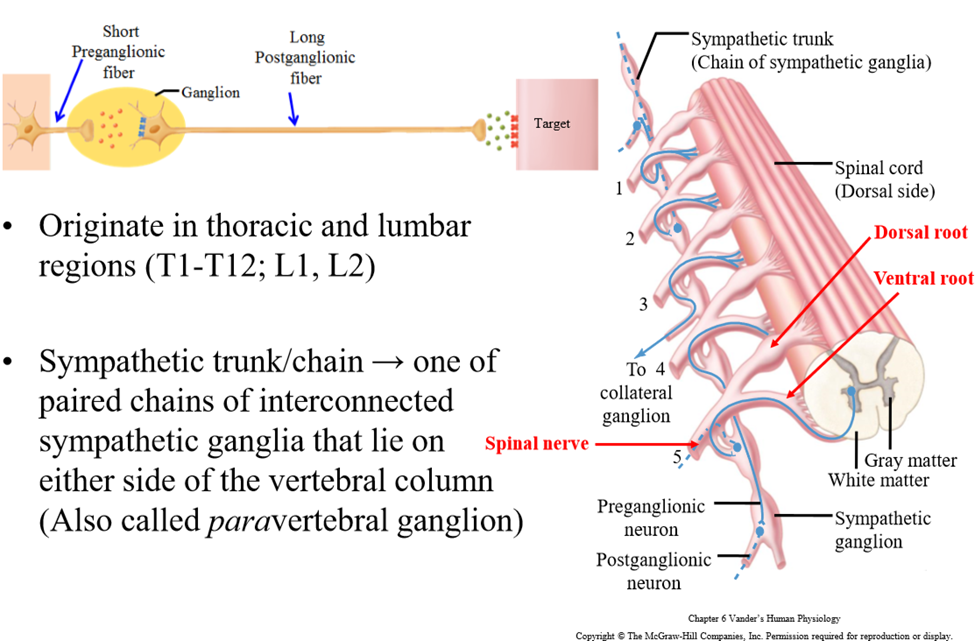
SNS Collateral ganglia (pre-vertebral ganglia)
Ganglia located in front of the vertebral column. Sympathetic pre-ganglionic axon leaves the spinal cord via the ventral root and passes through the sympathetic trunk. The axon travels into collateral ganglion to synapse
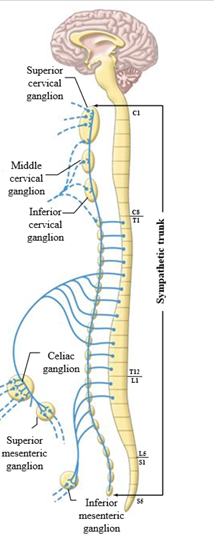
The 3 collateral ganglia
Celica ganglion, superior mesenteric ganglion, inferior mesenteric ganglion

Location of collateral ganglia
Lie close to the viscera (internal abdominal organs)

Collateral ganglia function
Innervate abdominal and pelvic viscera
3 pathways a sympathetic preganglionic fiber can take when it leaves the spinal cord
1. Synapse immediately with postganglionic neruon in sympathetic ganglion the same level
2. Travel up or down the sympathetic chain and synapse and ganglia at other levels of the vertebral column
3. Travel through the chain without synapsing, and continute to collateral ganglion as a splanchnic nerve
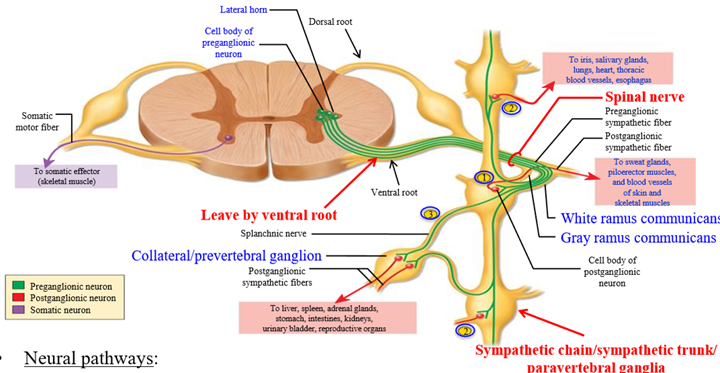
Communicating rami
Branches or connections between the spinal nerv and the ganglia
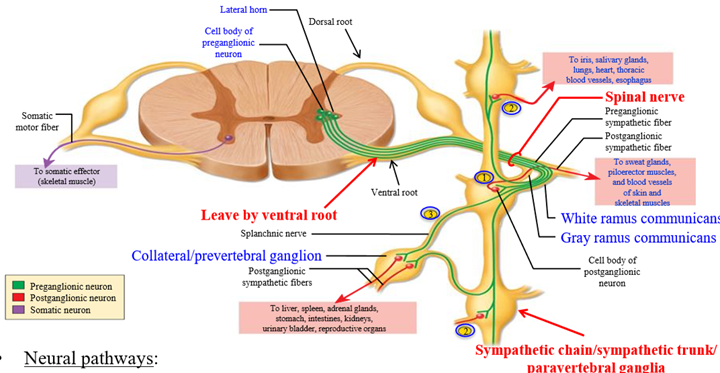
White ramus communicans
Branch that leads into the ganglion from the spinal nerve
