Exam 2 Flashcards
1/267
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
268 Terms
Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek
Father of Microbiology
Kochs’s Postulates
The microorganisms must be found in abundance in all organisms suffering from the disease, but should not be found in healthy organisms
The microorgansim must be isolated from a disease organisism and grown in a pure culture
The culutured microorganism should cause disease when introduced into a health organism
The microorgansim must be reisolated from the inoculated diseased experimental host and identified as being identical to the originial specific causative agent
Gerhard Domagk
Prontosil
What does prontosil Cure
streptococcal infections
Sir Alexander Fleming
penicillin
what does mold secreting penicillin kill
staphylococci
Selman Abraham Waksman
streptomyces
What does streptomycin kill
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Giuseppe Brotzu
discovered original cephalosporin (Cephalosporium
acremonium) from sewer outfall
Is there an ecological rationale for production of antibiotics by microbes?
Antibiotic resistance
When germs develop the ability to defeat the antibiotics designed to kill them, one of the greatest global heath challenges of modern time
Antibiotic Resistance infections affect
Sepsis Treatment
Surgery
Chronic conditions (ex, diabetes)
Organ transplants
Dialysis for advanced kidney disease
Cancer Care
Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae
Are a major concern for patients in healthcare facilities. Some bacteria in this family are resistant to nearly all antibiotics , leaving. more toxic or less effective treatment oprions
How do CRE spread antibiotic resistance?
They can carry mobile genetic elements that are easily shared between bacteria
Plasmids
Circles of DNA that can move between cells
Transpoons
small pieces of DNA that can go into and change the overall DNA of a cell. These can move from chromosomes (which carry all essential genes for germ survival) to plasmids and back
Phages
Viruses that attack germs and carry DNA from germ to germ
Transduction
Resistant genes can be transfered from one germ to another via phages
Conjugation
Resistant genes can be transfered between germs when they connect
Transformation
Resistant genes released from nearby live or dead germs can be picked up directly from another germ
Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms
Antibiotic degrading enzyme
Antibiotic Alterning Enzyme
Antibiotic efflux pump
Example of a drug class affected by antibiotic degrading enzymes
Beta-Lactams
Example of a drug class affected by antibiotic altering enzyme
Aminoglycosides
Example of a drug class affected by an antibiotic efflux pump
