WI DNR Wastewater Certification (General)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Which provides a better composite representative:
A. A smaller sample collected more often
B. A larger sample collected less often
A smaller sample collected more often
Which part of the treatment process uses biological processes?
A: Primary
B: Secondary
C: Tertiary
D: WAS
Secondary
The activated sludge (bio mass) collected in the final clarifier and returned to the secondary treatment process to mix with the incoming wastewater is:
A: Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS)
B: Waste Activated Sludge (WAS)
C: Return Activated Sludge (RAS)
D: Mixed Liquor Volatile Suspended Solids (MLSS)
Return Activated Sludge (RAS)
Define primary treatment
Clarification by solid and liquid separation that removes a substantial amount of suspended and floating matter.
True or False: Disinfection destroys all microorganisms?
False
What type of solids does a clarifier remove?
Floating and settled
Define F:M using BOD and MLSS
F:M = (food to micro-organism) ratio where the 'food' is BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) and the microorganisms are the MLSS/MLVSS.
What is a restriction in an open channel used to measure flow?
A: Weir
B: Box cord
C: Packing
D: Flume
Flume
What is a selector?
Part of the treatment system that selects a specific type of organism by providing an environment (Anaerobic, anoxic, or aerobic) that favors its growth.
____ are flows generated within the plant, usually from solids processing that has been recycled back through the plant.
Sidestreams
_ is the treatment process that uses physical, chemical, or biological processes to remove suspended solids and nutrients in wastewater to accomplish a level of treatment greater than what can be accomplished by secondary treatment.
Tertiary treatment
The activated sludge (except biomass or cell mass) removed from the secondary treatment process.
A: Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS)
B: Waste Activated Sludge (WAS)
C: Return Activated Sludge (RAS)
D: Mixed Liquor Volatile Suspended Solids (MLSS)
Waste Activated Sludge (WAS)
What are the two main reasons for treating wastewater?
To protect public health by destroying pathogens and to protect the environment by removing pollutants.
Discuss the effect of I&I (inflow & Infiltration) on a collection system
(1)Exceed capacity of the pipes = sanitary sewer overflows (SSO).
(2) Very high flows entering the treatment facility can lead to too much flow going through aeration basins and clarifiers washing out solids
A structure that allows a pipe to dip below an obstruction by forming a "U" shaped path. Liquid flowing in one end is forced up and out the over. It is typically used in collections when there is a river or other deep obstructions.
A: Gate Valve Structure
B: Torque Wrench
C: Pathfinder
D: Inverted Siphon
Inverted Siphon
Fill in the general characteristics for domestic wastewater: (mg/L)
BOD:
TSS:
Total Nitrogen:
Ammonia: _
Total P:
FOG: _
pH: _
BOD: 250
TSS: 300
Total Nitrogen: 40
Ammonia:25
Total P: 9
FOG: 100
pH: 6.5 - 8.0
What impacts can a dairy producer have on a treatment plant?
Dairy producers alternate cleaning tanks with very acidic and very caustic cleaners. They can potential create slug loads of one extreme of a pH.
They also tend to have very high BOD loadings (1k - 10k mg/L)
Milk products contain high amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and chlorides.
Dairy producers often require pretreatment or an equalization tank to prevent sending extreme concentrations due to the variable loadings.
What impacts can the food industry have on a treatment plant?
The food product can determine the impact. In general:
the food industry generally has high BOD, total nitrogen, TSS, phosphorus, and varying pH.
Food industries also might need to be equalized or pretreated.
What impacts can breweries have on a treatment plant?
High BOD (1,000-4,000 mg/L) from carbs and proteins; TSS from 200-1000; nitrogen from 25-80 mg/L; p from 1-50 mg/L; pH of 4-12.
Equalization is often necessary so discharge is relatively uniform.
What impacts can metal finishing industries have on a treatment plant?
little BOD but can have toxic pollutants that harm aquatic life in small concentrations. Pollutants may not easily be removed by the treatment process.
pH between 1-12, ww can contain phosphates, chromate, cyanide, and metals. Metals can concentrate in sludge; must be monitored and reported to DNR. Application of sludge with elevated metal concentrations cannot be applied or may be restricted due to soil accumulation concerns.
Discuss the impact cleaning agents can have on a treatment plant.
Many cleaners contain phosphates and can elevate phosphorus.
Quaternary ammonia from cleaners can be toxic and contribute ammonia to the waste stream.
