Cardiovascular System Review Guide
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy and Physiology H
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Arteries carry blood….
away from the heart.
Veins carry blood…
towards the heart.
____ carry oxygenated blood.
Arteries
Which artery is the exception that does not carry oxygenated blood?
The pulmonary artery.
What do you call the loose, outer layer of the sac around the heart?
The pericardium
What is the inner layer?
visceral
What is the outer layer?
parietal
When vessels expand, it is called…
vasodilation
When vessels contract it is called…
vasoconstriction
Epicardium
The outer layer of the heart wall.
Myocardium
muscle layer of the heart wall.
Endocaridum
inner layer of the heart wall, lining the chambers of the heart
Where is the heart located?
The center of the chest; within the mediastinum
What is the heart’s size?
about the size of a fist
What divides the left and right side of the heart?
the septum
Which side of the heart is more muscular?
left side
What bone lies directly in front of the heart?
the sternum
During systole, the aortic valve is…
open
During diastole, the aortic valve is…
closed
Veins and arteries meet at _____ where nutrients are exchanged with body tissues.
capillaries
Arteries branch into smaller vessels called…
arteriloes
Veins also have smaller branches called…
venuoles
What aids in bringing blood back to the heart?
The diaphragm, sphincter valves, movements of skeletal muscles
What is the pacemaker?
The SA node, regulates the pace of the heart.
What fibers cause a contraction in the ventricle?
Perkinje Fibers
Where is the AV node located? (AV stands for atrioventricular)
It is located between the right atrium and ventricle of the heart.
Tachicardiyum
Rapid heart rate
Bradycardia
Slow heart rate
Arrhythmia
Irregular heart rate
What is defibrillation?
A defibrillator shocks the heart back to its normal rhythm
How are the valves attached to the wall of the heart (2 structures)?
The chordae tendinae attached to papillary muscles
Generally speaking, when the ventricle contracts, the atrium…
relaxes
Any contraction (atrial or ventricular) is called…
systole
Relaxing is called…
diastole
What causes a P-Wave, the QRS complex and a T wave?
P is the first small bump, QRS is the large peak, and T is the small wave after the peak
What is an ECG?
*be able to analyze one for test
electrocardiogram
What are systolic pressure and diastolic pressure?
Systolic blood pressure is the first number. It measures the pressure your blood is pushing against your artery walls when the heart beats.
Diastolic blood pressure is the second number. It measures the pressure your blood is pushing against your artery walls while the heart muscle rests between beats.
What is the “normal” blood pressure for a human?
120/80
What two pieces of equipment are needed to take a person’s blood pressure?
A stethoscope and sphygmomanometer.
Describe the procedure for taking blood pressure.
The stethoscope is places at the brachial artery (elbow) and the cuff is wrapped around the arm, the cuff is inflated and then the valve is released slowly. The first time you hear the sound of a heart beat is the systolic pressure. The cuff continues to deflate until you no longer hear the sound, this is the diastolic pressure.
Blood that moves from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart again is in the ___________ circuit.
pulmonary
Blood moving throughout the body is in the_________circuit.
systemic
Identify the three major vessels that branch off of the aortic arch. You may want to draw a diagram.
Brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian
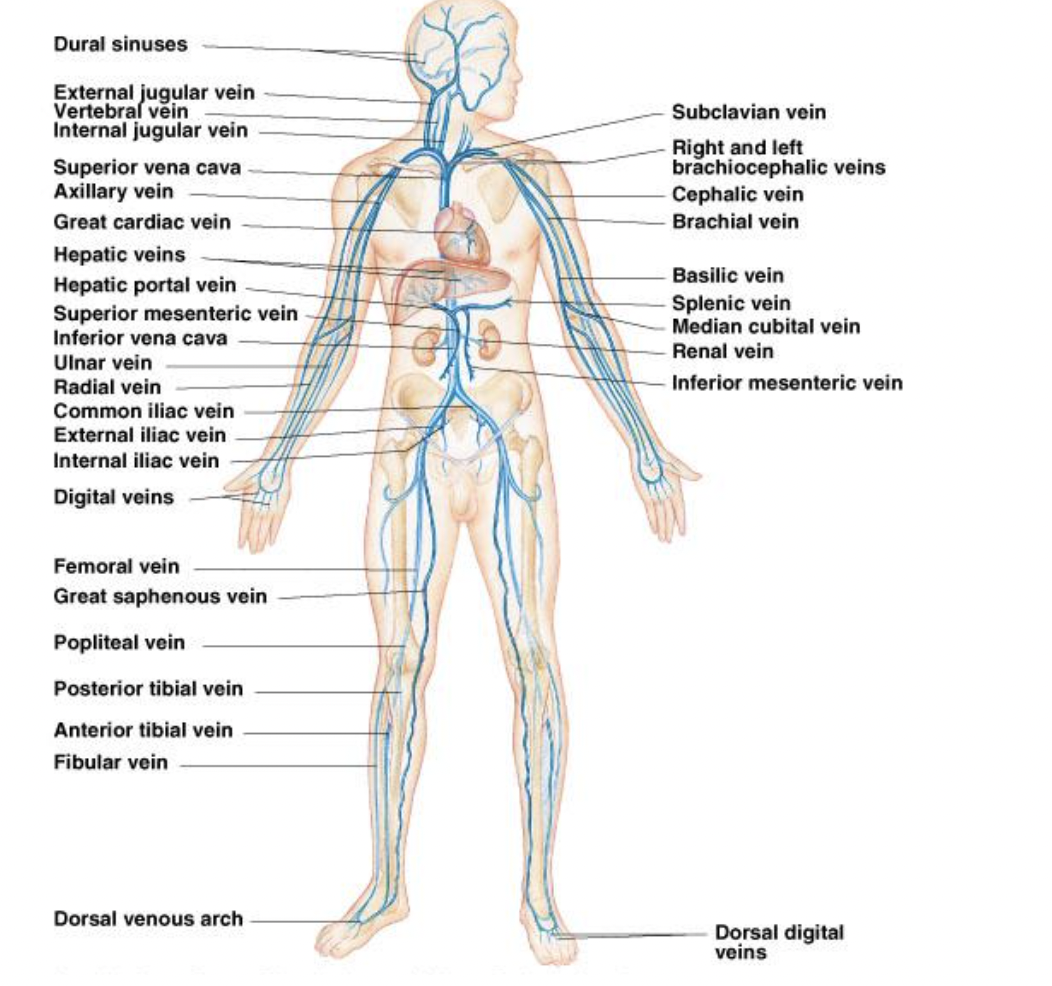
Label the heart and trace the flow of blood through the