NPTE Studying Stroke and TBI
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What are the two different types of CVA?
Ischemic - clock or blockage
Hemorrhagic - Rupture or leakage
The first ____ hours is critical to attend to for a ischemic CVA
72 hours
How does an Anterior Cerebral artery CVA present?
Contralateral motor and sensory loss greater in the LE > UE
Sensory loss LE > UE
Memory and behavioral impairments due to Frontal Lobe involvement
Problems with imitation and bi-manual tasks, apraxia
Urinary incontience
What is the most common ischemic stroke?
Middle Cerebral artery
How does a non dominant Middle Cerebral Artery CVA present?
Contra motor & sensory involving UE and face (UE > LE)
Contra Homonymous Hemianopsia
NonDominant Side (Right stroke)
Perceptual problem
Unilateral neglect, depth perception, spatial relations, agnosia, apraxia)
How does a dominant side middle cerebral artery CVA present?
Dominant Side (Left stroke)
Aphasia
Contra motor & sensory involving UE and face (UE > LE)
Contra Homonymous Hemianopsia
What would happen if you give a step up as a TherEx for a patient who had a non-dominant middle cerebral artery? What side of the brain is affected?
Right stroke
They do not know how much knee or hip flexion they will need in order to ambulate up the stairs
Will typically hear a stomp
What is Homonymous Hemianopsia?
loss of half of the field of view on the same side in both eyes
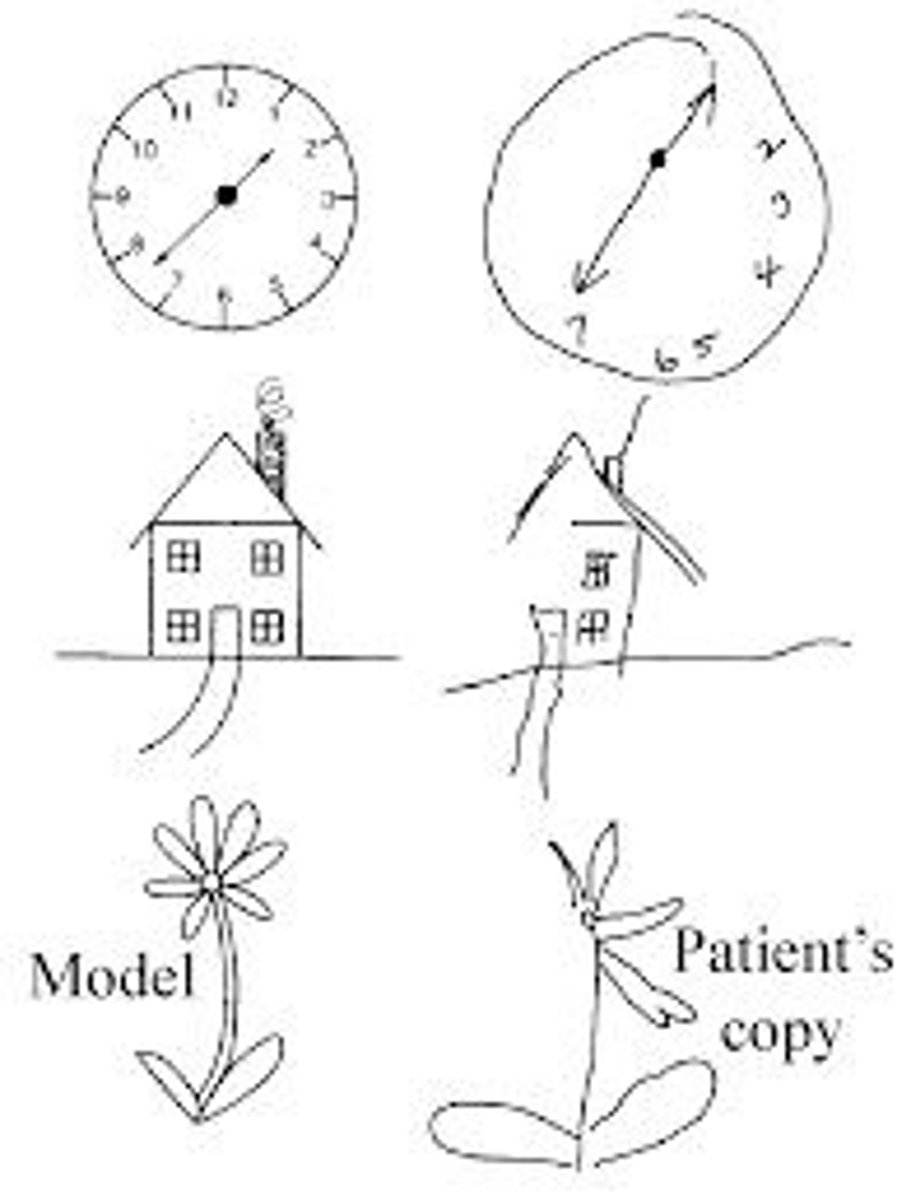
What is Hemineglect?