tetracyclines
What is a biofilm?
A biofilm is a community of bacteria encased in a self-produced extracellular matrix that adheres to surfaces and protects bacteria from external threats, including antibiotics.
How does a biofilm contribute to antibiotic resistance?
Biofilms act as a protective barrier, preventing antibiotics from penetrating and reaching bacteria, leading to increased resistance.
Kirby-Bauer Assay
A standardized method used to test bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics by measuring the zone of inhibition around antibiotic-impregnated discs on an agar plate.
How is the Broth Dilution Assay performed?
Bacteria are inoculated into tubes or wells containing liquid media with serially diluted concentrations of an antibiotic, then incubated and observed for growth.
MIC - Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
Lowest concentration of a drug that results in no visible growth of the bacteria
MBC - Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
Lowest concentration of the drug that kills 99.9% of bacteria cells in original inoculum
Bacteriostatic activity
An antibacterial drug that stops the growth of a pathogen but does NOT kill it at the site of infection after a therapeutic dose
Bactericidal Activity
An antibacterial drug that kills a pathogen at the site of infection after a therapeutic dose
Five major pathways/targets of clinically used antibacterial drugs
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Inhibition of protein synthesis
Inhibition of DNA or RNA synthesis
Inhibition of folate synthesis
Membrane distribution
Sulfonamides
Inhibitors of folic acid biosythnesis in bacteria
Sulfonamides MOA
inhibit dihydropteroate synthase
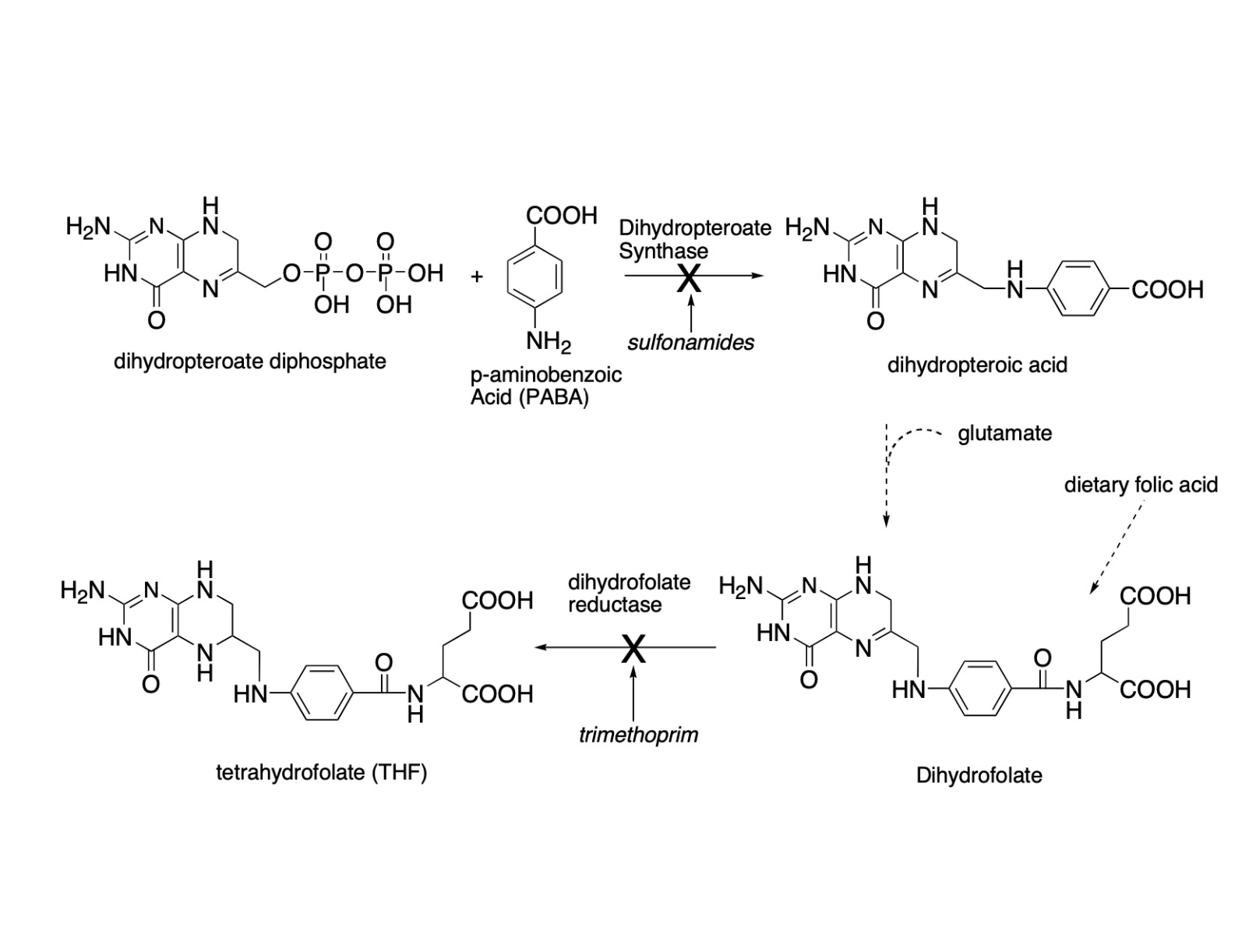
what does dihydropteroate synthase do
an enzyme necessary for folic acid biosynthesis
why is Tetrahydrofolate important
it is an essential coenzyme for the synthesis of thymidine, purines, and certain amino acidcs
What do sulfonamides mimic
PABA
Monotherapy of sulfonamide are
Bacteriostatic
Common allergic reactions to sulfonamides
Hypersensitivity reactions (rash, photosensitivity, drug fever)
Sulfadiazine
broad spectrum activity against Gram (+) and Gam (-) bacteria, toxoplasmosis, poorly soluble in urine and can cause crystalluria
Sulfamethoxazone
Used only in synergistic combination therapy with trimethoprim. Combination is known as co-trimoxzole or TMP-SMX
Trimethoprim (TMP)
Inhibitor of folate biosynthesis
trimethoprim MOA
inhibits bacterial dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) thus halting folate biosynthesis. Folate is needed for DNA synthesis.
Basis for Selectivity (trimethoprim)
Differences between bacterial and mamalian DHFR.