Surfactants can interfere with solids settling in clarifiers and create foam in aeration basins.
Discuss impacts of FOG (fats, oils, and grease) in the treatment plant.
SSOs due to blockages
can create settling problems
promotes growth of filamentous bacteria that create surface foam and scum
BMP is to have a FOG program which typically includes grease trap inspections and an ongoing information/education program for businesses and residents.
Which materials should be prohibited from discharge into the collection system?
Volatile organics
heavy metals
acidic and alkaline wastes (pH between 5 and 10)
FOG
High strength BOD/TSS loadings
High temperature wastewater
any debris including rags
other toxic materials that may interfere with the treatment process.
Why is it important to measure wastewater flow?
Treatment efficiency is dependent on loadings and detention time.
Required by DNR to report final effluent flows to the river.
To measure the influent entering a treatment plant from the community--where should flow measurements be taken?
before sidestreams
To know actual flow and loading to treatment units side streams need to be [included] or [excluded] from flow measurements?
included
Describe the following types of flow measurement devices:
Open Channel
Pipe flow
Open channel: measured through a flume or weir. Most common is parshall flume. Most common weir is a 60 or 90 notch (triangular).
Pipe flow: magnetic meter. operates on principal of electromagnetic induction. Pressure or ultrasonic meters can be used too.
Both flow meters must be calibrated annually with records kept according to WDNR.
Where are in-plant flow meters located?
Hint: 7 of them.
RAS (return activated sludge)
WAS (waste activated sludge)
Recycle flows
Sidestream flows
sludge flows to digesters
sludge feed rates to sludge dewatering equipment
sludge withdrawal volumes from storage tanks
How much of the sampler should be filled with liquid when determining ideal sample size for a composite sample?
1/4 to 1/2 the bottle volume.
Ex: 10 L bottle = 2.5 to 5 L
Describe a good sampling location and procedure for collecting representative influent wastewater samples.
Well mixed and after headworks (post-grit removal/screening)
Discuss the purpose of preliminary treatment
remove larger, inorganic materials, and grit from the wastestream
Which is NOT considered a type of preliminary treatment?
A. Screening and Grit Removal
B. Odor Control
C. Flow Equalization
D. Aeration
Aeration
True or False: The microorganisms used to treat wastewater are the same as those found in rivers and lakes?
True
True or False: One purpose of a WWTP is to satisfy the oxygen demand of the waste flow before it's discharged to the environment?
True
What are three problems that can result from sewage going septic (anaerobic)?
- Horrid smell
- Produces sulfur compounds (toxic hydrogen sulfide)
- Corrode pipes due to acid production
True or False: Sand is an example of organic matter found in raw sewage?
False
What percent of sewage is solid?
A. 10% solids
B. 1 % solids
C. 0.1% solids
D. 0.01% solids
0.1% solids
Define wet well
The tank where wastewater is collected. Water is pumped from the wet well and found in lift stations and at the headworks of the plant.
Which of the following is NOT a component of the sanitary sewer system?
A. Private building lateral sewer
B. Mainline sewer
C. Force mains
D. Lift (pump) stations
E. Inverted Siphon
F. Manholes
G. None of the above
None of the above -- private building laterals may not be owned by the collection system but they still feed to it.
What are control measures necessary for industrial discharges?
A. Enforce sewer use ordinances
B. Effective communication with industries
C. Grease Control Program
D. Monitoring
E. All of the Above
F. All except B
All of the above
Discuss how an aerated grit chamber works
Raw wastewater is introduced into the end of an aerated grit chamber, which is typically rectangular in shape. Injected air creates a spiral flow of wastewater as it moves through the chamber. As the flow velocity diminishes along the tank, heavier grit particles gradually settle from the water. The settled solids are typically gathered at the tank bottom by a rake mechanism and removed by pumping.
Discuss how a vortex-type (Pista®) grit chamber works.
Raw wastewater is introduced along the side of a cylindrical tank designed for vortex flow. The water and grit combination rotates slowly around the vertical access of the tank. The flow spirals gradually down the tank perimeter, allowing the heavier solids to settle to the tank bottom where they are then removed.
What is the purpose of primary treatment?
To settle solids and capture floatable materials
Which of the following are common primary treatment equipment
DAF unit and clarifiers
What materials are the baffles in a clarifier typically made of?
