Lecture 1
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Life, ecology, evolution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
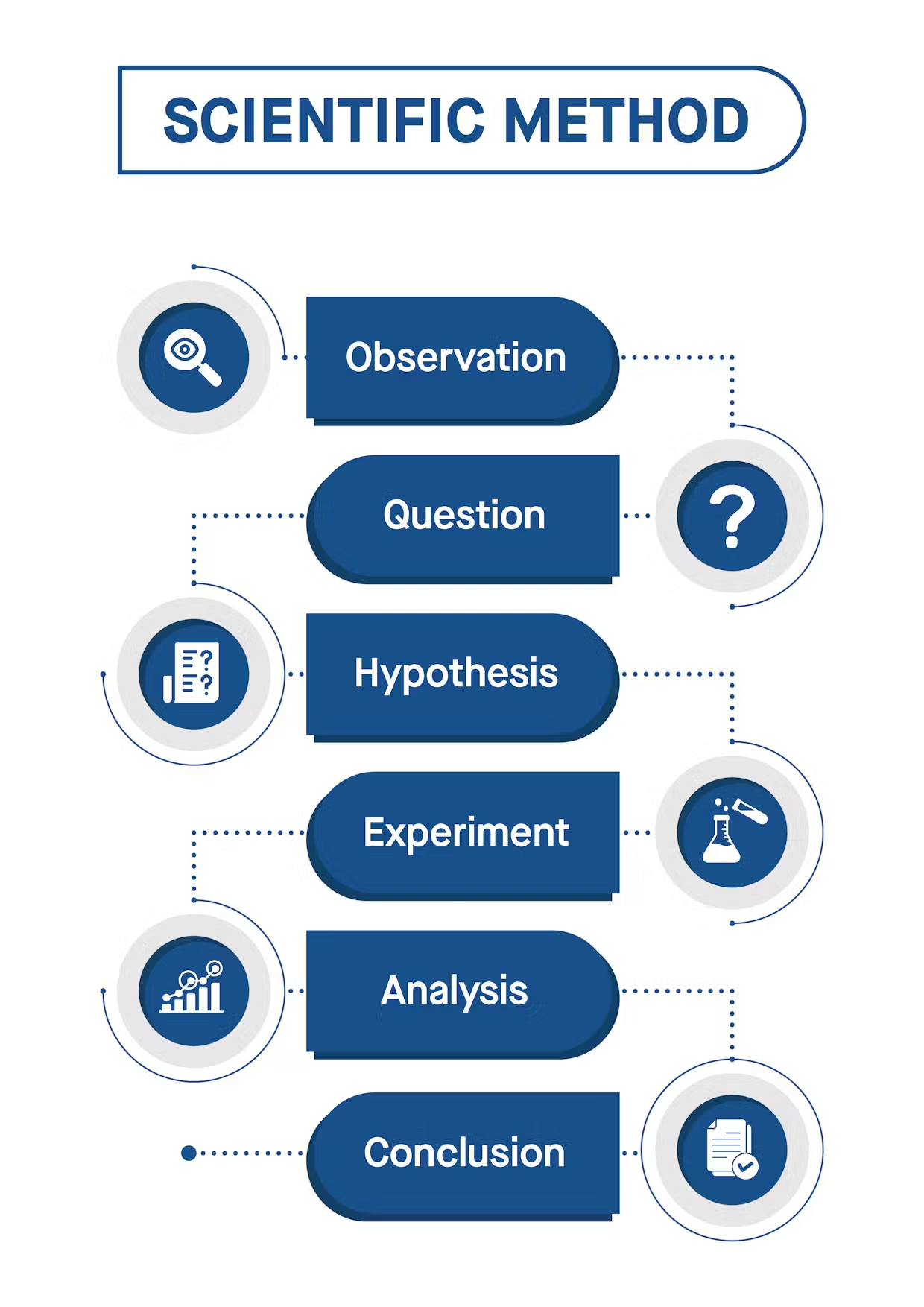
What is the process of science from observation to theory (evidence, iteration, repetition, etc.)?
Observation - Question - Hypothesis - Experiment (repeat multiple times) - Explanation (iteration) - Theory

What are the traits of all living things? (7)
order and organization, energy processing, growth and development, evolutionary change, regulation (homeostasis), reproduction, response to stimuli

How do non-living things fail to meet one or more requirements of living things?
an example could be fire, it checks off everything but having cells (such as atoms)

Why are ecology and evolution taught together?
evolution shapes ecology, ecology drives evolution, together they make more sense!