Patient may have distortions of the perception on the contralateral side. If drawn a clock, the numbers would be filled all on one side
What interventions would you use to treat those with Homonymous Hemianopsia or Hemineglect?
Strategies that encourage awareness and use of the environment on the hemiparetic side of the hemiparetic limb
Teach active visual scanning - active movement is important, need to turn head and axial trunk rotations to the more involved side
What is Aphasia?
loss of ability to understand or express speech, caused by brain damage
What is global aphasia?
Wernicke's and Broca's aphasia put together
Impairments in both production and comprehension of lanuage
Where would the lesion be if your patient has aphasia?
Dominant Hemisphere
Left hemisphere
What is Wernicke's Aphasia?
"Fluent Aphasia" - Word Salad
Lesion located in auditory associated cortex in the left lateral temporal lobe
Auditory comprehension is impaired with difficulty with comprehending spoken lanuage
What is Broca's Aphasia?
Nonfluent Aphasia - Broken Speech
Lesion in the premotor area of the left frontal lobe
Flow of speech is slow and hesitant, but comprehension is good
What is spatial perceptual Dysfunction?
Incorrect perception of self & illness
Incorrect perception of self in space (may neglect all input from the affected side (worsened by homonymous hemianopsia)
What is Agnoisa?
Unable to identify an object by sight, touch, or hearing
What is a huge part of treatment you need to be aware of with a spatial perceptual dysfunction?
Safety safety safety
A PT is ordered to examine a 76 year old patient who has suffered a recent stroke. The OT informs the PT that the patient has apraxia. She cannot drink from the bottle on command. However, she can point out the bottle and verbalize the purpose of the bottle. From this information, what sort of apraxia does this patient have? How should the PT approach treatment?
A. Ideomotor apraxia; The PT should speak in short concise sentences
B. Ideational apraxia; The PT should always give the patient 3-step commands
C. Ideomotor apraxia; The PT should always give the patient 3-step commands
D. Ideational apraxia; The PT should speak in short concise sentences
A. Ideomotor apraxia; The PT should speak in short concise sentences
The action of 3-step command is not going to change anything since they are unable to do the task on command
How does a Posterior Cerebral Artery present?
Contra Homonymous Hemianopsia
Memory deficits
Visual Agnosia
Prosopagnosia - difficulty naming people on sight)
Central post stroke (thalamic) pain
How does a Vertebrobasilar Artery: Locked in Syndrome present?
Basilar artery infarct of bilateral pons
Rapid progression from hemiparesis to tetraplegia
Cranial nerve paralysis (CN V-XII)
Rapid progression from dysarthria to anarthria
Result → Patient cannot move or speak but is alert and oriented
In PT session, the therapist commands the patient to wear a shirt, but the patient is unable to complete the task due to inability to find buttons on his shirt. Which of the following is MOST appropriate diagnosis and the best possible strategy to address this deficit?
A. Form discrimination, patient should be encourage to use touch to identify objects
B. Figure-ground discrimination, patient should be encourage to use touch to identify objects
C. Position in space impairment, orientating the patient with one object in relation to another
D. Ideational apraxia, having the patient perform one part of the task at a time, guiding the patient with the task if needed
B. Figure-ground discrimination, patient should be encourage to use touch to identify objects
A patient with right hemisphere damage would MOST likely have
A. Left unilateral neglect and difficulty reaching for objects presented on the Left side of the body
B. Left unilateral neglect and difficulty reaching for objects presented on the midline of the body
C. Difficulty crossing midline to reach objects on the right side of the body
D. Difficulty stabilizing gaze and locating objects on the right side of the body
A. Left unilateral neglect and difficulty reaching for objects presented on the Left side of the body
What are some Right side specific CVA symptoms?
