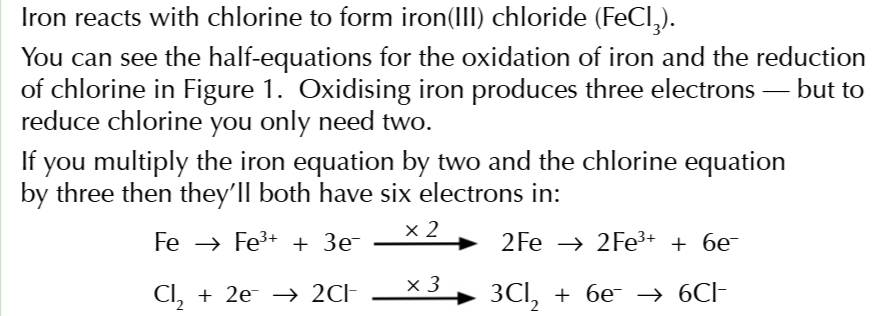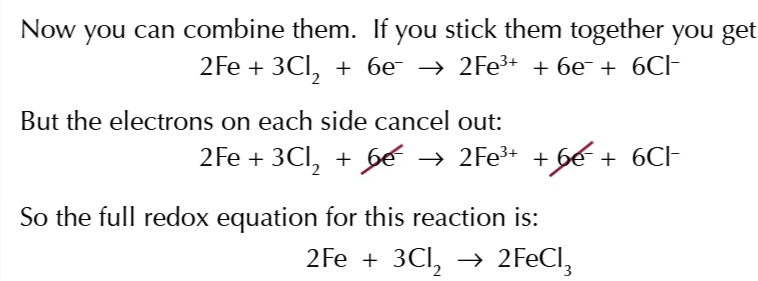EQHILIBRIA AND REDOX REACTION PART 2
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
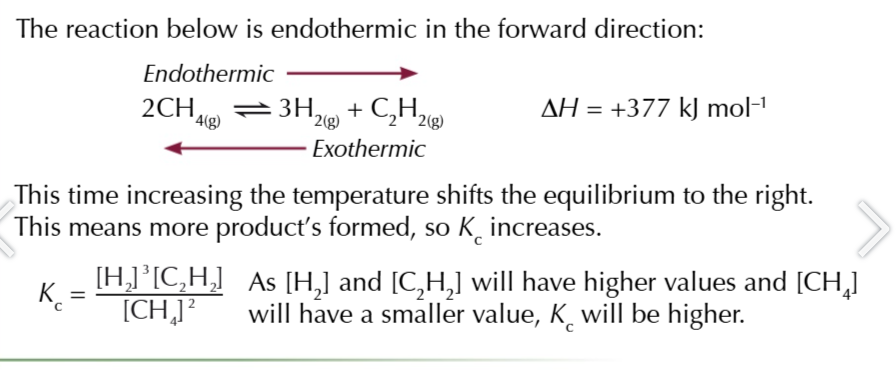
Increasing the temperature adds heat
the equilibrium shifts in the endothermic direction to absorb heat
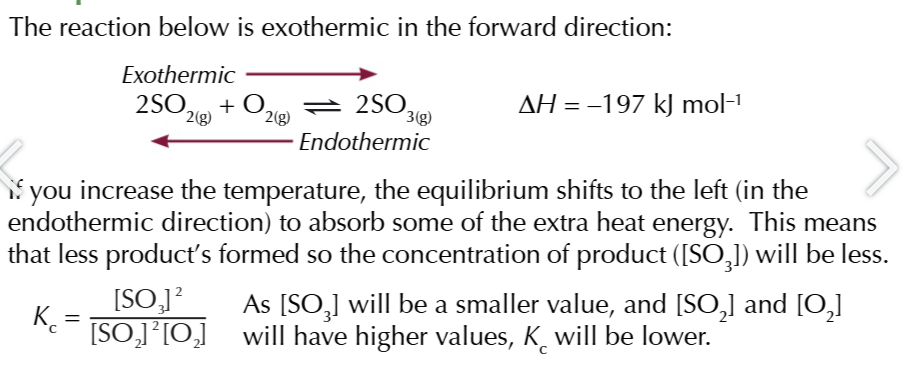
decreasing the temperature removes heat
the equilibrium shifts in the exothermic direction to replace heat
if you change the temperature and cause more product to form
Kc value increases
if you change the temperature and cause less product to form
Kc value decreases

changing the concentration…
does not affect the Kc value
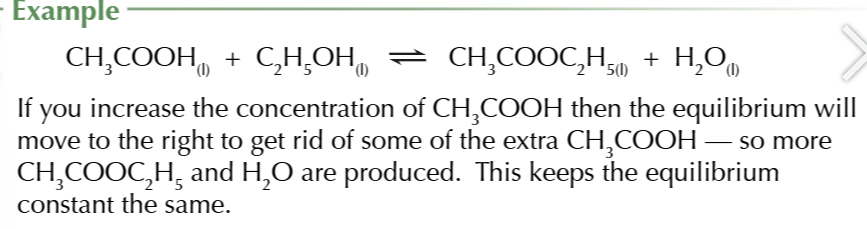
adding a catalyst
has no effect of the equilibrium position or Kc value because it increases the rate of both forwards and backwards reactions by the same amount so equilibrium will only be reached faster
how do catalysts increase the rate of reaction?