Who developed the theory of evolution as we know it today?
Not just Charles Darwin! But many others such as Aristotle, Humboldt, Lyell, Mary Anning, etc..

What is the smallest unit of life?
atoms

What is Ecology?
the study of how organisms interact with each other, and with the environment in which they live (biotic and abiotic interactions)
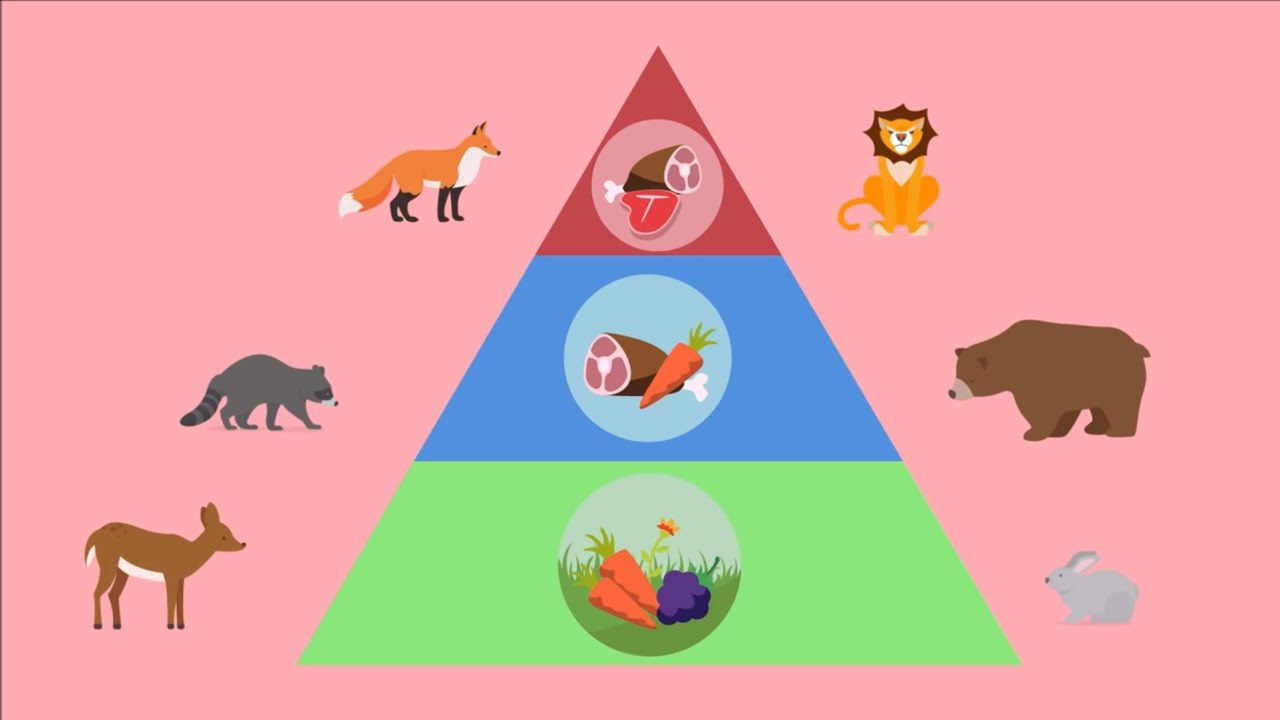
What are Biotic Interactions?
Living organisms interacting with other living organisms (competition, mutualism, predation, etc)
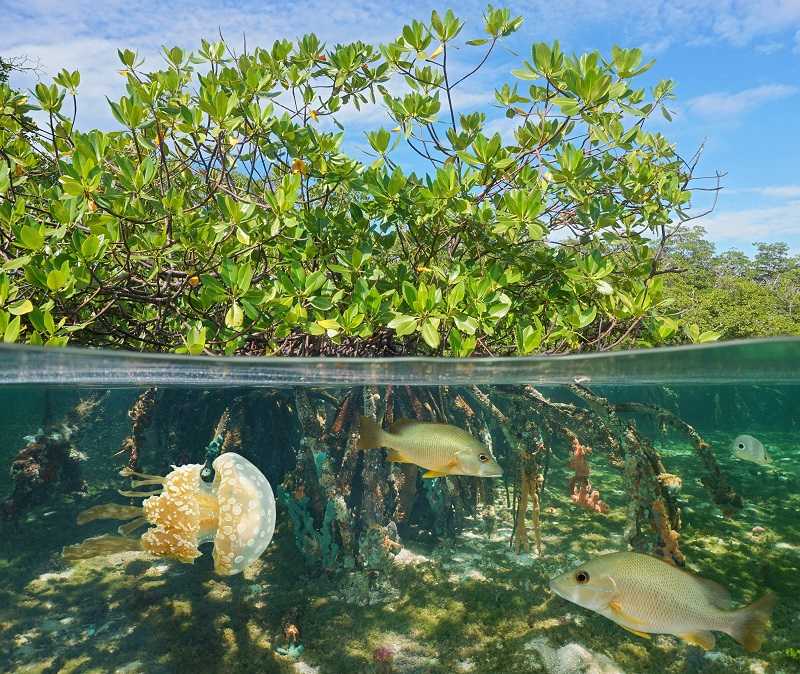