A. Metal and plastic
B. wood or fiberglass
C. glass or plexiglass
D. Aluminum
Wood or fiberglass
What is the purpose of secondary (biological) treatment?
A. Remove dissolved and suspended organic material
B. Disinfect the water
C. Remove microbes
D. Remove inorganics and volatiles
Remove dissolved and suspended organic material
What % of TSS(Total Suspended Solids)/BOD(Biochemical Oxygen Demand) can a secondary treatment system achieve?
A. 70-80
B. 75-85
C. 80-90
D. 85-95
85-95
What are common maintenance tasks for pumps? Select all that apply.
A. Lubrication
B. Amperage checks
C. Packing if leaking
D. Flushing water seals
E. Check for clogging
All of the above.
Describe cavitation, its cause and the sound it makes.
Occurs when vacuum pressure is lowered to vapor pressure of the liquid. Vapor bubbles form and collapse.
Usually occurs in pumps, on impellers, or at restrictions in a flowing liquid and may occur as suction cavitation or discharge cavitation.
It is very noisy--associated with a popping, clattering, or marble-like sound.
What are potential impacts of cavitation?
Reduced efficiency and possible equipment failure.
Pitting of the impeller and corrosion.
What should you do if cavitation is occurring?
Contact the consultant or pump service representative to determine the cause and corrective actions.
What are preventative spill measures/procedures for WWTPs? Select all that apply.
A. Storage tanks must have secondary containment equal to tank volume.
B. Containment pails for potential leakage points during unloading of chemical delivery vehicles
C. Inspect and maintain fill lines and valves
D. Inspect storage tanks and hardware
E. Pay attention to what is being done
F. Provide onsite containment equipment and seal the yard and storm drains
All of the above
How soon after a chemical spill should the DNR and local emergency response agencies be notified?
Within 24 hours
What is a potential safety hazard with anaerobic digestors?
A. Back harm from heavy lifting
B. Explosive atmosphere from methane gas
C. Carbon monoxide poisoning
D. Drowning during inspection process
Explosive atmosphere from methane gas
Which of the following are potential toxic gases at a WWTP? Select all that apply.
A. Hydrogen Sulfide
B. Methane
C. Carbon Monoxide
D. Chlorine
E. Neon Tetroxide
All except E.
Which of the following are required records an operator must keep when biosolids and sludge are land spread. Select all that apply.
A. Approved site used
B. Number of acres applied with sludge on that day
C. Amount of sludge applied that day and amount per acre.
D. Amount of nitrogen applied per acre
E. Method of application
All of the above.
What are the four analysis sludge must go through before being applied as Class B sludge?
- Nutrients (N&P)
- Metals
- Pathogen densities (Fecal coli)
- Vector attraction reduction
What are the 2 WI admin codes regulating municipal and industrial sludge?
- NR204 -- domestic sludge
- NR 214 -- Land treatment of industrial liquid wastes
What are common methods of sludge disposal?
Use in parks, gardens, golf courses, farms, and landfills
What % solids are dewatered sludge typically? What are they nicknamed?
15-30% solids, nicknamed cake sludge
What equipment is used to dewater sludge?
Belt press or plate press
Secondary biological treatment consists of ____, either mixed in suspension in a basin or attached to a media of some type where the _____ material is broken down and consumed. Most secondary treatment processes require ____ for the bacteria.
microorganisms, organic, oxygen
The mixture of microorganisms and wastewater in an aeration tank is referred to as:
Mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS)/Activated sludge
List common equipment used in suspended growth secondary biological treatment
Hint: 5 kinds
aeration tanks, blowers, diffusers, final clarifiers, and sludge pumps
What is the purpose of the final clarifier?
To settle MLSS.
What are the two places settled solids from the aeration tank can end up?
RAS -- back to aeration tank
WAS -- wasted from the treatment system
Anaerobic activity results in ___ gas which is extremely toxic
Hydrogen Sulfide
How does an operator determine what preventative maintenance a piece of equipment requires?
By reading the O&M manual
What are three possible reasons a centrifugal pump could lose its prime?
A. Air Leak
B. No liquid at intake
C. Check valve doesn't seal
Which of the following are preventative maintenance activities for valves? Select all that apply.