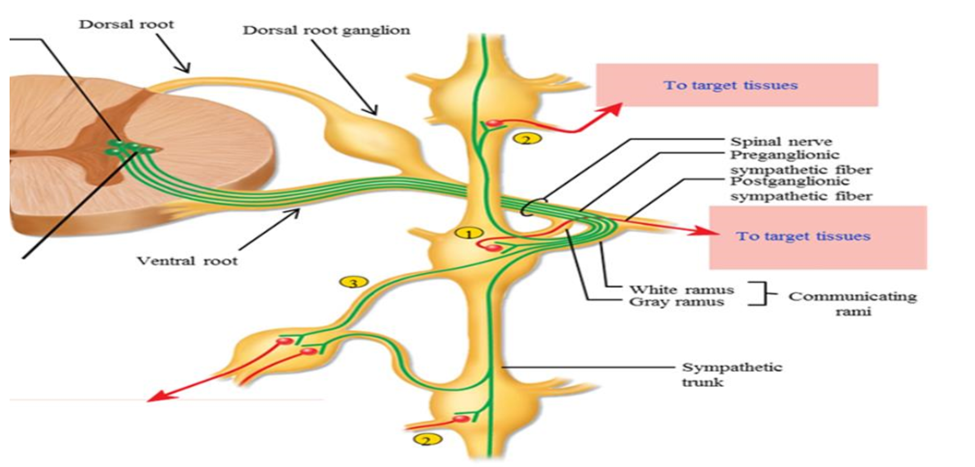
Why is the white ramus white
Carries myelinated pre-ganglionic fiber (white in color)
Grey ramus comunicans
Branch that goes back into the spinal cord
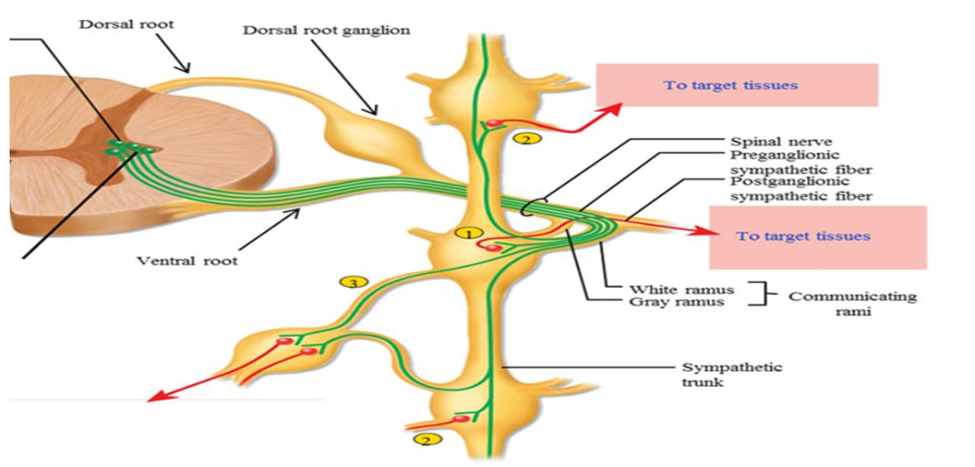
Why is the gray ramus grey
Carries unmyelinated post-ganglionic fiber (gray in color)
Though the pathways in the SNS are different, what is one similar feature
The pre-ganglionic neuron is short, and the post-ganglionic neuron is long
Function of the sympathetic nervous system
Fight or flight response - how the body reacts in a stressful/fearful situation
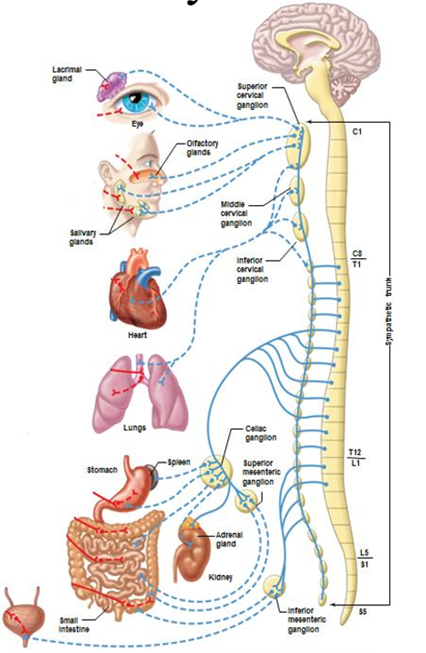
Sympathetic nervous system effect on eyes
Dilation of pupils, adjustment for far vision (can see danger better)
Sympathetic nervous system effect on Cardiovascular orgns
Increases heartrate and force of contraction (provide oxygen to muscles)
Sympathetic nervous system effect on arterioles and veins
Constriction - push blood to musles
Sympathetic nervous system effect on skeletal muscle blood vessels
Dilation - allow more oxygen into muscles to run away or fight
Sympathetic nervous system effect on lungs
Dilation of bronchioles and inhibition of mucous secretion - grab more O2 from environment and give to blood