Left side weakness/paralysis
Left neglect, spatial perceptual problems
Poor judgment, impulsivity
Short attention span and short term memory loss
Communication problems
Due to weakness of facial muscles
Cognitive problems
What are some Left side specific CVA symptoms?
Right side weakness/paralysis
Aphasia
Due to damage in Wernicke's and/or Broca's
Personality changes
Cautious, compulsive, disorganized
Difficulty with new information
Decreased memory
Difficulty generalizing or conceptualizing
What are the components of an UE flexor synergy?
Scap retraction, elevation, hyperextension
Should ABD, ER
Elbow flexion
Forearm supination
Wrist and finger flexion
What are the components of a LE extensor synergy?
Hip extension, ADD, IR
Knee Ext
Ankle PF, INV
Toe Extension
During the initial eval, PT asks the stroke patient to lift her left arm as high as she is able. Patient is able to lift her arm off of her lap; however, she is only able to move it with elbow flexion, shoulder elevation, and wrist flexion with significantly increased tone. Which of the following Brunnstrom's Stages Of recovery is MOST appropriate description for this patient?
A. Stage 3
B. Stage 4
C. Stage 5
D. Stage 6
A. Stage 3
What is the most important stage for therapy for Brunnstrom's Stages Of recovery?
Stage 4
Due to being able to create movements outside of the synergy patterns
What are the 7 stages of Brunnstrom's Stages Of recovery is
Stage 1 - Flaccidity, No active limb movement
Stage 2 - Beginning of minimal voluntary movement
In synergy, with associated reactions
Increase in tone
Stage 3- Voluntary control of movement synergy (spasticity at peak)
Stage 4 - Movement outside synergy
Decrease in tone
Stage 5 - Increased in complex movement, greater independence from limb synergies
Stage 6 - Individual join movement, coordinated movement
Stage 7 - Normal function
A PT is evaluating an 86 year old female, who sustained a Right CVA due to a MCA infarction 1 week ago. Patient has the classical signs and symptoms of MCA CVA. During the initial eval, the PT performs reflex testing on the patient. The PT would expect what?
A. Right side hyperreflexia and (-) Babinski
B. Right side hyporeflexia and (+) Babinski
C. Left side hyperreflexia and (+) Babinski
D. Left side hyporeflexia and (-) Babinski
Left side hyperreflexia and (+) Babinski
In a patient that has been Dx with a CVA, how would you position their UE affected side in supine?
Scapular protracted; shoulder forward and slightly ABD
Arm supported via pillow
Elbow extended with hand resting on pillow
Wrist neutral, fingers extended, thumb ABD
In a patient that has been Dx with a CVA, how would you position their LE affected side in supine to reduce common malalignments?
Hip forward (pelvis protracted)
Knee on small pillow or towel roll to prevent hyperextension
Nothing against soles of feet
In a patient that has been Dx with a CVA, how would you position them if they are side lying on the more affected side?
Head/neck: neutral and symmetrical
Trunk: aligned in midline
More Affected UE: Scapular protracted, shoulder forward, arm placed in slight abduction and ER, elbow extended, forearm supinated, wrist netural, fingers extended and thumb abducted
LE: Hip extended and knee flexed supported by pillows
In a patient that has been Dx with a CVA, how would you position them if they are side lying on the less affected side?
Want to elongate the hemiplegic side
Trunk: aligned midline; small pillow or towel can be placed under the rib cage to elongate the hemiplegic side
UE: Scapular protracted, shoulder forward; arm on a supporting pillow with elbow extended, wrist neural, fingers extended, thumb abducted
In a patient that has been Dx with a CVA, how would you position them if they are sitting in an arm chair or wheelchair?