A. Exercise and lubricate inactive valves
B. Inspect packing for leaking
C. Replace all screws quarterly
D. Annual replacement
A. Exercise and lubricate inactive valves
B. Inspect packing for leaking
In an open channel flow measurement, to measure amount of flow, a device must measure the:
Height (depth) of the water
Debris is lodged in the bottom of the v-notch weir. This would make the flow meter read:
A. Higher
B. Lower
C. The same
Higher
When is the DMR (Discharge Monitoring Reports) report due
21st day of the next month
T/F Trickling filters are a form of secondary treatment?
True
What is the most common way to dispose of sludge in Wisconsin?
Land application
What is the optimal DO range?
A. 0-1.0 mg/L
B. 1.0 - 3.0 mg/L
C. 1.5 - 3.5 mg/L
D. 2.0 - 4.0 mg/L
1.0 to 3.0 mg/L
What type of pump is a diaphragm pump?
A. Positive displacement
B. Negative displacement
C. Centrifugal
Positive displacement
This type of pump operates using a piston in a reciprocating motion to pump fluids. Commonly used for pumping sludges.
Positive displacement piston pump
Which of the following are attached growth systems? Select all that apply.
A. Rotating biological contactor (RBC)
B. Stationary biological contactor (SBC)
C. Trickling filter
D. Biotower
All except B
Process Control Equipment used for monitoring an activated sludge plant. Select all that apply.
A. DO meter
B. Settleometer
C. Sludge blanket finder
D. Microscope
E. pH/temp meter
F. Flow meter
All of the above
Process where nitrifying bacteria convert nitrogen in the form of ammonia to nitrite and nitrate under aerobic conditions.
Nitrification
Process where bacteria convert nitrate and nitrite to nitrogen gas under anoxic conditions
Denitrification
When would a plant be required to use denitrification to remove nitrogen?
When the WI DNR gives the plant a nitrogen limit.
What should the ratio of BOD to Nitrogen to Phosphorus be?
A. 10:1:1
B: 100:20:5
C. 100:5:1
D. 10:2:1
100:5:1
Where are common recycle streams from in a treatment plant?
Thickening and dewatering process
Stabilization and storage
Where are the two places settled solids can go?
RAS and/or WAS
[KNOW] be able to label final clarifier on pdf page 35
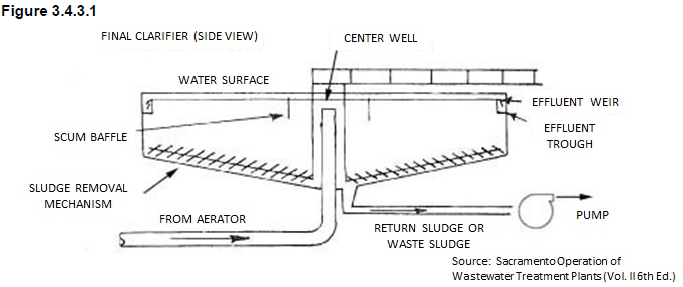
Which of the following are tertiary treatment methods? Select all that apply.
A. Ozone
B. Granular filtration
C. Carbon adsorption
D. Chemical precipitation
All except A
How many days is the detention time for lagoon/small pond systems?
A. 50 days
B. 100 days
C. 150+ days
150+ days
True or False: Stabilization ponds are aerated
False
True or False: Stabilization ponds are normally less than 10 feet deep
True
Centrifugal Pump
contains an impeller that rotates in a casing to pump large volumes of liquid through a pipe. This pipe is most commonly used for raw wastewater pump; at lift stations, recirculation flows, for RAS/WAS, and final effluent pumping.
A ____ pump is a type of pump and motor combination used for lift stations and wet wells. It is a type of centrifugal pump.
Submersible
True or False: Rotary lobe pumps are self-priming, valveless, positive-displacement pumps.
True
True or False: a peristaltic pump is a small positive displacement pump commonly used for sampling and chemical addition.
True
True or false: Progressive cavity pumps are unreliable and can often run dry and fill with excessive grit.
False--however, running dry and filling with excessive grit may cause equipment failure.
True or False: Air lift pumps are prone to plugging, especially as low return flow rates. Thus, operators should closely monitor these pumps to ensure sludge is being returned at all times.
True
What are diaphragm pumps commonly used for?
Adding chemicals or polymer. Larger pumps can be used for sludge.
What makes diaphragm pumps unique from other positive displacement pumps?
They protect the pumping mechanism from the material being pumped.
True or False: Trash pumps are non-clogging up to 3-4".
True -- they are often used for moving large volumes of wastewater quickly during dewatering