Sympathetic nervous system effect on digestive tract
Decreased motility, inhibition of digestive secretions - body focuses on running/fighting instead of eating
Sympathetic nervous system effect on endocrine glands (adrenal medulla)
Stimulation of epinephrine and norepinephrine secretion
Sympathetic nervous system effect on sweat glands (exocrine)
stimulation of secretion
Sympathetic nervous system effect on salivary glands (exocrine)
stimulate small volume of thick saliva (rich in mucous)
Sympathetic nervous system effect on bladder
Prevent urination
Sympathetic nervous system effect on genitals
Males - emission
Females - uterus contraction
Adrenal medulla
Part of the adrenal gland - acts like a modfied sympathetic postganglionic neuron (with no axon or cell body)
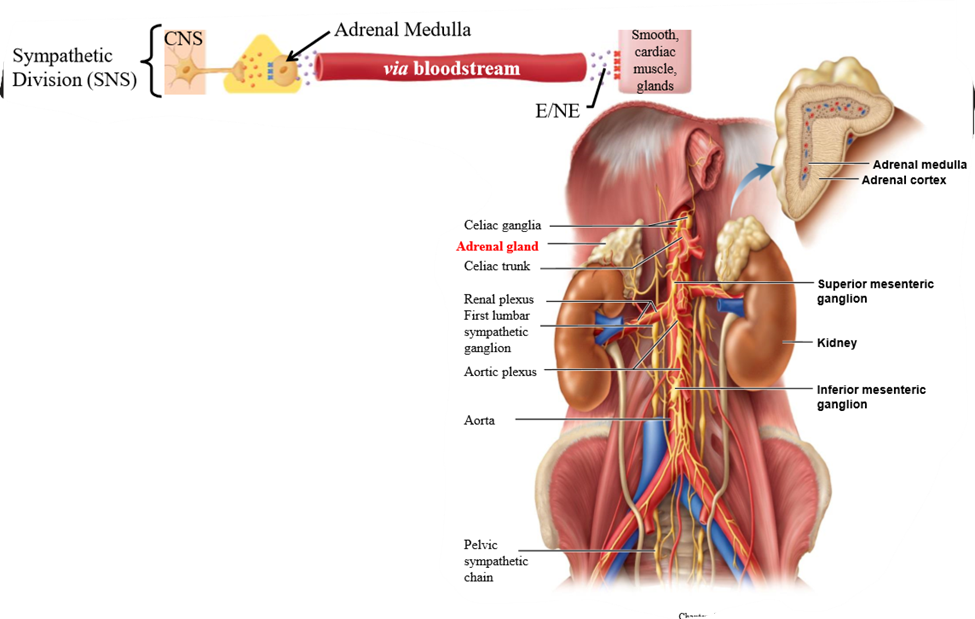
Function of adrenal medulla
Preganglionic neurotransmitters activate, cause secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine into the blood stream

Use of epinephrine and norepinephrine in bloodstream
Travel to different targe tissues/organs to produce a response, allowing hormones to reach places that do not receive nervous innervation
Use of adrenal medulla hormones being broken down in the liver
Allows for prolonged effect on the body