Head/neck: neutral and symmetrical; head directly above pelvis
Trunk: spine extension
Pelvic: aligned in neutral with WB on both buttocks
More affected UE: Shoulder protracted and forward; elbow supported on arm through or lapboard; forearm, wrist neutrals, fingers, and thumb abduction (resting splint as needed)
Both LEs: Hips flexed to 90deg, positioned in neutral with respect to ration
What is Pusher's Syndrome?
Altered perception of body orientation in relation to gravity
-Lateral postural imbalance due to pushing with stronger UE/LE towards weaker side
-Believe they are upright but are actually leaning towards affected/weaker side
-Seen in 10% of people after stroke (usually thalamic stroke)
What is the intervention for Pusher's Syndrome?
Therapist can sit on the patient's LESS involved side and instruct the patient to "lean over to me."
OR
the patient can be positioned with the LESS involved side next to a wall and instructed to "lean" towards the wall
Patient should be fully involved in problem solving
What are the clinical signs and symptoms of "Pusher's Syndrome"?
Spontaneous body tilting toward the more-affected side
Abduction and extension of the less-affected extremities
A 82 year old patient suffered a right sided CVA about a week ago. The therapist is educating him on various positioning strategies. Which of the following is the MOST appropriate while lying on the left side?
A. Head/neck: Neutral, left scap protracted; L arm in slight abduction and ER; elbow extended, forearm supinated, wrist neutral, fingers extended, and thumb abducted
B. Head/neck: Neutral, left scap protracted; L arm in slight abduction and IR; elbow extended, forearm pronated, wrist neutral, fingers extended, and thumb adducted
C. Head/neck: Neutral, right scap protracted; L arm in slight abduction and IR; elbow extended, forearm pronated, wrist neutral, fingers extended, and thumb adducted
D. A. Head/neck: Neutral, left scap protracted; L arm in slight adduction and ER; elbow flexed, forearm supinated, wrist extended, fingers flexed, and thumb abducted
A. Head/neck: Neutral, left scap protracted; L arm in slight abduction and ER; elbow extended, forearm supinated, wrist neutral, fingers extended, and thumb abducted
What is the PNF UE D1 Flexion pattern?
Flex, adduction, ER
Forearm supination
Wrist - radially flexed
What is the PNF UE D1 Extension pattern?
Ext, Abd, IR
Forearm pronated
Wrist ulnarly extended
What is the PNF UE D2 Flexion pattern?
Flex, ABD, ER
Wrist radially extended
What is the PNF UE D2 Extension pattern?
Ext, Add, IR
Wrist ulnarly flexed
What are head/neck and trunk chop patterns?
Lead arm (weak arm) goes through the required pattern
Assist arm (strong arm) holds from the top of the wrist and moves into the opposite PNF pattern
Ex: Lead arm begins in D1 Flex and moves into D1 Ext while the assist arms moves into D2 Extension
The trunk and head needs to follow these movements
What is an UE thrust pattern?
What is the D1 lower extremity extension pattern?
Hip Ext, abd, IR
Knee flexion or extension
Ankle PF, eversion and toe flexion
What is the LE D2 Flex/Ext pattern?