major vessels and all of the valves.
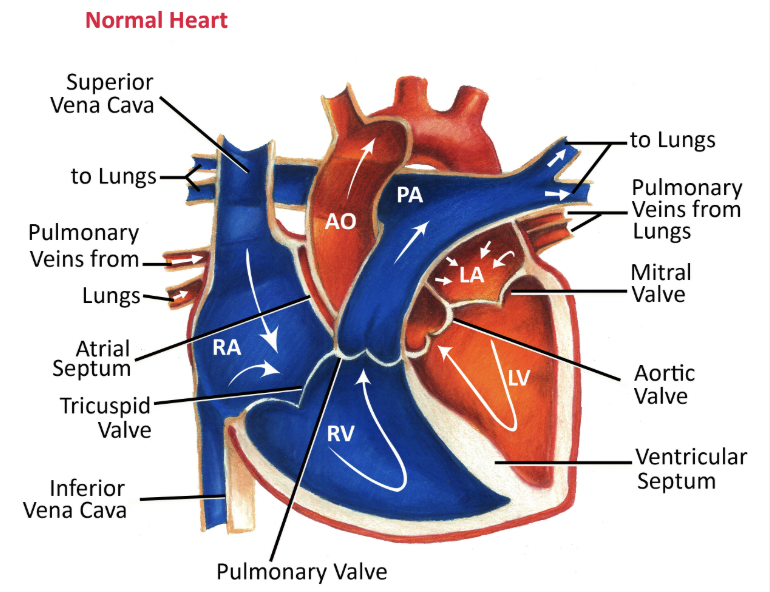
Label any 5 arteries
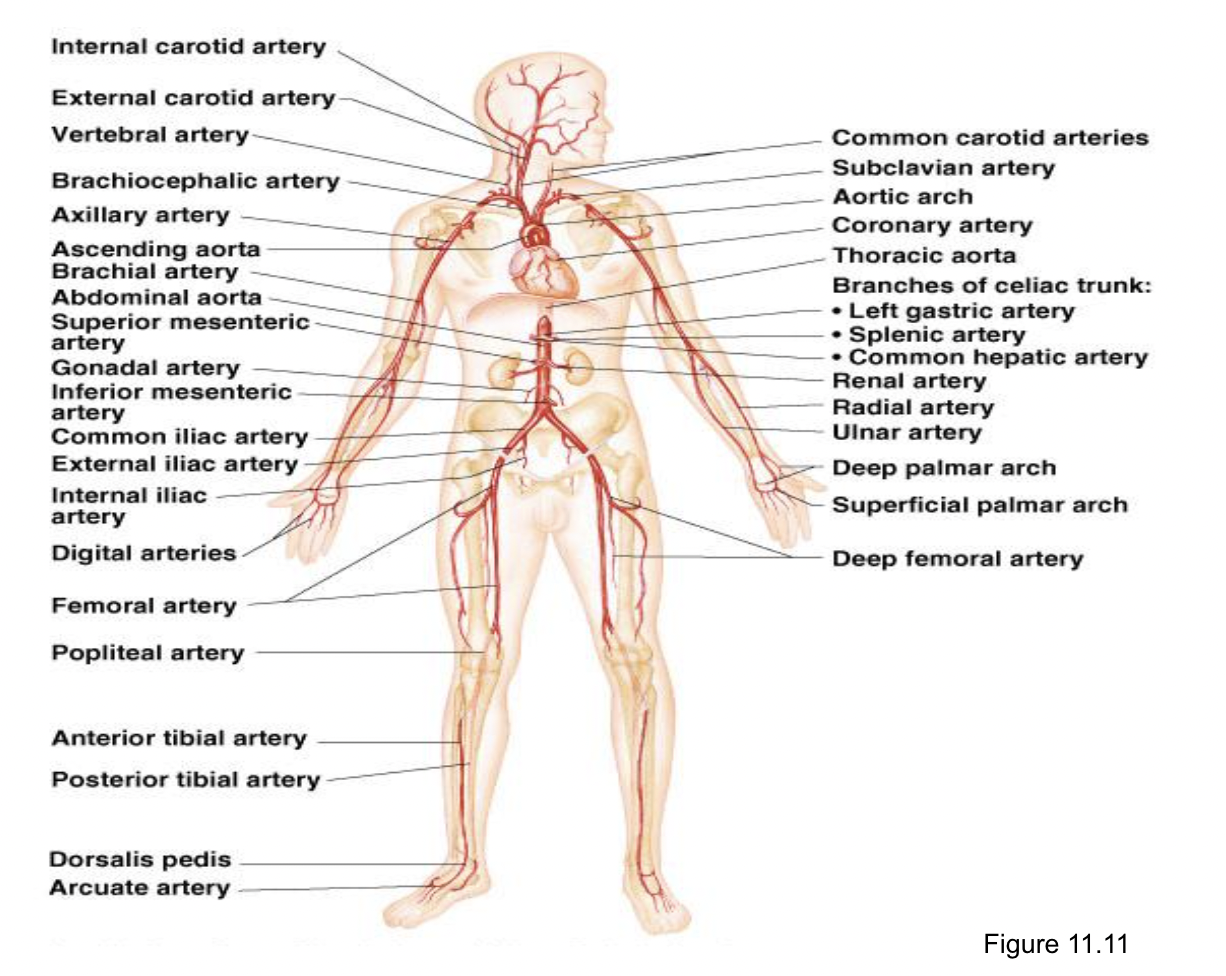
Label any 5 veins