What are Abiotic Interactions?
the relationship between non-living things and living things and how it affects their environment (temp, water, sunlight, etc)
What is Evolution?
they study of changes in heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations (microevolution and macroevolution)
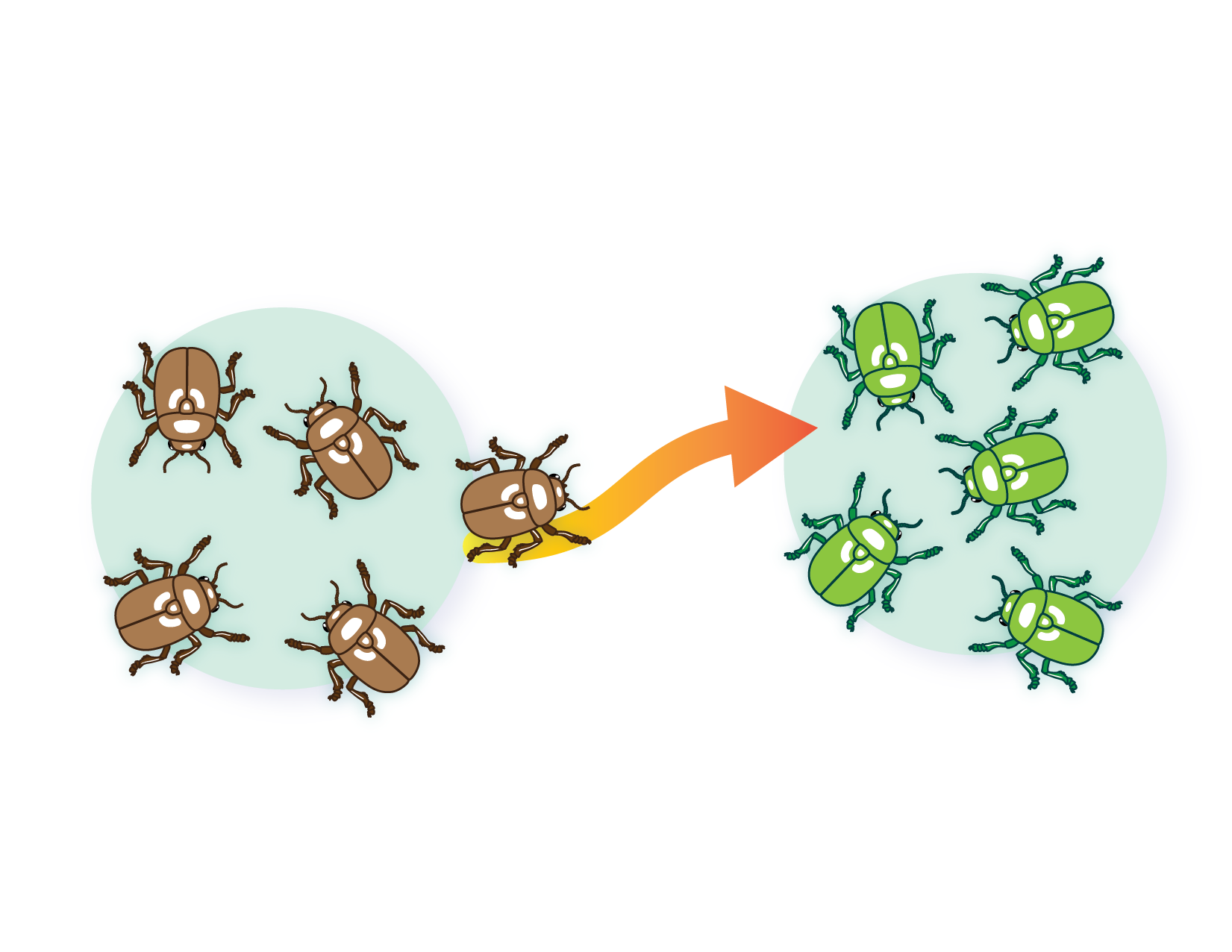
What is Microevolution?
small, gradual genetic changes within a single population over a short time. happens through