Karate kick
Kick your leg up and out
Pull your leg down and behind
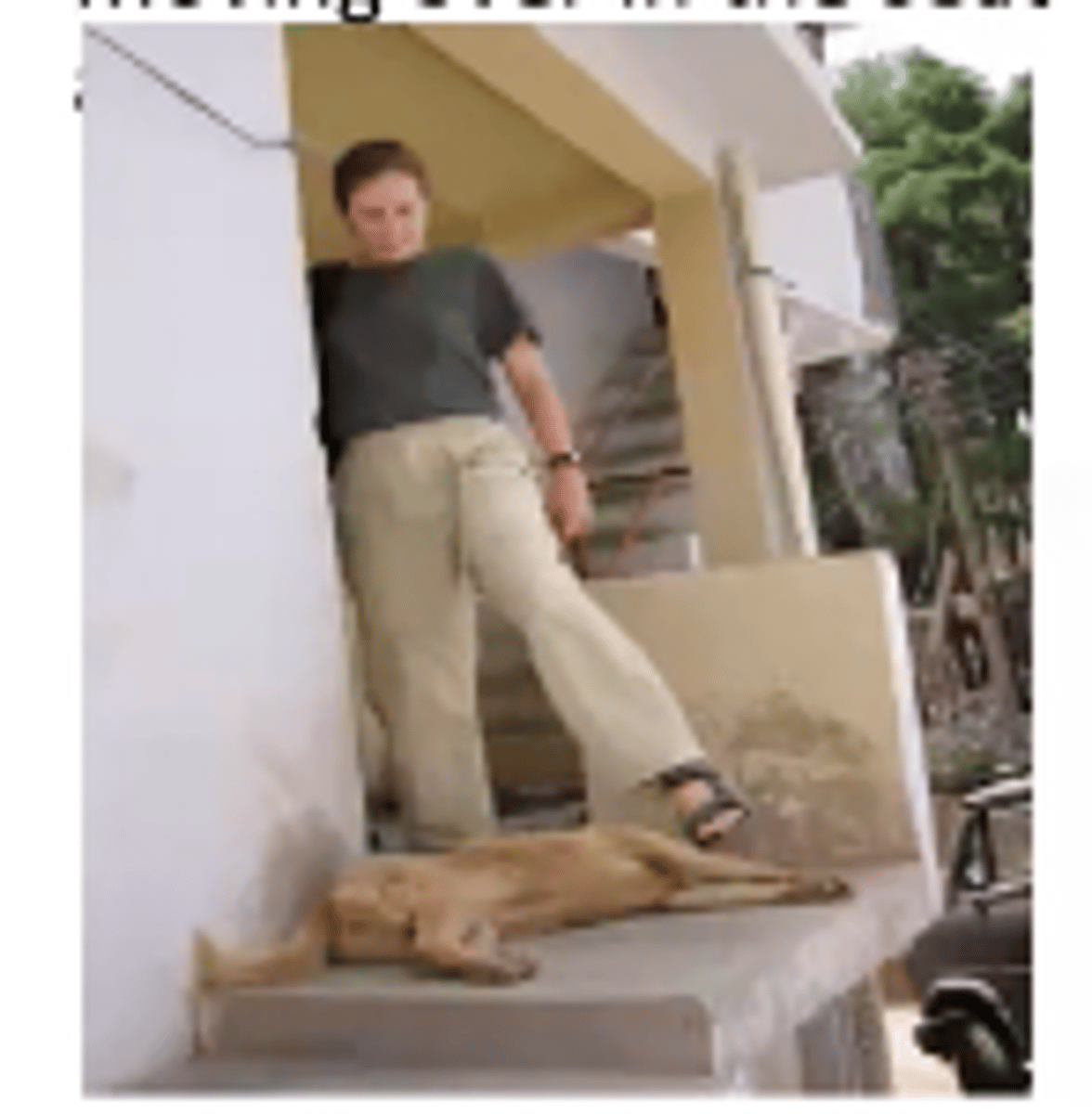
What is the LE D1 Flex/Ext pattern?
Soccer kick
Leg up and across
What is D2 Flexion pattern for LE?
Hip flexion, ABD, IR
Knee flex or extend
Ankle DF, eversion, Toe flexion

What is a D2 extension pattern for LE?
Hip extension, Add, ER
Knee flexion or extension
Ankle PF, inversion
Toe flexion

A patient diagnosed with Parkinson's disease exhibits a forward stooped posture. As part of the patient's care plan, the PT selects a number of active exercises that promote improved posture. Which PNF pattern would be the MOST appropriate to achieve the PT's objective?
a. D1 Extension
b. D1 Flexion
c. D2 Extension
d. D2 flexion
D. D2 Flexion Pattern
Helps open up the airway and helps eliminate the stooped posture
A therapist examines a 69 year old woman who has suffered a recent stroke. The therapist needs to focus on pre-gait activities. Which PNF diagonal best encourages normal gait?
A. D1
B. D2
C. PNF is contraindicated
D. Pelvic PNF patterns only
A. D1
This is very similar to walking
What is Decorticate posturing?