catalyst provide the surface for a reaction therefore increasing the surface area which increases the number of available active sites which increases the frequency of successful collisions
oxidation
loss of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
redox
reduction and oxidation occurring at the same time
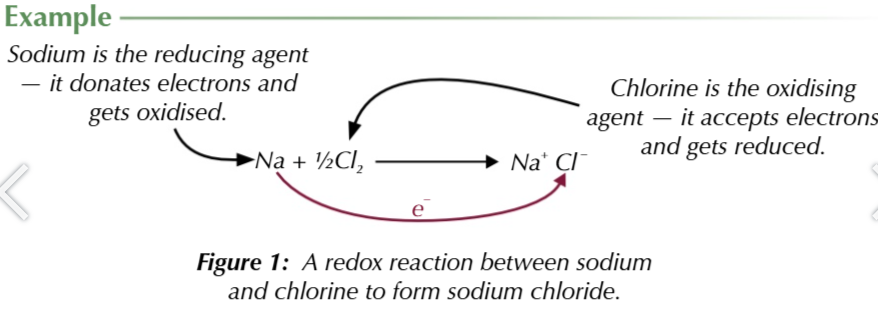
oxidising agent
accepts electrons and gets reduced
reducing agents
donates electrons and gets oxidised
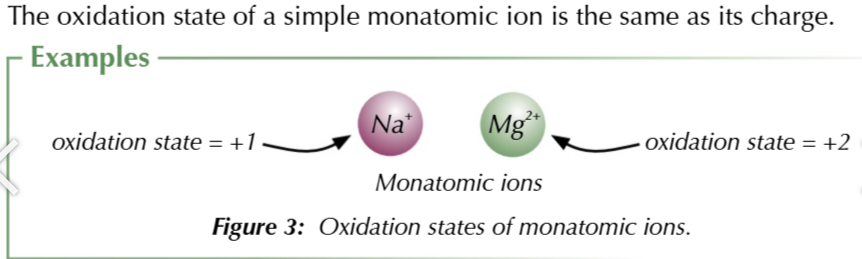
oxidation state/ number
total number of electrons an element has donated or accepted
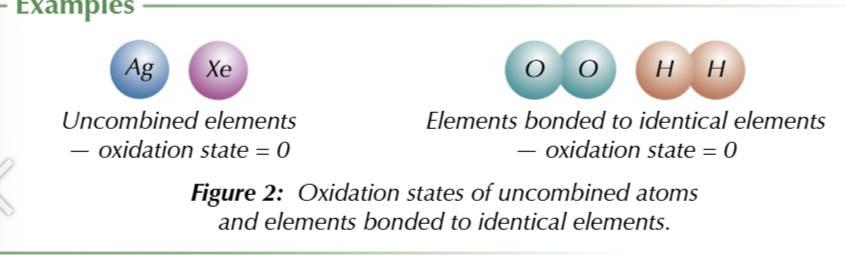
elements with an oxidation state of 0
uncombine elements
elements bonded to identical atoms
atoms in compounds/ compound ions
have their own oxidation states which sum up to make the compounds overall oxidation state
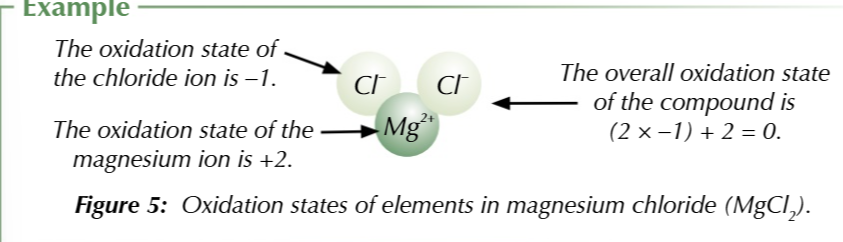
within compound ions
the most electronegative elements has a negative oxidation state while others have positive ones
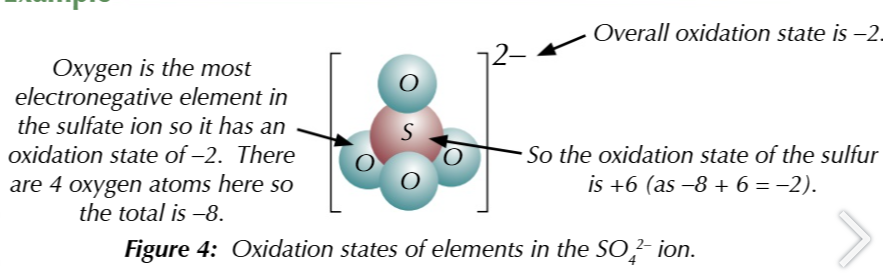
oxygen normally has an oxidation state of 2-
HOWEVER when in a PEROXIDE, oxygen has an oxidation number of -1
hydrogen usually has +1 oxidation state
when hydrogen is bonded to a metal like Li/Na etc its oxidation state is -1


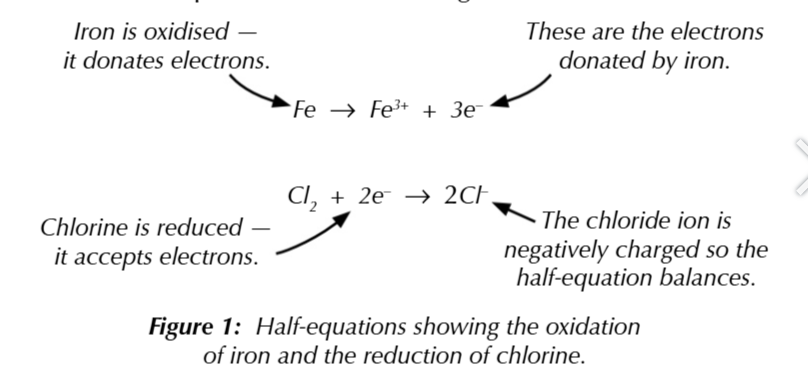
ionic half equations show oxidation or reduction
electrons are shown in a half equation so the charges balance