mutation, natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow.
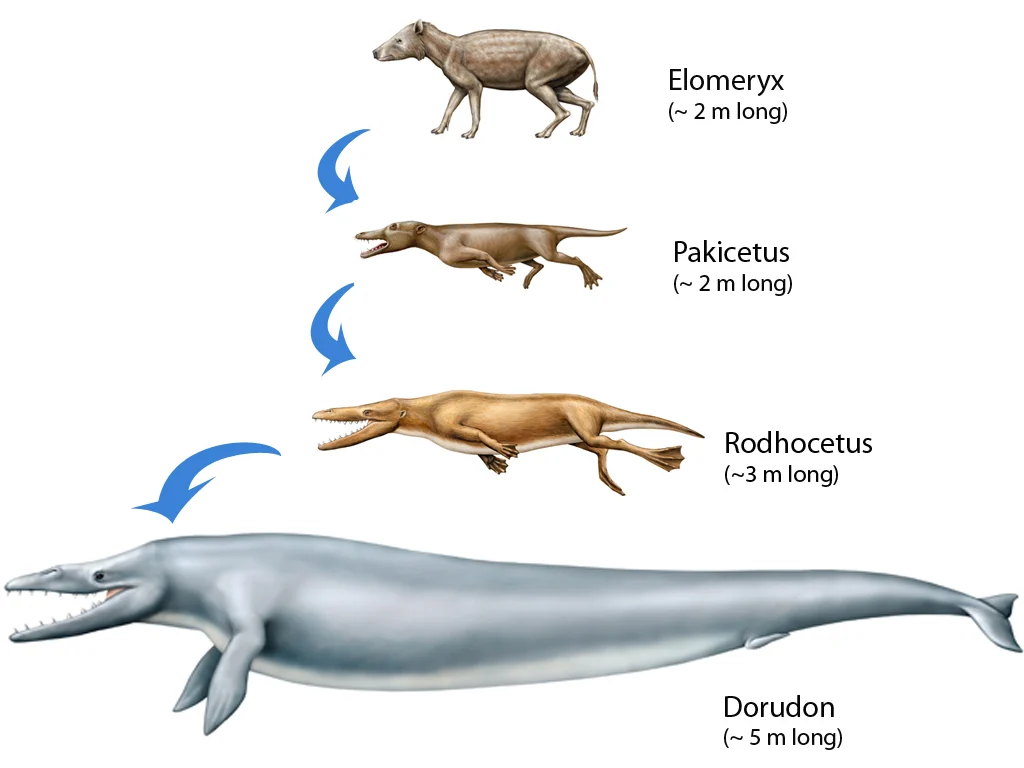
What is macroevolution?
large-scale changes that happen over millions of years, leading to new species, genera, or even entire groups of organisms. includes speciation (new species forming) and extinction events.

What are some examples of evolution AND ecology? (6)
natural selection, mutation, phenotype, mutualism, mate choice, competition, etc