Abnormal flexor response, sustained contraction and posturing of the UE in flexion & LE in extension
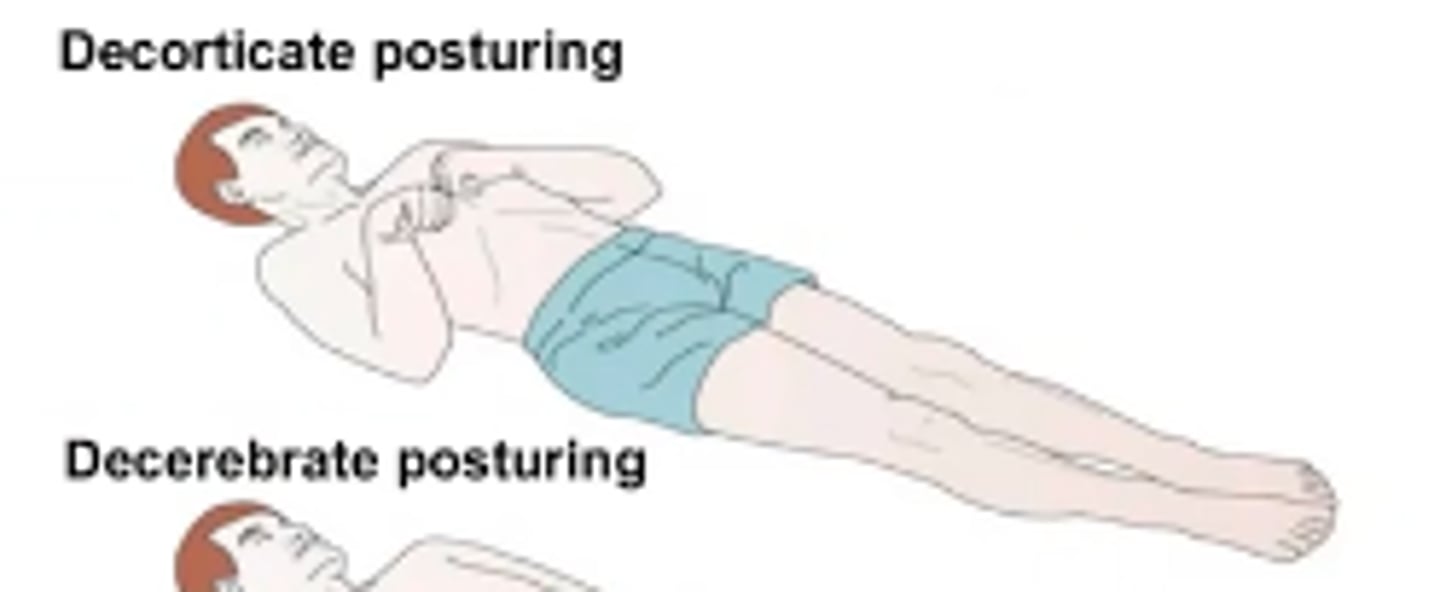
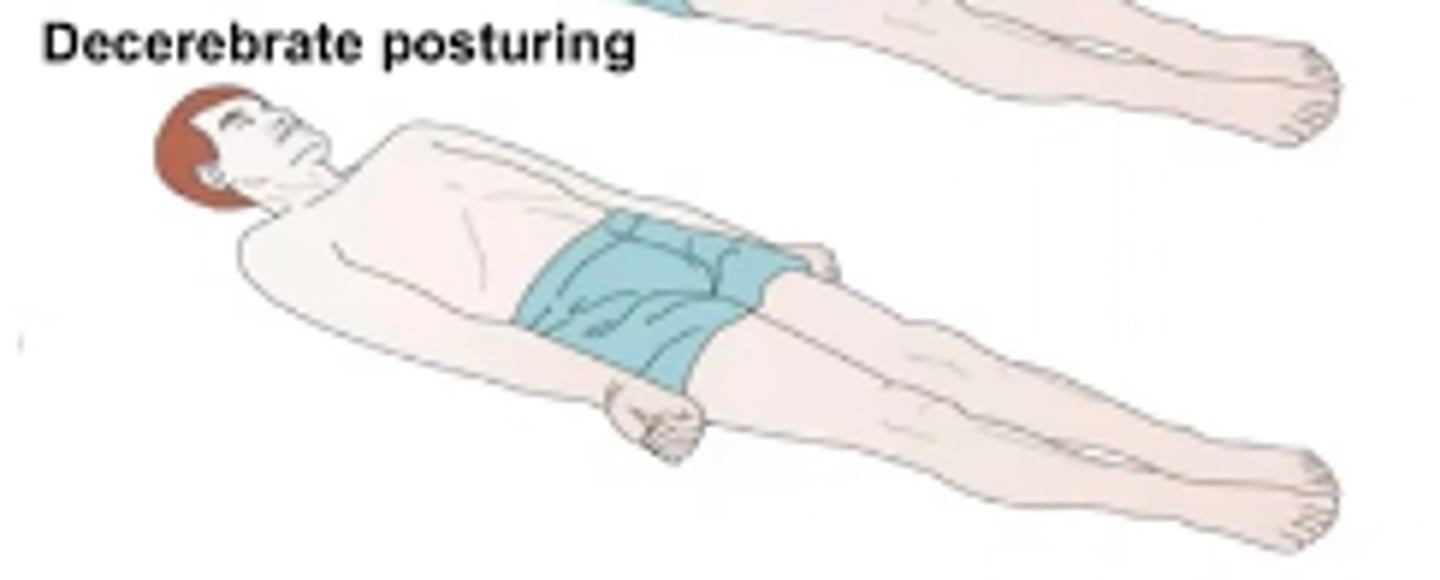