Trimethoprim - Resistance Mechanisms
Alteration of DHFR (weaker binding of TMP)
Increased DHFR production in bacteria cell
TMP does not penetrate into Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells
Trimethoprim & Sulfamethoxazole
Bactrim
Trimethoprim & Sulfamethoxazole
Formulated in a 1:5 ratio (TMP:SMX) to
produce a serum concentration of 1:20
Is TMP-SMX bactericidal or bacteriostatic
Bactericidal - Synergy from inhibiting two enzymes in same pathway
What is the brand name for TMP-SMX
Bactrim
How is TMP-SMX formulated
1:5 ratio (TMP:SMX)
What serum concentration does TMP-SMX produce
1:20
What are indications for TMP-SMX
Uncoomplicated lower UTIs (cystitis), MRSA (cellulitis)
How is the TMP-SMX Oral bioavailability
Excellent
TMP-SMX has signfigant drug intraction with
warfarin
A common side effect of TMP-SMX is
RASH (due to SMX)
Quinolones
Inhibitors of DNA Gyrase and Topoisomerase IV
First Gerneation Quinolone also called
Nalidixic Acid
First geranation Quinolones have low or high potency
Low potency
First gerneation quinolones are indicated for
Gram negative urinary tract infections
Seconnd genration quinolones (biocehmistry)
Fluroine atom at the C-6 Position which incrase the spectrim of activity (gram + and gram negative)
What is DNA gyrase needed for
to help unqind the supercoils
MA of quinolones
inhibit the nicking and closing activeties at DNA gyrase. At higher concenrtations they block the decatenating activity of toposiomerase
What happens when winding and unwiding of DNA is impated
DNA cannot be properly stored, replicated, repaired and trasncribed
IMPORANT: Quinolones have chemical icompatabilties with
Chelate polyvalent metals (ca2+, Mg2+, A3+, Fe2+) and form less water soluble complexes which ddecrease oral bioavibility, thereby losing potency
Quinolones and what are contraindicated
co-adminstration with antacids and after consuking dair products
What is the bassi of selectivity of quinolones
Human toposiomerase II is insensitive to uinolones at noraml achievalbe dosese
Bacteria resistance to quinolones
Binding site modifications, efflux pumps
What is the brand name for ciprofloxacin
Cipro
Compared to other fluorquionones ciproflacxin has the ____ activity against aerobic gram - organisims
MOST; ciprofloxacin (cipro) most active fluroquinlone agaisnt aerobic gram (-) organsisms
Is ciprofloxacin active against anerobic organsims
NO ciprofloxacin is not active agaisnt anaerobic organsims
Is hte plasma pritein bidning of cirpofloxacin low or high
low
Cirpofxacin is widely distributed into
most tissues
What is the brand name of ofloxacin
Floxcin
What is the aboslute bioavailabilty of ofloxacin
roughly 98 percent
Compared to ciprofloxacin ofloxacin is _____ potent compared
Less, ofloxacin is less potent than ciprofloxacin against most gram (-) bacteria
What is ofloxacin generally used to treat,
Mild to moderate urinary UTI, prostatitis, Lower respiratory tract infections, and skin infections
What are teh brand names of levofloxacin
Iquix, Levaquin, Quixin
Levoflxacin is
optically active L-isomer of ofloxacin
Levofloxacin exhbits
post antigbitoic effect (APE) against amny patherogens: organisms may not redsuke grwoth for about 0.5 - 4 hrs after exposrue to levofloxacin, despire undetectrable drug levels
MOA of nitrfuranotin
DNA damaging agent
Nitrofurantoin is used for
Limited to infections of the lower urinary tract (baldder, cystiis)
What is the concentration of ntrifuratoin in the urin
200 μg/mL
Who should avoid nitrofurantoin
Patientts with renal dysfunction due to insufficeint accumulation of drug
What does nitrofurantoin do to the urine
Colors the urine brown
MOA Summary
Sulfonamides: block biosyntheiss of terrahydrofolate by inhibiting the nexyme dihydropteroate synthase
Trimethoprim: inhibits biosynthesis of tetrahydrofolate by bidning to the enzyme tetrahydrofolate reductase
Fluroquinolones: Inhibitors of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV
Nitrfurantoin: Generates reactive species that lead to DNA damage
What is the main resistance mechansims for the for beta-lactam antibiotic famalines
The penicillins are incctivted bt amidases and lactamases
Penicillin binding proteins (PBS) have two crucial enxu,atic activeis for th sutnehsus of peptidogylane where
transpetidase (TP) that cross-links amino acid side chains
Glucosyltransferase (GT) that links subunits of the glycopetide polymer
Beta lactams inhibit peptidogylcan syntehsis by
bidning to transpeptidase
The biculic Beta-lactam structure mimics
D-alanul-D-alaanine
Beta-lactams onhbit peptidoglycan sytnehsis by covalenting bindign to
the transpeptidase at hte same stie that bidns to D-alanyl-D-alanine
What is penicillin G called
Benzylpenicillin
Penicillin G is primaruly active against
gram (+) cocci
procaine and benzathine saltes of penicillin G
water insoluble used for repositoruy pruposes follwing intramuscual injection when long term delivery is desired
Origin of b-Lactam Allergenicity
Haptenic reaction with host protein
porins are protiens that form channles providing
hydrophilic access
Penicllinase resitent, paternal penicllins
Methicillin
Nefecillin
Penicillinase resistant oral penicllins
cloxacillin, dicloxacilloin
Pencillinase sesnitve - braod spectrim oral penicllins
Ampicillin
Amoxicillin
Penicillnase senstive braod sepctrum parenteral penicllins
Ticarcilln
Piperacillin