What is Decerebrate posturing?
Abnormal extensor response
Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and limbs in full extension
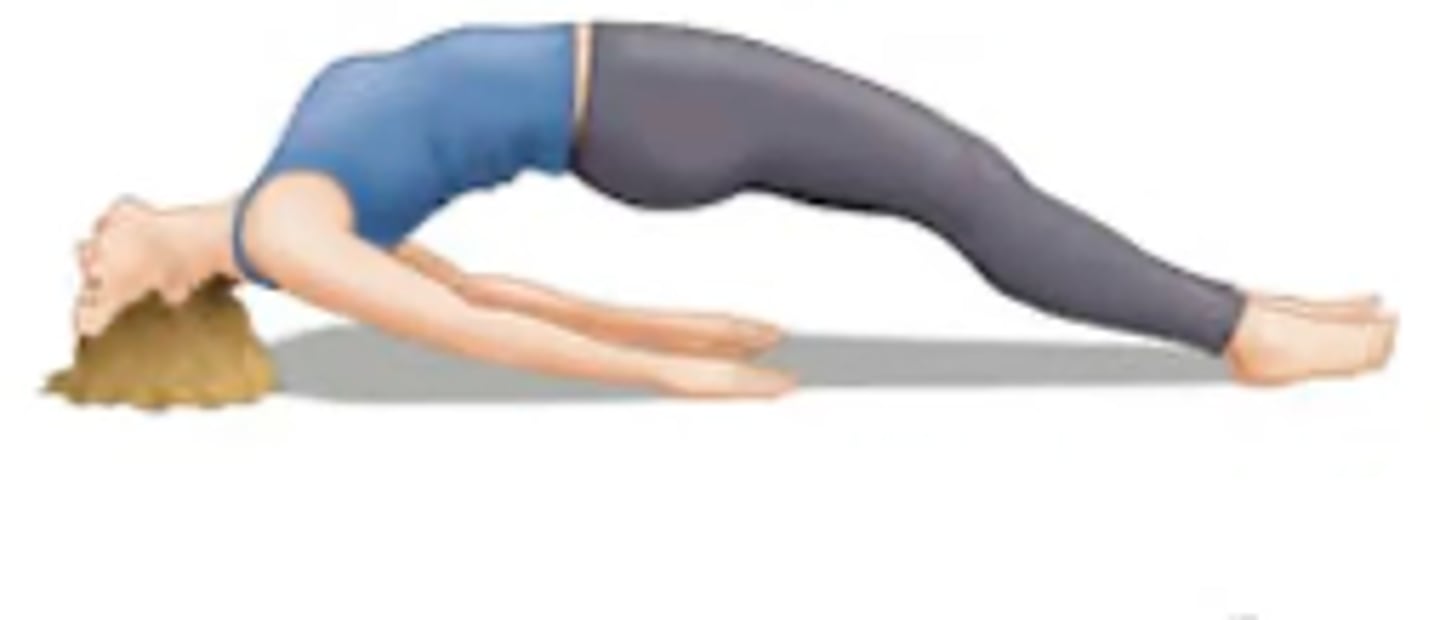
What is opisthotonus posturing?
Strong sustained contraction of the extensor muscles of the neck and trunk

What are stages I-III in the Rancho Los Amigos Level of cognitive functioning scale?
I. No response, Completely unresponsive to any stimuli
II. Generalized Response Patients react inconsistently and non-specifically to stimuli
III. Localized response Patients react inconsistent but specifically to stimuli
What is Rancho Level IV?
Confused/Agitated:
Alert and in heightened state of activity with potential aggressive behaviors
Absent short term memory
Unable to fully cooperate with treatment
When treating a patient that is a Level IV on the rancho scale, how should you set up the treatment session?
Quiet room
Remove all possible distractions
Remove objects that can be thrown or used aggressively
What is Rancho Level V?
Confused, inappropriate, non-agitated
Unable to learn new information, but can listen/understand simple commands
Frequent brief periods, non-purposeful sustained attention
Intervention
How would you structure your intervention plan for someone who is a rancho level v?
Quiet environment
Highly structured functional tasks
Need a routine
Can use assistive devices
Give options
What is Level VI of the rancho los amigos scale?
Confused and Appropriate
little carry-over for new learning
MaxA for new learning or no carry over
Consistently follows simple directions
Unaware of impairments, disabilities, and safety risks
How would you structure your intervention plan for someone who was on the level VI Rancho Los Amigos scale?
Highly structured functional tasks
Decreases cues/external direction
Decrease use assistive devices
Increase speed and complexity of tasks as able
A physical therapist is called to assess a patient with traumatic brain injury. The therapist documents that the patient has a cerebrate posturing pattern. Which of the following is MOST likely to be seen in this patient?
A. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and lower limbs in extension, and the upper limbs in flexion, fists clenched
B. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and lower limbs in flexion, and upper limbs in extension, fists clenched
C. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and limbs in position of full extension
D. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and limbs in a position of full flexion
C. Sustained contraction and posturing of the trunk and limbs in position of full extension
A patient recovering from TBI is functioning at stage IV on the Rancho Los Amigos level of cognitive functioning scale. During the therapist's initial examination, the patient becomes agitated and tries to bite the therapist. The BEST course of action is to:
A. Postpone the examination until later in the day when the patient calms down
B. Postpone the examination for 1 week and then try again
C. Document the behaviors and engage in calming activities
D. Restructure the formal exam so the therapist can complete it in 3 very short sessions
C. Document the behaviors and engage in calming activities
Other answers are too passive and will not work in this specific scenario
Restructuring will not change any of the behavior that will occur with this type of client
What is Level VII of the rancho los amigos scale?
Automatic, Appropriate
Min supervision for new learning, with carryover
Initiation and follow through of basic ADLs
Minimal supervision for safety in routine home and community activities
Able to attend to highly familiar tasks in a non-distraction environment for at least 30 min with minA to complete tasks
How would you structure a treatment session for someone who is a Level VII on the rancho los amigos scale?
Structured functional tasks
Increase complexity of tasks
Work on coordination and fine motor control
What is Level VIII of the rancho los amigos scale?
Purposeful, Appropriate (stand by assistance)
Consistent orientation to person, place, and time
Independent with familiar tasks for an hour in distracting environment
Uses memory devices to recall schedules
Able to recall and integrate past and recent events
How would you structure an intervention session with someone who is a level VIII on the rancho los amigos scale?
Structured and unstructured functional tasks
Increase complexity of tasks
Work on coordination and fine motor control
Immediate steps you should take when someone is experiencing autonomic dysreflexia?
Sit them up to lower BP
Look for the noxious stimuli (bladder distension most common cause)
How to treat orthostatic hypotension for someone with SCI?
Gradual progression to vertical position
Use abdominal binder and compression stockings to minimise effects